Content
Share on VKontakte Share on Odnoklassniki Share on Facebook
Every year, the number of people who are diagnosed with benign formations on the skin – fibromas – increases. This kind of disease can appear in both a child and an adult. Fibroma - what it is, what are its symptoms and treatment, what types of disease exist. Symptoms of a soft tissue defect are practically absent.
What is fibroma and why is it dangerous?
So, what is a fibrous formation? This is a benign node that is formed from connective tissue cells. The tumor affects different parts of the body and human organs: skin, mammary glands, uterus, ovaries, and so on. Soft tissue fibroma is a benign tumor, but if not treated in a timely manner, the tumor enters the malignant phase.
There are single or multiple (fibromatosis) lesions of connective tissue, soft and hard forms of the disease. Removal of the formation is carried out using different methods:
- surgical excision;
- cryodestruction;
- laser therapy;
- radio wave exposure.
Soft
The mild type of the disease refers to multiple tissue lesions. Appears on the face or neck, in the armpits, under the mammary glands. The neoplasm is distinguished by its color, which varies from flesh-colored to brown. A soft oncological defect looks like a round polyp on a stalk. If it is injured, pain is felt and bleeding occurs.
A solid fibrous tumor is a small tumor. It is located above the skin or mucous membrane. Often this type of disease has dimensions of no more than 1 centimeter and is formed on a spacious basis. It's not difficult to recognize her. Affects the limbs, internal organs (lungs, heart, stomach, uterus, vagina, etc.).
Soft tissue fibroma
Tissue tumors often develop in men and women on the skin, mammary glands, and tendons. The location of such oncology of all types is very diverse. The neoplasm mainly affects the soft tissues of the arms and legs, the torso area, the face, and the neck. Often benign oncology appears in internal cavities and organs. Let's consider the main forms of tumor.
Uterus
Uterine fibroids - what is it? This type of cancer forms in the muscle tissue of the uterus. Neoplasms are divided into fibroma, myoma and fibromyoma. The first type consists of connective tissues.
Myoma is an oncology formed from muscle tissue, and uterine fibroids, the symptoms and treatment of which are identical to the classical form of the disease - it is formed from connective and muscle fibers.
In most cases, a uterine tumor does not have pronounced symptoms, but sometimes its size or location gives the woman severe pain, and at times even bleeding occurs. The size of multiple nodes varies from small to extensive formations. It happens that the anomaly increases to very large sizes.
Mammary gland
Breast fibroma is detected in many women. The appearance of oncology is often closely related to hormonal changes in the female body (menstruation, menopause, childbirth).
Breast fibroma is classified into two types: fibroadenoma and fibroadenomatosis. The first type is a solid ball that moves.
The second one fills the mammary gland completely, which causes severe pain to the person.
Ovarian
A neoplasm of a round shape with a smooth or nodular surface, having a stalk, is an ovarian fibroma. If it is small in size, then the symptoms hardly appear. When the formation increases, it often leads to the following signs of the disease:
- severe weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- pain;
- bloating of the abdominal cavity.
Skin
Fibrous skin tumor is a benign connective tissue pathology. Formations of a soft structure are located on various parts of the body (in the folds of the groin, armpits, chest, fingers).
This type of cancer is often detected in females after 40-50 years of age. A solid tumor forms in both women and men.
It has a dense structure and protrudes above the surface of the skin.
Angiofibroma is a formation derived from fibroma. It consists of connective fibers, with vessels on a smooth surface. This type of benign fibrous abnormality forms as a noticeable small nodule that is flesh-colored or light brown in color. It is often diagnosed in males and females over the age of 45 years.
Lungs
Oncological diseases also affect the human lungs. Pulmonary fibroids - what is it, what are their features? A very dangerous tumor, often affecting both respiratory organs at once, and can increase in size.
Occurs at any age, multiple and solitary forms of the disease are observed. At first there are no signs, but with significant growth, there is a feeling of heaviness in the chest, pressure on the sternum organs.
On the tongue
A benign tumor of the oral mucosa, consisting of connective fibers, is called oral fibroma. A neoplasm is formed on the mucous membrane of the lips, gums, palate, tongue, and inside the cheeks. It looks like a round shaped knot with a stem or large base. If a tumor on the tongue or other part of the oral cavity is often damaged, it can transform into malignant.
On the face
Facial fibroma is localized in different parts of the face, affecting people of all ages. The main symptom of the disease is the sudden appearance of a small hard or soft growth. In general, pathology on the face occurs without symptoms, unless it is receptive to touch. Often forms in/on the nose, ears, eyelids.
Bone fibroma
Fibrous bone tumors often appear in young children and adolescents. Formed in the tibia or femur.
There are absolutely no symptoms of this type of disease (except for an unexpected fracture of a bone affected by a tumor). The neoplasm belongs to a rare type of benign osteogenic oncology.
Bone fibrosis in the leg or arm of the non-osteogenic form practically does not occur.
Video: is fibroid dangerous?
The video explains what soft tissue fibroids are and how dangerous this disease is to health and life. After watching the video, you can find out what types of tumors exist and how to deal with them. Such useful information will allow you to identify the disease in time and undergo examination by a doctor who will prescribe the optimal therapy.
Fibroma. Description of the disease
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Source: https://sovets.net/4169-fibroma-chto-eto-takoe.html
Uterine fibroids: Symptoms, Signs, Treatment, Diagnosis
Among the diseases that often worry women is uterine fibroids. The main “companion” of this disease is the lack of knowledge about diagnosing its symptoms and treatment methods in women. This article will discuss all the key points that will allow you to understand all the features of the disease and the fight against it.
The term “fibromyoma” refers to a formation located within the body of the uterus, which is a benign tumor.
Most women confuse fibroids with fibroids, which is not a critical mistake, but there are differences between these concepts. If fibroids are formed due to the growth of exclusively smooth muscle tissue, then fibroids have a connective tissue and smooth muscle basis.
Since fibroids are a formation consisting of various tissues, their appearance is possible both on the surface of the uterine body and inside. However, the basis for its formation is the muscle layer. The body of the formation is covered with an active system of vessels through which it is nourished and stimulates growth.
The main problem of this disease is a significant impairment of uterine contractility. Due to the lack of contraction, the vessels remain “open”, which leads to bleeding. Uterine fibroids, the symptoms of which are very diverse, significantly affect the overall muscle tone of a woman.
In medicine, it is customary to determine the size of fibromyomatous nodes, according to the classification adopted for use during pregnancy (the period is determined in weeks).
In the photo: Fibromyoma node
In appearance, the formation is similar to a compaction (knot), which has a rounded shape. In diameter, fibroids can range from a few mm to 20 cm in diameter on average.
There is no risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor. However, there have been cases of uterine sarcoma occurring due to the lack of treatment for this formation.
The disease poses a particular danger as the diameter of the formation increases. Depending on the location, there is the possibility of pressure on nearby organs. Additionally, significant deformation of the uterine body is possible.
Heavy bleeding, which may accompany the course of the disease, makes significant adjustments to the hemoglobin level. As a result, the woman’s condition worsens significantly.
The symptoms and course of the disease can cause significant harm to a woman’s body in the absence of timely assistance. Loss of blood can be fatal.
There is also a danger in the form of necrosis, which can develop at the tumor stalk. Most often, the cause is torsion of the leg and failure of the blood supply.
It has been scientifically established that the main cause of uterine fibroids is hormones. However, an additional factor is the presence of appropriate conditions for their influence, namely any damage to the uterus. We are not necessarily talking about mechanical damage. This could be the consequences of a disease that has a negative impact on the uterus.
Additional causes that may cause the disease include:
It is noted that the disease is more common in black women. One of the possible reasons also includes genetic predisposition.
There are two main types, which differ in location. These include:
These two types account for most of the formations, but there are also others:
Additionally, tumors should be distinguished based on quantitative characteristics. So, it can be a single node or a cluster of them.
The main risk group is women of childbearing age. The combination of estrogen activity and additional factors, which include:
- Disorders of uterine tissue (surgical interventions, congenital features, damage).
A special risk group consists of women in a state after an abortion and after infectious diseases. In such cases, estrogen activity manifests itself in its action on damaged tissue, thereby provoking the growth of a tumor.
Most often, the disease occurs in the age group of 35 to 40 years, but can also be found in young women (17-20 years old).
Uterine fibroids, the symptoms of which may not be detectable in the early stages, can be diagnosed in time with 1-2 visits to the gynecologist per year.
This disease poses a big problem for self-diagnosis, since in most cases it is practically asymptomatic.
Symptoms that can be diagnosed by a woman independently appear, as a rule, only at the moment when the formation reaches a large size. This is explained by the pressure that fibroids can exert on nearby organs (the ureters are most often affected).
A symptom that allows you to pay attention to it at the earliest possible stage of the development of the disease is bleeding. Bleeding may vary in intensity. In addition, cases of profuse bleeding in this disease are often recorded.
It is also worth paying attention to the amount of blood during menstruation. An increase in the amount and a change in the consistency of discharge to a more liquid state may also be a reason to contact a gynecologist.
Symptoms that complement the overall picture of the disease include:
- Aching pain that may change its position slightly
-
Reproductive problems;
(Inability to get pregnant, inability to bear a child).
- Changing the nature of the cycle
- Increased abdominal volume
-
Urinary disorders
Difficulty urinating, frequent urge to urinate.
In medicine, a case was recorded when a patient sought medical help for fibroids equal in size to a 40-week-old child. According to the woman, she began to feel discomfort more than a year and a half ago, but did not consult a doctor because she believed that it was the consequences of a large amount of food consumption.
When contacting a gynecologist, the patient’s symptoms and signs are analyzed, followed by an examination. The size of the tumor is determined as follows:
- Palpation is used to determine the approximate time of tumor growth
- Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size of fibroids
Early diagnosis allows you to avoid surgical intervention. The fact is that removal of uterine fibroids is mandatory only in the case of constant growth of the formation.
If it does not bring discomfort to a woman’s life, treatment of uterine fibroids is possible, which, to a greater extent, will consist of constant monitoring of the condition.
Control should be understood as regular visits to the gynecologist, ultrasound and other research methods.
However, if the presence of fibroids is accompanied by a number of symptoms that are associated with heavy bleeding and changes in pressure, treatment of uterine fibroids is carried out by surgical removal.
There are two main treatment options. These include:
Conservative treatment involves regular examinations and observation by a doctor. It is used in the early stages, if the tumor does not show aggressive growth. It is possible to prescribe any medications to improve the overall picture of the patient’s condition.
The basis of drug therapy is the use of drugs that control the patient’s hormonal levels. Additionally, medications can be taken that suppress the possibility of tumor tissue growth. The classic period of conservative treatment lasts about 8 months.
- Surgical removal of uterine fibroids is used in advanced cases when conservative treatment is powerless.
- In this section, it is necessary to highlight surgical methods of intervention that can stabilize the patient’s condition and prevent the harmful effects of the tumor on the body.
- The main ones include:
Embolization
In the figure: Schematic process of uterine artery embolization
The essence of the operation is as follows: a special conductor is inserted through the femoral artery, whose task is to approach the vessel supplying blood to the fibroids.
Next, when the main source of nutrition has been discovered, a substance - an embolus - is injected through the catheter. Its effect is as follows: by changing, or rather, blocking the blood supply system, fibroids lose the ability to receive nutrients.
As a result, it turns out not only to stop its growth, but also to create conditions for killing.
The advantage of this method is the absence of serious penetration into the body systems. As a result, the healing process and rehabilitation period are as short as possible.
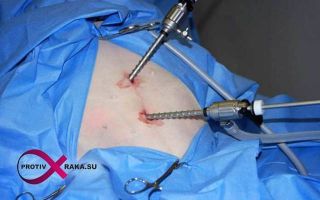
Laparoscopic surgery to remove fibroids
In the photo: Laparoscopic surgery to remove fibroids
This type of operation is an organ-preserving method. Its use is determined by the possibility of reducing injuries, as well as the possibility of intervention without serious consequences for the woman’s body.
Four trocars are being introduced. Three are installed in the suprapubic region, one in the umbilical region.
A trocar installed in the umbilical region serves to introduce a camera through which coordination of actions will be possible.
The operation is performed with the additional use of a special gas, the action of which allows you to expand the abdominal cavity. This way the surgeon gains access to the organ.
There are several types of laparoscopic operations. If the node is on the outside and has a thin stalk at its base, coagulation may be used. If access inside is necessary, the edges are compressed with forceps and an incision is made.
The tissue is then grabbed and then cut off. In this variation, a special role is played by the subsequent processing of the incision, namely suturing. The strength of the future scar depends on the quality of sutures.
Removal of tissue is done using a tool that crushes it and brings it out.
This type of operation is extremely rare. It is indicated for large formations. The incision is made in the suprapubic region. In some cases, a lower-median or median laparotomy may be performed.
Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy)
Removal is also possible laparoscopically. It is the extreme level of possible interventions.
Uterine fibroids, symptoms and body signals should be detected as early as possible. Early treatment will avoid major surgery.
It is not uncommon for the disease to occur during pregnancy, or to be diagnosed during pregnancy. There is no consensus regarding the danger of fibroids, but all doctors agree that in this case everything is decided by the size and location.
The occurrence of a tumor can seriously affect the course of pregnancy. Embryo development involves movement of the uterus. In this case, the tumor can make significant adjustments and even interfere with the normal development of the fetus.
The disease poses an additional danger during childbirth. The possibility of severe bleeding increases significantly.
The whole essence of prevention should be focused on constant monitoring, which includes:
Surgical treatment, unfortunately, is also a risk factor. Of particular danger is the removal of nodes from the body of the uterus and subsequent suturing of the incision. The postoperative period, even against the background of a minimally traumatic operation, should be accompanied by full adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
- visits to the gynecologist at least 2 times a year;
- compliance with medications, if prescribed;
- constant monitoring of hormonal levels;
- control of the menstrual cycle;
Thus, uterine fibroids are a disease that requires only one thing from a woman - attention. At the first symptoms that arise, you should consult a doctor.
Any delay can negatively affect your health. In addition, timely treatment allows you to bypass surgical intervention, and also with a high percentage of probability of getting rid of the recurrence of situations dangerous to health.
Source: https://ProtivRaka.su/dobrokachestvennye-opuholi/fibromioma-matki.html
Concept of benign fibroma
In medicine, there are a huge number of tumors of different types. One of the most common is fibroma. It has its own developmental characteristics, varieties and reasons for its appearance. What is fibroma and how to treat it?
Concept of pathology
Fibroma is a benign tumor formed from connective or muscle tissue. A growth can appear on any part of the human body. Patrology is also diagnosed in people of different ages.
There are soft and hard fibrous tumors. The first type occurs in large numbers. Fibroids form on the arm, leg, face, armpits, neck and other places. The color of the tumor can be different and change over time.
Typically, the color varies from flesh to brown. Soft fibroma has a round shape, soft structure, and has a stalk. When damaged, pain and bleeding are observed.
The solid type of pathology most often occurs under the skin or on the mucous membranes. Fibroids of the vagina, uterus, stomach and other internal organs are usually found. Solid growths are small in size, not exceeding one centimeter.
The types of fibromas, depending on the location of the tumor, are as follows:
- Bone fibroma.
- Fibroma on the leg and arm.
- Fibroma of the skin.
- Breast fibroma.
- Fibroma of internal organs.
- Fibroma on the head.
The following types of tumors are also distinguished:
- Desmoid fibroma. This type includes a formation that is dense to the touch and has a fibrous membrane. It is formed in most cases in the peritoneum, back, chest, arms and legs. The danger of this growth is its possible transformation into a malignant tumor.
- Non-ossifying fibroma. This type of neoplasm is distinguished by the fact that patients often experience a pathological bone fracture. The tumor is most localized in the lower extremities. Often the pathology disappears on its own after a few years.
- Non-osteogenic fibroma. This type of disease occurs in the tibia and femur. The exact cause of the phenomenon has not yet been established. The neoplasm is characterized by destruction of connective tissue, which is then replaced by fibrous tissue.
- Cystic fibroma. This form includes tumors that are more common in females due to hormonal imbalance. Cysts can appear in the uterus, ovary, and mammary glands.
According to the international classification of diseases ICD 10, fibroma is coded D10-D36. The exact code depends on the location of the tumor.
Causes
Doctors cannot name the exact reason why soft fibroma develops, because scientists have not yet identified it. Etiology still has many questions, the answers to which have not yet been obtained. But doctors clearly know what factors can provoke the onset of the disease.
For example, fibroma in the mouth may appear due to damage to the mucous membrane. Inflammation in the cavity also has a negative effect. Pulmonary fibroids occur as a result of smoking, exposure to harmful substances at work, and decreased immunity.
- Doctors also include heredity, hormonal imbalance, and taking certain medications as provoking factors.
- Fibroma of the soft tissues of the reproductive organs occurs with chronic inflammation, abortion, promiscuous sex life, disruption of the endocrine system, frequent stress, and complicated childbirth.
- Non-ossifying bone fibroma is formed as a result of trauma to bone tissue, inflammation, and infectious pathologies.
Symptoms
Fibroids manifest themselves in the same way in children and adults. Clinical signs depend on where the tumor is located. Therefore, it is worth considering them separately.
Bone fibroids usually do not cause discomfort because bone tissue does not have nerve endings. But if the patient experiences a pathological fracture, pain and swelling will occur.
A neoplasm in the uterus is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Heavy periods.
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lumbar region and external genitalia.
- Unpleasant sensations and a feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area.
- Frequent desire to empty the bladder.
- Constipation.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse.
A lung tumor is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Feeling of heaviness in the chest.
- Shortness of breath after exercise.
- Cough.
- Pain syndrome in the affected area.
- Excessive activity of the sweat glands.
Myofibroma of the skin causes the following symptoms:
- Increased mobility.
- Flesh color, which, as the size of the tumor increases, turns into a dark purple color.
- Bleeding in case of mechanical injury.
Fibrous neoplasm of the larynx is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Feeling as if there is a lump stuck in the throat.
- Dry frequent cough.
- Hoarse voice.
Source: https://opake.ru/dobrokachestvennaya-opuhol/fibroma/
Fibroids - causes, signs, symptoms and treatment
Fibromyoma is a benign formation that consists of fibrous tissue and muscle structures. Its main features are that it does not spread to nearby tissues and grows rather slowly.
The weight of the formed node can be from several tens of grams to several kilograms. Fibroids can occur in both men and women.
But it is worth noting the fact that among the fair half of humanity they are much more common.
Fibroids predominantly form in women between 30 and 40 years of age. But in recent years there has been a rapid “rejuvenation” of the pathology. Now a tumor can develop even in women over 20 years of age.
Doctors explain this trend by the fact that now the negative impact on a woman’s body has increased significantly. All this is directly related to the environment.
But one should also not exclude mechanical factors - abortions (especially out-of-hospital ones), various surgical interventions that can damage the internal and external genital organs. All this also adversely affects health and can cause the progression of fibroids.
Women most often develop fibroids of the breast, uterus, and ovaries. Depending on the location of the pathological process, symptoms may differ slightly. But the reasons for the progression of benign formations are usually the same in all cases.
Causes
A certain impetus for the development of fibroids is a certain hormonal imbalance. Clinicians also identify several other main factors that contribute to the progression of pathology:
- disturbances of blood flow in the pelvis;
- failure of the ovaries;
- infertility caused by disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries, pathologies in the uterus, etc.;
- infectious inflammation of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes;
- disorders in the cardiovascular system;
- genetic predisposition to the development of cancer;
- other underlying diseases.
Breast fibroids
Breast fibroids are formed due to the rapid proliferation of muscle and connective tissue. As a result, a dense knot forms in the chest, which is not painful upon palpation. The main reasons for the progression of this pathology are hereditary factors, hormonal imbalance in the body, as well as constant psycho-emotional stress.
In the first stages of the formation of a benign formation, a woman may not notice any symptoms at all. The presence of a lump in the chest can only be detected by palpation. The following symptoms indicate that fibroids have formed:
- as a rule, the formation of only one tumor is observed;
- when palpated, the seal is movable and measures no more than 1–5 cm;
- no pain syndrome is observed.
Fibroids of the breast
Breast fibroids come in several types: leaf-shaped, pericanalicular and intracanalicular. It is worth noting that only the leaf-shaped form of fibroids can eventually (in the absence of proper treatment) degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis of this pathology is complicated by the fact that the neoplasm does not cause any concern to the woman. Therefore, for a long time she does not notice him at all.
Only after its size becomes quite large can breast tenderness be observed before menstruation.
It is important to regularly perform breast self-examination so that if you suspect the development of fibroids, immediately consult a doctor. The diagnosis is confirmed through personal examination, palpation, based on ultrasound data.
Treatment of fibroids is surgical. The formed tumor is excised through a small incision, onto which a cosmetic suture is then applied.
After its removal, no scars remain, and the aesthetic appearance of the breast does not suffer. If it is not possible to carry out surgical treatment, then in this case doctors resort to another method - conservative.
The patient is prescribed hormonal and non-hormonal medications.
Uterine fibroids
If this pathology develops, the muscular layer of the uterus is affected. Medical statistics are such that uterine fibroids occur in 70% of patients.
The danger of the disease is that, due to common etiopathogenetic mechanisms, in most clinical situations the tumor develops simultaneously with hyperplastic processes of the endometrium.
This condition is extremely dangerous for a woman’s body, as it is a background for the further development of cancer.
Predisposing factors to the development of pathology:
- complications during childbirth;
- heredity;
- installation and long-term wearing of the IUD;
- history of abortion;
- anovulation;
- hysteroscopy.
For a long time, uterine fibroids can occur without a single symptom. But as the tumor grows, the following signs begin to appear:
- uterine bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the duration of menstruation increases, and the discharge becomes abundant;
- urination is impaired.
If these symptoms occur, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and prescribing the correct course of treatment. For diagnostic purposes the following is prescribed:
- Ultrasound;
- metrosalpingography;
- diagnostic curettage followed by histological examination of the scraping obtained.
The doctor will also perform a vaginal examination. If a woman’s fibroids progress, the uterus will be enlarged in size, its consistency will be dense, and nodes can be felt upon palpation.
Treatment of fibroids can be either conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment is used if the size of the fibroids does not exceed eight weeks. The following medications are prescribed:
- pure gestagens;
- combined oral contraceptives;
- antigonadotropins.
Surgical treatment of fibroids can be carried out both with the preservation of the organs of the woman’s reproductive system, and with their removal (the uterus is removed, but the ovaries remain). It all depends on the complexity of the disease, as well as on the size of the formed tumor.
Ovarian fibroids
Ovarian fibroids also consist of fibrous and muscle tissue. This pathology is extremely rare. The pathological formation develops quite slowly and does not show symptoms in the first stages of development. Ovarian fibroids are located on a stalk. Typically, only one ovary is affected. Bilateral lesions are extremely rare.
When ovarian fibroids form up to 3 cm in diameter, no symptoms are observed. The functions of the ovary are not impaired. The first signs appear when the tumor increases in size and begins to put pressure on neighboring organs.
Symptoms:
Diagnosis of the disease includes examination of the patient, vaginal examination, and ultrasound (the most informative method). Conservative treatment of the pathology is not carried out, since this tumor cannot be resolved.
Treatment should only be surgical. Removal of the formation is carried out laparoscopically. Fibroids are removed immediately with the capsule, which makes it possible to preserve both the menstrual and generative functions of the ovary.
Laparoscopy
ethnoscience
Treatment of fibroids using folk remedies can only be carried out in tandem with drug therapy. Under no circumstances should you rely only on herbs and decoctions. You can use any folk remedies only after consulting your doctor.
Effective folk remedies used for treatment at home:
- Birch tar;
- potato juice;
- burdock;
- celandine;
- propolis;
- bee bread
Prevention
There is no specific prevention that could protect a woman from developing fibroids. But if you adhere to the measures below, you can reduce the risk of developing pathology:
- rational lifestyle;
- timely detection and treatment of infectious diseases;
- exclusion of abortion;
- correction of hormonal disorders;
- correct and complete treatment of existing gynecological diseases.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/1126-fibromioma-simptomy
What is fibroma and its types?
wow. Most often, it looks like a pale pink or flesh-colored skin formation. Does not cause any inconvenience to humans, except cosmetic ones.
Fibroids can be present in a child from birth or develop during life. Such a disease can be located anywhere and is completely independent of gender or age. However, inflammation often occurs inside organs.
There are many types of fibroids, we will look at some of them.
Dermatofibroma
Dermatofibroma, or otherwise hemangioma, is a neoplasm of connective tissue and skin that sometimes looks like a wart. Dermatofibroma most often has a round shape, the main part of the inflammation is in the skin.
Usually, dermatofibroma is a single formation, but there have been cases when several neoplasms appeared at once. Most often found on the arms, legs, neck, face and other parts of the body.
Dermatofibroma has been seen most in middle-aged women.
Dermatofibroma
Doctors associate the causes of this inflammation with several factors:
- polluted environment;
- heredity;
- infection;
- permanent skin injury.
Dermatofibroma can be dangerous, especially when it occurs in children. This is explained by the fact that with constant irritation, painful sensations may occur. The following symptoms can be considered signs of inflammation such as dermatofibroma.
- bleeding due to mechanical damage;
- if you press, the dermatofibroma will bend inward;
- increased sensitivity, painful sensations when touched, as well as itching cannot be ruled out.
Dermatofibroma can only be treated in one way - removal, either laser or surgical.
It is important to know! Any neoplasm that has been removed, including dermatofibroma, requires morphological tissue analysis.
Angiofibroma
Angiofibroma is a benign neoplasm that consists of fibrous and vascular tissue. The diameter of angiofibroma ranges from three millimeters to several centimeters.
The surface of the tumor itself is transparent, capillaries are visible, they are especially visible during dermoscopy.
The disease develops slowly; as a rule, angiofibroma becomes progressive after a person reaches the age of forty to fifty years. Angiofibroma is a rare skin disease.
Angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis
As a rule, angiofibroma forms on the skin of the extremities, but there are cases when the tumor appears on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. There is no tendency to malignancy in this pathology.
Angiofibroma in terms of its diagnosis is no different from other types of fibromas.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a histological examination, and only after a positive result it is necessary to draw up a course of treatment.
Desmoid fibroma
Desmoid fibroma is an extremely rare disease that usually affects the walls of the abdominal cavity. For quite a long time, there was only one method of treatment - surgical, but with the development of medicine, combined methods appeared that effectively affected the tumor without surgical intervention.
Odontogenic fibroma
Odontogenic fibroma is a rare tumor located in the jaw area. Its main difference from other similar diseases is the presence of a cyst-like cavity with multiple dense inclusions.
Kidney fibroma
Kidney fibroma is one of the benign tumors, but it still cannot be neglected. Pain in this organ does not always indicate problems in the kidney; other causes are possible. If you notice symptoms of this pathology, we strongly recommend that you consult a medical specialist.
Many believe that this disease can only be cured through traditional medicine, spells and other non-medical methods. This opinion is wrong. Of course, there were cases when a person was able to recover using only traditional medicine, but such cases are extremely rare.
With modern medicine, refusing its help is, at a minimum, stupid.
Chondromyxoid fibroma
Chondromyxoid fibroma is an extremely rare cartilage-forming inflammation. As a rule, it most often occurs in the metadiaphyses and metaphyses. It can also progress in other bones of the human body. The prognosis for a disease such as chondromyxoid fibroma is favorable, but there is one drawback. Chondromyxoid fibroma is prone to recurrence, and sometimes the development of cancer is possible. Relapses occur in ten to fifteen percent, usually in the first two years after surgery. Chondromyxoid fibroma is treated only with surgery. Usually, marginal resection is used, which guarantees a minimum number of relapses. If treatment is not started in time, chondromyxoid fibroma can become malignant. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you respond appropriately to the manifestation of symptoms.
Bone fibroma
Bone fibroma is one of the most common tumor diseases. Typically, bone fibroids most often occur on the leg. It is noteworthy that after surgery to remove inflammation there is no scar or stitch left. Therefore, treatment of this pathology occurs, most often, without complications.
Non-ossifying fibroma
Neossifying fibroma and metaphyseal defect are one of the most common skeletal diseases in childhood. These terms can be considered synonyms, since they have almost no differences in their lexical meaning and mean the same thing. You should not be afraid of doctors or not follow their recommendations and advice at all. Nowadays, medicine has reached such a level that it is able to remove any type of fibroma without consequences, be it non-ostegenic fibroma or non-ossified fibroma, or any other. Many people don’t even know what a puncture is, but our medicine has been using it for a long time! Inflammation of the prostate or pancreas, soft tissues, thighs, pelvis, mammary glands, ears, tibia, tendons, on the nose, near the eyes, in the abdomen or some others. Our medicine can handle everything!
The most important thing to remember is to always listen to your healthcare professional.
If he says that you need to take these pills for 12 weeks, then that’s what you need to do. Many people decide for themselves when they can stop taking pills - this is wrong.
If your symptoms go away, it does not mean that you are completely healthy. It is necessary to adhere to a healthy diet, as well as a postoperative course of prevention. Particular attention should be paid to prevention in case of pregnancy.
If you managed to move from diagnosing the disease to undergoing a course of treatment in time, you have nothing to worry about!
Source: http://opuholi.org/dobrokachestvennaya-opuxol/fibroma/chto-takoe-fibroma.html
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a5c6286865165fdcc876cb5/5afe6d9e2f578ccc52f53c68
Benign tumors of the uterus
Currently,
there
is an increase in
benign tumors of the uterus,
which
are associated with the influence of
unfavorable
environmental factors on the women’s body,
neuropsychic stress,
which affects
hormonal
function (hyper-
or hypofunction of the gonads).
Every
4-5 women consult
a gynecologist about uterine fibroids, or
-25% of women over 35 years of age.
According to the results of pathological
studies, uterine fibroids are diagnosed
in 50% of women.
According to the literature,
of fibroids in young women
is currently increasing .
II.
Educational goals. The student
must know:
- 1) theories of the occurrence of
benign uterine tumors; - 2)
morpho-functional
types of benign
uterine formations; - 3) clinical
symptoms of uterine fibroids; - 4) methods for diagnosing
uterine fibroids; - 5)
differential
diagnosis between malignant and
benign tumors
of the uterus; - 6)
methods of treating uterine fibroids (conservative
and surgical); - 7) methods of surgical
interventions; - 8) methods of prevention.
-
As
a result of the practical
lesson, the student should be able to: - 1)
select from complaints and anamnesis data
that reflect the presence of a
uterine tumor; - 2)
draw up
a plan for examining the patient to
diagnose uterine fibroids; - 3) evaluate the results
of examination of a patient with uterine fibroids; - 4)
conduct
a differential diagnosis of
uterine fibroids; - 5)
draw up
and examine
an individual treatment and
rehabilitation plan for a patient with uterine fibroids; - 6)
conduct
an examination of the disability of a patient
with uterine fibroids.
III. Basic knowledge
1. Anatomy of the internal
female genital organs.
2. Hormonal
regulation of the menstrual cycle.
3.
Etiology
and pathogenesis of the development of benign
formations.
4. Collection of general and
gynecological history.
5.
Methods of general examination of the patient by
organs and systems.
6.
research methods in
gynecology.
7.
Interpretation of the results of clinical,
biochemical and invasive
studies.
IV. Contents of educational material
fibroids
, or leiomyoma,
are a benign, well-separated,
encapsulated
tumor that
develops from the muscular
layer
of the body or cervix, in a hormone-dependent
organ.
In
the literature
there are numerous terms
used to call this disease:
fibromyoma, myofibroma,
leiomyofibroma,
fibroleiomyoma,
fibroma, fibroid
and
myoma.
According to modern research, uterine fibroids are a dishormonal tumor
with a disorder in
the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal-ovarian system.
The dyshormonal nature is due to
the presence of a number of
metabolic
disorders,
functional liver failure
and often impaired
fat
metabolism.
- Patients with
uterine fibroids have a high
infection index, often have
infertility
and
menstrual dysfunction. - factors
for uterine fibroids are: - 1) heredity;
- 2)
menstrual
dysfunction menarche,
hyperestrogenism; - 3) sexual infantilism;
- 4)
reproductive
dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian
system; - 5)
recurrent
inflammatory
diseases of the genitals; - 6)
numerous curettages of the mucous
membrane of the uterine body and induced
abortions; - 7)
extragenital
pathology with disturbances of carbohydrate,
lipid and other types of metabolism.
The clinical
picture depends
on
the patient’s age, time of illness, localization
of myomatous
nodes, premorbid
background, and
concomitant pathology.
Main
complaints :
uterine bleeding, signs of
distension,
dysfunction
of neighboring organs, pain in
the lower abdomen, there may be
dysuric
disorders,
infertility, anemia and symptoms of insufficiency
of the cardiovascular system, constipation.
In 50% of patients, menstruation is heavy, with
clots, for more than 5 days, bleeding
can be acyclic
.
There are
nodular
and diffuse forms of uterine fibroids.
Most often - nodal forms.
Diagnosis is not difficult; bimanual
examination reveals an enlarged
uterus of dense consistency with a nodular
surface.
Differential diagnosis is carried out between uterine fibroids
,
ovarian cysts,
tumors of the ovaries, bladder and
intestines.
Additional
examination methods: ultrasound,
hysteroscopy
with targeted biopsy, hysterosalpingography,
probing of
cavity
with separate
curettage of the cervical
canal and
uterine cavity, diagnostic
laparoscopy is possible.
Depending
on the location of the myomatous
node, the following types of fibroids are distinguished:
1)
subserous
(subperitoneal) nodes, i.e.
growth towards
the
serous covering
of the uterus;
- 2)
interstitial
(intramural)
- in
the thickness
of the uterine wall; - 3)
submucous
(pidmucosal)
- growth of the node into
cavity
; - 4)
atypical
- retrocervicalae,
retroperitonealae,
antecervicalae,
subperitonealae,
perecervicalae,
intraligamentaram. - The body
of the uterus is affected in
95% of cases, the cervix in
5%. -
Complications
of uterine fibroids :
“birth”,
necrosis, suppuration
of the myomatous
node, torsion
of the node’s legs, rupture of the capsule and vessels
of the node, malignant
degeneration.
Most
women with fibroids
have preserved
. Those who have it impaired are currently being successfully treated; the number of
women having pregnancies with uterine fibroids
is constantly increasing.
This is very
important because medical, social
and psychological
problems
arise in all women with uterine fibroids.
Pregnancy occurs in
the uterus,
as a rule, in the case of intramural
subserous
location
of the nodes.
In
the case of
pidlistal
node, pregnancy does not occur or
ends in spontaneous abortion.
Throughout pregnancy, the following may be
observed: threat of miscarriage, pain
in the lower abdomen and lower back, dysfunction
of the bladder and rectum,
necrosis of the myomatous
node, gestosis
in the second half of pregnancy.
A complication of fibroids in
the postpartum period is hypotonic
uterine bleeding.
-
Treatment of
uterine fibroids is possible
in two
ways: conservative
with
caution for cancer,
surgical
- radical. - Indications
for
surgery are: - 1.
Heavy and prolonged
menstruation or acyclic
bleeding, which
leads to
anemia
in the patient; - 2.
The size of the tumor is 12
weeks or more, even in the absence of complaints; - 3.
The size of the tumor, at which
symptoms of impaired function of neighboring
organs occur (impaired
kidney function, frequent
urination, impaired
bowel movements);
4.
Rapid
tumor growth (4-5 weeks per year).
In such cases, malignancy
of the tumor is always suspected;
5.
Subserous
nodes on the stalk.
Such a knot can lead to
torsion and urgent surgical
intervention;
6.
Necrosis of myomatous
node;
7.
Submucous
uterine fibroids.
Such fibroids lead to
uterine bleeding.
Regardless of the size of the fibroids, such patients require
surgical treatment;
- 8.
Intraligamentary
nodes lead to
pain as
a result of compression
of the nerve plexuses and impaired
renal function due to compression of
the urinary tract; - 9.
Nodes growing from
the vaginal part of the cervix; - 10.
Combination of fibroids with other pathological
conditions
of the genital organs: ovarian tumors,
prolapse
endometrial hyperplastic processes
11.
Combination of uterine fibroids and infertility.
Surgical
treatment can be conservative (in
women of reproductive age,
advantage is given to
reconstructive plastic surgery)
and radical (supravaginal
amputation or hysterectomy
, the issue
of
removing
appendages
and cervix is decided depending
on the age
of the patient and their condition).
During
surgical treatment, a number of
questions arise: complete or partial
removal
of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix
.
What kind of
access - abdominal, vaginal
or endoscopic.
The extent of the operation depends
on
the woman’s age, her condition,
concomitant diseases, the location
and size of the nodes, the condition
of the cervix and ovaries.
If, during
the operation, young women develop
cystic
changes
in the ovaries,
they are resected; if there is an ovarian tumor, then
is
removed
.
For women under the age
of 50, they are not removed during surgery if
the ovaries are unchanged.
If
there are no changes
in the cervix (colposcopy,
cytological examination), it is left during
the operation.
Also, the issue of removing
the fallopian tubes during surgery is decided
individually.
If uterine fibroids
are accompanied by
adhesions
, the fallopian tubes must be removed.
This also applies to necrosis
of the mimatous
node, purulent melting of the uterine nodes.
In
all other cases, the fallopian tubes
must be left, because when
they are removed, the innervation and
blood circulation of the ovaries are disrupted, which leads
to
a rapid
decline in their function.
Approach
to
conservative treatment of uterine fibroids .
When
fibroids are detected, the reliability of clinical
cure using even
modern methods of conservative
therapy is low.
It is possible to use modern laparoscopic
surgery, hysteroresectoscopic
surgery and additionally combined
hormonal therapy
regimen
: functional surgery +
fixing hormone therapy or
stabilizing hormone therapy +
functional surgery + fixing
hormone therapy.
According to
the literature, an attempt to preserve
an organ
in a young woman without early surgical
intervention leads to up to 100% of its loss
over the next 5-10 years after
is detected
.
Conservative therapy for uterine fibroids is not an alternative
to surgical treatment.
If there are indications
for
surgical
treatment, then it must be performed.
Uterine artery
embolization treatment method.
There is no need for
pre- and postoperative treatment.
- The goal
of hormone therapy is to relieve the pain symptoms
of uterine fibroids or prevent
its growth. Hormonal drugs: - gestagens
(norkolut,
prima-lyut-nor)
from 16 to 25 days of the menstrual cycle, 5
mg for 3-6 cycles; - 12.5%
oxyprogesterone
capronate,
in the 2nd
phase of the menstrual cycle on days 14-17-21
, 125-250 mg, 6 months.
Analogues
- gonadotropin-releasing
hormones (GnRH):
zoladex,
deferelin,
buserelin.
The treatment method is aimed at a 6-month
course of taking the drug.
The first injection is performed
from days 1 to 5
of the menstrual cycle, the drug is administered
every
28 days.
- Specific
prevention of the development of uterine fibroids: - a) prevention
of unwanted pregnancy; - b)
systematic fight against chronic
stressful cases, correction
of pathological and psychosomatic
factors; - c)
early detection
and timely correction of luteal
insufficiency; - d) complete
therapy of common diseases
of the uterine appendages; - e)
widespread
use of oral
contraceptives
and gestagens
as “maintenance” therapy for
pathological conditions. - In
order to prevent precancerous
diseases and uterine tumors, it is necessary
to conduct preventive examinations
of women once a year after 30 years with
a cytological examination of the contents of
the cervical
canal,
ultrasound, and
timely treatment
of identified diseases.
Source: https://studfile.net/preview/1607478/page:3/