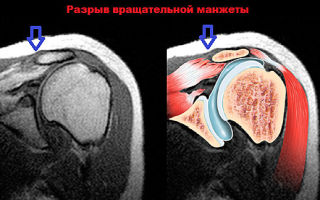
An MRI of the shoulder joint is necessary for people who are constantly bothered by pain and stiffness of movement.
The procedure uses high-quality equipment that can show a detailed image of the joint and nearby tissues.
MRI can also be performed with the addition of contrast, which helps to observe blood circulation in the shoulder and see the smallest inflamed areas.
Reasons for ordering the study
MRI of the shoulder is prescribed in cases where difficulties arise in making a diagnosis, it is necessary to monitor treatment or assess the extent of damage. Magnetic tomography of the shoulder joint is performed for complaints of severe pain; it is also prescribed for dislocations, polyarthritis or arthritis.
Pain can be caused by a large number of different pathologies, each of which has its own cause. Sometimes treatment involves mutually exclusive methods. Often, due to a number of difficulties, it is necessary to do an MRI of the shoulder joint, which will show comprehensive information on the basis of which a diagnosis is made.
The cost of the procedure varies depending on the region. For example, in Moscow the minimum price for an examination will be 3 thousand rubles, and in Yekaterinburg - 2.2 thousand rubles.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in the following cases:
- Constant pain.
- Rupture of the joint capsule.
- Injuries (dislocations, fractures, etc.).
- Tumor and inflammation of soft tissues.
- Arthritis.
This method is also sometimes used to determine the location of a pinched nerve when monitoring indicators in the postoperative period.
In any of the listed cases, this examination will give clear results that will help to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Principle of operation
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the examination methods. The conduction involves placing the shoulder joint in a magnetic field.
All structures and tissues of the body contain hydrogen ions in different concentrations. Their number directly depends on the density of the substance.
When protons are placed in a magnetic field, they begin to change their characteristics - spatial orientation, charges, direction of movement.
The tomograph is able to detect these changes and transmit the received information to a computer. The device collects data and produces images colored in different colors.
Most of the photo is occupied by shades of gray. Their saturation depends on the density of the specific structure. You can also make a three-dimensional image. The procedure is most informative with the use of contrast agents.
Diagnosis of diseases
An MRI of the shoulder joint can detect various injuries and their consequences. If there were complex fractures or ligament ruptures, then scars remain in their place, which greatly disrupt trophism.
In this case, there is a risk of post-traumatic arthrosis - a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the joints. If it is detected in the early stages, the pathology can be quickly stopped and stable remission can be achieved.
Most often, an MRI of the shoulder joint shows:
- Chronic pathologies of the articular region (osteoarthrosis, arthritis). An exacerbation of the disease can also be diagnosed.
- Various rotator cuff disorders.
- Systemic pathologies that can affect connective structures.
- Diseases caused by infection.
- Bleeding formed in the joint cavities, hematomas, the presence of exudate.
- Plexitis is inflammation of the nerve plexuses.
- Shoulder periarthritis. They usually occur due to inflammation of the synovial capsule.
- Osteochondropathies are tissue necrosis caused by malnutrition.
- Joint hypermobility.
- Benign and malignant tumors, as well as other small cancer lesions.
- Anomalies in the structure of the joint that occur in utero or during life.
- Neuropathies are nerve lesions that are not inflammatory in nature.
An examination is also prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. Surgeons monitor tissue regeneration, and rheumatologists monitor the effect of medications.
To obtain results, doctors can use native or contrast tomography. Using a native one, you can take a photograph of the entire shoulder region. The image is displayed in three planes:
- The first is necessary in order to examine the shoulder cuff.
- The second captures the muscles and head of the bone.
- The third is needed to examine the tendons.
A contrast analysis of the shoulder joint is performed to detect problems with the functionality of parts of the forearm. They can be static and dynamic.
Direct contrast MRI is performed to detect abnormalities in mechanical function and show intra-articular changes. For example, a benign or malignant neoplasm can be detected.
Purpose of examination with contrast agents
Quite often, doctors need to identify inflammation in the shoulder joint. Some time before the examination, the person is intravenously injected with contrast, which often contains a paramagnetic agent. MRI using contrast agents is done if the following pathologies are suspected:
- The appearance of new tumors and the spread of metastases. Malignant and benign formations receive blood stained with a contrast agent, and this is clearly displayed on the resulting images. The contrast helps determine what caused the tumor, as well as the number of recently formed metastases.
- Inflammatory processes in tissues. The contrast agent enters the inflamed areas of the muscles and ligaments.
- Vascular pathologies. Certain diseases develop because blood circulation in tissues is impaired. This leads to insufficient supply of necessary substances. The development of the disease is caused by the poor condition of the capillaries, veins and arteries in the shoulder girdle.
Before the procedure begins, the person is tested to determine his individual sensitivity to the contrast agent. Usually it does not have any side effects, and the patient tolerates the administration of the paramagnetic well.
MRI technique
An MRI of the right shoulder joint is usually prescribed, since the right arm is the working arm for most people, and therefore is damaged more often. Carrying out a tomography does not require any special preparation.
If you need to use a contrast agent for the examination, it is better not to eat for several hours before the procedure.
Immediately before starting, you need to remove all metal and metal-containing items (jewelry, clothes with buttons and zippers, etc.).
The doctor must consult the patient and tell him how the procedure will be carried out. People who have developed neurological and mental disorders, as well as patients with claustrophobia, should take tranquilizers or sedatives before tomography.
Procedure for performing an MRI of the joint:
- First, a special coil in the form of a hemisphere is applied to the sore spot.
- The patient lies down on a retractable table and rides it into the capsule. Old equipment provides for a vertical position of a person, but such devices are practically not used anymore.
- A layer-by-layer examination of the damaged section begins, which takes about half an hour. If a contrast agent is used, the procedure lasts about 40 minutes.
- First, a special coil in the form of a hemisphere is applied to the sore spot.
- The patient lies down on a retractable table and rides it into the capsule. Old equipment provides for a vertical position of a person, but such devices are practically not used anymore.
- A layer-by-layer examination of the damaged section begins, which takes about half an hour. If a contrast agent is used, the procedure lasts about 40 minutes.
Usually the examination does not cause any discomfort. In rare cases, patients experience dizziness.
Most often, the cause of this is discomfort due to being in a cramped and confined space.
Decoding the results
The interpretation is made by a doctor specializing in diagnostics. Interpretation most often takes approximately 2 hours. But if the radiologist is too busy, then patients have to wait about a day. An MRI of the shoulder joint may show the following:
- Atrophying, degenerative and inflammatory changes in bone and cartilage tissue. In the picture they are shown as colored areas.
- Cavities in tissues. This indicates the formation of inflammation.
- Cancer and benign tumors. Their structure is much denser than that of the surrounding tissues. The formations are intensely colored and are located between the muscles.
- Displacement of ligaments into the articular cavity. This happens when there is a break.
- Destruction of cartilage. The disease is called osteoarthritis. The overgrown edges of the plates indicate it.
- Reducing joint space. This suggests that surgical methods need to be used.
- The appearance of dead tissue. Indicates infectious arthritis.
- Change in heat transfer. This pathology can cause the development of many diseases.
When the results are deciphered, the condition of the cartilage and bones is assessed. They should not show any defects. Nearby tissues are also examined. If any changes are found in them, this may mean that there is a weak chronic inflammatory process.
Contraindications to tomography
MRI is the safest way to study the body. Compared to X-rays, tomography is performed without irradiating a person. Arthroscopic analysis is performed if there are soft tissue abnormalities. But nevertheless, MRI also has absolute contraindications:
- Presence of electronic implants.
- Presence of hemostatic clips in the body.
- If a person has undergone surgery to implant heart valves, then an MRI is strictly prohibited.
- Presence of electronic implants.
- Presence of hemostatic clips in the body.
- If a person has undergone surgery to implant heart valves, then an MRI is strictly prohibited.
Other devices implanted into the body are not contraindicated, but there is a possibility that the results will be distorted. The final decision must be made by the radiologist.
The disadvantages of this procedure include the rather high cost, the unavailability of the device in small towns, and absolute contraindications.
At the moment, MRI is the safest and most informative way to diagnose the disease, thanks to which pathologies can be detected in the early stages of development. The device also allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis.
Source: https://Artroz.guru/mrt-plechevogo-sustava.html
MRI of the shoulder joint: how they do it, what it shows, interpretation
MRI of the shoulder joint is indicated for patients complaining of pain and crunching in the joint, and stiffness of movement. During the procedure, equipment is used that allows one to obtain high-quality images of bones, cartilage, and ligamentous-tendon apparatus. MRI performed with contrast helps to assess blood circulation in the shoulder and visualize the smallest inflammatory foci.
An example of an MRI image of a healthy joint.
Radiography is usually used to diagnose pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. But it is not always informative when examining the shoulder joint, which has a complex structure. MRI reveals not only destructive changes in bone and cartilage tissue, but also damage to the synovial capsule, ligaments, muscles, and nerves.
Operating principle
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists...” Read more...
Magnetic resonance imaging is an examination method in which the shoulder joint is placed in a magnetic field.
Cartilage, bones and connective tissue structures contain different concentrations of hydrogen ions, which are directly dependent on tissue density. In a magnetic field, protons change their characteristics - charges, motion vectors, spatial orientation.
This is detected by the tomograph sensors and the collected information is transmitted to the computer. The device reads the changes that have occurred and converts the data into images colored in different colors.
The images are dominated by gray shades, the intensity of which depends on the density of the structures being examined. If necessary, a three-dimensional image is created on the monitor screen, which is most informative when performing MRI with a contrast agent.
Indications for use
Shoulder joint diseases can develop under the influence of many external and internal negative factors. The task of performing an MRI of the shoulder is not only to detect foci of pathology, but also to establish the cause of their occurrence. Therefore, the diagnostic procedure is indicated for patients in the following situations:
- stiffness of the joint at rest and (or) during flexion and extension;
- morning puffiness, joint swelling;
- painful sensations that disappear or intensify during physical activity and movement;
- blocking movements;
- crepitus - clicking, crunching when bending, turning, changing body position;
- previous injuries - dislocations, fractures, ligament and tendon ruptures;
- discomfort in the shoulder joint.
The causes of one of these symptoms or their combination can be either banal muscle strain or the formation of malignant neoplasms. X-rays are most informative when examining bone tissue, and MRI will allow you to visualize rotator cuffs, tendons, labrums and other connective tissue structures.
This is an x-ray that shows the absence of joint space. MRI imaging will be even better.
What the examination can show
MRI is performed to diagnose sports and household injuries, as well as their consequences. In case of complex fractures or complete separations of ligaments and tendons, scars remain that disrupt trophism.
There is a risk of developing post-traumatic arthrosis - a progressive degenerative disease. Detecting it at an early stage allows you to stop the pathology and achieve stable remission.
What else can be discovered during an MRI of the shoulder joint:
- acute and chronic articular pathologies of an inflammatory and degenerative nature - osteoarthritis, rheumatic, psoriatic, juvenile, gouty arthritis;
- various injuries of the rotator cuffs;
- diseases of infectious etiology - osteomyelitis, synovitis, bursitis;
- plexitis - inflammatory processes of large nerve plexuses of various localizations;
- osteochondropathy (Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, Ostgood-Schlatter disease, Köhler disease, Scheuermann-Mau disease, Schinz disease) - disturbances in the nutrition of bone tissue and their subsequent necrosis;
- bleeding into the joint cavities, formed hematomas, accumulation of pathological exudate;
- humeroscapular periarthritis, occurring against the background of an inflammatory process in the synovial capsule, muscles, ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- abnormalities in the structure of the shoulder that arose during intrauterine or postpartum development;
- systemic pathologies affecting connective tissue structures (lupus erythematosus);
- hypermobility of the shoulder joint;
- neuropathies - non-inflammatory nerve lesions of traumatic or non-traumatic origin;
- benign neoplasms, cancerous tumors, distant foci of the oncological process.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also prescribed to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. Surgeons monitor the rate of tissue regeneration, traumatologists and rheumatologists monitor the effect of pharmacological drugs.
The head of the humerus is affected by arthritis.
Why is MRI performed with contrast agents?
Doctors often need to determine the presence of an inflammatory focus in the shoulder joint. To do this, patients are given a contrast agent intravenously a few minutes before the examination. Most often, it contains a paramagnetic substance - the rare earth metal gadolinium, which is absolutely inert in relation to the body. MRI with contrast is performed if the following is suspected:
- neoplasms and metastases. Tumors are supplied with blood, which is clearly visualized in the resulting images. The use of a contrast agent helps to establish the origin of the tumor, the number of formed metastases, the degree of their penetration into neighboring tissues, and the characteristics of the blood supply;
- inflammation of the joint. Using contrast, you can detect small inflammatory foci in ligaments, tendons, and muscles. It is impossible to identify them during radiography;
- vascular pathologies. Some diseases of the shoulder joint develop due to insufficient supply of nutrients and biologically active substances to the tissues. The cause of the resulting deficiency is the poor condition of the veins, arteries and capillaries of the shoulder girdle.
“Doctors are hiding the truth!”
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day...
>
Before diagnostics using contrast, the patient is prescribed testing to establish sensitivity to a rare earth metal. Typically, gadolinium does not provoke any external or systemic side effects and is well tolerated by humans.
Technique of diagnostic procedure
No special preparation is required for an MRI. If contrast is used for diagnosis, it is advisable not to eat food for 1-2 hours. All items containing metals should be left in the pre-preparation room.
The diagnostician will inform you about the progress of the study and indicate how to contact him if your health worsens. Patients with mental disorders, claustrophobia or neurological disorders are advised to take tranquilizers or sedatives.
How to do an MRI of the shoulder joint:
- the joint being examined is covered with a special coil shaped like a hemisphere;
- The patient is placed in the tomograph in a horizontal position. Shoulder examinations using outdated equipment can be performed in a standing position, but most clinics do not use such installations;
- A layer-by-layer scanning of a joint takes about half an hour, and 40 minutes when using contrast. The patient should not move during the examination.
The procedure does not cause any discomfort. It is extremely rare for subjects to complain of dizziness, which is explained by being in a confined space.
Decoding
The radiation diagnostics doctor interprets the results obtained. Deciphering usually does not take more than 2 hours, but when the radiologist is busy, patients have to wait for results within 24 hours. What does an MRI of the shoulder joint show:
- inflammatory foci, destructive and degenerative changes in bones and hyaline cartilage are visualized as intensely colored areas;
- inflammation is indicated by cavities formed around the tissues;
- benign and malignant neoplasms look like areas with a denser structure. They are intensely colored and localized at the border between bones and muscles;
- when the ligaments rupture, there is a noticeable displacement of the torn parts into the articular cavity;
- overgrown edges of bone plates and calcified areas signal the irreversible destruction of cartilage tissue and the development of osteoarthritis;
- complete or partial fusion of the joint space indicates ankylosis (immobility of the joint) and the need for surgical intervention;
- the formation of sequestra (dead tissue) is a characteristic sign of infectious arthritis;
- the accumulation of fluid in the synovial bursa indicates bursitis, and the presence of effusion in the joint cavity indicates synovitis;
- changes in heat exchange, also determined during examination, accompany many diseases of the shoulder joint.
During interpretation of the results, the condition of the bone surfaces lined with cartilage tissue is assessed. Normally, there should be no obvious defects on them. Ligaments, tendons, nerve bundles, and muscle fibers located near the joint are also examined. Changes in soft tissue structures often indicate a low-grade inflammatory process.
Contraindications
MRI is the safest way to examine the shoulder joint. Unlike radiography, during diagnosis there is no unwanted radiation exposure to the human body. And an informative arthroscopic examination occurs when the integrity of the soft tissues is violated. But MRI has absolute contraindications:
- the presence of ferromagnetic or electronic implants;
- implantation of artificial heart valves;
- surgical implants located in one of the organs of the central nervous system, for example, hemostatic clips.
Surgical devices installed in other parts of the body do not serve as absolute contraindications to the study. But there is a possibility of distortion of the results due to artifacts (interference) formed under the influence of the magnetic field. The decision to use magnetic resonance imaging to detect a specific pathology is made by the radiologist.
The disadvantages of the diagnostic procedure include the rather high cost, the presence of serious contraindications, and the unavailability of equipment in sparsely populated areas. But the advantages of MRI far outweigh its disadvantages. The study is minimally invasive, absolutely safe and highly informative.
Source: https://sustavlive.ru/diagnostika/mrt-plechevogo-sustava.html
MRI of the shoulder joint: indications and contraindications for its implementation
If it is necessary to determine the cause of pain in the shoulder joint, the doctor will prescribe an x-ray or ultrasound. In cases where traditional research methods are unsuccessful, the patient is referred to an MRI of the shoulder joint. Magnetic resonance imaging is a high-tech way of obtaining images of tissues and internal organs. Diagnostic screening allows you to accurately determine the signs of pathology. In this article we will talk about who is recommended for an MRI of the shoulder joint, how the procedure is performed, and what contraindications there may be for prescribing the study.
The essence of the MTP method of the shoulder joint
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is actively used in modern medicine. MRI is an effective, very informative and safe method of instrumental diagnostics.
High intensity magnetic waves affect a specific area of the human body and influence the hydrogen atoms inside cells, causing them to move in a certain order.
Against the background of cell movement, energy is released.
A specially designed device scans these processes and creates a tomogram. A picture is displayed on the monitor screen, which the doctor can print on a special film.
To diagnose the shoulder joint, classical research procedures such as radiography or ultrasound are more often used. But MRI of the shoulder joint differs from traditional methods in its high accuracy and information content. This completely eliminates the impact of harmful ionizing radiation on the human body.
In some cases, gadolinium contrast agent is used to clearly determine the structure and size of pathological changes.
Benefits of MRI of the shoulder joint
- Unlike X-rays or CT (computed tomography), the influence of harmful radiation on the human body is completely excluded.
- MRI is an absolutely safe diagnostic method that does not cause adverse reactions in the body. There may be a risk of an allergic reaction when using a contrast agent.
- The procedure is minimally invasive and painless. Magnetic resonance imaging does not use ionizing radiation harmful to the body.
The main advantage of magnetic resonance technology is the high accuracy of the results.
MRI of the shoulder joint allows you to diagnose even the most minor pathological changes:
- In just one research procedure, a doctor can obtain complete information about the condition of all tissues of the shoulder joint, muscle tissue, tendons, and nerve fibers. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to diagnose vascular changes.
- The image clearly shows the boundaries between healthy and damaged tissues.
- 100% reliability of the result. Due to the complex structure of the shoulder joint, other diagnostic methods do not always accurately determine the area of pathological changes.
- The device records any tissue damage, necrosis, congestion, tumors, neoplasms of various etiologies, even at the initial stage of development. Other methods are not always so accurate and informative.
- MRI of the shoulder joint allows you to clarify the need for surgical intervention.
- Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to determine the area of bone tissue damage even in cases where radiography in two projections is unsuccessful.
- If all traditional methods of examining the shoulder joint are unsuccessful, MRI will help establish the correct diagnosis.
A significant advantage is the absence of age-related contraindications to the procedure. Tomography can be performed at any age. To ensure immobility and reduce mental stress, young children (up to 1 year) and patients suffering from claustrophobia are immersed in medicated sleep.
Source: https://www.salonveronika.ru/info/blog/mrt-plechevogo-sustava/
MRI of the shoulder joint: how and where it is done, what it shows, contraindications
MRI of the shoulder joints is one of the most expensive, but informative ways to diagnose the condition of the articulation of the corresponding bones. Doctors prescribe procedures only in cases where the problem cannot be solved using traditional X-rays or ultrasound.
The essence of the method
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a modern method of instrumental diagnostics. The essence of the technique is to expose a certain area of the body to high-tension magnetic waves. As a result of the corresponding influence, hydrogen atoms inside the cells are “lined up” in a certain order.
Against the background of the movement of these structures, energy is released, which is recorded by the apparatus with the construction of a tomogram. The doctor receives a picture on the screen with the ability to print it on a special film.
It is important to note that magnetic resonance imaging is qualitatively different from traditional x-rays and ultrasound, which are usually used to diagnose pathologies of the shoulder joint. MRI of joints eliminates the harmful effects of radiation and increases information content compared to ultrasound diagnostics.
The procedure can be performed with the use of a contrast agent (gadolinium) to increase information content.
Indications and contraindications
MRI is indicated when simpler methods of instrumental examination are ineffective. The procedure is expensive, so doctors prescribe it only when difficulties arise in diagnosing pathologies of the corresponding structure.
Indications:
- Injuries and mechanical damage to the cartilage, muscles, and ligaments of the shoulder joint. It is worth noting that MRI is more relevant for soft tissue diseases. Bone tissue is relatively difficult to visualize using nuclear magnetic resonance.
- Tumor process inside the joint.
- Diagnosis of infectious or reactive arthritis. Read more about arthritis →
- Pain syndrome in the shoulder joint of unknown origin.
Despite the high information content and demand for the technique, MRI is not indicated for all patients. The procedure affects any metals, which limits doctors in certain situations.
Contraindications for MRI (NMR) of the shoulder joint:
- Metal objects inside the patient's body that cannot be removed - pacemakers, prostheses, artificial heart valves, etc.
- Heart or kidney failure if a contrast agent is used.
- Pregnancy and children under 7 years of age.
- Claustrophobia. This contraindication is relevant when using closed-type tomographs (in the form of a tunnel).
- Tattoos using dyes containing metals.
Before performing an MRI, the doctor assesses the patient's condition and indicates whether the patient can undergo the appropriate examination.
What diseases can be diagnosed?
What does an MRI of the shoulder joint show and what can be detected with appropriate research? The technique allows you to evaluate the state of the joint in a comprehensive manner with the establishment of mechanical and functional changes.
Diseases that can be diagnosed using MRI:
- Inflammatory pathologies – bursitis, arthritis.
- Degenerative diseases of cartilage and ligaments (bundles of collagen fibers).
- Osteoporosis is a lack of bone tissue.
- Infectious arthritis.
- Joint tumors.
- Injuries, hemorrhages into the joint cavity.
In addition to changes in the anatomy of the shoulder joint, MRI shows the presence of indirect signs of functional disorders, which helps the doctor select adequate treatment.
Preparation
MRI is a procedure that does not require specialized training. The patient leads a normal lifestyle, which contributes to the person’s comfort and adherence to this technique. Only immediately before the examination, the patient is asked to remove all metal jewelry and objects to prevent deterioration in image quality.
When using a contrast agent, the patient should refrain from eating and drinking liquids 4-5 hours before the examination to prevent complications.
Additionally, it is necessary to establish the presence of an allergy to gadolinium. To do this, the patient is given a small dose of the appropriate substance.
If reactions such as urticaria or suffocation occur, further diagnosis is prohibited.
Carrying out the procedure
How is an MRI of the shoulder done? The procedure lasts 30 minutes, and when using a contrast agent - about an hour. After removing the metal jewelry, the patient lies down on a special table.
Key stages of the study:
- To prevent spontaneous movements of the limbs, the arms are secured with straps, and a soft cushion is placed under the head.
- The table slides into the tunnel (when using devices with a closed circuit).
- The patient lies quietly while the tomograph is working.
- After the procedure is completed, the patient goes home.
The person does not feel any discomfort during the examination. The patient can freely communicate with medical staff. The main thing is to avoid sudden movements to prevent image distortion.
The procedure for examining the right or left shoulder is no different for the patient. The doctor enters the necessary data into the computer to select a specific side of the body. The process is automated.
Decoding the results
Interpretation of the results is based on the doctor’s visual assessment of the resulting image. After constructing a computer tomogram, the doctor examines the pathological abnormalities and makes a diagnosis. Depending on the specifics of the work of the relevant departments, the patient can receive the result in 30 minutes or in 1-2 days.
Price
Where can I get an MRI of the shoulder joint? The procedure requires the availability of appropriate expensive equipment. In most cases, only large regional hospitals have the ability to provide patients with this diagnostic method. If desired, you can use the services of private centers.
The average cost of an MRI of the shoulder joint is 3,200 rubles. When contrast is used, the price increases.
Advantages and disadvantages
MRI is a modern method for diagnosing various diseases. The procedure has established itself as the optimal way to verify soft tissue pathologies inside the patient’s body.
Main advantages:
- No harmful radiation influences the human body, unlike traditional X-rays or computed tomography (CT).
- High information content. Modern technologies make it possible to identify the slightest deviations in the structures of the shoulder joint.
- Safety. The technique is not accompanied by the development of adverse reactions. The exception is episodes involving the use of a contrast agent. There remains a risk of allergy progression.
The negative aspects include:
- Impossibility of diagnostics in the presence of metal implants.
- Problems with the examination of patients suffering from claustrophobia. The solution remains modern open-circuit devices.
- Expensive. Not every patient can afford to carry out appropriate diagnostics, given the need for further medication.
MRI of the shoulder joint is an important diagnostic method widely used in practice. The procedure allows you to identify changes in the internal structures of the joint that cannot be determined in any other way. When used correctly, it is possible to quickly select adequate treatment and improve the patient’s condition.
Denis Volynsky, doctor,
especially for Ortopediya.pro
Source: https://ortopediya.pro/diagnostika/mrt/plechevogo-sustava.html
MRI of the shoulder joint
October 29, 2015 Admin Home page » MRI and CT of joints Views:
3279
MRI examinations of the shoulder joint use a powerful magnetic field to take detailed photographs of the bones, tendons, muscles and blood vessels in the shoulder joint.
This method is mainly used to assess sports, work-related and domestic injuries.
A special form of magnetic resonance imaging is MR arthrography. She uses contrast injections so the radiologist can see the structures inside the joint.
Indications for use of MRI of the shoulder joint
When is it necessary to do an MRI of the shoulder joint? This method is used for diagnosis in the following cases:
- degenerative joint diseases (arthritis)
- fractures
- rotator cuff disorders
- sports, domestic and work injuries
- infections (osteomyelitis)
- tumors and metastases involving bones and joints
- pain, swelling, or bleeding in and around tissues
- unexplained shoulder pain
- decreased mobility in the shoulder
- control after shoulder surgery.
What is MRI of the shoulder joint: video
Preparing for an MRI of the shoulder joint
It is required to notify the health care provider about the operations performed and any health problems. Like, for example, severe kidney disease. In this case, there may be restrictions on the administration of the contrast agent.
Women should be notified of the possibility of pregnancy.
Although the MRI procedure does not have negative consequences for pregnant women and the fetus, it is recommended to refuse the procedure in the 1st trimester of pregnancy if there are no serious reasons for undergoing it.
Metal items must be removed. Jewelry, watches, hair clips, metal zippers, hearing aids, and removable dentures can cause image distortion.
Do not perform an MRI if the body contains: a cochlear (ear) implant, clips used for the brain of an aneurysm, some types of metal coils placed in blood vessels, cardiac defibrillators and pacemakers, shrapnel, bullets and other pieces of metal that may have remained after some or previous accidents.
How to do an MRI of the shoulder joint
To perform the examination, you will be asked to sit on a mobile table. To fix the patient's position, they can be secured with belts and bolsters. This will help you maintain the required position during the examination.
If a contrast agent will be used, your healthcare provider will inject it into a vein in your arm.
After this, the table moves into the magnetic block of the device. The provider performs the test outside the room.
The procedure consists of several stages. Depending on the procedure and the tomograph, it lasts from fifteen to forty-five minutes.
An MRI scan is painless. However, some patients may experience discomfort. You will be fitted with headphones to reduce the intensity of the sounds produced by the machine. When undergoing an MRI with contrast, the intravenous needle may cause some discomfort. There may be some slight irritation on your skin where the tube inserted. A number of patients feel a metallic taste in the mouth after injection of the drug. Sometimes allergies or nausea from the contrast may occur.
It is important that you remain still. The provider can hear and talk to you using two-way communication.
Benefits of MRI
- Non-invasive method (unlike X-ray angiography and CT).
- Valued in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases, including muscle and bone pathology
- Helps determine when shoulder injuries require surgery
- Allows diagnosis of a bone fracture if the results of x-rays and other examinations do not provide an accurate analysis
- MRI allows you to detect bone abnormalities that were hidden by other research methods
Contrast agents used in MRI are less likely to cause allergies in the patient than, for example, iodine-based drugs for conventional X-rays and CT scans.
Contraindications for MRI of the shoulder joint
- High quality tomography images will be achieved only if you remain completely still during the examination. If the patient is afraid of something, he is in severe pain, and it is difficult for him to lie still, then it will be very difficult to obtain high-quality images.
- Too much weight that will not allow the patient to fit in the tomograph.
- The presence of an implant or other metal objects in the body. Their presence will not allow you to obtain the desired images or may cause harm to your health.
- Pregnant women are advised not to undergo an MRI procedure in the first trimester.
Basically, MRI is performed on tomographs with a power of at least 1.5 Tesla. Images can be constructed as regular flat or three-dimensional.
The images are provided to the patient in 3 projections – oblique coronal, sagittal and axial. Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder is performed without the use of contrast.
After receiving the images, the specialists who conducted the examination will interpret the scan results. As a rule, the patient receives such a conclusion and images 1-2 hours after the examination; sometimes the interpretation can be completed within 24 hours. With the conclusion and photographs, the patient must contact the doctor who referred him for such an examination.
What does and what can be detected on an MRI of the shoulder joint
After deciphering the results, the specialist draws up a conclusion, which will indicate the features of the anatomical structure, as well as deviations from the norm. Such deviations may be:
- detection of tumors, growths
- detection of inflammatory or infectious processes
- detection of fluid accumulation
- damage to ligaments, tendons, and cartilage is detected
- identification of multiple injuries, as well as signs of bone destruction.
Most often, MRI of the shoulder is used in traumatology. In everyday life and sports, joint injuries are not uncommon: fractures, cracks, dislocations, displacements, hematomas.
MRI allows you to see and examine bone structures, tissues, and tendons. An MRI of the shoulder joint makes it possible to determine the nature of the displacements and damage that occurs and determine the need for surgical intervention. Inflammatory processes occurring in the joint are available for diagnosis; the presence of sprains and bruises of the soft tissues surrounding the joint is determined.
In cases of studying tumors in the shoulder area, the patient is administered a contrast agent intravenously. Since tumor formations have a well-developed system of blood vessels, after spreading and accumulation of contrast in the bloodstream, the examination area becomes colored, and the visibility of the tumors increases.
In this way, the location and size of tumors can be determined. The difference between malignant and benign tumors and the presence of metastases can be very clearly determined. Typically, drugs containing gadolinium ions are used.
Tomography using contrast agents is carried out after a little preparation of the patient and an analysis to determine whether the patient is allergic to contrast. The drug is eliminated from the body within one or two days and is harmless to the patient’s health.
However, for people with kidney failure, such a procedure will be contraindicated, as it may cause a deterioration in the patient’s condition.
The cost of an MRI of the shoulder joint using a 1.5 Tesla machine is approximately from 3.5 to 5.5 thousand rubles. If contrast is used or an MRI procedure is performed on devices of higher power, the cost of the procedure will be higher. It should be noted that images from tomographs with higher power differ not only in price, but also in higher quality.
MRI today is a completely harmless, painless and reliable way to diagnose a wide range of diseases in various areas of the human body, including joints.
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS AND VOTE
(3
Source: https://tomografpro.ru/mrt-sustavov/mrt-plechevogo-sustava.html
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the shoulder joint - examination procedure, contraindications, what it shows
The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the body, so magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder joint is considered a popular procedure. It visualizes the condition of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus, bone structures, cartilage, and blood movement in the shoulder.
The anatomy of the human structure is such that pain can radiate from different origins, therefore tomography is carried out both of one shoulder and in combination with the cervical spine.
The price of diagnostics depends on this, so it is impossible to answer unequivocally how much the examination costs.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are detected by different research methods. If you ask doctors, CT scan or better MRI, most will give preference to resonance imaging.
Firstly, it is safe and does not irradiate the body, and secondly, it is much better at recognizing the pathology of soft tissues and neoplasms at the initial stage. Arthroscopic reconstruction is performed only based on the results of MRI, as a more reliable method of examination.
No preliminary preparation is required for diagnosing the shoulder joint without intravenous contrast.
Often, magnetic resonance imaging allows one to avoid such unpleasant procedures as puncture and biopsy, and measurement of intraosseous pressure. The accuracy of the data obtained reaches 95%.
Get an MRI of the shoulder joint at the MIRT clinic
A lot of questions arise from our patients - whether tomography is done in childhood, how long the examination lasts, when diagnostics are prohibited, etc. First things first.
Indications and contraindications
If there is pain without pathologies, which intensifies with movement, flexion-extension, physical activity and at rest, but it is not known where the source of pain is hidden, then this is a reason for an MRI of the shoulder joint. Other indications are:
- stiffness in hand movement;
- crunching, crackling in the limb when bending, turning;
- shoulder injuries - dislocations, fractures, ligament tears, joint falling out of the bag, sprains;
- swelling, swelling, redness of the skin around the joint;
- suspicion of vascular pathologies. Around the shoulder, the condition of the blood vessels, veins and arteries deteriorates, so nutrients do not reach the joint.
- The examination is prescribed by surgeons as preoperative preparation and to monitor tissue regeneration after operations, by traumatologists and rheumatologists to monitor the therapy performed.
- The list of contraindications is standard - magnetic metal components in the body, first trimester of pregnancy, pacemakers, tattoos on the body made with metallic inks.
- The doctor at our clinic may refuse a contrast scan in case of chronic liver and kidney diseases, as well as an allergy to gadolinium, but these conditions are rare and usually an MRI of the shoulder joint is well tolerated.
It is worth noting that the MIRT clinic has unique equipment that allows it to examine overweight people. Claustrophobia, childhood, nervous system disorders and hyperexcitability are not prohibitions to tomography.
Preparation
Preliminary preparation is required only for MRI of the shoulder with contrast. It is advisable to have a light snack the day before - this is necessary in order to prevent unwanted nausea during the administration of gadolinium.
Before entering the office, the patient puts on a disposable medical gown, turns off the phone, and takes off his watch, hairpins, and jewelry.
How to do an MRI of the shoulder joint
The procedure goes as follows:
- the patient lies down on the couch, covers the shoulder with a special coil to concentrate the magnetic field;
- If necessary, contrast is injected into the vein or directly into the articular bursa.
- the table slides into the machine so that the upper part of the body fits into the machine, and scanning begins. During the examination, you need to lie still so that the clarity of the layer-by-layer images is not distorted. The procedure does not cause any discomfort, but in extreme cases the patient can stop the scan and report discomfort via two-way communication;
- at the same moment, the doctor behind the glass observes the process. The tomograph processes sections in the coronal, sagittal, axial and oblique planes in different programs, then the images are sent to the doctor’s computer for processing and evaluation of changes.
Sometimes MRIs of the shoulder joint will be supplemented with contrast enhancement. Indications for the administration of gadolinium-based drugs are suspicion of oncology and the growth of metastases, vascular pathologies.
The fact is that neoplasms are well supplied with blood, and when gadolinium is concentrated in the circulatory system, it brightly colors the tumor.
Thus, the number of metastases, the boundaries and size of the tumor, and the degree of spread to surrounding tissues are determined.
The average duration of the examination is 40-60 minutes, depending on the use of contrast.
What does an MRI of the shoulder joint show?
During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to the components of the shoulder joint:
- labrum;
- rotator cuff;
- biceps muscle and its tendon;
- head of the humerus;
- coracoacromial ligament;
- deltoid muscle;
- intra-articular fluid;
- coracoid process;
- collarbone;
- subdeltoid and subacromial bursae;
- tendons, bones and other connective tissue structures.
The specialist conducts a detailed examination of the tissue structure and evaluates motor activity disorders. Normally, the surface of the bones, lined with cartilage, should not have defects.
It is worth considering if there are intensely colored areas and cavities, changes in soft tissue structures - they signal inflammation. Dense structures with intense coloration indicate swelling between the bones and muscles.
Ligament rupture can be recognized by disruption of their structure, integrity, and displacement of parts. The doctor diagnoses osteoarthritis if the image shows overgrown edges of the bone plates. Rarely, partial or complete fusion of the shoulder joint space is possible.
This is what ankylosis looks like.
In the picture you can find:
- hypermobility of the shoulder joint;
- infectious infection - synovitis, bursitis, osteomyelitis, etc.;
- inflammatory processes in the surrounding muscles, ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- degenerative-dystrophic changes - different types of arthritis, gout, osteoarthritis, etc.;
- rotator cuff injury;
- nerve inflammation;
- malnutrition of bones with and without necrosis;
- hematomas, bleeding into the joint cavity;
- accumulation of exudate in the joint cavity;
- neoplasms of benign and malignant types;
- neuropathy associated with damage to nerve trunks;
- rotator cuff tears.
The procedure for decoding the received images takes 1-2 hours. At this time, the radiologist compares the normal values with the detected changes and records them in the description. The specialist only interprets the results, and the attending physician is responsible for establishing the diagnosis.
Where to get an MRI of the shoulder joint in Kostroma
Residents of Kostroma do not need to look for a medical center where MRIs are performed. In the very center of the city on Sverdlova, 8, the MIRT clinic has been opened. Experienced doctors, modern equipment, and competitive prices attract many visitors.
The clinic is open from 8 am to 11 pm, so it is not difficult for the patient to choose the optimal hour and date of appointment. Registration is carried out by phone and electronically on the website.
Source: https://mirt-med.ru/departments/diagnostika/mrt-plechevogo-sustava/