An important organ in the human body is the thymus gland. Its work is disrupted in various pathologies. Diseases of the thymus negatively affect the immune system. The body's defenses weaken.
As a result, people become less resistant to the influence of unfavorable environmental factors and get sick more often. Pathologies can be identified using ultrasound of the thymus.
After receiving the results, specialists make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A little bit of anatomy
The thymus is an endocrine gland. It is a small organ located in the chest area behind the sternum (in the upper part of the anterior mediastinum). The thymus gland consists of two lobes. They vary in size. The lobes are attached to each other due to a layer of connective tissue.
Thymus in newborns and adults
The role of this gland is enormous. The thymus produces several hormones that participate in the development of the body's immunological reactions and stimulate the formation of antibodies. Another function of the organ is to control the development and distribution of lymphocytes.
Ultrasound of the gland - a method of accurate diagnosis
Ultrasound examination is a highly informative diagnostic method. With its help, the condition of various internal organs and tissues is studied. Very often, children and adults are prescribed ultrasound:
- hearts;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- brain;
- kidney;
- pelvic organs;
- thyroid gland.
This list can also include ultrasound examination of the thymus. An ultrasound of the thymus gland is performed to assess its size. The volume and mass of this organ are also calculated.
Indications for examination
Ultrasound examination of the thymus is sometimes prescribed for young children. Indications for ultrasound before the age of 1 year are:
- severe diathesis;
- severe dysbacteriosis;
- other immune system disorders.
Diathesis in a child
For older children and adults, such a study is prescribed in the following cases:
- with frequent colds, aggravated by bronchitis, sinusitis, pneumonia;
- with enlarged lymph nodes in children;
- in the presence of a pronounced vascular cell on the chest;
- with a strong predisposition to allergies;
- with general weakness, fatigue, pain for unknown reasons in the chest area.
Pros and cons of the study
Ultrasound examination of the thymus has many advantages:
- no radiation exposure;
- affordable price for examination;
- no need to use contrast agents;
- quick results.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound. During the procedure, some people report a feeling of cold. Discomfort occurs due to the pressure exerted by the ultrasonic sensor. If the skin is hypersensitive, the ultrasound procedure is quite unpleasant, but it does not pose any danger.
Preparing for the examination
Ultrasound of the thymus gland is performed at a time prescribed by specialists. No special preparation is required. However, one nuance is still worth taking into account.
If an ultrasound is prescribed for a child, then he should be reassured before undergoing the examination, because due to anxiety and fear, the thymus gland may not be measured accurately.
You can also try to distract your little patient with toys while the scan is being performed.
When going for an examination, it is recommended to wear comfortable clothing that can be quickly unbuttoned and removed. You should take a small towel or napkins with you. They are useful for wiping traces of gel from the chest after an ultrasound examination.
How is the examination carried out?
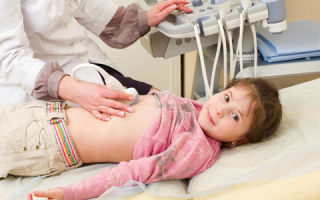
The examination of the thymus gland is carried out using an ultrasound machine. To perform scanning, a linear sensor with a frequency of 7.5 to 12 MHz is used. The patient undergoing the examination is required to stand while the specialist performs the scan.
Ultrasound of the unchanged thymus gland in newborns: a – frontal scan, cross-section of the gland (the outline is outlined in a dotted line).
During an ultrasound, the width of the thymus is measured. To do this, the sensor is placed transversely in the projection of the upper third of the sternum. Sometimes it has to be shifted significantly down. This is done by specialists in cases where the thymus gland is significantly enlarged.
The length and thickness of the thymus lobes are also determined. The measurement is carried out by longitudinally positioning the knot sensor parasternally on the left and opposite side of the upper part of the sternum. In general, the thymus assessment takes no more than 10 minutes.
Ultrasound of an organ in childhood
The thymus begins to develop in the fetus at the 6th week of a woman’s pregnancy. In the 3rd trimester, this organ is already fully formed. It begins to function before the baby is born. After birth, some children are prescribed an ultrasound of this organ to identify pathologies.
Indications for the study
Sometimes specialists, when performing an X-ray of the chest organs of a child, notice that the size of the thymus gland does not correspond to the norm. Suspicion of enlarged thymus syndrome serves as the basis for an ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound of the thymus may also be prescribed if there are signs of reduced immunity. For example, an examination is necessary if the child’s body temperature remains at 37.1-37.5 degrees, and there are no signs of the development of any diseases. An ultrasound examination is necessary if there are indirect signs of an enlarged thymus gland - shortness of breath, heart rhythm disturbances.
Features of ultrasound
During the scan, newborns are placed on their back and a small cushion is placed under their neck. Children over 2 years of age are examined in a standing position. If the child is worried, he is allowed to sit on his mother’s lap facing the specialist performing an ultrasound scan of the gland.
Norms and results of the study
In the absence of any pathologies, the thymus gland in children looks like a formation with average echogenicity. The norm is smooth contours, uniform structure. The organ is also characterized by a clear demarcation from soft tissues and other structures of the anterior mediastinum. At the posterior part of the thymus there is a smooth border.
When scanning, specialists determine the width, length, and thickness of the lobes. Then, taking into account the data obtained, the volume of each lobe and the thymus gland as a whole is calculated. The following formulas are used:
- Volume of the right (left) lobe = X * Y * Z * 0.523, where X is the length (in cm), Y is the width, and Z is the thickness of the measured lobe.
- The volume of the thymus in children = the volume of the right lobe + the volume of the left lobe.
The next stage is calculating the mass of each lobe and the thymus, determining the thymic index (TI). Experts use the following formulas:
- Mass of the right (left) lobe = X * Y * Z * 0.704.
- Thymus mass = right lobe mass + left lobe mass.
- TI in children = Thymus mass / Child body weight * 100%
The resulting thymic index is compared with special tables. After this, appropriate conclusions are drawn: whether the norm has been achieved, whether there are deviations.
Table. Centile distribution of thymic index
| Patient age | TI, % | TI (centiles, %) | ||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | ||
| Newborn | 0,18−0,66 | 0,18 | 0,19 | 0,26 | 0,35 | 0,42 | 0,51 | 0,66 |
| From 1 to 3 months | 0,24−0,73 | 0,26 | 0,34 | 0,38 | 0,49 | 0,58 | 0,67 | 0,72 |
| 4 to 6 months | 0,13−0,58 | 0,14 | 0,21 | 0,24 | 0,31 | 0,39 | 0,49 | 0,57 |
| From 7 to 12 months | 0,13−0,57 | 0,14 | 0,17 | 0,21 | 0,26 | 0,31 | 0,40 | 0,53 |
| From 1 year to 4 years |
0,08−0,37 | 0,08 | 0,10 | 0,14 | 0,19 | 0,25 | 0,32 | 0,36 |
Conclusions:
- From 3 to 25 centile – value below average. The size of the thymus gland does not correspond to age. They are smaller than normal.
- From 25th to 75th centile. The values included in this interval correspond to the norm.
- From 75 to 97 centile and more. These values are higher than normal. Diagnosis: thymomegaly (enlargement of the thymus gland) degree I, II or III.
Ultrasound indicators in adults: norms and deviations
Thymus pathology can be diagnosed in a child by a pediatrician when signs of weakened immunity appear. In adults, an enlargement of the thymus gland is detected randomly during an X-ray examination of the lungs or heart.
When scanning, this organ is visualized as small in size. With age, glandular cells are replaced by adipose tissue. After 50 years of age, the thymus gland can no longer be visualized using ultrasound. This is the norm.
Thymus pathologies
One of the serious problems related to the thymus gland is thymomegaly. Medicine does not know why exactly this pathology occurs in children and adults. Experts suggest that the development of the disease is influenced by predisposing factors such as birth injuries, prematurity, and malnutrition.
Thymomegaly (dotted line) in newborns due to severe illness
Clinically, thymomegaly is manifested by the following symptoms:
- long-term course of infectious diseases (due to decreased immunity);
- shortness of breath, cough, noisy breathing (due to compression by the enlarged lobes of the thymus of the vagus nerve, trachea, superior vena cava);
- decreased appetite (due to disruption of metabolic and endocrine processes occurring in the body).
Thymomegaly is not easy to diagnose. Examination of the thymus gland is difficult due to the presence of insurmountable obstacles in the path of ultrasound - lung tissue and sternum bone. Despite this, such examination is still prescribed by specialists. During it, the linear dimensions of the thymus are determined. If they are larger than normal, then this indicates the presence of thymomegaly.
Tumors are sometimes detected during an ultrasound. They have a hypoechoic structure. Neoplasms stand out well against the background of healthy tissues of the mediastinum in children and adults. However, ultrasound is slightly inferior to computed tomography in detecting tumors.
Further actions
With a slight increase in the thymus, patients do not need special treatment measures. A balanced diet and the exclusion of strong stressful stimuli are what experts recommend for this pathology. Babies in the first year of life should be fed mother's milk. Children who are bottle-fed should be given the following diet: fermented milk or adapted formulas.
With severe hyperplasia or enlargement of the thymus (thymus gland), patients are prescribed drug therapy. Antihistamines, immunomodulators, and vitamins are prescribed.
If symptoms of compression of other organs or acute thymus-adrenal insufficiency are detected, then hormones are used. For tumors, the main treatment method is surgery.
Many researchers also recommend radiation therapy after surgery.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the thymus gland can be examined in different ways (using radiography, computed tomography). The simplest and safest of them is ultrasound of the thymus. In addition, this method is quite informative. Thanks to it, you can notice the enlargement of the organ and visualize tumors.
Source: https://uziprosto.ru/ultrazvuk/grudi/uzi-vilochkovoj-zhelezy-chto-eto-takoe-rezultaty-obsledovaniya.html
Why do ultrasounds of the thymus (thymus gland) be done for children and adults and what does the norm look like?
Home › Chest
07.05.2019
Ultrasound of the adult and pediatric thymus gland involves exposure to ultrasonic waves. The examination does not irradiate the body and does not cause harm. It helps to identify any negative changes in the thymus, which are often the cause of reduced immunity.
What does the thymus look like in adults and children?
The thymus is located in the chest cavity, under the anterior wall, in the center of the sternum. It takes part in immune processes by cloning and differentiating (training) immune T cells. The organ is most active in children under 5 years of age. With age, the thymus gland gradually loses its importance.
The organ got its name because of its shape. When healthy, it resembles a fork with two prongs. A damaged thymus usually looks like a butterfly.
In children, the thymus gland is well defined and easily visible on ultrasound. It has a pinkish-gray color. Over time, the organ involutions (degrades) and atrophies. By the age of 30, the thymus gland acquires a yellowish tint. After 10–15 years, it significantly decreases in size and completely ceases to perform its functions.
Previously, doctors preferred to examine the thymus gland using x-rays. Unlike ultrasound of the thymus gland in adults and children, x-rays irradiate the body.
What can a gland examination reveal?
Ultrasound of the thymus is an examination that allows you to identify a number of diseases and begin their treatment in a timely manner. In most cases, the procedure is prescribed for children:
- abnormal development of the thymus gland;
- DiGeorge syndrome;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- Bernard-Horner syndrome;
- thymomegaly (enlargement of the thymus gland);
- underdevelopment of the thymus (aplasia);
- Nezelof's syndrome.
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor pays attention to a number of parameters. They allow you to determine the correct development of the thymus gland:
- sizes (the parameter is checked in accordance with age standards);
- organ tissue structure;
- contours of the thymus.
Indications for the study
Ultrasound of the thymus in children has no contraindications. The diagnostic method does not have a negative effect on the body.
An ultrasound of the thymus gland is necessary if there are symptoms indicating improper functioning of the immune system. This is especially important for children.
Indications for ultrasound of the thymus gland:
- a person suffers from acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections more than 10 times a year;
- colds are severe;
- frequent complications of colds (pneumonia, sinusitis, etc.);
- frequent allergic reactions that occur when foods that act as irritants are excluded from the diet;
- unreasonable increase in temperature several times a month;
- the appearance of a network of blood vessels in the chest area;
- signs of lymphadenitis in the fossae under and above the collarbones;
- muscle weakness;
- abnormally rapid weight gain;
- frequent regurgitation and heavy breathing in children under one year of age;
- symptoms of bronchial asthma;
- increased fatigue, lethargy;
- arrhythmia and chest discomfort;
- enlarged tonsils and adenoids.
Ultrasound of the thymus gland is mandatory for premature babies and people in whose family there have been cases of sudden death.
Some doctors believe that a study of the thymus gland should be done before DTP (complex vaccination against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus). If an ultrasound shows negative changes in the thymus, the vaccination will have to be postponed.
Dr. Komarovsky talks about the thymus gland in children in his program:
How to prepare for the examination
Preparation for an ultrasound examination is minimal. The procedure is carried out at any time of the day. Before the examination, it is important to know the patient's weight. Depending on the indicator, the normal weight of the thymus gland is determined.
Take with you a diaper for the couch and paper towels to remove any remaining gel. In paid clinics, all supplies are issued on the spot.
When examining a child aged 3 years and older, he needs to be explained in advance how the procedure will take place. This will help the baby not to worry during the ultrasound.
For more information about the procedure, watch the video:
How is the procedure performed?
Ultrasound is one of the most popular methods for checking the condition of internal organs. The procedure lasts only 10–15 minutes. This time is enough for the doctor to study the condition of the thymus in detail.
Ultrasound examination of the thymus gland in adults and children has several differences:
- The patient undresses to the waist. All jewelry is removed from the neck.
- The doctor asks the patient to take the desired position. Children under one year old are held in the arms of their parents during the procedure. A child under 13 years of age lies down on the couch. Adults stand or sit during the procedure.
- The doctor applies a special gel to the chest.
- The specialist moves a sensor across the chest and examines the image that appears on the screen.
- Once the ultrasound is complete, the gel is removed from the patient's chest.
See below for what the thymus looks like on an ultrasound:
Interpretation of diagnostic results
Ultrasound checks the weight of the thymus gland in children, which is normally 0.18–0.38% of body weight. The weight of the thymus also depends on the age of the patient:
| Age | Gland mass per 1 kg of weight | Width of shares | Lobe thickness | Length of beats | |||
| left | right | left | right | left | right | ||
| up to 1 g | 4.2 g | 3–9,2 | 2,7–9 | 0,6–3,2 | 0,7–3,3 | 0,4–1,8 | 0,4–1,6 |
| from 1 g to 5 | 2.3 g | 5–15,1 | 6,1–11,3 | 1,4–3,5 | 1–4,2 | 0,8–2 | 0,9–1,9 |
| from 6 to 10 | 1.2 g | 5–13,6 | 6,6–11,8 | 2–3 | 2–3,4 | 06, –1,7 | 0,6–1,9 |
| from 11 to 15 | 1 g | 8,5–12,5 | 7,3–15,6 | 2,5–2,7 | 1,6-3,4 | 0,7 –1,3 | 0,6–1,6 |
| from 16 to 25 | 0.5 g | 7,1–13,8 | 7,1–9,9 | 1,5–2,5 | 1,5–2,9 | 0,6–1,4 | 0,6–1,2 |
In people aged 25 years and older, there is normally 0.3 g of gland per kilogram of weight. If the indicator significantly exceeds the norm, then thymomegaly is diagnosed (usually with this disease the thymus gland has an irregular shape). A reduced volume indicates aplasia.
The contours of the normal thymus are clear. In the image of a healthy patient there is a curved light stripe, the gland itself is a uniform gray color, its shape is clearly visible in the image and is separated from other organs.
Abnormal development of the thymus is easy to determine from an image. The organ in the photo has an irregular shape and unclear boundaries. The presence of light and dark spots in the gland also indicates problems. For example, darker spots with clear boundaries are characteristic of tumor formations.
How much does the examination cost?
Ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus in paid clinics will cost from 1000 to 2000 rubles. The cost depends on the pricing policy of the establishment. In government institutions, ultrasounds are performed only on the direction of a doctor. In this case, the examination is carried out free of charge.
Ultrasound of the thymus gland is a safe procedure that, if indicated, is prescribed at any age. It does not have a negative effect on the body and does not require special preparation.
Have you encountered ultrasound of the thymus gland? Did the procedure help in making the diagnosis? Share your experience in reviews and articles on social media. networks. Be healthy.
Why do ultrasounds of the thymus (thymus) be done for children and adults and what does the norm look like? Link to main publication
Source: https://uziman.ru/grudnaya/uzi-vilochkovoj-zhelezy
Ultrasound of the thymus gland: indications for examination and its results
Ultrasound diagnostics is becoming increasingly popular. This method is highly informative. Moreover, this is the most accessible research method. It is his help that is resorted to if difficulties arise with making a diagnosis. Almost all organs, including the thymus gland, are examined using ultrasound.
For some diseases, it is very important to examine the thymus gland
What is ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnostics involves a painless and non-invasive research method. It is worth noting that this is the most informative diagnostic method. However, he was not always like this. For example, 20 years ago it was used exclusively for one purpose - to identify sand and kidney stones.
During the research, special equipment is used. The sensor, which is moved by a specialist over the area under study, transmits the image to the monitor. They get a fairly clear image that allows you to see the smallest details.
Consequently, the doctor has the opportunity to notice even those pathologies that are in the initial stages of development. It is noteworthy that this is extremely important for diagnosing not only ordinary pathologies, but also neoplasms.
That is why, if cancer is suspected, doctors also prescribe this examination.
When is an ultrasound of the gland performed?
The thymus gland is scientifically called the thymus. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of this gland. It is this small organ that provides the body's resistance to various infections.
Consequently, any deviations in the functioning of the thymus are extremely dangerous. If the doctor suspects that the patient has any problems with the functioning of the thymus, he will definitely prescribe an ultrasound diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the thymus gland in adults is a fairly common procedure.
An ultrasound scan of the thymus is indicated for frequent colds.
Indications for it will be:
- The patient quite often seeks medical help to recover from various colds.
- A person very often suffers from diseases such as bronchitis, sinusitis or pneumonia.
- If we talk about preschool children, their alarming symptom is a sudden enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- The vascular pattern in the chest area also indicates that a pathology affecting the thymus gland is rapidly developing in the body.
- Frequent allergies, severe fatigue and weakness, as well as fatigue indicate the development of thymus diseases.
If a patient comes to the clinic and complains of similar symptoms, the doctor necessarily recommends that he undergo an ultrasound examination. After all, only with its help can this diagnosis be confirmed or refuted.
Sometimes problems with the thymus gland can be indicated by fatigue and fatigue.
How to prepare for the procedure
There can be no talk of any special training. However, doctors remind that immediately before the study it is necessary to inform the specialist exactly what medications the patient is taking.
Even if you do not use synthetic drugs, but replace them with conventional dietary supplements, you need to inform your doctor, since they may slightly distort the results obtained.
Of course, the best option in this case is to stop taking any medications. However, if this is not possible, you should simply inform your doctor. Because he will take this into account when making a diagnosis.
Ultrasound is performed using a special device; no special preparation is required for the procedure.
How is ultrasound performed?
The order of the procedure is as follows:
- The specialist applies gel to the test site. This is a special substance that does not cause allergies and helps obtain a clearer image.
- The specialist passes the sensor over the area under study. This sensor uses high frequency sound waves to penetrate layers of tissue.
- The sound echo that is created is reflected from the organ that is being examined and goes to the equipment.
- An image of the organ being examined is then displayed on the monitor screen, which allows you to assess its condition.
The duration of the procedure is approximately 20 minutes. Immediately after its completion, the patient can return to the normal rhythm of life.
On a special monitor, the doctor can see the condition of the gland during an ultrasound scan.
What indicators are normal?
To identify a disease, it is necessary to understand which conditions are normal and which are not. That is why doctors have developed certain standards. It is believed that deviation from the figures indicated in the table is pathological.
Width (mm)Length (mm)Thickness (mm)| 30-40 | 35-50 | 17-25 |
Such indicators should be normal on ultrasound of the thymus. It is noteworthy that the size of the thymus remains virtually unchanged during adolescence. However, if the study is carried out on a child, the doctor pays much more attention to studying the size of the thymus. Because even the slightest deviation from the norm may indicate a developing disease.
Want to learn more about thymus ultrasound? Then watch this video:
What pathologies are detected
As a result of the study, it is possible to identify:
- DiGeorge syndrome is a fairly rare disease that is accompanied by a decrease in the activity of T-lymphocyte production.
- Nezelof syndrome - this disease is usually classified as a primary immunodeficiency disorder.
- Ataxia-telangiectasia - this disease is most often diagnosed in young children. However, the most pronounced symptoms do not manifest themselves immediately, but when the child begins to walk.
- Bernard-Horner syndrome is the most severe disease. Because its treatment requires a thymus transplantation operation.
In addition, as already written above, ultrasound diagnostics helps determine the nature of neoplasms on the thymus.
Tumors in this organ often appear, while cancerous ones are not so common.
Can everyone have an ultrasound?
This research method has no contraindications. Therefore, it can be used to diagnose not only adults, but also children. But ultrasound of the thymus gland in children is especially important.
Children also often undergo ultrasound examinations of the thymus gland.
However, it is necessary to take into account the presence of factors that may affect the effectiveness of the study. Such factors include excess weight, the presence of skin diseases, burns and open wounds.
Did the article help? Rate it (No Ratings Yet) Loading…
Source: https://infouzi.ru/ultrazvukovoe-issledovanie/brjushnaja-polost-2/vilochkovaja-zheleza.html
Indications for ultrasound of the thymus gland
The thymus gland, or thymus, is a small but very important organ. It consists of two lobes and is located behind the sternum.
Here, maturation, differentiation and “training” of T-lymphocytes take place, which are directly involved in the fight against foreign agents, while ignoring “native” cells.
The main function of the thymus is immunological; if the organ’s functioning is disrupted, immunity also decreases.
In order to determine the immune status, they resort to ultrasound of the thymus (thymus gland). This is such a simple, informative, safe and comfortable study that can be done at any age.
If an enlarged thymus gland was detected in childhood (which usually goes away with growing up), then an adult needs to regularly check this internal secretion organ using ultrasound diagnostic tools.
Why are they doing it? Indications and contraindications
If an adult or child constantly has colds, allergic reactions, or constantly enlarged lymph nodes, this may indicate reduced immunity. The patient is referred for an ultrasound scan of the thymus. By studying its size, structure, homogeneity, the doctor judges the functionality of the organ, the absence or presence of pathologies.
If the functioning of the gland in question is disrupted, immune dysfunctions may occur in adults, which are especially dangerous during pregnancy. Due to a malfunction of the immune system, the body begins to produce T-lymphocytes incorrectly.
It is especially important to monitor the condition of the thymus during pregnancy week by week. Its increase is a sign of an inflammatory process occurring in the expectant mother’s body. Many neonatologists associate developmental disorders, fetal heart defects and premature birth with inflammation.
Indications for ultrasound of the thymus gland in children under one year of age:
- symptoms of dysbiosis;
- diathesis that is difficult to treat;
- other skin rashes;
- persistent low-grade fever;
- enlarged adenoids and lymph nodes;
- intense weight gain;
- other signs of reduced immunity.
For older children and adults, thymus scanning is recommended for:
- frequent colds that develop into complications;
- vascular network on the chest;
- predisposition to allergies;
- fatigue, weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, pallor;
- unstable heart rhythm;
- pain in the sternum of unknown etiology.
Preparation
There is no need to prepare specially for the ultrasound scanning procedure of the thymus. The patient only needs to take a towel with him to remove the gel from the skin and put on comfortable, easily removable clothing. While examining the organ, the doctor will move the sensor, so the patient’s clothing should have a wide neckline or a comfortable fastener that allows you to adjust its depth.
How is the examination carried out?
An ultrasound of the thymus is performed using a special device. Its emitters form a sound wave of a given frequency. Penetrating inside the human body, it is reflected from obstacles encountered along the way - internal organs located behind the sternum, and returns, transmitting to the screen visual information about what the organ itself, as well as the tissues and joints surrounding it, look like.
The thymus gland is checked using ultrasound using a special sensor that performs the functions of an emitter of sound pulses and a transducer (converter) simultaneously.
During the procedure, the sensor is located in the area of the sternum, behind which this organ is located.
To obtain an accurate image, the sonologist uses a medical gel, which is applied to the patient’s skin in the area of contact with the contact surface of the device.
When conducting an ultrasound examination prescribed by specialists, the following is determined:
- the size of the organ, which depends on the age of the patient and is checked against the normal values from the table;
- structure and contours of the gland;
- foreign formations and inclusions.
Based on the information received, the specialist fills out a research protocol.
To kid
Ultrasound of the thymus in older children is usually performed, as in adults, standing. Babies aged 9 months to one and a half years can sit. In newborns, ultrasound of the thymus is performed in the supine position. During an ultrasound, which takes no more than 10 minutes, gland pathologies are detected in infants, older children and adults. They are judged by its size.
For adults
Adults are most often in an upright position during the examination. The doctor tries to study different parameters of the thymus:
- length;
- width;
- thickness;
- structural and functional characteristics.
To solve this problem, a sensor with an ultrasonic attachment is placed in the upper third of the sternum and moved in different directions.
Norms and decoding
All results are recorded in a special protocol for ultrasound examination of the thymus gland.
The basis of the study is to determine the size, volume and mass of the thymus. Metric characteristics (length, width and thickness) are obtained during scanning.
The volume of the lobe is calculated as the product of three dimensional values, multiplied by a factor of 0.523; mass – the same, only the index changes to 0.704.
Normally, the gland gradually grows from the first year of life (13.26 g) until approximately 11-15 years, when its weight reaches 37.52 g. From the age of 16, the thymus gradually decreases and, for example, by the age of 25-30 it weighs only 22. 30 g.
Another analyzed indicator is TI (thymic index). It is calculated as the ratio of the mass of the thymus gland to body weight. The result is presented in centiles. Normal values are considered to be 25-75 centile. If TI is less than normal, this indicates that the size of the thymus does not reach normal; if it is more, they speak of thymomegaly.
Over the course of life, the weight of the gland decreases per 1 kg of body weight. If in infants its value should be 4.2 g, in children under 5 years old - 2.2 g, under 10 years old - 1.2 g, under 15 years old - 0.9 g, then, starting from the age of 25, 0.2-0.3 g is considered normal.
Pathologies
Pathological results of ultrasound scanning are considered:
- thymogamy – enlargement of the organ compared to the norm;
- aplasia – lack of visualization. This happens due to the underdevelopment of the gland or its involution, that is, reverse (age-related) development, during which the parenchyma is replaced by adipose tissue.
Timomegaly
One of the common diagnoses entered into the protocol based on the results of an ultrasound examination of the organ is thymomegaly, or enlargement of the thymus. In most cases, young children do not require treatment, since the gland returns to normal size after some time.
The reasons for the development of this pathology are not clear. Doctors tend to believe that the cause of the development of thymomegaly is birth trauma and premature birth. In adults, it can develop against the background of deteriorating nutrition. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- cough;
- shortness of breath and heavy breathing, which occur due to an increase in the size of the gland;
- prolonged course of infectious diseases as a result of a decrease in the body’s protective functions;
- poor appetite.
Patients with this diagnosis are not prescribed special drug treatment. They are prescribed a gentle regimen and a visit to the doctor after a certain time to re-scan the enlarged organ.
Other diseases
Based on the indicators obtained during ultrasound of the thymus gland, the following is also diagnosed:
- MEDAC syndrome is an autoimmune polyendocrine abnormality of genetic origin;
- thymoma – neoplasm;
- T-cell lymphoma - a blood disease;
- myasthenia gravis is a muscle pathology.
In newborns the following is determined:
- hyperplasia (hypertrophy) of the gland;
- hypoplasia (DiGeorge syndrome);
- tumors.
Based on the diagnosis, a treatment regimen for the disease is selected.
Where to do it and how much it costs
An ultrasound of the thymus can be done in any public or private clinic, not only by yourself, but also with your children. This must be done if children often suffer from infectious diseases, get tired quickly and are prone to allergies.
The procedure will be performed free of charge if you have an insurance policy and a doctor’s referral. In private centers, you will have to pay from 850 to 2000 rubles for the examination. This price range is due to several reasons.
Firstly, medical services in the capital and large cities are more expensive. The cost is influenced by the type of equipment and personnel qualifications. Finally, in high-status clinics the price lists usually contain more “zeros”.
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/uzi/pokazaniya-k-uzi-vilochkovoj-zhelezy
Ultrasound of the thymus gland in children: indications for performance, how it is done, what it shows - medsi
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a procedure that is safe for a child of any age. It allows for accurate diagnosis quickly and painlessly. In this case, X-ray radiation is not used, which is harmful to the child’s body. The principle of its operation is based on the effect of different reflections of high-frequency sound waves from different types of organs and tissues.
What is the thymus gland?
The thymus gland (thymus) is an important part of the body responsible for the production of T-lymphocytes for human immunity. It is located in the upper region of the chest (in the upper mediastinum).
The size and weight of the gland changes throughout a person’s life:
- At birth she weighs 15 grams and is about 5 cm long
- By the end of puberty and throughout the main period of adult life, its weight is 20–37 grams, and its length is 7.5–16 cm
- By old age (about 75 years old) her weight decreases to 6 grams
The thymus gland has a gray-pink tissue color, and in old age it is yellowish.
For what purpose is an ultrasound of the thymus performed?
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the thymus gland for children when there are complaints about the child’s constant illnesses (colds, acute respiratory infections, etc.) and low immunity. This is necessary to determine the causes of regular ailments.
Ultrasound examination reveals a pathological increase in the size of the thymus - thymomegaly. As a result of its appearance, the immune system is weakened, and the child begins to regularly become infected with various diseases from other children and adults. In this case, allergies, gastrointestinal upset, and high fever may occur against the background of a common cold.
Indications for use
Ultrasound of the thymus is prescribed for symptoms such as:
- The child gets sick regularly (up to 10 times a year)
- The common cold often becomes more severe and is accompanied by complications (pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis)
- The temperature often rises to 37.5 and lasts for a long time
- Excessive regurgitation, excessive and heavy breathing
- The appearance of bronchial asthma, allergic reactions that are not eliminated even with a more proper diet
- For general weakness, chronic fatigue, chest pain
- If the network of blood vessels on the chest is clearly visible
- If your heart rhythm is abnormal (arrhythmia)
- With enlarged lymph nodes, tonsils or adenoids
What can an ultrasound reveal?
Ultrasound of the thymus gland in children helps to identify the following types of diseases and disorders:
- Timomegaly
- Pathologies of thymus development
- Aplasia (underdevelopment of the gland)
- Neoplasms (benign and malignant)
- Bernard-Horner syndrome (autosomal disorder)
- Nezelof's syndrome (appears due to the fact that the thymus gland cannot cope with its functions)
- DiGeorge syndrome (characterized by low T cell production)
Ultrasound examination will also allow you to determine parameters such as:
- Change in size (it should change within age norms)
- Correctness of organ tissue structure
- Contours (normally should be clear and uniform)
How is it carried out?
The process of performing an ultrasound scan of the thymus gland is quite simple:
- The child takes the body position necessary for the study:
- Until the age of one year, he should be in the arms of his parents
- From a year - he sits or lies down on the couch
- If the child is a teenager, then he must stand
- Clothes are removed from the upper body
- Gel is applied to the chest to improve sound conduction
- The doctor moves the sensor along the upper chest
- The image is displayed on the screen, and from it the specialist draws conclusions about the condition of the organ
The whole procedure takes about 10–15 minutes.
Preparation
Before performing an ultrasound examination of the thymus, no complex preparation is required:
- It is necessary to warn your doctor if you are taking various medications.
- You should find out the exact weight of the child and inform the doctor about it
- Clothing should be chosen that is easy to remove before the procedure.
- It is recommended to explain to the child what kind of examination is ahead and how it will be carried out so that he does not get nervous
Decoding the results
To decipher the results, the doctor must know the exact body weight of the child, since the determination of the normal volume and weight of the thymus gland (their compliance with age standards) depends on this value.
Normally, the weight of the gland is 0.3% of the total body weight. If this value is exceeded, a diagnosis of thymomegaly is made. It comes in three degrees, and its value is measured by a special CTTI index:
- I - with a CTTI index value from 0.33 to 0.37%
- II - with a CTTI value from 0.37 to 0.42%
- III - with an index value of more than 0.42%
Also, a sonogram (ultrasound result) can reveal changes in the gland such as: tumor, excessive tissue growth, etc.
Is it possible to examine the thymus in other ways?
Ultrasound of the thymus gland as a technique has been used relatively recently. Previously, X-ray examination was used to identify disturbances in the functioning and structure of the thymus gland. But such an analysis cannot be carried out frequently, unlike ultrasound, since X-ray irradiation is harmful to the child’s body.
If the results of an ultrasound scan of the thymus are not clear enough or contrast enough, the doctor may prescribe additional types of examination:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Heart scan
- Blood tests (general and biochemical) and urine tests
- Retroperitoneal scanning
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- The MEDSI network of clinics conducts more than fifty different types of ultrasound examinations using modern expert-level devices (models Pro Focus 2202, Philips iU22)
- Interpretation of the survey results is done by experienced specialists who have high qualification categories and regularly improve their skills at major scientific conferences and seminars
- To make an appointment with a specialist, you need to call 8 (495) 7-800-500
- There are more than 20 clinics in Moscow, so it’s easy to find a convenient place for examination
- MEDSI clinics have comfortable waiting areas for children and parents
Source: https://medsi.ru/articles/uzi-vilochkovoy-zhelezy-u-detey-pokazaniya-k-provedeniyu-kak-delaetsya-chto-pokazyvaet/