Most often, the disease is a complication of the wound process. Gas gangrene is caused by anaerobic microorganisms. Microorganisms from the genus Clostridia. Extensive wounds with tissue crushing are important.
The disease occurs when massive muscle destruction occurs. Contamination of the wound surface with soil, dust or scraps of clothing also plays a major role. Wounds become infected with anaerobic bacteria.
Anaerobic bacteria live in soil and street dust. Patients with extensive wounds, which are accompanied by massive crushing of tissue, are especially predisposed to the disease. Areas with poor blood supply appear.
Gas gangrene is a severe wound infectious process. There are several forms of gas gangrene. These forms of gas gangrene have the following characteristics:
- classic shape;
- edematous-toxic form;
- phlegmonous form;
- putrefactive form.
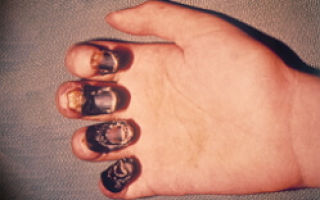
In the classic form of gas gangrene, tissue necrosis occurs, followed by the release of gas. There is no pus. When pressure is applied to the wound, gas and sanguineous fluid are released.
In the edematous-toxic form of gas gangrene, swelling quickly spreads. The swelling increases every minute. There is no purulent discharge, gas is released in small quantities.
The phlegmonous form of gas gangrene proceeds more favorably. This form can develop in a limited area. The swelling is minor. At the bottom of the wound there are muscles with areas of necrosis.
The putrefactive form of gas gangrene develops as a result of a combination of anaerobic and putrefactive microorganisms. This form is characterized by lightning-fast flow. The infection spreads quickly.
go to top
Causes
What are the main causes of gas gangrene? Gas gangrene occurs with extensive wounds. The disease is caused by clostridia. Clostridia live:
- Earth;
- street dust;
- cloth;
- feces;
- people's skin.
Gas gangrene occurs with extensive crush wounds. Traumatic separations of limbs are also important. Much less common causes of gas gangrene are:
- injury to the large intestine;
- entry of foreign bodies.
In some cases, gas gangrene can be caused by small wounds. This occurs as a result of contaminated scraps of clothing or soil particles entering the wound. Therefore, it is imperative to carry out primary treatment of the wound surface.
go to top
What are the main clinical signs of gas gangrene? The main symptoms of gas gangrene appear on the first day of the disease. Usually after injury.
The tissue around the wound swells. A foul-smelling discharge with gas bubbles appears. The swelling spreads to adjacent tissues. The human body is poisoned by tissue decay products, since gas gangrene is directly caused by tissue decay.
General and local symptoms depend on the type of clostridia. Symptoms for various forms of the disease have the following types:
- necrotic course of the disease;
- bloody tissue swelling;
- small amount of gas released;
- destruction of red blood cells.
The patient's general condition deteriorates. In this case, the clinical signs of gas gangrene are as follows:
- increased body temperature;
- decreased blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- thirst;
- chills;
- headache;
- insomnia.
The central nervous system may also be disrupted. In this case, the patient is either excited or depressed. First, there is either a decrease in the volume of urine or an absence of urine. Severe cases of gas gangrene are manifested by a decrease in body temperature.
Patients exhibit anemia. This includes swelling of the surrounding tissues. Gas is formed and muscle tissue is destroyed. In the classic form of gas gangrene, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- the skin in the wound area is cold and pale;
- sensitivity is lost;
- the pulse disappears.
The edematous-toxic form of gas gangrene speaks for itself. This form is accompanied by extensive swelling. Necrosis of the limb appears, the limb becomes brown.
In the putrefactive form of the disease, necrosis of fiber, muscles and fascia occurs. Secondary bleeding is observed. In addition, this form of the disease is characterized by lightning-fast progression.
For more detailed information, please visit the website: bolit.info
This site is informative!
go to top
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of gas gangrene, the clinical picture of the disease is of great importance. But more research is also needed. Additional studies include blood picture data. It observes:
- anemia;
- decrease in the number of red blood cells;
- leukocytosis with a shift of the formula to the left.
Diagnostics when measuring pulse is of great importance. There is no pulse in the peripheral arteries. The nature of the secreted liquid is also studied. When examining the fluid discharged from a wound under a microscope, clostridia are detected.
X-ray examination is widely used. It confirms the presence of gas in the tissues. At the same time, diagnosis is based on a differentiated study of the disease. A differentiated study of the disease includes the exclusion of phlegmon.
Diagnosis in most cases of gas gangrene is based on consultation with a specialist. Especially if repeated manifestations of gas gangrene are noted. In order to diagnose a complication it is necessary to study:
- nature of care for injuries;
- primary surgical treatment.
go to top
Prevention
Prevention of gas gangrene is based on primary surgical treatment of the wound. In this case, a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed. During wound treatment, the following results should be achieved:
- all non-viable tissues were excised;
- the bottom and edges of the tissue are excised;
- wound treatment.
Antibiotics should be used for large wounds. Especially if the wounds are heavily contaminated and are accompanied by tissue crushing. Prevention of gas gangrene also includes the use of serums. But they are often ineffective and lead to anaphylactic shock.
The patient must be isolated. At the same time, he is assigned a separate nursing station. It is advisable to burn the dressing material. Tools and linen are processed.
Instruments must be processed under high pressure conditions. A steam sterilizer is preferably used. The dry-heat oven matters.
Any medical procedure is carried out with rubber gloves. Rubber gloves are burned or processed. The following disinfectants are used:
- Lysol;
- carbolic acid;
- chloramine
Prevention is aimed at directly calling medical workers. Or an ambulance. Only a specialist can carry out initial wound treatment.
go to top
Treatment
The treatment process for gas gangrene includes emergency medical care. Active general therapy is also necessary. The treatment process includes the following activities:
- the wound is opened with striped incisions;
- non-viable tissues are excised;
- the wound is washed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide;
- Suspicious areas are also opened.
The wound must be left open. It is loosely drained with gauze soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate. Or hydrogen peroxide. During the first two days, it is advisable to carry out dressings three times a day.
When limbs become necrosis, amputation is performed. Amputation is carried out with cutting off all layers. The wound is left open. The following procedure is also performed:
- striped cuts;
- wounds are drained;
- use gauze soaked in an antiseptic solution.
Massive infusion therapy is widely used in the treatment of gas gangrene. Infusion therapy includes:
- use of plasma;
- use of albumin;
- use of solutions of proteins and electrolytes.
Antibiotics are used in high doses, intravenously. When identifying the causative agent of the disease, monovalent serum is used. If the pathogen is not identified, polyvalent serum is used.
go to top
In adults
Gas gangrene in adults is a rather severe pathology. In adults it is observed in any age category. Gas gangrene of the extremities comes first. Gangrene can be described as a type of necrosis in tissue.
The causes of gas gangrene in adults vary. The most common etiology of gas gangrene is:
- extensive injuries;
- frostbite;
- deep burns;
- lightning or electric shock;
- contact with strong acids.
However, in adults there are two forms of gangrene. In the first case, it is wet gangrene. In the second case, it is dry gangrene. If the above reasons are present, the gangrene is wet.
Necrosis can lead to the development of gangrene. Necrosis occurs in various diseases. At risk are adults with various pathologies. Pathological data of the following nature:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- embolism;
- thrombosis.
Gas gangrene is similar in symptoms to dry and wet gangrene. Symptoms of gas gangrene in adults are as follows:
- pain;
- edema;
- rotting flesh;
- gas release;
- dead tissue.
go to top
In children
Gas gangrene in children is quite rare. There are cases of morbidity among the youthful age category. The usual causes of gas gangrene in children are:
- extensive injuries;
- extensive wounds;
- lack of proper assistance.
Children are rarely susceptible to gas gangrene. Usually at school age when injured. If you do not help the child, gas gangrene occurs. Treatment for children includes general measures. In particular, primary surgical treatment.
Gangrene in children has common symptoms. Most often, the clinical signs of gangrene in children are as follows:
- pain;
- blackening of the wound;
- chills;
- headache;
- tachycardia;
- increase in body temperature.
In addition, it should be noted that gangrene in children leads to irreversible phenomena. Most often this is fatal if proper assistance is not provided. In addition, the child’s body has not developed immunity. Clostridia easily penetrates the child's body.
go to top
Forecast
With gangrene, the prognosis is often unfavorable. This is associated with a severe infectious process. And also with tissue necrosis as a result of this process.
The prognosis improves if proper assistance is provided on time. The man came to his senses. Undesirable consequences were prevented.
The prognosis is also influenced by the patient's condition. Namely, the presence of various diseases. With severe chronic diseases, the prognosis worsens.
go to top
Exodus
The most common outcome of gas gangrene is death. This is due to failure to provide timely assistance, or insufficient treatment of the wound. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor this process.
Recovery from gas gangrene occurs if doctors act correctly. Although gangrene can often be cured surgically. But surgical treatment includes amputation.
Naturally, with amputation, we can talk about an unfavorable outcome of gas gangrene. A person after amputation is considered inferior. This leads to disability.
go to top
Lifespan
With gas gangrene, life expectancy depends on many circumstances. With timely assistance, life expectancy increases. Although sometimes patients become disabled.
Disability leads to a decrease in quality of life. Accordingly, the patient loses interest in life. And thus its overall duration is reduced.
Life expectancy with gas gangrene is influenced by the patient's condition. If the body temperature drops significantly, then we can talk about a critical condition. Only a qualified specialist can provide proper assistance.
Source: http://bolit.info/gazovaya-gangrena.html
Gangrene in diabetes
Surgeons at the Innovative Vascular Center manage to preserve the leg and the ability to walk in more than 90% of patients with diabetic gangrene. Amputation in our clinic is prescribed only in case of complete purulent decay of the limb, when there is nothing left to save. At the first signs of wet gangrene in diabetes mellitus, contact the Innovative Vascular Center and we will definitely help you.
In Russia, out of 80,000 amputations per year, more than 60,000 are associated with the development of gangrene of the limb due to diabetes mellitus.
The poor development of services for the prevention of vascular complications of diabetes, the lack of a network of diabetic foot clinics leads to the fact that almost 30% of diabetics lose their legs from amputation.
Rare endocrinologists explain to patients the rules of foot care, carry out visual monitoring and examination of the feet of these patients. Most often, communication between an endocrinologist and a patient comes down to adjusting sugar levels and writing prescriptions for insulin.
Dry gangrene in diabetes
Dry gangrene in diabetes mellitus develops as a result of diabetic macroangiopathy, that is, damage to the vascular wall by calcified plaques. The amount of calcium in the vessels is such that even with a non-contrast x-ray examination, the vessels affected by plaques are clearly visible on the pictures.
Dry gangrene develops in patients with compensated diabetes and arterial insufficiency. With diabetes, there is always a risk of dry gangrene turning into wet gangrene, with the development of life-threatening complications. Treatment for dry gangrene involves restoring blood flow and removing only dead tissue. The difficulty lies in the nature of the damage to the vessel walls.
Most often there are extensive narrowings of the arteries and closed lateral flows. Treatment of patients with dry gangrene due to diabetic angiopathy differs from ordinary atherosclerosis. It is necessary to have the technical ability to perform hybrid interventions, a combination of angioplasty and bypass surgery.
Removal of necrosis can be carried out after restoration of blood flow, since there is no immediate threat of general blood infection with dry gangrene.
Wet gangrene in diabetes mellitus
Unlike dry, wet diabetic gangrene is almost always associated with infection and often develops against the background of existing diabetic foot syndrome.
Crush injuries and acute blood clot blockage (embolism) can quickly cut off blood supply to the affected area of the leg, causing tissue death and an increased risk of infection.
Against the background of diabetes mellitus, microbes in the wet form of necrosis can quickly spread throughout the body.
Gas gangrene is a rare but very dangerous disease. It begins when the infection reaches deep into muscles or organs, often as a result of injury. The bacteria that cause gas gangrene are called clostridia. They release dangerous toxins that cause severe damage to the body.
A characteristic symptom of this form of gangrene is the formation of blisters in the tissues. With the development of gas gangrene, the skin becomes pale and gray in appearance, and when pressed, a characteristic cracking sound (crepitus) is heard, due to bubbles in the tissues.
If left untreated, without qualified help, death can occur within 48 hours.
The tactics for treating wet gangrene in diabetes mellitus consists of emergency intervention at the site of putrefactive tissue melting (necrectomy, opening of phlegmon) with urgent vascular surgery to restore blood flow. If gangrene can be stopped, then a stage of restorative treatment follows with healing of residual wounds.
Causes of wet gangrene
The development of destructive processes in the leg is possible in patients with reduced immune defense due to diabetes mellitus or other factors weakening the body. For dry gangrene to transition into wet gangrene, it takes quite a long time and the formation of significant edema due to the forced lowering of the affected leg.
The development of diabetic gangrene of the lower extremities can often be associated with attempts to treat initial dry necrosis of the fingers with the help of “folk remedies” - beef liver, bread crumb and the like.
These “recommendations” require long-term closure of the gangrenous focus with “folk remedies.” Accordingly, an excellent environment is created for the proliferation of bacteria and the progression of the purulent process.
Purulent-necrotic gangrene of the lower extremities in diabetes mellitus develops at lightning speed due to the spread of infection along the tendons.
The main risk factor for leg loss is diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation with damage to the arteries of the leg (angiopathy) and poor foot care in the initial stage of diabetic foot syndrome.
Complications
The main complication of wet gangrene is the development of general infection of the body. This condition is observed in 85% of patients who have not undergone active surgical treatment. Sepsis inevitably leads to death. Gangrene of the legs in diabetes leads to death in 60% of patients who do not receive qualified and timely assistance.
Deep vein thrombosis is one of the very common complications that worsens the circulatory situation. Thrombotic masses can be infected and carry the infection throughout the body through the bloodstream. Deep venous thrombosis of the legs often contributes to pulmonary embolism and leads to sudden death.
Forecast
In the absence of surgical care, all patients with wet gangrene die from sepsis. The main approach to treatment is still emergency high amputation. Therefore, we can say that for most patients with wet gangrene, the latter ends in the loss of a leg.
To prevent the development of the disease, a diabetic needs to change his lifestyle, lose excess weight, carefully approach the treatment of the foot, and monitor minor finger injuries and abrasions.
It is necessary to promptly, at the first signs of changes in the feet and nails, seek help from diabetic foot specialists - podiatrists.
Source: https://angioclinic.ru/zabolevaniya/vlazhnaya-gangrena/
Gas gangrene
Gas gangrene is an infectious pathology, the development of clinical manifestations of which occurs with the active growth and reproduction of clostridial flora in human muscle fibers, localized mainly in the projection of the extremities. The entry of a pathogenic microorganism during gas gangrene occurs only if the integrity of the surface layers of the skin is damaged with further spread to deeper layers.
Anaerobic gas gangrene can develop as a result of various types of pathogenic clostridia entering the human body, among which the specific pathogen Clostridium perfringens plays a major role.
A special feature of the causative agent of gas gangrene is its ability to produce exotoxins that destroy soft tissues, as well as gas formation, which contributes to the rapid spread of pathomorphological processes to the deep layers of soft tissues.
The pathogenesis of gas gangrene ends with the development of irreversible changes in the form of necrosis of a large area of skin and muscles, which requires immediate surgical correction in order to prevent further spread of the pathological process.
It is extremely rare that anaerobic gas gangrene is localized not in the skeletal muscles, but in the muscle tissue of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
The pathogenesis of gas gangrene most often begins against the background of any extensive crushing of soft tissues of a gunshot, laceration, laceration-contusion origin, in which the wound channel is often contaminated with earth or scraps of clothing.
There is a clear correlation between the risk of developing gas gangrene and the depth of soft tissue damage.
The routes of transmission of gas gangrene are limited and involve the entry of the pathogen in the form of pathogenic clostridia into the human body through the damaged surface of the skin.
Among the pathognomonic local symptoms of gas gangrene, the following should be highlighted: regional swelling of soft tissues, their melting, accompanied by gas production. Along with the above symptoms, a specific sign of gas gangrene, which allows differentiation from other soft tissue diseases, is the complete absence of signs of inflammation.
In addition to the appearance of specific local clinical markers of the disease, gas gangrene is characterized by the development of a general intoxication symptom complex in the form of cardiac dysfunction, psychomotor agitation, febrile fever, and increased breathing.
With the development of the hemolytic form of the disease, the patient rapidly progresses to clinical signs of anemia.
In the absence of timely surgical and drug correction, gas gangrene in 90% of cases is fatal, which occurs within a maximum of three days.
Causes and causative agent of gas gangrene
The source of gas gangrene is represented by representatives of an anaerobic infection, capable of forming spores, and also characterized by pronounced resistance to environmental factors.
For the causative agents of gas gangrene, the most favorable conditions are soil contaminated with putrefactive organic matter. When a microbe enters the soft tissue of a susceptible macroorganism, severe necrotic pathomorphological changes develop, and pathogens such as Cl.
perfringens and Cl. Oedematiens provoke the development of swelling of soft tissues and gas in the intermuscular spaces.
The clinical picture of gas gangrene, as a rule, develops when not one, but several representatives of anaerobic flora enter the body. The occurrence of one or another clinical form of gas gangrene directly depends on the specificity of the pathogen.
The source of gas gangrene in the form of an anaerobic microbe constantly lives in the intestinal lumen of any domestic herbivore. In addition, pathogens of anaerobic infection can be cultured from the skin and feces of a healthy person.
Necrotic muscle tissue acts as a breeding ground for representatives of anaerobic infection.
For the active reproduction of gas gangrene pathogens, a prerequisite is the absence of oxygen, since the vital processes of microorganisms are accompanied by the release of gas.
The clinic of gas gangrene is prone to a lightning-fast increase in the intensity of symptoms, which is due to the rapid spread of anaerobic infection and the development of a general intoxication syndrome.
The entry gate for the penetration of pathogens is the skin with signs of disruption of integrity, which occurs with traumatic injury to the extremities, crush wounds, ingress of foreign bodies and damage to the intestinal wall.
During the initial examination of the patient, it should be taken into account that even minimal damage to the integrity of the skin may be accompanied by the development of a severe clinical form of gas gangrene.
The development of the pathogenesis of gas gangrene occurs, as a rule, in the first day after traumatic exposure, although in some situations more distant phases of the clinical development of the disease may be observed.
The favorite localization for the proliferation of gas gangrene pathogens is an extensive wound surface with the presence of a large array of non-viable tissues, in which there are signs of impaired blood supply, and, accordingly, a complete lack of oxygen. Such conditions are favorable for the active reproduction of gas gangrene pathogens and their release of toxins, which is accompanied by the development of a severe general reaction of the human body.
The most intense pathological processes in gas gangrene are localized in the muscle fibers of the buttocks and thighs. The pathological process in gas gangrene is prone to rapid spread along the vessels from the skeletal muscles of the limbs to the torso.
Gunshot wounds are the most favorable for the further development of gas gangrene, since in them the remains of clothing and projectile fragments accumulate in the wound channel.
In addition, intense blood loss, exhaustion, and prolonged compression of soft tissue with a tourniquet should be considered as factors contributing to the development of gas gangrene.
Currently, complications of gas gangrene develop, as a rule, after the criminal termination of an unwanted pregnancy, which is performed under inappropriate conditions.
Another option for the development of gas gangrene is the spread of anaerobic infection with a massive bedsore, which is a closed area of soft tissue necrosis.
Paths of transmission of gas gangrene are also realized when aseptic conditions are not observed during primary surgical treatment of the wound surface or postoperative treatment is not applied in full.
Symptoms and signs of gas gangrene
The development of one or another clinical form of gas gangrene directly depends on the specificity of the pathogen.
When Clostridia perfringens gets on the wound surface, toxic-hemolytic, fibrinolytic and necrotic changes develop. Such a causative agent of gas gangrene as Cl.
septicum provokes the development of bloody-serous edema of soft tissues with minimal gas production in the intermuscular spaces, and the production of exotoxins is accompanied by hemolysis of red blood cells.
Under experimental conditions, the following properties of Cl toxins were determined. septicum as a tendency to lower blood pressure, development of cardiac rhythm disturbances. Feature Cl.
oedematiens is its ability to provoke a rapid increase in soft tissue edema, which is accompanied by the release of gas. The most aggressive in terms of destructive effects on the soft tissues of the human body is Cl. Histolitycum, which for 10 - 12 hours.
capable of completely melting the muscle mass and ligamentous apparatus of the limbs, up to skeletonization of the bones.
The classic version of the clinical picture of gas gangrene consists of local and general manifestations. Taking into account the characteristics of local symptoms, several clinical forms of gas gangrene are distinguished.
Thus, the classic form of the disease is emphysematous, the pathomorphological substrate of which is the development of local swelling of soft tissues, their destruction and pronounced local gas formation. The wound surface with gas gangrene remains dry and has no signs of granulation, but is characterized by the formation of extensive necrosis.
When palpating the affected area, the release of bloody fluid and gas bubbles is noted, and the surrounding skin has a whitish color. Subsequently, the muscle tissue acquires a gray-green color, which is accompanied by severe pain and disappearance of the pulse in the peripheral arteries.
The skin adjacent to the wound surface turns purple, sensitivity in the affected area is completely absent. This form of gas gangrene is not characterized by the formation of pus.
The initial manifestations of the edematous-toxic form of gas gangrene is the formation of a large area of soft tissue edema in the complete absence of gas and pus formation.
As a result of increasing edema, there is an increase in the volume of the muscle mass, which is pale in color and protrudes from the wound surface.
A characteristic manifestation of the edematous-toxic form of gas gangrene is a change in the color and structure of subcutaneous fat, which has a gelatinous-jelly-like appearance. As edema increases, blood supply disturbances develop and massive necrosis of soft tissue develops.
Phlegmonous gas gangrene is the most favorable clinical form, since with it the pathological changes in the soft tissues are limited.
A distinctive feature of this variant of gas gangrene is the formation of purulent discharge in the wound.
The spread of the inflammatory process occurs through the intermuscular spaces, and there is almost never any disruption of the blood supply to the affected area.
Putrid or putrefactive gas gangrene is characterized by a rapid increase in clinical symptoms, which is caused by massive necroticization of soft tissues.
The spread of the pathological process occurs not only through the fiber, but also through the intermuscular spaces. Necrotic soft tissues have a dirty gray color and are covered with putrefactive discharge, which has a pronounced unpleasant odor.
Complications of gas gangrene in this situation are caused by the addition of a putrefactive bacterial component.
This form of gas gangrene is characterized by the development of secondary erosive bleeding, which is caused by massive breakdown of proteins contained in the walls of blood vessels. Pathological changes in the putrefactive form are localized mainly near the rectum, as well as paramediastinal.
Diagnosis of gas gangrene
To carry out microbiological diagnosis of gas gangrene, the fundamental element is the isolation of the pathogen by examining biological material taken from the patient, followed by its identification based on morphological, cultural, biochemical, and toxigenic study of the pathogen.
As a biological material for further microbiological analysis, a biopsy of the affected tissue, fluid aspirated from the wound surface, as well as blood culture should be used.
In a situation where it is necessary to carry out post-mortem microbiological diagnostics, biological material must be removed no later than five hours after death in order to exclude possible post-mortem contamination of tissues.
After carefully selecting the biomaterial for research, fingerprint smears should be prepared and then stained with Gram. Laboratory confirmation of gas gangrene in this situation is the detection of gram-positive rods of large size and round shape in the smear.
The bacteriological research method involves preliminary rubbing of soft tissues, diluting them with physiological solution and dividing them into two equal portions. The first portion should be heated for 15 minutes at a temperature of 80°C.
Subsequently, portions of the prepared biomaterial are sown on a casein nutrient medium containing petroleum jelly and 1% glucose solution for four days, subject to a temperature of 37°C. With such seeding, gas gangrene is characterized by maximum germination of clostridia within 36 hours.
Subsequently, the resulting culture of the pathogen is subjected to microscopic examination and a neutralization reaction is carried out, confirming toxin formation.
Unfortunately, all types of laboratory diagnostics of gas gangrene are very labor-intensive to carry out and require a large amount of time, while the patient’s clinical manifestations require immediate surgical correction. In this regard, laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis has retrospective significance.
Treatment of gas gangrene
The principles of treating patients common to all variants of gas gangrene is an integrated approach, which involves the use of not only surgical treatment methods, but also conservative ones.
First aid for gas gangrene involves the use of immediate surgical intervention in the form of a wide dissection of the wound channel, which is the entrance gate for the penetration of the pathogen.
The surgical treatment for gas gangrene consists of making deep stripe-type skin incisions down to the tendon aponeurosis, which must be opened. Then it is necessary to excise the necrotic tissue down to healthy tissue and treat the incisions with a solution of potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide.
The aseptic dressing must be thoroughly soaked in a hypertonic sodium chloride solution. In severe cases of gas gangrene with the development of massive extensive melting of soft tissues up to skeletonization of bones, the scope of surgical intervention consists of amputation or disarticulation.
Amputation should be carried out using the guillotine method, after which it is necessary to leave the amputation surface open with additional strip cuts and drainage of the wound.
As therapeutic measures of non-specific significance, detoxification therapy should be used by administering a large amount of crystalloid solutions intravenously and expanding the drinking regime. During the entire period of treatment, a patient suffering from gas gangrene must adhere to bed rest and a high-calorie diet.
Specific drug therapy for gas gangrene involves the use of anti-gangrenous serum in the early postoperative period by intravenous administration of 50,000 AE.
As a preventive measure to prevent the development of anaphylactic shock during gas gangrene, intravenous administration of 10 ml of a 10% solution of calcium chloride and antihistamines (Pipolfen in a daily dose of up to 500 mg) should be used.
In addition, specific drug treatment for gas gangrene should include an anaerobic bacteriophage in a dose of 50 ml, diluted in 500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution intravenously by drip for three days. Application of an anaerobic bacteriophage to the wound surface is also allowed.
In order to prevent the possible addition of a bacterial component and the development of a complicated course of gas gangrene, antibacterial drugs with the preferred parenteral route of administration should be included in the general drug therapy regimen. The fundamental element of postoperative treatment of patients is the use of hyperbaric oxygenation.
Prevention of gas gangrene
Preventive measures for gas gangrene consist of immediate hospitalization of the patient in a purulent-septic surgical hospital, where he must be isolated from others for the entire period of treatment.
First aid for gas gangrene should be provided at the prehospital stage, which helps prevent the development of severe complicated forms of the disease.
In order to prevent the possible intrahospital spread of the pathogen, it is necessary to comply with all sanitary and hygienic standards, including thorough sterilization and disinfection of instruments, and the use of disposable dressings. The preferred method of sterilizing instruments is air, in which a critical maximum temperature of up to 1500°C develops in a dry-heat oven, which allows you to completely kill not only vegetative forms of the pathogen, but also spores.
Surgical specialists, as well as junior medical personnel, should pay special attention to compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, as well as wearing special medical clothing that prevents the spread of pathogen spores. It is mandatory to use barrier protective methods in the form of wearing disposable latex gloves every time you have contact with a sick person.
Gas gangrene - which doctor will help? If you have or suspect the development of gas gangrene, you should immediately seek advice from a doctor such as a surgeon.
Source: https://vlanamed.com/gazovaya-gangrena/
Газовая гангрена
RS‚Р° форма гангрены Реначе называется анаэробной, РїРѕС ‚РѕРјСѓ что ее выз S‹РІР°СЋС‚ РјРеРєСЂРѕР±С‹, живущие Ryo SЂР°Р·РјРЅРѕР¶Р°СЋС‰РёРµСЃСЏ без доступ Р° кислорода.
Патогенные SЃРїРѕСЂРѕРѕР±СЂР°Р·СѓСЋС‰РёРµ бактерии РёР· СЂРѕРґР° клост SЂРёРґРёР№ попадают РІ организм S‡РµР»РѕРІРµРєР ° РїСЂРё нарушенги целостности RєРѕР¶РЅРѕРіРѕ РїРѕРєСЂРѕРІР°.
Р—Р° очень короткое время RѕРЅРё SЂР°СЃРїСЂРѕСЃС‚раняются РІ РіР» СѓР±РѕРєРѕ расположенные структуры тела, РЅР °СЂСѓС€Р°СЏ РёС… функцРеРё Рё часто RїСЂРІРІРѕРґСЏ Rє R»РµС‚альному РѕЃС…РѕРґСѓ .
Содержание:
RљР°Рє РїСЂРѕРёСЃС…РѕРґРёС‚ разввитие RіР°Р·РѕРІРѕР№ гангрены?
Р' РЅРѕСЂРјРµ клостридии обитают РІ кишечнмке домашних Р¶РёРІРѕС ‚РСых. Оттуда бактерии попадают РЅР° одежду кожу S‡РµР»РѕРІРµРєР°, РЅР° землю. РћРЅРё РЅРµ представляют опасности для людей РґРѕ S‚ех РїРѕСЂ, R їРѕРєР° РЅРµ окажутся РІ обширной раз RјРѕР·Р¶РµРСРЅРѕР№ СЂР°РСРµ. Раневая поверхность RјРѕР¶РµС‚ быть РЅРµ очень большой, РЅР * опасность внедрения RєР»РѕСЃС‚СЂРёРґРёР№ СЃРѕС… SЂР°РЅСЏРµС‚СЃСЏ, если РІ SЂР°РЅСѓ RїРѕРїР°Р»Рё S‡Р°СЃС‚ицы почвы или RѕРґРµР¶Р ґС‹ пострадавшего S‡ еловека.
Чаще всего газовая гангрена диагностируется РЅР° СЃРєР µР»РµС‚РЅРѕР№ мускулатуре, однако РІ редких СЃР» SѓS‡R°SЏS… RїSЂРё SЂР°РЅРµРЅРІС… брюшной RїRѕR»РѕСЃС‚Рё RєРёС€РµС‡РЅРѕР№ SЃС‚енки R ѕРЅР° поражает органы мал РѕРіРѕ таза Рё желудочно-кишечный тракт.
Самое главное SѓСЃР»РѕРІРёРµ для запуска RїР°С‚ологического R їСЂРѕС†РµСЃСЃР° – отсутствне РІ І ране оксигенац РёРё, нарушение снабжения ее RєРёСЃР»РѕСЂРѕРґРѕРј. RS‚РѕРјСѓ SЃРїРѕСЃРѕР±СЃС‚вует затрудненвое кровообращениРµ РЅР° травмированном участке.
Особенностанаэробной гангрены:
- РџСЂРёС‡РеРЅС‹ нарушения оксигенации – SЃR»РёС€РєРѕРј долго налож " СЊРЅРѕР№ артерии, хроническая артериальная РЅРµРґРѕСЃС‚Р°С‚РѕС ‡РЅРѕСЃС‚СЊ РІ анамнезе, массивна СЏ кровопотеря.
- R'Рѕ время SЂР°Р·РјРЅРѕР¶РµРЅРёСЏ RєР»РѕСЃС‚СЂРёРґРёРё вырабатывают SЌРєР·Рѕ S‚РѕРєСЃРеРЅС‹, разрушающие мышцы, СЃРІСЏР·РєРё, кожу, СЃРѕСЃСѓРґС‹.
- Спровоцированное РёРјРё газообразованве SЃРїРѕСЃРѕР±СЃС‚РІСѓР R їСЂРѕС†РµСЃСЃР° некротизации мышц Рё кожи.
- Общая тяжелая реакция человека РЅР° онтоксикацию РѕСЂР іР°РЅРёР·РјР° развивает SЃСЏ РІ первые сутки РѕС‚ начала заражения.
RќР°РёР±РѕР»РµРµ RјР°СЃСЃРёРІРЅРѕРµ RїРѕСЂР°Р¶РµРЅРёРµ RїСЂРё газовой гангрене РІР ѕР·РЅРёРєР°РµС‚ РІ мышцах СЏРіРѕРґРёС† Рё бедер.
Rнфекция SЂР°СЃРїСЂРѕСЃС‚раняется RїРѕ S…РѕРґСѓ RєСЂСѓРїРЅС‹С… SЃРѕСЃСѓ RґРѕРІ конечностей, RїРѕ SЃРѕСЃСѓРґРёСЃС‚Рѕ-нервным RїСѓС‡РєР°Рј.
РкзотоксРеРЅ напрямую влияет РЅР° тромбообразование РІ РІ " РёС‡ Рё нарушение микроциркуляции.
RќР°РёР±РѕР»РµРµ S‡Р°СЃС‚ые RїСЂРёС‡РёРЅС‹ RїРѕРІСЂРµР¶РґРµРЅРёР№ РїСЂРё R°РЅР°СЌСЂРѕР±РЅРѕ Р№ гангрене:
- RћРіРЅРµСЃС‚рельное SЂР°РЅРµРЅРёРµ;
- Криминальное прерывание беременности;
- RFILLLYYCHRѕPѕR ± p »CћrґrµRѕRERHERPELEL ° ° ° ° ° °” ° ° С Сarch РРр РіРѕ іsђr… Сѓ ‡rіrtyy ‡ РµSѓrѕrѕr € € ° С ° Сњ °. RIR ° RER »RYOSHYSHYRO RARѕSѓR» RPRRIRARARHRARHARIR ° C † RRPHRPHRPHRѕRAP »RPRES ‡ ении;
- Глубокие массивные пролежни.
RнкубацРеонный период RїСЂРё RіР°Р·РѕРІРѕР№ гангрене длится Rѕ S‚ нескольких часов РґРѕ 15-20 дней, ча S‰Рµ всего РѕС‚ РѕРґРЅРёС… суток RґРѕ RѕРґРЅРѕР№ недели. Чем короче RїРµСЂРёРѕРґ инкубации, тем тяжелее течение Р· аболевания Рё хуже РїСЂРѕРіРЅРѕР· его SЂР°Р·РІРёС‚РёСЏ.
RЎРЎРјРїС‚РѕРјС‹ газовой гангрены
ЗаболеванРеРµ начинается SЃС‚ремительно, уже РЅР° первыР№-третий день после СЂР° нения или S‚равмы развивается отек S‚каней, РІ ране РїСЂРѕР ґСѓС†РёСЂСѓРµС‚СЃСЏ мутное отделяемое СЃ РїСѓР·С ‹СЂСЊРєР°РјРё газа ккрайне неприятным запахом. Отечность быстро распространяется, РЅР° коже RїРѕСЏ RІР»СЏСЋС‚СЃСЏ пузыри СЃ геморрагическим SЃРѕРґРµСЂР¶РёРјС‹Рј внутри, пятна зеленого цвета. RљРѕРЅРµС‡РЅРѕСЃС‚СЊ становится S…олодной, RјС‹С€С†С‹ приобрет ают РІРеРґ вареного РјСЏСЃР°, РёС… волокна СЂР° SЃСЃР»Р°Реваются. Р—Р° 10-12 часов РѕРґРёРЅ РєР· РІРІрґРѕРІ клостридии SЃРїРѕСЃРѕР±РµРЅ СЂР°Р·СЂСѓС€РёС ‚СЊ подкожную клетчатку РґРѕ РєРѕСЃС‚ ей.
Нарастают СЃРемптомы общей онтокскации организма:
- Учащенное сердцебРеение;
- R“ипертермия РґРѕ 39-40В°;
- R›РѕРјРѕС‚Р° РІ мышцаС...;
- Частое дыхание;
- Жажда;
- Р'ессонница;
- R“оДовная боль;
- Повышенная возбудимость или, наоборот, подавленноS ЃС‚СЊ;
- Уменьшение RєРѕР»РёС‡РµСЃС‚РІР° выделяемой мочи, далее ее РїРѕ R»РЅРѕРµ отсутствие;
- Крепитация (треск) при нажатии на поврежденные тка ни.
Р' РєСЂРѕРІРё стремительно разрушаются эритроциты, РІРѕР·Р Sикает анемия гемолитическая R ¶РµР»С‚СѓС…Р°.
R' SЃРІРѕРµРј SЂР°Р·РІРёС‚РёРё гангрена РїСЂРѕС…РѕРґРёС‚ 4 стадии:
- Стадия отграничендой РѕР°Рхгрены. Отек тканей отделяемое RјРёРЅРёРјР°Р»СЊРЅС‹, рана сухая, имеется боль, кожа бледная.
- Стадия распространения. Поражение некроз S‚каней продвигаются RїРѕ RєРѕРЅРµС‡РЅРѕ сти, боль приобретает SЂР°СЃРїРёСЂР°СЋС‰РёР№ С…Р °СЂР°РєС‚ер, мышцы обескровлены, кожа желтеет, РЅР° ней Р·Р° метны пятнР°.
- Третья стадия. Р'оль SѓРјРµРЅСЊС€Р°РµС‚СЃСЏ или прекращается SЃРѕРІСЃРµРј, конечность SѓРІРµР»РёС‡РёРІР°РµС‚СЃСЏ, холодеет, РїСѓР» ьсация прекращается. Отечность газы распространяются РїРѕ большой РїР»РѕС ‰Р°РґРё тела, РЅР° РєРѕР¶ Рµ образуются пузыри СЃ бурым SЃРѕРґРµСЂР¶РёРјС‹Рј.
- Стадия сепсиса. RнтоксРекация RѕСЂРіР°РЅРёР·РјР° R·РЅР°С‡РёС‚ельна, рана РЅР°РїРѕР»РЅСЏРµС ‚СЃСЏ гноем, очагго СЃ РіРЅРѕР№РЅС ‹Рј содержимым фиксируются отдаленно РѕС‚ первичн РѕРіРѕ внедрения бактерий.
Если больной РЅРµ получает SЃРІРѕРµРІСЂРµРјРµРЅРЅСѓСЋ RїРѕРјРѕС‰СЊ, С‡РµС ЂРµР· 2-3 РґРЅСЏ наступает Р»РµС‚Р°Р»СЊРЅС ‹Р№ РёСЃС…РѕРґ.
СнмптоматРеРєР° анаэробной гангрены заввисит РѕС‚ ее С„РѕС ЂРјС‹.
Различают 4 формы SЌС‚РѕРіРѕ заболевания:
- Рмфизематозная, или классическая форма . Отек ткани небольшой, РѕС‚ раны РѕСЃС…РѕРґРёС‚ трупный запах. Нет РіРЅРѕСЏ, РЅРµ отделяется SЌРєСЃСЃСѓРґР°С‚. ввагностоЂСѓРµС‚СЃСЏ значительное газообразование, РІС‹С ЂР°Р¶РµРЅРЅС‹Р№ болевой SЃРЅРґСЂРѕРј. РЎ развитием заболевания S‚кани мышц приобретают зелеРSоватый S†РІРµС‚, кожа багровеет, исчезает пульсация артерии.
- Отечно-токсическая форма. Отек стремительно нарастает, вследствие чего RјS ‹С€С†С‹ сдавливаются. РЅРЅРѕСЏ нет, газ выделяется РІ РјРенимальном RєРѕР»РёС‡РµСЃС‚РІРµ. RљРѕР¶Р° RІРѕРєСЂСѓРі SЂР°РЅС‹ S…олодная, RїРѕРґРєРѕР¶РЅР°СЏ RєР»РµС‚чатка SЃРЅР° чала принимает Р· еленый цвет, затем буреет, ткани RїРѕРґРІРµСЂРіР°СЋС‚СЃСЏ нео братимому некрозу.
- Флегмонозная форма. омеет РЅР°Реболее благоприяS‚ный РїСЂРѕРіРЅРѕР· развптия, обла сть поражения РѕРіСЂР°РЅРёС ‡РµРЅР°, РѕРЅРѕ РЅРµ распространяется SЃР»РёС€РєРѕРј быстро. Р' ране Ремеется РіРЅРѕР№, ее кровоснабжение РЅРµ нарушено.
- ннилостная, или путридная форма. Клиника заболевания Р±СѓСЂРЅРѕ нарастает, РјСЏРіРєРёРµ ткани РїРѕР ґРІРµСЂРіР°СЋС‚СЃСЏ обширному некрозу. РѕР· раны отделяется гнилостная субстанция СЃ исклюS ‡РёС‚ельно неприяS‚ным Р·Р° RїR°S…RѕRј. РџСЂРё этой форме РёР· раны выходит газ, разрушаются стен RєРё SЃРѕСЃСѓРґРѕРІ.
RљР°Рє диагностКаковую RіР°РЅРіСЂРµРЅСГ?
RќР°РёР±РѕР»РµРµ S‚очным RјРµС‚РѕРґРѕРј RґРёР°РіРЅРѕСЃС‚РёРєРё SЏРІР»СЏРµС‚СЃСЏ RјРёР єСЂРѕР±Реологический анализ Р±РеРѕРїС‚Р°С ‚Р° тканей очага поражения, аспната РёР· раны, гемокуль S‚СѓСЂС‹.
Поскольку проведение Псследованввзанимает РјРЅРѕРіРѕ R ІСЂРµРјРµРЅРё, Р° больному необходима незамедлительная РјРµРґРёС †РеРЅСЃРєР° СЏ помощь, Ђабораторная диагностика уступает РїРѕ важ ности оценке клинической РєР°СЂС ‚РёРЅС‹ заболевания. РџСЂРё проведении РЈР—Р Рё SЂРµРЅС‚геновЁкого кследования R јРѕР¶РЅРѕ SѓРІРёРґРµС‚СЊ пузырьккгаза РІ пораженных тканяS….
RџСЂРё диагностПровании врачом RїСЂРёРЅРјРјР°РµС‚СЃСЏ РІРѕ внимани Рµ скорость нарастания отечности тканей Рё РёС… некроза, наличРеРµ хруста (крепитацРеРё), окраска кожи Рё РјС‹ шц.
Терапевтические Ryo S…ирургические RјРµС‚РѕРґС‹ лечения R іР°Р·РѕРІРѕР№ гангрены
Неотложное мероприятие RїСЂРё RѕР±РЅР°СЂСѓР¶РµРЅРёРё SЃРемптомоРІ газовой гангрены – рассечение SЂР°РЅРµРІРѕРіРѕ канала. Р'доль конечности делают глубокие лампасные СЂР°Р·СЂРµР·С ‹, затем иссекают некротизированные мышцы. РќР° открытую рану накладывают рыхлый дренаж РёР· марганца Рё перекиси RІРѕРґРѕСЂРѕРґР°. RS‚Сѓ РїРѕРІСЏР·РєСѓ меняют несколько раз РІ сутки, РїСЂРё улучше РЅРёРё состояноЏ больного – делают это ежедневно . Р' течение всего РєСѓСЂСЃР° лечения больной соблюдает РїРѕС ЃС‚ельный режим, питается РІС‹ SЃРѕРєРѕРєР°Р»РѕСЂРёР№РЅС‹РјРё продуктами.
Еслгангрена принимает тяжелое S‚ечение, наблюдает SЃСЏ массивное SЂР°СЃРїР»Р°РІР»РµРЅРІРµ С ‚каней, доходящее РґРѕ костей, врачом RїСЂРёРЅРёРјР°РµС‚СЃСЏ СЂР µС€РµРЅРеРµ РѕР± ампутации.
RџРѕРІРµСЂС…ность SЂР°РЅС‹ RїРѕСЃР»Рµ R°РјРїСѓS‚ацРеРё оставляют откр ытой, СЂСЏРґРѕРј РїСЂРѕРёР·РІРѕРґСЏС‚ Р»Р°РјРїР°СЃРЅС ‹Рµ разрезы, устанавливают дренаж раны перекисью РІРѕ RґРѕСЂРѕРґР° марганца.
РЎ самого начала комплексной S‚ерапии проводится леч ение антРеР±РеРѕС‚Реками.
Препараты выбора:
- РљРѕРјР±РенацРеРё пенициллинов СЃ амРеногликозидами;
- РљРѕРјР±РенацРеРё цефалоспоринов СЃ аминогликозидамми;
- РљР»РендамицРеРЅ;
- РифамппицРеРЅ;
- R”РёРѕРєСЃРёРґРёРЅ;
- Хлорамфеникол;
- МетронидазоД.
RR°R·РЅР°С‡Р°СЋС‚ капельнвцы СЃ альбумном, РїР »Р°Р·РјРѕР№ РєСЂРѕРІРё, СЂР° SЃС‚ворами белков Рё электролитов, введение RїСЂРѕС‚РёРІРѕРі ангренозной сыворотки, переливанве РєСЂРѕРІРё, Р°РїРїР»РёРєР°С †РеРё анаэробного бактериофага РЅР° рану. R”R”СЏ SЃРЅРёР¶РµРЅРёСЏ RєРѕРЅС†РµРЅС‚рацРеРё R±Р°РєС‚ерий применяюS‚ R»РµС‡Р µРЅРёРµ РІ барокамере.
ПрофилактРеРєР° распространення газовой РіР°Рхгрены
Чтобы газовая гангрена РЅРµ вознвла Сѓ пациентов СЃ размозженными Рё Р·Р °РіСЂСЏР·РЅРµРЅРЅС‹РјРё ранами, РёС… ссазу же обрабатывают СЃ гссеч ением нежизнеспособны S... S‚каней. Р'ольному СЃ такими повреждениями назначают Р°РЅС‚РёР±РёРѕС ‚РёРєРё S€РёСЂРѕРєРѕРіРѕ спектра действия.
Очень важно РїСЂРІ»РµС‡РµРЅРёРё пациента СЃ газовой гангрено Р№ соблюдать строгие меры Р°РЅС ‚исептики.
R»R»СЏ него SЃРѕР·РґР°СЋС‚ RїРµСЂСЃРѕРЅР°Р»СЊРЅС‹Р№ сестрРеРЅСЃРєРёР№ РїРѕСЃС‚, РїРѕ мещают больного РІ отдельную пала S‚Sѓ.
Р'СЃРµ манипуляцРеРё СЃ РЅРёРј выполняются RјРµРґРїРµСЂСЃРѕРЅР°Р»РѕРј РІ Р ѕРґРЅРѕСЂР°Р·РѕРІС‹С… перчатках, врачи Рё медсестры надевают специальную RѕРґРµР¶РґСѓ, бахилы.
Rспользованный инструмент, белье RїР°С†РёРµРЅС‚Р° РѕР±СЂР°Р±Р°С ‚ывают РІ СЃСѓС…РѕР ¶Р°СЂРѕРІРѕРј шкафу или РІ стерилизаторе.
Перевязочный материал после ппользования подлежи S‚ немедленному SЃР¶РёРіР°РЅРёСЋ.
RљРепяченРеРµ РЅРµ SЃРїРѕСЃРѕР±РЅРѕ SѓРЅРёС‡С‚ожить SЃРїРѕСЂС‹ RєР»РѕСЃС‚СЂРёР ґРёР№, поэтому S‚акой метод дезинфекции РЅРµ RїСЂРёРјРµРЅСЏРµС‚СЃ СЏ РїСЂРё РіР °Р·РѕРІРѕР№ гангрене.
R”R”СЏ RїSЂRѕS„РеДактРеРєРё SЂР°СЃРїСЂРѕСЃС‚ранения RІРЅСѓS‚рибольничнРѕР№ инфекции требуется С‚С‰Р°С ‚ельно соблюдать РІСЃРµ РЅРѕСЂРјС‹ санитарно-гггиеничесРєРѕР№ обработки RїРѕРјРµС‰РµРЅРёР№ предметов, соприкаса SЋS‰РёС…СЃСЏ СЃ больным.
RџРѕРґРµР»РёС‚СЊСЃСЏ:
Source: https://web.archive.org/save/https://www.ayzdorov.ru/lechenie_gangrena_gazovaya.php