What kind of procedure is densitometry, every postmenopausal woman should know, since during this period the likelihood of developing osteoporosis is highest. Such a study makes it possible to detect it effectively and absolutely painlessly at the earliest stages.
Densitometry refers to instrumental diagnostic methods, and allows you to determine the density of bone tissue, more precisely, to do its quantitative and qualitative analysis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtFc4nw8XVw
There are ultrasound and x-ray densitometry. The two methods are based on different operating principles and use different equipment. Sensors are used to read indicators, after which the data is transferred to a computer for calculation:
- relative bone density;
- thickness of the cortical layer;
- architectonics (spatial structure) and other parameters.
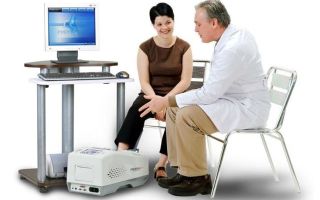
Equipment for densitometric examination can be stationary, with a table and sleeves. It is usually used to examine the spine, as well as the bones and joints of the pelvis.
Monoblock device Stationary equipment
Monobloc equipment is also used in the form of a small device that allows scanning hands, feet and other individual joints and bones.
Preparing for densitometry involves following simple rules:
- The day before the procedure, you should stop taking medications containing calcium and phosphorus, as well as eating calcium-rich foods (cheese, cottage cheese).
- A week before the procedure, MRI or CT with contrast, as well as isotope scanning, should not be performed.
- You should not come to the examination wearing clothes with metal elements (zippers, rivets, buttons), which may affect the information content of the results.
- When starting the procedure, you need to take off your watch and hide your mobile phone in your bag.
X-ray densitometry
X-ray bone densitometry is based on the ability of X-rays to pass through soft tissue, being retained in the dense structure of bones, which are characterized by a high concentration of calcium salts and other minerals. Based on the rate of absorption of X-rays by bone tissue, specialists calculate the degree of mineralization of its various sections.
X-ray densitometry is considered more accurate than ultrasound. It is carried out on a stationary table with a “sleeve”, where the patient is placed for 10-30 minutes.
During the procedure, the spine or its parts, hip and wrist joints, or the entire skeleton are examined. The technique is very accurate, but it cannot be used in all cases: for example, pregnancy is a contraindication for it.
The cost of the procedure ranges from 1,300 to 3,000 rubles, it is determined by the scope of the study and the type of clinic. If there is a need to conduct combined densitometry using a computed tomograph (CT densitometry), then the cost will be about 5,000 rubles.
Diagnostic features
The development of osteoporosis is provoked by many factors. It is important to start treatment on time to completely restore bone tissue. It is spinal densitometry that determines the risk of developing the disease. The following patients should undergo such examination regularly:
- men over 60 years of age;
- women over 45 years of age or at the onset of menopause;
- in case of a fracture without objective reasons;
- patients with spinal diseases;
- when taking hormonal medications, glucocorticosteroids and anticonvulsants;
- people with endocrine diseases and rheumatoid arthritis;
- patients with osteoporosis to determine the effectiveness of treatment;
- people with short stature or low body mass index.
The procedure is simple and takes only 10-20 minutes. Most often, to detect osteoporosis at an early stage, an examination of the lumbar spine is performed. It is in this place that the skeleton experiences the greatest load, and deformation occurs most often.
The procedure is carried out using special equipment, which is a table under which the emitter is placed.
The patient lies down on it, and a sensor is placed above him, which transmits information to the computer about how X-rays are absorbed by bone tissue. If the spine is being examined, the legs should be bent at the knees.
A special stand is placed under them. It is advisable not to move during the procedure.
You can also read: Drugs for the treatment of osteoporosis
The densitometry apparatus contains information about normal indicators of bone tissue mineralization. After the diagnosis, two results are given. Based on this, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
- The first result is the T-test. It shows how the patient's tissue density differs from that of a healthy person. With indicators from 2 to -1, skeletal mineralization is considered normal. If the result is below -2.5, this indicates the development of osteoporosis.
- The Z-score indicates the ratio of the patient’s tissue density to the average values for people of the same age and gender.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DWrjuzWylAs
Spinal densitometry has now become a popular method for preventing complications of osteoporosis. It can be done at any medical center, the cost of the examination is not very high - from 1200 to 4000 rubles. But it allows you to determine the presence of osteoporosis at an early stage and begin treatment on time.
The only method that allows you to detect osteoporosis at an early stage is densitometry.
When examining patients in medical institutions, a standard X-ray examination is used, which detects the disease when there is a loss of more than 30% of skeletal mass.
Densitometry records a weight loss of 2%. The method is non-invasive, without incisions or surgical interventions, and provides a quantitative assessment of the detected changes.
Diagnostics will determine the extent of bone tissue damage.
The study is carried out using special devices - densitometers, which have a built-in computer and special software. The intensity of the scanning beam, after passing through the tissues of the body, depends on their density and structure. The receiving sensors of the device record changes in radiation intensity and reflect them on the monitor screen.
The doctor will evaluate the densitometry results and make a diagnosis.
T-criterion indicators| Norms | Standard deviation no more than 1 in any direction |
| Low bone density | From 1 to 2.5 |
| Osteoporosis | More than 2.5 |
Osteoporosis is a serious socio-economic problem.
After the age of 60, patients with fractures of the vertebrae and femoral neck spend more time in a hospital bed than those suffering from diabetes mellitus or myocardial infarction.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis using densitometry reveals skeletal pathology in the early stages, before the occurrence of fractures. The procedure allows you to prolong life, avoid complications and disability.
Of all the results that densinometry shows, the most important are:
- Bone density (T-score), compared with the norm for young people in points. The norm is considered to be 1 point or higher; at 1-2.5 they speak of osteopenia, less than -2.5 - osteoporosis is diagnosed.
- Bone density compared to the norm for a specific age group (Z score). This indicator must be within the specified age limits.
The list of diseases for which densitometry is indicated is presented:
- Osteopenia.
- Osteoporosis.
- Spinal fractures.
- Bone fractures
X-ray and ultrasound densitometry are effective methods for early diagnosis of such an insidious disease as osteoporosis. Thanks to their sensitivity and information content, regular examinations can promptly identify signs of the disease and prevent its progression.
Ultrasound densitometry
This densinometry method is similar to X-ray, but its accuracy is lower. Ultrasound densitometry is considered an indirect method for determining bone density. Ultrasound waves travel at different speeds through areas of bone tissue that have different densities. The process is recorded by a sensor, processed and provided in the form of data to a specialist for analysis.
The cost of this type of examination ranges from 700-2000 rubles.
Despite the lower accuracy of the results, this method is also used quite widely, due to its absolute safety, speed and ability to be performed without additional examinations. The procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes and can be performed for pregnant and lactating women.
Indications for densitometry
Recently, ultrasound diagnostics have been used more often. It is safe and allows you to examine even children and pregnant women. The X-ray method is used to clarify the diagnosis if osteoporosis is suspected. It may not be possible for all patients. X-ray densitometry is contraindicated in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- women during breastfeeding;
- if there are metal implants;
- if radioisotope diagnostics or CT scanning using a contrast agent was performed within 5 days before.
Also, the examination is not recommended in the presence of arthritis of the spine and recent fractures, as well as other conditions that prevent the patient from lying motionless on a hard surface for a long time.
Bone loss due to osteoporosis
Densinometry is performed when osteoporosis is suspected, as well as as a preventive examination associated with this disease.
This type of examination is used to determine:
- The amounts of minerals in any one of the bones or in the entire skeleton.
- General condition of the spine.
- The presence of osteoporosis or osteopenia (a disease characterized by a slight decrease in calcium content in bone tissue), the degree of development of the pathology.
- Fractures of bones and vertebrae.
That is, undergoing densitometry makes sense for any person who is at risk of developing osteoporosis. This is especially true for people exposed to risk factors.
The list of these factors is presented:
- Metabolic disorders.
- Pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies.
- Diseases of the spine (spondylolisthesis, osteochondrosis), injuries.
- Endocrine diseases - hypothyroidism, diabetes, pathologies of the parathyroid gland.
- Long-term use of hormonal and other drugs that remove calcium.
- Some neurological disorders.
- Recurrent fractures.
- Rheumatism.
- Poor nutrition, frequent adherence to strict diets.
- Low body weight, alcohol abuse and smoking.
- Densitometry of the lumbar spine and femoral neck can provide a 10-year prognosis for fracture and can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- When conducting such an examination on a child, it is possible to determine whether there is enough calcium and phosphorus in his body so that the child’s body can cope with intensive bone growth.
- The amount of calcium in the bones after 30 years begins to decrease over time, so from about 40 years of age you need to control this indicator.
How often can densitometry be done? It should be carried out once every 2 years. Thanks to screening examinations, osteoporosis can be detected and treated in a timely manner. This examination regimen is recommended for women over 30 years of age who have close relatives susceptible to osteoporosis. Men should be screened for prevention starting at age 60.
- A bone fracture, especially a minor injury, and any bone trauma.
- Early menopause (before 50 years).
- For men, this is the age after 60 years.
- Orchiectomy (surgical removal of the testicles).
- Pathologies of the parathyroid glands.
- Taking oral contraceptives, tranquilizers and glucocorticoids (steroid hormones).
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Frail physique.
- Genetic predisposition to osteoporosis.
Patients who are susceptible to the listed risk factors for osteoporosis should undergo densitometry at least once a year. And if there is loss of bone mass density, it is necessary to begin preventive measures as soon as possible.
ABOUT CALCIUM
How is densitometry done?
When performing X-ray densitometry, the patient is placed on a table equipped with a stationary device, after which the specialist leaves the room. When examining the spine, a special stand is used to support the legs.
When examining the pelvic bones, the legs are placed in a brace. After this, the arm of the device moves, during which a series of photographs are taken, and the data is transferred to a computer.
Movement during the procedure is prohibited unless such a command is given by the doctor. He may also ask the patient to hold his breath.
How is ultrasound densitometry performed? In this case, the patient lies on a medical couch, and the doctor performs an ultrasound procedure using a special attachment with a sensor. Both types of examination are absolutely painless and are performed fairly quickly.
In this way, you can examine any area: the lumbosacral spine, femoral region, heel bone, etc.
Ultrasound densitometry has no contraindications. X-rays are strictly prohibited for pregnant and lactating women, and for children it is done in case of urgent need.
Source: https://osustavaxt.ru/densitometriya-kostey-pozvonochnika-metod-diagnostiki-osteoporoza/
How is bone and spine densitometry performed?
Bone densitometry is a procedure performed to assess the condition of the bone tissue structure. This type of study is prescribed for a number of diseases.
With its help, you can identify pathology in time, which will prevent the occurrence of complications. The technique is presented in several options.
The choice is determined by the severity of the disease and the localization of bone tissue lesions.
More about densitometry
The procedure allows you to determine bone mineral density. The method is non-invasive, which means there is no need to violate the integrity of the skin.
If you are interested in the question of what densitometry is, you need to find out how it is carried out.
Various equipment is used for the examination; the purpose of the procedure is to determine quantitative indicators of the content of essential minerals, primarily calcium.
If degenerative processes develop in the bones, densitometry of the lumbar spine and femoral neck is first prescribed. Based on the results of the study, the condition of the bones of the musculoskeletal system is analyzed. It is important to exclude the possibility of a fracture, since damage to the femoral neck and spine can result in complete immobility.
- microarchitecture of bone tissue;
- mineralization;
- the presence of microdamages of bone beams;
- bone turnover.
Typically, examination of the spine and hip joints is required. If necessary, the bone structure of the entire skeleton is assessed.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
There are a number of factors that can provoke degenerative processes in bone tissue:
- bone fractures (even a single case sometimes leads to the development of pathology);
- in women, bone demineralization is diagnosed more often, especially after the age of 65;
- menopause;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids (more than 3 months), which is often a necessary measure for rheumatic diseases (vasculitis, lupus erythematosus);
- if relatives have been diagnosed with osteoporosis;
- minor developmental delays (pronounced thinness, short stature);
- physical inactivity;
- alcohol, drugs;
- surgery to remove the ovaries;
- prolonged immobilization of joints;
- lack of vitamin D and calcium.
If one of these factors occurs, then the likelihood of developing pathology is reduced. However, densitometry can also be performed to monitor therapy. This method has few contraindications.
The pregnancy period is noted, but this limitation occurs only with certain types of densitometry. In addition, it is not recommended to perform this procedure if there is immobility.
In this case, the patient will not be able to take the desired position for the examination.
Overview of types of techniques
Assessment of the structure of bone tissue, namely the mineral density indicator, can be carried out in different ways. Types of techniques:
- Ultrasound bone densitometry. There is no harm to the body. The disadvantage of this technique is a less accurate result. Ultrasound-based densitometry has no contraindications. It is permissible to perform it even for pregnant women and women during lactation. Ultrasound is often prescribed for initial examination if degenerative processes in the joints are suspected. This procedure takes little time and does not cause discomfort. However, for further monitoring and control of therapy, it is recommended to use a more accurate method.
- X-ray densitometry. This is a highly informative technique. If you are interested in how such a procedure is carried out, you need to know that the assessment of the structure of bone tissue is based on the intensity of radiation passing through the bones. A special device is connected to the equipment, which determines the quantitative indicators of minerals. X-ray densitometry allows you to examine the entire skeleton or its individual parts. This method evaluates the structure of the bone tissues of the lumbar, thoracic spine, wrist joint, femur, etc. The disadvantage of the technique is the need to expose the patient to radiation. For this reason, it is not prescribed during pregnancy and to patients in childhood.
- Absorption photon densitometry is an expensive method, which is also quite labor-intensive. For this reason, it is not as common as x-rays. In this case, the intensity of absorption of radioisotopes by bone tissue is assessed. One of the methods of carrying out the procedure is prescribed: monochrome and dichrome. In the first case, the dose of isotopes is minimal. Monochrome densitometry is used to assess bone density. The dichrome method is more informative; it also determines the degree of looseness of bone tissue.
There are other methods that are types of x-ray densitometry:
- quantitative magnetic resonance densitometry;
- computed bone densitometry or quantitative computed tomography.
They are prescribed less frequently - for example, in cases where it is necessary to obtain more extensive information about the condition of the skeleton and identify other disorders. This will allow you to make a correct diagnosis, excluding a number of pathological processes. In addition, CT and MRI are expensive methods and therefore are available to a narrower range of patients.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Unlike a number of other techniques, densitometry does not require adjustments to the diet in anticipation of its implementation. However, it is still necessary to prepare for the procedure; to do this, you need to follow the following recommendations:
- Stop taking medications that contain calcium. Densitometry is precisely carried out to determine the quantitative component of this indicator. If you take additional calcium, the result will be inaccurate, which may affect further treatment. Avoid supplements containing this mineral about a day before densitometry.
- It is important to warn the doctor about other studies that have been performed previously: CT, MRI, etc. The procedure may be affected not by the fact of the study itself, but by the substance that is introduced to create contrast in the image, for example, containing barium. If this element is present in the body, the result will be inaccurate. It is necessary to take a pause between different procedures, but the decision to prescribe the next examination must be made by the doctor.
If it is necessary to perform a bone structure analysis on hairy areas of the body, it is important to remember that hair removal is not required for the densitometry procedure. As you can see, the preparation is not labor-intensive; it is only important to discuss with the doctor all the aspects of the procedure. Early pregnancy must be reported prior to testing.
If the ultrasound method is safe for the woman and baby, then with X-ray densitometry the period of gestation is a contraindication.
How is the procedure performed?
The main condition is to remain still. Even weak movements can lead to worse results. The person must take a position that is comfortable for the examination.
The body position is selected taking into account the localization of bone tissue lesions. Densitometry is carried out with a special small sensor.
It comes into contact with the skin and transmits radiation that reaches bone tissue. The result is displayed on the monitor.
The whole body examination may take some time (30 minutes or more). Densitometry of peripheral areas is carried out in a few minutes. If an x-ray is performed, all metal objects must be removed. This applies to X-rays, CT and MRI. You should tell your doctor about implants. The ultrasound-based procedure is carried out in two ways:
- "Dry" sensor. The method requires the use of a special gel, which is applied to the area where the lesions are localized. The substance that allows the densitometer probe to slide is different from that used during standard ultrasound procedures of any other type.
- "Water" method. In this case, the patient's body is completely or partially immersed in water, for which distilled water is used. The procedure is carried out in a bath.
X-ray densitometry is performed while wearing clothes. However, you should check that there are no metal fittings on it.
Decoding the result
Bone tissue can have a different structure when degenerative processes develop in it. When densitometry, two criteria are analyzed: T- and Z-score. The first of them is the result of a comparison of the reference indicator, as well as an assessment of the density of the patient’s tissues. The Z-score is obtained by comparing the patient's bone density and the average for his age group.
Decoding the results:
- A result greater than 1 is normal.
- If the value of the main indicators varies from -1 to -2, osteopenia is diagnosed. This is a condition characterized by low bone mineral density.
- An indicator of less than -2 indicates that osteoporosis is developing.
- A decrease in the indicator to -2.5 or below gives grounds to diagnose a severe stage of osteoporosis, when the risk of fracture due to minor injury is extremely high.
Price and where to go for the procedure
Ultrasound is performed in outpatient departments and diagnostic centers. This is a simpler and more affordable method. If X-ray densitometry has been prescribed, this procedure is available in hospitals and general medical centers. If you are interested in the average price, then it is necessary to take into account the type of joint being examined and the location of the lesions.
The cost varies from 700 to 6000 rubles. Thus, an extensive examination, when the condition of all the bones of the skeleton is assessed, will cost more than other procedures. Studying the tissue structure of one joint can cost an average of 700–1400 rubles. A comprehensive examination, when it is necessary to obtain results on the condition of 2 or more joints, will cost 2,200 rubles and more.
Source: https://OrtoCure.ru/diagnostika/densitometriya-kostej-i-pozvonochnika.html
Densitometry, what is this procedure?
Densitometry, what is this procedure?
Osteoporosis is a dangerous disease that leads to rapid bone depletion. Cases of fractures are becoming more frequent, and the ability to move is limited.
If you have an illness, you have to change your lifestyle. Against the background of osteoporosis, other serious diseases develop, often leading to death.
- Treating a disease is much more difficult than stopping it at the initial stage of development or preventing its occurrence.
- Densitometry helps to make a timely diagnosis - a diagnostic procedure that allows instrumental identification of the structure and mineral density of bone tissue, the thickness of its surface layer.
- The study is carried out during the treatment of the disease to assess the quality of the therapy.
- It is necessary to consider what indications are taken into account when scheduling an examination, how to prepare for it, how the procedure is carried out, and whether it is allowed for everyone.
Types of densitometry
Densitometry is carried out exclusively by specialists in a clinical setting, in public and private diagnostic centers. There are two types, but it is always painless.
*Read more: EHF therapy indications and contraindications
It does not require anesthesia of the part being examined or the use of anesthesia. The types differ in the apparatus used to examine the patient.
When using x-rays it is called x-ray, when examining with ultrasonic waves it is called ultrasound.
Each type has its own characteristics and indications for implementation or categorical prohibitions and restrictions on the procedure.
X-ray
- X-ray densitometry is the most accurate modern diagnostic tool for identifying osteoporosis in the early stages of development.
- Diagnosis is provided using devices that illuminate bones with X-rays.
- The method for identifying the disease is simple: the denser the bone of the person being examined, the fewer rays pass through it.
Consultation with a doctor before densitometry
The radiation exposure to organisms is low. However, it is not recommended to undergo the procedure more than once a year.
Most often, patients are prescribed densitometry of the lumbar spine, although the method is suitable for studying the bones of the pelvis and shoulder joint.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic densitometry is completely safe. The method is common, but less accurate compared to the previous one.
To obtain results on bone density, elasticity, and stiffness, a sound wave is used, directed to a specific section.
*Also read: How does High Tone Therapy work?
Reflecting from the bone or scattering through its thickness, the wave signals the presence or absence of osteoporosis and other diseases that lead to deformations of the skeletal system.
How is the procedure performed?
The method of densitometry is determined by the type of examination:
- The X-ray examination is carried out on a special table, on the surface of which the patient is laid. Below the table there is a generator that scans the bones, and on top there is a device that takes several pictures. The data is immediately sent to the monitor. The patient is prohibited from moving while the device is operating. A stand or brace is placed under the legs or lower back.
- Ultrasound diagnostics are performed on a couch next to the installed device. The patient lies down straight, sits, and the doctor scans the desired area with a special attachment, supplemented with a sensor that transmits ultrasound. A computer is connected to the device, and the results are displayed on the monitor.
Step by step instructions
Densitometry of the femoral neck or other part is performed, usually at the time prescribed for the patient. There is no need to undress before the procedure.
*Also read: Hip fracture in old age
It is recommended to remove jewelry or clothing that has metal fittings.
Densitometry procedure
It is also advisable to put a watch and mobile phone in your bag and set it aside.
*Also see: How diadynamic therapy works
Procedure:
- Lie down on a table or sit on a couch.
- Take the position recommended by the doctor. Hold your breath for a few seconds if necessary.
- Leave the premises after completing the study.
What the study shows
The doctor prescribing the procedure must decipher the densitometry result. However, the patient can read something in the conclusion, seeing the score indicators.
The device contains a program that knows what parameters of bone density should normally correspond to a certain age.
Densitometry results
Having received data on a specific patient, they are compared with the established ones.
- The “T” indicator reveals the ratio of the existing results to the norm. Indications above -0.9 are considered optimal, the disease has not been detected. In the range -1 - -2.5 - the development of osteopenia, numbers below -2.5 - indicate osteoporosis, an increased risk of fractures.
- The “Z” score indicates bone density in comparison with reference normative data for the corresponding age group and gender of the patient. If low numbers are obtained, a repeat study is required to adjust the treatment and stop bone destruction.
How to prepare for densitometry
If there are suspicions or a diagnosis of osteoporosis has been made, densitometry is mandatory.
*Also see: What is SCENAR therapy
Preparing for the procedure does not imply lifestyle changes, but it is necessary to follow several recommendations to obtain reliable information:
- During the day preceding diagnosis, exclude from the diet dishes containing cottage cheese and various cheeses.
- Stop taking medications that increase phosphorus and calcium levels (1-2 days before the tests).
- If MRI or CT was performed, then densitometry is allowed no earlier than a week, after a radiator examination - after 2 - 3 days.
Indications and contraindications
Bone densitometry is prescribed both to examine the entire spine and to obtain results on the condition of individual sections: the hip, shoulder, and limbs.
The procedure is not recommended for everyone, but for people prone to developing the disease and suffering from osteoporosis.
*Read more: Inductothermy, therapeutic effects
Indications for examination are:
- pregnancy;
- spine pathologies;
- metabolic disorders;
- constant back pain;
- long-term treatment with hormonal drugs.
The circle of patients constituting a risk group has been determined. They are recommended to have spinal densitometry at least once every 10–12 months:
- women who have reached the age of fifty, men - sixty years of age;
- patients suffering from frequent fractures;
- old people whose height is below 1 m 50 cm;
- individuals of any age who are underweight;
- women who have reached menopause;
- patients with rheumatic and endocrine diseases, scoliosis and intervertebral hernias.
Knowing what densitometry is and how the study is carried out, patients themselves can take a referral for an examination if they believe that they have problems with their bones.
Healthy bone and bone affected by osteoporosis
Reasonable suspicions arise in the presence of bad habits, which include:
- addiction to frequent fasting, malnutrition;
- systematic diets with limited consumption of healthy foods;
- passion for alcoholic drinks;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking in large quantities over a long period.
It is recommended to go to the clinic and undergo examination if you have relatives suffering from osteoporosis.
*Read more: How to quit smoking in old age
- Densitometry of the lumbar region or other part of the spine is not always permitted.
- The ban is imposed by the doctor, but patients should know in advance about contraindications to the procedure.
- Factors that do not allow you to undergo diagnostics using an X-ray machine:
- pregnancy at any stage;
- period of breastfeeding.
There are no contraindications for ultrasound densitometry, since the procedure is considered harmless.
Conclusion
Densitometry is an ideal method for detecting bone diseases at an early stage.
By performing the procedure systematically, it is possible to avoid the development of pathology and progression of the disease called osteoporosis.
Video: Densitometry (measuring bone density)
Source: https://noalone.ru/infocentr/zdorove/densitometriya-chto-yeto-za-procedura/
Densitometry (diagnosis of osteoporosis)
Osteoporosis is an extremely common disease characterized by decreased bone density. To a certain extent, the increasing frequency of diagnosed cases of osteoporosis is explained not so much by the deterioration of the health of the population, but by an increase in life expectancy (the disease mainly affects people in the older age group).
The development of the diagnostic capabilities of modern medicine has played a certain role in the increase in the number of patients with increased bone fragility. The most informative method for diagnosing osteoporosis is bone densitometry, which allows not only to determine the percentage of bone loss, but also to identify structural disorders of bone architecture.
The mechanism of development of bone tissue pathology
Bone is a highly specific tissue that contains three structural elements:
- protein matrix, which makes up the main connective tissue that holds minerals in the bone;
- mineral component consisting of calcium and phosphorus;
- bone cells responsible for the reconstruction of bone tissue.
Contrary to popular belief, bone does not have a permanent, once formed structure. Essentially, it is a living structure whose main purpose is to provide optimal maintenance to the human body. During life, the nature of the loads on the load-bearing apparatus of the human body changes repeatedly; the reasons for the changes can be:
- weight gain;
- lifestyle changes (increasing or decreasing mobility);
- increase in external loads (systematic lifting of weights), etc.
The influence of these factors forces the bone to constantly carry out internal restructuring, allowing it to maintain stability and maximally resist changing loads.
In this case, bone tissue is destroyed in a place that does not require increased strength, and harder tissue is formed in the most “loaded” area.
The remodeling process is constant, and bone cells are responsible for it - osteoblasts, which form a new matrix and osteoclasts, which destroy it.
Regular physical activity stimulates metabolic processes in the bone structure
The age period up to 20-30 years is characterized by a high rate of metabolic processes, in which bone formation occurs under the influence of various factors (strength loads, amount of calcium consumed, hormonal changes). Once maximum bone mass is reached, the processes of loss and restoration are balanced. The main cause of osteoporosis is the predominance of resorption (destruction) processes over formation processes.
Important! If in young people the rate of metabolic processes in bones is 50% during the year, then in the age category over 50 years old it is no more than 5%, while resorption processes inevitably prevail over formation processes.
Since loss of bone mineral density (BMD) is always a consequence of some disease or condition, there are certain categories of people for whom screening for osteoporosis is indicated.
So, the indications for the examination are:
- age over 45 for women and over 55 for men;
- postmenopausal women;
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- multiple pregnancies (more than 3) or prolonged breastfeeding;
- several cases of bone fractures within 3–5 years;
- patients taking drugs from the corticosteroid group, as well as tranquilizers and anticonvulsants;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle (long-term bed rest, use of a wheelchair);
- sudden weight loss or constant low weight;
- presence of relatives diagnosed with osteoporosis.
Important! Insufficient intake of vitamin D in the body can cause the development of osteoporosis. Smoking and drinking alcohol are one of the causes of osteoporosis.
Diagnostics
Among the list of tests for osteoporosis, densitometry rightfully occupies a leading place, as it allows for a quantitative assessment of the condition of bone tissue.
A urine test for the amount of excreted calcium and hydroxyproline, which in patients with progressive osteoporosis are usually excreted in the urine to a greater extent than absorbed by the body, has a certain informative value, applicable to assessing the intensity of bone destruction.
- In addition, the initial examination includes testing the urine for deoxypyridonoline (DPID), which is excreted unchanged (unbound) in the urine as a result of slow or absent metabolic processes in bone tissue.
- Since the main goal of diagnosing osteoporosis is to identify a category of patients prone to low bone mass, it is advisable to carry out a comprehensive assessment of osteoblast activity, determined by the amount of osteocalcin per day, parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase and deoxypyridonoline.
- Table. Normal values of biochemical markers
| Indicators | Unit change | Norm | |
| men | women | ||
| Total calcium | mmol/l | 2,2–2,65 | 2,2–2,65 |
| Phosphorus | ** | 0,80–1,5 | 0,80–1,5 |
| Parathyroid hormone | pmol/l | 0,7–5,5 | 0,7–5,5 |
| Deoxypyridonoline | DPID/mol | 2,3–5,5 | 2,9–7,5 |
| Osteocalcin | ng/ml | 12,0–52,0 | 5,5–59,0 |
Determining the concentration of female and male sex hormones has a fairly high diagnostic value, since it is endocrine disorders that often become the cause of the development of osteoporosis.
X-ray densitometry
The most commonly used method for examining bones for osteoporosis is densitometry. The term “densitometry” combines several methods of obtaining images that allow a quantitative assessment of the bone mineral density (BMD) of the patient being examined. Certain results in assessing BMD have been achieved using conventional x-rays.
However, it is not possible to obtain any significant quantitative results with its help. The determining factor that excluded radiography from the list of methods used to diagnose osteoporosis was the fact that even when assessing the image by an experienced doctor, it was not possible to detect bone loss of less than 40%.
Carrying out a dynamic assessment of the progression or regression of the disease is also quite difficult due to the low sensitivity of the equipment. Despite this, radiography is successfully used when it is necessary to assess the degree of deformation of bone structures, for example, vertebrae, since a similar phenomenon often occurs with the development of osteoporosis.
Important! It is advisable to study the degree of changes in BMD in areas of the skeleton where the proportion of trabecular tissue predominates (femoral neck, lumbar spine, wrist joint), since osteopenic changes affect it first.
Minor bone loss cannot be diagnosed using an x-ray.
The most popular methods of X-ray examination of the BMD are considered to be:
- dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA);
- morphometric X-ray absorptiometry (MRA);
- quantitative computed tomography (QCT).
All x-ray methods for studying the degree of BMD reduction are based on the movement of ionizing radiation from a source located outside through the bone to a fixing detector. In this case, a narrow beam of X-ray radiation is directed to the object under study and the final result, that is, the intensity of the radiation transmitted through the bone is recorded by a computer system.
How often can x-rays be taken?
The main principle of the DEXA method is the use of double radiation, which allows the error to be reduced as much as possible due to the registration of two options for energy absorption (in soft tissues and bones).
The MRA method is a variant of DEXA, however, the use of a fan-shaped radiation flux has improved image quality and reduced scanning time, and accordingly reduced the radiation dose to the patient.
The QCT method allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image and not only determine BMD, but also obtain data on the layer-by-layer structure of bones, that is, assess the condition of the trabecular and cortical layers.
The negative side of using CCT is the high radiation dose, 10 times higher than DEXA, and the dependence of the accuracy of the readings on the amount of bone marrow, the percentage of which increases with age.
Ultrasound computer densitometry
The method of ultrasonic densitometric research is based on calculating the speed of movement of an ultrasonic wave through tissues of different densities. Differences in the density of the bone being examined cause differences in the speed of ultrasound transmission, that is, denser bone (well mineralized) transmits ultrasound faster than less dense bone.
The received data is recorded by the sensor and converted using computer software into quantitative indicators. A characteristic property of ultrasound densitometry is its extremely high sensitivity to the slightest changes in bone density. In this regard, it can be used to diagnose osteopenia, when the loss of mineral substances does not exceed 3–5%.
The undoubted advantages of ultrasonic computer densitometry methods include:
- sufficiently high information content;
- no negative impact on the body;
- speed of the procedure;
- affordability;
- no contraindications.
Thanks to such a large list of positive aspects, ultrasound densitometry can be used not only for diagnosing osteopenia and osteoporosis, but also for monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
Due to significant deviations that appear when examining bones deeply embedded in soft tissue (proximal femur), ultrasound densitometry is performed exclusively on the extremities (wrist joint, calcaneus, etc.).
Long bones are the most informative when performing ultrasonic densitometry
Conduct and results
The technique of X-ray densitometry consists of performing a set of measurements using radiographs at several standard points most susceptible to osteopenic changes:
- lumbar spine;
- femoral neck;
- radius.
After taking a series of images, the software processes the results obtained by comparing them with the database included in it. The comparison is made according to two criteria:
- the result obtained with the optimal indicator for patients of the same sex (T-criterion);
- the result obtained with the average statistical indicator of patients of the same sex and age (Z-criterion).
The most informative when making a diagnosis is the T-criterion; checking the degree of its deviation from normal indicators has a significant diagnostic value:
- readings above “-1” indicate normal BMD;
- readings ranging from “-1” to “-2.5” indicate osteopenia (the initial stage of osteoporosis);
- readings below “-2.5” indicate the development of osteoporosis.
Ultrasonic densitometry is carried out by determining the density of the cortical (outer) layer of tubular bones.
To do this, using an ultrasound sensor, an ultrasonic wave is passed along the bone, determining the MIC by the speed of its propagation.
In a short period of time, the device performs thousands of measurements and calculates Z and T-criteria based on the results. Standard projections for ultrasonic computer densitometry are:
- phalanx of the middle finger;
- radius or wrist bone.
Important! The results obtained using X-ray and ultrasound methods may have some differences, but the final indicators are usually interpreted the same (normal or osteoporosis).
Structural changes in bones: on the left – normal, on the right – osteoporosis
Due to the individual characteristics of the course of the disease, there may not be obvious signs of bone tissue destruction, such as fractures. However, timely diagnosis can significantly reduce the risk of such a serious complication as a femoral neck fracture.
Despite the fact that the pathology is not fatal, a long-term decrease in motor activity and expensive treatment (prosthetics), which is also impossible to carry out in severe stages of osteoporosis, often lead to death.
Today, doctors have a large number of medications in their arsenal to treat osteoporosis, but due to the fact that the recovery process is extremely long, it is optimal to start it as early as possible.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/prochee/densitometriya-diagnostika-osteoporoza
Densitometry: indications and contraindications for examination
Do you know what osteoporosis is? Maybe. However, most of us do not take this disease seriously, despite the fact that osteoporosis, according to the World Health Organization, is among the leaders and ranks fourth among the causes of death and disability in humans. The first three are assigned to oncology, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
So, osteoporosis is a disease characterized by a decrease in the density of bone tissue, and therefore the bones themselves. The chemical composition of bone matter per unit volume of the bone itself does not change. Osteoporosis appears due to disruption of metabolic processes in the body, i.e.
the process of formation (synthesis) of new tissue and destruction of old tissue, and is expressed in a decrease in bone mass. It is not difficult to guess what the consequences of osteoporosis are. Decreased bone density reduces bone strength and therefore increases the risk of fractures.
If there is an imbalance between synthesis and breakdown, healing of a bone fracture will proceed extremely slowly, which can ultimately lead to disability, and in extremely severe cases, death.
- The risk group includes:
- - persons over 45 years of age;
- - women after menopause;
- people taking prednisolone (glucocorticoid hormones), NSAIDs (diclofenac, etc.), thyroid hormones, diuretics, steroids (metipred, etc.)
To determine osteoporosis today, it is enough to undergo densitometry - a modern, safe, painless method that allows you to make an absolutely accurate diagnosis. What is densitometry , who is it indicated for, and who cannot undergo this type of examination?
So, densitometry is a study of bone tissue to determine its mineral density.
It allows you to estimate the loss of bone mass with an accuracy of 2%, thanks to which the doctor can select the most effective treatment for osteoporosis and prescribe medications that are suitable for you.
In most cases, bone mineral density can be almost completely restored, thereby preventing the development of the disease and the likelihood of fractures.
How is densitometry performed in the clinic?
Preparation for densitometry does not require special diets or a special diet. The day before the test, simply stop taking calcium supplements. You should come to the examination itself in comfortable clothes without metal parts (buttons, zippers, rivets).
The entire examination takes no more than 30 minutes, the duration of the procedure depends on the parts of the body being examined. You can analyze the condition of the entire skeleton, or you can undergo densitometry of only a certain part of the body. As a rule, doctors examine the bone tissue of the hip joint and spine - the places most susceptible to fractures.
You lie down on a soft table, above which there is a sensor, and below it is a radiation source. The device illuminates your bones with thin beams invisible to the human eye with a low dose of radiation (less than 0.1 dose of standard radiography - fluorography). After which the doctor receives information about bone mineral density.
During densitometry, you will periodically take short periods of time in positions that are uncomfortable for you.
- Who is densitometry indicated for, and what are the contraindications?
- Densitometry is indicated for the above-mentioned risk group, as well as for those who:
- - has 2 or more risk factors for osteoporosis;
- - had at least one or, moreover, several fractures not associated with serious trauma over the age of forty years;
- — was injured as a result of an accident, playing sports, or falling from a great height;
- - has a suspicion of osteoporosis;
- — takes medications for the treatment of osteoporosis in order to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Densitometry has no absolute contraindications. Relative ones can be called: pregnancy, changes in the lumbosacral spine, due to which the patient will not be able to take the position necessary for the examination or remain in a supine position on a sufficiently hard surface during the analysis.
- In addition to densitometry, the following may additionally be prescribed:
- - X-ray (if you have more than 20% bone loss);
- — markers of bone tissue metabolism, or biochemistry of metabolic processes in bone tissue;
- — bone tissue biopsy (performed during surgical interventions)
- For a qualitative analysis of bone density and a correct diagnosis, it is strongly recommended that you undergo an examination at a reputable medical institution specializing in the treatment of osteoporosis and other problems with the spine, such as the Spine Clinic in St. Petersburg.
Source: http://romasky.ru/63/32698