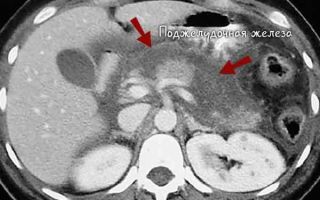
- A number of pathological changes in the area of soft tissues and vital internal organs, such as the pancreas, require high diagnostic accuracy.
- Such changes cannot be detected using x-rays, ultrasound or computed tomography.
- The necessary accuracy of research is achieved using non-invasive methods such as magnetic resonance imaging.
- The results of an MRI of the pancreas make it possible to determine the nature of the pathology in the early stages, which means they significantly increase a person’s chances of recovery.
The implementation of digestion and metabolic processes in the body is impossible without the participation of the pancreas - the pancreas. Any, even minor, disturbance in the functioning of the second largest endocrine gland leads to the development of chronic diseases that are difficult to treat.
Thus, no doctor can guarantee a complete cure for diseases such as diabetes mellitus or pancreatitis. In most cases, maintenance treatment must be continued until the end of the patient's life. This prognosis is a compelling reason for immediate, high-precision diagnostics.
The resulting tomographic images are sent to the monitor screen.
The doctor is able to identify fibrous changes, the presence of cysts or dense tumor formations. Depending on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed.
The main indications for diagnostics using MRI are:
- presence of stones inside the pancreas ducts detected by ultrasound;
- unconfirmed diagnosis of calculous pancreatitis;
- conducting an assessment examination of the structure of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis;
- unreasonable pain in the epigastric region;
- the presence of pus in the peripancreatic tissue;
- identified cysts or benign formations;
- the need to confirm the development of a malignant tumor;
- post-traumatic conditions;
- the likelihood of metastatic lesions;
- history of chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- confirmed carbohydrate metabolism disorder;
- routine monitoring if treatment is ongoing or has already been completed.
The doctor may prescribe an examination if unclear symptoms are detected, similar to both pathological changes in the pancreas and diseases of other abdominal organs. In such cases, diagnosis of pancreas is carried out as part of a general examination.
Abdominal MRI. Pancreas
In addition to providing assistance in making a final diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging allows one to monitor the processes of recovery of the pancreas after surgery and record the current state of the pancreas during treatment.
Carrying out diagnostics using the MRI method provides results with an accuracy of up to 97%, which is especially important when identifying malignant formations of small (within 2-3 cm) malignant formations, or small stones located in the area of dilated pancreatic ducts.
People suffering from claustrophobia should not insist on diagnostics using open-type equipment. The power of such equipment does not exceed 0.5 Tesla and directly affects the quality of the image displayed on the monitor screen.
The required accuracy in diagnosing the pancreas can only be provided by a closed tomograph (from 1.5 Tesla).
What does an MRI show?
For a patient, the duration of a magnetic resonance imaging session of the pancreas is no more than half an hour. You will have to wait a little longer, about two hours, for the results of the study.
During this time, the doctor, processing the resulting high-quality layer-by-layer images, assesses the condition of the pancreas according to the following parameters:
- gland shape;
- organ size;
- tissue density, determined by signal intensity;
- the contours of the gland itself, as well as formations, if any were discovered;
- the presence of neoplasms of any kind;
- deviations from the norm in the condition of the ducts;
- the presence of changes in the blood supply system (vascularization) of the pancreas.
The high accuracy of MRI results allows a specialist to identify minimal structural changes, which is important for diagnosing diseases in the early stages of development.
Depending on the indications, contrast enhancement is used to obtain more reliable data (for example, when studying vascularization features).
Preparing for an MRI of the pancreas
Preliminary preparation for the session will help increase the quality of images, as well as their information content.
The clinic administrators must inform you about the necessary preparatory measures before an MRI of the pancreas when registering for a session. Thus, a person does not need to memorize everything necessary to successfully complete the study and action.
With the exception of some additions related to the peculiarities of diagnosing the abdominal organs, the usual list of preparatory activities includes:
- a gentle regime for the digestive system during the day before the session;
- refusal to drink alcohol;
- stopping taking medications containing alcohol;
- quit smoking at least 3 hours before the test.
Medicines
There is a strict ban on taking medications containing alcohol. Any medications are also prohibited if magnetic resonance imaging with contrast is prescribed.
It is allowed to take sedatives as prescribed by a doctor if a person suffers from claustrophobia or is afraid of conducting research . The doctor should be notified in advance of the slightest anxiety or fear. Timely taking of the drug prescribed by your doctor will help you get rid of unnecessary and unfounded worries.
Diet
The patient should pay special attention to foods consumed during the day before the MRI. To reduce the load on the digestive system as much as possible, one day before the MRI (or better yet, increase the duration of the fasting diet to three days), it is necessary to eliminate the following:
- any fatty foods;
- spicy;
- salty;
- canned fruits and vegetables;
- coffee;
- black strong tea;
- any drinks containing alcohol.
The diet should be fractional. Eat small meals every three hours. Instead of black tea and coffee, drink clean, not boiled water, not strong green tea. It is good to diversify your diet with milk, oatmeal or berry jelly.
Special requirements are imposed to prepare for magnetic resonance imaging with contrast. In this case, it is prohibited to eat for 12 hours before the session.
The ban also applies to taking any medications.
If there is a need to relieve tension, anxiety or eliminate fear, sedation is performed by an anesthesiologist immediately before the MRI.
The maximum information content of the images directly depends on the patient’s ability to remain still during the MRI session. Minimal anxiety or fear interferes with the ability to be in a relaxed state.
The doctor should be informed about any disturbances in the emotional state associated with the upcoming procedure several days before the start of the study.
Applying Contrast
The results of magnetic resonance imaging are significantly different from the results of examinations using ultrasound or radiography due to the high accuracy of the data obtained.
However, for examining the pancreas, if, for example, we are talking about confirming the development of a malignant tumor, or identifying features of the vascularization of the organ, the accuracy of the information obtained should be even higher. It can be increased by using special paramagnetic compounds (contrast agents).
Contrast agents can not only determine the state of the pancreas blood supply system. MRI with contrast gives a clearer idea of the size, boundaries, degree of development, features of vascularization of the tumor, and the presence of metastases.
Pancreatic head cancer with contrast
Drugs used for MRI with contrast enhance the signal due to the inclusion of gadolinium.
Contrast drugs with gadolinium (Gadovist, Omniscan and others), unlike compounds containing iodine, rarely cause allergic reactions and can be used for magnetic resonance imaging even in pregnant women (with the exception of the first trimester).
The drug is administered into the body in one of two ways:
- Manual. A single administration is performed intravenously.
- Bolus. The drug enters the body by droplets (a special dispenser is used).
The amount of the drug is calculated taking into account the body weight of the person undergoing the examination. There is no discomfort or pain during the administration of paramagnetic agents.
In case of allergies, bronchial asthma and pregnancy, the use of contrast is permissible only in exceptional cases.
Conducting research
- clothing containing metal parts;
- credit cards;
- any metal objects (keys, money, jewelry, costume jewelry, watches, hairpins);
- Hearing Aids;
- removable dentures;
- mobile phone;
- wig.
Before an MRI, representatives of the fairer sex will have to wash off all cosmetics if they contain metal particles.
There is no need to get rid of metal crowns. They usually do not affect the quality of the resulting images. However, you will have to inform your doctor about the presence of such crowns. Next, the patient receives disposable clothing in which he can comfortably and safely undergo an MRI session.
After being invited to the room where the apparatus is located, the subject must lie down on a special table. The next step is to move into the so-called magnet tunnel, which looks like a large pipe.
The patient’s task is to remain still throughout the entire examination.
Communication with a doctor observing the person being examined using a video camera is ensured by a special intercom.
The MRI process itself is accompanied by a loud and rhythmic sound of varying tone and strength. Such sound should not cause concern. On the contrary, its presence indicates that the device is functioning normally. Headphones help reduce noise intensity.
The patient can obtain MRI results as follows:
- pick up in person the next day after the tomography;
- notify the doctor of the need to transfer the report to the attending physician;
- receive the result on the day of the study after prior agreement with the doctor (possible in exceptional cases).
Feelings of discomfort and anxiety should not be ignored. Information about any negative changes should be reported to the doctor. This can be done using an intercom. The presence of a loved one also helps reduce the level of emotional stress.
Contraindications
Despite all the advantages of magnetic resonance imaging, it cannot be recommended for everyone who needs diagnostics. The good news is that in addition to absolute contraindications, there are also relative ones, which, in case of emergency, you can try to circumvent under the guidance of a doctor.
Absolute contraindications
You will have to refuse diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging if:
- presence of a pacemaker;
- replacement of heart valves with prostheses (except biological);
- artificial joints;
- installed medical devices (Ilizarov apparatus, brackets, filters);
- epilepsy disease;
- convulsive seizures;
- frequent loss of consciousness;
- the presence of foreign ferromagnetic objects (splinters, pieces of shavings);
- pregnancy (first trimester).
Relative contraindications
The so-called relative contraindications that allow magnetic resonance imaging with restrictions include:
- presence of tremor;
- the patient's inability to hold his breath;
- installed bracket system;
- fixed denture;
- the presence of vena cava filters (clot traps), stents and postoperative clips;
- performed coronary artery bypass grafting;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- pregnancy (except the first trimester);
- claustrophobia;
- lack of ability to remain in a stationary position due to pain;
- tattoos made using dyes containing metal particles;
- obesity (weight more than 120 kg).
If it is impossible to quickly remove the reason why an MRI is undesirable, it is better to use one of the alternative research methods.
Alternative research methods
If there are contraindications to MRI, the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, will suggest one of the alternative diagnostic methods. The most accurate data will be provided by:
- Spiral computed tomography. The resulting images are of high resolution. The number of contraindications is significantly less than for MRI (weight over 150 kg, pregnancy, lactation, renal failure, allergic reaction to drugs used for contrast).
- Multislice computed tomography. Gives a picture of the condition of blood vessels, ducts, lymph nodes.
- 3d sonographic examination (ultrasound examination). A highly informative method that detects malignant neoplasms and the presence of stones.
- X-ray. With its help, cancer, polyposis, and diverticulosis are successfully diagnosed.
- Radiography. It will help in diagnosing the condition of the head of the pancreas and bile ducts.
The information picture provided by one of the alternatives will not be as complete as that provided by magnetic resonance imaging. However, if the diagnosis needs to be carried out on an emergency basis, the data obtained is sufficient for the doctor to make the most accurate conclusion and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Video on the topic
Source: https://gormonexpert.ru/zhelezy-vnutrennej-sekrecii/podzheludochnaya-zheleza/zabolevaniya/mrt-3.html
MRI of the pancreas: indications, what it shows, preparation
Diseases of the pancreas are quite common these days.
An incorrect lifestyle, bad habits, and dietary errors play a large role in the formation of pathological processes. Early diagnosis helps prevent the development of dangerous complications.
In this situation, you cannot do without a magnetic tomograph. What does an MRI of the pancreas show and do you need to prepare for it?
Principle of operation
The pancreas is one of those organs that are poorly visualized using standard diagnostic procedures. For example, X-rays and ultrasound may not even detect a medium-sized tumor. In this case, you cannot do without an MRI of the pancreas.
Modern techniques help to identify space-occupying formations in the organ in the early stages and begin treatment of the pathology. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner provides a three-dimensional image of the endocrine gland. The picture is created using a magnetic field.
Important! MRI is based on the relationship between a magnet and the human body. The magnetic field activates hydrogen. This interaction allows for clear visualization of the organ under study.
Using instantaneous images, you can examine all areas of the pancreas, as well as see any changes in the structure of the organ. The equipment allows you to take more than a hundred pictures in sections at various levels. The quality of the resulting images largely depends on the power of the equipment.
The examination, which is carried out on a closed tomograph, provides higher image quality. The use of a contrast agent can have a positive effect on the results. This allows you to visualize not only the slightest changes in the organ, but also to assess the condition of the vessels approaching the organ.
Nuclear magnetic resonance makes it possible to learn everything about the human body, thanks to its saturation with hydrogen atoms and the magnetic properties of tissues. MRI is the only radiation diagnostic method today that provides accurate information about the state of internal organs, metabolism, structure and the course of physiological processes.
During the examination, organs and tissues are displayed in different projections. Thanks to this, they can be seen in cross-section. Around the organ being examined there are radio frequency sensors that read the signals and transmit them to a computer. Next, the images are processed, after which a high-quality image is produced.
The pictures are recorded onto a compact disc.
Using this modern technique, you can visualize tissues, blood vessels, nerve fibers, as well as estimate the speed of blood movement and measure the temperature of any internal organ.
MRI of the pancreas is performed with and without contrast. The use of a contrast agent makes the device more sensitive. Pictures are taken before and after the injection of the dye.
The popularity of MRI is due to the absence of the harmful effects of X-ray radiation
The procedure is absolutely painless. The influence of the magnetic field and radio waves is not felt in any way. During the examination, the patient feels various signals, tapping, and noises. Some clinics provide earplugs so that extraneous sounds do not irritate a person. To diagnose pancreas pathologies, open and closed type devices are used.
In the first case, the person is not in a confined space. This is a very important point for patients suffering from claustrophobia. Such devices can support people whose weight exceeds 150 kg. Tomography should be performed only when indicated. The doctor will explain where it is best to get an MRI.
Indications
MRI of the pancreas is done in various cases:
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- primary diagnosis of pancreatitis or dynamic observation;
- chronic pathologies of the digestive organs;
- control of the treatment;
- disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism;
- detection of any formations by ultrasound;
- intraductal hypertension;
- purulent process;
- search for metastases when a primary focus is detected;
- unclear ultrasound picture;
- chronic digestive disorders;
- cystic lesion;
- girdle pain in the stomach of unknown etiology (cause);
- traumatic injuries;
- stones in the pancreas ducts.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is not suitable for everyone. Its implementation is contraindicated in the following cases:
Cyst in the pancreas
- serious mental or neurological disorders;
- claustrophobia;
- too much weight;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of metal structures in the body: stents, pacemakers;
- severe general condition.
Some restrictions are relative. In this case, the doctor can individually determine the appropriateness of the diagnosis. Relative contraindications include severe heart, liver and kidney diseases, and the third trimester of pregnancy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each diagnostic technique has its positive and negative sides. Among the “advantages” of MRI of the pancreas are the following:
- no pain;
- obtaining high quality images;
- absence of harmful radioactive radiation;
- there is no need for any special long-term preparation;
- no side effects from the use of contrast agents;
- obtaining fast and highly accurate results;
- lack of recovery period;
- early detection of pathological changes;
- high resolution images. This makes it possible to enlarge the picture for viewing;
- the need for hospital stay of the patient is eliminated.
Still, it is worth understanding that MRI is not a panacea, and it, like other diagnostic methods, has a number of “disadvantages”. Let us highlight the main disadvantages of the procedure:
- late detection of hematomas;
- impossibility of conducting research in the presence of metal structures in the body;
- patient movement negatively affects the quality of images;
- impossibility of carrying out the procedure due to fear of confined spaces.
High image resolution allows you to enlarge the image
What will it show?
Experts prescribe MRI of the pancreas to obtain the following information:
- structure;
- structure;
- shape, density;
- condition of the ducts;
- presence of formations;
- fiber condition;
- detection of differences between tumors and cysts;
- tumor prevalence;
- features of vascularization;
- presence of metastases;
- identification of stones in the ducts;
- the condition of the blood vessels supplying the endocrine organ.
Preparation rules
Preparing for an MRI of the pancreas does not pose any difficulties. There are no restrictions on food and drink. When using dyes, the procedure should be carried out on an empty stomach. If the study is carried out for the first time, an allergy test is required.
Before diagnosing pancreatic disorders, it is important to relieve the gastrointestinal tract as much as possible. For this purpose, one day before the proposed test, fatty, salty, and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. For three days, you need to remove foods that contribute to gas formation: legumes, confectionery, sweet juices, cabbage, baked goods, raw vegetables and fruits.
It is also necessary to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and medications that contain ethyl alcohol. It is better not to drink coffee or tea the day before the MRI. Experts strongly recommend not to carry out procedures that involve the introduction of a dye into the pancreatic ducts before the examination.
Preparation immediately before the procedure includes the following: getting rid of metal objects on the body, including piercings, taking the required position on a retractable table, and injecting a contrast agent into a vein. The study is usually scheduled in the morning. It is better to arrive earlier than the appointed time.
You should take with you a referral from a doctor and a passport proving your identity. If you are allergic to dyes, you should definitely inform your doctor about this. The administration of contrast is not recommended for pregnant women and nursing mothers, as the substance can cross the placenta to the baby and into breast milk.
Two to three hours before diagnosis, it is forbidden to consume food and water. It is recommended to follow a low-carbohydrate diet for a few days. In case of increased gas formation and constipation, it is recommended to take a laxative or enterosorbent the day before. Half an hour before the MRI, you should take an antispasmodic tablet, for example, No-shpu.
Features of the event
The patient lies down on a sliding table. He will have to remain motionless for some time, so he should immediately take a comfortable position. Soft straps are used for secure fixation. This will prevent involuntary movements that could blur the image.
Attention! The contrast that is introduced into the body does not accumulate and is excreted within two days by the kidneys.
If tomography is performed using contrast, a test is performed before the study to exclude an allergic reaction. The dye is administered intravenously. It quickly reaches the pancreas. The study allows us to identify even small tumors, which is impossible without the use of a dye.
The procedure provides information about the degree of malignancy of the tumor and shows with extreme accuracy the size of the affected area. The contrast spreads throughout the body within a few minutes.
The accumulation of this component is observed in places of strong blood flow. This is observed in areas of tumors and their metastases.
Contrast enhances the clarity of healthy and pathologically altered structures.
Specialists manage to obtain a series of images with millimeter distances between them. Gadolinium-based dyes are used for diagnostic purposes.
Unlike iodine-containing components, it rarely causes allergic reactions. The contrast agent contains a chelating agent as an adjuvant.
It allows the drug to be evenly distributed throughout the organ under study and avoid accumulation in the body.
The patient should breathe calmly, lie still and follow the doctor’s instructions, which he will transmit through the microphone
The substance is injected into a vein once based on body weight. In rare cases, adverse reactions to the administration of a coloring agent may occur:
- redness;
- edema;
- itching;
- hypotension;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- cough, sneezing;
- burning and tearing in the eyes.
Separately, it is worth noting the features of diagnosing children. Due to their age, they are very mobile, it is difficult to force them to stay in one position for thirty minutes or more.
In some cases, the procedure is delayed. It is also worth considering the fact that the child will have to lie in a confined space. Needless to say, if such manipulation scares even adults.
Children may be frightened by noise coming from the equipment.
Some tomographs are equipped with built-in screens that show cartoons. This smooths out unpleasant sounds and helps achieve stillness. In addition, open-type devices are often used to diagnose children, so parents and medical staff can be nearby.
In some cases, MRI is prescribed for infants. Typically, children under five years of age are put into a state of medicated sleep. The duration of the procedure is about one hour.
Before the examination, parents need to psychologically prepare their child. He should explain the importance of the procedure and convey how everything will go.
It is better to warn him that noises will appear, and also that he cannot move.
Which is better - MRI or CT?
Many patients wonder why overpay for examination if CT provides a high level of information content.
It is worth noting that both magnetic resonance and computed tomography are widely popular in diagnosing pancreatic pathologies. Each of these methods has a number of advantages and disadvantages.
As for radioactive studies, MRI in this regard is an absolutely safe procedure.
CT scans carry a significant radiation load on the body. If you look at this issue from a financial point of view, then, of course, computed tomography will cost less. The magnetic resonance method has a much higher quality of soft tissue diagnostics. But when internal organs are damaged, CT is more often used. Unlike computed tomography, MRI is rarely performed with contrast.
Important! For chronic pancreatitis, a combination of two techniques at the same time is often prescribed - CT and MRI.
The choice of device in most cases remains with the doctor. This takes into account contraindications, concomitant pathologies and the availability of a tomograph. Currently, CT and MRI are rapidly developing, thanks to which visualization of the pancreas and liver using both methods occurs at a high level.
Decoding the results
The images obtained during the magnetic resonance examination are examined by a radiation diagnostics specialist. Its task is to identify and describe pathological changes presented in the images. He should also identify the connection between the existing disorder and other dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Interpretation of the results usually takes about an hour. To guarantee the reliability of the study, the patient is given a specialist’s report with the doctor’s signature and seal, as well as photographs on film, paper and digital media.
A cystic lesion of the pancreas looks like a round formation with clear contours without obvious walls. Pseudocysts are presented in the form of multi-chamber structures with a thickened wall. Often such a formation extends beyond the contours of the pancreas. The presence of granulation tissue along the periphery and air bubbles inside indicate the formation of an abscess.
More than ninety percent of all tumor processes in the endocrine organ are adenocarcinoma. Most often, the neoplasm affects the head of the pancreas. The images show changes in the contours of the pancreas and a local increase in the affected part of the pancreas.
Dilatation of the pancreatic ducts cannot confirm the presence of cancer. This symptom also characterizes chronic pancreatitis and obstruction. Adenomocarcinoma may visually resemble a cyst. A specialist will be able to recognize cancer by the absence of calcification. The tumor will have a thicker and more uneven wall.
Key Thoughts
MRI of the pancreas is most often prescribed when cancer is suspected. Doctors may refer you for diagnostics if you have persistent epigastric pain of unknown cause. The examination provides complete information about the functional state of the organ, its structure, structure and blood vessels. To study the pancreas, open and closed tomographs are used.
The use of a contrast agent makes the device more sensitive and helps to identify the slightest pathological foci. MRI does not require lengthy or special preparation. The main requirement is the absence of metal utensils. For consultation on MRI of the pancreas, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/zhkt/podzheludochnaya-zheleza/mrt-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy
Magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas
MRI of the pancreas is the most effective method for diagnosing pancreatic diseases - acute and chronic pancreatitis.
The inflammatory process in the pancreas is characterized by the appearance of a clinical picture with a significant time lag from the moment of its occurrence. In this regard, pancreatitis is a difficult to diagnose disease.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides the most complete information about the volumetric formations of the pancreas and its structure at any stage of the disease. This information, used as the basis for assessment and analysis, allows the doctor to make a diagnosis with 100% accuracy.
Medical practice has reliably documented the superiority of MRI over computed tomography.
It is also significant that with magnetic resonance imaging the patient is not exposed to radiation, as happens when diagnosing the disease by other methods, for example, with fluoroscopy.
An MRI examination of the pancreas can diagnose the following disorders:
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- cystic formations;
- benign and malignant formations;
- stones in the pancreatic duct.
Despite the high cost of this procedure, in some cases, making an accurate diagnosis, and therefore prescribing effective treatment, is impossible without it.
What is magnetic resonance imaging
This diagnostic method uses such properties of the magnetic field as its uneven reflection from various structural formations in the pancreas and adjacent abdominal organs.
The tomograph is designed in such a way that the patient's body is located inside a magnetic field.
The magnetic signal is reflected from hydrogen atoms, which are known to be present in every cell of the body’s tissues, and is processed by special computer programs, and as a result, the doctor observes a clear and three-dimensional image of the pancreas and its smallest details on the monitor screen.
The resolution of the tomogram, that is, the clarity and detail of the image of the organ, depends on the power of the equipment. Without going into technical details, we note that proper quality images can be obtained on a device with a power of 1.5 Tesla or more.
Unfortunately, not all medical institutions in the country are equipped with such equipment.
Therefore, if an MRI examination of the pancreas is prescribed to a patient using a lower-power tomograph, spending money on such a procedure is completely pointless, due to the impossibility of obtaining reliable examination results due to the low power of the equipment.
The second important factor that ensures the possibility of obtaining visualization of an organ with acceptable clarity and contrast is the introduction of a special substance that enhances the echo signal and affects the contrast enhancement. Failure to use this substance when examining an inflamed organ results in unreliable diagnostic results.
Indications for examination
If the symptoms are unclear, or if the attending physician concludes that one of the following indications is present, an MRI examination is performed:
- primary diagnosis of chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- constant pain in the epigastric region;
- stones in the pancreatic ducts;
- identified formations of any nature in the epigastrium;
- chronic digestive disorders;
- disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism;
- pancreatic cyst;
- control of the treatment performed, primarily surgical intervention;
- purulent swelling in the peripancreatic tissue.
It is advisable to undergo a tomography examination in case of unclear results of ultrasound examination, as well as in cases of injuries to the abdominal organs.
Contraindications for MRI
Despite its safety, tomography examination has a number of contraindications.
The main limitation is related to the inadmissibility of placing a patient in the magnetic field of the device whose body contains elements made of magnetizable metal, for example, a pacemaker, stents, insulin pump, etc.
The induction of a magnetic field causes heating of the metal in it, which can lead to various kinds of negative consequences.
MRI is also contraindicated in the following situations:
- general serious condition of the subject;
- excess, over 150 kg, body weight:
- diseases of a neurological and mental nature;
- during pregnancy - in the 1st and 3rd trimester.
The conditions listed above, except for the presence of metal elements in the body, are not imperative, that is, mandatory for fulfillment. The final decision on whether to prescribe a tomograph examination for a particular patient is made by the attending physician.
Preparing for an MRI of the pancreas
No special preparatory actions are required for a long time before the procedure. It is not recommended one day, or better yet two days before the examination, to stop drinking alcohol, spicy and salty foods, fatty meats, smoked meats, canned food, as well as strong tea and coffee.
The examination is carried out on an empty stomach, so the fasting period before the procedure should not be less than 6 hours. If the patient has not previously been tested for allergic reactions to contrast agents, it is necessary to do such a test for allergy to contrast before the study.
Also, if there is stagnation in the upper intestines, it is recommended to evacuate the intestinal contents through a probe, or perform a cleansing enema.
Magnetic resonance imaging procedure
The doctor conducting the study should advise the patient about his actions during the procedure. The patient must remove all jewelry, costume jewelry, and metal objects. Wear clean clothes - disposable, if provided by the clinic, or brought with you.
- The doctor helps the patient lie down on a special platform in a horizontal position.
- The head is fixed in a special applicator.
- The platform with the patient is moved in to remove the device, or, in the case of an open-type tomograph, a magnetic camera is placed above the pancreas area.
- The subject is injected with a gadolinium-based contrast agent - “Magnevist”, “Prohanks” and others.
- The doctor turns on the equipment and receives volumetric visualization of the pancreas on the monitor.
Magnetic field scanning of the pancreas is carried out through several passes of the magnetic camera. The figure demonstrates the trajectory of its movement: after each pass of the camera, the direction of its movement shifts by 20-30 degrees in the horizontal area.
As a result, the organ is scanned in all directions.
The duration of the MRI procedure is from 30 to 60 minutes. As a rule, a conclusion with a prescribed pathology or norm is provided to the patient the next day after the procedure.
During the entire examination, the patient should remain motionless, relax as much as possible, lie in a horizontal position and not hold his breath. Perhaps the doctor, through a microphone, will inform the patient about the need to perform certain actions. The instructions should be followed after first making sure that the doctor’s wording is correctly understood.
MRI results
The main goal of diagnosis is to determine complications of pancreatic inflammation and the degree of its intensity.
In a mild form of acute pancreatitis, the pancreas is enlarged as a whole, or in any part of it, in most cases, in the tail. The organ is affected by interstitial edema. The tomogram displays the blurriness of all contours. If contrast is administered to the patient, a non-homogeneous enhancement of the organ parenchyma is recorded.
Acute pancreatitis in the severe stage is characterized by uneven structure of the gland and its significant increase in volume. The contrast enhances the clarity of healthy tissue, while areas affected by necrosis remain unchanged. Necrosis appears hypodense, sequesters appear isodense, and hemorrhages appear hyperdense.
The chronic form of pancreatitis is characterized by disturbances of exogenous and endogenous functions. A tomogram can record enlargement or atrophy of the pancreas, expansion or blockage of the pancreatic duct, the presence of calcifications and pseudocysts.
Despite its very high diagnostic accuracy, MRI of the pancreas should be carried out in conjunction with laboratory tests and the clinical picture of the disease.
Source: http://pancrea.ru/treatment-mrt.html
MRI pancreas
The pancreas is a parenchymal organ located quite deep in the abdominal cavity.
Routine diagnostic methods are not always able to provide sufficient information about it to make a correct diagnosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging is increasingly used to determine its diseases. This method has proven itself to be the most informative and safe for patients.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the ability of various neoplasms developing in parenchymal organs to reflect magnetic waves with different intensities.
Naturally, the quality of the images that will be displayed on the computer screen that provides image processing will depend on the power of the tomograph used.
The more powerful the device, the higher the image quality and the more reliable the research.
You can also improve image quality by using special contrast agents. Contrast in combination with MRI allows not only to visualize the smallest changes in an organ, but also to assess the condition of the vessels that feed it.
What functions does the pancreas perform?
The main function of the pancreas is to provide the digestive tract with various enzymes necessary for normal digestion and absorption of food. The most significant of them are trypsin, chymotrypsin, pancreatic lipase and amylase.
The second function, which is no less important, is to provide the body with hormones involved in the metabolism of glucose and glycogen. It is thanks to the formations of the pancreas, called the islets of Langerhans, that insulin and glucagon are synthesized. With an excess or deficiency of these hormones, severe metabolic pathologies develop, the most famous of which is diabetes mellitus.
Indications for MRI of the pancreas
Many organ diseases are asymptomatic or with minimal complaints from the patient. This makes diagnosis very difficult, especially when it comes to a tumor.
Most often, MRI of the pancreas is performed when the following complaints are presented:
- pain in the area of the stomach and the gland itself, which is girdling in nature;
- chronic digestive problems;
- suspicion of a tumor or cyst;
- the presence of chronic pancreatitis of any form;
- previously diagnosed hypertension inside the bile ducts to exclude their obstructive overlap.
Since MRI does not carry radiation, it is also often used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the selected therapy if necessary.
What does an MRI of the pancreas show?
The study can show minute changes in the structure of the organ. The most valuable data is considered to be obtained if a mass formation in the pancreas is detected in a patient during an MRI.
Based on the results of the images, the following is determined:
- position and internal structure of the organ;
- dimensions of the head, body and tail of the gland;
- state of parapancreatic tissue;
- parenchyma structure, presence of pathological formations;
- density of tissue pathology, which will distinguish a tumor from a cystic formation;
- the shape and size of the pathology, this will help differentiate the tumor; smooth contours and rounded shapes indicate the benign nature of the formation;
- tumor growth into surrounding tissues;
- metastasis from other organs;
- the condition of the ducts located inside the gland;
- the presence of stones in the ducts;
- the condition of the vessels that provide nutrition to the organ, etc.
When is an MRI of the pancreas with contrast indicated?
Contrast is used mainly when it is necessary to confirm the presence of large tumors in an organ. Cancer cells retain the contrast for a longer time, thereby providing improved visualization of the tumor.
Contrast MRI of the pancreas can also be used to diagnose pathologies of the vessels feeding the organ.
Preparing for the examination
MRI of the pancreas requires minimal preparation. First of all, it is recommended that the patient undergo the examination on an empty stomach. If the examination is in the morning, then breakfast is moved to a later time. If the examination is during the day, then a ban on eating is imposed at least 5 hours before the examination.
Two days before the test, it is recommended to avoid foods that lead to gas formation (bread, soda, sweets, juices, legumes, etc.).
Before the procedure, be sure to remove all metal jewelry and warn the doctor about allergic reactions to contrast, if it has already been used previously.
It is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of implanted electronic devices or metal prostheses, as this may be a contraindication for the study. If the patient uses a hearing aid, it will be removed before the procedure.
Order of conduct
MRI of the pancreas is a diagnostic procedure that is carried out in a specially equipped room where the tomograph is located. The patient is placed on a movable table, which will later be inside the device.
If the scan takes place without contrast, the table slides into the machine and the procedure begins. During the procedure, patients should not move, as moving will blur the images. All the patient has to do is lie motionless in the tomograph for 20-30 minutes.
If a decision is made to carry out a procedure with contrast, then before the study the patient is given an allergy test. It is necessary to exclude unexpected reactions of the body to the administered substance. If no allergy is detected, then the contrast is administered intravenously, and then the procedure proceeds according to the standard plan.
During the procedure, some patients experience claustrophobia. You can deal with it by talking to a doctor through a microphone built into the tomograph. Usually, even during an attack of claustrophobia, the study is not interrupted, but if the patient begins to panic, it can be stopped.
Which is better MRI or CT scan of the pancreas?
Today, when it comes to choosing between MRI and CT, preference is given to the first method. This is due to the higher resolution of the method and fewer contraindications.
With magnetic resonance imaging, unlike computed tomography, the body is not irradiated with x-rays. Often this factor is a priority when choosing a survey technique.
It is also important that MRI allows you to diagnose even very small pancreatic tumors (from 2 mm) and their metastases. CT does not have such resolving power, making it possible to determine the presence of a tumor only at later stages.
Which is better: MRI or ultrasound of the pancreas?
Ultrasound of the pancreas is one of the routine studies that are performed on all patients with complaints about the functioning of this organ.
The resolution of ultrasound for visualizing the pancreas is not very high. This is due to the deep location of the organ. Using ultrasound, you can diagnose large tumors and determine the presence of problems with the ducts, but more specific information can only be obtained using tomography.
Doctors often prescribe both of these examination methods to patients, since data from ultrasound can complement the picture obtained as a result of an MRI study.
This article contains general information only, is not scientific material and should not be construed as a substitute for medical advice.
Source: https://mrt-kt.info/vidy-mrt/bryushnoy-polosti/podzheludochnoy-zhelezy/