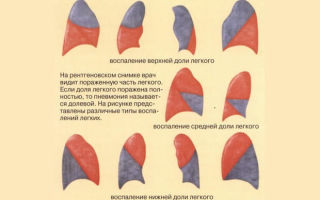
Identifying signs of pneumonia in children is a rather difficult task. To suspect a disease, you need to know what the main clinical signs of this condition may be in a baby.
An inflammatory process in the lungs can develop in a baby as a result of exposure to a variety of factors. The most common “provocateur” is bacterial flora .
Various representatives of staphylococci, streptococci, as well as atypical microbes lead to the appearance of clinical signs of the disease.
The latter quite often cause the development of pneumonia in the baby, which can occur without high body temperature.
The incubation period for this disease varies greatly. In most cases, manifestations of the disease develop within 1-2 weeks from the moment the baby is infected . Many infectious diseases are transmitted from a sick child to a healthy one. The airborne method of spreading these diseases is the leading one, especially in crowded children's groups.
Pneumonia is manifested by the appearance of many different clinical signs. The severity of their manifestation is usually different and is determined by the primary well-being of the baby. The age of the child also plays a significant role.
Infants, as a rule, suffer pathology much more severely than schoolchildren. A severe course of the disease can also occur in weakened children, as well as in children with concomitant diseases.
A pathological process that arises in the respiratory tract and occurs without high fever, but with a cough, most often develops in children with an atypical course of this pathology. The child coughs quite a lot.
A severe form of the disease is accompanied by an annoying cough, which brings significant discomfort to the baby.
When a child coughs, he produces phlegm. In bacterial diseases, it has a yellow or greenish tint. Viral infections occur with the release of mucous or gray sputum.
After coughing, severe pain appears in the chest area, and in certain situations even severe pain.
This manifestation of the disease may also intensify when getting out of bed.
The amount of sputum discharge is a very significant indicator. The usual form of the disease is characterized by the separation of several teaspoons of such pathological fluid. The severe version is accompanied by sputum production of up to 1/3 cup or more. When standing for a long time, it can stratify into separate layers that differ from each other in density.
This clinical variant of the pathology develops over a very long time. This is largely due to the fact that the child does not complain about having adverse symptoms. Quite often it happens that parents cannot determine that their baby is sick, since the baby’s well-being may suffer slightly. The child may become slightly distracted or get tired quickly.
A cough with this pathological variant of pneumonia does not always develop. Sputum production is also not a permanent symptom. Some sick children can only cough. The cough in this case is unproductive - “dry”. Usually this symptom becomes the first signal for parents to contact a pediatrician.
Some doctors believe that pneumonia, which occurs with normal body temperature, appears only in children suffering from various immunodeficiency pathologies. A decrease in immunity causes their long-term and protracted development of the disease. In some children, the disease occurs with normal body temperature for quite a long time.
A characteristic symptom of this pathology is the development of manifestations of intoxication. Their severity is usually minimal. You can notice the occurrence of such manifestations in a baby only by changing his behavior. A sick child becomes more nervous. Outdoor games with other kids do not delight the child and do not occupy his attention.
If a viral infection led to the development of manifestations of the disease, then the baby will also develop other nonspecific signs. Thus, adenoviruses cause a severe runny nose in a sick baby. Discharge from the nasal passages is usually copious. The breathing of a sick baby is severely impaired. He stops breathing through his nose and starts inhaling through his mouth.
Many children experience a characteristic “bruising” in the chest. This situation is characterized by the appearance of a feeling of strong pressure. A persistent and prolonged cough only aggravates the development of this condition. When inflammation passes from the lungs to the pleura, severe pain occurs, which is a manifestation of a very dangerous clinical condition - pleurisy.
Intoxication of the body with bacterial or viral toxins causes thirst to increase in a sick child. The baby's lips become very dry and may even crack. In some babies, you may notice pathological pallor of the skin of the face. In some cases, the child's lips begin to turn blue.
Prolonged course of the disease often leads to the development of respiratory failure. Parents may suspect this manifestation if rapid breathing occurs - shortness of breath. In the initial stages of development of this pathology, this manifestation develops only when active actions are performed. Subsequently, such clinical signs appear at rest.
As intoxication increases, the child's skin becomes very pale and his cheeks become red. The area of the nasolabial triangle turns blue. In some cases, a sick child begins to whistle during normal breathing. This symptom only intensifies when performing active movements.
A striking manifestation of severe intoxication, in addition to shortness of breath, is the appearance of a rapid heartbeat. This manifestation is due to insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body due to impaired breathing and subsequent oxygen hypoxia. Tachycardia also first appears in a sick child only during active walking, and then at complete rest.
The spread of inflammation to the bronchial tree makes it difficult for the child to inhale air. In this situation, the child also develops general weakness. This symptom is quite distinct in schoolchildren. A sick child begins to study poorly; it becomes difficult for him to concentrate on completing first complex and then simpler tasks.
In most cases, inflammation develops on only one side of the body. Too weakened immunity contributes to the spread of the process to the neighboring lung.
Double pneumonia, which develops without high fever, is recorded quite rarely in children.
This condition can develop in infants, especially those babies who were born prematurely or have a critical birth weight.
Existing disturbances in the structure of the lung tissue can also lead to the fact that the pathology can become bilateral.
If unfavorable clinical signs appear in a baby immediately after birth, then the prognosis for the development of this pathology is usually extremely unfavorable.
In babies with low weight, you can even see some displacement of the affected area of the chest to the right or left side.
The long course of the disease can lead to the fact that the sputum released during coughing becomes very dense and difficult to separate. This condition contributes to an increase in congestion and pain in the chest.
Attempts to cough up thick mucus only lead to a deterioration in the child’s well-being. In such a situation, the child coughs up dense clots or lumps.
Increasing intoxication causes the child to develop sweating . Usually it bothers the baby in a state of complete rest. In this state, the baby feels quite bad.
He may also develop a headache or become increasingly dizzy . If the disease progresses further, it can lead to the development of severe respiratory failure in the child.
Pneumonia should be recognized as early as possible. Timely diagnosis allows for quick treatment. Without specific therapy, it is impossible to get rid of unfavorable symptoms.
It can be quite difficult for fathers and mothers to suspect pneumonia in a child, especially if it occurs without developing a high fever.
In this case, all that is required is careful attention to the baby’s mood and behavior in everyday life.
Regular patronage and visits to the pediatrician will help identify hidden signs of the disease at fairly early stages. Conducting a clinical examination in this case plays an important diagnostic role.
During such a study, the doctor will definitely conduct auscultation (listening) of the lungs.
The appearance of dry or moist wheezing, as well as weakening of breathing are signs that the baby has damaged areas in the lungs.
Laboratory tests will help confirm the diagnosis. All children suspected of having pneumonia must undergo a general blood test. This pathological condition is characterized by an increase in immune cells - leukocytes. ESR also increases during pneumonia. In severe cases of the disease, it can increase 2-3 times relative to normal.
An increased number of neutrophils in the leukocyte formula usually indicates that a bacterial infection led to the development of unfavorable symptoms in a sick child. With viral pathologies, lymphocytes usually increase. These immune cells guard the child’s body from various infections.
To determine the causative agents of infectious diseases, several bacteriological studies are carried out. To conduct such tests, biomaterial is taken. It usually becomes phlegm. To establish the cause of the disease, a bacteriological analysis of sputum for nutrient media is carried out. The result of the study is ready approximately 5-7 days from the moment the material is collected.
X-ray is the main method used in children to verify inflammation in the lung tissue.
It should be noted that this study is not carried out on all children. There are strict medical indications for this. Only the attending physician can determine the need for this study.
In complex diagnostic cases, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can also be performed.
These studies have good resolution and detect any pathological changes in the lungs even at the earliest stages.
Small pathological lesions are also quite well determined by CT and MRI methods. The tests can be performed on all babies, as they do not cause any pain.
For a child to recover quickly, it is very important to follow the correct daily routine. It is better not to walk with your child in the cold season , as this can only aggravate the course of the disease.
To improve the functioning of the immune system, it is necessary to include a sufficient amount of protein products in the baby’s daily diet . These include: lean beef and pork, poultry, fresh fish.
Fermented milk products will be a good addition to your child’s diet.
Drinking regimen also plays a very important role in eliminating the symptoms of intoxication. Water entering the body eliminates from it all toxic products formed during infectious diseases. Suitable drinks include fruit drinks and compotes made with dried fruits or berries. Frozen fruits can also be used to make drinks.
In the treatment of any inflammation in the lungs, which occurs even without an increase in temperature, antibacterial agents are necessarily used. They are necessary to eliminate microbes from the body that caused the development of this pathology in the baby. Cephalosporins, macrolides and modern penicillins help cope with most infections quite quickly and effectively.
The use of anti-inflammatory drugs will help eliminate the manifestations of intoxication syndrome .
They not only help reduce inflammation in the lung tissue, but also lead to a noticeable improvement in the well-being of the sick baby.
For children with signs of reduced immunity, interferon-based medications are used. They have a stimulating effect on the immune system, leading to a noticeable improvement in the child’s condition.
You can restore immunity and speed up recovery only with the help of multivitamin preparations. Such complex products contain the necessary combination of all vital vitamins and microelements. Multivitamin complexes can be prescribed both for the treatment of pneumonia and for the prevention of any inflammation in the lung tissue.
Next, we recommend watching a video in which Elena Malysheva will talk about what pneumonia is and where it comes from.
Source: https://o-krohe.ru/bolezni-rebenka/pnevmoniya-bez-temperatury/
Pneumonia without fever: does it happen, does cough always occur with pneumonia, treatment
Respiratory diseases are accompanied by cough and fever. But sometimes with bronchitis and pneumonia the temperature remains normal. In this case, the symptoms resemble a cold, and the person is in no hurry to see a doctor. As a result, treatment is not started on time, and the disease can lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms
Pneumonia with a normal temperature does not have the manifestations characteristic of ordinary pneumonia, and you can suspect something is wrong only if you carefully monitor your well-being. The first sign of pathology is causeless weakness, drowsiness and fatigue.
Shortness of breath after exercise
Indirect symptoms of non-temperature pneumonia include:
- shortness of breath and increased heart rate after exercise;
- sweating;
- difficulty breathing;
- pale facial skin.
A common sign of pathology is blush on the cheeks. It is brighter on the side of the diseased lung.
A severe cough that does not stop and whistling breathing can lead one to think about pneumonia. Pain in the back and chest is common, often when moving. They can radiate to the abdomen, simulating the picture of a heart attack. Headache is also associated with pneumonia.
Parents should be especially attentive, because the child cannot always understand and explain what is happening to him.
With pneumonia, he becomes moody, refuses to eat and play, and complains that something hurts. Infants are at risk.
In babies under one year of age, the disease manifests itself as lethargy, poor sleep and loss of appetite, heavy and frequent breathing, and nasal congestion. Sometimes pneumonia is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea.
Main reasons
The main causes of non-temperature pneumonia include:
Weak immunity
- Weakening of the immune system. The infection easily penetrates the body, microbes multiply quickly.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics. Due to the large number of antibacterial agents, the body reacts to infection in a dull manner. This happens after untreated bronchitis.
- Taking antitussive tablets. They suppress the reflex, and sputum containing pathogenic microorganisms is not removed from the bronchi. As a result, purulent-inflammatory processes develop in the lungs.
In pregnant women, the fetus causes the lungs to sit higher. This and a weakened immune system often cause atypical pneumonia, which occurs without fever.
In infants, manifestations of pneumonia often occur after a viral infection.
Diagnostic procedures
Listening to the lungs
Diagnosis of the disease begins with examination of the patient. Attention is paid to the pallor of the skin, frequency and depth of breathing. Lung sounds are carefully listened to. For pregnant women, this is the main type of examination, since x-rays are contraindicated for them. At the initial stage of pneumonia, sometimes wheezing in the lungs is not heard, which sometimes causes misdiagnosis.
It is difficult even for an experienced doctor to recognize atypical pneumonia. Therefore, diagnosis cannot be done without a blood test, which records an increase in ESR and leukocytes, and a decrease in the level of lymphocytes.
An X-ray of the lungs is required, but sometimes even the image does not show changes in the lung tissue.
Methods of treating the disease
UHF therapy
Treatment of pneumonia without fever is carried out comprehensively. These are drug therapy and auxiliary treatment methods. The latter include physiotherapy: microwave, UHF, electrophoresis, inhalation, massage. They reduce the inflammatory process, promote the removal of sputum, and activate blood circulation. Therapeutic exercise improves pulmonary ventilation and strengthens the respiratory muscles. Traditional medicine helps increase immunity and reduce cough.
Bed rest and diet - high-calorie foods, plenty of drink - compotes, fruit drinks, natural juices, herbal teas are of great importance in the treatment of pneumonia.
Pneumonia in adults and adolescents, if there are no complications, can be treated at home if the doctor’s orders are strictly followed. Treatment without the recommendations of a pulmonologist aggravates the patient’s condition. In case of complicated pneumonia, children and people over 60, as well as pregnant women, are better off receiving treatment in a hospital.
What medications to take
Ingavirin capsules
To treat pneumonia, antibiotics (or antiviral drugs), anti-inflammatory, detoxification, immunostimulating, antihistamine, mucolytic and expectorant drugs are used.
Antiviral drugs (Nazoferon, Alfarekin, Ingavirin) are prescribed for the treatment of viral pneumonia. If the infection is caused by bacteria, you should definitely take antibiotics for 7-14 days.
They are selected taking into account the type of pathogen or wide spectrum of action. Children are often prescribed Amoxicillin with or without clavulanic acid, Cefuroxime by injection, adults - Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav.
In practice, antibiotics of 2-3 groups are used simultaneously to treat pneumonia.
Immunomodulators are used (Arbidol, Kagocel, Immunal). Vitamin complexes accelerate tissue regeneration and increase the body's defenses. Sometimes newborns are given immunoglobulins.
Zodak drug
Anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Analgin) are taken to relieve inflammation, reduce the symptoms of pneumonia and intoxication.
Antihistamines (Loratadine, Aleron, Zodak) are used in the treatment of pneumonia to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes. If the nose is stuffy, use vasoconstrictor nasal drops (Naphthyzin, Galazolin).
For dry cough, mucolytics (Acetylcysteine, Fluimucil, Ambroxol, Mukobene) are used to thin the mucus and facilitate its movement, and expectorants (Mukaltin, Gedelix, Stoptussin) are used for complete coughing.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine recipes in the treatment of pneumonia are used provided that they are in addition to drug therapy and are agreed upon with the attending physician.
Aloe juice with honey
To boost immunity, drink tea with lemon, raspberries, currants, strawberries, rose hips, mint, and linden.
At home, they do steam inhalations, breathe over boiled potatoes, apply compresses, mustard plasters, and jars. Warming up in saunas and baths is contraindicated for pneumonia.
Indispensable assistants in the treatment of pneumonia are aloe vera and agave. The juice and pulp of these plants are taken orally with honey. A drink made from oats relieves inflammation well.
Forecast
If treatment for pneumonia is started on time and carried out at the proper level, the patient recovers. The prognosis is optimistic if the patient feels well, has satisfactory laboratory tests and a minimum of chronic pathologies. If there are no complications, pneumonia goes away in 2-3 weeks. After recovery, residual cough may still persist for up to 1 month, which is quite normal.
Preventive actions
Hardening
Prevention of pneumonia – strong immunity. To do this you need to eat well and strengthen your body. The diet should include dairy products, meat, fish, all kinds of fruits and vegetables - sources of vitamins and minerals. To harden the body, you need to walk in the fresh air in any weather, dress according to the season so as not to freeze, but also not to sweat. Strengthening massage is useful, especially for newborns.
The correct temperature (22-23°C) and humidity in the house (45-60%) are important. Cleanliness of the room, absence of mold, dampness, heat, drafts - all this also improves health. Smoking and harmful fumes harm the lungs.
To avoid catching an infection during the peak period of colds, you just need to avoid contact with infected people, wear a medical mask in public places, and rinse your nose with saline solution.
For those who are prone to respiratory diseases, regular breathing exercises and physical exercise should become the rule of life.
Possible complications
With pneumonia without fever, there is a high risk of complications, which include:
Pleurisy
- pleurisy;
- swelling or suppuration of the lung;
- pulmonary abscess;
- bleeding;
- blood poisoning;
- respiratory failure.
Often there are complications in the heart (myocarditis) and damage to the central nervous system. Children experience neurotoxicosis, in which the temperature can rise sharply. The fever is accompanied by convulsions and respiratory arrest.
Pneumonia occurring without fever is a very dangerous pathology. Without treatment, it always ends in serious complications, sometimes the patient dies.
Source: https://pulmohealth.com/pnevmoniya/pnevmoniya-bez-temperatury/
Pneumonia without fever
There are cases when pneumonia occurs without fever; this course of the disease is especially dangerous. Patients know that the main symptom of pneumonia is fever. The disease is diagnosed late, often leading to complications.
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
The site provides reference information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
Pneumonia without fever and its main pathogens
Pneumonia is an acute lung disease of an inflammatory-infectious nature.
It affects the entire surface of the lungs and all their structures, including the alveoli. Inflammatory exudations develop in them.
Doctors distinguish 4 groups of pneumonia:
- Community-acquired form. This is a common form of the disease. It affects people regardless of gender and age. The main reason for its appearance is weakened immunity.
- In-hospital form. The causative agents are bacteria and microorganisms that are common in the air of hospital wards and departments. These microorganisms are resistant to drugs used to treat pneumonia.
- Aspiration group. The causative agent of this group is bacteria that live in the microflora of the stomach and enter the nasopharynx or oral cavity.
- A group of pneumonias that occur against the background of a severe disorder of the immune system. In this condition, any type of infection or bacteria can cause the disease. The disease is severe and difficult to treat.
There are main types of microorganisms that cause the disease:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
Patients at risk are:
- Children under 1 year of age or older people;
- Smokers;
- Those suffering from alcoholism;
- Drug addicts;
- With a congenital disorder of immune processes or patients with AIDS;
- Suffering from diseases of internal organs, for example, kidneys, liver.
There are several known scenarios for the development of pneumonia:
- Microaspiration within the nasopharynx. On the surface of the mucous membrane of the oral and nasal cavities there are many bacteria - and the causative agents of pneumonia. During sleep, a small amount of secretion flows from the nasopharynx into the respiratory tract, which is sterile. Normally, the immune system is able to overcome microorganisms that enter the respiratory tract. If it is weakened, then the sterility of the lungs is already compromised and pneumonia develops against this background.
- Getting into the lungs air with a high content of pathogens. This is possible during a long stay in a hospital department, where the environment is filled with many bacteria. The longer the patient inhales this environment, the higher the risk of disease.
- The entry of microbes into the lungs from a source of inflammation located on the patient’s body. Pneumonia pathogens enter the organ through the circulatory system. These cases are common in patients with untreated inflammatory diseases or drug addicts.
- The infection can affect the lungs from nearby organs, for example, with liver or pancreas disease. There is a risk of contracting pneumonia if there is a penetrating wound to the chest area.
Symptoms of pneumonia in adults
The main symptom of pneumonia is a sharp increase in body temperature. Sometimes it can reach 39-40 degrees.
In cases of a latent form of the disease, the temperature rises by only a few tenths of a degree compared to normal.
But the person constantly complains of weakness and malaise. If a severe cough is added to this, then this is a reason to send the patient for an x-ray.
Symptoms of latent pneumonia:
- Nasal congestion and runny nose;
- Headache;
- Increased sweating;
- Decreased appetite;
- Severe shortness of breath;
- Pain in the chest area and numbness in part of it;
- Strong whistling sound when inhaling and exhaling;
- Drowsiness.
Pneumonia that occurs without fever is a consequence of medications taken or a reduced body response to infections. The disease occurs without fever in people who are accustomed to treating any ailment with antibiotics.
At some point, the body stops fighting viruses and bacteria, and the disease acts poorly.
Elderly people or infants do not have strong enough immunity to resist a complex disease. Among such patients, there is a high probability of complications or even death.
In cases where there is even a slight suspicion of pneumonia, especially if the symptoms include a cough and sputum with a greenish tint, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The appearance of a cough in a person
Pneumonia, which occurs without fever but is accompanied by a cough, is easier to identify. It often occurs against the background of colds that have not been completely cured. Then a weak cough develops into a long one, with copious sputum production.
Pneumonia cannot be asymptomatic.
Symptoms if there is no fever, but there is a cough:
- The patient is very thirsty and almost does not want to eat;
- With minimal physical exertion or activity, heavy sweating occurs;
- Rapid breathing due to disruption of one of the lungs;
- Blush on one half of the face, corresponding to the side of the affected lung, which does not go away from the face;
- Painful sensation in the chest with sudden movements or turns of the body.
A cough helps in making a diagnosis and alleviating the patient’s condition.
When you cough, phlegm is expelled, and along with it the infection that has accumulated in the lungs. Its presence always indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the body. Sometimes patients do not consider these symptoms a reason to see a doctor and try to overcome them on their own. Cough or cold tablets and folk remedies are used.
These remedies do not bring relief, but only worsen the situation. The patient arrives at a medical facility in a serious condition and with little opportunity for recovery.
Diagnosis of this disease
Determining pneumonia without fever requires the doctor's skills and experience; it is difficult to verify the correctness of the diagnosis by ordinary listening.
The doctor should listen to the patient, especially pay attention to his well-being. During the examination, the specialist pays attention to the symmetry of the movement of the lungs during breathing, sounds during inhalation and exhalation.
When diagnosing the disease, the doctor may prescribe a number of tests - sputum, blood and urine. To determine exactly the affected area of the lung, the patient is sent for an x-ray. https://feedmed.ru/bolezni/organov-dyhaniya/pnevmoniya-temperatury.html
The x-ray is taken in 2 projections so as not to miss the affected area. Darkening of the lungs indicates the presence of pneumonia.
An x-ray does not always contain all the information and may not show where the source of inflammation is located. The doctor orders a CT scan.
The type of diagnosis is justified in the following cases:
- When all the symptoms indicate pneumonia, but the x-ray does not indicate the source of inflammation.
- If there is inflammation in the same lobe of the lung, which causes a relapse of the disease. If the number of relapses exceeds 3 times, then computed tomography is required.
- If the results of radiography are inconsistent with the symptoms of the disease.
For complications associated with pneumonia, bronchoscopy is prescribed. A study is carried out: a flexible tube is inserted through the nose into the lumen between the bronchi. This allows you to determine the cause of the complication and determine the method of its treatment.
Video
Differential diagnosis with bronchitis
Both pneumonia and bronchitis have similar symptoms, and only an experienced doctor can easily distinguish these 2 diseases from each other. The course of bronchitis is usually not accompanied by fever; there are cases when pneumonia does not have this symptom.
It is important to make an accurate diagnosis in order to begin the correct treatment in time and avoid complications.
You can distinguish bronchitis from pneumonia without fever by the following signs:
- These 2 diseases are caused by different pathogens: viruses give impetus to the development of bronchitis, bacteria - for pneumonia;
- Bronchitis is characterized by the appearance of scars and swelling in the respiratory tract; with pneumonia, fluid accumulates in the alveoli;
- The sounds of wheezing: with bronchitis they are whistling, with pneumonia the wheezing will be both dry and wet;
- With bronchitis, the sounds that accompany breathing are so loud that they can be heard without special equipment;
- Bronchitis is not diagnosed using an x-ray, but with pneumonia, the focus of inflammation is visible in the image.
Bronchitis is treated at home, without hospitalization. Treatment of pneumonia requires constant medical supervision in a hospital setting.
Treatment methods without coughing
Treatment of symptoms of pneumonia without fever in an adult should be comprehensive and carried out in a hospital setting. The slightest changes in the patient’s condition should be assessed by a specialist and measures taken to improve the condition or achieve a stable state.
All drugs used in treatment can be divided into 2 groups. The first group of drugs is necessary to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and alleviate the patient’s condition. The action of the second group is aimed at combating bacteria that cause inflammation.
The treatment complex includes antimicrobial medications and those that facilitate the removal of sputum. They are used in the form of solutions and syrups.
If there is difficulty breathing, the patient is advised to take inhalations with medications. They help dilate the bronchi, making breathing easier.
A simple but effective remedy is fir or eucalyptus essential oil. To alleviate the condition, I use these oils for inhalation, but they also rinse the mouth or take baths.
To overcome pneumonia, the patient must remain in bed. This will help direct all the body’s forces to fight the disease and lead to a speedy recovery.
Effective fight against cough
Coughing with pneumonia is a good sign; pathogens leave the body with sputum. The doctor prescribes 2 types of medications - for removing sputum and mucolytic drugs, for example, ACC or Bromhexine.
Antitussives and expectorants are not always prescribed. If the patient complains of a dry cough, then they will not bring relief, and there is no point in prescribing them.
To alleviate the patient's condition, you can use traditional medicine, but only after consulting a doctor. Physical therapy gives good results.
Help of medicines
All medications for the treatment of pneumonia without fever are prescribed by the attending physician. Self-medication is not acceptable.
In the treatment of this disease, the use of antibiotics gives good and lasting results. Mucopront, Mucodin, Acetylcysteine, Ambrobene and Lazolvan are often prescribed.
- Mucopront. This medicine is available in 2 forms: syrup or capsules. Adults are recommended to take 3 tablespoons or 2 capsules three times a day. For children under 12 years old, 1-2 spoons of Mucopront three times a day is enough. Capsules are not prescribed to children.
- Mukodin. Doses and method are similar to the previous medicine. Children are allowed to take the product only in the form of syrup, one spoon 2-3 times a day.
- Acetylcysteine. The dosage of this drug is selected for each patient based on the severity of the condition. It is not recommended to take more than 200 ml of medication per day. For children, the dose should not exceed 100 ml.
- Ambrobene. The drug is available in tablet form. They must be taken according to a regimen developed by the attending physician. It looks something like this: from the first to the third day - 1 tablet 3 times a day, then - 1 tablet twice a day.
- Lazolvan. The product is available in the form of syrup. Recommended dosage: for adults - 2 spoons twice a day, for children - one spoon 2-3 times a day. The medicine is taken with meals and washed down with plenty of water.
For a speedy recovery, it is necessary to take medications and proper nutrition. It is better if the food is light and contains a minimum of fat. Food should be nutritious and fortified.
Don't forget about water. She's important too. The consequence of tissue dehydration will be high temperature.
Possible complications of the disease
Pneumonia, regardless of the cause, must be cured. Otherwise, this leads to serious consequences and complications.
Doctors call the most common complications due to improper treatment:
- Acute respiratory failure;
- Pleurisy;
- Broncho-obstructive syndrome;
- Problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Severe pulmonary edema;
- Shock caused by toxins or infection.
Against the background of pneumonia, heart failure can develop, which is the main cause of most deaths in patients. Despite the rapid development of medicine, pneumonia, especially without fever, is the cause of death for patients.
This disease should not be treated with disdain, self-medication or not treated at all. Timely contact with specialists will save life and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor
Source: https://FeedMed.ru/bolezni/organov-dyhaniya/pnevmoniya-temperatury.html
Signs of pneumonia in an adult without fever with cough
Pneumonia without fever in adults is a dangerous condition that develops primarily with weakened immunity.
A distinctive feature of the disease is that there is no risk of infection for others, but the nature of its course is not much different from an infectious one.
It is important to promptly identify the main signs of pneumonia in an adult without fever with cough in order to avoid the development of dangerous complications and risk to the patient’s life.
Types of pneumonia without fever
Pneumonia without fever can be:
- focal;
- segmental;
- share;
- total;
- staphylococcal.
With the development of a focal form, small round dark spots are detected in the lungs. A dry cough is replaced by a wet one and has a long-lasting course.
In the case of segmental pneumonia, the cough is mild . Increased sweating, sleep disturbances and appetite disturbances become more striking symptoms.
The lobar form of the disease involves one or more lobes of the lungs. Total is dangerous because it spreads to the entire lung or involves both. These types of pathology are accompanied by periodic bouts of coughing and difficulty breathing.
The staphylococcal form has the most unfavorable course. A hysterical cough is accompanied by the release of purulent sputum, clearly visible wheezing, shortness of breath and nausea.
Proceeding without fever, pneumonia indicates the body’s inability to resist a progressive disease. Often a person is unaware of his condition and does not take appropriate measures, aggravating the dangerous situation even more.
Read more about wet cough
Main causes and development of the disease
Pneumonia without fever in adults can be caused by :
- bacterial flora (staphylococci, streptococci, mycoplasma, chlamydia, Haemophilus influenzae, leginella);
- viral agents (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, herpes, chickenpox);
- the presence of parasites in the body (ascaris, pulmonary fluke, echinococcus);
- fungal infections (candida and aspergella);
- uncontrolled use of medications (antibiotics);
- severe hypothermia.
The first two reasons are the most common. As a bacterial infection develops, a focal form of the disease often develops.
Viral diseases can cause dangerous complications, including pneumonia. Inflammation of the lungs often develops against the background of weakened immunity after an illness.
Fungi and parasites are relatively rare causes of pneumonia. Candida can cause disease in patients with HIV infection, with severely weakened immunity, and bone marrow pathologies.
Self-administration of antibiotics at the initial signs of the disease often leads to the development of resistance to the antibacterial agent in the infection.
In addition, they note the inability of drugs to have a sufficient effect on pathogenic bacteria.
The result is the further development of the disease, with the involvement of new areas of lung tissue in the pathological process.
Signs of pneumonia in an adult
The main signs of pneumonia in an adult :
- increasing shortness of breath;
- the appearance of bloody streaks in the sputum released during coughing;
- soreness in the sternum, increasing with each breath;
- malaise, apathy and lethargy;
- rapid pulse;
- sickly blush combined with a pale complexion of the face and limbs.
The last sign allows you to independently determine the nature of the development of the disease. The blush becomes especially noticeable with unilateral pneumonia, when it appears on one cheek. With bilateral inflammation, it is less noticeable, since it is located on both.
Cough and sore throat are integral signs of pneumonia in an adult without fever with cough. Gradually, a dry cough is replaced by a wet cough. It is often accompanied by the release of mucopurulent or purulent-rusty sputum.
Read more about how to treat a cough
Why does my back hurt when I have pneumonia?
Back pain is a less common but significant symptom of pneumonia. Most often, this condition occurs with a bacterial form of the disease, as well as with severe bilateral pneumonia.
Pain syndrome develops as a consequence of the impact on the nerve endings that penetrate the spinal canal of the spine and the internal organs adjacent to the lungs.
In the lobar form of the disease, the back hurts as a result of the transition of the pathological process to the serous membrane - the pleura.
An increase in pain in the back area is often associated precisely with this, and becomes a pronounced signal of increasing pathology.
Another cause of back pain with pneumonia is an increasing cough . In this case, strong pressure appears on the bundles of nerve endings, and acute pain occurs.
How to treat pneumonia?
Treatment of pneumonia that occurs without fever should be under the supervision of a specialist. Only a doctor can determine how to treat pneumonia in each specific case.
On average, the course of treatment lasts about 3 weeks. The main method is antibiotic therapy. Most common application :
- Penicillin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Cefazolin;
- Cefotaxin.
Along with antibiotics, you will need to take drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora . The course of restoring balance is about 1 month.
If the disease is of viral origin, Acyclovir , Ingavirin , Tamiflu . Cycloferon and Esberitox are indicated as immune modulators . To ease expectoration, you will need to take mucolytics .
If there is indications from the attending physician, inhalations are performed using expectorant and anti-inflammatory drugs . It is also often recommended to perform breathing exercises to speed up the healing process and avoid the development of complications. Special exercises help stretch adhesions and adhesions and strengthen the respiratory muscles.
An important point of treatment is plenty of warm drinks . This is necessary for the accelerated introduction of toxins from the body.
Traditionally multivitamins , and a specific diet containing foods rich in natural vitamins and minerals is discussed with the patient.
After suffering from pneumonia, a rehabilitation course is provided, including physiotherapeutic procedures. A sanatorium on the seashore or in a coniferous forest will benefit an organism weakened by illness.
Is it possible to carry out treatment on your own at home?
Pneumonia that occurs without fever is no less dangerous to human life than the traditional form of the disease. For this reason, it is necessary to exclude self-treatment at home and uncontrolled use of medications.
Only a doctor can correctly identify the signs of pneumonia in an adult without fever with cough . You should not rely on yourself or your friends to make a diagnosis and choose medications. It is important to remember that pneumonia tends to progress, and the last, 3rd stage of the disease, poses a serious threat to life.
If the patient's condition allows, treatment can take place simultaneously on an outpatient basis and in a hospital. In this case, health workers are responsible for the correctness of its implementation and the preservation of the patient’s health.
For a speedy recovery, the patient is recommended to :
- organize a good rest;
- drink enough fluid (at least 2.5 liters per day);
- give up active and passive smoking;
- avoid staying in places with a polluted atmosphere;
- increase the air humidity in the room and carry out wet cleaning daily.
If signs of pneumonia appear in an adult without fever with cough, it is important to exclude self-diagnosis and self-medication in any form. Only modern therapeutic methods will allow you to maintain health and prevent the development of severe complications.
Source: https://lechu-kashel.ru/priznaki-pnevmonii-u-vzroslogo/
Pneumonia - symptoms in adults without fever but with a dry cough, signs of pneumonia, treatment if without wheezing
Do your loved ones have symptoms of pneumonia, but they are not accompanied by fever? It can also be pneumonia, only in a latent form.
So that you can recognize this disease in time and cope with it, let's figure out what features this particular type of pneumonia has, how it can be identified, and what treatment such a disease will require.
And also what to do if the cough does not go away after pneumonia.
Definition of disease
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung tissue that can spread to segments or lobes of the lungs. Pneumonia is usually accompanied by severe symptoms, including cough and fever in adults.
But in some cases, this disease can occur in the so-called silent form, in which the patient will not experience the main symptoms of the disease. This form of pneumonia is often perceived by patients as a normal, long-term illness.
It is for this reason that patients suffering from it rarely seek help in a timely manner, and therefore have a higher chance of developing complications, as well as death, than patients with ordinary pneumonia.
In recent years, this form of pneumonia has become most widespread. A special risk group for this disease includes those patients who have already suffered from pneumonia at least once or suffer from reduced immunity.
Causes
Like other forms of pneumonia, latent pneumonia occurs against the background of a viral or bacterial infection.
The source of such an infection is often the upper respiratory tract, less often – teeth (caries can also lead to the development of such pneumonia) or other organs and systems.
The reason why this disease is not accompanied by an increase in temperature may be low immunity or uncontrolled use of antibiotics, which reduces the body's defenses.
In some cases, the cause of the development of such a disease is the uncontrolled use of antitussive drugs, which could occur with bronchitis. It is he who provokes stagnation of mucus in the bronchi, which further causes pneumonia.
Symptoms
Pneumonia in a latent form, as a rule, gives few symptoms characteristic of such a disease of a bacterial or viral nature. The main signs of such an illness in the described case will be:
- General weakness, prolonged loss of performance, increased human fatigue. This symptom will be observed even several weeks after the onset of the disease.
- Cough, which will be accompanied by sputum. This sputum will have a greenish or rusty tint, but in some cases it may also contain blood clots.
- Characteristic wheezing. Often it will be more pronounced at night.
- Shortness of breath. With this disease, it can appear even in cases where the patient’s physical activity was minimal.
- Chest pain. With this disease, they are usually minor and can only appear when taking a deep breath or after vigorous physical activity.
- Breast distortion. This sign is visible if you look at the patient from the side. It is caused by the fact that in such patients the affected lung is usually less active in work than the normal one, therefore only part of the chest moves when breathing.
- Unhealthy blush. With this form of pneumonia, a person usually experiences pale skin, against which red spots of blush appear. Often this is the sign that allows you to determine the presence of pneumonia in a silent form.
A patient with a latent form of pneumonia may not even experience all, but only some of the stated symptoms. Such cases are quite common in medical practice. For this reason, even those patients in whom the disease has only some manifestations should consult a doctor, since they also belong to a special risk group.
Possible complications
Pneumonia in a latent form quite often leads to various complications, since this particular variant of the disease is extremely difficult to diagnose in a timely manner and treat correctly.
The pathologies that it can provoke include heart and pulmonary failure, liver and kidney diseases, pleurisy, and lung gangrene.
Also, in advanced cases of the disease, patients with this disease may develop sepsis, which often leads to death.
If there are any signs of deterioration in the condition of a person suffering from pneumonia, you should immediately call emergency help. Remember that the above complications are extremely dangerous for the patient and can result in his death. Only emergency help from specialists will give him a chance to survive in such a situation.
Treatment
Pneumonia not accompanied by a cough requires long-term drug treatment. It is carried out mainly in a hospital setting and involves taking a huge number of specialized medications. Also, such therapy may involve the additional use of traditional methods of treatment. Let's take a look at them in more detail.
By medication
Treatment of this type of pneumonia must be carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of experienced specialists. As part of such therapy, a course of antibiotics (or antivirals, if the disease is viral in nature) is usually prescribed. Basically, for this disease, penicillin drugs or macrolides are prescribed.
Patients are also prescribed immunostimulants, agents that facilitate sputum discharge and symptomatic medications. Additionally, various physical agents are used. procedures, including electrophoresis and magnetic therapy. To restore lung function, patients are also prescribed massage and special breathing exercises. For the entire duration of treatment, the patient is prescribed bed rest and a special diet.
The duration of treatment for such a disease will vary depending on the general condition of the patient and will range from several days to several weeks.
In any case, the patient must undergo a full course of drug therapy and follow all other doctor’s recommendations.
Violation of these can significantly reduce the effectiveness of treatment and lead to various complications of the disease.
Folk remedies
In most cases, with this form of pneumonia, doctors allow patients to take folk remedies, but only simultaneously with standard drug therapy. Such remedies usually help relieve individual symptoms of the disease, increase the patient’s immunity and speed up recovery. The most effective among them are:
- Herbal decoctions. As such, it is best to use a ready-made pharmacy breast mixture or St. John's wort. This decoction can be given to a person up to 3 times a day, ensuring they drink plenty of fluids.
- Fruit drinks, compotes, teas with berries. These drugs help reduce the patient’s temperature and replenish the lack of vitamin C in the body. The most effective in this case will be drinks made from raspberries, blueberries, and currants. You can drink them in almost unlimited quantities.
- Inhalations. They can be made using either a herbal decoction or regular mineral water or boiled potatoes. Such remedies are best used during the recovery stage. They help restore the mucous membrane and facilitate the removal of sputum.
- Massages with essential oils or animal fat. They are used at different stages of the disease. They allow you to warm up the chest and promote rapid removal of mucus.
- Compresses. Crumpled boiled potatoes and cottage cheese cakes are used as such remedies at home. They are softer analogues of conventional mustard plasters. They can be done once a day.
Also, when treating pneumonia that is not accompanied by fever, many recommend using cups. This remedy is really quite effective for this disease. However, it can only be used with the permission of the attending physician. It is recommended to entrust this procedure to medical personnel, since it is very difficult to perform.
Prevention
In many cases, the occurrence of such a disease can be prevented by using general simple preventive recommendations. They provide:
- Strict control of antibiotic intake for any disease, including respiratory diseases. It is this factor that most often leads to the appearance of pneumonia, not accompanied by cough and fever.
- Timely treatment of ARVI, influenza and other respiratory diseases. It is precisely such ailments that most often provoke a silent form of pneumonia. If necessary, get vaccinated three weeks before the onset of respiratory disease epidemics.
- General strengthening of the body. Regular exercise, hardening, taking vitamins as prescribed by your doctor.
- To give up smoking. This habit greatly weakens the protective functions of your lungs, which can lead to the appearance of such diseases.
A particularly important part of the prevention of such a disease is timely examination by the attending physician and regular fluorography, which is required once a year.
These measures will allow you to detect such a disease in the early stages, as well as identify a predisposition to it, which will give you the opportunity to immunize the body in a timely manner and in the future avoid an unpleasant illness.
The first signs and symptoms of tuberculosis
The first signs of pneumonia are described in this article.
Pathogenesis of COPD //drlor.online/zabolevaniya/legkix/xobl/pathogenez.html
Video
conclusions
As you can see, pneumonia, not accompanied by pneumonia, is an extremely dangerous disease that occurs due to reduced immunity or uncontrolled use of medications.
It can be recognized only by indirect signs.
However, even if they exist, patients need to seek qualified help as quickly as possible and undergo a full examination in order to cope with this illness with minimal consequences for their health.
Source: https://drLOR.online/zabolevaniya/legkix/pnevmoniya/s-kashlem-bez-temperatury-opisanie-bolezni-i-lechenie.html