N. K. Vitko, Candidate of Medical Sciences A. B. Bagirov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Yu. V. Bukovskaya, S. V. Zinin
Clinical Hospital No. 1 of the Medical Center of the Administration of the President of the Russian Federation, Moscow
Fractures of the bones of the foot and ankle are the most common traumatic injuries to the skeleton. Their share, according to various authors, is at least 10-15%.
A feature of bone fractures in the ankle joint is the high frequency of intra-articular injuries. Destruction of articular cartilage and subchondral plates significantly aggravates the course of the disease and worsens the prognosis of treatment and rehabilitation of such patients. Unsatisfactory results in the treatment of intra-articular fractures of the ankle joints are up to 28%.
A similar trend can be seen in fractures of the foot bones. Damage to the calcaneus and talus bones are of greatest clinical importance. Thus, calcaneal fractures account for about 60% of tarsal bone fractures and 2% of all fractures.
The results of conservative treatment are often unsatisfactory. Fractures of the calcaneus in 75% of cases involve the subtalar joint, while 80% of them are accompanied by displacement of fragments.
Hence the discrepancy and violation of congruence of articular surfaces, early degenerative changes, late pain attacks and disability.
Considering that the majority of patients with fractures of the bones of the foot and ankle are able-bodied people, the need for their extended and detailed radiation examination becomes clear.
When examining the ankle joint, standard positions are used in the lateral, external, posterior and posterior projections with internal rotation (10-150). The methods for carrying them out are described in many radiology manuals and do not require separate consideration.
However, radiography cannot provide all the information a traumatologist needs. Therefore, a patient with an ankle fracture is advised to undergo an X-ray computed tomography (CT) scan.
The accuracy of a CT examination largely depends on the thickness of the “slice” and the table feed pitch. A collimation width of more than 3 mm is considered by many authors to be inadequate for identifying fractures without displacement of fragments. The ideal “slice” thickness for traditional CT is 2 mm or less. The table feed pitch should also not exceed 2 mm.
Spiral computed tomography is preferred due to its short examination time.
In all cases, the study is carried out in the axial plane. For stepwise CT scans with a slice thickness of 3 mm, a coronal projection can additionally be used. Tomography with a collimation width of 1-2 mm allows one to limit oneself to axial studies. The possibility of multiplanar and three-dimensional reconstructions improves the information content of CT without additional radiation.
It should be noted that the radiation dose to the patient is quite low during computed tomography of the ankle or foot. Thus, when performing 60 axial scans on a Somatom plus 4 tomograph (Siemens), the effective absorbed dose is less than 0.1 m3v, which is comparable to an x-ray examination.
The main advantage of computed tomography is the ability to study in detail the horizontal articular surface of the tibia. CT scans often reveal additional fracture lines and fragments. CT allows you to accurately determine the total area of the articular surface of fragments, diastasis between them, angular and multiplanar displacement, and the position of small fragments.
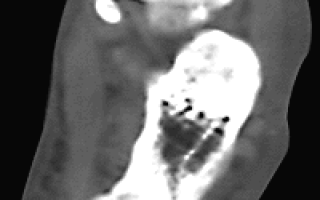
| Figure 1. Lateral radiograph of the right ankle. Fracture of the posterior edge larger than the tibia with displacement of the fragment upward and posteriorly |
Tomography data determines treatment tactics. Thus, in case of fractures of the posterior process (third malleolus), the approximate area of its articular surface is determined (Fig. 1, 2). In cases where the area of the fragment exceeds 1/3 of the entire horizontal articular surface of the tibia and there is a backward and upward displacement of the fragment by more than 2 mm, the patient is indicated for osteosynthesis.
Destruction of the articular surface of the tibia does not occur chaotically, but is determined by the mechanism of injury and in accordance with the action of tension forces on the ankle joint ligaments. There are fractures of the tibia with the formation of four types of fragments: anterior internal, posterior internal, anterior external, posterior external.
Most often, posterointernal fractures are detected.
| Figure 2. Axial computed tomography scan of the ankle joints after plaster cast application. Two additional tibial fracture lines are identified in the oblique frontal plane. The area of the articular surface of the fragments exceeds |
CT allows one to visualize the transition of fracture lines to the medial malleolus, which are not visible on radiographs.
In a series of sequential scans, the x-ray joint space between the ankles and the talus trochlea in both legs is measured with an accuracy of 1 mm.
An undoubted advantage of computed tomography is the ability to visualize damage to the distal tibiofibular joint. Quantitative assessment of X-ray fibular gap diastasis and fibular rotation reveals another possible cause of ankle instability and pain (Fig. 3).
| Figure 3. Axial computed tomography scan of the ankle joints. (a) Pathological diastasis between the medial malleolus and the trochlea of the right leg. (b) Diastasis of the distal tibiofibular joint. A screw is visualized in the epiphysis of the tibia |
Computed tomography is a good tool in assessing the effectiveness of conservative or surgical treatment. Even despite multiple linear artifacts from metal fixing structures, it is almost always possible to determine the correct alignment of fragments and the elimination of pathological diastasis between fragments or bones (Fig. 3).
Topographically, anatomically and functionally, the foot is inseparable from the ankle joint. This applies more to the back of the foot.
X-rays of the heel and talus and the joints they form occur simultaneously with the examination of the ankle joint. Additionally, radiography of the calcaneus in the axial projection can be performed. However, more often it is difficult due to severe pain.
Mandatory in the study of the fore and middle sections of the foot are its radiography in plantar, oblique and strictly lateral projections.
However, due to the complexity of the anatomical structure of the foot and the projection of the bones involved in the formation of several joints, radiography cannot satisfy surgeons.
This problem is only partially solved by direct magnification radiography. Therefore, fractures of the foot bones are an indication for computed tomography.
The CT scan technique of the foot is no different from examining the ankle joint. The scanning area includes the entire foot, starting from the horizontal joint space of the ankle joint.
The participation of the calcaneus in the formation of three joints, as well as the gravitational load of the entire body acting on it, determines the increased attention of traumatologists to this bone.
| Figure 4. Axial computed tomography scan of the calcaneus after plaster cast application. (a) Fracture of the right calcaneus at the subtalar joint. The fracture line passes through the sinus of the tarsus. Fracture of the right scaphoid (b) Many |
A calcaneal fracture usually occurs due to compression on the subtalar joint between the talus and the ground. The fracture line passes obliquely through the posterior talar articular surface (Fig. 4).
In this case, two main intra-articular fragments are formed: anterior-internal (sustentacular) and postero-external. The sustentacular fragment is firmly attached to the talus by the interosseous ligament of the sinus tarsus. The fixing role of the anterior internal fragment is of fundamental importance.
One of the main tasks of the traumatologist is to compare the free posteroexternal fragment with it.
Regardless of the method of intended fixation of fragments - intraosseous or extraosseous - there are a number of clinically relevant questions to which computed tomography can provide unambiguous answers.
First of all, this concerns the number of intra-articular fragments. The treatment prognosis worsens if more than two fragments are visualized.
The second important aspect is the proximity of the fracture line to the medial surface of the calcaneus. The worst prognosis is for fractures passing through the sinus of the tarsus. Fixation of both fragments to the talus may not be sufficient for full functioning of the joints.
In contrast to the sustentacular fragment, the posteroexternal one, as a rule, has a subluxation in relation to the talus, planar and angular displacement. Their exact quantitative measurement with CT specifies the task for the traumatologist when fixing fragments.
| Figure 5. (a) Lateral oblique radiograph of the foot. Fracture of the calcaneus in the area of the subtalar joint with the formation of a subtalar fragment. Upward displacement of the posterolateral fragment (b) Axial computed tomogram of the calcaneus. Main l |
When performing intraosseous osteosynthesis with a lateral approach, it is important to know in advance whether the posteroexternal fragment will be hidden by the lateral wall of the body of the calcaneus. Their relative position is better visualized in the coronal plane (Fig. 5).
Axial images assess the integrity of the process supporting the talus. This is explained by the fact that the metal structures that fix the fragments are optimally passed through the sustentaculum.
To restore foot length, the integrity of the lateral wall of the body of the calcaneus is necessary. Axial topograms enable the radiologist to assess the integrity of the cortical layer of the lateral wall.
The calcaneus is involved in the formation of the calcaneocuboid and talocaleonavicular joints. In this case, the main load from the human body is distributed to the calcaneal-cuboid joint. The presence of intra-articular fractures of these joints is a poor prognostic sign.
In addition to detailing the identified fractures, it is important to study the shape of the damaged heel in order to normalize it. Anteroposterior shortening, superior inferior collapse, and angular (varus or valgus) rotation of the calcaneus are quantified.
| The main advantage of computed tomography is the ability to study in detail the horizontal articular surface of the tibia. CT scans often reveal additional fracture lines and fragments. CT allows you to accurately determine the total area of the articular surface of fragments, diastasis between them, angular and multiplanar displacement, and the position of small fragments |
Fractures of the talus do not have such strict patterns as the heel. More often they are multi-fragmented and complicated by aseptic necrosis (Fig. 6).
| Figure 6. Axial computed tomogram at the level of the subtalar joints. Multi-comminuted long-standing fracture of the right talus. Aseptic necrosis of the talus |
The trochlea of the talus is the most typical site of occurrence of separating osteochondritis, after the knee joint. Typical places of their detection: posterointernal and anteroexternal segments of the block. In addition, the talus is the second most common site (about 25%) of stress fractures, after the tibia. In half of the cases they are not detected radiographically and almost always arise in the trochlea of the talus.
Stress fractures of the tarsal bones are detected in no more than 9% of cases. They are called “marching fractures,” although they occur not only in the military, but also in athletes and simply obese people.
| Figure 7. Axial computed tomography scan of the right foot at the level of the navicular bone. Additional external tibia is visualized - development option |
The cause of pain in the foot area can be damage to the synchondroses between the accessory bones and bones of the foot, and the ligaments next to the sessamoid bones. The most typical sites of this type of injury are the connections of the accessory external tibia and scaphoid bones, the synchondrosis between the posterior process of the talus and the triangular bones, as well as the area of the sessamoid bones: the second cuboid and triangular bones (Fig. 7). Computed tomography helps to identify not only development options, but also the presence of injury.
Thus, traumatic injury to the foot and ankle requires extensive x-ray examination. Computed tomography should become a routine method for studying this area due to its high information content.
New computer tomography software emerging in recent years allows us to predict even greater interest in this research method on the part of traumatologists.
Thus, computer disarticulation will provide complete spatial information about the state of the articular surfaces. The fluoroscopic computed tomography mode will make it possible to carry out minor invasive measures under CT control in real time.
All this promises an increase in the number of scientific studies on X-ray computed tomography of trauma patients in the coming years.
Source: https://www.lvrach.ru/2000/02/4525737/
What does a CT scan of the foot show? Preparation, indications and contraindications
- Content
CT scan of the foot is a modern non-invasive diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of tissues and blood vessels in this area, differentiate pathology and determine the method of treatment. The study is based on the ability of X-rays to penetrate the structural formations of the human body. The use of special equipment makes it possible to convert the signal into an image, which shows pathological changes in tissues and organs. The method is as informative as possible when diagnosing diseases of bone and cartilaginous structures, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and when assessing the nature of the blood supply to the area being studied.
Arthrosis of the talonavicular joint on CT
What does a CT scan of the foot show?
Computed tomography of the foot reveals structural abnormalities in the bone and cartilaginous elements of the metatarsus, ankle joint and toes. The use of CT scans with contrast will help determine the condition of the blood vessels supplying this area and detect tumors and foci of inflammation.
The method is used to differentiate the following pathological changes:
- traumatic damage to the elements of the ankle joint (fractures, dislocations, ligament rupture, hemorrhages in the area of the joint capsule);
- inflammatory changes in arthritis, bursitis;
- foci of destruction in osteomyelitis;
- aseptic necrosis of bone structures of various etiologies;
- primary neoplasms and metastases;
- pathological position of the elements of the foot with transverse flatfoot, hallux valgus;
- impaired blood supply, the presence of vascular thrombosis, changes in the structure of the walls of veins and arteries.
As a result of the examination, the doctor receives a series of layer-by-layer images, on the basis of which, if necessary, a three-dimensional image can be recreated.
Calcaneal fracture on CT scan of the foot, 3D image
The method allows you to determine the location of the lesion and the degree of development of pathological changes.
How is a CT scan of the foot performed?
The procedure is carried out using a tomograph - special equipment capable of reading information during the examination and transmitting it to a computer monitor in the form of photographs of thin sections of the studied area.
The device has a wide annular part in which emitters - X-ray tubes - are located. The latter perform rotational movements during the procedure, which ensures that the area is illuminated in the desired plane. At this time, the tomograph ring is static, only the table on which the patient is located moves.
The examination takes place in a separate room, the doctor and technical staff are located behind a special partition. Communication with the patient is carried out through an intercom. The subject is positioned on a horizontally mounted table surface, his feet are fixed with straps to increase the accuracy of visualization.
The whole procedure takes up to 10 minutes, then the patient is asked to wait for the results of the study and the doctor’s conclusion. All information is placed on a CD, and the radiologist gives an additional oral consultation.
When performing a CT scan of the foot with contrast, the duration of the examination increases. First, the radiologist takes a series of native images, then the patient is injected with an iodine-containing solution that has high radiopacity.
The procedure is continued, resulting in layer-by-layer photos showing the circulatory network and pathological changes in the area being studied.
By comparing the images, the doctor makes a conclusion about the condition of the elements and structures of the examined part of the body.
Preparing for the study
Computed tomography does not require special preparation. The patient needs to approach 10-15 minutes before the start of the procedure and remove items of clothing that may affect the quality of the images.
Carrying out contrast computed tomography involves the following steps:
- the patient takes a blood test for creatinine, which will assess the condition of the kidneys and identify violations of their functionality;
- If you have an individual intolerance to iodine preparations, you must notify your doctor - this will make it possible to avoid unwanted allergic reactions.
The Magnit Medical Diagnostic Center offers patients a free preliminary consultation, at which the radiologist will provide the necessary information, explain the features of performing a computed tomography scan of the foot and preparing for this study.
The ankle joint and foot bones bear the main load when walking, taking on the weight of the human body. Some pathological processes can only be differentiated with the appropriate position of the leg, when the appearance of physiological work of this part of the body is created. To identify them, the method of computed tomography of the foot with a load is used.
Indications for this type of CT scan include suspicion of transverse flatfoot in the initial stage, deformation due to valgus or varus structure of the legs.
Measuring the angle and height of the longitudinal arch of the foot with MSCT
Identifying pathology at an early stage allows for timely treatment and preventing the development of complications.
MRI or CT scan of the foot – which method to choose?
The main difference with magnetic resonance imaging is the use of a magnetic field that penetrates the tissue of the human body and is converted into an image using a computer program. MRI is safe for human health; there is no X-ray radiation when using this method. This type of diagnosis is informative in identifying diseases that affect the soft tissues of the foot.
The method is indicated if the patient has contraindications to x-ray examination, if there is damage to muscle tissue, ligaments of the ankle joint, metatarsus and toes. When choosing a diagnostic method, it should be taken into account that the price of an MRI is significantly higher than a CT examination of a similar area.
Computed tomography of the feet provides visualization of the condition of bone and cartilaginous elements and is informative regarding inflammatory processes and neoplasms. The procedure takes less time than a similar MRI examination.
The choice of method depends on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient.
CT scan of a child's foot
CT scans of the feet are usually performed on children over the age of five. Radiation exposure when using modern tomographs is minimal and does not have a pronounced pathological effect on the child’s body. CT makes it possible to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis and determine the localization of the process.
If you follow the radiologist's recommendations, the positive effect of the procedure significantly outweighs the possible risk, and the doctor receives information about the condition of bone and cartilage structures and sees an objective picture in real time.
CT scan of the foot with contrast in children is highly informative and is used to identify neoplasms, inflammatory changes, and assess the blood supply to the area being studied.
Registration of a child for a tomography is carried out on the website of the Magnit clinic, by contact numbers and during a personal visit to the center. You can choose a convenient time to visit and receive a free consultation on each specific case.
Indications and contraindications for CT scans of the feet
Diagnosis of foot diseases using computed tomography is carried out at the initiative of the patient and upon the direction of the doctor. It is worth making an appointment if you notice the following symptoms:
- foot pain of unknown etiology;
- swelling, feeling of heaviness in this area;
- history of traumatic foot injuries;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms;
- external change in the shape of the foot;
- suspicion of the occurrence of inflammatory and degenerative processes in this area;
- impaired blood supply to the feet.
Visualization of foot fractures on CT
Patients are referred to a computed tomography scan before surgery in order to determine the scope and location of the upcoming actions. During the recovery period after surgery, CT is prescribed to monitor tissue regeneration processes.
The method has a number of contraindications, which is associated with the use of X-ray radiation in the research process. CT scans of the feet are not performed:
- pregnant women;
- children under 5 years of age (anesthesia is required due to the child’s inability to lie still for the required time);
The use of contrast is not possible in the following cases:
- in the presence of individual intolerance to the contrast agent;
- with severe thyrotoxicosis;
- with renal failure;
- if you are taking certain medications for diabetes;
- with caution in children under 12 years of age.
If a CT scan is not possible, the doctor may recommend that the patient undergo a magnetic resonance examination or ultrasound examination of the feet. When choosing a diagnostic method, the specialist takes into account the indications, clinical picture and data from other examination methods.
Source: https://spb24mrt.ru/kt-info/chto-pokazyvaet-kt-stopy
CT scan of the lower extremities: what pathologies are determined, interpretation, contraindications
Computed tomography involves a research method during which a person is exposed to x-rays.
There is a CT scan procedure of the lower extremities - it allows you to timely identify pathologies that are beyond the reach of other methods. Tomography is often performed with contrast; this procedure will be minimally invasive, but it reveals pathologies of blood vessels and tissues. Thanks to the technique, the doctor can find malignant neoplasms in time, and this is important because in case of oncological processes, therapy begins as soon as possible. In this publication we will look at what a diagnostic method is, when it is carried out, how to properly prepare and other interesting information.
Indications and contraindications
The main advantage of the procedure is that the diagnostician visualizes small joints, blood vessels, and the condition of bone tissue. A CT scan of the leg is prescribed after an x-ray, but this is necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
To find out whether certain parts of the body are normal or pathological during an examination is the main question that computed tomography solves.
Another name for CT of the lower extremities is angiography, and this method is indicated in the following cases:
- there is pain in the calf area;
- even after minor exertion, a person feels an unpleasant tingling sensation in the lower part, sometimes soreness;
- the legs or toes below become numb;
- if you palpate the lower limbs, the pulse is not felt;
- Even in the warm season, the feet remain cold and freeze.
It is mandatory to conduct regular examinations if the following pathological conditions are found in a person:
- embolism;
- thrombosis in acute form;
- phlebeurysm;
- allows you to see venous insufficiency in a chronic form;
- pathologies of the vascular system;
- angiopathy caused by diabetes.
In addition, medical personnel recommend undergoing an examination if surgery is to be performed. After surgery, examinations are carried out to monitor the patient's condition.
If a person has suffered an injury, then a CT scan is performed to determine the nature and extent of the injury. To monitor the condition of the vessels, a CT scan of the lower extremities with contrast is performed, having previously specified whether there is any individual intolerance to the active substances included in the administered drug.
A study is carried out if a person has a history of arterial disease with a serious degree of circulatory impairment.
The diagnostic method of the lower extremities is popular and is considered relatively safe, but not everyone can be tested in this way. Let's consider contraindications to the procedure:
- lactation period, if a study with contrast is planned;
- It is undesirable to undergo it during pregnancy due to the likelihood of exposure of the fetus to radiation, which can subsequently provoke the occurrence of pathologies;
- with contrast - not done in case of acute renal failure, since the substance is predominantly excreted by the kidneys;
- diabetes mellitus – the radiologist independently decides on the advisability of conducting the examination;
- in severe condition, CT scan of the lower extremities can be harmful;
- too much weight - the devices are not designed for overweight people.
If a woman is breastfeeding and needs to undergo examination, milk is expressed for some time (2-3 days). At this time, the baby is transferred to artificial formula.
When a contrast agent is administered to examine the lower parts of the body, allergy tests are done. Some people have an individual intolerance to iodine; it is part of the contrast agent and provokes undesirable effects: nausea, dizziness, rash, suffocation.
Doctors recommend that many people undergo examination, but it is worth carefully studying the list of contraindications, as well as possible side effects. Usually the therapist explains everything about this method during the consultation.
Special conditions
CT scan of the lower extremities is a minimally invasive procedure, so it is important that the room where the examination is performed is kept sterile. The task of health workers is to limit the transmission of infections; it is also important that disinfection procedures are carried out in the places where the puncture will be carried out.
Specialists should have medicines and instruments on hand if the person being examined needs urgent medical care. In the office there are:
- radiologist;
- anesthetist;
- resuscitator.
Before the procedure, written consent is taken, despite the fact that the attending physician recommends a CT scan of the lower extremities. The patient is explained in detail what the essence of the procedure is and what complications arise during its implementation.
If necessary, before CT angiography of the vessels of the lower extremities, drugs that have an anti-allergenic or sedative effect are administered. If it is planned to administer contrast, laboratory tests will be ordered: they will determine the level of creatinine and urea in the body.
The examination method requires some preparation - the patient needs to stop eating for 8-10 hours, so the best option is to go for a CT scan of the lower part in the morning.
It is not recommended to drink water before the study, especially if you plan to administer a contrast agent.
You also need to undergo allergy tests to find out whether you have an individual intolerance to iodine-containing substances.
Why contrast is needed
Why use a contrast agent if a CT scan is planned to examine the vessels of the lower extremities - this question is relevant for many patients. It is this technique that allows us to examine the condition of the blood vessels in detail.
The image will clearly show whether there are pathologies of the arteries, the diagnostician will determine whether surgery is necessary, or whether conservative therapy can be used.
If a CT scan of the vessels of the patient’s lower body is to be performed, then the use of contrast is a prerequisite. The specialist will be able to examine in the image all the features associated with the blood supply to the extremities: the structure of the capillaries and even their very small branches.
Thanks to the connection to a computer, you can see the state of the tissues in a three-dimensional image, and this factor significantly expands the possibilities of the study. It is possible to perform a CT scan of the lower part without contrast, but often this technique is not very informative, so examination is rarely prescribed.
How the actual procedure works
The equipment used for the procedure is called a tomograph; it works on the principle of X-ray irradiation. Advantages of the technique: the degree of radiation is much lower than if the patient were prescribed radiography, while the results are several times more reliable and informative.
The procedure itself is carried out as follows:
- Before the scan, the subject is given special disposable clothing that does not contain metal elements. It is comfortable, spacious, and does not restrict movement.
- It is also important for the patient to remove all metal jewelry.
- The person is placed on a special moving platform, which operates automatically. During the procedure, the device moves the human body under a special tomograph ring in exactly those areas that are intended for examination.
- During the procedure, the subject must be alone in the office, but a team of specialists is present in the next room. They monitor the progress of the procedure and, if necessary, will always provide first aid.
- It is forbidden to leave the platform, you cannot even move during the procedure - this will distort the results of the examination.
- If there is discomfort, unusual and unpleasant sensations, or dizziness, then you need to urgently notify the doctor about this using a special device.
The maximum duration of the examination is 30 minutes with the introduction of contrast. Consists of the following stages:
- a puncture is performed on the patient using a catheter;
- contrast is introduced;
- A CT scan takes a series of pictures;
- a few hours later the patient receives the examination results.
Before performing a scan on a patient, the doctor must tell him about the possible risks associated with this examination. Many people ask to provide the results of certain examinations: data on the absence of allergic reactions to the contrast agent, or that the patient does not have intolerance to the contrast agent.
Medical opinion
In addition to the radiologist, a vascular surgeon can also interpret the resulting images. Upon completion, specialists can identify any disease - from atherosclerosis to the growth of scar tissue. If necessary, the patient is provided with additional images, where emphasis is placed on areas and areas with pathologies.
During discharge, the patient is given a report that clearly indicates the presence of pathological changes, anomalies and other information that the specialist was able to obtain during a CT scan of the lower parts of the body. If the method turns out to be insufficiently informative, other examination methods may be prescribed: MRI or ultrasound.
Advantages and disadvantages
The method is in great demand due to its high information content and relative safety. Let's look at the advantages of this technique:
- During the study, possible pain or discomfort was excluded. All that is required of the patient is to remain completely immobilized during the procedure; the procedure is not prescribed even in an emergency after physical activity; the patient must be calm. Otherwise, sedation is required.
- The radiation dose is much lower than with radiography - CT scans of the lower parts of the body can be performed twice a year without risk to health.
- The likelihood of harmful microorganisms entering the area of lymphatic spaces is reduced to zero.
- 30 minutes is enough to obtain the maximum necessary information about the condition of the patient’s body.
- You can assess the condition of the diseased organ and find out how far the pathological process has spread. To obtain maximum information, the CT method will be quite sufficient.
- The accuracy of the results is the highest; this method is popular among diagnosticians due to the fact that it allows you to see tissues, organs, and vessels in a three-dimensional image.
The doctor can easily identify even minor pathological changes and find out how widespread the pathological process is. This point plays an important role, since a disease detected in time is much easier to cure.
Disadvantages include contraindications to CT. For example, the examination is not carried out if the patient has an individual intolerance to the contrast agent, since there is a high probability of side effects.
If we talk about the harm that the patient is exposed to during the examination, it is insignificant if the procedure is not performed frequently. For example, radiography is much more harmful, and also does not give clear results, especially when it comes to the condition of blood vessels.
If you need to find out about vascular pathology, then the CT method of the lower extremities is the most informative.
How much does a CT scan of the lower extremities cost?
One scan of the patient’s lower extremities will cost up to 6,000 Russian rubles. In general, the cost of the examination directly depends on the chosen clinic, the diagnostic equipment installed in it, and the qualifications of the medical staff.
CT with contrast will be more expensive, but this method is preferable due to the fact that it allows you to see the condition of the vessels in detail. If you need to find out separately the condition of the knee joint, femoral neck or other parts of the lower extremities, the price is negotiated individually in each specific case.
Alternative methods of examination or instead of a conclusion
One of the most common methods that can replace CT scans of the lower body is MRI. The difference is that with magnetic resonance imaging a person does not receive a dose of radiation; the examination takes place under the influence of a powerful electromagnetic field.
MSCT is also considered a popular examination method, the difference is in the device used - a multislice tomograph takes a large number of images in different sections. This method of studying the lower extremities is much more expensive than CT - it will cost from 8 to 10 thousand rubles.
Source: https://mrtdom.ru/diagnostika-kt/kt-sustavov-i-konechnostej/kt-nizhnih-konechnostej
CT scan of the foot or hand
The method by which it is possible to determine damage in the area of the feet and hands, as well as visualize their structure, is called computed tomography. This diagnostic method is the most accurate, so even an inexperienced doctor can determine any deviation.
A CT scan of the foot produces images that show all the structures of the foot down to the small joints. Based on the final results of a CT scan of the foot, the doctor makes a diagnosis with maximum accuracy. If with the help of X-rays it is possible to determine exclusively internal damage to bone tissue, then a CT scan of the feet allows you to track all the processes occurring in this area of diagnosis.
Computed tomography is a last resort method, which is prescribed due to the uncertainties of a particular type of foot ailment. For example, a disease such as tuberculous destruction can only be determined using a CT scan of the feet.
This material will tell you exactly about the technique of performing a CT scan of the foot. Let's also consider in what cases the doctor can refer for such a study, when a CT scan of the foot is not recommended, and what results the doctor receives at the end of the procedure.
What does a CT scan show?
A CT scan of the foot allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of a given area using X-rays and ultimately create a model in three-dimensional visualization. The resulting images show the following organs:
- phalanges of fingers;
- metatarsus;
- tarsals;
- ankle joints;
- lower parts of the leg bones.
The photographs show even the slightest deviations in these organs and the feet as a whole. Through examination, the following ailments can be determined:
- various injuries;
- inflammation;
- degenerative processes;
- tumors;
- chronic diseases.
In addition to the fact that a CT scan of the foot is the most accurate and effective way to diagnose various abnormalities in this area, it is also not capable of causing harm to a person and his health, which cannot be said about radiography.
Indications for the procedure
The reasons for prescribing a CT scan of the foot are the following factors:
- fractures;
- dislocations and subluxations;
- various pathologies in this area;
- abnormalities in ligaments and tendons.
CT scan of the foot is prescribed for a fracture
A CT scan of the foot is also prescribed to identify the following diseases:
Through the study, various types of neoplasms (malignant and benign tumors), as well as the appearance of metastases, are identified. If you plan to perform surgery on the ankle area, then a preliminary CT scan of the foot can increase the effectiveness of the surgical intervention.
In frequent cases, doctors prescribe a computed tomography scan to clarify a preliminary diagnosis.
If a person suffers from pain in the ankle joint, detects crunching in the joints, as well as an increase in the range of motion in the joints, then one should immediately consult a doctor to clarify the cause of the ailment, which causes such symptoms.
Computed tomography is performed in any medical institution if it has such a device.
Contraindications for CT scanning
Although computed tomography is considered the most harmless and safest method of examination, even it has some prohibitions for its implementation. CT scanning is prohibited for women who are at any stage of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, even practically harmless x-ray radiation for the mother can cause irreparable damage to the baby’s health.
As a result, the development of pathological abnormalities in the fetus and unborn child may occur, therefore, CT scanning is not recommended during pregnancy.
In exceptional cases, strictly as prescribed by a doctor, tomography can be performed on young children, but not earlier than from the age of seven.
Tomography is allowed for children from the age of 14, but only as prescribed by a doctor and when absolutely necessary. It is often impossible to perform tomography for people whose weight exceeds 120 kg.
Depending on the design, the devices are designed for a maximum patient weight of 120 to 200 kg.
This study is not prescribed for people who have a tendency to the following diseases:
Breastfeeding mothers are allowed to undergo examination; only after the process, the baby can be breastfed no earlier than 48 hours later.
CT technique
Computed tomography requires preparatory measures only if the patient is scheduled to receive a contrast agent intravenously. In this case, the patient must be prepared, and, therefore, come for examination on an empty stomach, without eating before for at least 6 hours.
The foot examination process consists of the following steps:
- The patient is placed on a special retractable tomograph table.
- The foot or both are secured with special straps.
- Next, the device is started and the required organ or part of the body is examined. During the examination, the ring of the device rotates, that is, scanning is carried out.
During the procedure, the patient hears only the noise of the device, but the person does not experience any unpleasant sensations. The duration of the tomography procedure takes from one to 20 minutes, depending on the use of contrast or without it.
Carrying out a CT scan of the foot
Contrast and its necessity
Contrast is a special substance or drug that is administered to the patient intravenously before the start of the foot examination procedure. Contrast is necessary to improve visualization of the structures being examined.
The dosage of drug administration depends, first of all, on the patient’s weight and is selected for each patient strictly on an individual basis. The contrast is introduced over 1.5 days, so the preparation process is quite long.
But it should be noted that contrast in the study of the foot is used in very rare cases. It is administered only when tumors are suspected. But often CT does not require contrast, since the method of non-contrast examination of the foot provides a more than complete picture of the processes occurring in the joints.
Conclusion
After the computed tomography has been completed, in 15–20 minutes the results will be deciphered and handed over to the patient personally. If necessary, the results are recorded on electronic media or sent by e-mail. With these results, the patient turns to his doctor, from whom he received a referral.
Often, the health worker who performs a CT scan of the foot does not give any explanations for the final results, so the full picture of the disease can only be learned from a doctor.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis, through which future treatment for the patient is prescribed. It is also worth noting that conducting research in the early stages allows you to identify and avoid serious diseases of the joints and feet.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/metody/kt-stopy
MRI and CT scan of the foot: what does tomography show, how is it done and how much does the study cost?
Typically, an x-ray will be prescribed to examine the extremities. However, this type of diagnosis only shows the condition of the bones, which is why it is used mainly after injuries.
If there is a suspicion of disease or damage to other tissues, other types of examination are required.
Let's figure out together why magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the foot are prescribed, how these diagnostics differ and what results they give.
Indications for MRI and computed tomography of the foot
An MRI of the foot is necessary in the following cases:
- foot and ankle pain;
- when walking there is pain in the muscles;
- the foot has increased in size;
- swelling or redness is noticeable in the joint or foot;
- the joint has become inactive;
- there is discomfort in the joint or foot;
- the toes or the entire foot are deformed;
- the skin has turned pale, the pulse cannot be felt;
- noticeable expansion of the vascular network;
- sensitivity in the foot or joint is impaired;
- there was an injury on the limb;
- after an infection, inflammation developed in the joint;
- examination required before surgery;
- other methods do not provide an unambiguous picture of the disease.
Indications for CT are:
- previous injuries;
- suspicion of bone cracks;
- suspicion of neoplasms (primary or secondary);
- purulent-destructive processes in the bones of the foot (osteomyelitis, tuberculosis);
- inflammation in the ankle joint;
- After surgery, it is necessary to determine the condition of the limb and the degree of effectiveness of the surgical intervention.
Contraindications for research
Contraindications for both procedures are almost identical:
- installed permanent metal or electronic implants;
- diseases accompanied by convulsions and uncontrolled movements (epilepsy, hyperkinesis);
- allergy to contrast (if necessary);
- pregnancy.
Computed tomography with contrast is not allowed for breastfeeding mothers and patients suffering from renal failure.
If a person has kidney problems, the contrast may cause poisoning or other side effects. In the case of lactation, the substance enters the mother's milk.
If you can’t do without a CT scan, the young mother will have to interrupt breastfeeding for 2 days after the examination.
Preparation for each procedure and their stages
MRI
Immediately before the procedure, the subject changes into a loose shirt or robe without metal fasteners. You should also remove jewelry, watches and other items with metal parts during the diagnosis. The same applies to removable dentures and other dentures. You must leave your phone, plastic cards with chips, and items with electronic devices outside the office.
MRI machines are either closed or open:
- If the examination is carried out in a closed tomograph, then the couch with the patient is moved into the tunnel part, where the scanning is performed. The device makes quite a lot of noise, so wear headphones or earplugs to reduce discomfort.
- An open-type tomograph works similarly to a closed one, only outwardly it looks like an open couch with a scanning device located above it. This type of tomograph was created specifically for those who are overweight or claustrophobic and simply physically cannot be in a closed tunnel.
CT scan
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI? The only thing you need to do before a CT scan of the foot is that if contrast is used, do not eat food 6 hours before the procedure. This is due to the fact that the contrast agent can provoke an allergic reaction. However, such cases are very rare in medical practice.
Preparations before the procedure are similar to those before an MRI. The patient also needs to change clothes and get rid of metal objects and electronics.
A computer tomography machine consists of two parts - a couch and a scanning device. The patient lies down on a couch, which during the procedure moves along the tomograph tunnel, and the ring part of the device rotates around and, through filming, receives data, which is then transmitted to the computer. The procedure is also accompanied by sounds, but less noisy than with an MRI.
Both procedures are painless and do not cause any discomfort to the patient.
The staff is located in the next office, but if necessary, a specialist can be contacted through a special device. During both types of examination, you must remain still.
If this is not possible due to specific diseases or due to the psycho-emotional state, it is allowed to put the patient into a state of sleep.
A CT scan takes several minutes. Magnetic resonance imaging requires a little more time - from 20 minutes to half an hour. In particularly difficult cases, as well as when a contrast agent is used, the MRI time can be increased to one and a half hours.
If the patient has previously undergone any other types of examination, you should take their results with you. Thanks to this, the specialist will create a more complete picture.
What MRI and CT scans show: interpretation of foot examination results
MRI is one of the most detailed and sensitive methods for diagnosing the body. When the foot is examined on an MRI, the images will show an almost complete picture of its condition, as well as the entire ankle joint:
- foot structure;
- the condition and development of all surrounding tissues;
- pathologies of bones and joints;
- blood supply and vascular condition;
- soft tissue pathologists;
- presence of neoplasms.
A CT scan of the foot is examined mainly to identify the most serious pathologies:
- damage to soft tissues, bones and tendons;
- degenerative-dystrophic processes;
- malignant tumors, etc.
A computed tomography scan is usually ordered after an x-ray. Its main purpose is to clarify the results of the preliminary study.
The transcripts of the images in both cases contain only a description of the pathologies and do not include information on areas that are normal. The photo shows examples of conclusions based on the results of MRI and CT scans of the lower limb.
How much does it cost to diagnose a foot using MRI and CT?
The cost of magnetic resonance imaging of the foot largely depends on the power of the tomograph. The accuracy of the result also depends on this.
On average, the price for an MRI of the foot starts from 3-4 thousand rubles. How much does a CT scan cost? The price tag for a computed tomography scan of the foot is no different from a magnetic resonance scan. It also ranges from 3000-4000 rubles.
Additional factors that increase the cost of both types of examination are:
- use of contrast agent;
- use of anesthesia;
- professional level of the radiologist;
- clinic level;
- location of the center where the examination is carried out;
- additional services (for example, consultation with a doctor based on the results of the images).
Source: https://vedmed-expert.ru/mrt/sustavi/mrt-stopy.html