Men's health and strength are important elements of harmonious personal development. If a man experiences problems with sexual function , he begins to feel inferior.
Prostatitis is a fairly common disease. However, according to science, this disease is highly treatable in the early stages, so it is important to recognize the disease at the very beginning of its development and consult a doctor. In the article we will look at what prostatitis happens .
Hide content
What kind of disease is this
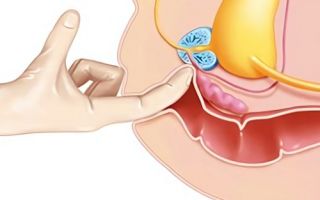
The disease affects the prostate gland of the male body (prostate). This organ is responsible for the harmonious functioning of the human reproductive mechanism, as well as how well the sperm will perform its main function.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the prostate; if it is neglected, it can become the cause of prostate adenoma .
Important: prostate adenoma is a neoplasm on the organ caused by the proliferation of prostate cells.
There are several different types of prostatitis. Let's look at the types of prostatitis in men.
Spicy
Inflammation is a consequence of the vital activity of organisms, the presence of which is normal for the human body. The cause of the inflammatory process, in this case, is their abnormal reproduction. However, sometimes the disease occurs in the body and due to infections that were brought in from outside.
One way or another, an abnormally high concentration of microorganisms leads to damage to the prostate gland, which is the main cause of acute prostatitis. Its peculiarity is that it develops very quickly . Symptoms:
- General disorder of the body (fever, frequent changes in body temperature, lethargy).
- Acute pain in the groin , anus, and lower back.
- Problems with urination (frequent urination with difficulty, stagnation of urea).
- Sexual dysfunction ( difficulty with erection ).
- Purulent secretion (usually if the disease is advanced)
Chronic
Chronic prostatitis is a consequence of two main reasons: pathogenic organisms entering the prostate tissue; and processes associated with stagnation. Due to its structure and location, the prostate is vulnerable to any infections and stagnant effects. The disease manifests itself as chronic inflammation of this gland.
The disease is a rather dangerous disease because it develops in stages, and the symptoms of this type of prostatitis are not pronounced, so most men do not pay attention to the first signs of the disease.
With this disease, the patient usually complains of:
- problems with urination
- regular sharp pain in the groin area
- feeling of weakness
- nervous state of mind
- apathy
- decreased interest in sex.
Calculous
The cause of calculous prostatitis is the formation of stones in the prostate . Stones can form due to endogenous (stagnant processes) and exogenous factors (chronic processes).
Symptoms Pain in the area of the reproductive mechanism (may intensify when moving, after sexual intercourse, during long walks, or when the lower spine is in an uncomfortable position). Seminal fluid may also contain blood. There are general symptoms inherent in the above types of prostatitis.
Latent
In relation to latent prostatitis, it is incorrect to use the term “species”, since it, along with the chronic and acute forms, is more associated with the stage of its development. The latent course of prostatitis is usually characterized by the absence of symptoms .
A correct diagnosis can only be made with a special examination. The disease can manifest itself when the body’s condition is complicated (it is exhausted, there is no regular sexual intercourse, blood flow in the pelvic organs is disrupted). Then the symptoms are similar to the course of the disease described above (chronic form).
The disease can be diagnosed by taking prostate secretions , or by more detailed analysis of the functioning of this organ.
Bacterial prostatitis is caused by the activity of pathogenic organisms on prostate tissue against the background of factors that reduce the body's resistance to foreign bodies. It can occur in acute and chronic form .
In the acute form, the following symptoms are observed:
- general inflammatory reaction of the body (fever, frequent changes in body temperature, feeling of weakness, pain in muscle tissue);
- local inflammation of individual organs (pain in the groin and anus, frequent urination, pain in the penis, problems with erection);
- specific changes in the composition of urine, blood serum, and prostate secretions.
If the patient is sick with a chronic form, then the symptoms are the same. But their severity is reduced. As the patient's condition worsens, the presence of all of the above signs can be observed.
Infectious
This type of disease is similar to bacterial. At least the symptoms completely coincide with it. The difference between infectious prostatitis and bacterial prostatitis is that the second is caused by the activity of bacteria, while the first can be provoked by foreign bodies of a different kind (for example, fungi or protozoa).
Non-infectious
The disease is associated with inflammation of the prostate, which is caused by disruption of the flow of lymphatic fluid and blood in the pelvis. Despite the fact that modern realities are beneficial for the development of the disease (sedentary lifestyle), doctors see the main cause of the disease in hormonal disorders .
With abacterial prostatitis, infection of the prostate gland does not occur. The disease does not develop clearly . At first, vague painful sensations appear in the groin area. After this, the patient begins to urinate very often (usually at night).
When urinating, mild aching pain may occur, which becomes stronger if a man has stood for a long time or has an irregular sex life. This symptomatology can be observed for several years. This type of prostatitis is also called nonspecific .
Viral
- Viral prostatitis occurs when the prostate gland is infected by a virus.
- For reference: This type of prostatitis is currently very little studied.
- The peculiarity of this type is that it can spread throughout the organ from a specific focus and can affect the superficial tissues of the prostate, or the entire body of the organ.
- Symptoms:
- heat
- frequent changes in body temperature
- urination disorder
- painful sensation in the prostate gland.
When examining an organ, you can find that it has a tense, painful shape, but does not differ from its normal appearance. The boundaries of the prostate gland are clear, and associated organs may also not be subject to abnormal changes.
Attention: this type of disease is most often caused by herpes, papilloma, and influenza viruses.
Chlamydial prostatitis occurs in the human prostate gland due to infection with a special bacterium - chlamydia . This microorganism is transmitted only through sexual contact. In the first stages of the disease, it does not manifest itself in any way, so the patient can infect a large number of sexual partners.
Usually the first sign of infection is very frequent urination . Symptoms of the disease also include:
- Painful sensations during urination
- A thin stream of urine
- Opaque urine with purulent formations
- Heat
- Headache, lack of normal sleep
- Erection and libido problems
- Partial bladder release
- Abnormalities of sexual function
- Sharp passing pain in the lower spine
Here it is necessary to clarify that signs of the disease may not be all at once, but several symptoms. Moreover, their presence may be temporary.
Fungal
Fungal prostatitis occurs due to infection of the prostate by a fungus . Microorganisms of the Candida are the most common cause of the disease. This type is also often called candidal prostatitis .
As with other infections of the prostate gland by foreign organisms, in this case, general signs of the disease can be observed.
However, the peculiarity of this type of prostatitis is that it is usually a sign of complex infection of the patient’s body.
In some cases, the ailment may be mistakenly mistaken for another, associated with inflammation of the organs responsible for removing urea from the human body. Symptoms: fever, pain in the lower spine, problems with urination.
Gonorrheal
Very often, gonorrheal urethritis develops into gonorrheal prostatitis . The mechanism of infection is as follows: the back of the urethra is affected by gonococci, which enter there through the excretory canals of the prostate. An inflammatory reaction begins on the infected prostate gland, which, like all types of prostatitis, can occur in acute and chronic forms.
The acute form of the disease can be focal, can be localized on the surface of the organ, or can affect the entire organ.
Each type of disease has its own symptoms: in the focal form , one can observe intense heat in the pelvic organs, pain during urination, purulent secretion, and in special cases (when individual lobes of the prostate are subject to the inflammatory process), pain during bowel movements.
Manual examination of the prostate can reveal scars and soft areas filled with pus. And there may be pressure in the anus.
If the disease has affected the upper layers of the organ, then usually the disease is practically asymptomatic . The only thing is that frequent urge to go to the toilet can be a sign of illness. Purulent formations may be found in urea . When palpating the prostate, pain is either minimal or not observed at all.
If the disease affects the entire body of the organ, then the urea will become either very light or cloudy. Manual examination of the organ can reveal severe enlargement of the gland .
But gonorrheal prostatitis can also occur on a chronic basis. In this case, the patient may experience slight irritation in the urethra, spreading pain in the lower spine, groin, and pressure in the rectum.
purulent formations in the urea , and urination itself will become abnormally frequent.
Fibrous
Fibrous prostatitis occurs when, due to benign tissue growth, the prostate begins to put pressure on neighboring organs . This results in problems with sexual function and urination. Symptoms:
- problems with urination
- partial emptying of the bladder
- urinary retention
- pain in the perineum and anus
- abnormalities of the reproductive mechanism.
Herpetic
Herpetic prostatitis occurs in the body when the prostate gland is infected by the herpes virus . This results in symptoms similar to viral prostatitis. Herpes is a rather dangerous virus. Therefore, the consequences of this disease can be very serious.
The main symptom of this disease is discomfort during urination . Sometimes the disease proceeds without expressing itself in any way. Then, if prostatitis is suspected, such a patient should contact the clinic for a laboratory examination of prostate secretions.
Purulent
Purulent prostatitis in men is a severe type of acute infectious. Its main symptoms are fever and purulent secretion from the urinary canal. The disease occurs in several stages . Each of them has its own symptoms.
Symptoms of catarrhal prostatitis (when the disease affects the upper tissues of the prostate): pain in the pelvic organs and frequent urination. Symptoms of follicular prostatitis (focal): pain in the lower spine, fever, purulent secretion.
Symptoms of parenchymal prostatitis (when all prostate tissues are affected): severe pain, fever, intense discharge of pus. Symptoms of abscessive prostatitis (complication): high temperature (up to 39 degrees), severe pain in the groin, very strong purulent secretion.
Current classification
The modern classification of prostatitis, which was developed by the American National Institute of Health (1995), identifies the following categories of prostatitis:
- Category one includes acute prostatitis
- category two includes chronic bacterial prostatitis
- category three includes chronic prostatitis
- Category four includes asymptomatic chronic prostatitis.
There are also two subcategories: “three a”, under which chronic prostatitis with signs of inflammation are combined, and “three b”, under which chronic prostatitis without signs of inflammation are combined.
The disease in question is quite dangerous , but with due vigilance and timely measures it can be treated quite well. Non-infectious prostatitis is also called nonspecific.
In order to avoid many problems, it is enough to closely monitor your health : do not let nonspecific prostatitis develop into infectious.
Video
Video about types of prostatitis
Source: https://LechenieBolezney.com/urology/prostatitis/vidy
Classification and types of prostatitis: course of the disease at various stages of prostatitis
Among the diseases of the male genitourinary system, prostatitis is the most common. Inflammation of the prostate gland is formed under the influence of unfavorable external conditions or is a complication of existing pathology of the urinary organs.
There are several known forms of the disease, for the ordering of which a convenient classification has been developed, and the types of prostatitis are divided depending on the causes, the nature of the pathology and the stage of the pathological process.
Men try to delay visiting a doctor, waiting for the unpleasant symptoms to disappear, or resort to unconventional methods on their own.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
The danger of inflammation of the prostate gland is that in the absence of timely treatment, the disease easily becomes chronic, creating conditions for the development of kidney disease and increasing the risk of early hyperplastic changes.
Types of prostatitis according to course
The simplest and most convenient classification of prostatitis is based on the stage of development of the pathological process.
A feature of inflammatory diseases is the presence of an acute stage, when pronounced symptoms become the body’s reaction to the presence of unfavorable conditions.
Timely detection and treatment of the disease at the initial stage reduces the risk of transition to a chronic form, which is characterized by periods of exacerbation and temporary lull.
Inflammation of the prostate gland in men develops according to a pattern common to all inflammatory reactions. To denote the form of the disease, doctors use the terms acute and chronic prostatitis, which form the basis of the standard classification. Additionally, the type of pathogen identified based on laboratory data is indicated.
Spicy
New acute prostatitis is a consequence of the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the male genitourinary system.
The causes of infection may be violation of personal hygiene measures, unprotected intimate contacts, transfer of the pathogen from other parts of the urinary system, or penetration of the pathogen into the general bloodstream.
The risk of development increases when the immune system is weakened, when the body’s protective functions suffer due to stress, colds, hypothermia and insufficient intake of nutrients.
Primary inflammation is accompanied by a clear clinical picture, on the basis of which an experienced doctor makes an accurate diagnosis at the stage of examination and history taking, even before laboratory or instrumental studies are carried out. The symptoms are confirmed by diagnostic data and the man must undergo a full course of treatment to eliminate the risk of the disease becoming chronic.
The disease develops quickly, accompanied by signs of general and local inflammation:
- Pain and burning when urinating during the acute period of prostatitis is a consequence of the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which lead to the formation of microcracks in the mucous membranes of the urinary tract. The passage of urine is accompanied by burning pain.
- The appearance of symptoms of intoxication. The waste products of pathogenic microorganisms poison the body by being absorbed into the general bloodstream. The temperature rises, weakness increases and appetite disappears.
- Increased diuresis is accompanied by a weakening of the urine stream, heaviness in the lower abdomen and pain. The inflamed prostate partially blocks the urethral canal, which causes pain in the perineum and groin area.
- Decreased erection. Constant pain, deterioration in general well-being, increasing congestion in the prostate gland inevitably lead to erectile dysfunction, and attempts to engage in intimate intimacy are accompanied by sharp pain attacks.
- Purulent discharge from the urethral canal and anus. They indicate extensive advanced inflammation of the prostate and prolonged lack of treatment.
Detection of one or more symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible. By treating prostate inflammation at the initial stage, you can get rid of the unpleasant disease forever.
During the initial examination, the doctor carries out the necessary manipulations, prescribes an ultrasound of the prostate gland, takes a smear of prostatic secretion to identify the type of pathogen and determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Newly detected acute prostatitis is best treated in a hospital. This is the most reliable way to completely eliminate pathology, reduce the risk of infection of the urinary system and the disease becoming chronic.
For treatment, doctors use specific anti-inflammatory drugs; for this purpose, they prescribe antibiotics in the form of tablets or injections, antiviral and antifungal drugs, depending on the type of pathogen.
Symptomatic therapy is used to reduce pain, improve urinary function, and stimulate immune defense. Subject to a course of conservative therapy and recovery, the acute stage can be cured without consequences.
A prolonged absence of specific treatment can cause a prostate abscess, which will require urgent surgery to eliminate.
Chronic
Fully treated prostatitis does not cause complications, but if the course of therapy is interrupted, there is a possibility of encountering a chronic form of the disease.
The presence of a focus of inflammation in the prostate gland increases the risk of early hyperplastic changes, creates conditions for the development of diseases of the urinary system, worsens erectile function and affects a man’s performance.
It is dangerous to start the acute stage, since further treatment becomes more difficult, and diagnosing the disease becomes more difficult due to the frequent asymptomatic course.
The causes of chronic prostatitis, in addition to the transition of temporary pathology to a permanent form, are:
- Injuries and damage to the prostate gland.
- Stress, physical and nervous overload.
- Sedentary lifestyle and irregular sexual activity.
- Bad habits, including addiction to junk food.
- Diseases of the urinary system.
- Weakening of the immune system by frequent colds.
- The presence of a source of infection in a man’s body – caries, bronchitis.
- Hypothermia of the lower body.
It is difficult to determine the presence of chronic prostatitis; for preventive purposes, men over 35 years of age are recommended to see a urologist at least once a year. Paying attention to your own health will help you detect and begin to treat the disease.
A sluggish disease may not manifest itself in any way, but when exposed to unfavorable conditions, an exacerbation will certainly occur, the symptoms of which resemble the first attack:
- Problems with urination. In the chronic course, pain during urination periodically occurs, nagging pain in the lower back, perineum and anal area.
- Decreased erection. Inflammatory edema disrupts the secretory function of the prostate gland and provokes disorders in the intimate area.
- General deterioration in health. There may be no temperature, since the body is already accustomed to living with inflammation, but lethargy, weakness and constant fatigue are observed.
Chronic prostatitis must be treated to avoid even more dangerous consequences.
The main principle is to prevent exacerbation of existing pathology and reduce the risk of irreversible changes in prostate tissue.
Prostatitis is considered one of the provoking factors in the formation of hyperplasia, which can take on both a benign and malignant nature.
The choice of treatment depends on the clinical picture of the disease. At home, in order to prevent exacerbation, traditional methods are used, using the beneficial properties of medicinal plants and herbs.
Natural decoctions and teas help get rid of the symptoms of the disease and also reduce the need for medications, but it is impossible to do without antibacterial drugs to eliminate the source of infection.
Classification by reason of occurrence
Inflammation of the prostate gland can be provoked by various types of pathogens or be a reaction to pathological changes in tissues. Depending on the cause, there are several types of prostatitis. In clinical practice, there are cases of a combination of several etiological factors, then a complex effect is required to eliminate all sources of infection.
Bacterial
Pathogenic microorganisms provoke an inflammatory reaction in the prostate and are the causative agents of the bacterial form of the disease. Prostatitis is often caused by E. coli, streptococci and staphylococci.
These pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the urethral canal or enter the prostate gland from an existing source of infection in the body. Treatment requires the mandatory use of antibiotics according to the regimen proposed by the doctor, as well as the prescription of symptomatic correction to eliminate signs of the disease.
Viral
Several types of viral prostatitis have been described, which cause damage to the cellular structure of the prostate gland. Pathogens of influenza, herpes, and papillomas often affect prostate tissue and cause the disease.
Viruses are capable of rearranging their protein composition and integrating their genetic code into the cells of the body. Symptoms include muscle pain and a significant rise in temperature.
Treatment requires the prescription of specific antiviral agents, as well as increasing the body's own immune forces.
Infectious
The course of infectious prostatitis in the acute phase is similar to the bacterial form of the disease. The main difference is that the causative agent can be conditionally pathogenic and fungal flora.
Infectious inflammation of the prostate often becomes a complication of a sexually transmitted disease, quickly becomes chronic and latent and is the main cause of male infertility.
Treatment is lengthy; identification of the pathogen is required using special tests in order to select an effective means of control.
Non-infectious (non-specific)
The causative agent of the infection is absent, and the cause of nonspecific inflammation is prolonged stagnation in the tissues of the prostate gland. This type of prostatitis is also called stagnant.
The main cause of the non-infectious form of the disease is a sedentary lifestyle, low sexual activity, as well as hormonal imbalances that provoke disorders in the prostate tissue.
The acute phase is practically absent, the disease develops over a long period of time and is characterized by an asymptomatic course until signs of urinary disturbances develop against the background of one of the provoking factors.
Sedentary lifestyle
Other types
Prolonged stagnation of prostatic secretion leads to its thickening and the formation of stones. The presence of a mechanical obstruction to the outflow of waste products from the prostate gland is the cause of the development of calculous prostatitis, which is accompanied by severe pain.
The fibrous form of the disease often becomes a complication of past inflammation of the prostate and is characterized by degeneration of organ tissue with excessive development of connective tissue structures.
International classification by category
In the international classification, the division of types of prostatitis is based on the principles of danger in the current period and forecasts for further development.
All possible options were divided into 4 categories, each of which is characterized taking into account frequently occurring indicators.
The international standard takes into account latent and atypical forms of the disease, stage and clinical picture, and with regard to the cause, an additional classification is used:
- 1st category. This group included all types of acute prostatitis, regardless of the nature of the course and the type of pathogen. The prognosis is favorable provided high-quality treatment in the early stages.
- 2nd category. Chronic bacterial prostatitis, which developed as a complication of diseases of the urinary system or an incompletely cured acute form of the disease. The main goal of therapy is to maintain the remission stage for a long time.
- Category 3. Chronic prostatitis of the abacterial type, developing as a separate form of pathology or involving the urinary organs. The prognosis depends on the effectiveness of conservative treatment measures.
- Category 4. Atypical and latent forms of chronic pathology in an advanced stage, with pronounced dysfunction of the genitourinary system and an increased risk of complications.
Regardless of what classification the doctor uses, prostatitis poses a threat to men's health and requires timely treatment. Compliance with simple and effective preventive measures reduces the risk of developing a dangerous disease, so you should pay attention to your own health and try to follow the recommendations of urologists. Routine examinations, a properly organized lifestyle, timely treatment of genitourinary infections and strengthening the immune defense will help reduce the likelihood of developing the disease. At the first symptoms of the acute stage of the disease, you should consult a doctor to get rid of the threat of the pathology becoming chronic.
Source: https://dostami.ru/predstatelnaya_zheleza/prostatit/klassifikatsiya-i-vidy-prostatita/
Chronic prostatitis and its consequences for men
Chronic prostatitis (ICD 10 code - N 41.1) is the most common disease of the male genital area. Pathology is an inflammatory process in the prostate gland, which occurs against the background of stagnant processes or infection of the organ by various microorganisms.
Chronic prostatitis can be primary or secondary; it is often a complication of acute prostatitis that was treated incorrectly or untimely. The disease most often occurs in mature men, older than 50-60 years. But in severe cases, the pathology is also diagnosed in patients of fertile age: from 30 to 50 years.
Causes of chronic prostatitis
There is a huge list of causes and factors that can provoke chronic prostatitis. First of all, these are infectious diseases of the prostate gland and age-related changes, congestive processes in the prostate.
Acute prostatitis very often becomes the cause of the development of a chronic form of the disease. The fact is that men in most cases do not dare to consult an andrologist for pain in the pelvis. As a result, the inflammatory process can go away on its own, if the immune system copes, or provoke suppuration. In any case, a complication arises in the form of chronicity of the process.
In older patients, chronic prostatitis is associated with poor circulation in the pelvis and lack of sexual life.
The prostate secretes a special secretion that enters the ejaculate during ejaculation. If a man does not have sex and does not masturbate, the fluid stagnates, thickens, and the prostate gland degrades.
The same thing happens when there is insufficient blood circulation, the prostate lacks nutrients.
Stagnant processes in the prostate can also be provoked by interrupted sexual intercourse or unrealized arousal. If a man has an erection, the synthesis of prostate juice increases, but ejaculation does not occur - the excess fluid stagnates.
Doctors identify a number of factors that contribute to the development of chronic prostatitis in men:
- A passive lifestyle is a direct path to the formation of stagnant processes in the pelvis, poor circulation, and the appearance of adhesions.
- Poor nutrition, an abundance of fatty and unhealthy food, obesity.
- Incorrect sexual activity.
- Hypothermia of the genitals.
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the body, including the upper respiratory tract, caries, history of urogenital infections, etc.
- Chronic constipation.
- Endocrine disorders, hormonal imbalances.
- Injuries to the genital organs.
- Weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency.
- Chronic fatigue, depression.
Regular consumption of alcohol and smoking increases the risk of chronic prostatitis. The fact is that these substances provoke a spasm of the vascular system, disrupting blood circulation. If this happens constantly, the vessels stop functioning normally, and the internal organs do not receive nutrition.
Signs of chronic prostatitis in men
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis appear to varying degrees. During the period of remission, the symptoms can be very mild, so patients are in no rush to see a doctor. Exacerbation of chronic prostatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the perineum and lower abdomen, which radiates to the penis and rectum.
- Pain during ejaculation.
- Various forms of urination disorders: frequent urge, urinary retention, pain and burning, sluggish stream of urine.
- The addition of infection is accompanied by an increase in temperature and a general deterioration in health.
- Infertility during the year may be a sign of chronic prostatitis, since the disease disrupts the process of sperm production.
- The advanced form of the disease is accompanied by various forms of erectile dysfunction: rapid ejaculation, weakening of erection during sexual intercourse, impotence.
During remission, patients complain of dull pain, especially after active physical activity or a hard day at work. As the pathology progresses, the signs become more pronounced.
If at the first stage, disorders of the excretory system are practically invisible, only frequent urination is observed, and the man begins to get up to go to the toilet at night. Then at stages 2-3 of the disease, patients begin to actively push so that urine production begins. The last stage of the disease is accompanied by acute urinary retention.
The same thing happens with erectile function. At the initial stage of the disease, only slight deviations are visible: the duration of sexual intercourse decreases, an erection is sometimes insufficient if the man is tired. At the last stage of chronic prostatitis, patients complain of complete impotence, not even wet dreams occur.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis with drugs
Many men are sure that chronic prostatitis is forever, so there is no need to treat it, it is just a waste of money and time. This is a complete misconception. It is necessary to treat chronic prostatitis, and it is better to start doing this as early as possible.
Of course, no one can guarantee that after a course of pills, prostatitis will go away and never bother you again. Any chronic process requires constant monitoring and adequate treatment. But we can say with confidence that the right approach to therapy will help restore normal urination and return a man to healthy erectile function.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis is a long and quite labor-intensive process. The patient is prescribed to take medications, attend physiotherapeutic treatment, diet, sanatorium holidays, and regular sex life. You definitely need to reconsider your lifestyle, start eating right, doing exercises, and pay attention to your psychological health.
First of all, the patient is prescribed medications. If a bacterial infection is detected, then antibiotics are prescribed for chronic prostatitis:
- Amoxiclav;
- Azithromycin;
- Wilprafen et al.
Antispasmodics are prescribed for pain and spasms:
For normal excretion of prostatic fluid, alpha-blockers are indicated:
- Urorek;
- Omnic;
- Silodosin et al.
It is strongly not recommended to use these groups of drugs for self-medication. It is very important to choose the right remedy and select the dosage, otherwise the therapy may not only be ineffective, but also significantly harm the body. It must be remembered that all medications have side effects, and even uncontrolled use of ascorbic acid can cause serious complications.
In the complex treatment of chronic prostatitis, vitamins and immunomodulators must be prescribed. This is necessary to compensate for the lack of nutrients. If problems with blood circulation are observed, venotonic drugs and blood thinners are indicated. The decision to prescribe such medications is made by the doctor based on test results.
Massage for chronic prostatitis
The most important stage of treatment for chronic prostatitis is prostate massage and physiotherapy. It is worth immediately noting that such methods are used exclusively during the period of remission.
During an exacerbation of chronic prostatitis, with infectious inflammation, in the presence of cysts, tumors, stones, massage cannot be done.
Stimulation of the prostate in such cases can lead to increased pain, swelling of the gland, and damage to it.
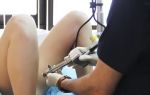
You can massage the prostate at home, but you should not try to do it yourself; it is better to ask your wife, or go to a medical facility. For many men, this procedure is quite unpleasant, because the massage is performed through the anus.
The man undresses to the waist, lies on his side, pulling his knees to his stomach, or takes a knee-elbow position. The massage therapist puts on a glove and applies medical Vaseline to the index finger.
The finger is carefully inserted into the rectum, while it is better for the patient to relax as much as possible. If the anus is tense, the massage will seem very painful. For a couple of minutes, the massage therapist gently strokes the prostate area.
If a man is categorically against this method of treatment, he can massage the prostate through the perineum, but this method is less effective. You can also improve the outflow of fluid and blood circulation in the pelvis with the help of exercises on the pubococcygeus muscle, through active cycling and long walks.
Physiotherapeutic treatment helps improve blood circulation, activate local immunity, and helps destroy adhesive processes. For chronic prostatitis, the following treatment methods are used:
- Magnet;
- Laser;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Electrical stimulation, etc.
The attending physician chooses the method of therapy, and he pays attention to the stage of the disease and the cause of its occurrence.
Traditional treatment of chronic prostatitis
In the complex treatment of chronic prostatitis, traditional medicine recipes are actively used. But they cannot be used for exacerbation of prostatitis, tumors, infectious diseases, and personal intolerance to the components of the product is also a contraindication.
Recipes for chronic prostatitis:
- Pumpkin seeds have been used since ancient times to treat prostatitis and impotence. To speed up recovery, you need to eat 30 grams of peeled seeds daily. They can be added to salads or used as a healthy snack.
- For chronic prostatitis, pear compote is very useful. But before consuming such a compote, you need to make sure that it is prepared without sugar.
- It is recommended to take medicinal baths with herbal decoctions and sea salt 3 times a week. To prepare a decoction, you can use sage, chamomile, calendula, and pine needles. The herb is brewed in boiling water, filtered, and then poured into a bath of warm water. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. It is very important to remember that the water should not be hot, and the genitals should not be allowed to overheat.
- Parsley seeds and juice are very useful; the herb can also be added fresh to various dishes. Parsley contains many useful vitamins and also has a positive effect on the reproductive system.
- A well-known remedy is rectal suppositories with propolis. You need to mix propolis with cocoa butter, form candles and store them in the refrigerator. Every month you need to insert 1 suppository into the anus before going to bed.
Traditional recipes for prostatitis are not a panacea for all diseases. For chronic prostatitis, they can only be used in complex therapy after consultation with an andrologist.
Prevention of chronic prostatitis
The prevalence of chronic prostatitis makes us think about the need to prevent the disease. To prevent this pathology, you must follow the following recommendations:
- At the first signs of prostatitis, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner treatment begins, the less likely it is that the process will become chronic.
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
- Quit alcohol, drugs and tobacco.
- Have sex regularly, and when arousal occurs, try to satisfy your needs.
- Avoid questionable sexual relations, protect yourself with condoms.
- Treat all infectious diseases promptly.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Dress for the weather.
These recommendations should be followed by all men, especially those who have already been diagnosed.
Conclusion
Chronic prostatitis is not a death sentence. Many men live with this pathology for many years, and I don’t know any problems, all thanks to timely treatment and a responsible attitude towards their health. To maintain potency for as long as possible, you need to be regularly examined by an andrologist, as well as take a responsible approach to the treatment of detected diseases.
You might be interested
Source: https://prostatits.ru/prostatit/hronicheskij-prostatit.html
Chronic prostatitis: classification, symptoms and treatment of the disease
Article on the topic: “chronic prostatitis: classification, symptoms and treatment of the disease.” Find out more about treating the disease.
The prostate gland is the most vulnerable organ in the male body. Prostate diseases occur in every third man over the age of 20. Moreover, prostate hyperplasia and adenoma, leading to erection problems, are most often a consequence of chronic prostatitis. That is why you should know the characteristic signs of chronic prostatitis and how to treat it.
Chronic prostatitis - what is it?
Chronic prostatitis is a long-term inflammatory process in the prostate gland. The term combines several forms of the disease, manifested by similar clinical symptoms.
Categories of chronic prostatitis:
- Infectious - caused by bacteria, fungus or virus;
- Non-infectious (stagnant) - otherwise called chronic pelvic pain syndrome, occurs with or without signs of inflammation;
- Asymptomatic - in the complete absence of clinical manifestations, inflammation is detected only with a thorough examination of the prostate.
In 95% of cases, non-infectious chronic prostatitis is diagnosed. At the same time, stagnation in the prostate - its secretion or blood circulation in the veins - comes to the fore in the development of inflammation.
The risk of chronic prostatitis is increased in people:
- leading an irregular sex life, regularly practicing interruption of sexual intercourse to avoid pregnancy of a partner;
- office employees and drivers (sedentary work provokes stagnation of blood in the pelvis);
- those who prefer to wear tight underwear;
- alcohol and smoking abusers.
Chronic prostatitis: signs of exacerbation
Chronic prostatitis develops gradually and may not cause concern for many years. From time to time a man may notice:
- Unpleasant sensations in the perineal area;
- Pain of minimal intensity with characteristic irradiation to the sacrum, rectum, genitals;
- Some increase in urination with the occurrence of pain and minor pathological discharge from the urethral canal, a weak stream of urine;
- Pain in the glans penis after ejaculation (disappears within 30 minutes);
- Burning in the urethra, pain during intercourse.
Stress, hypothermia, previous infection leading to weakened immunity, and consumption of spicy food/alcohol can trigger an exacerbation of chronic prostatitis. At the same time, the intensity of painful manifestations increases and resembles acute inflammation.
With the development of the disease and the involvement of nerves in the pathological process, erectile dysfunction intensifies, which significantly affects the psychological state of the patient.
However, chronic prostatitis is fraught not only with impaired potency - weak erection, decreased sensations during orgasm or their complete absence, and premature ejaculation.
Often the disease leads to the development of cystitis, pyelonephritis and inflammation of the testicles, aggravating the course of the underlying pathology. In addition, the risk of formation of prostate stones, adenomas, or the appearance of a malignant tumor increases significantly. With a long course of chronic prostatitis, infertility develops.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis by forms and stages
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis depend on the form of the disease and the stage of the disease (exacerbation or remission).
Bacterial chronic prostatitis
Signs of chronic prostatitis caused by pathogenic microflora periodically occur with varying intensity. During an exacerbation, the symptoms of inflammation are most pronounced. Infectious, chronic prostatitis manifests itself:
- Common signs of inflammation in the body are fever, weakness, chills, muscle pain (occurs during exacerbation);
- local inflammation syndrome - pain in the lower abdomen, increasing during sexual intercourse, after defecation and urination, with prolonged absence of intimacy;
- Disorders of the genitourinary system - intermittent urination, impaired erectility;
- Deviations in laboratory tests - detection of bacteria/fungi in prostate secretions and urine analysis, signs of inflammation in blood tests (leukocytosis, increased ESR) and urine (leukocyturia, protein).
Without exacerbation of inflammation, the signs of chronic prostatitis are erased. The patient's complaints are more indicative of impaired urination, decreased sexual desire and other erectile disorders that cause severe nervousness.
Non-infectious chronic prostatitis : chronic pelvic pain syndrome
The name itself indicates the predominant symptom of this type of chronic prostatitis - pain. Due to the low intensity of pain, chronic prostatitis of a non-infectious nature is often ignored.
Over time, the pain intensifies somewhat, and the clinical picture shows symptoms of sexual dysfunction caused by the progression of congestion and a decrease in muscle tone of the pelvic floor and urinary sphincter.
Often the disease is completely asymptomatic. The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is made when signs of inflammation of the prostate and its hyperplasia are detected during diagnostic studies. A urine test may periodically detect leukocyturia.
Treatment methods for chronic prostatitis
In each case, treatment of chronic prostatitis requires individual selection of a therapeutic regimen. This takes into account the cause of the disease (infection, stagnation of secretions or venous blood), duration of the course and the presence of aggravating pathology.
Drug therapy:
- Antibacterial drugs - treatment with antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Azithromycin, Levofloxacin, Clarithromycin) is indicated only for severe inflammation, identification of a bacterial agent in the urine or prostate secretion. Antibiotic therapy lasts 2-8 weeks. At the end of the course, the symptoms of the disease often remain in full, although the infectious factor is completely eliminated.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers (Terazonin, Tramsulosin, Alfuzosin) - are prescribed for increased intraurethral pressure, hypertonicity of the bladder muscles. Their use has no effect in cases of impaired innervation of muscles and pelvic floor myodystrophy.
- Symptomatic treatment of chronic prostatitis - NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Ketorolac) are often used in tablets to relieve pain; to eliminate anxiety, it is recommended to take selective antidepressants (Imipramine, Fluoxetine). Hormone therapy - treatment with antiandrogens and androgens is carried out in accordance with the deviations in hormonal levels.
- Immunostimulants are prescribed only for laboratory-proven immunodeficiency.
- Medicines that regulate uric acid levels are only advisable if stones are detected in the prostate. Most often, the doctor prescribes Allopurinol. However, the drug is effective only against urates.
- Vitamin therapy - vitamin and mineral complexes are becoming available as the means of choice in the treatment of chronic prostatitis. Replacing them with advertised dietary supplements does not bring any therapeutic results, except for unnecessary waste of money.
Surgical treatment of prostatitis
Depending on the pathological process that provoked chronic prostatitis, transurethral resection of the prostate (often replacing open surgery), endoscopic drainage of a formed prostate cyst, and surgical correction of the seminal vesicles in case of impaired secretion outflow are used.
For widespread sclerosis, prostatectomy is performed. For prostate hyperplasia, ablative methods are effective - microwave thermotherapy and laser ablation.
Other treatments for chronic prostatitis
Some doctors actively prescribe various methods of physical stimulation of the prostate to patients with chronic prostatitis. However, most of them have a number of contraindications and are prescribed only in certain cases:
- Massage of the prostate (only a small part of the gland is accessible) with hyperplastic changes in the organ can provoke acute urinary retention and contributes to the spread of the inflammatory process (up to the development of sepsis). Also, massage cannot be performed with prostate stones and cysts, severe venous stagnation. The best way to free the prostate from stagnant secretions is through natural ejaculation.
- Gymnastics for the bladder - special exercises for lengthening the intervals between urination to 4-5 hours are effective in cases of impaired muscle tone of the bladder and its sphincter. However, their effectiveness is noticeably reduced in myofascial syndrome caused by neurodystrophic changes.
- Instillation - deep infusion of medications into the urethra is very painful and fraught with complications.
- Electrical stimulation, transrectal ultrasound and phonophoresis, magnetic therapy and other methods of muscle stimulation are advisable to use only with reduced tone of the pelvic floor muscles. Physiotherapy provides only temporary relief, and a lasting effect is achieved by eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Traditional methods - home recipes (pumpkin seeds with honey, alcoholic infusion of aspen bark and others) are used only with the approval of the treating andrologist and in no way replace drug therapy.
Prognosis: can chronic prostatitis be cured?
The prognosis for chronic prostatitis directly depends on the timeliness of the patient seeking qualified help. As you may have noticed, the symptoms and treatment of chronic prostatitis in men are closely related - in the absence of hyperplastic changes in the gland and neurodystrophy, with comprehensive treatment, a lasting improvement in the condition can be achieved.
- It is also important to radically reconsider your life: eliminate factors that provoke stagnation, get rid of bad habits and eat well.
- (Visited 11,612 times, 18 visits today)
Source: https://prostatitguru.ru/hronicheskiy-prostatit-klassifikaciya-simptomy-i-lechenie-zabolevaniya/