The narrowing of the foreskin opening makes it difficult to expose the head of the penis.
This anatomical and physiological feature can be congenital or acquired.
If physiological phimosis, which is considered normal for newborns, does not disappear by 2-3 years of life, surgical intervention is necessary to eliminate obstacles to the movement of the foreskin. Phimosis in a child: photos before and after surgery, how it goes and whether it is necessary, also everything about postoperative care for children.
Hide content
Prerequisites for prescribing the operation
In the first years of life, there is no point in treating phimosis, since at this stage of the baby’s development, the presence of phimosis does not interfere with the functioning of the genitourinary system. In boys under 4-5 years of age, the head of the penis is completely covered by the foreskin.
The skin proboscis hangs down, the flesh has an insufficiently wide opening. When hormonal changes occur in the body, the penis grows. The fold of skin, called the preputial sac, is moved apart by the head, which is brought out quite freely.
The head of the penis is connected to the inner layer of the foreskin using delicate embryonic adhesions. Smegma accumulates here, creating a breeding ground for microbes, especially if the hygienic care of the boy’s genitals is unsatisfactory.
In this case, balanoposthitis develops, in which the head and foreskin become inflamed. The resulting inflammation tends to subside, but does not exclude the appearance of scars. Disruption of the urination process is considered a natural result of such pathological changes.
The consequence of obstructed urine outflow is an ascending infection, causing cystitis and pyelonephritis. In addition, the removal of the head is hampered by scar changes, which bring discomfort and suffering. If cicatricial phimosis is diagnosed, the child demonstrates restless behavior and strains greatly when urinating.
Urine pours into the preputial sac, filling and inflating it. Then it flows out in a thin stream. The inflammatory process is expressed by pain, swelling and redness of the genital organ, and the release of pus.
IMPORTANT! The head of the penis should not be forcibly removed. This injures the foreskin and aggravates the severity of symptoms. Early contact with a doctor and a careful examination by a specialist makes diagnosis timely and simple.
The main thing in this situation is the differential diagnosis of types of phimosis. With hypertrophic, the foreskin is overdeveloped. In the atrophic variant, there is a tight fit of the head, an opening with calloused edges.
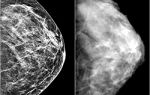
Appearance of the penis. Photo before surgery:
Surgical treatment of phimosis in children
Once an accurate diagnosis is established, surgery for phimosis in children is performed. How does the operation go for boys? Cicatricial phimosis is eliminated by circular excision of the leaves of the foreskin. People call this circumcision, scientifically it is called circumcision. The surgery lasts about 20 minutes.
In case of developed balanoposthitis, conservative therapy includes the following measures:
- warm baths with a solution of potassium permanganate - 5 times a day for 4 days;
- treatment with furacillin - according to the same scheme;
- introduction of antiseptic ointments into the preputial sac - 3 times a day for 6 days;
- lubricating the affected area with petroleum jelly - 2 times a day, 7 days.
External antibacterial therapy can be different and is determined in each specific case individually. Antibiotic-based emulsions and powders may be prescribed. When performing the procedure, the foreskin must be moved from the head.
After the elimination of scar changes and the inflammatory process, the child should be under observation, the period of which is determined by the attending physician. Recurrent balanoposthitis, unresponsive to conservative measures, is an indication for circumcision even in the absence of scar changes.
When the narrowed ring pinches the head, the flesh is cut longitudinally. This is how children are relieved of paraphimosis. The goal is to free the head and restore normal blood circulation.
Appearance of the penis. Photo after surgery:
The result of surgical treatment largely depends on the effectiveness and safety of anesthesia. The anatomical and physiological characteristics of children and their psychological status indicate the need for general anesthesia (anesthesia). In the postoperative period in children with phimosis, child care is of great importance.
There may be difficulty emptying the bladder due to pain during the first acts of urination. To relax the muscles, the penis is placed in a container of warm water. The child is asked to urinate, trying to calm him down with conversations on abstract topics.
After urinating and washing the head of the penis, what should you use to treat the surgical site? An antibacterial ointment dressing is applied, which is prescribed by the surgeon. After a week, the bandages are removed. Relapses and negative consequences of surgical treatment are usually absent.
Photo
Phimosis in boys before and after surgery in the photo:
- The head is partially exposed during an erection.
- Erect state without exposing the head; Difficulties arise with this even in a calm state.
- The head does not release in any condition; the child can urinate without problems, which cannot be said about the fourth degree of the disease.
- The difficulty is in the strong swelling of the preputial sac, urine is released in drops, and the head cannot be opened slightly; severe pain appears.
Regular, long-term application of corticosteroid drugs increases tissue elasticity to some extent. The foreskin stretches, the symptoms of the disease improve somewhat. Ointments based on this group reduce swelling and inflammation. Microcracks heal faster. You can find a review of ointments prescribed for phimosis here.
But this method does not play a decisive role in the treatment of the disease. It is good only when used in combination, during treatment after surgery.
It is possible to spend many months using corticosteroids without stopping the progression of phimosis in boys. The treatment strategy should be determined by a qualified urologist.
Conclusion
Complete circumcision of the foreskin at the last stage of phimosis in a child (see photos before and after the operation).
above), is considered the most optimal method of treatment ; physiological phimosis does not require surgical intervention.
The earlier treatment is started, the less likely it is to develop complications (balanoposthitis, paraphimosis, impaired urine outflow, inflammation of the urethra, etc.).
This allows us to hope for positive results during surgical and therapeutic procedures.
Medical tactics are determined by the patient’s age, the degree of phimosis, the presence of concomitant diseases, the general condition of the body and the conditions of the medical institution.
ATTENTION! In the history of mankind, teaching a boy the norms and rules of behavior accepted in a given society, taking into account his gender, developed gradually, focusing on the subsequent life of a man.
The main aspects of sex education include hygiene issues. The goal of working with children is to, by promoting the harmonious development of the body, instill in the child gender-specific hygienic skills from early childhood.
Prevention of phimosis and accompanying inflammation in children allows one to avoid skin ruptures, bleeding, and sexual dysfunction in adults. As for the surgical treatment of phimosis in children, this is a necessary measure, although it is very effective.
Source: https://samec.guru/zabolevaniya/andrologiya/fimoz/u-detej/lechenie-operativnim-putem.html
Phimosis: surgery in children, how it goes and how to care after removal
If it is impossible to expose the head of the penis, conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Surgery for phimosis is recommended in cases where the problem cannot be eliminated with the help of ointments and folk remedies, and the man has complications of various types.
To treat the disease, intervention is carried out in various ways, depending on the age of the patient - an adult or a child, the type and stage of the disease, etc. Let's consider how surgery is performed for phimosis in children and adults, and when is it better to refuse it?
Stages and techniques of surgery for phimosis
In medical practice, physiological and pathological phimosis are distinguished. In the first case, this is a variant of the norm inherent in all newborn boys.
Over time, the head becomes exposed on its own. If this has not happened by the age of seven, then they speak of a pathological form of the disease.
Regardless of the type, complications may arise, resulting in the need for surgical intervention.
For phimosis, surgery is necessary at the third and fourth stages of the disease.
If at the second stage the patient experiences pain when emptying the bladder, smegma accumulates in the preputial sac, which leads to inflammatory processes, then surgical treatment is also indicated.
Other indications include the scar form of the disease - it can only be treated surgically, since scar tissue is inelastic and does not have the ability to stretch.
It’s worth knowing: phimosis surgery in children and adults is a “one-day manipulation.” In other words, it is carried out on an outpatient basis: in the morning the patient is hospitalized, after which the procedure is performed, and after a few hours the patient can leave the medical facility.
Phimosis surgery in men can be performed using various methods. The choice is determined by the age group of the patient, the type and severity of the disease, as well as the skills of the surgeon, the presence/absence of an assistant, and the equipment of the clinic.
Surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia method depends on the person’s age. For example, it can be done on a newborn under local anesthesia, provided that the baby is sufficiently fixed. For older children, general anesthesia is required - the drug is administered intravenously. This eliminates mental and emotional trauma to the child.
Adults and adolescents tolerate local anesthesia quite well. The drug is injected directly into the skin of the penis. However, if there is an allergy to the drug, or there are pathological changes in the skin at the injection site, general anesthesia is performed.
Circular resection method
- This surgical option is recommended for patients who have prominent saphenous veins of the reproductive organ, since the circular resection method minimizes the likelihood of bleeding.
- To remove phimosis, the doctor does the following:
- First, the doctor outlines the line of the future incision on the inside and outside of the foreskin. Using a scalpel, a medical specialist makes an incision along the intended lines, dissecting the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- A flap of skin is dissected and separated from the trunk of the reproductive organ. Afterwards, the doctor applies securing sutures;
- Upon completion of the intervention, a bandage is applied.
Note: the advantages of the method include a good cosmetic effect - the scar is not noticeable, and there is a low risk of bleeding. Disadvantages of manipulation - it requires good surgeon skills and the help of an assistant.
Preputioplasty
If scar tissue is located at the tip of the prepuce, then surgery is performed. Phimosis in children of this form is extremely rare. If such a picture is observed, then the preputioplasty method is chosen. The manipulation is carried out under general or local anesthesia; there are no special preoperative preparations.
Manipulation progress:
- Using scissors, the surgeon makes a longitudinal incision of the prepuce along the dorsal surface (the incision is similar to the dorsal technique).
- As necessary, adhesions located between the head of the penis and the foreskin are dissected.
- The doctor’s actions neutralize phimosis. After the operation, transverse sutures are applied to connect the inner and outer parts of the prepuce to each other.
A distinctive feature of the procedure is that with circumcision using the dorsal incision method, the skin is dissected more than with preputioplasty. The duration of the manipulation is 15-20 minutes. The procedure is characterized by a minimum of possible complications and the absence of painful sensations. Phimosis after surgery is leveled out; the attending doctor will tell you how to care for it in each specific case.
Preputioplasty is not recommended for all patients. When the prepuce is significantly narrowed, compacted and there are scar changes, manipulation is not performed, since there is a high risk of relapse of the disease.
Meatoplasty
Meatoplasty is a surgical treatment for narrowing the external opening of the urethral canal in men. In most clinical situations, this procedure is not an independent manipulation. It appears as an addition to the intervention when it is necessary to trim the foreskin or to preputioplasty.
During meatoplasty, cystoscopy is performed - a visual examination of the urethral canal using endoscopic equipment to exclude narrowing of the urethra. If the assumption is confirmed, then an operation is performed to expand the lumen of the urethra.
Using clamps
The birth process is a serious stress for the newborn, which is accompanied by a significant increase in the concentration of anti-stress hormones. Therefore, the healing process in the postoperative period after removal of phimosis is somewhat faster, and modern techniques make it possible to eliminate the need for sutures.
Important: Surgical techniques include methods that help protect the penis from damage during preputial incision. The MOGEN clamp (introduced into medical practice in 1945) and Plastibell (used since 1955) are widely used.
You can remove phimosis in children using the following methods:
- Dorsal dissection method;
- Via MOGEN clamp;
- Using a Plastibell clamp.
Plastibell is a clamp made of a sterile plastic ring with a handle and a deep groove. This method of therapy allows for circumcision, which eliminates the need for sutures. In the United States of America, this clamp is used in 60% of cases.
After the dorsal incision, a bell is inserted into the space of the foreskin, and the prepuce is tightly fixed above it using a ligature with a groove, which is tightened. Excess prepuce is trimmed a few millimeters below the applied ligature. Then the handle of the bell is broken off. After about a week, the ring falls off on its own. Treatment with antiseptics is carried out within a week.
The duration of the procedure varies from 5 to 10 minutes. Negative consequences are extremely rare. However, the experience and skill of the surgeon circumcising the child is of great importance.
Bells come in different sizes. But the maximum clamp size is designed for boys of 11-12 years of age.
There are no bells for teenage boys or adult men because the procedure is associated with the following risks:
- Slipping of the ring during an erect state.
- Impossibility of tightly fixing the ring.
- High probability of infection due to improper isolation of necrotic tissue.
It is important to choose the right ring. If it is too small, it cuts heavily into the genital organ and can lead to complications - tissue death or disruption of the urinary process. A large diameter ring will slip off.
Circumcision using a MOGEN clamp is performed under local anesthesia using an anesthetic cream, a local injection or under general anesthesia (mainly in children of the older age group).
The essence of the method is that after separating the prepuce, it is stretched so that the penis slides backwards towards the scrotum.
The MOGEN clamp is then applied 10 mm below the edge of the foreskin, but in front of the head of the reproductive organ.
After making sure that the head is safe, the doctor closes the clamp tightly and waits a certain time interval. For example, during an operation on children under six months old - approximately 30 seconds, for a child from 6 months and adolescents - five minutes. After time, the surgeon uses a scalpel to circumcise the prepuce above MOGEN, after which it is removed, and the foreskin is moved behind the penis.
Note: unlike the Plastibell clamp technique, where the bells are disposable “tools,” the MOGEN clamp is a reusable device that must be sterilized after manipulation, which significantly reduces the cost of the intervention.
Contraindications for surgery
If a man or child has inflammatory pathologies of the genitourinary system, the procedure is not performed until the infection is cured. This criterion is met in case of ulcerative lesions of the reproductive organ.
When a patient has a congenital curvature of the genital organ, preputioplasty is performed. This method does not require the need to completely cut the foreskin. In the future, the birth defect is eliminated.
Absolute contraindications include genetic diseases of the circulatory system - blood clotting disorders, tendency to bleed, etc. Uncompensated diseases, which include diabetes mellitus, regardless of type, are an obstacle.
When is it better to refuse surgery?
Despite the low invasiveness of modern intervention techniques, many men try to avoid surgery whenever possible.
In some cases this is possible, in other cases - circumcision is the only way to solve the problem.
Of course, there is a possibility of complications, but if you choose a clinic with a good reputation and treat the wound surface with antiseptics during the rehabilitation period, then they can be avoided.
If the disease can be treated with conservative methods, then the doctor will not recommend surgery. Practice shows that the first stage, and in some cases the second, can be successfully treated with corticosteroid ointments and antibiotics that neutralize the inflammatory process.
When using topical medications, you need to do specialized exercises aimed at stretching the foreskin. The process is not quick; a man will need several months to get rid of phimosis.
Other treatments
As an alternative to surgery, laser treatment technology is used. The advantage is a minimal risk of bleeding, no stitches, a quick healing process, complications associated with swelling, hyperemia and suppuration of the genital organ practically do not develop.
It’s worth knowing: the disadvantage of laser manipulation is the high cost of the procedure – from $400. Since the method does not involve sutures - they are sealed, there is a high risk of their divergence due to an increase in the size of the penis during erection, which requires repeated intervention.
Alternative therapies:
- The use of baths based on decoctions of medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antibacterial effects;
- Stretching the prepuce with your fingers for 2-3 months;
- The use of glucocorticosteroids is effective at stages 1 and 2 of the disease. Creams and gels have many contraindications and should only be prescribed by a doctor.
The choice of treatment method remains with the medical specialist and the patient. The treatment technique is determined by the age of the patient, the form of the disease, stage and other criteria, on the basis of which a method of solving the problem is selected.
Surgery is an effective method of treating phimosis, helping to get rid of the pathology. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period, the likelihood of complications is reduced to zero.
Source: https://ManExpert.ru/andrologiya/anomalii-razvitiya/fimoz-operatsiya.html
Surgical treatment of phimosis in children
- Phimosis in children is a pathological condition that can lead to various complications in adolescence and adulthood.
- At the age of about 6 years, a child with signs of phimosis must be shown to a urologist.
- Moreover, this disease is easily diagnosed.
- It is necessary to treat phimosis as early as possible , since in adulthood it can lead to infertility or the appearance of a cancerous tumor.
What is childhood phimosis?
Phimosis in childhood is a narrowing of the foreskin. As a result, the head of the penis either does not open at all or does not open completely. With this disease, pathogenic bacteria begin to develop under the skin, causing inflammation.
Stages of the disease, its symptoms and causes
Phimosis in children occurs in several stages.
The first degree of this disease is characterized by the fact that when a boy has an erection, the head of the penis is only partially exposed. But in a calm state this problem is not observed.
The second degree of the disease is manifested in the fact that the head of the penis is not exposed at all. The same happens when he is in a calm state.
The third degree is characterized by difficulty opening the head in any condition. But the child does not experience difficulty urinating.
With the fourth degree of phimosis, swelling of the preputial sac is observed during urination. As a result, urine flows out literally in droplets, but sometimes in a thin stream. The head of the penis does not open at all. This is the most complex degree of the disease, which is accompanied by severe pain.
Most often, phimosis in children appears at birth. But if it has not passed before 3 years, then the disease ceases to be considered physiological.
Phimosis can occur in several forms:
- the physiological form of the disease can be treated by observing normal hygiene rules and requires regular consultations with a doctor;
- the pathological form is treated with medications or requires surgery.
The causes of phimosis in children can be different:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- infections of the foreskin;
- damage to the genital organ;
- complications after operations.
In a newborn child, the cause of phimosis is considered to be heredity , which manifests itself in the gluing of the foreskin to the head of the penis. This makes it impossible to completely expose it. This condition occurs due to exposure to toxins or infections. Regardless of the cause, if you have phimosis, you should immediately contact a urologist.
Symptoms of the disease appear when the inflammatory process is at its peak of development.
They are expressed as follows:
- the head of the penis does not open freely;
- problems with urination begin. It becomes painful, so urine is excreted very poorly;
- the cavity next to the foreskin swells as urine and lubricant accumulate in it;
- erection is impaired;
- pain and pus appear;
- temperature rises;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
Video: “Phimosis in children”
Diagnosis of phimosis
This disease is diagnosed after examining the child by a urologist.
Phimosis treatment methods
It is necessary to treat phimosis in order to avoid possible complications with erection at a later age.
During erection, the head of the penis becomes larger in size, which leads to stretching of the foreskin and the appearance of microcracks. After healing, scars form in their place. They are inelastic and therefore lead to severe discomfort. Advanced phimosis can subsequently lead to problems in sexual life and possible bleeding.
In newborns, phimosis is not treated , but simply monitored for its progress. It often goes away on its own. It is very important for boys to maintain body hygiene. It is better to use baby soap for washing. But it should not get into the preputial sac.
In adolescence, phimosis can go away on its own due to the production of sex hormones. However, complications of the disease are very rare. They can appear when a child has allergies, overheating, or poor hygiene.
Treatment of phimosis in children can be carried out by a pediatrician or urologist. It consists of introducing furacilin under the foreskin . This procedure is performed until the pus is completely washed out. After this, you can instill a few drops of Vaseline oil.
In addition, ointments are used to treat phimosis , which are applied to the foreskin and glans penis. This helps to heal cracks faster and remove swelling.
Treatment of the disease with surgery and its advantages
The most effective treatment for phimosis is surgical removal of the foreskin , which is called circumcision. As a result, problems with exposing the head of the penis disappear.
At what stage of the disease is surgery required?
The operation is called circumcision or circumcision. It is prescribed only for grade 4 narrowing of the opening near the foreskin.
This procedure is used if conservative treatment does not lead to the expected effect. It is not prescribed when the head of the penis and the foreskin are in an inflamed state.
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed in two main ways. For this, a scalpel is used, with which a classic circumcision is performed. The second option is a laser beam.
The operation in children is performed under general anesthesia. During it, complete or partial excision of the prepuce occurs. The classic operation is performed for at least one hour. It is characterized by increased bleeding, since there are a lot of blood vessels in this organ.
After surgery, the child may have problems urinating, as well as severe pain. Tissue swelling is also possible. It will take at least a month to fully recover from surgery.
Thanks to the surgical method, it is possible to remove the foreskin of the penis, which is the cause of the disease. But, as with any other operation, complications are possible. They are expressed in decreased sensitivity of the glans penis or relapse of the disease . An experienced doctor will not allow this to happen or will minimize the risk of complications.
Using a laser beam, you can quickly seal the vessels, so there is practically no bleeding after this procedure. There is also no pain syndrome of long duration and tissue swelling. The entire operation takes no more than 20 minutes. The patient can be discharged from the hospital immediately after the procedure. The stitches take about a week to heal.
Video: “Circumcision of the foreskin”
Recovery after surgery
Within a week after surgery, there may be signs such as:
- pain;
- swelling;
- high sensitivity of the genital organ.
This should not cause concern to parents, since all signs are a normal reaction to surgery. It is important to fully follow all doctor’s recommendations and child care rules.
The gauze bandage should always be clean, the same applies to wounds. This will avoid infection of the inflamed sutures. But if swelling and inflammation of the wound occurs, or discharge appears from the penis, you should urgently consult a doctor. The same should be done when body temperature rises.
During the postoperative period, it is important to carefully monitor the boy in order to provide him with timely medical assistance. It may be required if you are allergic to any medications.
The child does not need to be bathed for two days after surgery. Instead of water procedures, it is wiped with a towel soaked in warm water. After 48 hours, the boy can be completely bathed. The food is normal, but the portions should be a little larger.
After the operation, the boys need to be given proper care, since at first they cannot even put on underwear and clothes. The rehabilitation period of recovery will allow all scars to heal and get rid of pain.
Medicinal herbs, for example, calendula, string, barley, chamomile, will help you recover faster after surgery. They remove swelling and inflammation well, as they have bactericidal and antiseptic properties.
Herbs are used in the form of decoctions for lotions, which are applied to inflamed areas. But they should only be pharmaceutical grade to avoid additional infection.
Postoperative procedures
After surgery, it is important to provide conditions for rapid healing of the sutures. That's why so much attention is paid to their processing. First, the treatment is performed by the doctor himself, and then all procedures can be performed by the child’s parents. Bandages must be applied for at least 10 days.
To remove the bandage during dressing, it must be moistened with hydrogen peroxide so that it can be easily removed. This will prevent tissue injury and help avoid infection. When the bandage can be easily removed, hydrogen peroxide can no longer be used.
For bleeding and ulcers, antiseptic ointments are used. They are applied in a thin layer and covered with a sterile bandage. Most often, the doctor prescribes Levomekol ointment, which has excellent antiseptic properties. It is also necessary to treat the seams with potassium permanganate or brilliant green. Sometimes a solution of furatsilin is used.
You can take methyluracil tablets orally, but only after a doctor’s prescription. Salt baths, which are also prescribed by the doctor, help relieve swelling.
Prognosis after treatment
Timely treatment of phimosis allows you to avoid possible complications. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of removing phimosis naturally as the boy grows. That is, he can outgrow his problem and phimosis will disappear by itself.
Conclusion
Phimosis occurs in many children and is expressed in a narrowing of the foreskin. If the child is under 6 years old, this disease cannot be considered pathological. Therefore, it does not require special treatment. Very often, phimosis disappears as the boy grows older. To treat phimosis, the main method is circumcision surgery, which allows you to restore all functions of the genital organ.
Source: https://kakbyk.com/bolezni/khirurgicheskie-zabolevaniya/khirurgicheskoe-lechenie-fimoza-u-detej.html
Phimosis!? You just have a boy growing up. Treatment of phimosis: surgery to remove adhesions or circumcision
Content:
During a preventive examination of boys under three years of age, doctors often diagnose “phimosis.” For some, this incomprehensible word sounds like a sentence and a call for immediate surgery. Parents in a panic begin to look for specialists who can cure this “disease”. Is this a disease and should it be treated?
Male anatomy
First, let's take a quick look at the normal anatomy of the foreskin.
The penis consists of a body, a head and a root. On the head there is an external opening of the urethra (meatus). Through it, urine is released during urination, and sperm is released during ejaculation.
The head of the penis is hidden by skin - the foreskin (prepuce), which in an adult man is easily displaced, exposing the head. The foreskin consists of two sheets: the outer one, not different from the skin, and the inner one, tender and soft, reminiscent of a mucous membrane.
Between the head and the inner layer of the foreskin there is a space - the cavity of the foreskin. Into this space (preputial space) the secretion of glands located under the foreskin is secreted and forms a special lubricant (smegma), which facilitates the displacement of the skin from the glans.
Along the lower surface of the penis, the foreskin is connected to the head by the frenulum of the foreskin - a fold of skin in which blood vessels and nerves are located.
In a newborn boy, the skin of the foreskin is usually fused to the head of the penis through synechiae, a kind of adhesions that prevent or completely eliminate the free removal of the head.
This temporary anatomical structure is called physiological phimosis (phimosis, from the Greek phimosis - tightening, compression, - narrowing of the foreskin, preventing the removal of the head of the penis), which is a normal condition for boys under 3-6 years of age and does not require any treatment .
Only 10% of children have the glans penis fully or partially open in the first year of life.
Moreover, the fusion of the head with the foreskin can be considered as a protective mechanism to reduce the likelihood of infection entering the preputial space and the development of inflammation.
Gradually, in the process of growth of the penis, the glans spreads the foreskin, a slow independent separation of the synechiae and opening of the glans occurs. This process can continue until the boy reaches puberty, when sex hormones are activated, which make the foreskin tissue more elastic and stretchable.
Sometimes smegma accumulates in the preputial space, limited by synechiae, in the form of a dense formation similar to a tumor. In case of a large accumulation of smegma, minimal medical assistance is required: - a special probe, similar to a thin stick, is used to separate the synechiae that prevent the discharge of secretions.
Boy hygiene
During infancy, proper hygiene care is limited to daily bathing of the child and washing after the baby poops. During bathing, water gets under the foreskin, which naturally washes away the accumulated secretions.
You should wash your penis and scrotum with soap at least once a week. To do this, it is better to use baby soap or special baby bathing products. Daily use of bactericidal (germ-killing) soaps or gels is not recommended.
If used frequently, they can disrupt the balance of the normal microbial environment on the skin.
To avoid urinary tract infections, children should be washed from front to back. When washing the penis, you should not move the foreskin .
If you still try (on the advice of some doctors) to gradually move the skin of the penis and expose the head, then this procedure must be performed very carefully, without causing the slightest pain to the child.
It should be remembered that the area of the glans penis contains a large number of pain nerve endings, and rough manipulation of the penis can lead to mental trauma and fear. Immediately after toileting the head, the foreskin should be returned to its place, in order to avoid the development of paraphimosis - pinching of the head in the foreskin (see below).
Pathological phimosis
Some boys may develop pathological phimosis , a disease that most often requires surgical intervention.
It is customary to distinguish between atrophic (cicatricial) and hypertrophic pathological phimosis .
The first is characterized by the presence of rough scars that narrow the foreskin; in the second case, there is an excess of foreskin that prevents the removal of the head. There are two main reasons for the development of pathological phimosis:
- Inflammation of the foreskin and glans penis - balanoposthitis.
- Complication after rough manipulation of the penis associated with the removal of the head.
Rough, immediate removal of the head of the penis is one of the most common causes of the development of phimosis.
Pathological phimosis can lead to disruption of the act of urination , which will flow in a thin stream, swelling the foreskin. This condition requires surgery.
Also, pathological phimosis sometimes leads to acute urinary retention . This condition is reflexive in nature and is more common in young children, as a reaction to pain due to pinching of soft tissues. The child cannot urinate for a long time, becomes restless, and often complains of pain in the abdomen and above the womb, where an enlarged bladder can be felt.
Acute urinary retention is an emergency and requires immediate medical attention.
In this case, the baby is given painkillers, a cleansing enema is given (so that the intestines with feces do not put additional pressure on the bladder and impede the outflow of urine), and then a warm bath with potassium permanganate, during which the child tries to urinate. If unsuccessful, urine is removed using a catheter.
If there is phimosis, as a result of an attempt to remove the head of the penis, it may become pinched in the narrowed ring of the foreskin - paraphimosis . In this case, the blood supply and lymphatic drainage in the penis are disrupted, which leads to swelling of the foreskin and glans, and subsequently to their necrosis (death) and the development of purulent complications.
The development of paraphimosis requires emergency medical attention. With a short duration of the disease, manual reduction of the strangulated head is possible (sometimes with the use of short-term anesthesia). If this is not possible, then surgical dissection of the pinching ring is performed. In the future, treatment of balanoposthitis is carried out (see.
further) and, after the inflammatory changes subside, circumcision of the foreskin.
Balanoposthitis is an inflammation of the foreskin and glans penis.
It develops when the preputial space is infected, poor genital hygiene or urinary tract infection - urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys). The chance of developing balanoposthitis increases in children with reduced immunity or against the background of other infectious diseases.
Balanoposthitis can be both a cause and a consequence of atrophic (scar) phimosis. The narrowed foreskin prevents the preputial space from being cleared of smegma and remaining drops of urine, complicates hygienic manipulations, which creates favorable conditions for inflammation.
Inflammation of the foreskin is characterized by swelling, redness (hyperemia), pain, and purulent discharge from the preputial space. The result of inflammation can be cicatricial degeneration of the skin of the foreskin and, as a consequence, the development of phimosis.
When the head of the penis is roughly removed for the treatment of balanoposthitis or separation of synechiae, the delicate inner layer of the foreskin is injured, microcracks appear, which form a cicatricial narrowing during the healing process.
Balanoposthitis is a disease that requires emergency medical attention. The doctor inserts a special probe between the head of the penis and the skin of the foreskin, which carefully separates the existing synechiae and creates conditions for the outflow of accumulated pus. After which the preputial cavity is washed with a solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) or furatsilin.
In the future, the child needs to take daily baths with a warm, weak solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction (1 tablespoon of herb per 200 ml of water, leave for 10 minutes in a water bath, strain, cool).
Several crystals of potassium permanganate are completely dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water and a few drops are added from the resulting solution to the container where the procedure will be carried out until the water appears slightly pink.
The main danger is making too concentrated a solution of potassium permanganate, which can lead to a chemical burn to the penis. For young children, you can use a basin or bathtub for baths, but for older children, it is enough to hold the penis in a solution poured into a glass or tray.
The procedure is performed for 5-10 minutes, 3-4 times a day for 5 days. Depending on the severity of the inflammation, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can use various antibacterial ointments (syntomycin liniment, levomekol, dioxidine ointment, etc.), which are placed in the preputial space.
Balanoposthitis is rare, but can be complicated by the spread of infection to the overlying urinary tract with the development of urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) and even pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys).
To prevent these complications, it is enough to give your child plenty of fluids.
If painful urination or fever occurs, a consultation with a urologist is necessary, as well as additional examination and treatment.
Conservative (non-surgical) treatment of phimosis
In case of hypertrophic phimosis (excess of the foreskin, which prevents the removal of the head), when there are no complications (repeated inflammation of the foreskin, urinary disorders), conservative treatment is possible, which consists of gradual stretching of the foreskin. The manipulation can be performed by parents at home. Three times a week, while bathing with herbal decoctions (chamomile, chamomile), the foreskin is displaced until the child begins to feel pain, after which a few drops of sterile Vaseline oil are injected into the preputial space. The duration of treatment is several months. The procedure should be performed very carefully to avoid paraphimosis. Success depends on the persistence of the parents and the severity of phimosis. If there is a scar zone of narrowing, conservative treatment is not very effective.
In recent years, correction of phimosis has been used with hormonal ointments, which are placed in the preputial space. They make the fabric easier to stretch. Treatment is carried out by parents with mandatory medical supervision.
In the absence of complications and gross scar changes, treatment of phimosis should begin with conservative measures that preserve the foreskin with its protective, sensitive (sensory) and sexual function, and only if conservative treatment fails, surgery should be resorted to.
Surgical treatment of phimosis
Indications for surgery:
- pronounced changes in the foreskin due to scars;
- repeated repetitions of balanoposthitis;
- urinary disorders.
The operation is performed at any age, immediately after diagnosis, as planned, i.e. if the child is in full health: there are no infectious diseases during the last month before the operation and after the examination, if the tests are normal.
The most commonly performed circumcision of the foreskin is circumcision - a circular excision of the leaves of the foreskin. This operation lasts 10-15 minutes and is usually performed under general anesthesia. The foreskin is cut off circularly (in a circle), while preserving the frenulum.
The inner and outer layers of the foreskin are sutured with catgut (a suture material that dissolves on its own and does not require further removal of sutures). After the operation, a bandage with Vaseline oil is applied.
A few hours after surgery, the child can walk and independent urination is restored.
In some countries, the so-called hygienic circumcision is quite popular - the removal of a healthy foreskin in order to avoid, as supporters of the procedure claim, possible complications in the future (penile cancer, sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation of the foreskin, etc.). Parents should be aware that there is not a single medical, confirmed indication for preventive circumcision, which was decided by the American Academy of Pediatrics back in 1975.
Complications after surgery performed in a hospital setting by an experienced surgeon are rare and do not exceed 0.1-0.2%. If they do appear, they are divided into acute (bleeding, acute urinary retention, suppuration of a postoperative wound), occurring immediately after surgery, and chronic .
Bleeding occurs when stitching is poorly performed, blood vessels are damaged during excision of the foreskin (this complication is especially common when the operation is performed at home for religious purposes) and when diseases of the blood coagulation system are not identified. In most cases, applying a tight bandage to the postoperative suture is sufficient to stop bleeding.
If bleeding continues, it is necessary to suture the bleeding vessel.
Chronic complications include meatitis (inflammation of the meatus - the external opening of the urethra), meatostenosis (narrowing of the external opening of the urethra), and excessive retention of the foreskin .
After the operation, the mucous membrane of the external opening of the urethra is deprived of the protection of the foreskin, as a result of which local inflammation may occur - meatitis .
This complication is characterized by redness of the meatus, sometimes painful urination, and changes in urine tests indicating inflammation.
Treatment: baths with a solution of potassium permanganate and antibacterial drugs, the most effective in treating urinary tract infections (as prescribed by a doctor).
As a result of inflammation of the meatus, its cicatricial narrowing may develop - meatostenosis , when urination is performed in a thin stream, with straining, for a long time.
The diagnosis is confirmed by examination by a urologist-andrologist with uroflowmetry, a special study that determines the rate of urine flow. For a child, this procedure is no different from regular urination, only into a special toilet connected to a computer.
Meatostenosis requires surgical treatment - dissection or formation of the correct contours of the external opening of the urethra (meatus plastic).
Excessive foreskin retention is diagnosed when there are uneven flaps of excess foreskin left by the surgeon. In this case, repeated circumcision is indicated to achieve a cosmetic effect.
Sometimes, especially if the foreskin is left excessively around the entire circumference, a recurrence of phimosis is possible. At the request of the parents, plastic surgery of the foreskin can be performed. In this case, the narrowing is eliminated, but most of the foreskin is preserved.
This operation is somewhat more technically complex and is accompanied by a large number of complications (mainly relapse of phimosis).
Congenital anomalies of the penis
Even before circumcision of the foreskin, the surgeon must make sure that the meatus is located correctly - at the top of the glans penis.
If an incorrect location of the external opening of the urethra is detected - hypospadias (a congenital disease, occurs in 1 in 150 boys), the operation of circumcision of the foreskin is not performed, since the issue of tactics for surgical treatment of hypospadias must first be decided.
Often phimosis is combined with a short frenulum of the foreskin , which deforms the meatus and bends the head of the penis. In this case, simultaneously with circumcision, dissection and plastic surgery of the frenulum are performed.
Advice for parents.
It is advisable after birth (in the first week of life) to consult a boy with an andrologist who deals with issues of the male reproductive system, who will examine the child and determine whether he has any pathology or not.
If it is not possible to see an andrologist, the baby should be examined by a urologist or pediatric surgeon. In the future, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations, especially during the onset of puberty.
Oleg Staroverov pediatric urologist-endrologist, Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 9 named after. G.N. Speransky, Ph.D.
Source: https://www.7ya.ru/article/Fimoz-Prosto-u-vas-rastet-malchik/
Phimosis and paraphimosis
Phimosis and paraphimosis
At the first signs of phimosis, you should immediately consult a specialist. In the early stages of the disease, conservative therapy can be used. In more complex cases, circumcision is indicated.
Signs of phimosis cannot always be detected immediately. Often the narrowing of the foreskin begins unnoticed by the man. At an early stage, there are practically no problems with urination. However, releasing the head of the penis during an erection causes pain. If you notice this phenomenon, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to prevent the development of complications.
Later stages are characterized by the appearance of other signs of phimosis:
- pain when retracting the foreskin when the penis is at rest,
- problems with urination,
- soreness of the skin in the head area.
A complication of phimosis is often balanoposthitis - inflammation of the scalp. Develops under the influence of pathological microbes accumulating under the skin. The most complex and dangerous cases of complications are paraphimosis and the formation of synechiae - tissue fusions. In this case, urgent surgical intervention is required.
A timely visit to the doctor will help prevent the consequences of phimosis. The andrologist diagnoses the causes of the pathology based on existing signs and chooses the appropriate treatment method.
Causes of phimosis
There are several causes of the disease:
- insufficient elasticity of connective tissue - due to a genetic factor,
- physiological gluing of the head and the foreskin is the norm in newborn boys; in most cases, skin mobility is normalized by 6-7 years of age,
- mechanical injuries to the penis - lead to the formation of scars, due to which the foreskin narrows,
- inflammatory diseases of the penis - like trauma, leads to tissue scarring.
Depending on the causes and current manifestations, one or another method of treating the pathology is chosen. In case of inflammation, diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections is indicated. Based on the results of the study, a treatment program is drawn up.
At the first signs of phimosis, you should immediately consult a specialist. In the early stages of the disease, conservative therapy can be used. In more complex cases, circumcision is indicated. In our clinic, this operation is performed using radio wave and laser technologies. The procedure is as safe as possible, shortening the recovery period.
Phimosis treatment methods
Currently, the most effective, fastest and safest way to treat phimosis in both children and adults is surgery to circumcise the foreskin of the penis.
Treatment methods for phimosis are selected depending on the current condition of the patient. Today, both conservative and surgical methods of therapy are used. The andrologist at our clinic will select the most effective one in accordance with your wishes and capabilities.
Conservative treatment of phimosis
A conservative method of therapy is based on the use of an ointment containing male sex hormones. When applied, the foreskin is stretched. The ointment helps expose the head by reducing the density of the tissues of the preputial ring.
The method is used only in two cases:
- with physiological phimosis, when gluing of the head and the foreskin occurs,
- in the early stages of cicatricial phimosis - before the formation of a dense scar.
The disadvantage of this method is the need for long-term use of the ointment - up to 12 months. Therefore, today, to eliminate the narrowing of the foreskin, the surgical technique most often used is circumcision.
Surgical treatment of phimosis
Circumcision of the foreskin is a safe and effective treatment for phimosis. Modern medical technologies can significantly reduce the trauma of surgery. Our clinic’s specialists perform circumcision using a laser and radio wave scalpel.
The most commonly used technology for removing the foreskin is the Surgitron device. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes about half an hour. Using a radio wave scalpel, the surgeon makes an incision and electrocoagulates the tissue. Thanks to high-frequency radiation, rapid “evaporation” of skin cells occurs.
This method has a number of advantages over traditional mechanical circumcision:
- minimal trauma,
- local impact only on the desired area,
- minimal risk of complications and infection due to the non-contact method of incision,
- short recovery period.
Complete healing after surgery occurs within a few days. During the recovery period, the use of healing ointments is indicated.
Circumcision can also be performed using traditional methods using conventional tools. The patient chooses the appropriate treatment technique for phimosis in accordance with his own wishes and financial capabilities.
You should consult a doctor at the first symptoms of phimosis. Timely professional help will help not only avoid complications, but also reduce the cost of treatment.
Paraphimosis
A pathological condition that can develop as a complication of phimosis
Complications of paraphimosis include an inflammatory process. Due to injury to the organ, hygienic care is impossible. Smegma accumulates in the preputial sac. Paraphimosis is a pinching of the head by a narrow foreskin.
Squeezing usually occurs when the patient pushes the skin beyond the coronary sulcus and does not return it. Swelling of the glans penis develops and blood circulation is impaired. Urgent medical attention is needed, as the next stage is tissue necrosis.
At the stage of tissue necrosis, radical treatment is most often performed - removal of the dead part of the penis.
(sebum). The secretion of the glands is a good nutrient medium for the development of microorganisms. Balanoposthitis begins - inflammation of the skin of the penis and the inner layer of the prepuce.
Etiology, diagnosis of paraphimosis
The most common reason for the development of paraphimosis in boys is an attempt by parents to push the foreskin beyond the coronal sulcus.
Paraphimosis develops quite often in boys The occurrence of infringement is caused by a congenital narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis), less often - acquired, that is, secondary. The anomaly is more common among boys aged 10-12 years. The complication also occurs in adult men.
The most common reason for the development of paraphimosis in boys is an attempt by parents to push the foreskin beyond the coronary groove. The narrowing prevents the tissue from coming back. This situation leads to swelling of the skin. In a man, strangulation can be caused by trauma during sexual intercourse.
The disease may occur with a short, inelastic frenulum. When the skin is pulled back, the head deviates downward, and the groove on the upper side of the circumference of the head deepens. The prepuce forms a fold, making it difficult to reposition the tissues to their original position.
Diagnosis of paraphimosis
To diagnose paraphimosis, an examination of the boy by a urologist is sufficient. The clinical picture in the first stages of the pathology is not expressed. After opening the head, it cannot be closed.
There is no severe pain yet; the boy may experience minor discomfort.
The absence of severe pain in the initial stages increases the risk of complications, since the child does not see the danger to health and does not tell the parents anything.
After 2-3 hours the prepuce swells. The size of the swelling quickly increases. At this stage, it is possible to treat paraphimosis using the reduction method, without surgery.
If medical assistance is not provided, the pathology develops rapidly. Lymph and blood circulation are disrupted, diagnostics shows the appearance of a characteristic bluish-red tint of the skin (cyanosis). Due to severe pain and significant swelling, the boy is unable to urinate.
In the later stages of development, ulcers appear. Using palpation, the doctor determines the lumps. An alarming signal is the disappearance of the painful syndrome. If measures are not taken, paraphimosis will cause necrosis - death of the tissues of the foreskin and penis. If you have signs of injury, you should immediately consult a doctor.
First, the head is cooled, treated with an antiseptic solution and vaseline oil or glycerin to facilitate sliding. The inner leaf of the prepuce is also lubricated. The doctor clasps the penis with the thumb and index finger of the left hand behind the pinching ring.
With his right hand he presses lightly and kneads the head. A gentle impact is needed to reduce swelling of the head and inner layer of the foreskin. Gradually, the edematous fluid is moved behind the ring.
Starting from the dorsum of the penis, the specialist simultaneously tightens the foreskin and pushes the head into the foreskin ring.
Conservative treatment is painful and is performed only under anesthesia. The use of local anesthesia is usually inappropriate because it increases swelling. In some cases, according to indications, adult patients are still given local anesthesia. If the patient is a child, then general anesthesia is used.
Upon successful completion of the reduction, the penis is tied to the abdomen to drain the edematous fluid. For the same purpose, the patient is prescribed treatment of the penis with special preparations.
Methods of surgical treatment of paraphimosis
If reduction is impossible, then doctors suggest surgical treatment. Several basic techniques are used in surgery. The first is a dissection of the pinching foreskin under local anesthesia. A grooved probe is placed under the ring to prevent damage to deeper tissues. After the dissection, as well as after the reduction, the penis is tied up.
After removal of the swelling and healing of the ulcers, circumcision of the foreskin (circumcision) is recommended. Surgery will prevent paraphimosis from recurring. According to indications, specialists can immediately perform circumcision (instead of dissection).
The operation involves excision of the prepuce around the circumference, with the application of sutures or clamps. Today, the Surgitron radiosurgical device and local anesthesia are used for circumcision. Circumcision with Surgitron takes no more than 40 minutes, the patient goes home on the day of the operation.
Using the equipment provides several advantages. During the treatment of paraphimosis, the device reduces bleeding and disinfects the incision site.
The high accuracy of the device ensures the removal of only preputial tissue, without damaging adjacent integuments. The use of the device has a minimum of contraindications and complications.
At the preliminary consultation, the doctor will tell you about the features of eliminating the infringement.
Source: https://www.ncagp.ru/index.php?_t8=527