Mastopathy is a pathological condition accompanied by the proliferation of glandular breast tissue. The disease can be diagnosed not only in women of reproductive age, but also in men and even newborn children. The provoking factors are the same everywhere - hormonal imbalance and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body.
Symptoms and types of mastopathy in children
The first benign changes in the mammary glands occur soon after the child is born. In medicine, this phenomenon is called “physiological mastopathy” or “neonatal mastopathy”. According to statistics, more than 50% of young parents encounter this phenomenon. The definition of “physiological” implies the natural course of events and the baby’s adaptation to new conditions.
During development in the womb, the child receives a large concentration of female hormones, thanks to which full development occurs.
Soon after birth, this process stops, which encourages the body to produce everything on its own. The first symptoms of a hormonal crisis usually appear on days 3-5 of life.
The peak occurs on days 7-11, when the newborn’s body has not yet fully adapted and the estrogen concentration is minimal.
Physiological mastopathy
Clinical picture of physiological mastopathy:
- Swelling of the mammary glands, especially the nipples and parapapillary area. A swelling size not exceeding 30 mm in diameter is considered within normal limits.
- Various skin rashes are possible, but rare.
- Slight redness of the skin around the nipple, no significant pain is noted.
- A concomitant symptom may be slight swelling of the genital organs.
- There may be slight discharge of secretions from the nipples. It is important not to squeeze the mammary glands yourself, as this can cause infection of healthy tissue and injury.
When several symptoms appear simultaneously, the newborn becomes capricious and restless. Gradually, the disease goes away on its own after 3-5 weeks.
Enlargement of the mammary glands with mastopathy
Mastopathy in children after one year is accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- Swelling of one mammary gland, redness of the skin and swelling.
- Bursting sensation, as if there is a foreign object under the skin.
- Enlargement of the mammary gland.
- Discharge from the nipple of a liquid and sticky secretion, usually colorless or yellow in color.
- Discomfort or pain when touched, burning and itching.
It is necessary to immediately show the child to a specialist.
Diagnosis and causes of development of childhood mastopathy
Ultrasound is prescribed to diagnose the disease
To confirm a hormonal imbalance, the child will need to be examined by highly specialized specialists and undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations. A mammologist or gynecologist or endocrinologist can help in this matter. A laboratory blood test for hormone levels is required, as well as an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands (ultrasound).
If there is a suspicion of infectious inflammation, a surgeon should examine the child. In most cases, the inflammatory process in the chest develops against the background of Staphylococcus aureus entering the body. It can penetrate through the excretory ducts in the mammary glands or through the damaged upper layer of the epidermis if it is not properly cared for. These factors provoke the development of mastopathy.
In severe cases of infection, the development of phlegmon is possible - a severe pathological condition accompanied by extensive purulent inflammation, which has no clear boundaries.
This condition is especially dangerous for young girls, since the disease can lead to irreversible structural changes in the mammary glands. Complications include underdeveloped breasts at an older age, as well as blockage of the excretory ducts.
This form of mastopathy requires complex treatment, including surgery.
Causes of physiological mastopathy in newborns
Ambient temperature influences the development of physiological mastopathy in a newborn
The development of the disease in newborns indicates the course of a hormonal or sexual crisis. This pathological condition develops as a result of the penetration of a large concentration of the hormone estrogen from the mother’s body into the genitals or mammary glands of the child.
According to statistics, mastopathy develops more often in girls, due to the removal of maternal hormones. Also, a list of negative phenomena from the external environment leads to the appearance of the physiological form of the disease.
- Constant contact of the child with external stimuli, as a result of which all the baby’s senses are involved: visual, auditory, tactile and taste buds.
- During birth, the baby is faced with such a natural phenomenon as gravity. She was absent during intrauterine development.
- Ambient air temperature. The indicators are significantly lower in comparison with the temperature environment in a woman’s body. For example, it was stable 37 degrees, but it became no more than 25. For a child, this is a sharp change and not every body is able to adapt to this in a limited period of time.
The physiological form of mastopathy in newborns rarely becomes pathological.
Treatment and prevention
In newborns and children under one year of age, in most cases, diagnosed mastopathy does not require treatment unless its course causes pain. In adolescence and adults, it is mandatory to undergo a therapeutic course, especially for people with a predisposition to developing cancer.
Treatment of mastopathy in children under one year of age
If therapy does not produce results, surgical intervention is necessary
In a child under 9 months, the development of pathology is considered a consequence of hormonal imbalance. To relieve symptoms, the doctor can develop a preventive treatment course, including mild medications and observation.
In severe cases of the disease, hormone replacement therapy is required. If it does not bring positive dynamics, mandatory surgical intervention is required.
It is forbidden to self-medicate, especially with taking hormonal drugs, since hormonal imbalance can unpredictably affect the condition of a still fragile body, complications can be irreversible.
It is prohibited to copy standard treatment protocols, since each organism is individual and the genetic level of hormones is different for everyone.
Treatment of the disease in adolescent children
Mastopathy in teenage girls can become diffuse
In teenage girls, breast mastopathy develops in a diffuse form. This pathological condition is accompanied by the formation of a large number of small nodules, which are almost impossible to detect upon palpation. The total mass of tissue in the chest increases, provided that the specific mass of breast tissue remains unchanged - this state of affairs aggravates the functioning of the endocrine and thyroid glands, which leads to hormonal imbalance.
Treatment includes the following steps:
- Examination. As a rule, making a diagnosis requires the opinion of three specialized doctors - a surgeon, an endocrinologist and a mammologist. Everyone evaluates the condition and proposes an effective treatment regimen. To make a diagnosis, blood tests for thyroid hormones, growth hormone and sex hormones, as well as an ultrasound, are prescribed.
- Based on the results obtained, taking into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body, a therapeutic course is drawn up. Physiotherapy sessions are sometimes added to traditional treatment, for example, UV radiation, vibration therapy, electrophoresis.
If surgical intervention is required, the procedure can be carried out in several ways - traditional excision of excess tissue and laser removal, during which the integrity of the skin is not compromised.
Source: https://NogoStop.ru/grud/lechenie-yunosheskoj-mastopatii-molochnoj-zhelezy-u-podrostkov.html
Mastopathy of newborn girls and boys
After birth, serious hormonal changes occur in the child's body. The body is rebuilt and gradually gets used to life outside the womb, which is what causes the fairly frequent occurrence of a sexual crisis. The main symptom of this condition is swelling of the mammary glands.
This phenomenon is observed in infants of any gender, both girls and boys. The color of the skin may also change and a rash may appear, but it is worth remembering that specific treatment should not be used in such cases.
Sexual crisis is a special physiological manifestation of the child’s condition, characterizing his ability to adapt.
What is the phenomenon
The development of the crisis is due to the fact that during gestation, female hormones related to the reproductive sphere enter the fetus’s body. They cross the placenta and support the normal development of pregnancy.
After birth, the level of this hormone decreases significantly. The advantage of this feature is observed in the first 4 weeks of life. A sharp decrease in the level of this hormone provokes significant jumps in other substances in the body. The main cause of changes occurring in the mammary gland is hormonal changes.
Physiological mastopathy gradually increases, after which it goes away on its own within a few weeks.
On average, mastopathy in newborns, both boys and girls, is observed in 70% of cases.
Mastopathy occurs in full-term infants. As for premature babies or children with developmental delays, signs of crisis appear much less frequently. Many experts agree that the absence of such manifestations must be equated to a pathological process.
The crisis manifests itself mainly in healthy children or in those who adapt well to intrauterine life. In this case, the period of gestation should pass without various kinds of deviations or pathologies. Crisis plays an important role in the development of the hypothalamus; in addition, children with crisis are less likely to develop jaundice.
The development of mastopathy in a newborn is a normal reaction of the body to a lack of female sex hormone. It does not require special treatment or separate influence.
Signs of crisis development
There are many signs of a hormonal crisis developing in a newborn:
- The appearance of mastopathy in a newborn.
- Discharge of fluid from the vaginal area in girls.
- Rashes.
An increase in diameter of up to 3 centimeters is considered a normal indicator, provided that there are no visible changes on the skin. In some cases, neonatal mastopathy may be accompanied by the release of a small amount of fluid from the mammary glands.
Mostly mastopathy develops a few days after birth. Its decline occurs at the end of the first week. A phenomenon such as neonatal mastopathy does not require special treatment. Experts emphasize that it is impossible to influence the mammary glands using physiological methods or use various medications.
For a child, this phenomenon does not cause discomfort. During this period, you need to be especially careful about the friction of clothing in this area. It is not worth taking any measures, since physical impact can cause infection in the wound. The penetration of infection causes the development of a rather serious complication - mastitis. This disease is difficult to treat and quite often leads to a tragic outcome.
Mastitis in babies
A disease such as mastitis can occur due to improper care of the child, that is, if his hygiene is not taken care of, when ulcers appear, caused by sweat, as well as when infections penetrate through the nipple area.
Symptoms of the disease and treatment measures
In the final stages of inflammation, the skin becomes quite red. The development of the disease is accompanied by a disturbance in the general condition of the child. Characterized by a significant increase in body temperature.
The child refuses the breast and becomes lethargic. As the disease develops, a significant increase in size of the mammary gland is observed. As the disease progresses, the affected areas become denser.
Features of mastitis treatment
If you have certain symptoms indicating the development of mastitis, you should consult a doctor. Treatment of this disease is carried out exclusively under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital setting.
First of all, specialists conduct an analysis and determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to various influences. Based on the test results, the specialist selects the optimal treatment.
Treatment of this disease takes place in several stages:
- At the initial stage, special compresses and antibacterial agents are used to prevent the development of inflammation.
- When the purulent form develops, the accumulated pus is opened and removed. After the intervention, special dressings and antibacterial drugs are used.
Mastopathy in newborns is quite common. Thus, the so-called hormonal crisis manifests itself. This phenomenon is quite normal for a baby and does not require any additional exposure. However, the child’s condition should be constantly monitored in order to notice the development of mastitis in time.
Source: https://grud03.ru/bolezni/mastopatiya/u-devochek-novorozhdennyih.html
Mastopathy in children (newborns, 1 year old, adolescents)
Mastopathy is a common childhood pathology that occurs quite often, regardless of age group. Many adults, having discovered signs of illness in their child, do not know how to behave correctly and how to help their child. Let's try to figure this out. Mastopathy in children is an active proliferation of glandular tissue in the mammary glands, which is mainly benign in nature. If there is no treatment, the tumor can transform into malignant, and then it will pose a serious threat not only to the life, but also to the health of the baby. Interestingly, the development of mastopathy in newborn boys or girls is not perceived critically by doctors. But if we are talking about a teenager, then the disease requires immediate treatment.
Pathology of newborns
Causes
What are the main reasons for such active development of the mammary glands in young children? The fact is that while the fetus is in the womb, a fairly large amount of female sex hormones (estrogens) enters the baby’s body through the placenta. After the birth of the child, the level of hormones in his blood dropped, which led to the appearance of specific symptoms.
Symptoms
The development of mastopathy in infants is manifested by the following signs:
- an increase in size and noticeable engorgement of the mammary glands in children of both sexes;
- the appearance of discharge from them;
- temporary increase in the size of the genital organs;
- rashes on the skin;
- discharge from the genitals in newborn girls (can be either white or bloody).
In some cases, neonatal mastopathy is accompanied by a rise in body temperature.
Therapy
Mastopathy in newborns in most cases does not require specialized treatment and goes away on its own within a few weeks. During the period of disease activity, careful medical monitoring of the child’s condition is recommended.
Some doctors recommend lubricating pathological lesions with a weak solution of manganese. This must be done to prevent the development of infection.
It is imperative to consult a doctor if the symptoms of the disease do not disappear within the first six weeks.
What is prohibited to do
If signs of mastopathy appear in children under one year of age, it is strictly forbidden to put any pressure on the mammary glands. The secretion secreted by the breasts should not be squeezed out under any circumstances!
What is the danger?
Mastopathy in children is dangerous due to the development of such a serious complication as purulent mastitis. Pathology develops due to non-compliance with basic hygiene rules, as well as due to improper handling of sore breasts.
The disease is characterized by inflammatory processes, severe pain and a jump in temperature. Purulent mastitis is most often provoked by a pathogenic bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus. In advanced cases, the complication can lead to complete death of the mammary glands.
Disease in children 1 year and older
The development of mastopathy in girls and boys older than the first year of life is accompanied by the same symptoms as mastopathy in a child under one year old or a newborn.
Causes
Unlike a child who has not yet turned 1 year old, in older children the reasons for the development of the disease are not physiological in nature. Mastopathy in boys and girls can be provoked by:
- endocrine pathologies;
- liver pathologies;
- neurological diseases;
- some medications.
Treatment approaches
Unlike infants, in older children the disease is not ignored. First of all, the cause that led to the development of the disease is established.
All efforts of doctors and parents should be aimed at eliminating it. If mastopathy in children has developed due to the use of specialized medications, it is recommended that they be discontinued under the supervision of a physician.
If discontinuation of the drug is not possible, a replacement is selected.
Illness in teenagers
Mastopathy in adolescents is most often characterized by diffuse changes. At the same time, multiple compactions form in the mammary glands, mainly in girls, which can be easily palpated. In rare cases, the nodes are large. In young men, this disease is called gynecomastia.
Causes
Pathology in most cases is caused by hormonal changes that any growing organism goes through. Such mastopathy, like a disease in a newborn or infant, can be considered physiological; it goes away as soon as puberty is completed.
It is important to remember that in adolescents the disease can be not only physiological. Its development can be caused by stress, complications due to diseases of other organs and systems, and taking certain medications. It is necessary to carefully determine the cause of the disease in order to treat it.
Diagnostic methods
- Mastopathy is a disease that is diagnosed in adolescents through a thorough collection of complaints and an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
- If problems with hormones are suspected, the girl may be sent to take tests for them.
- Mammography is not used as a diagnostic method before the age of 35!
Treatment
Preventive actions
There is no specific prevention of pathology. It is recommended for adolescents to prevent the development of the disease:
- avoid psychological pressure and stress;
- get enough sleep;
- Healthy food;
- control of chronic diseases and regular medical examinations
- to refuse from bad habits;
- take daily walks in the fresh air.
Mastopathy is a disease that in most cases does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child. The main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner so that he can determine the causes of the disease and help select the correct treatment.
Source: https://GrudExpert.ru/bolezni-msh/o-mastopatii/u-detej/
Manifestation of mastopathy in newborns
Mastopathy is considered a disease of the mammary glands. Characterized by tissue growth in the chest area. This disease has several varieties, all of which have the same symptoms. It responds well to treatment, but in some cases surgery is necessary.
Newborn boys and girls are equally susceptible to mastopathy
Mastopathy occurs in newborns. It happens to girls and boys. In most cases, it goes away on its own and only occasionally requires special treatment.
Mastopathy and sexual crisis
From a medical point of view, physiological mastopathy occurs as a result of a sexual crisis, which is recognized as a certain transitional state for a newborn child, when it adapts to the world outside the mother’s belly. Mastopathy is the most common symptom. About seventy out of a hundred infants are susceptible to it. More common in girls than boys.
During the entire long period of pregnancy, the child receives a large amount of hormones from the mother through the placenta. These are estrogens. They help the baby grow and develop throughout the entire gestation period.
Their level in the blood of a newborn is very high and begins to fall sharply immediately after birth. The maximum peak of this decline occurs at the end of the first or beginning of the second week of the baby’s life.
Due to everything that is happening, other hormones in the bloodstream begin to change their concentration and their level in the body increases. A so-called “hormonal explosion” occurs. Mastopathy occurs against its background.
Additionally, its development is helped by breastfeeding, which also contains a certain amount of hormones.
It disappears on its own when the body’s adaptation is complete and the hormone levels return to normal.
Mastopathy usually occurs on the second or third day of a newborn’s life. Lasts from ten days to one month. The duration depends on the characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth, breastfeeding and the child’s body itself.
Main symptoms of mastopathy:
- A slight increase in the size of the mammary glands. It happens on one or evenly on both glands. The degree of swelling rarely exceeds two or three centimeters.
- Slight redness around the nipples. Observed due to breast engorgement.
- Whitish or grayish discharge. In small quantities, they resemble mother's colostrum. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze them out.
There are several additional signs of a sexual crisis, which include: swelling of the external genitalia and discharge (menarche) from them, vulvovaginitis and a whitish-yellow rash on the face (milium). All of the listed symptoms rarely bother the baby, which cannot be said about his mother.
Separately, it is worth saying that the absence of a pain symptom helps to distinguish mastopathy from purulent breast diseases. If the discharge of the mammary glands becomes abundant, then this is a serious reason to show the baby to the doctor. In other cases, all symptoms are considered a normal reaction of the child’s body to the loss of maternal hormones.
Mastopathy in a newborn is manifested by painful swelling of the breast
About treatment
As has already been said many times, physiological mastopathy is an adequate response of a newborn child to adapt to the outside world. That is why it does not require any special treatment.
It’s enough just to be very careful and gentle with your baby’s mammary glands so as not to cause unnecessary skin irritation. Protect them from friction with clothing. Massaging the breasts and tightly swaddling the baby is strictly prohibited.
But there are exceptions to all rules. In some cases, some treatment will still be required. This applies to situations where all the symptoms of mastopathy are pronounced and there is significant swelling and copious discharge from the breast.
Treatment options:
- gentle treatment of the baby’s mammary glands with a weak solution of manganese or fucarcin;
- applying a sterile, warm and dry dressing to the child’s chest;
- Warm camphor oil helps a lot, which should be applied to the chest for five minutes using a gauze pad soaked in it.
In exceptional cases, mastopathy can be pathological. This development of events occurs when the characteristic symptoms persist for more than one month or two and additional signs of a sexual crisis are added to them. It is in such situations that urgent assistance from a specialist is required.
For additional diagnostics, your doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the mammary glands and a blood test to determine hormone levels. The help of a surgeon is often required if the tissue enlargement does not stop and nodules begin to form in the chest.
Sometimes hormonal medications may be prescribed for use by the mother. The child will receive them through her milk. This treatment requires great care so as not to harm the baby.
Another reason to see a doctor would be the baby’s frequent crying for no apparent reason, moodiness, and breast refusal. All this may be signs of purulent mastitis. It requires immediate treatment, as late presentation may result in surgery and possible loss of one or both breasts.
Unreasonable crying may signal mastopathy
A few facts
Many experts believe that mastopathy, along with other manifestations of the sexual crisis, plays an important role in the formation of sexual differentiation and the development of the hypothalamus.
An interesting fact is that mastopathy most often occurs in full-term babies. Premature babies or those born with intrauterine growth retardation, as well as immature babies, are less likely to have this symptom.
Some parents worry about the appearance of symptoms of the disease and begin to squeeze out the contents of the glands, massage the breasts, thereby introducing microbes into the cracks of the papillae. As a result, a serious complication develops – mastitis of newborns.
Therefore, such procedures are strictly contraindicated for mastopathy. But preventive measures will help:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before handling your baby, especially after walking or using the toilet;
- bathe your baby every day;
- change diapers and nappies in a timely manner, wash them;
- Keep sick people away from your child.
If the parents are still young and inexperienced or are simply very worried, and there is no one to ask questions, then do not hesitate to contact a medical professional - a nurse or a pediatrician. They will be able to assess the baby’s condition and give the necessary recommendations.
The process of adaptation to a new and unknown world for a child is very difficult. He learns to breathe, eat and perceive a lot of information on his own. Physiological mastopathy is one of the signs of the successful occurrence of these processes.
But it often frightens parents and raises many questions about the health of their beloved child. There is no need to be afraid, you just need to follow the specialist’s recommendations and follow preventive measures.
Then everything will pass on its own, leaving no trace.
Source: https://vrachlady.ru/mastopatiya/mastopatiya-u-novorozhdennyh.html
Mastopathy in newborn girls and boys: treatment
More than half of all newborn children, both girls and boys, may experience a state of genital (hormonal) crisis.
One of the manifestations of such a hormonal crisis in a newborn is considered to be physiological mastopathy. This is just one of the possible transitional states, which is associated with the adaptation of a newly born child to a new life for him.
Is it necessary to treat infants in such cases, and is this not dangerous to health? Let's find out.
Why does physiological mastopathy occur and how does it manifest?
Every future baby, while in the womb of the mother during pregnancy, constantly receives a significant amount of female hormones, which are vital for him at this time.
After childbirth, this hormonal supply ends; naturally, the child’s hormonal background changes somewhat, and the levels of female sex hormones, in general, drop quite sharply.
Moreover, the peak point of drop in the level of certain hormones of the child can usually occur on the seventh, maximum tenth day of the newborn’s life. Most often, physiological mastopathy still manifests itself in newborn girls, although boys do not always avoid this fate.
At the same time, while the baby is breastfeeding, a small but still increase in size, swelling and swelling of the mammary glands begins to occur.
Such changes in the glands, in most cases, are strictly symmetrical. The very degree of swelling (enlargement) of the breast usually does not exceed two centimeters.
Swelling is often accompanied by subtle discharge from the glands themselves. Typically, this discharge may resemble colostrum released from the mother's breasts.
Similar symptoms are usually observed on the third or fourth day of the baby’s life. And by the seventh or tenth day of life, this state reaches its maximum.
In most cases, mastopathy in newborns does not bother the babies themselves; rather, new mothers begin to get nervous about this.
A little later, say, after the tenth day of life, mastopathy, or rather its symptoms, gradually begins to decrease. And approximately, by the beginning of the second month of life of newborns, all manifestations disappear.
It must be said that in some cases, mastopathy in newborn girls may have slightly more significant manifestations. Namely, this form of hormonal crisis in newborns can be accompanied by:
- Significant swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands.
- Noticeable redness of the skin around the baby's nipples.
- Moderate whitish discharge from the mammary glands, which is strictly forbidden to squeeze out.
It is important to remember that if suddenly the discharge from the baby’s chest becomes abundant, the baby must be shown to the doctor.
Is it necessary to treat physiological mastopathy?
It should be understood that the described state of hormonal crisis (a form of crisis called mastopathy) is a physiological condition, and therefore does not require strictly specific treatment at all.
Usually, a simple careful and careful attitude towards the baby’s mammary glands is more than enough, which will prevent unnecessary irritation of the baby’s skin.
However, doctors still sometimes prescribe restorative treatment. For example, treatment may be required if the manifestations of mastopathy are too pronounced, and to a greater extent, we are talking about the abundance of discharge from the mammary glands.
In such cases, treatment includes the most gentle treatment of children's mammary glands with a weak solution of liquid potassium permanganate or a solution of fucarcin.
Sometimes such treatment also involves applying a dry, necessarily sterile, warm bandage to the chest (but this can only be dry heat).
Unfortunately, there are rare cases when neonatal mastopathy is not a physiological condition, but a very specific pathology. When symptoms persist for more than a month or two, when the baby is bothered by other manifestations or concomitant pathologies.
Naturally, in this case, the newborn requires other strictly specific treatment, which depends on the problems that the doctor notices.
Source: http://OMastopatii.ru/o-zabolevanii/gormonalnyj-kriz-novorozhdennyx-mastopatiya.html
Neonatal mastitis
Neonatal mastitis is an acute infectious and inflammatory disease of the mammary gland in children in the first weeks of life. It manifests itself as external changes in the breast area in the form of engorgement, a bluish-purple tint of the skin over the affected area and local hyperthermia. There is always a general increase in temperature to 39C° or more, and pus may be separated through the central duct of the mammary gland. Neonatal mastitis is diagnosed clinically and laboratory. Conservative and surgical treatment is carried out, tactics are determined by the stage of abscess formation.
Neonatal mastitis is quite rare. In some cases, this condition is mistakenly attributed to neonatal mastopathy with somewhat similar clinical symptoms, but the causes of the latter are hormonal and not associated with infection.
Neonatal mastitis is equally common in girls and boys. The relevance of the disease in pediatrics is associated with the general anatomical features of children of this age, the severity of the pathological process, and its danger to the life and health of patients.
Rapid generalization of infection with the development of sepsis is possible, which significantly increases the risk to the baby’s life.
On the part of parents, there is often overdiagnosis associated with physiological engorgement of the mammary glands (mastopathy of the newborn), and subsequent self-medication, which can seriously worsen the child’s condition and negatively affect his health.
Neonatal mastitis
Neonatal mastitis develops due to infection of the tissues of the anterior chest wall. The main pathogens are staphylococcus and streptococcus.
As a rule, a violation of the norms of care for newborns predisposes to the development of infection, leading to the appearance of diaper rash, in the area of which the pathogen is detected. Microcracks and injuries in the area of the mammary glands play a certain role, where the formation of the primary focus of infection occurs.
Neonatal mastitis most often develops during the period of physiological engorgement of the baby’s mammary glands, which occurs in the first two weeks of life.
Neonatal mastitis usually appears between 7-10 days of a child’s life. The development of typical signs of the inflammatory process is characteristic. First, attention is drawn to a lump in the breast area, usually one-sided. At the same time, there is an increase in body temperature, often significant, up to 39C° and above.
Palpation is painful, but the area above the affected gland is not changed at the initial stages. Later, the skin over the source of infection acquires a bluish-purple tint, and the infiltration zone is replaced by a site of fluctuation. This means that an abscess has already formed in this area. Hyperthermia continues to increase, and the child’s general condition suffers due to intoxication.
Upon palpation, slight discharge of pus is possible, sometimes pus is released spontaneously.
The basis of diagnosis is physical examination and history taking. Upon examination, the pediatrician detects an infiltrate or a zone of fluctuation, a local and general increase in temperature. On palpation, purulent discharge can be noticed. A general blood test reveals leukocytosis with a shift to the left and other signs of infection.
The causative agent is reliably determined after examining the contents of the abscess. It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of mastitis in newborns with mastopathy, which occurs in almost all children after birth. This condition is also manifested by engorgement of the mammary glands and hyperemia (there are some signs of inflammation).
The main difference is the absence of infection as such.
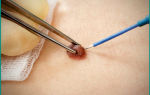
During the infiltration phase, conservative therapy is carried out. Physiotherapy using UHF and UV irradiation methods and treatment with local remedies are indicated. Already at this stage, antibiotic therapy begins, the drug is selected empirically. After the formation of a focus of infection, surgical treatment of neonatal mastitis is carried out. Mastitis is opened using radial incisions that do not affect the areola.
More often than not, multiple incisions are used. After opening, the pus is separated. The incisions are drained for several days, and bandages with a hypertonic solution are added to the treatment for faster sanitation of the source of infection. Antibiotic therapy continues, and it is possible to select a drug taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen established during the study of purulent discharge.
The prognosis for neonatal mastitis is favorable. The outcome is usually a complete cure. In some cases, infection may spread through soft tissues with the formation of phlegmon. This complication is life-threatening due to the rapid development of sepsis with multiple organ failure.
Treatment is surgical only, the child is observed in the intensive care unit and resuscitation room. Complications of neonatal mastitis are rare and, as a rule, are the result of late diagnosis, and therefore the inattention or inexperience of parents, since the infection often develops after discharge from the hospital.
Preventive measures include following the rules of caring for a newborn and regular examinations of the child’s body.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/children/neonatal-mastitis
masstop.ru
Despite the fact that there are several types of mastopathy, it always manifests itself in the same way: when palpated, a thickening is felt, and when pressed, a clear liquid is released. This disease occurs not only in women, men, but even in newborns.
The child, while in the womb, receives female hormones that are so necessary for him during this period. After childbirth, hormonal levels change dramatically and a sexual crisis occurs. It occurs in 70% of newborns and its absence is more likely a deviation from the norm than a normal condition of the newborn. Physiological mastopathy is considered one of the main signs of a sexual crisis, and it is expressed in the swelling of one or two mammary glands. Normally, the enlargement of the gland should be no more than 3 cm and should not have any redness of the skin. Sometimes a gray or milky white substance is released from the breast, resembling maternal colostrum. Swelling of the glands usually appears on the second day after birth. Special treatment for physiological mastopathy is not required, because this phenomenon is temporary and, for the most part, goes away after 4 weeks. It is very important at this time to protect the baby’s mammary glands from compression and try not to swaddle him tightly.
Mastopathy or mastitis?
Mastopathy and mastitis are two terms, the difference between which not everyone understands. Despite the fact that the symptoms of these diseases, at certain stages, are the same, these diseases are still different. Mastitis is a disease in which an infection (for example: staphylococci or streptococci) enters the breast tissue.
With mastitis, a newborn's temperature may rise sharply, and the mammary glands may become red and inflamed. This condition can be provoked by a young mother’s failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, and physiological mastopathy in a short time develops into purulent mastitis.
There are two types of mastitis: • physiological;
- • purulent.
- Physiological mastitis does not require treatment, it goes away on its own, you just need to maintain hygiene when caring for the child.
If the baby becomes capricious, often cries for no apparent reason and refuses to breastfeed, this may be a sign of purulent mastitis. It is this type of disease that requires immediate treatment. Purulent mastitis is especially dangerous for girls, because late treatment or improper treatment can result in complete or partial loss of the mammary glands.
Treatment of mastopathy in newborns
In order not to harm the growing body, the question of treatment should be decided only by a doctor, because mastopathy develops under the influence of many factors and an individual approach is required in each individual case.
Most often, treatment of physiological mastopathy is limited to treating the mammary glands of a newborn child with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or applying warm compresses to them. Sometimes, when the symptoms of the disease persist for more than a month, doctors prescribe hormonal drugs to the mother, which she will use, and the child will receive them through breast milk.
If the discharge does not stop and additional signs appear that bother the baby (for example, nodes), then specific treatment may be required, which is prescribed by the doctor after conducting an additional examination. Sometimes, you have to resort to surgery, after which all symptoms disappear, but, fortunately, such serious cases are rare.
Any mother needs to remember that mastopathy in a newborn is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance, and in no case should it be treated on its own. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is imperative to show the child to a pediatrician, who, if necessary, will write a referral to an endocrinologist or surgeon.
Source: http://masstop.ru/mastopatija-u-novorozhdennyh.html
What is mastopathy in newborn boys and girls?
In newborn children, a hormonal crisis quite often occurs, which can result in physiological mastopathy.
And this disease affects not only girls, but also boys. This is due to the transition of a newborn child from one state to another.
When a child is in the womb of a woman, he receives hormones from the mother, which affect his development. After birth, the child finds himself in a completely different environment, as a result of which his body stops feeding the female hormones that it needs during the adaptation period.
Due to changes in hormonal levels, a child experiences a powerful sexual crisis, which leads to the appearance of mastopathy in newborn girls and boys.
70% of children experience this disease.
The crisis is characterized by a sharp decrease in female hormones in the newborn’s body. This peak occurs on days 7-10 of a child’s life.
This is expressed in the swelling of one or two mammary glands in the child.
Another cause of the disease is the consumption of breast milk by the child of a mother who has a hormonal imbalance in the body. Swollen mammary glands should not have any redness.
Newborn boys and girls are susceptible to mastopathy. But according to medical statistics, girls more often experience a hormonal crisis after birth, which leads to the manifestation of physiological mastopathy.
Mothers should be more attentive to their babies if they have this problem. During this period, special care for the mammary glands of children is required. Women are not recommended to swaddle their baby tightly so as not to disrupt the blood flow in the body.
Symptoms
Symptoms of mastopathy in newborns have their own characteristics. The most important thing is the swelling of the mammary glands, which exceed the established norm.
This can also include:
- the appearance of rashes on the skin that resemble acne;
- swelling or enlargement of the child’s genitals may appear;
- girls may have discharge that resembles menstrual discharge;
- there may be a whitish discharge from the swollen glands;
- the skin around the nipple may turn slightly red;
- swollen glands are symmetrical;
- The baby does not experience pain in the mammary glands.
IMPORTANT If the newborn's discharge becomes profuse, it is necessary to show the baby to the doctor.
Physiological mastopathy is not included in the group of diseases of newborns that would threaten their life or health. This is a passing disease that in most cases does not require special treatment.
- While the baby is in the womb, he receives a large amount of estrogen from the woman with nutrients.
- As soon as a child is born, the flow of hormones into the body abruptly stops, as a result of which, after a few days, the newborn experiences changes in the mammary glands and genitals due to a lack of this female hormone.
- The so-called hormonal crisis is associated with the newborn’s adaptation to a new lifestyle, nutrition, cold or heat, bright light, loud sounds.
During this period, complex processes occur in the newborn’s body that are no longer associated with the mother’s body. And the most important thing is a sharp reduction in the child’s intake of estrogen.
The mother has an excess of these hormones in her blood, and when they enter the baby’s food through breast milk, they cause an imbalance in the baby’s body. Therefore, this disease in newborns is considered a normal condition without deviation from the norm.
At what age does it go?
The peak of symptoms appears after the 2nd day of the child’s life. It is on days 3-4 that signs of physiological mastopathy appear. By the 10th day of the baby’s life, they reach their maximum, and then begin to go away on their own. By the second month of life, the child has no signs of physiological mastopathy.
IMPORTANT If the symptoms of the disease last more than 2 months, the newborn must be shown to a doctor.
Since this type of disease is not a pathology, in most cases mastopathy goes away on its own. But with pronounced symptoms, especially if it is more profuse discharge or severe redness in the mammary glands, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
Read more in the article about the course of mastopathy during and after pregnancy. And also wondering whether a woman can cure mastopathy by breastfeeding? Find out the answer here.
Treatment for a newborn is as follows::
- The baby's mammary glands must be regularly treated with a slightly pinkish solution of potassium permanganate. In addition to this solution, you can use fucorcin.
- It is very important that your baby's clothes are spacious. It is necessary to avoid rubbing the mammary glands.
- Tight swaddling of a newborn is contraindicated.
- A sterile dressing should be applied to the mammary glands. It should be warm and dry.
- If the symptoms do not go away for more than a month, the woman is prescribed hormonal drugs so that they enter the baby’s body along with breast milk.
Forbidden:
- Warm up the glands. This can cause inflammation or mastitis. You can only apply a slightly warm sterile cloth.
- It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out the contents of the glands.
- Massage is not allowed.
- Ointments, decoctions and compresses from traditional medicine recipes are strictly prohibited for a child.
- Physiological mastopathy in a newborn child in most cases goes away on its own and does not threaten the baby’s health.
- But in any case, it is best to consult a doctor about this so that he can monitor the course of the disease.
- You can find more information on this topic in the Mastopathy section.
Source: https://nesekret.net/mastopatiya/u-novorozhdennyx