From this article you will learn:
- what causes caries,
- what role do individual characteristics play?
- theories of caries occurrence.
Caries of hard dental tissues is a process of their destruction, which occurs with the obligatory participation of cariogenic microorganisms of the oral cavity (as part of soft microbial plaque) and food debris stuck between the teeth. Cariogenic bacteria metabolize food debris and secrete a lot of organic acids, which, when in contact with tooth enamel, wash minerals out of it - primarily calcium in the form of hydroxyapatite.
Thus, the main cause of dental caries is irregular or insufficiently effective oral hygiene.
However, it is worth recognizing that for different people, even with the same level of oral hygiene, the situation with the development of caries is different. This is due to the individual characteristics of each person.
For example, different people have different levels of enamel resistance to acids, which depends on the structure of the enamel, determined by a genetic factor.
What caries looks like in the oral cavity and on a tooth cut -
Among other individual factors that increase the caries resistance of enamel are the high buffering capacity of saliva (i.e., its ability to neutralize acids), the rate and volume of saliva secretion, and the content of lysozyme in the oral fluid.
Thus, the risk of caries is affected not only by poor oral hygiene, but also by the degree of effectiveness of protective factors - 1) the degree of caries resistance of tooth enamel to acids, 2) the volume and composition of oral fluid.
For example, under conditions of low rate and volume of salivary secretion, there will be a more pronounced rate of plaque growth, as well as a higher rate of tooth decay.
In people who have the habit of snacking between main meals (for example, chips, flour, sweets) or who often consume sugar-containing drinks, the risk of developing caries becomes maximum, even if tooth enamel is highly resistant to acids.
Why caries appears: 414 theories
Now the causes of dental caries have been fully researched and understood. But historically, scientists have argued about the question: why caries appears throughout the last centuries. Believe it or not, a total of about 414 theories have been proposed.
We will not list all the theories, but will focus only on the currently generally accepted theory of the development of caries, which was developed in 1898 by Miller. In the original, this concept is called “chemical-parasitic”, and the main role here is given to dental plaque (Fig.
3-4).
In principle, at the very beginning of the article, we already presented this concept, according to which the main role is given to cariogenic bacteria of the oral cavity in the composition of dental plaque - primarily streptococci, actinomycetes and lactobacilli.
If there are food residues in the mouth (especially fast carbohydrates), these bacteria produce acids that dissolve tooth enamel.
In the process of demineralization of enamel, a gradual destruction of its structure occurs, which leads to the formation of a carious cavity.
Poor oral hygiene –
What bacteria cause dental caries?
The bacteria that cause caries are primarily Streptococcus mutans. And to a much lesser extent these are “Streptococcus sanguis”, as well as actinomycetes and lactobacilli.
It should be noted here that the effect of these cariogenic bacteria is not expressed equally in all people - in some people the activity of these microorganisms, and accordingly their pathogenic effect, is more pronounced, and in some less.
This difference is also associated with the state of general and local immunity.
Thus, it has been established that in people with weakened immunity, soft plaque forms more actively than in people with strong immunity.
Moreover, if soft plaque can still be removed with a regular toothbrush, simply by brushing your teeth, then tartar can no longer be removed on your own.
Tartar adheres very tightly to the teeth, and it can only be removed at a dentist’s appointment using, for example, ultrasonic teeth cleaning (24stoma.ru).
Soft plaque turns into hard tartar gradually (over several days), due to the impregnation of the plaque with calcium salts.
Consequently, as soon as tartar has formed, the negative impact of microorganisms continues constantly, even if you suddenly start brushing your teeth regularly after meals, carefully removing soft plaque and food debris.
→ Methods for preventing dental caries
Additional causes of caries -
We have already said above that in addition to the main factors (dental plaque and food debris), there are also causes in the oral cavity that predispose to the appearance of caries. These include:
- The presence of crowded teeth (Fig. 6) – this contributes to food getting stuck between the teeth and also complicates the process of oral hygiene. Therefore, such patients almost always experience rapid formation of dental plaque, gum inflammation, and dental caries.
- Low rate and amount of saliva secretion - salivation helps to some extent to wash away food debris from the teeth after eating. So per day, normally about one and a half to two liters of saliva should be produced. If a person’s salivation is low, then this is a prerequisite for faster development of caries.
- Neutral indicator of saliva acidity – saliva has an alkaline environment, which is determined by its buffer capacity. Therefore, it can to some extent neutralize organic acids produced by cariogenic bacteria. However, if a person has a low buffering capacity of saliva, it will have a neutral pH and, accordingly, will no longer be able to neutralize organic acids that dissolve enamel.
- Dietary disorder – one of the decisive factors is the frequency of consumption of carbohydrates (sucrose, glucose, fructose, lactose and starch). Therefore, periodic snacks between main meals in the form of cookies, sweets, buns, etc. (provided there is no subsequent immediate brushing of teeth) – leads to the development of caries.
Where does dental caries most often occur?
First of all, caries forms in places where soft plaque and food debris accumulate. These critical areas in the oral cavity include:
- Tooth necks (Fig. 7) – accumulations of plaque and tartar can most often be seen in the area of tooth necks (along the gingival margin). It is under the layer of dental plaque that demineralization of tooth enamel actively occurs, which leads to the formation of carious defects. Therefore, in dentistry there is even a separate form - the so-called cervical form of caries.
- Interdental spaces (Fig. 8) – food debris gets stuck in these spaces and cannot be cleaned out with a toothbrush. For these purposes, it is necessary to use dental floss, and most people either do not use it at all or use it irregularly. As a result, so-called interdental caries occurs, which can be quite difficult to diagnose in time, and treatment requires complex manual skills from the doctor (restoring the contact point between the teeth).
- Dental fissures (Fig. 9) - the chewing surfaces of large teeth (molars and premolars) have deep grooves on the surface called fissures. The latter are a good place to retain food residues. In dentistry, there is even a separate form called fissure caries. By the way, it was precisely for its prevention that a method of sealing fissures with liquid-flowing filling materials was invented.
Forms of caries (stages of development) –
In the development of the carious process, it is customary to distinguish 4 stages, each of which reflects the depth of tooth destruction:
- Caries in the white spot stage is visually determined in the form of a white or chalky spot, with a matte surface (devoid of shine). White spots are areas of demineralization in which the enamel has lost a lot of calcium. At the same time, the formation of a carious defect at this stage does not yet occur. The surface of such spots is rough; when mechanically applied with a sharp instrument, the enamel is easily scraped off.
- Superficial form of caries - a defect is formed within the enamel, without damaging the dentin (dentin is the tooth tissue that is located under the enamel). Thus, the bottom of the carious cavity will not be deeper than the enamel-dentin border.
- Medium caries - the process spreads to dentin, but without affecting its deep layers (immediately surrounding the tooth pulp).
- Deep form of caries - the destruction process extends to the deep layers of dentin near the pulp of the tooth, thus, only a very thin strip of healthy dentin remains between the pulp and the bottom of the carious cavity.
Consequences of caries -
Caries, if not treated on time, gradually leads to the development of pulpitis.
The difference between caries and pulpitis is that during caries, only the destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs without concomitant inflammation of the dental pulp (neurovascular bundle).
When the destruction process goes very deep and the cariogenic flora penetrates the tooth pulp, its inflammation occurs, which is accompanied by acute or chronic aching pain.
Lack of timely treatment of pulpitis leads to the development of periodontitis (a disease in which inflammation already extends beyond the boundaries of the tooth). In this case, granulomas (purulent sacs) form in the area of the apex of the roots of the diseased tooth, and fistulas form on the gums. We hope that our article: Dental caries causes - was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in therapeutic dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dentist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook” (Borovsky E.),
5. “Practical therapeutic dentistry” (Nikolaev A.).
Source: https://24stoma.ru/karies-prichiny.html
Causes of caries
Caries is characterized by softening of the enamel and the formation of a defect in the form of a carious hole. The health of our teeth leaks into these “black holes”. The disease has not one, but a whole variety of causes: hygiene, nutrition, the chemical composition of the secretion of the salivary glands, heredity and others.
There are more than 400 theories of the occurrence of caries, but only one of them is unambiguous: teeth are spoiled by “bad” cariogenic bacteria (Streptococcus mutans, Aktinomyces viscosus, etc.). They live in the mouth of every person, including you personally.
5 theories of the occurrence of caries
Neurotrophic
According to this 1934 concept, disease arises from the nervous system's response to environmental stimuli. For example, stress, emotional overstrain, and unfavorable social conditions worsen the condition of the central nervous system (CNS). As a result, pathological reflexes arise that disrupt the trophism (nutrition) of hard tissues.
Proteolysis-chelation
According to this paradigm, caries is promoted by the simultaneous processes of proteolysis and chelation:
- Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins under the influence of enzymes (enzymatic attack of microbes on enamel proteins).
- Chelation is the destruction of the enamel layer due to the combination of calcium ions with aions (negatively charged ions) of acids.
Scheme of action of caries
Miller's chemical-parasitic theory
Back in the 19th century, the German dentist W. Miller conducted research and proved that caries is a consequence of the destructive effects of organic acids. Bacteria in the mouth ferment carbohydrates (sucrose), resulting in fermentation.
As a result of fermentation, acids are released (formic, acetic, etc.), which destroy the dental coating. It is Miller's theory that underlies modern ideas about the etiology of caries.
Entin's physicochemical theory
This model states that tooth enamel is a membrane that separates two environments (saliva and blood). The membrane passes osmotic currents caused by different pressures of the internal and external environment. Due to metabolic disorders, as well as the chemical composition of the secretion of the salivary glands, the strength and direction of the current changes. As a result, resistance to adverse factors decreases.
Trophic (biological) theory according to Lukomsky
Lukomsky claims that the basis of caries pathogenesis is a deficiency of vitamins (especially vitamin D), as well as insufficient or excessive content of minerals (calcium, fluorine) in food.
Because of this, the nutrition of enamel and dentin deteriorates, their composition changes, and therefore a destructive carious reaction occurs.
External conditions also matter, because it is known that vitamin D is produced in the body under the influence of sunlight.
Scheme of the influence of various factors on teeth
Why does caries develop in adults?
The main danger to teeth is the bacterial microflora of the oral cavity. Bacteria literally “stick” to the enamel along with saliva, forming a dense biofilm.
The main causative agents of caries are streptococci, actinomycetes and veillonella. During their life, they process sugar, releasing organic acids. Acids “corrode” the enamel and wash away calcium.
The source of sucrose and other carbohydrates are microparticles of food that remain in the mouth after eating. Sweet and flour products are a real nutritional paradise for bacteria. The first 20 minutes are especially dangerous; during this period, the acidity of the oral cavity increases sharply. Therefore, it is very important to rinse your mouth after eating, or even better, use a toothbrush.
Now it is obvious that caries is a problem for people who neglect hygienic care, therefore:
- Bacteria must be removed daily.
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day.
- Use a mouthwash with an antiseptic.
- Remove pieces of food stuck between teeth with floss.
Here are other conditions for the appearance of caries that are typical for adult patients.
Gum recession
Recession is a decrease in gum level. This problem is a consequence of age-related changes. Due to a lack of nutrients and oxygen, the gums lose elasticity and recede. Plaque adheres to the exposed roots of the teeth, and caries begins.
Decreased saliva production (xerostomia)
Saliva plays an important role in the fight against tooth decay. This liquid contains valuable immunoglobulin proteins with antibacterial properties. It also neutralizes lactic, acetic and other organic acids due to its alkaline environment.
Many older people experience a decrease in the production of oral fluid and, as a result, dry mouth. Such patients have a high risk of developing caries. The appearance of insufficient salivation is also facilitated by taking medications - antidepressants, hormonal drugs, etc.
Bad habits
Smoking and alcohol abuse have never improved anyone's dental health. Cariogenic bacteria feel perfectly protected under the yellow nicotine coating. In addition, hot smoke together with resin particles dries out and injures the enamel. Microcracks form on the surface of the teeth, where bacteria and acids penetrate.
The occurrence of caries in children
The cause of caries in children is exactly the same as in adult patients: violation of hygiene rules and accumulation of microbial plaque. However, children's teeth decay faster and are more prone to caries.
The highest caries activity is observed between the ages of 2 and 11 years. And that's why:
- baby teeth are covered with a thin enamel layer with high permeability;
- dentin (inner tissue) of baby teeth has a special structure; it is penetrated by hundreds of microtubules;
- local immunity is still very weak and cannot fully cope with harmful bacteria.
Caries of baby teeth
About 30% of children under 2 years of age have dental caries. The upper and lower incisors are destroyed first. Behind these troubles is a bottle filled with a sweet drink. If you give your baby juice, compote or fermented milk products before bed, cariogenic bacteria will actively multiply in your mouth.
At night, the salivary glands “sleep”; fluid is not produced in sufficient quantities, so nothing prevents microbes from destroying tooth enamel. It is also not recommended to introduce a child to sweets, chocolates and other sweets under 3 years of age.
Infant bottle caries is often a consequence of calcium deficiency in the mother in the first trimester of pregnancy. Severe toxicosis at the beginning of the period, viral and infectious diseases also affect the formation and growth of dental tissues.
Caries in teenagers
Wearing braces contributes to the formation of caries in adolescents. Of course, braces themselves are not dangerous, but after their installation, dental care becomes much more difficult. Food particles constantly accumulate between the grooves, which are difficult to remove with a regular toothbrush. Here you need a special brush.
But if a child does not take care of his teeth during the period of orthodontic correction, and is also fond of chips, toffees, popcorn and other prohibited foods, then caries is guaranteed! All pulling and crunchy foods get stuck between the elements of braces and create a favorable environment for bacteria.
Another nuance: caries in adolescents is often activated due to hormonal changes.
Risk factors for caries formation
Local
- Crowding of teeth - it is impossible to carry out high-quality hygienic care; food particles remain between the teeth, which contributes to the process of fermentation and decay;
- excessive consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates - this applies to lovers of sweets, cakes, sweet soda, flour products;
- reduced pH of the oral cavity - within a few minutes after taking sucrose (sugar), the pH level drops from 6 to 4. The destruction of the surface enamel layer begins at a pH of 4.5;
- lack of rough food in the diet - rough food of natural origin, for example, apples, carrots, pumpkin, provide natural mechanical cleaning of the enamel;
- the presence of fissures - small tubercles on the chewing surface; plaque often accumulates in such areas and caries occurs.
Another “popular” reason is the accumulation of tartar. Due to poor hygiene, a soft coating forms, which over time turns into hard, rocky deposits. They can no longer be removed at home; it is necessary to undergo ultrasonic cleaning at the dentist.
Neglect of hygienic care also leads to the formation of pellicles. This is a thin organic film covering the enamel, it helps to attach microorganisms to the tooth surface.
Fissure caries
Are common
- Lack of calcium, fluorine and phosphorus - these minerals are the main building materials for teeth;
- vitamin D deficiency – calcium is absorbed thanks to vitamin D, which is produced by the body under the influence of ultraviolet rays and also comes from food (fish, caviar, fatty dairy products);
- weakened immunity - the fight against any bacteria, including caries pathogens, becomes difficult with low immunity;
- systemic diseases of the body - chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, endocrine systems;
- various extreme effects on the body - radiation, high, low temperatures, stress;
- poor quality drinking water;
- heredity - determines the shape, size of teeth, as well as the structure of hard tissues and the chemical composition of saliva.
Source: https://MyDentist.ru/blog/prichiny-kariesa/
Causes of caries - theories of the disease
What problem do people most often come to the dentist for? There is no need to think and guess - of course, with caries.
Where does it come from in healthy people? In fact, there are several good reasons - we’ll talk about them in today’s article, and we’ll reveal all the secrets of the development of caries, and dwell on its varieties and treatment methods.
We will also learn about the problem “first hand” - from patients and dentists. Read the detailed material and you will find out everything.
What is known about caries
According to WHO statistics1, caries is one of the most common diagnoses in the modern world. It affects about 98% of adults and 75% of children of preschool and school age. As for children, this pathology ranks first, surpassing even bronchial asthma, which is the “scourge” of our time.
Caries is a very insidious disease, because in the early stages it does not make itself felt. Therefore, a person begins to sound the alarm when he notices a hole in a tooth or a sudden pain.
For a number of reasons (which are the subject of today’s article), there is a gradual destruction of hard dental tissues - enamel and dentin, which can ultimately lead to various complications and tooth loss.
Interesting fact! Translated from Latin, “caries” means “rotting.” Initially, this was the name for purulent-necrotic inflammation of the bone marrow, which, in fact, had nothing in common with carious lesions of the teeth.
Causes of caries development
So what are the main causes of dental caries in adults and children? Let's figure it out. Previously, people made many guesses about what causes caries, until at the end of the 19th century2 they put forward the theory that the disease was of a chemical-parasitic nature.
This theory formed the basis of the modern generally accepted concept of caries formation, which is used by all professional dentists. Its essence lies in the fact that under the influence of microorganisms that make up bacterial plaque, irreversible destruction of dental tissue occurs.
The combination of the following factors causes the development of carious lesions in the oral cavity.
1. Bacterial plaque and tartar
A toothbrush, even when used correctly, removes only soft plaque, but is completely useless in the presence of interdental calculus, which also consists of microbes (streptococci, staphylococci and actinomycetes). Pathogenic microflora produces organic acids, toxic enzymes and allergens, which negatively affect the mineral composition of the enamel, causing its destruction.
The photo shows tartar
2. Poor nutrition
Increased consumption of sugar, starch and carbohydrates (found in baked goods and flour products) creates increased acidity in the oral cavity, which negatively affects the density and stability of enamel.
The main constituent substance, hydroxyapatite, begins to deteriorate in it. In addition, under the action of salivary enzymes, sucrose is formed, which serves as an excellent source of nutrition for microorganisms.
Therefore, sweet tooth lovers are more likely to suffer from tooth decay.
3. Decreased salivation
The volume of saliva of a healthy person secreted by the salivary glands during the day is 1.5-2 liters. Saliva, in addition to its enzymatic properties, has the ability to wash away food debris from the teeth. With decreased secretion, less fluid is produced. Accordingly, more food will settle on the teeth, which is directly related to the formation of a bacterial film.
4. Violation of the mineral composition of the enamel
Proper nutrition promotes dental health
Demineralization of enamel occurs due to poor nutrition, when a person receives little calcium and phosphorus from food. These essential microelements are found in cottage cheese, cheese, sunflower seeds, red beans, oatmeal and buckwheat. Violations of the mineral composition and thickness of the enamel can be hereditary or occur due to problems during fetal development.
Fluorine plays an important role in mineralization, which is well absorbed in drinking water. In recent decades, in regions where the fluoride content is extremely low, this trace element has been added to the water supply system.
5. General diseases of the body
Thyroid diseases, diabetes and hormonal disorders affect metabolism, which makes minerals less absorbed. Therefore, in patients with such ailments, carious lesions are detected more often than in others.
6. Poor environmental conditions
Unfavorable environmental conditions in a certain region (where there are many factories with harmful atmospheric emissions) or in production (where alkalis, salts of heavy metals and acids are used) affect the entire body as a whole and the absorption of necessary minerals by tooth enamel.
Harmful emissions into the atmosphere have a bad effect on tooth enamel
Varieties and classification
Currently, when making a diagnosis, the dentist is guided by several widely used classifications. Let's look at them in more detail.
1. Classification according to the stage of the process
- initial: the stage of the “chalk” stain, the very beginning of the destruction of the enamel surface and the leaching of minerals. Difficult to diagnose at home, but is considered completely reversible under favorable conditions, i.e. correct and timely treatment,
- superficial: the infection penetrates the tooth enamel and appears as a yellow or gray stain. The patient sometimes notes increased sensitivity to sweets and sours,
Source: https://anZub.ru/lechenie-zubov/prichiny-kariesa/
Stages of caries - Symptoms and manifestations of caries
Caries, like any disease, develops gradually. Carious disease does not occur suddenly; the development of even initial caries requires time and favorable factors, since carious disease occurs as a result of a group of factors, and not just one cause. The stages of caries are characterized by the depth of penetration into the tooth tissue and the degree of destruction. Caries, if left untreated, is an irreversible process that can lead to the development of complications, tooth loss, and the development of caries on adjacent teeth.
Symptoms of caries development
Caries has several striking manifestations. In the initial stages of the disease, the symptoms are almost invisible, they do not bother the patient or cause discomfort. Over time and the development of the disease, the manifestations worsen, the intensity of the symptoms increases, and additional external and internal signs appear, noticeable to the patient and the people around him.
The initial stage is a change in the color and structure of the tooth
A change in tooth color indicates the beginning of a pathological process.
Caries in its initial form is characterized by almost imperceptible changes in the structure of the tooth surface - the appearance of lines, grooves, irregularities, roughness, as well as the appearance of white, yellowish or dark spots on the tooth enamel.
A change in the color of dental tissues is a sign of demineralization of the enamel, that is, its gradual destruction; if the resulting stains are brown or black, the demineralization process has transferred to the dentin.
Cavity formation
The formation of cavities or as we call holes in the dental tissue is the main sign of caries. In the initial stages of the formation of the disease, the cavities are hardly noticeable and cause almost no inconvenience.
As caries progresses, cavities can be easily felt with the tongue and change color. Also, the resulting cavities are sensitive to temperature changes.
In some cases, at this stage of the disease, patients are often bothered by aching toothache.
Dentin damage
Increased tooth sensitivity
One of the most striking manifestations of caries is increased sensitivity of teeth to temperature and taste of food. Damage to tooth enamel causes a sharp reaction to cold, hot food and drinks, and is also expressed by acute pain when eating sugary foods.
The severity of the symptom varies, depending on the level of damage to tooth enamel and the degree of development of carious disease. Sometimes tooth sensitivity occurs not only during eating, but also during changes in ambient temperature. With progressive caries, the affected tooth may react with pain when moving from a warm room to the street and back.
Brushing your teeth with a regular toothbrush can also cause discomfort and pain.
Uncomfortable sensations while eating food
In addition to the increased sensitivity of teeth to the temperature of food, with caries the very process of chewing food causes discomfort or pain.
The patient has the impression that the tooth is pierced by pain to the very root; the pain can be described as sharp, sharp, strong, even unbearable.
However, when the stimulus disappears, it goes away quite quickly on its own.
Toothache
The development of caries can cause spontaneous toothache of various types (from mild aching to severe acute) for no apparent reason. Painful sensations occur suddenly, at any time of the day, regardless of food intake and activity. In this case, toothache is easily relieved with a painkiller or goes away on its own after a while.
Having bad breath
Bad breath is a constant companion for patients suffering from dental caries. The nature and intensity of the smell can be different and completely depend on the amount and degree of damage to dental caries. It is noteworthy that in the vast majority of cases the patient himself does not feel the unpleasant odor.
If you are concerned about at least one of the listed symptoms, call us at 8 (495) 221-21-18 or leave your information in the recording form. The Dentistry clinic on Shchelkovskaya “Diamed” is attended by a team of highly qualified specialists.
We use modern methods of pain relief with insulin syringes, work with current filling materials, and provide a guarantee for the work performed.
Make an appointment with the dentist now, don’t wait until caries reaches an acute stage and causes excruciating toothache!
Stages of caries
Spot
The initial stage of carious disease in the form of a light or dark spot is considered the easiest to treat, since it does not require significant dental interventions and is most often treated with several procedures to restore tooth enamel. In some cases, it is difficult to identify caries on your own at the stain stage due to the specific location of the tooth.
Superficial caries
Superficial caries destroys tooth enamel and affects the top layer of dentin. The structure of the tooth surface changes - the damaged area of dental tissue becomes uneven, rough, and sometimes grooves or lines appear on it. At this stage, the damaged tooth becomes more sensitive and reacts to temperature changes.
Median caries
Median caries is characterized by damage to the deeper layers of dentin. Caries at this stage causes increased tooth sensitivity, sharp pain during eating, and also for no apparent reason.
Deep caries
Deep caries is a complex form of the disease, characterized by a tendency to rapid progression and the development of complications.
Damage to the deep layers of dental tissue most often contributes to the transition of carious disease to the dental pulp.
Deep caries is manifested by acute pain that occurs at any time of the day, regardless of the patient’s activities, for no apparent reason. Sometimes the pain can last up to several hours, varying in intensity.
How to identify caries at home
Carry out a daily inspection of the visible surface of the teeth immediately after hygiene procedures once a day. The timing of the inspection is not important, the main thing is that you can devote enough time to it. Carefully examine all visible teeth for changes in surface structure: the appearance of white, yellowish, brown or black spots; the formation of stripes, grooves, grooves, irregularities, roughness.
If you find even a small stain that differs in color from normal dental tissue, try to determine the possible source of its appearance: remember if you ate coloring foods that day (berries, strong coffee or tea, spicy dishes, seasonings, etc. .), have you used any new dental or oral care products (toothpaste, rinse, whitening or strengthening agents, etc.). If the detected stain does not disappear after brushing your teeth again the next day, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Pay attention to tooth sensitivity. Healthy tooth enamel without damage will not allow you to experience discomfort or pain when drinking cold or hot drinks. Even if the discomfort does not cause severe inconvenience or lasts only a few seconds, you should still visit the dentist as soon as possible.
Particular attention should be paid to those teeth that have previously undergone dental treatment. There are forms of caries that develop under a filling, so if you suddenly feel pain in an already treated tooth, immediately visit a doctor. A change in tooth color, chipping of a filling, or the appearance of roughness on the surface of a filling are also reasons to contact a dentist.
The reason for an urgent visit to the doctor is a tooth injury.
If, due to chemical or mechanical action, a part breaks off from a tooth, a crack appears on its surface, the structure of the surface or the color of the dental tissue changes, you must contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Regardless of the location of the tooth, even minor damage can lead to disastrous consequences. Particularly dangerous are cases when the damage entails the loss of a significant part of the tooth or its fracture along the growth from the edge to the root.
Source: https://smile4you.ru/blog/lechenie-zubov/stadii-kariesa/
Dental caries
Dental caries is the process of demineralization and destruction of hard tooth tissues with the formation of a cavity defect. It is characterized by the appearance of a yellowish-brown pigment spot on the enamel, bad breath, a tooth reaction to sour, sweet, cold or hot foods, and aching pain. With the development of deep caries, the formation of cysts, the addition of pulpitis, and then periodontitis are possible. Advanced caries can lead to tooth loss. The presence of unsanitized carious cavities increases the risk of developing acute and chronic diseases of the body.
Dental caries is a destructive process of a dystrophic or infectious nature, occurring in the bone or periosteum and ending in complete or partial destruction of the tooth. Carious disease is the most common disease among the adult population.
According to WHO, the incidence of dental caries in different countries and among different populations ranges from 80% to 98%.
In the last two decades, there has been a trend of increasing incidence among children, especially in economically developed countries, and by the age of 6-7 years, 80-90% of children have caries of varying depths.
Dental caries is not an independent disease, and pathological conditions of the body as a whole are an important pathogenetic link in its development. Thus, a decrease in general and local immunity, pathology of the gastrointestinal tract and errors in diet contribute to the development of caries.
Today, there are about four hundred theories about the occurrence of caries, but most of them are based on the fact that due to poor oral hygiene, plaque appears on the enamel, which leads to the development of caries.
Plaque appears due to improper and irregular brushing of teeth, especially in places that are difficult to reach for cleaning and in places where it is not removed naturally during chewing (the side surfaces of the teeth, the recesses of the chewing surfaces).
Dental plaque firmly binds to the surface of the tooth and is a habitat for bacteria, most of which are streptococcal flora. Mineral salts contained in saliva help thicken plaque. Such formations of plaque and mineral salts are called dental plaque.
Bacteria living in dental plaque produce lactic acid, which demineralizes tooth enamel. Demineralization of tooth enamel is the first stage of the carious process. The polysaccharide dextran, which is produced by streptococci from sucrose, promotes the process of demineralization, which is why the development of caries is associated with eating large amounts of simple carbohydrates.
The activity of microorganisms in dental plaque and the demineralization process depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
In most people, resistance to cariogenic bacteria is weakly expressed, while in people with a good immune system and in the absence of concomitant diseases, resistance is quite high.
In people who have immunodeficiency conditions, caries develops more actively. And in children with exudative diathesis and rickets, caries disease is diagnosed 2 times more often.
When the composition of saliva changes, when the ratio of mineral salts in it is disrupted and its natural antibacterial properties are reduced, the risk of developing caries increases.
Somatic diseases and errors in a diet with a deficiency of minerals, especially during the period of tooth formation, significantly reduce resistance.
Hereditary enamel pathologies (enamel aplasia or hypoplasia) and extreme exposure to the body, in combination with other factors, increase the likelihood of carious disease.
Living in industrial areas, unfavorable environmental conditions and poor drinking water reduce the overall protective functions of the body, which can become an important pathogenetic link in the occurrence of caries.
Sticky residues of carbohydrate foods and deviations in the biochemical composition of hard dental tissues are the main local factors that contribute to the development of the carious process.
The state of the dentofacial system during the period of formation, development, eruption and formation of teeth is of great importance in the further state of the dentofacial system.
Depending on the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, 4 forms of caries are distinguished.
- At the stage of a carious stain, clouding of the tooth enamel occurs. There is no visible destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth; instrumental examination with a probe is not very informative, since at this stage there are still no signs of changes in the structure of the hard tissues of the tooth. Sometimes the stain may regress; the reasons for this phenomenon are not clear, but dentists associate self-healing with the activation of the immune system.
- The second form of caries is superficial caries. Dark pigmentation appears on the surface of the tooth; during an instrumental examination, softening of the enamel is revealed in the pigmentation area. Sometimes, already at the stage of superficial caries, all layers of tooth enamel are involved in the destructive process. But usually the defect is limited and does not extend beyond the enamel. A carious lesion appears as a dirty gray or brown spot with a rough bottom.
- With average caries, enamel and dentin tissues are affected.
- With deep caries, complete destruction of all tooth tissues occurs, up to complete destruction of the tooth. Subjective sensations depend on the depth of the lesion and the severity of caries. Typically, patients complain of acute pain when sour, sweet or cold food gets on the affected surface or in the carious cavity. When the irritating factor is eliminated, acute toothache subsides; as a rule, spontaneous pain due to caries does not occur.
In the acute course of caries, a number of teeth are simultaneously affected, the affected tissues are dirty gray in color, softened, the focus of destruction has an irregular outline, its edges are undermined, and the pain syndrome is more pronounced. The most acute course of caries is characterized by damage to almost all teeth, with each tooth having several foci of carious lesions.
The chronic course of caries disease is characterized by pigmentation of the affected areas, their compaction and smoothness of the edges. Individual teeth are affected, usually the process is sluggish. If left untreated, caries is complicated by pulpitis and periodontitis, which is the main cause of tooth destruction and subsequent removal.
Caries is diagnosed during visual and instrumental examinations of the dentist. The patient’s subjective sensations allow us to judge the depth of the process, but are not the main diagnostic criteria. During the diagnostic process, targeted radiography of the tooth and electroodontometry are performed.
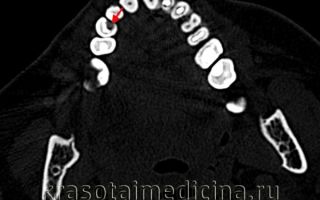
CT scan of the jaws in the bone window. Carious cavity on the mesial side of the canine crown of the lower jaw.
The main principle of caries treatment is to remove the affected tissue and restore the tooth with filling materials. During the sanitation of a carious cavity, all affected tissue is removed.
The cavity is thoroughly disinfected, sometimes for this purpose temporary fillings are installed, under which there are disinfectants. The better the disinfection of the carious cavity, the stronger the filling will hold.
High-quality strengthening of weakened tissues depends both on the high-quality removal of the carious lesion and its disinfection, and on what stage of the development of carious disease treatment began.
Classical preparation of a carious lesion occurs using a drill, but today there is an alternative option - laser preparation. The procedure is characterized by painlessness, noiselessness and the quality of preparation of the tooth cavity for further filling.
Treatment of superficial caries is possible in several ways. A common method is tooth preparation and subsequent filling of the carious cavity.
A prerequisite for this treatment method is the creation of a cavity within the dentin, but when creating a small cavity, the conditions for creating a two-layer filling from an insulating spacer and the filling itself are not sufficient.
These factors are taken into account when filling carious cavities on the chewing and contact surfaces of premolars and molars.
Another technique is to use new composite materials with high adhesive properties, which will make it possible to fill superficial caries without deep preparation of tooth tissue. The third method is to grind off the carious area followed by remineralization.
Remineralization of enamel is carried out using applications or electrophoresis with a 1% solution of sodium fluoride (deep fluoridation of teeth) or using other approved remineralizing drugs.
In case of average caries, only the method of preparing the hard tissues of the tooth with subsequent filling of the carious cavity is possible.
Treatment of deep caries is associated with certain difficulties, since the restoration of an almost completely destroyed tooth requires not only professionalism from the doctor, but also the choice of technique. Sometimes, with deep caries, the tooth pulp is covered with a layer of intact dentin; in some cases, the doctor is forced to leave pigmented and softened dentin in the carious cavity.
Such cases of deep caries require the application of a therapeutic pad to the bottom of the carious cavity (calcemin paste is most often used). This pad has an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulates dentinogenesis.
That is, a filling for deep carious lesions consists of three layers: a therapeutic pad, an insulating phosphate cement pad and a permanent filling material, most often an amalgam.
The choice of filling material is based on the group of teeth.
In order to restore the anatomical shapes of the front teeth - incisors and canines, as a result of filling, requirements are imposed on the filling, both in terms of strength and aesthetics.
For filling these groups of teeth, the material is selected in accordance with the color of the patient’s teeth, which is possible with silicate cements and composite materials.
It is imperative to comply with the technological process when preparing filling material, because the use of good components without following the technology for preparing the material and if the technique for installing the seal is not followed significantly reduces its durability.
Preparing a carious cavity for filling involves carefully removing dentinal filings using a stream of water or air. Next, the cavity is disinfected and dried, because even slight traces of moisture significantly impair the adhesion of cements, light polymers and composite fillings.
After the filling has hardened, it is ground and polished, first removing excess protrusions. The better the surface of the filling is polished, the less microorganisms and food debris are retained on its surface.
The uniformity of the outer layer reduces the likelihood of corrosion of the filling and prevents its rapid destruction.
Treatment of even chronic and advanced caries with filling allows you to restore the integrity of the tooth surface, prevent pulpitis and complete tooth destruction.
Prevention of caries is the fight against soft plaque, which includes the use of high-quality toothpastes and toothbrushes, the use of dental floss, and regular professional oral hygiene procedures.
If tooth enamel is weakened, then fluoridation of teeth using fluoride-containing preparations: pastes, solutions and varnishes is indicated to strengthen it. A balanced diet high in solid foods and low in simple carbohydrates prevents the growth of microorganisms in the mouth.
In areas where the quality of drinking water is poor, it is recommended to use water from other regions.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology/dental_caries