Literary editor Elena Berezhnaya and scientific editor Sergey Fedosov worked on the article by Dr. Ignatenko T.A.
Published January 12, 2018 Updated July 20, 2019
The term “leukoplakia” (translated from Greek as “white plaque”) was proposed by Schwimmer in 1887 to describe whitish areas of the mucous membranes of the cheeks, which were regarded as precancerous changes. In Russian literature and clinical practice, the term remains generally accepted to this day. Abroad, the preferred term is “dyskeratosis.”[2]
The focus of leukoplakia can be located on the mucous membrane of the lower lip, corner of the mouth, floor of the mouth, cheeks, in the anogenital area, on the vulva, clitoris, in the vagina, on the cervix, less often - in the area of the head of the penis, in the circumference of the anus.[11 ]
According to statistics, the incidence of cervical leukoplakia is only 0.7 per 100,000 cases of gynecological morbidity, among cervical diseases - 5.2%.[11]
Cervical leukoplakia is most common in the age group 17-39 years.[9]
In most countries in Europe and the United States, where organized screening for cervical cancer is carried out, cervical leukoplakia is not actively searched for until cytological smears reveal the initial stages of cervical dysplasia (precancer). In our country, the tactics for monitoring and managing cervical leukoplakia are more active.
The causes of the development of cervical leukoplakia are divided into:
- internal (endogenous): hormonal imbalance, immune disorders in the body;
- external (exogenous): infectious, chemical, traumatic.
Hormonal imbalance often means a chronic lack of ovulation, which leads to an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone in the body with a predominance of the former.
Relatively increased concentrations of estrogen, in turn, act on target organs (breasts, body and cervix), leading to hyperplastic processes (an uncontrolled increase in the number of cells).
[4] Often, patients with cervical leukoplakia are diagnosed with increased prolactin levels. Immune disorders are often manifested by inflammatory processes of the uterus and its appendages (vaginitis, salpingo-oophoritis, cervicitis).
[9] A domestic study revealed an increase in the concentration of secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA) in patients with such underlying cervical diseases as ectopic columnar epithelium and cervical leukoplakia.[8]
Chemical and traumatic effects often mean intensive and inadequate treatment for “pseudo-erosion” of the cervix: approximately a third of patients with leukoplakia had previously undergone diathermocoagulation and other destructive interventions on the cervix. An important factor in the development of cervical leukoplakia is prolapse and prolapse of the uterus/cervix, which is accompanied by inevitable disruption of the vaginal flora and, in severe cases, a permanent contract between the cervix and the external environment.[5]
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Often the disease is asymptomatic. Only about a third of patients complain of profuse leucorrhoea and contact bleeding (after sexual intercourse, use of tampons, gynecological examinations).
The mechanism of development of leukoplakia is not precisely understood. It is believed that under the influence of causative factors, the mechanisms of keratinization of the normally non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium of the cervix are activated. Horny scales, cells with a deformed nucleus and intracellular components, form on the surface of the cervix.[2]
According to the classification of Ya.B. Bohman (1976), leukoplakia, along with pseudo-erosion, ectropion, polyp, cervical endometriosis, cervicitis, true erosion of the cervix, is included in the group of background diseases of the cervix, in which cells with atypical signs are not detected, but the long-term existence of which can serve as a factor risk of developing precancer.
Abroad, cervical leukoplakia with cellular atypia is classified as a group of precancerous pathology of the cervix - CIN (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, or dysplasia, of the cervix).[2]
Leukoplakia can spread from the cervix to the vaginal vaults. Malignant degeneration of leukoplakia cells is observed in 31.6% of patients according to domestic authors, 4.9-9% - according to foreign data.[11]
A comprehensive examination for leukoplakia includes:
- a survey identifying risk factors for the development of the disease (menstrual cycle disorders, past inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, long-term existence of “pseudo-erosion” of the cervix);
- inspection;
- colposcopy (examination of the vaginal part of the cervix with magnification). It is worth noting that extensive foci of leukoplakia are visible to the naked eye. With colposcopy, you can evaluate in detail the tender or coarse whitish deposits on the surface of the cervix that are not stained with Lugol's solution (an aqueous solution of potassium iodide).
During colposcopy, the type of transformation zone (the transition zone at the junction of two types of integumentary epithelium of the cervix - stratified squamous and cylindrical) and the location of leukoplakia are determined.
The vaginal part of the cervix (exocervix) is covered with stratified squamous epithelium. In the cervical canal (cervical canal, endocervix) there is a cylindrical epithelium.
The place of transition of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal into the multilayered squamous epithelium of the surface of the cervix is called the transformation zone.
This area is of great clinical importance because it is where more than 80% of cases of cervical dysplasia and cancer occur.
Type 1 transformation zone - the transition zone is completely visible. This is the most optimal and prognostically “favorable” version of the colposcopic conclusion.
Type 2 transformation zone - the transition zone is partially hidden in the cervical canal. It is difficult to adequately assess such a picture, since the most altered areas may not be visible and may be missed.
Type 3 transformation zone - the transition zone is located deep in the cervical canal and cannot be assessed colposcopically. Colposcopy in this case is considered uninformative, since the depth of the pathological focus remains unknown.
- cytological (PAP test) and histological (obtained by biopsy) examination of cells and tissues of the cervix; The difficulty of diagnosing leukoplakia using a simple cytological scraping from the cervix lies in the impossibility of assessing the full cellular composition, since due to dense horny scales on the surface of the multilayered squamous epithelium of the cervix, cells from the deep layers may not be included in the scraping. In this way, precancerous transformation or even cervical cancer may be missed.[3] That is why the main method for diagnosing cervical leukoplakia is the examination of cervical tissue obtained through a mandatory targeted biopsy against the background of colposcopy. Transformation zones of types 2 and 3, determined during colposcopy, can serve as a reason for performing not only a biopsy, but also curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. A more gentle method of assessing the condition of the cervical mucosa is possible using microcolpohysteroscopy (office hysteroscopy). The advantage of the method is the possibility of non-traumatic passage of the cervical canal (cervical canal) under visual control without anesthesia. During the procedure, a targeted biopsy can be performed. In histological examination, leukoplakia is characterized by the terms: keratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis.
- bacterioscopic and bacteriological examination (examination of vaginal smear and bacterial cultures for flora and sexually transmitted infections). Research is important because in the presence of cervical inflammation, the results of cytological and histological analyzes may be distorted;
- study of HPV DNA of high oncogenic risk in scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal. The effect of viral infection on the development of leukoplakia is currently being studied. Some authors believe that keratinization processes can be considered as an indirect marker of human papillomavirus infection. Leukoplakia that exists outside of HPV infection often does not become malignant. When combined with a virus, there is a possibility of malignancy, but there is no serious evidence of this fact yet.[12][13]
The most commonly used treatment methods for cervical leukoplakia are:
- radio wave surgery;
- high-intensity CO2 laser radiation;
- diathermocoagulation (as undesirable, due to the large number of potential complications, but a possible method of treatment).
Manipulations are performed in the first half of the menstrual cycle (4-7 days from the start of menstruation). To more accurately determine the pathological tissue, the procedure is controlled by colposcopy, and the cervix is treated with Lugol's solution.
Complete healing and the patient’s return to normal life (the possibility of sexual activity, the use of vaginal tampons, visiting the pool, etc.) is often expected 28-40 days after the procedure.
Correction of hormonal disorders and adequate hormone therapy, according to some data, can speed up the healing time of postoperative wounds and reduce the frequency of recurrence of benign diseases of the cervix.[10]
When leukoplakia is combined with deformation and hypertrophy of the cervix, it is advisable to perform reconstructive plastic surgery (cervical plastic surgery) to restore the anatomy of the cervical canal.[14][15]
When leukoplakia of the cervix is combined with inflammatory processes of the vagina, vulva and cervix, the priority is to eliminate the inflammatory process. You should not use products that affect tissue metabolism (sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, aloe preparations, etc.).
If the results of a cervical biopsy do not reveal cells with signs of atypia, cervical leukoplakia can be observed without exposing it to destructive effects.
Modern foreign researchers regard leukoplakia as a benign physiological process and in most situations recommend preventive monitoring.
With cervical leukoplakia, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Principles for preventing the development of cervical leukoplakia include:
- rational treatment of pathological processes of the cervix, excluding unreasonable repeated traumatic effects on the cervix of outdated methods (diathermocoagulation, chemical coagulation). Patients who have had diathermocoagulation or chemical coagulation of the cervix in the past require annual follow-up, especially if they have HPV;
- timely detection and treatment of inflammatory processes of the genital organs;
- elimination of menstrual irregularities;[1]
- An annual smear test (PAP test) reliably reveals the presence of HPV-related cell changes and precursor lesions of precancerous cervical pathology.[6]
- National Guidelines for Gynecology. Ed. G.M. Savelyeva, G.T. Sukhikh, V.N. Serova, I.B. Manukhina, V.E. Radzinsky, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2017. 541-545 p.
- National Guidelines for Gynecology. Ed. IN AND. Kulakova, I.B. Manukhina, G.M. Savelyeva, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. 746 p.
Source: https://ProBolezny.ru/lyaykoplakiya/
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a complex and at the same time complex gynecological disease.
It affects, as the name suggests, the mucous membrane of the cervix.
A descending course of the disease is possible, in which the tissue of the vagina and birth canal, as well as the external genitalia, are involved in the process. The ICD code is N88.1.
The essence of the process is the thickening of epithelial tissues, their compaction and keratinization. Translated, leukoplakia means “white plaque,” which well characterizes the pathogenic process.
Indeed, areas of leukoplakia look like white thickenings on the walls of the mucous membranes.
What it is?
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a condition in which its epithelium acquires a property uncharacteristic for this place - keratinization.
In a healthy woman, only skin cells are normally subject to this process - they are exfoliated and thus renewed. An abnormal property can appear not only in the cells of the squamous epithelium of the cervix, but also in the vagina, perineum, and oral cavity. The danger of leukoplakia is that its presence increases the likelihood of cancer developing in this area several times.
Leukoplakia is a precancerous disease. However, timely detection and treatment will avoid such disastrous consequences. Reviews from women who have suffered this illness confirm this. In each specific case, therapy is selected individually. For some, cauterization of cervical leukoplakia is suitable, while for others, laser or liquid nitrogen is better.
Causes of cervical leukoplakia
The most likely causes of leukoplakia on the cervix currently include:
1) Infectious and inflammatory diseases. Recurrent infectious inflammatory processes in the vagina negatively affect the condition of the squamous epithelium, provoking its desquamation, and also deplete the immune system. It has been reliably established that in women of reproductive age, the occurrence of cervical leukoplakia is often preceded by inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages.
Over 50% of patients with cervical leukoplakia have a diagnostically confirmed human papillomavirus. It penetrates into the mucous membranes through existing microtraumas and, roughly speaking, damages their genetic memory.
2) Hormonal dysfunction, namely absolute or relative hyperestrogenism. All processes occurring in the mucous membranes of the external genitalia depend on the state of the hormonal function of the ovaries, especially on the level of estrogen. Increased secretion of estrogen (predominance of estradiol) leads to excessive proliferation of stratified epithelium.
In women with menstrual irregularities, cervical leukoplakia occurs in 13%, and in those whose menstrual rhythm is preserved - only in 3%.
3) Injuries to the mucous membrane of various origins: abortion, childbirth, diagnostic traumatic manipulations, barrier and spermicidal contraceptives, incorrect use of vaginal hygienic tampons, aggressive sexual intercourse and others.
Leukoplakia of the cervix due to trauma to the mucous membranes is always combined with the presence of ectopia on the cervix. The resulting microdamages to the mucous membranes often heal incorrectly, this leads to the formation of pseudo-erosions, and leukoplakia appears at one of the stages of its formation.
Exogenous factors that increase the chances of developing leukoplakia include endocrine pathologies (especially diabetes mellitus) and deformation of the immune status.
Classification
According to morphological criteria, cervical leukoplakia is divided into two types: simple or proliferative.
- Simple cervical leukoplakia is a background change in the epithelial layer, representing parakeratosis or hyperkeratosis. This form of pathology is characterized by pronounced keratinization and thickening of the surface epithelial layer, but the parabasal and basal cell structures do not change.
- Proliferative leukoplakia - this pathological variety is characterized by impaired differentiation, proliferative changes in all tissue layers and the presence of atypical cellular structures. The proliferative form is classified as a precancerous condition; it is also called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical dysplasia.
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia
The disease is not accompanied by a specific clinical picture and subjective complaints.
More often, cervical leukoplakia is detected during a regular examination by a gynecologist. In some cases, indirect symptoms of cervical leukoplakia may be present - significant leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor, contact discharge of a small amount of blood after sexual intercourse.
In this case, pain does not accompany leukoplakia. Its appearance is associated with the onset of complications or other diseases.
Leukoplakia and pregnancy
Planning pregnancy if you have leukoplakia is not recommended. Doctors advise to first cure the disease and then start conceiving.
The pathology does not affect the course of pregnancy. But under the influence of hormonal changes, damaged epithelial cells can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
An additional provoking factor in this case is a decrease in immunity.
Leukoplakia itself does not prevent conception. The ability to fertilize decreases due to the reasons that provoked the pathology. Very often, gynecological diseases are accompanied by anovulation.
If the disease appears during pregnancy, therapy is postponed until the postpartum period. Labor is most often carried out naturally.
With intensive growth of horny scales, a cesarean section is indicated.
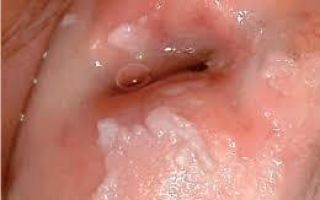
Photo
With leukoplakia, white spots appear on the cervix, which are formed after structural changes in normal tissues. The affected area differs from the surrounding healthy area in color, increased dryness and lack of elasticity.
Below is what the disease looks like in the photo:
Similar tissue degeneration can occur in the vulva and clitoris area. There, a woman can easily notice pathological changes and consult a doctor in time. For early diagnosis of problems with the cervix, it is necessary to undergo annual examinations with a gynecologist and do colposcopy.
Diagnostics
Cervical leukoplakia can be diagnosed by characteristic spots on the surface, which are detected during a routine gynecological examination. In order to determine what type of keratosis affects the cervix, whether there are atypical or cancer cells in the mucosa, and how deep the affected area is, the following examination methods are used:
- A general blood and urine test to determine the presence of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Biochemical blood test for sugar, protein (allows you to diagnose metabolic disorders that contribute to the occurrence of hormonal shifts in the body).
- Blood test for hormones. Necessary for determining the ratio of sex and other hormones, the content of which determines the nature of the cycle and the duration of menstruation.
- Blood test for tumor markers, for various types of infection.
- Bacteriological analysis of a smear from the cervix to determine the nature of the microflora.
- Biopsy of tissue from the surface of the cervix followed by examination under a microscope (histological analysis to determine the types of infection), colposcopic examination of the cervix.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs allows you to detect pathologies in the structure and shape of the uterus, the presence of areas of inflammation in its various parts.
All these methods determine the cause of cervical leukoplakia in a woman, the degree of danger of malignant degeneration, and allow you to choose the optimal method of treatment.
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia
The treatment strategy is determined by the form of detected cervical leukoplakia (simple or proliferative). The goals of treatment are the elimination of underlying diseases and the complete removal of pathological foci.
In the case of simple leukoplakia, the treatment is carried out by a gynecologist, but if signs of atypia are identified, the treatment of the disease is determined and carried out by a gynecologist-oncologist.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the affected areas of the cervix.
The question of how to treat cervical leukoplakia most effectively has not yet been resolved. Quite a few methods of influencing the pathological focus have been proposed, in particular:
- diathermocoagulation;
- exposure to liquid nitrogen;
- laser treatment of cervical leukoplakia using high-intensity radiation;
- radio wave surgery;
- general drug treatment;
- use of drugs locally.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to make sure that the patient does not have inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina caused by viruses, chlamydia, trichomonas, and fungi. According to indications, treatment is carried out with appropriate antimicrobial drugs.
Drug treatment
The following medications are used.
- Antibiotics. Prescribed for concomitant genital infections, the presence of inflammation, for example, in areas of scratching. If there are no such signs, antibacterial drugs are not used.
- Antiviral. If a concomitant lesion of HPV or HSV (herpes simplex virus) is detected.
- Immunomodulatory. Often included in regimens to increase the body's resistance. These are biological supplements, drugs from the interferon group in the form of suppositories.
- "Solkovagin". This is a solution consisting of a mixture of acids. It is used to treat the cervix in affected areas, after which a local small tissue burn is formed in these areas with subsequent restoration. Typically two to three treatments are required, spaced seven to ten days apart. But treatment with Solkovagin cannot be carried out if dysplasia or inflammation is suspected or present.
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia with folk remedies is not recommended. Substances such as sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, aloe-based products and other popular recipes can increase the proliferation of pathological cells and cause the appearance of atypical cells. We advise women not to risk their health, but to be treated according to modern ideas.
Methods for removing leukoplakia
Surgical methods that can be used to treat cervical leukoplakia:
- Thermocoagulation . The affected area is exposed to electric current, which leads to a burn, death of the affected epithelium and its replacement with healthy cells. The procedure is painful, easy to perform, and is accompanied by a high risk of bleeding and prolonged healing.
- Cryodestruction . Cold treatment is considered a modern and highly effective method. Liquid nitrogen destroys the affected area and atypical cells stop growing. The procedure has many advantages - painlessness, high efficiency, no scars.
- Laser therapy . One of the best treatment methods to date. The procedure does not require pain relief, the cervix heals quickly and does not bleed. The method is non-contact - a laser beam processes pathological cells, after which they are destroyed. At the end of the procedure, a protective film is formed on the affected surface, which prevents infection from entering the wound. The method is quite expensive.
- Radio wave therapy . It is also a non-contact and effective method that destroys the focus of leukoplakia using radio waves.
- Chemical coagulation . The affected area of the mucosa is treated with the drug Solkovagin, which contains a mixture of acids. The method is painless. However, it is effective only for superficial leukoplakia, since the product does not penetrate deeper than 2 mm.
In each case, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of treatment. Particular attention should be paid to women planning pregnancy or who have not yet given birth. The surgical technologies used in relation to them should imply the minimum possible removal of tissue, otherwise in the future the consequences of such treatment of cervical leukoplakia may lead to problems with pregnancy.
Some reviews from women:
- Evgenia, 27 years old: when cervical leukoplakia was discovered, the doctor offered a choice of cauterization or laser removal. On the recommendation of a gynecologist I knew, I opted for laser therapy, which I don’t regret at all. The procedure went without complications, quickly and painlessly. I recommend.
- Ekaterina, 38 years old: I was treated for cervical leukoplakia with traditional cauterization. There were no complications. After treatment, a year and a half later, she safely gave birth to a son. Therefore, we can safely say that the treatment was successful.
In the postoperative period, doctors strongly recommend maintaining sexual rest for 1.5 months. Lifting heavy objects, taking hot baths, and going to baths and saunas are also prohibited.
In addition, douching and the use of sanitary tampons are prohibited. It is also necessary to observe the rules of intimate hygiene.
In the first 10 days after any method of treating the cervix, heavy liquid discharge may appear, which should not frighten the woman. This is a response to treatment and indicates healing of the wound surface.
Prevention
For timely detection of pathological changes, all women are strongly recommended to undergo examination by a gynecologist at least once every 6 months.
During reproductive age, it is also necessary to take measures to eliminate menstrual irregularities. Any diseases of infectious-inflammatory origin require timely and adequate therapy.
Treatment prognosis
Yes, complete cure is guaranteed in almost 99%.
The prognosis for this disease is favorable, in case of timely treatment and elimination of provoking factors. Otherwise, the process may recur, and in 15%, leukoplakia may degenerate into dysplasia and malignant degeneration of the cervix.
Source: https://doctor-365.net/lejkoplakiya-shejki-matki/
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Update date: 05/14/2019
Cervical leukoplakia (CLM) is a gynecological disease characterized by keratinization of the epithelial cells of the cervix. The etiology of the disease includes exogenous (chemical, traumatic, infectious) and endogenous (problems with the immune system, disturbances in hormonal homeostasis) factors.
In most cases, the appearance of cervical leukoplakia was preceded by various inflammations of the uterus and appendages. In addition, various traumatic and chemical influences play a significant role in the occurrence of the disease.
Women with various menstrual irregularities, pseudo-erosions of the cervix and diseases of the genital organs are often at risk for cervical cancer.
There are two forms of the disease:
- Simple leukoplakia of the cervix. This form of pathology is classified as a background change - parakeratosis or hyperkeratosis. During diagnosis, keratinization and significant thickening of the epithelial layers are detected;
- Proliferative form. Characteristic symptoms of this form are proliferation and differentiation of all layers of the cervix, as well as the appearance of new atypical structural elements. Doctors consider this form of pathology as a precancerous condition.
Prevention of cervical leukoplakia
Prevention of cervical leukoplakia It is quite possible to prevent the occurrence and worsening of the disease. To do this, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive measures. In particular, infectious and inflammatory processes should be treated promptly. As well as cervical erosion.
In addition, it is also worth excluding abortions, as well as injuries to the uterus during gynecological operations and childbirth.
Since one of the symptoms of the disease may be menstrual irregularities, women with this pathology need to be observed by a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Regular gynecological examinations and vaccination against HPV play an important role in the prevention of the disease. Certain preventive measures should be followed even after treatment. Namely, the patient must attend a colposcopy procedure every six months, as well as undergo tests for HPV and smear tests for oncocytology.
Prognosis for cervical leukoplakia
When cervical leukoplakia is diagnosed in a young nulliparous woman, gentle methods of treating the pathology are chosen that would not cause scars to appear on the cervix. Namely, in this case, treatment methods such as laser vaporization, chemical coagulation, radiosurgical treatment, and cryodestruction are used.
If after treatment no atypia occurs, background factors have been eliminated, and no human papillomavirus infection has been detected, then the prognosis for the patient’s health is favorable. However, if the root cause of the pathology remains, its manifest course and even transition to cervical cancer is possible.
Therefore, it is very important to see a gynecologist, without missing examinations every six months.
The causes of the disease are not fully understood. However, it is possible to identify the main factors that most often cause this pathological condition.
In most cases, the disease becomes a consequence of injuries or even scratches of the cervix or infections.
As for infections, these include primarily the following: ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, gonorrhea, thrush. In rare cases, pathology develops against the background of cervical cancer or dysplasia.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, cervical leukoplakia does not manifest itself with any symptoms at all, so it can only be detected during an examination by a gynecologist.
However, if the disease develops against the background of an infectious disease, various symptoms may appear, including vaginal discharge, pain during sex, and genital itching. In addition, the woman usually feels discomfort and an unpleasant burning sensation.
If the disease has spread to the vulva, severe itching is possible, which leads to minor abrasions, scratches and scratching. In rare cases, bleeding may appear immediately after intercourse.
Have you noticed any symptoms of this disease? Call Our specialists will advise you!
The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Gynecological examination with a mirror. It is during this period that clinical manifestations of the disease are often detected. Namely, examination on a chair using mirrors helps to detect a whitish coating in the form of plaques and spots of different sizes, which take on an oval shape and have pronounced contours. Their surface may be covered with keratinized epithelium;
- Colposcopy. This technique is used specifically to detail information obtained during a gynecological examination. Namely, the doctor clarifies the size and nature of the lesion of the cervix. This procedure allows you to see white plaques, their precise and even contours, and the absence of a network of blood vessels. Colposcopy allows you to determine the size of cervical leukoplakia, which can vary from one point to a large area;
- Scraping of the cervix. Allows you to detect accumulations of epithelial cells that have signs of hyper- or parakeratosis. Nucleated keratinized scales usually indicate hyperkeratosis. With parakeratosis, an increase in the color and density of the cytoplasm of small cells is detected. For a more detailed diagnosis, doctors use histological examination of exorcervis tissue and a knife biopsy of the cervix. These two studies are aimed at identifying a precancerous condition. To exclude cervical cancer, curettage of the cervical canal is used;
- Clinical and laboratory tests. Microscopic tests, immunological and hormonal studies, HPV typing and bacteriological examination of smears are prescribed;
- In some cases, patients require consultation with an endocrinologist.
Removal of cervical leukoplakia involves the use of a whole arsenal of techniques, the most used of which are:
- cryogenic exposure;
- diathermocoagulation;
- high-intensity laser radiation;
- medicinal methods.
FSM often develops against the background of inflammatory processes in the vagina or vulva.
Therefore, before starting treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammation. For this purpose, antibacterial, antifungal, antichlamydial and antiviral drugs are used. During treatment, the patient must abstain from sexual activity for 4-6 weeks. The exact period depends on how quickly all damaged cervical tissue is restored.
If you are interested in how to treat cervical leukoplakia, then please note that this pathology is often considered as a benign process.
However, it is worth noting here that the appearance of atypical cells during the study may still indicate a precancerous process. The doctor can give a final conclusion only after a biopsy.
Therefore, we strongly recommend that you choose a clinic on our website and sign up for a diagnostic examination so that you can decide on a treatment regimen.
Chemical coagulants
In this group of drugs for the treatment of pathology, Solkovagin, consisting of a mixture of inorganic and organic acids, is primarily isolated. This drug has a coagulating effect on the epithelium. Moreover, the depth of its penetration into tissue can reach 2.5 millimeters. Treatment with this drug is completely painless, and its effectiveness is about 73%.
Diathermocoagulation
This is the most common and most frequently used method of getting rid of pathology. However, clinical studies show that, unfortunately, the method does not always give positive results. Moreover, it can cause a number of side effects:
- endometriosis;
- exacerbation of inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- pain syndrome;
- menstrual irregularities;
- relapse of the disease.
Cryotherapy
This treatment method is considered one of the most effective today, which is not at all surprising. It involves exposing pathological areas of tissue to an intense laser, which leads to their necrosis.
The procedure is carried out contact-wise, in one go and quite quickly - in just 2-5 minutes. The advantages of cryotherapy are undeniable: the procedure is painless and carried out on an outpatient basis.
However, this technique also has its drawbacks - a relapse of the disease is possible, especially if the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
Laser coagulation
A highly effective technique that allows painless, contactless, bloodless and aseptic coagulation of pathological tissue areas.
At the same time, a thin film is formed on the surface of the tissue, which prevents the penetration of infections. This technique can even be used to treat extensive tissue damage to the uterus and vagina.
In this case, laser coagulation of the cervix is first performed, followed by the removal of the epithelium itself.
It is also worth noting that in some cases it is not possible to do without surgical intervention. Namely, surgery will be needed if there is deformation of the cervix. To treat the pathology in this case, knife and laser conization, reconstructive plastic surgery, cone-shaped or wedge-shaped amputation of the cervix are used.
Of course, today medicine offers a large selection of methods for treating cervical leukoplakia. However, the choice of a specific method that is suitable in a given situation must be approached very carefully. In addition, you should know that none of the methods for treating pathology is perfect, so in many cases it is necessary to use combined treatment.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice. Consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Still have questions?
Enter your information and our specialists will contact you and provide free advice on issues that concern you.
Gynecological diseases
Source: https://www.medcentrservis.ru/disease/lejkoplakiya-shejki-matki/
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Reading time: min.
No time to read
Unfortunately, the number of diseases in the field of gynecology is increasing every day. Cases of detection of cervical pathologies in women of childbearing age are becoming increasingly common. Cervical leukoplakia is common.
What it is? This is an abnormal condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix, which does not have a specific clinical picture, and therefore is most often detected during a routine examination. So, what is cervical leukoplakia? Doctors describe this disease as a violation of the covering layer of epithelial tissue located on the vaginal part of the cervix.
I would also like to note that leukoplakia is a pathology that occurs not only on the organs of the reproductive system, but is also localized on the mucous membranes of the mouth and skin of the body.
The described disease in translation means a white plaque, which is a clinical sign of the disease when examined in a mirror. The incidence of the disease is about 15% of all cases of pathological conditions of the cervix. In addition, the risk of developing leukoplakia increases in women with irregular menstrual cycles (in such women, pathology occurs in 18-20% of cases).
Leukoplakia of the cervix causes
The reasons for the development of this pathology are eso- and endogenous factors, against the background of which structural changes in the epithelium of the cervix occur. Among the endogenous factors are:
- hormonal imbalance, which is accompanied by a decrease in progesterone levels and an increased amount of estrogen. This combination of hormonal imbalance leads to ovarian dysfunction and, as a rule, anovulation;
- inflammatory processes of the organs of the female reproductive system (uterus - endometritis, ovaries - adnexitis and cervix - cervicitis, vagina - vaginitis);
- impaired metabolism due to diabetes mellitus;
- decreased immunity, the body’s inability to respond to the penetration of a viral pathogen;
- previous diseases of the cervix, such as ectopia or the presence of ectropion, also lead to the occurrence of leukoplakia;
- the provoking factor is the presence in the woman’s body of a human papillomavirus infection or herpes virus, as well as an STI;
- vitamin deficiency, which is accompanied by a lack of vitamin A;
- age-related changes in the cervix.
Endogenous causes include:
- mechanical impact on the cervix, leading to traumatization of cervical tissue (artificial termination of pregnancy, curettage, difficult childbirth using obstetric auxiliary instruments, surgical methods for treating previously suffered cervical erosion);
- destructive effect on the epithelium covering the cervix;
- long-term use of spermicidal drugs, as well as the influence of other chemical agents, for example, when using douching;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- lack of sex education, accompanied by a large number of sexual partners.
Is leukoplakia of the cervix cancer or not?
This issue is most troubling for women with identified pathology. Answering this question, doctors describe the fine line between these diseases. It should be noted that simple leukoplakia is a background disease of the cervix.
Under certain conditions, background diseases have the ability to degenerate into oncopathology. If leukoplakia with atypia is diagnosed, the development of cancer is almost inevitable. There is no clear answer to the question posed.
Since the degeneration of leukoplakia into an oncological process depends on the cellular structure.
Nevertheless, leukoplakia is a pathological result of colposcopic examination, which causes special attention and requires long-term observation.
So, simple leukoplakia of the cervix, what is it? A simple form of the disease is the initial stage of the pathological process, which is accompanied by slight compaction and keratinization of the integumentary layer of the epithelium.
The pathological process is insignificant and the changed tissues do not rise above healthy tissues, the changes do not penetrate into the deeper layers. This leukoplakia without cervical atypia does not lead to the formation of intraepithelial cancer.
Basically, this form of the disease is treated without serious consequences.
Severe cervical leukoplakia with atypia is characterized by damage to the epithelial layer, which is accompanied by the formation of keratinized scales that rise above the surface of healthy tissues.
In addition, the visually rough form of leukoplakia is visualized by a white plaque against the background of a pale pink neck. With this form of the pathological process, damage to deeper layers is detected.
Atypia cells are formed in the deep layers, therefore, for the treatment of the diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia, conization is the most effective method. Most often, this method of treatment is recommended when determining glandular atypia in cervical leukoplakia. Removing part of the cervix in a cone-shaped manner will stop the process, which will prevent degeneration into an oncological process.
But let's get back to the fact that gynecologists identify another form of leukoplakia - focal leukoplakia of the cervix without atypia.
This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of keratinization areas with clear boundaries (foci), which rise above the surface of the cervix and have the appearance of a white plaque.
During cytological analysis, despite their clinical manifestations, atypia cells are not detected.
Classification according to ICD
Leukoplakia of the cervix in the International classification is among diseases of class XIV. This class includes diseases of the genitourinary system. Encryption of pathologies of the genitourinary system begins with N00 and ends with N99.
Since leukoplakia is a disease of the female genital organs, its coding belongs to the code block N80-N98. Behind these codes are non-inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. To be more precise, cervical leukoplakia according to ICD 10 has N88.
Other non-inflammatory diseases of the cervix. Namely, cervical leukoplakia is coded under the code N88.0.
In turn, leukoplakia is divided into: simple and lekoplakia with atypia. Simple leukoplakia of the cervix is manifested by the formation of keratinized cells on the surface of the cervix, which form a plaque. The cells that form this form of leukoplakia contain keratin. In addition, the tissues do not have microstructural changes.
Lekoplakia of the cervix ICD 10 is a background benign change and in most cases does not require radical treatment.
Lekoplakia of the cervix ICD 10 is a background benign change and in most cases does not require radical treatment.
Symptoms
Leukoplakia of the cervix, symptoms and signs in the vast majority of cases appear from a concomitant disease. As a rule, leukoplakia develops against the background of an inflammatory and/or infectious disease.
Thus, the disease is detected during a preventive examination by a gynecologist. Basically, the course of this pathology is manifested by such symptoms as discharge of an unusual color from the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse.
In addition, cervical leukoplakia is characterized by a burning sensation, itching, and contact bleeding that appears after sexual intercourse.
Treatment
When such symptoms are detected, the question arises: how is cervical leukoplakia treated? This pathological condition is treated both conservatively and using surgical methods. The choice of treatment method for the disease depends on the severity of the pathology.
In most cases, gynecologists prefer to remove pathological areas of the cervix. After which complex, specifically targeted therapy should be carried out. It should consist of prescribing antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as vitamin complexes.
Currently, there are several most common ways to treat cervical leukoplakia. These are methods of removing lesions using laser therapy, radio wave therapy, diathermocoagulation, or excision of the pathological area.
But, as a rule, before starting treatment for leukoplakia, it is necessary to undergo a series of studies. These include a smear on the vaginal flora, cytological analysis of the smear, and determination of sexually transmitted infections. A blood test to determine a woman’s hormonal levels is also recommended.
After conducting research, provided there are no concomitant pathologies, they begin directly to treat this disease.
If any of the pathologies are detected, especially the inflammatory process of the genitourinary system or the definition of a sexually transmitted infection, it is recommended to initially undergo a course of treatment for the identified diseases. In addition, cytology is an important analysis.
If the results of this analysis are questionable, a cervical biopsy is performed. For leukoplakia, a targeted biopsy is performed with sampling of the keratinized area of the cervix.
After receiving the results and preliminary therapy, therapy can be carried out regarding the diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia. Histology is necessary for differentiation from the oncological process.
Since when cancer cells are detected in histology, the treatment of the disease will be different.
So, the choice of treatment method depends on many factors that the attending physician takes into account. In each individual case, the technique is selected according to individual indications. The advantages and disadvantages of the method are taken into account. This is especially important when treating women of reproductive age.
One of the effective, but traumatic methods is cauterization of cervical leukoplakia with electric current. This method is usually called diathermocoagulation. The essence of the method is the effect of electric current on pathological areas.
As a result, a burn forms in its place, which is then replaced by healthy tissue. The method is effective, but due to its disadvantages it is currently used quite rarely. In addition, it is used only for women who have given birth. The method is cheap and accessible, but with the development of technology it is fading into the background.
Currently, preference is increasingly being given to more gentle methods, for example, cryodestruction.
Cryodestruction is carried out by exposing the pathological area to liquid nitrogen, which has a low temperature. Thus, the pathological cells freeze and die. The advantage of the method is its painlessness and the absence of scar tissue formation.
If a nulliparous woman is confirmed to have cervical leukoplakia, what should she do? In such cases, gynecologists decide to prescribe laser vaporization. This is the most gentle and effective method. As a result of exposure to rays, liquid evaporates from pathological cells, which leads to their death and death. The risk of relapse of the disease after this method is negligible.
Radio wave treatment of cervical leukoplakia is also a gentle method. With this method of treatment, a special device “Surgitron” is used. This is the latest method and is quite effective. The disadvantage of this method is the absence of antenatal clinics in all offices and its price.
With a confirmed diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia, treatment with folk remedies is not recommended. Gynecologists are categorically inclined towards such methods. Since some traditional medicines can do more harm than good. Most medicinal plants used in folk medicine provoke the growth of pathological cells.
In the vast majority of cases, at home, women use the douching method and/or tampons soaked in medicinal decoctions and infusions. Both methods can have a traumatic effect on the fate of leukoplakia. This in turn can lead to a worsening of the disease.
In addition, today there are no methods of traditional medicine, the administration of which could be appropriate and effective. Unfortunately, studies do not confirm the therapeutic effect of folk remedies in the case of leukoplakia.
Pregnancy
Cervical leukoplakia and pregnancy, as shown by long-term studies, can coexist absolutely normally. The disease does not have any negative effect on the course of pregnancy, as well as on the growth and development of the fetus.
But it is worth noting that, as we know, during pregnancy a woman’s hormonal levels actively change, which leads to the development of a sharp progression of pathology.
If leukoplakia is discovered while planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo treatment and then become pregnant. If the pathology is detected at the stage of pregnancy, its treatment is delayed until the onset of childbirth.
After this, therapy is prescribed. Childbirth is mainly carried out through the natural birth canal; in rare cases, a cesarean section is recommended.
Reviews
Most reviews about the treatment of cervical leukoplakia are based on personal experience. But in addition to reviews of women with this disease, there are reviews and recommendations based on data from many years of research. Treatment of the diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia reviews are generally positive. It is important to understand that timely initiation of therapy is the key to a favorable outcome of the disease.
The treatment of this pathology does not differ from the treatment of diseases such as erosion and ectopia of the cervix. Most women speak positively about laser treatment of pathology. The most important point before treatment is the results of cytology and determination of the form of the disease.
In fact, there are many different reviews of treatment methods. Reviews about the treatment depend on the characteristics of the recovery period. Some women underwent therapy without complications, while others experienced complications.
It all also depends on how the women followed the recommendations of their doctors. Nowadays, it is not difficult for women to use the Internet to find out what cervical leukoplakia is and reviews about the treatment of this disease.
Knowledge about the disease, as well as the methods and consequences of treatment, allows you to prepare mentally.
Photo
Currently, gynecological diseases are becoming more common. Knowing this, every woman is interested in their causes, as well as what this disease looks like. Such a disease as cervical leukoplakia is no exception. Photos and other sources of information will help you understand what it is. Thanks to the development of technology and the emergence of the Internet and social networks in our lives, women are able to find a fairly large amount of information of interest.
First of all, leukoplakia is a pathological condition of the cervix in which areas of the covering layer become keratinized. But at the same time, no changes are noted in the cervix itself. If you translate the diagnosis from Greek into Russian, you get a description of a characteristic type of pathology, i.e. “white plaque”.
Depending on what form cervical leukoplakia has, what it is, a photo will help you figure it out. With a simple form in the photo, we will see areas of whitish color that are localized level with the mucous membrane, without rising above it.
If we consider the verrucous form, it will look like whitish elevations in areas of the healthy cervix. Thus, the neck takes on a lumpy appearance. As for the erosive form, cracks or abrasions are noted in the whitish areas.
Video: What is “Cervical Leukoplakia”
Source: https://lecheniye-matki.ru/lejkoplakiya-shejki-matki.html
Leukoplakia of the cervix - causes, symptoms, treatment
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a pathological condition in which thickening and keratinization of the integumentary epithelium that lines the cervix is observed. This disease is included in the group of background precancerous pathologies.
If adequate treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, leukoplakia can develop into cancer. Pathological formations can be seen during a gynecological examination.
White or gray plaques are observed on the vaginal part of the cervix.
Causes
Factors that can cause the progression of cervical leukoplakia are divided into exogenous and endogenous.
Clinicians consider endogenous disorders in the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary-uterus chain. As a result, anovulation develops with further progression of hyperestrogenism. Also, with this condition, there may be a lack of progesterone. Such changes do not leave a woman’s body without leaving a trace. Because of them, hyperplastic processes begin to occur in certain organs.
Exogenous factors:
- chemical;
- infectious;
- traumatic.
In most clinical situations, it is infectious factors that cause the occurrence of cervical leukoplakia. It is often preceded by disruptions in a woman’s menstrual cycle, as well as pathologies of an infectious and inflammatory nature.
Background factors for the development of pathology:
- nonspecific colpitis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- cervicitis;
- herpes and so on.
Traumatic and chemical injuries can occur when:
- cauterization of cervical erosion;
- curettage for diagnostic purposes;
- abortion;
- diathermocoagulation.
Kinds
- simple leukoplakia. It is also called simple. This form of pathology is characterized by the appearance of whitish lesions that do not rise above the epithelium. Usually no unpleasant symptoms occur in this case. Therefore, the presence of pathology is detected during a gynecological examination for a completely different reason. But if leukoplakia has just begun to develop, then the doctor may not notice its manifestations on the mucous membrane;
- erosive form. White spots form on the cervix. Around them there are cracks, as well as areas with erosion;
- warty form. The affected areas of the epithelium are clearly visible on the surface of the epithelium. They have a dense structure. Often such lesions are layered on top of each other. This form of the disease can develop into oncology. Therefore, when a warty form is detected, a biopsy is performed to detect atypical cells.
Leukoplakia of the cervix
Symptoms
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia directly depend on its type. With focal or simple leukoplakia, signs of pathology may not be observed. Discomfort and burning are observed with the warty form.
The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly with erosive leukoplakia. Ich oozes from the affected area. It is released more abundantly after sexual intercourse. If the plaques spread to the vulva area, then the patient begins to feel burning and itching.
This leads to scratches, cracks and abrasions. But the appearance of such symptoms can also be observed with other diseases of the internal and external genital organs. Therefore, if they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnostics and an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia are very similar to those of other pathologies, so the doctor will need to conduct a thorough differential diagnosis to accurately diagnose. Instrumental diagnostic methods are also used:
Treatment
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia must begin as soon as possible, since this disease has a tendency to degenerate into cancer. Now in medicine there are quite a large number of techniques that make it possible to cure this pathology:
- chemical coagulation. The essence of the technique is that the doctor acts on the affected area of the epithelium with chemicals, under the influence of which the affected cells die;
- cauterization or electrocoagulation. Doctors use this technique most often, as it is accessible and relatively inexpensive. But it is worth noting that cauterization has several significant disadvantages. This procedure is quite painful and traumatic for a woman and, along with pathological foci, healthy tissues are also affected. The consequences of doing so can be quite unpleasant. The healing process takes a very long time. After cauterization, there is no guarantee that the pathology will not recur.
- cryodestruction. The essence of this technique is that the affected areas are exposed to cold. This procedure is not only effective, but also painless. After it is carried out, there are no complications and no scars form on the surface of the epithelium. But this manipulation also has some disadvantages. It is not effective if the foci of inflammation are very deep. After it is performed, the cervix may shorten slightly;
- laser exposure. The method has a lot of advantages and only a few disadvantages. It is painless, there are no scars left after it, the epithelium is restored quickly and the disease does not relapse;
- radio wave surgery. A gentle method that can be used even by girls who have not given birth. In this case, the pathological focus is affected by radio waves, under the influence of which the affected cells simply evaporate.
In the event that leukoplakia is accompanied by severe deformation and hypertrophy, radical treatment is resorted to - the cervix is removed.
If, along with leukoplakia, inflammatory processes in the genital tract are observed, then they must first be treated. In this case, conservative treatment is resorted to. Prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- broad spectrum antibiotics;
- drugs for the correction of concomitant pathologies;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Treatment with folk remedies in case of development of this condition is not advisable, since they are ineffective.
You should also not self-medicate, as there is a danger that without adequate treatment the disease can develop into cancer. Folk remedies can only be used in combination with traditional treatment methods.
They should not be the main therapy. Treatment with folk remedies can only be carried out with the permission of the attending physician.
Treatment of the pathology should be carried out as early as possible to avoid the development of adverse consequences.
Is everything in the article correct from a medical point of view?
Answer only if you have proven medical knowledge Thrush (matching symptoms: 6 out of 6)
What is thrush? This is an inflammatory process, the cause of which lies in yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Under normal conditions, these components are contained in the microflora of the oral cavity, vagina and colon. If their permissible norm is exceeded, then the described pathological process occurs.
... Vulvitis (matching symptoms: 3 out of 6)
Vulvitis in women is an inflammatory process affecting the external genitalia, called the vulva.
This area includes the clitoris, labia (both major and minor), pubis, and the entire hymen (in girls).
In addition, the vulva includes the vagina itself, the glands contained in it, and the formation that covers the urinary canal and is located in the labia (bulb).
... Ganglioneuritis (overlapping symptoms: 3 out of 6)
Ganglioneuritis is an inflammation of the nerve ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system, accompanied by damage to the nerve processes. The fundamental cause of this disease is the occurrence of an infectious process in the body, both acute and chronic. In addition, there are several predisposing factors.
... Hyperkeratosis (matching symptoms: 3 out of 6)
Hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium is a pathology during which growth and thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin is observed. In a normal state, in a healthy child or adult, the upper layer dies and new cells grow to make up for the losses. With this disease, the processes of death and replenishment are disrupted.
The causes of this disease can be both the consequences of various diseases and genetic predisposition. This disease causes the top layer of skin to grow from a few millimeters to three centimeters, which causes severe discomfort.
The most common is follicular hyperkeratosis, which affects the skin of children and adults.
... Gonorrhea in women (overlapping symptoms: 3 out of 6)
Gonorrhea in women is a disease that is transmitted sexually or transplacentally. The causative agent is the pathogenic organism gonococcus. During vaginal sex, the risk of infection is 100%, slightly less during oral sex, but only due to the antibacterial properties of salivary fluid.
…
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/1187-leykoplakiya-sheyki-matki-simptomy