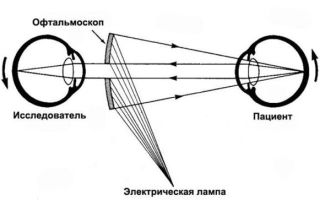
The retina of the eye is responsible for human vision. Due to the development of macular degeneration, this part of the eye is damaged. Therefore, a person sees a blurry picture. In the presence of macular degeneration of the retina, drug or surgical treatment is prescribed depending on the form and severity of the disease.
What is retinal macular degeneration
Macular degeneration of the eye is a lesion of the central part of the retina. The main reason for the development of pathology is insufficient blood flow. A yellow pigment accumulates near the macula. Because of this, the light-sensitive cones are damaged. First, vision deteriorates in one eye, and later in the second.
Dystrophic changes rarely appear at 17–18 years of age. The disease most often occurs in people over 50 due to age-related changes. The disease usually affects both eyes.
With macular degeneration, the first symptoms do not appear immediately. In such cases, people turn to an ophthalmologist when they have the last stage of the disease. Therefore, it is impossible to completely restore vision.
In the presence of macular degeneration, disability is given, but the group depends on the severity and form of the disease. If visual acuity decreases to 0.03, the person is assigned disability group 1. With a slight decrease to 0.1, group 3 is given. In other cases, group 2 is assigned.
Macular degeneration does not lead to complete loss of vision. The disease affects a person’s ability to work. It makes it difficult to drive a car, watch TV, recognize others, or count money.
Classification
In ophthalmology, pathological changes in the macular zone of the retina come in dry and wet forms. In the first case, the disease is treated successfully. Macular degeneration in the dry form is characterized by slow development. Wet macular degeneration of the retina is dangerous for humans as it progresses quickly. Therefore, vision rapidly deteriorates.
Wet macular degeneration with age-related changes is characterized by the proliferation of blood vessels that are directed towards the macula. Therefore, fluid from the new capillaries flows out and permeates the retinal tissue. As a result, the area swells.
The wet form of macular degeneration is the result of advanced dry macular degeneration. Unlike the dry form, the wet form leads to complete loss of vision. Dry dystrophic changes in the macula are distinguished by stages of development:
- Initial. There are no symptoms. The disease is diagnosed randomly during a medical examination. An ophthalmological examination of the fundus of a person reveals yellow spots. These growths are called drusen. At the beginning of the development of macular degeneration, they are small, almost invisible.
- Intermediate. The examination reveals medium and large drusen. A person with this stage is no longer able to distinguish objects.
- Expressed or last. When light-sensitive cells are destroyed, vision decreases sharply. Dystrophic changes lead to disruption of central vision. A person sees one continuous spot of black color.
Causes
The exact causes of retinal macular degeneration are not known in ophthalmology today. Many doctors are sure that vascular changes in the macular area provoke the disease.
Scientists say that the disease occurs mainly in older people. According to medical statistics, only 2% of people by the age of 55 develop macular degeneration. But at age 75, the risk increases sharply to 30%. Wet macular degeneration appears in rare cases.
Symptoms
Macular degeneration of the retina varies according to the stages and forms of the disease. Let's look at the general symptoms:
- distortion of vision;
- hallucinations in the form of distorted straight lines;
- difficulty reading books;
- poor visibility in the dark;
- spots, dots before the eyes.
The listed symptoms appear in one or two eyes. In the second case, the person gradually gets used to the new state, and therefore triggers the disease.
How does a person with macular degeneration of the retina see:
You can watch the following video for more information about the symptoms of this disease:
Diagnostics
First, the ophthalmologist conducts an examination of the fundus. Special drops are dropped into both eyes of a person to dilate the pupils. Afterwards, the ophthalmologist examines the eye for 15 minutes.
Sometimes a diagnostic method is used at home - the Amsler test. In this case, a special mesh and fluorescein angiography are used. In the presence of dystrophic changes in the central region of the retina, a person does not see a spot in the center of the field.
Treatment
Treatment of dry macular degeneration of the retina is carried out using medications. During therapy, a person is prescribed special drops and ointments. In the treatment of wet macular degeneration of the retina, surgical and laser operations are used.
Conservative
Treatment of the initial stage of macular degeneration of the retina involves the use of drops. To cure the disease, visual pigments, antioxidants and drops containing zinc and copper are instilled into the eye.
A person may be prescribed vitamin-mineral complexes, the task of which is to slow down the development of pathological changes in vision. Complete vitamin-mineral complexes against retinal macular degeneration contain the following components:
- zinc;
- vitamins of groups A, C, E;
- copper;
- lycopene;
- lutein;
- omega-3 fatty acids;
- beta carotene.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications containing vitamins and minerals:
- “Complivit Ofthalmo”, prescribed for periodic visual fatigue;
- “Lutein Complex”, used as a food supplement for vitamin deficiency;
- “Metmorphine” is used as a prophylactic against ophthalmic complications for people with diabetes;
- “Vitrum Vision Forte” is prescribed for changes in the macular area in the central or peripheral part.
In addition to taking these medications, a person should eat a balanced diet. If there are dystrophic changes in the central part of the retina, it is forbidden to eat fatty foods:
- rich soups;
- pork;
- smoked meats;
- fried, salty foods.
When sick, it is recommended to eat green vegetables, fruits and berries. Lenten dishes predominate in the diet.
Surgery and laser
Laser coagulation of the retina is used for the wet form of macular degeneration. During the operation, fragile, leaking vessels that have formed over the course of the disease are removed. The laser is aimed at the vessels and destroys them, preventing vision loss.
But sometimes surgery and laser surgery damage healthy blood vessels. Because of this, vision deteriorates. The surgical treatment method is used only when the newly formed vessels are located away from the central fossa of the macula.
Watch a video about laser coagulation of the retina below:
Modern methods
Today, age-related macular degeneration of the retina is treated with progressive methods. This therapy is effective for severe dry or wet forms. The essence of modern treatment is to prevent the proliferation of small vessels and destruction of the macula. For this purpose, special glasses Argus 2 were invented in the UK.
Folk
It is impossible to completely restore vision in the presence of dystrophic changes in the retina. Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina involves the use of folk remedies. Let's look at recipes for non-standard medicine:
- The washed, sorted wheat is laid out in a thin layer and filled with water. After germination, the wheat is washed. The resulting consistency is passed through a meat grinder. The resulting medicine is stored in a cool place. People with macular degeneration should eat up to 5 tsp of this wheat every morning. Berries and honey are added for taste.
- To restore vision you will need mumiyo infusion and aloe juice. 5 g of mumiyo is mixed with 100 ml of fresh juice. The resulting solution is stored on the top shelves of the refrigerator. It is necessary to instill the prepared drops 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 15 days. Then there is a break for a week. If necessary, therapy is resumed.
- Following a diet prevents further development of the disease. It is important to eat foods that are filled with vitamins and beneficial microelements.
Prevention
Age-related dystrophic changes in the retina now appear at an early age. Therefore, it is necessary to observe measures to prevent macular degeneration:
- Rejection of bad habits. It has been proven that alcohol and cigarettes age the body.
- Eye protection in sunny weather. Ultraviolet exposure negatively affects the structure of the retina. Therefore you need to wear sunglasses.
- Annual examination by an ophthalmologist. Timely consultation with a doctor is a guarantee of health.
- Partial exclusion from the diet of foods high in cholesterol.
- Arterial hypertension cannot be ignored. The disease must be treated.
- Take vitamin complexes if there is a hereditary predisposition to the disease. Many beneficial elements are found in vegetables, berries, fruits and seaweed.
At the first suspicion of retinal macular degeneration, you should consult a doctor. If treated in a timely manner, the disease will not lead to irreversible consequences.
Have you encountered this disease? Tell us about your story of fighting the disease. Share the article with your friends on social networks. Be healthy. Anti-inflammatory eye drops, read our article.
Source: https://ozrenieglaz.ru/bolezni/drugie/makulodistrofiya-setchatki-glaza-lechenie
Macular degeneration of the retina: wet, dry, treatment, symptoms and causes of age-related macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is a large group of ophthalmological diseases that are characterized by damage to the macular region of the retina. Mostly elderly people are affected. According to statistics, macular degeneration of the eye develops in 2% of people over 50 years of age. After 65 years, the risk of getting sick increases to 10%, and after 75 – to 30%.
In people with macular degeneration, the macula, the area responsible for central vision, is damaged. The disease leads to the destruction of the retinal nerve cells responsible for the perception of light waves.
As a result, patients' visual acuity decreases. It becomes difficult for them to read, watch TV, recognize acquaintances on the street, and even do their usual daily work. Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina can slow down the progression of the disease, but does not cure it.
Causes
The reliable cause of macular degeneration of the retina has not yet been established. However, there are several theories to explain the appearance of degenerative changes in the macula. Scientific research has shown that they all make sense.
Theories of the development of macular degeneration:
- Lack of vitamins and microelements. Many scientists believe that a deficiency of certain vitamins, antioxidants, carotenoids, zinc, zeaxanthin and lutein contributes to the development of the disease. Due to the lack of biologically active substances, the retina begins to gradually deteriorate, and the person begins to go blind.
- High cholesterol and “wrong” fats. Scientific studies have shown that age-related macular degeneration occurs more often in people who consume a lot of saturated fatty acids and cholesterol (these substances are found in animal products, some vegetable oils, and confectionery products). But people who eat enough monounsaturated fats (in particular omega-3 fatty acids) get sick much less often.
- Smoking. It is known that cigarette abuse increases the risk of developing the disease by about three times. The connection was established through thirteen different scientific studies.
- Cytomegalovirus infection. Scientists claim that CMV is one of the factors causing the development of the wet form of age-related macular degeneration. It is worth noting that more than 80% of the world's population is infected with this virus, however, the majority are only asymptomatic carriers.
- Hereditary predisposition. British scientists have discovered six mutations of the SERPING1 gene associated with the development of pathology. This explains the fact that the disease occurs much more often in close relatives. Statistics show that females are more susceptible to macular degeneration.
Dystrophy of the macular zone develops due to circulatory disorders in the small vessels of the retina. The reason for this may be atherosclerotic changes, sclerosis of capillaries or their spasm in smokers. Lack of blood leads to oxygen starvation of the retina. As a result, the patient’s macula begins to gradually deteriorate.
The macula consists of a huge number of cones - nerve cells responsible for visual perception. For their normal functioning, vitamins, minerals and pigments are needed. Therefore, a lack of zinc, vitamins A, E and C, lutein and zeaxaltin in the body leads to disruption of the rods and the development of macular degeneration.
Forms of the disease
Ophthalmologists distinguish dry and wet forms of age-related macular degeneration. The first occurs in 90% of cases and has a relatively favorable course. It develops very slowly and rarely leads to complete blindness. The wet form of the disease is much more dangerous. It progresses quickly and causes a sharp deterioration in vision.
Dry
Yellow pigment accumulates in the macula area, which over time damages the light-sensitive cones. Initially, the disease affects one eye, later the second one is also involved in the pathological process.
In the dry form of macular degeneration, symptoms appear gradually and very slowly. As a rule, people consult a doctor in the later stages of the disease. It is almost impossible to restore vision in this case.
Wet
The wet form of age-related macular degeneration is characterized by pathological proliferation of blood vessels towards the macula. Fluid from the newly formed capillaries leaks and permeates the retinal tissue, which leads to its swelling. As a result, the patient's vision is greatly distorted.
Wet macular degeneration almost always develops against the background of dry macular degeneration. This means that it affects sick people who already have degenerative changes in the macular area. The wet form of the disease is ten times more likely to lead to complete blindness than the dry form.
Stages
In its development, dry macular degeneration goes through several successive stages. An ophthalmologist can distinguish them after examining the patient. To assess the severity of the disease, he needs to examine the fundus. For this purpose, he performs direct or indirect ophthalmoscopy.
Stages of dry macular degeneration:
- Early. Has an asymptomatic course. The disease is detected by chance during routine examinations. During ophthalmoscopy, the doctor detects small and medium-sized drusen in the fundus. Externally, these formations look like round yellow-white spots.
- Intermediate. During the examination, drusen of medium and large sizes or geographic atrophy of the macula that does not affect the central fossa are detected. At this stage, patients notice the appearance of a fuzzy spot in front of their eyes. Visual acuity begins to gradually decrease.
- Expressed . Due to the destruction of light-sensitive cells (cones), the patient's vision is greatly deteriorated. Geographic atrophy spreads to the fovea, causing a large black spot to appear before a person’s eyes, making it difficult to see the world normally. At an advanced stage of the disease, signs of neovascular maculopathy appear in the macular area.
Subsequently, active proliferation of blood vessels continues in the macular area. Soon they begin to rupture with the formation of hemorrhages. Thus, the patient develops a wet form of the disease. Photoreceptors quickly die, and a person permanently loses vision.
Symptoms
The dry form of age-related macular degeneration is characterized by a slow development of symptoms. At first, the patient notices that he needs brighter light for reading.
It becomes difficult for him to navigate in the dark, especially when entering a dark room from a lit one. The person does not feel any pain in the eyes.
Over time, the patient's vision becomes distorted, which greatly interferes with reading and disrupts the usual way of life. The patient has difficulty recognizing familiar faces and has poor spatial orientation.
Some people experience so-called Charles Bonnet hallucinations. They are characterized by the appearance before the eyes of non-existent geometric figures, animals and even human faces. Many patients are hesitant to talk about this symptom because they are afraid that they will be taken for crazy.
The wet form of macular degeneration is manifested by a rapid decrease in visual acuity. In some cases, a dark spot (scotoma) appears before the eyes, preventing the patient from seeing normally. To a person with a wet form of macular degeneration, straight lines appear curved, wavy, and distorted.
Which doctor treats macular degeneration of the retina?
The dry form of the disease is treated by an ophthalmologist. At the appointment, he carefully examines the patient and prescribes appropriate medications. Then the doctor registers the patient at the dispensary and explains that he will have to come for routine examinations once a year. Regular visits to an ophthalmologist allow you to notice the progression of the disease and take appropriate measures in time.
If the wet form develops, a person requires the help of a vitreoretinal surgeon or laser ophthalmologist. These specialists diagnose and treat diseases of the retina and vitreous body. They are qualified to perform intravitreal injections and laser surgeries.
Diagnostics
Macular degeneration can be suspected based on the patient’s characteristic complaints and progressive deterioration of vision. To confirm the diagnosis, ophthalmologists use a number of additional research techniques. With their help, you can determine the form and stage of the disease.
Methods used to diagnose macular degeneration:
| Method | Target | results |
| Visiometry | Determine visual acuity of each eye | A decrease in visual acuity indirectly indicates damage to the macular region of the retina |
| Perimetry | Identify scotomas (defects in the visual field) | The appearance of a central scotoma (spots before the eyes) indicates the presence of pathological changes in the macula of the retina |
| Amsler test | Check if a person has vision distortion | A sheet of paper with a drawn even grid is placed in front of the patient and asked to look at it with each eye in turn. If the lines appear crooked or wavy to a person, the test is positive. |
| Ophthalmoscopy | Detect pathological changes in the retina of the eye | In various forms of macular degeneration, the doctor can see drusen, newly formed vessels, areas of hemorrhagic impregnation and hemorrhage |
| Fluorescein angiography (FA) | Examine retinal vessels. | In the image you can see absolutely all the vessels of the fundus and their location. The release of the contrast agent beyond the vascular bed indicates capillary ruptures and hemorrhages. |
| Optical coherence tomography (OCT) | See structural changes in the macular area | In the early stages of the disease, OCT allows one to see the initial degenerative changes in the retina. In the wet form, the image usually reveals macular edema |
Conservative treatment
In the initial stages, macular degeneration of the retina is treated conservatively. To combat pathology, antioxidants, visual pigments, carotenoids and certain trace elements (zinc, copper) are used. In some cases, courses of anticoagulant therapy are carried out, sometimes preference is given to regular use of drugs.
Vitamin-mineral complexes (VMC) inhibit the progression of the disease and help delay the development of irreversible changes in vision. Many doctors are skeptical about this treatment, but recent scientific studies have proven its effectiveness. Read more about tablets and vitamins for the eyes →
Effective IUDs must contain the following components:
- lutein;
- zeaxaltin;
- anthocyanins;
- lycopene;
- beta-carotene;
- vitamins E, A, C;
- copper;
- zinc;
- omega-3 fatty acids.
Among the vitamin-mineral complexes, the most effective drugs in the treatment of macular degeneration are:
- Focus;
- Nutrof Total;
- Lutein Complex;
- Vitrum Vision Forte;
- Complivit Oftalmo;
- Okuwait Lutein.
They have the richest and most balanced composition, thanks to which they actively nourish the retina and protect it from destruction.
Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina cannot be done without a balanced diet. The patient should eat more green vegetables, carrots, fresh fruits, and berries. Sprouted grains and legumes are very useful in this regard. But it is better to exclude rich broths, fatty meats, fried, salted and smoked foods from the diet, as they can aggravate the course of the disease.
To treat macular degeneration of the retina, you can additionally use folk remedies. Among them are:
- aloe;
- mumiyo;
- calendula;
- caraway;
- celandine;
- medical leeches.
It should be noted that traditional medicine methods do not always give the expected results and cannot replace traditional treatment.
Modern methods of treatment
Nowadays, several progressive techniques are used to treat age-related macular degeneration of the retina. They are effective in the last stage of dry and wet forms of the disease. With their help, you can stop the proliferation of small vessels and the destruction of the macular region of the retina.
Intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF drugs
Since in the final stages macular degeneration of the retina is accompanied by neovascularization, patients are prescribed drugs that destroy abnormal vessels and prevent their further growth. Medicines are administered intravitreally, that is, into the vitreous cavity.
Anti-VEGF agents include:
- Lucentis;
- Ilia;
- Makugen.
After administration of the drug, patients soon notice an improvement in vision. However, to obtain lasting visible results, at least 5 injections per year are required. The duration of anti-VEGF therapy should be at least 2 years. Unfortunately, due to the high cost, many people cannot complete the full course of treatment and are limited to 2-3 injections.
Laser coagulation of the retina
The procedure is aimed at destroying newly formed vessels. The doctor uses a laser to clog the bleeding capillaries, thereby preventing the appearance of hemorrhages and foci of hemorrhagic leakage.
Unfortunately, laser coagulation does not affect the cause of the disease and does not prevent further neovascularization. Moreover, laser cannot remove vessels located in the macular area. This means that laser coagulation itself is ineffective. Therefore, the procedure is usually performed in conjunction with intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF drugs.
Photodynamic therapy
The essence of the procedure is the intravenous administration of light-sensitive drugs followed by exposure of the retina to laser beams. With the help of photodynamic therapy, it is possible to remove fluid accumulated under the retina and even partially restore lost vision. The procedure is especially effective in the treatment of wet macular degeneration of the retina.
Due to the high cost of drugs, such treatment is practically unavailable in our country. Abroad, photodynamic therapy is used together with intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF drugs.
When is surgery needed?
Surgical treatment of macular degeneration is necessary in the case of massive hemorrhages under the retina and the appearance of subretinal membranes. Surgical intervention helps remove the severe consequences of the disease and partially restore vision. Read more about eye surgery →
Types of operations for macular degeneration:
- Retinotomy. Using special equipment, the surgeon removes the vitreous humor, which allows him to gain access to the macular area. He then cuts the retina and removes the accumulated fluid from underneath it. Instead of vitreous, he injects a special solution.
- Macular translocation. The operation also begins with vitrectomy. During surgery, the doctor carefully moves the macular area of the retina to the desired location. This allows for improved vision.
- Pneumatic displacement of a submacular hematoma. The surgeon introduces air into the eye cavity, which displaces the spilled blood. After the procedure, the retina returns to its place, and the person sees much better.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle is very important to prevent the disease. A person needs to stop smoking and eliminate unhealthy foods from their diet. In bright sunshine, he should wear wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses. Regular exercise will also help.
People over 50 years of age whose relatives suffered from macular degeneration should take vitamin and mineral complexes for preventive purposes. Regular visits to an ophthalmologist are also required. At this age, it is necessary to attend preventive examinations at least once a year.
Alina Lopushnyak, ophthalmologist,
specially for Okulist.pro
Source: https://okulist.pro/bolezni-glaz/setchatka/makulodistrophiya.html
Macular degeneration of the retina: causes, treatment
To understand what macular degeneration of the retina is, you must first understand how the eye as a whole works. To greatly simplify it, the mechanism looks like this:
- through the cornea, which protects the eye from external influences, light enters the lens;
- the lens, which looks like a piece of glass, refracts light;
- refracted light falls on the retina, which covers the fundus of the eye;
- nerve cells concentrated in the retina interpret the light, converting it into electrical impulses, and send it further to the optic nerve;
- The impulses travel along the optic nerve to the brain, where they are read and become an image that a person understands and comprehends.
Problems in this process can begin at any stage, but macular degeneration is said to occur when the macula is damaged - a particularly nerve-rich and therefore sensitive area of the retina that is responsible for central vision.
Causes of the occurrence and development of the disease
The damage that leads to the development of the disease is always the same: the macula is no longer sufficiently supplied with oxygen. As a result, nerve cells receive less nutrition, work less well, and some even die. The factors due to which such a deficiency can develop are very diverse:
- Heredity. If there is already a patient in the family, the chance that it will manifest itself in the next generation is many times greater. Therefore, macular degeneration is a hereditary disease.
- Genetics. Statistics show that Caucasians are more susceptible to macular degeneration than Asians, and light-eyed people are more susceptible to macular degeneration than dark-eyed people. Therefore, this disease may be genetic in nature.
- Age. The small vessels that nourish the retina simply wear out over time. Once a person turns seventy, the chance of developing macular degeneration increases by thirty percent.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Anything that damages blood vessels can contribute to the development of macular degeneration. These include hypertension, atherosclerosis, consequences of heart attack or stroke, thrombosis.
- Poor nutrition. Food rich in fats and calcium contributes to the thinning of blood vessels and the appearance of cholesterol plaques in them, which impede blood flow.
- Smoking and addiction to alcohol. Bad habits increase the rate at which blood vessels wear out and stretch.
- Lack of vitamins. Without proper nutrition, the entire body weakens.
And, of course, an unhealthy lifestyle in general has a negative impact on blood vessels: lack of at least a little physical activity and walks in the fresh air, lack of a sleep schedule, constant stress, insufficient attention to chronic diseases. All this weakens the body and makes it an easy target for macular degeneration.
Stages of development
How quickly the disease will develop and how easy it will be for the patient to notice it depends on how many factors coincide. There are only three stages of development:
- Early. At this stage, the patient himself does not notice anything, but the retina is already suffering from a lack of oxygen. However, if you undergo routine examinations with an ophthalmologist every year, there is a chance that the disease will be noticed by the doctor - when examined with an ophthalmoscope, small white-yellow spots, “druze,” are visible in the fundus of the eye.
- Intermediate. At this stage, the patient begins to notice problems, but in most cases attribute them to circumstances. This is all due to fatigue. Due to poor lighting. Because of stress. The text is simply too small, the TV is simply too far away, you just need to sit at the computer less. The decrease in vision is not too significant; small brown spots are observed in the field of vision. At this stage, the ophthalmologist sees medium and large drusen, as well as a noticeable change in the pigmentation of the retina: it darkens where the nerve cells die.
- Expressed. At this stage, the patient can no longer use circumstances as an excuse; the symptoms become too pronounced. A large black spot appears in the field of vision, which interferes with normal viewing. Visual acuity drops significantly. Upon examination, the ophthalmologist sees severe retinal dystrophy.
If nothing is done, the nerve cells will continue to die and gradually die completely, leaving the person blind.
Types of macular degeneration
Macular degeneration occurs in two types:
Dry form
It occurs in most patients and is actually the main one. It develops slowly, from an early stage to a pronounced one, and can remain unnoticed for a long time. Over time, it gradually turns into a wet form as the body, in an attempt to compensate for the lack of oxygen, forms new capillaries designed to nourish the retina.
Wet form of macular degeneration
The newly formed capillaries saturate the retina with fluid, but this usually does not lead to anything good: swelling occurs, and the patient’s vision is greatly distorted. Moreover, quite quickly the capillaries begin to burst, hemorrhages occur, after which the retina almost completely loses the ability to perceive light.
The wet form develops in about ten people out of a hundred, and in most cases, if the disease was not detected on time, at the dry stage. Leads to blindness quickly and without the possibility of treatment. To prevent this, you need to at least roughly know the symptoms of the disease in order to track it in a timely manner.
Symptoms of pathology
Macular degeneration is an unpleasant process, but absolutely painless. That’s why it’s difficult for a person accustomed to brushing off everything except pain to notice it.
The following symptoms are observed:
- blurriness of objects - observed at all stages, only becomes stronger over time, making it very difficult to read, watch TV and even navigate;
- problems with color perception - the retina is also responsible for this, so the patient may begin to confuse colors that are completely dissimilar from the point of view of healthy ones;
- problems with “twilight vision” – it is difficult for the patient to navigate in the dark;
- dark spot - at first it is small in size and occupies only a small part of the central field of vision, but over time it grows and covers it completely;
- problems with light perception - in bright light it is difficult for the patient to look around, he feels as if his vision is falling even more than before;
- hallucinations - straight lines in the patient’s field of vision are distorted, plus the brain makes efforts to decipher the received signal, and all this can lead to the person perceiving completely harmless objects, like animals or other people.
Interestingly, hallucinations are not typical for the dry form and appear in most cases only when the wet form develops.
Headaches can complement the picture, but they are not directly related to the disease and do not arise due to problems with the retina, but due to constant tension.
Diagnostics
To cure a disease, it must first be diagnosed. This is done by an ophthalmologist, and in most cases, the equipment of a treatment room is sufficient. Apply:
- viziometry - a classic test with a table that allows you to determine visual acuity;
- perimetry - a test that allows you to determine how distorted the patient’s field of vision is and, accordingly, see a dark spot;
- Amsler test - show the patient a sheet of paper with an even grid of thin lines, and ask whether he sees them straight or curved;
- Ophthalmoscopy – allows you to examine the fundus of the eye and get an idea of the condition of the retina.
Already these four tests, equipment for which is available in every eye office, are enough to detect macular degeneration in a person. And in order to check exactly how bad everything is, tomography and angiography are used, which allow you to look at the pattern of blood vessels and distortions of the fundus.
Based on the results, the patient is prescribed treatment.
Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina
To cure macular degeneration, you need to take an integrated approach and combine conservative therapy with lifestyle changes and folk remedies. If this does not help, surgery will be prescribed. And in order to improve the quality of life, which invariably worsens when vision decreases, adaptive devices can also be used.
Conservative therapy
If a patient has a dry form of the pathology, he is usually prescribed conservative therapy to begin with. It includes the following tools:
- helping to strengthen the walls of blood vessels - this will prevent hemorrhages and help saturate the nerve cells with oxygen;
- relieving swelling - this will remove excess fluid and reduce the likelihood of developing a wet form;
- vitamins and immunomodulators - increase immunity, strengthen the body and generally have a positive effect on health.
It is impossible to completely remove the effects of macular degeneration. You can only maintain vision at a certain level and prevent the pathology from leaving stable remission.
Laser treatment
The dry form can also be treated with laser. This operation takes place on an outpatient basis, after an injection of anesthetic. It does not require any special preparation and does not affect health too much at any age. It takes up to ten minutes - the doctor simply burns out the drusen with a laser.
This will not help raise your vision to the previous level, but it will prevent your vision from falling.
Surgical methods of treatment
If the disease has passed into a wet form, conservative treatment and laser surgery will no longer help - only surgical intervention will help.
Before it, the patient needs to avoid taking alcohol and medications for some time, keep his head warm and refrain from physical activity.
On the day of the operation, it is recommended to take a bath, wash your hair and not eat breakfast - the operation is performed under anesthesia, food may make you sick.
Regardless of which method is used (there are three in total and for the patient the difference does not matter), the doctor displaces the retina, removes excess fluid that has accumulated there due to hemorrhages, and fixes it back.
The patient is then kept in the hospital for some time, the dynamics are monitored and the medications are taken accurately. As a result, vision becomes more stable, the dark spot decreases, and the patient may even feel as if they have begun to see better.
Folk remedies
They can be of help in the early stages of the disease, but if macular degeneration has reached the wet form, they will no longer help. They can only be used with the permission of a doctor, and their main function is supportive: to improve health, facilitate blood flow through the vessels, and increase the oxygen content in the blood. The therapeutic function can only be performed by drugs.
There are several popular recipes:
- mix red rowan, blueberries and sea buckthorn in equal proportions, add a few tablespoons of honey, consume every day before meals - this composition is rich in vitamins;
- mix grated carrots and grated walnuts with honey, eat as a dessert;
- chamomile, mint, sage are soothing and strengthening herbs that can be drunk instead of tea.
But you should not drip plant juice or herbal decoctions into your eyes. Not only will this not help restore the retina, but it can also damage the cornea.
Application of adaptive devices
To make the life of a patient with macular degeneration more comfortable, additional adaptive means can also be used:
- magnifying glasses - help to read;
- glasses - help to remove blurriness and better navigate;
Source: https://oculistic.ru/bolezni/drugie-zabolevaniya/prichiny-simptomy-diagnostika-i-sposoby-lecheniya-makulodistrofii-setchatki
How to treat macular degeneration of the retina - I see super
Many people wonder how to treat macular degeneration of the retina, especially in old age. It is after 50 years that this pathology is detected in most patients. However, it can also bother young people and even children. They usually develop Stargardt macular degeneration.
What is macular degeneration
The macula is the layer in the center of the retina that is sensitive to light. It provides excellent vision of objects that are directly in front of a person. But if it is damaged, the patient loses the ability to do basic things: move in space, read, watch movies. Some patients simultaneously develop color blindness. This is exactly what happens with macular degeneration. Sensitive cells change and can no longer perceive the picture. A person sees a blurry dark spot in the center of the field of vision. Only peripheral vision works without failures. Over time, complete blindness occurs.
Stargardt's macular degeneration
This disease occurs in adolescents and children. It is transmitted exclusively by inheritance, and has no other reasons. At the same time, children whose parents suffer from macular degeneration have a low chance of getting sick. For every 10,000 healthy children and schoolchildren, there is one sick person.
Dry macular degeneration - what is it?
90% of macular degeneration diagnoses are due to this form of the disease. It represents the initial stage, during which the extra vessels have not yet had time to rejoice. Dry macular degeneration is characterized by thinning of the retina and the presence of yellow pigment in it.
Dry macular degeneration occurs in three stages:
- Early. Asymptomatic, small drusen may be present;
- Intermediate. Drusen merge into one large spot or several small ones. Spots begin to appear before the eyes;
- Expressed. The spots before the eyes become larger and darker, which indicates the death of light-sensitive cells.
If dry macular degeneration is not treated, it develops into wet macular degeneration. At this stage, abnormal blood vessels grow and vision deteriorates significantly. Everyone should understand what the diagnosis of “dry macular degeneration” means, what it is, and what its causes are. If risk factors are addressed, the early development of this disease can be delayed and even prevented.
Reasons for the development of macular degeneration
Among the risk factors, doctors most often identify several at once.
- Poor nutrition. If the body does not receive the necessary microelements and vitamins, any disease progresses faster.
- Sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation damages the retina.
- Frequent eye strain. The risk is aggravated by working at a computer, regularly watching TV for long periods of time, and reading in a poorly lit room.
- Smoking. Nicotine causes pathologies of blood vessels, which also nourish the retina.
- Pathologies of the circulatory system. Here, too, the risk lies in the insufficient supply of blood and nutrients to the retina.
- Advanced retinal diseases. Macular degeneration develops in the absence of timely treatment of other ophthalmological pathologies
How to treat retinal macular degeneration
Modern medicine does not have a way to completely eliminate this disease. Treatment is mainly aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and stopping the development of pathology. Surgeries or drug therapy are prescribed according to indications. Sometimes these methods are combined with each other. The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of development of macular degeneration.
Age-related macular degeneration of the retina - treatment and prognosis
With this diagnosis, the disease progresses slowly and painlessly, but is practically untreatable. However, this does not mean that treatment in this case is useless - it can significantly slow down vision loss and enable a person to maintain independence longer.
Macular degeneration, dry form, treatment and nutrition
If the patient is obese, it is urgent to normalize body weight by reducing the calorie content of the daily diet. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fat, especially animal fat, cholesterol, and fast carbohydrates.
The patient's menu should include:
- fish high in omega-3, such as salmon;
- fresh vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins;
- greens containing lutein.
Blood sugar levels need careful monitoring. The reason for this is the high risk of significant deterioration of the condition if diabetes develops.
Therefore, it is better to limit sweets and, if possible, replace them with honey. It is also better not to drink lemonade and natural juices, preferring green tea.
A healthy diet is also necessary to control blood pressure. The eyes are one of the first to suffer from hypertension.
Complications include bleeding and retinal detachment.
Lifestyle during treatment for macular degeneration
When deciding how to treat macular degeneration of the retina, doctors recommend an active lifestyle to all patients. Intense exercise is unacceptable, but physical exercise and walks in the fresh air are still necessary. This helps strengthen the vascular system and improve oxygen supply to organs, including the eyes.
It is enough to exercise in the morning and walk for an hour every day. When walking outside in the morning and during the day, you need to wear good sunglasses. This is true not only for summer, but also for the cold season. The negative influence of ultraviolet radiation on the visual organs should not be allowed. For the same reason, visiting the solarium is strictly prohibited.
It is imperative to give up bad habits.
Specific treatment of macular degeneration of the eye
The treatment method is chosen based on the stage of the pathology and its type. At an early stage, treatment is rarely prescribed due to the fact that diagnosis at this time is difficult. But even when diagnosed at an early stage, developing a treatment concept is difficult and sometimes impossible.
Macular degeneration, dry form - treatment
The main recommendation for patients with early macular degeneration is to eliminate risk factors. Drug therapy in this case consists of prescribing vitamins E, A, B, and antioxidants.
All people diagnosed with early stage macular degeneration are advised to visit an ophthalmologist at least once every six months to monitor the condition.
This is especially true for patients over fifty years of age.
If you have age-related macular degeneration of the retina, treatment and monitoring should be systematic. In the transitional and severe stage, as with the diagnosis of “macular degeneration, dry form,” treatment also very rarely gives a positive result.
Most often, such patients are prescribed laser correction. Overgrown drusen are removed, resulting in slightly improved vision.
Despite this, it is completely impossible to restore it, since photoreceptor cells are not restored under any circumstances.
Macular degeneration, wet form - treatment
The therapy is carried out in a similar way, although its effectiveness is slightly higher. However, even with this type of disease, you can only slow down the process, but not stop it. If the doctor's recommendations are followed correctly, the patient may never lose vision completely.
Analgesic injections
One of the most modern methods of treating this disease is biological therapy. Substances are injected into the eyeball to block the formation of new blood vessels.
Their effect on tissue makes it possible to slow down degradation and prolong the relatively normal functioning of the eyes for many years.
For patients diagnosed with macular degeneration, especially the wet form, treatment takes several weeks.
Photodynamic therapy
The course of treatment includes intravenous injections of verteporfin followed by exposure of the affected vessels to a laser beam. The drug begins to actively affect tissue, destroying new vascular beds.
Laser coagulation
The procedure is carried out with the preliminary administration of local anesthetics. The doctor directs the laser at the abnormal vessels, which, under the influence of high temperatures, are sealed and evaporated.
The radiation frequency allows healthy tissues not to be affected even if the laser beam hits them. However, this rarely happens, since the beam is very thin, which allows for almost one hundred percent accuracy.
The laser can only be used to eliminate newly grown vessels located in a limited area.
Adaptive devices for the treatment of macular degeneration
Palliative methods of vision correction provide a certain effect when blindness has not yet occurred, but vision has already seriously deteriorated. Because macular degeneration does not impair peripheral vision, patients can use it more effectively than healthy people.
To adapt patients to the disease, the following are used:
- glasses with special lenses;
- special devices for reading text and viewing screens;
Source: http://vizhusuper.ru/kak-lechit-makulodistrofiyu-setchatki-glaza/