The female reproductive system is susceptible to a variety of pathologies. One of them is an endometrioid ovarian cyst, which can lead to infertility and hormonal disorders. Therefore, it is so important to detect the disease in a timely manner and undergo treatment.
Full content
Content
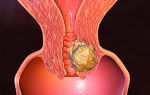
An endometrioid ovarian cyst is a neoplasm in which brown fluid accumulates. It can form on the surface of the organ or inside, and the size is usually no more than twelve centimeters.
Endometroid ovarian cyst
If left untreated, the tumor grows and over time may rupture, causing fluid to leak into the abdominal cavity. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women of reproductive age.
Left ovarian cyst
Endometrioma on the left side is not diagnosed as often as on the right. Its main feature is that they can appear against the background of pathology of the large intestine and after surgery on it. The size of the tumor varies from five millimeters to thirteen centimeters. Among the main signs of pathology are:
- abdominal pain;
- heavy menstruation;
- temperature increase;
- discomfort after sexual intercourse;
- painful urination.
The disease is characterized by abdominal pain, disrupted menstrual cycle and fever
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately treat the endometrioid cyst of the left ovary. If this is not done, negative consequences are possible.
Right ovarian cyst
Statistics prove that cystic formations appear most often on the right side, although they may not manifest themselves in any way. The provoking factor is surgical interventions in this area. If a tumor is found on both sides, the disease is clearly advanced.
Bowel and bladder problems may occur
Endometrioma on the right is accompanied by symptoms such as irregular cycles, pain, problems with the intestines and bladder.
Until now, doctors have not been able to reliably determine the causes of tumors.
The prevailing opinion in the medical community is that during menstruation, blood clots connect with cells located in the endometrium and accumulate on the ovaries, resulting in the formation of a cyst.
In addition, blood can accumulate after an abortion, curettage, or genital surgery. There are other assumptions as to what causes an endometrioid cyst of the right and left ovary:
- hereditary factor;
- drinking alcohol, smoking;
- hormonal disorders;
- increased prolactin levels;
- diseases of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- depression;
- keeping the intrauterine device for longer than the permitted period;
- overweight and obesity.
Smoking and alcohol may be causes of the disease
The following factors also contribute to tumor formation:
- pregnancy over the age of thirty;
- operations on the uterus;
- abdominal trauma;
- inflammation and sexually transmitted diseases;
- weakened immunity.
Even if endometrioma reaches a large size, the clinical picture of the disease does not have pronounced manifestations. It is usually detected incidentally during an ultrasound examination. The neoplasm is not dangerous to health, since it very rarely develops into a malignant form.
But when the tumor grows, it compresses the ovarian tissue, as a result of which it cannot fully perform its functions. This condition threatens complete loss of the organ. However, there are certain symptoms of endometrioid ovarian cysts that require mandatory treatment.
The initial stage is characterized by the following symptoms:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- heavy periods;
- intermenstrual bleeding with blood clots;
- pain after intimacy;
- painful sensations during menstrual periods;
- weakness, lack of appetite;
- temperature increase;
- urinary disturbance.
Characterized by general malaise and disruptions in the monthly cycle
In the absence of treatment, the patient’s well-being worsens, and the duration of menstruation increases to a month. In addition, the pathology can lead to infertility.
A small tumor does not interfere with conception and does not affect the development of the child.
Therefore, if a woman is diagnosed with a cyst, the pregnancy is not interrupted. If the diagnosis is made before conception, the neoplasm is recommended to be removed. The final decision is made by the patient herself.
It should be taken into account that during surgical intervention, ovarian tissue is inevitably damaged, as a result of which its functions suffer. In addition, an adhesive process is possible, which can lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes. In such conditions, pregnancy is impossible.
A woman must decide what is more important to her – a child and a small tumor or the likelihood of serious complications.
A small tumor does not interfere with conception
During the period of bearing a child, the body is completely rebuilt. As a result of hormonal changes, the tumor may disappear or, conversely, begin to grow actively, which is dangerous if interrupted. Therefore, pregnant women diagnosed with endometrioma should visit their doctor regularly.
The disease develops gradually, and each stage has its own characteristics and signs:
| Initial | The tumor size does not exceed a centimeter, only one ovary is affected |
| Moderate | The number of neoplasms increases, and their size reaches six centimeters |
| Heavy | Cysts spread to both ovaries, foci of inflammation are found on neighboring organs |
| Complicated | The size of the tumor exceeds ten centimeters, and the disease affects not only both ovaries, but also other organs |
Depending on the stage of the disease, the clinical picture may vary. When choosing a treatment method, the doctor must take into account the severity of the disease and the general well-being of the patient.
Cystic neoplasms under unfavorable conditions can cause negative consequences:
- Acute - require immediate medical attention. Usually this is a cyst rupture or torsion.
- Long-term complications occur hidden and do not manifest themselves for a very long time.
One of the dangerous complications is apoplexy - rupture of the cyst membrane, in which its contents end up in the abdominal cavity. There are many nerve endings there, so the patient suffers from severe pain.
In addition, a blood vessel may be damaged, resulting in intra-abdominal bleeding. If the vessel is large, significant blood loss is possible. The main symptom of apoplexy is sharp pain. It appears suddenly and is accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting.
If a woman loses a lot of blood, weakness, dizziness, and loss of consciousness are noted. In such a situation, immediate medical attention is required.
Most often, the consequences of cyst rupture can be eliminated with conservative therapy - with the help of painkillers and hemostatic drugs. If they do not help, surgery is performed.
Quite often, a complication such as torsion of an ovarian cyst occurs. It is possible with strong physical stress or active sexual intercourse. As a result, the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted and they die. This pathology can only be eliminated through surgery.
In some situations, surgery is necessary
Long-term consequences include disturbances in the functioning of the ovary, infertility, and the formation of oncological tumors.
The reason is the gradual disappearance of normal tissue, deterioration of blood supply, lack of oxygen and nutrients. For a long time, the problem may go unnoticed, since the second ovary works normally.
But over time, infertility develops. In two to three percent of cases, the cyst provokes the formation of a malignant tumor.
Features of therapy largely depend on the size of the tumor and the stage of the disease. A small tumor identified by ultrasound is treated for several months with hormonal drugs. Subsequently, the doctor decides whether to remove the endometrioid ovarian cyst or not.
Conservative methods
If the cyst has formed as a result of hormonal changes, you can first treat it with contraceptives. They inhibit the functioning of the ovaries, normalize hormonal levels and the menstrual cycle. As a result, the tumor may decrease in size.
Treatment with contraceptives
Sometimes patients are prescribed medications containing progesterone. One of the reasons for the formation of a hand is a deficiency of this hormone. Treatment with Duphaston is possible - it normalizes the cycle and prevents the growth of the endometrium.
If a woman is diagnosed with endometrioma, the drug prevents the formation of new tumors and is used in combination with surgical treatment methods. The specific dosage and duration of therapy is selected by the doctor.
Self-administration of Duphaston can harm the female body.
Folk remedies
In the early stages of the disease, alternative medicine recipes can be used to treat cysts. One of the most popular is honey, which is inserted into the vagina using a tampon. Honey can be mixed with viburnum - it has excellent antibacterial properties. The medicine is taken in the morning on an empty stomach for three to four months.
Flaxseed oil has a positive effect on the body. And to normalize hormonal levels, you can use a decoction of flaxseed. Walnut partitions have similar properties.
Infusions prepared from boron uterus give a good effect. Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts with folk remedies is quite acceptable. The main thing is to identify the disease in a timely manner, consult a specialist and follow all his recommendations.
Most often, a tumor is not a dangerous condition; only complications pose a threat.
Laparoscopy
The only method of treating a cyst that gives a one hundred percent guarantee is surgery to remove it using laparoscopy, performed under general anesthesia.
The doctor makes incisions above the ovary, inserts a laser into one of them and excises the tumor. The treatment method is considered painless, has a gentle effect and does not cause serious consequences.
The stitches heal quickly, and the patient can return to normal life. Full recovery occurs within two weeks.
Removing the cyst at an early stage of the disease allows you to restore reproductive function and subsequently become pregnant. If surgery is performed on an advanced tumor, infertility most often occurs.
Source: https://gynecolg.ru/opyh_zab/bol_yaich_mat_tr/endometrioidnaya-kista-yaichnika.html
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cyst without surgery: remedies - Women's Doctor
Endometrial cells line the inner walls of the uterus and are responsible for the attachment of the fertilized egg. Under the influence of various factors, the endometrium tends to grow outside the uterus, causing a common gynecological pathology - endometriosis. A common manifestation of the disease is endometrioid ovarian cyst.
The disease poses a serious threat to women and requires proper treatment. Complications are fraught with infertility, cyst rupture, peritonitis and other sad consequences.
Causes and symptoms
Doctors still have not thoroughly figured out the exact reasons for the development of pathology. Many experts agree that the main prerequisites for the formation of a cyst are:
- hormonal disorders;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- prolonged stress;
- heredity;
- long-term use of an intrauterine device;
- abortions;
- curettage and gynecological operations.
At the initial stage, the signs of the cyst are mild and manifest as heavy, painful menstruation, cycle disruptions, and discomfort during intimacy. If you do not undergo examination and start treatment in time, the symptoms intensify. Acute pain in the lower abdomen, general weakness, and a worrying lack of appetite and intestinal upset appear.
Diagnosis and treatment
A cyst can form on both the left and right ovaries. Its growth causes pathological changes in the reproductive system. Painful symptoms increase with palpation. Often in the middle of the ovarian cycle, spotting is disturbing.
- Diagnosis of the neoplasm is carried out through a gynecological examination.
- If the doctor suspects abnormalities, he sends the patient for an ultrasound and recommends an MRI.
- If the diagnosis is confirmed, the gynecologist prescribes treatment on an individual basis, taking into account the clinical picture.
At the initial stage of cyst formation, conservative therapy is used, including potent drugs. When the size of the formation is large and there is a threat of rupture of the walls, surgical intervention and removal of the cyst is required.
Unconventional methods
If the gynecologist considers it appropriate, you can use traditional methods of eliminating endometrioid ovarian cysts for auxiliary treatment. Herbs have proven themselves in the fight against disease and are considered a worthwhile alternative to hormonal drugs . The main thing is not to self-medicate. All actions must be taken with the approval of a doctor.
Hog queen
An ancient folk remedy for solving gynecological problems is boron uterus. The herb has valuable properties:
- resolves neoplasms;
- relieves inflammation;
- cleanses the genitourinary system of harmful bacteria.
The plant contains tannins, vitamins, organic acids, minerals, phytoestrogens and flavonoids. Together they normalize hormonal levels and heal the female reproductive system.
The complex chemical composition of boron uterus requires scrupulous adherence to the recommended dosage and not exceeding it . The course of treatment should begin on the day the menstruation ends and continue without interruption until the first day of the next menstruation.
Therapy must be repeated for 3 months.
- To prepare a decoction, pour a tablespoon of dried herb into 250 ml of boiling water and place in a water bath. After 10 minutes, turn off, strain and take 1 tablespoon 5 times a day before meals.
- To enhance the effectiveness of treatment, boron uterus is used in combination with the grass of wintergreen and red brush. Taking medicinal herbs is divided into three cycles. In the first week after menstruation, take an infusion of boron uterus, 2 tablespoons three times a day before meals. In the second week, the red brush is drunk in the same way. During the third week - infusion of winterweed. After the end of menstruation, the course is repeated. To prepare the infusion, you need to brew 1 teaspoon of the raw material in 250 ml of boiling water, leave for a quarter of an hour and strain.
- The alcohol infusion of boron uterus has high healing properties. To prepare the medicine, 50 g of herb is poured into 0.5 liters of vodka. Seal tightly and leave for 2 weeks. The bottle needs to be shaken regularly. The finished liquid is filtered and used as an effective folk remedy for the treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts. The course of therapy is three weeks. The tincture should be drunk 4 times a day before meals, dissolving 30 drops in a glass of cool water. Afterwards you need to take a break and continue treatment from the beginning of a new menstrual cycle.
Dandelion
This wildflower is widely used in folk medicine as a tonic, antitumor and cleansing agent. To eliminate the cyst, the rhizomes of the plant are used. A decoction of it reduces the amount of fluid in the tumor and prevents the formation of a cyst.
- You need to cut clean dried dandelion root with a knife and grind it in a coffee grinder.
- Measure a teaspoon of raw materials, pour 250 ml of boiling water in a ceramic bowl.
- Cover with a lid and leave for 30 minutes.
- The liquid passed through the filter is ready for use.
Instead of infusion, you can prepare a decoction by pouring 2 large tablespoons of chopped root into 0.5 liters of boiling water and placing it in a water bath. The medicine should be simmered on low heat for an hour, turn off, cool, and pour into a glass container with a lid. The liquid can be stored in a cool place for 3 days.
The decoction and infusion should be taken in the same way. Treatment begins 5 days before the start of menstruation and drink 2 tablespoons three times a day an hour before meals.
Herbal infusions
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts using medicinal herbs is effective.
- You need to mix chamomile flowers, sweet clover, coltsfoot in the same proportions. Measure out 2 tablespoons of raw materials and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water into a thermos. After 3 hours, strain and drink in equal portions throughout the day.
- To eliminate ovarian cysts, a folk remedy based on the root of pink radiola is useful. To two tablespoons of the main component you need to add the same amount of viburnum bark, chamomile, dry rowan berries, and motherwort. Stir, take 2 large spoons and pour 500 ml of boiling water. Wrap the container in a towel and strain after 3 hours. Drink half a glass 4 times a day.
The recommended course for using infusions is 3 months. Treatment should be interrupted during menstruation.
Green walnuts
Unripe nuts contain a high concentration of alkaloids necessary for the resorption of tumors. Requires milk nuts that can be easily pierced through with a needle. The optimal time for collecting raw materials is from May to mid-June. It is better to prepare the drug with rubber gloves. The nut shell contains a lot of pigment, which turns your hands a bright brown color.
The nuts must be filled with water, washed and cut into small pieces. Fill a liter jar one third full. Fill the remaining space with vodka, seal tightly and place in a dark place for 2 weeks. Filter the finished medicine and store it in the refrigerator. Take 1 spoon three times a day before meals. The course should begin on the day the menstruation ends and continue until the first day of the new menstruation.
Natural honey
Products based on natural honey have proven themselves to be excellent. You will need to squeeze the juice out of the viburnum berries and mix them in a glass jar with liquid honey in a 1:1 ratio. Therapy should be started with minimal doses.
- in the first week after menstruation - half a teaspoon;
- in the second week - 1 teaspoon;
- during the third week - 1 tablespoon;
- for 4 weeks - 1 tablespoon twice a day, morning and evening.
Then a break of 30 days is required, after which the therapy must be repeated, adhering to the reverse dosage regimen. The maximum course is 3 months.
Other recipes:
- It is useful to use another effective recipe. You need to crush 100 g of ripe viburnum berries, mix them in a glass container with the same amount of honey, freshly squeezed nettle juice and aloe. Place in the refrigerator and take 1 small spoon, slowly dissolving the medicine in the morning. The tasty drug can be drunk, interrupted by menstruation, for about six months.
- You can use tampons with honey. To make them, you will need a thick, hardened product. A small amount of honey should be wrapped in several layers of bandage, tied tightly with a thread and inserted into the vagina before bed.
- You need to mix honey with Kalanchoe or aloe juice 1:1, soak a gauze swab in the liquid and use it for treatment. To achieve a positive result, honey tampons should be used for at least a month.
Pine nuts
- Place 100 g of shelled pine nuts in a glass jar, add a spoonful of honey and pour a bottle of vodka over the ingredients.
- Shake and place in the dark to infuse. After two weeks, the liquid can be used.
- Treatment should begin with 5 drops of the product, which dissolve in a spoonful of water, and gradually increase the dosage to 25 drops.
- The course of therapy is a month. It is advisable to repeat it after a thirty-day break.
Acacia
Acacia flowers are a proven folk recipe for the treatment of endometrioid cysts of the left and right ovaries. Four spoons of fresh or dried flowers should be poured into 0.5 liters of vodka and left in a dark place for 2 weeks. Drink 1 spoon three times a day before meals for a month.
For treatment to be effective, it is important to detect the disease in its infancy. This requires prevention, which includes a gynecological examination of the woman at least once every six months. At the initial stage, endometrioid ovarian cyst can be eliminated by combining folk and drug treatment.
Source:
Treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery
Content
Source: https://mjk1.ru/operatsii/lechenie-endometrioidnoj-kisty-yaichnika-bez-operatsii-sredstva.html
Endometrioid ovarian cyst: causes, symptoms and signs, why it is dangerous, diagnosis and removal by laparoscopy, treatment of endometrioid cyst
An endometriotic cyst on the ovary is a neoplasm that appears as a result of the proliferation of the endometrium. It is a pathological cavity consisting of menstrual blood, which is surrounded by a membrane of endometrial cells.
Many experts insist that women undergo gynecological examinations in a timely manner, since endometrial ovarian cysts tend to malignize (degenerate into a malignant tumor).
Timely diagnosis and treatment allows you to completely get rid of the formation without loss of reproductive function.
The endometrium is the lining that covers the inner surface of the uterus. During the menstrual cycle, the endometrium increases in thickness and prepares to receive a fertilized egg. Rejection of the endometrioid mass occurs if pregnancy does not occur.
Endometriosis and ovarian cysts are gynecological hormone-dependent diseases. Which definitely require treatment.
The formation of an endometrioid cyst occurs gradually. Initially, a small lesion appears on the surface of the ovary, which increases in volume after each menstruation.
The blood accumulated inside the lesion eventually acquires a dark brown color and thick consistency. Therefore, the endometrioid ovarian cyst has a second name - “chocolate cyst”. Such a cyst can reach significant sizes (up to 12 centimeters in diameter).
As a rule, the pathology affects women of reproductive age from 20 to 50 years.
In the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, the diagnosis: “Endometrioid cyst” is made based on the conclusion of a gynecological examination in a chair, ultrasound examination, as well as additional diagnostic methods. Experienced doctors will help you get rid of this dangerous pathology in a timely manner, using modern treatment tactics.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst: symptoms in women
The endometrioid cyst of the right ovary, according to many experts, appears much more often than the endometrioid cyst of the left ovary, and also causes difficulties in diagnosis due to similar symptoms of appendicitis. The main symptoms of such a neoplasm are:
- Lack of a regular menstrual cycle;
- Pain in the corresponding side of the abdomen;
- Brown discharge;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Disruption of the urinary system;
- Abnormal bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea);
- Bloating.
The pain associated with an endometrioid ovarian cyst is usually dull and nagging, which intensifies during menstruation and exercise.
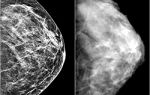
The main problem of this pathology is the impossibility of pregnancy. It is with this problem that women most often turn to a gynecologist for the first time, where they learn about their illness. An endometrioid ovarian cyst can only be diagnosed by ultrasound.
Why is an endometrioid ovarian cyst dangerous?
An endometrioid cyst is dangerous because, due to improper treatment or delay in seeking medical help, a number of serious complications can arise. The most common ones include:
- Cyst rupture. When the size of the cyst increases significantly, it bursts and the internal contents spill into the abdominal cavity. This is a very dangerous condition that can lead to the development of peritonitis or even death if the woman is not provided with medical assistance in time;
- Dysfunction of the internal organs of the pelvis. In some cases, the cyst can put pressure on neighboring organs and tissues, which impairs their function. The functioning of the genitourinary system and intestinal tract is most often disrupted. But the main threat is infertility. Sometimes, the only chance to have children is IVF after removal of an endometrioid ovarian cyst;
- Diseases of the female reproductive organs. Under the influence of endometrioid cysts, not only the ovaries, but also other reproductive organs are affected. In some cases, the formation leads to the development of endometriosis and some infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Twisting of the cyst stalk. This ovarian formation has some anatomical features - the legs, which reach a certain size, can twist, thereby stopping the flow of blood to the ovary. As a result of lack of blood circulation, tissue necrosis occurs, which leads to removal of the ovary along with the endometrioid cyst;
- The appearance of malignant tumors. The danger of an endometrioid cyst lies in the malignancy of its tissues, that is, the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one. In such cases, there is a huge risk of developing ovarian cancer. Of particular danger are cysts that remain in a woman’s body for a long time.
With an endometrioid ovarian cyst, consequences can be avoided if examinations and therapy are started on time.
Diagnosis of ovarian cyst
Diagnosis and treatment of formations of the uterine appendages is carried out by a gynecologist. During the examination, the specialist may detect enlargement of the ovaries, their compaction or adhesions in the pelvic cavity. During a two-handed examination, a woman may experience painful sensations, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the internal genital organs.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe:
- A blood test for the content of the tumor marker CA-125 - an increase in its level often indicates the presence of an endometrioid cyst;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs - with the help of ultrasound it is possible to detect a cyst, understand its location and size. Such formations consist of a dense capsule and finely dispersed contents;
- MRI of the pelvic organs - makes it possible to distinguish endometrioid from any other cyst, to assess the prevalence of the tumor;
- Laparoscopy of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is a diagnostic procedure that provides the opportunity to visually assess the formation and its contents. This procedure often turns into a therapeutic endoscopic operation.
At the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, they carry out the most reliable diagnosis of gynecological diseases according to European protocols. Doctors are engaged in effective treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts thanks to the involvement of foreign partners.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst: treatment of pathology
Many women who are faced with ovarian pathology ask the question: “How to treat endometrioid ovarian cyst?” Treatment of ovarian cysts is prescribed after a complete diagnosis and has several directions:
- Conservative therapy with the use of medications;
- Surgery;
- Complex therapy.
In the presence of lesions, hormonal drugs are first prescribed. After completing the course of treatment, it will become clear whether the endometrioid ovarian cyst should be removed or not. According to gynecologists, the formation can be treated with hormonal treatment only in the early stages.
Hormonal therapy is prescribed after all tests and examinations have been completed and has minimal effect on the woman’s body. Today, there is a huge selection of drugs that contain small doses of hormones necessary for effective therapy.
Sometimes the only treatment is surgical removal of the endometrioid ovarian cyst. The most innovative invention of the 21st century is laparoscopy.
The operation to remove an endometrioid ovarian cyst allows you to carry out all manipulations without rough incisions. It can minimize trauma to healthy organs and tissues, and will also allow the woman to have children in the future.
Surgery for an endometrioid ovarian cyst is prescribed only if drug treatment has not produced positive results.
In the presence of a very large tumor, the size of which would be a contraindication for laparoscopic access, puncture is used. Aspiration of an endometrioid ovarian cyst occurs under the control of transabdominal ultrasound.
Endometrioid cyst of the left and right ovary has the same treatment.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate symptoms and normalize hormonal levels. After personal selection of the treatment method, it is necessary to undergo a rehabilitation course.
Endometriotic cyst on the ovary: treatment in Moscow
The Yusupov Hospital employs the best specialists, professionals who know and love their job. Our hospital uses an individual approach to each patient, since no two cases are alike.
Innovative equipment allows diagnostics to be carried out comfortably, accurately and quickly. The oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is constantly introducing advanced technologies for the treatment of gynecological pathologies.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst does not tolerate treatment with folk remedies. At the first symptoms, contact a specialist. You can make an appointment and consultation by phone.
Natalya Aleksandrovna Vyaznikova
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Cherenkov V. G. Clinical oncology. — 3rd ed. - M.: Medical book, 2010. - 434 p. — ISBN 978-5-91894-002-0.
- Shirokorad V.I., Makhson A.N., Yadykov O.A. The state of oncourological care in Moscow // Oncourology. - 2013. - No. 4. - P. 10-13.
- Volosyanko M.I. Traditional and natural methods of preventing and treating cancer, Aquarium, 1994
- John Niederhuber, James Armitage, James Doroshow, Michael Kastan, Joel Tepper Abeloff's Clinical Oncology - 5th Edition, eMEDICAL BOOKS, 2013
*The information on the site is for informational purposes only. All materials and prices posted on the site are not a public offer, defined by the provisions of Art. 437 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For accurate information, please contact the clinic staff or visit our clinic.
Download price list for services
Source: https://yusupovs.com/articles/oncology/chto-takoe-endometrioidnaya-kista-yaichnika/
Endometrioid ovarian cyst
An endometrioid ovarian cyst is a pathological cavity formation on the surface of the ovary, consisting of accumulated menstrual blood surrounded by a membrane of endometrial cells. An endometrioid ovarian cyst in some cases may not manifest itself for a long time, in others it may be accompanied by abnormal menstruation, infertility, pain, up to the clinic of an “acute abdomen”. Diagnosis of endometrioid ovarian cyst is based on ultrasound and laparoscopy data. Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts includes surgical removal of the pathological formation and long-term hormonal therapy.
Endometrioid ovarian cysts, unlike functional cysts, have a different mechanism of development and in the vast majority of cases are bilateral.
In gynecology, an endometrioid ovarian cyst refers to a common manifestation of the genital form of endometriosis, in which cells of the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the uterus are found in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, vagina and abdominal cavity.
An endometrioid ovarian cyst develops in women of reproductive age (30-50 years), usually against the background of internal endometriosis, and can be combined with uterine fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia. The size of an endometrioid ovarian cyst can reach 10-12 cm.
Endometrioid ovarian cyst
Despite the large number of theories about the origin of endometriosis, the exact causes of the disease are still unknown. According to the implantation hypothesis, endometriosis and endometrioid ovarian cysts can occur during retrograde menstruation, when endometrial cells migrate with blood and take root in the tissues of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and abdominal cavity.
The introduction of endometrial fragments is also possible during surgical procedures that injure the uterine mucosa: gynecological and obstetric operations, diagnostic curettage, medical abortion, diathermocoagulation of the cervix. It is also believed that endometrioid lesions may be the result of metaplasia of remnant embryonic tissue, genetic defects (familial forms of endometriosis) or weakened immune responses.
Risk factors
There is a connection between the development of endometrioid ovarian cysts and endocrine disorders in the body: decreased levels of progesterone, increased levels of estrogen (hyperestrogenism) and prolactin, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex. Provoking factors in the development of endometriosis can be:
- any emotional stress;
- long-term use of the IUD;
- endometritis, oophoritis;
- liver dysfunction;
- obesity;
- unfavorable environment.
The resulting endometrioid lesions are functionally active and hormonally dependent, and therefore cyclically undergo a menstrual-like reaction.
The proliferation of monthly bleeding endometrial tissue in the ovarian cortex leads to the formation of endometriotic ovarian cysts (“chocolate” cysts), filled with thick, dark brown contents that cannot find a way out.
The histological sign of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is the absence of glands in its wall.
The severity of the clinical manifestations of an endometrioid ovarian cyst depends on a number of factors: the degree of spread of endometriosis, the presence of concomitant diseases, the psychological state of the patient, etc. In some cases, the formation of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is asymptomatic or manifests itself as impaired reproductive function (infertility).
An endometrioid ovarian cyst may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, which intensifies during menstruation and during sexual intercourse. Sometimes the pain can be very severe, and if the cyst capsule is large and ruptures, the clinical picture of an “acute abdomen” develops.
Endometrioid ovarian cysts are characterized by heavy periods, prolongation of the menstrual cycle with spotting before and after menstruation. Symptoms of intoxication may appear: weakness, nausea, fever.
The growth of an endometrioid ovarian cyst can lead to local changes in ovarian tissue: oocyte degeneration, follicular cysts, and the appearance of scars that disrupt the normal functions of the ovary.
With the long-term existence of an endometrioid ovarian cyst, an adhesive process in the small pelvis can be detected with dysfunction of the intestines and bladder (constipation, flatulence, urination problems).
An endometrioid ovarian cyst is a serious gynecological pathology that can be complicated by suppuration, rupture of the cyst walls with spillage of its contents into the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis.
A gynecological examination does not always reveal signs of endometriosis. With an endometrioid ovarian cyst, one can detect the presence of a sedentary, painful formation in the ovary and its enlargement before menstruation. The diagnosis of endometrioid ovarian cyst is established based on the results of ultrasound of the pelvic organs with Doppler measurements of the uteroplacental blood flow, MRI and laparoscopy:
- Ultrasound with Doppler. Determines the lack of blood flow in the walls of endometrioid ovarian cysts.
- Tumor marker study . When determining the level of tumor marker CA-125 in the blood, its concentration may be normal or slightly increased.
- Diagnostic operations . In the presence of infertility, hysterosalpingography and hysteroscopy are performed. Diagnostic laparoscopy is the most accurate method for diagnosing endometrioid ovarian cysts. A biopsy and subsequent histological examination of the focus of endometriosis in ovarian tissue is necessary to identify the likelihood of its malignancy.
MRI of the pelvis. Endometrioid cyst of the right ovary with a uniformly hypointense signal.
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cysts can be conservative (hormonal, nonspecific anti-inflammatory and analgesic therapy, taking immunomodulators, vitamins, enzymes), surgical (organ-preserving removal of endometrioid lesions using laparoscopic or laparotomic access) or combined.
Comprehensive treatment of endometriosis is aimed at eliminating symptoms, preventing the progression of the disease and treating infertility.
Treatment tactics for endometrioid ovarian cysts depend on the stage, symptoms and duration of endometriosis, the patient’s age and the presence of problems with conception, concomitant genital and extragenital pathology.
Conservative treatment
If the size of the endometrioid ovarian cyst is small, it is possible to carry out long-term hormonal therapy using low-dose monophasic COCs, norsteroid derivatives (levonorgestrel), prolonged MPA, androgen derivatives, synthetic GnRH agonists. Pain syndrome associated with the growth of endometrioid ovarian cysts is relieved by taking NSAIDs, antispasmodics and sedatives.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective for endometrioid ovarian cysts larger than 5 cm, a combination of endometriosis and infertility, the risk of complications and oncological alertness, only surgical treatment is indicated.
In women of reproductive age who want to have children, they try to avoid radical operations (oophorectomy, adnexectomy). The preferred methods of surgery for endometrioid cysts are enucleation of heterotopic formations or resection of the ovary. It is advisable to remove foci of endometriosis and endometrioid ovarian cysts with pre- and postoperative hormone therapy.
Postoperative management
Preoperative hormone therapy can reduce foci of endometriosis, their blood supply and functional activity, and the inflammatory reaction of surrounding tissues. After surgical removal of an endometrioid ovarian cyst, appropriate hormonal treatment promotes regression of remaining endometriotic lesions and prevents relapse of the pathology.
In the postoperative period, it is advisable to prescribe physical therapy for the purpose of correcting endocrine imbalance, preventing infiltrative and adhesive processes, relapses of endometrioid ovarian cysts (electrophoresis, ultrasound, phonophoresis, endonasal galvanization, SMT therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, radon baths, etc.).
After removal of the endometrioid ovarian cyst, in most cases, pain is significantly reduced, and normal menstrual and reproductive functions are restored. After treatment of an endometrioid ovarian cyst, dynamic observation by a gynecologist with ultrasound monitoring and testing of CA-125 levels is recommended.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/endometrioid-ovarian-cyst
Endometrioid ovarian cyst - causes, treatment methods, symptoms
Want to create a site? Find Free WordPress Themes and plugins.
Currently, many women suffer from a disease such as endometrioid ovarian cyst, abbreviated as endometrioma or chocolate cyst (we will discuss the origin of this name below).
This disease can affect both a very young girl and a woman of Balzac’s age; nulliparous women are at particular risk . According to statistics, eight out of ten women, one way or another, have encountered this disease.
What are endometrioid ovarian cysts , its symptoms, factors influencing the occurrence and methods of treatment, as well as the consequences that may occur if this disease is not treated, we will tell you in today’s article.
Why is an endometrioid cyst dangerous?
If the disease is not treated, the consequences can be very tragic: the cyst can burst and the blood in it can leak out, which in turn will lead to infection and death.
A tumor can also cause infertility , and if a pregnancy has already occurred, it can cause a miscarriage. There is a possibility that the cyst will develop into a cancerous disease , with all the “delights” that accompany this, such as removal of the uterus and uterine appendages. Therefore, doctors insist on mandatory treatment of endometrioid cysts.
What are endometrioid ovarian cysts?
An endometrioid cyst is a benign formation on one or two ovaries. Experts include it in a group of diseases under the general name “endometriosis”. Inside the ovary, tissue forms that is similar to the tissue that forms the basis of the uterine lining, the “endometrium.”
This tissue begins to bleed, a blood bubble appears, the blood in this bubble begins to oxidize and thicken, acquiring a brown-brown color, hence the other name for the “chocolate” cyst. Endometrioma comes in different sizes, sometimes its size can reach more than 10 cm .
Causes of endometrioma
Doctors are currently arguing about the cause of endometrioid ovarian cysts. One of the popular versions is the migration of endometrial cells from the uterus to the fallopian tubes and to the ovaries .
The disease begins with a small lesion, but after each menstruation the size of the affected tissue increases, blood begins to accumulate in them, which leads to the appearance of the cyst itself.
The development of cysts is greatly influenced by female sex hormones, hence the occurrence of the disease, primarily at a young age.
A woman’s body is simply not designed for frequent menstruation, which is why such disruptions occur; women, by postponing the birth of a child, thereby increase the likelihood of developing an endometrioid cyst .
One of the reasons for the occurrence of pathology may be various disorders in the functioning of the body as a whole. Weakened immunity, excess weight, and the use of IUDs can cause endometrioma . Advanced forms of various sexually transmitted diseases can also give rise to the disease. If a woman has undergone surgery in the abdominal area or had an abortion, then she is more likely to develop the disease.
Stages of disease development:
- At the first stage, tissue damage is minimal; isolated foci of the disease occur.
- The second stage is characterized by the immediate appearance of a cyst on one of the ovaries, not large in size, about 5-6 cm. Adhesions appear in the appendages and abdominal area.
- At the third stage, the lesion covers both ovaries, the size of the cyst increases. Inflammatory processes spread to the entire abdominal cavity, uterus and fallopian tubes. New foci of the disease are observed in the appendages.
- The fourth stage, the size of the cyst reaches large sizes, the disease affects the internal organs.
Symptoms of the disease
Sometimes the symptoms of the disease in women can go unnoticed, the woman does not feel any discomfort and learns about the presence of a cyst when, having failed to get pregnant, she consults a doctor and he diagnoses her with infertility.
Symptoms may also depend on whether there is any other underlying disease. Typically, a woman feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, painful menstruation, as well as pain during sexual intercourse.
The main signs by which a woman can judge whether she has the disease are severe pain during menstruation , periods themselves become longer, and vaginal discharge appears .
The nature of the pain can be described as dull, the lower abdomen and lower back hurt. Vomiting, problems with the digestive tract, constipation, bloating, flatulence. Dizziness, loss of consciousness, weakness, and high fever also accompany endometrioma.
It must, however, be clarified that weakness can also manifest itself simply during menstruation.
During sexual intercourse, severe pain often occurs due to the fact that the internal tissues are inflamed. Not being able to get pregnant for any period of time is also a reason to contact a gynecologist. If you notice all of the above symptoms, then a medical examination is necessary .
The presence or absence of various symptoms is influenced by the woman’s age and the stage of the disease . If the cyst ruptures and the internal contents enter the body, the temperature rises, the patient feels severe pain in the abdomen, and blood pressure becomes high.
In this case, urgent medical attention and surgery are necessary, as death is possible.
Diagnosis of the disease
When diagnosing a disease such as endometrioid ovarian cyst , several methods are usually used, the very first is an examination by a gynecologist , during the examination a small pathology is revealed, which increases in size as menstruation approaches. To make a final diagnosis, ultrasound, laparoscopy, and MRI methods are used.
During an ultrasound examination, the cyst is very clearly visible , like a thick capsule that practically does not move, but other various formations look exactly the same.
Therefore, in order not to make a mistake with the diagnosis, it is necessary to periodically conduct an ultrasound, for example, a corpus luteum cyst may decrease in size over time , or even disappear altogether , while an endometrioid cyst will only increase .
During diagnostic laparoscopy, the doctor can examine the tumor with his own eyes and answer whether it is an endometrioma. Laparoscopy does not require making major incisions on the patient's body; the procedure itself is performed under local anesthesia. Laparoscopy today is the most common method for diagnosing endometrioid cysts.
During laparoscopy it is also possible to take a puncture.
A puncture is the removal of tissue from the tumor itself . It is carried out under local anesthesia, a special tube with a needle is inserted into the vagina, a puncture is made and the liquid is sucked out with a pump. A puncture is both a medicine and a diagnosis rolled into one. When performing a puncture, alcohol enters the tumor (which disinfects) and all the liquid is pumped out.
Treatment of endometrioid ovarian cyst
, treatment for endometrioma begins . Treatment is divided into medication, surgery , and a combination of two methods is also possible .
During drug treatment, the patient is prescribed a course of drugs in order to remove the signs of the disease and its further progress. The doctor selects medications according to the severity of the disease. In late stages of the disease, surgical removal of the tumor is used. Today, laparoscopic surgery .
The advantages of this method are obvious to both the doctor and the patient. The operation does not require deep incisions, and therefore no stitches. The postoperative period is painless.
The operation itself is performed under local anesthesia; after several punctures, the doctor inserts special equipment into the person being operated on, with the help of which the tumor is removed . When using this type of operation, the patient’s reproductive organs are kept intact , which means that the chance of becoming a mother increases.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed to take various vitamin and strengthening medications to fully restore the body after the illness. After surgical removal, the likelihood of relapse is negligible due to the fact that all formations are removed from the patient’s body.
Many experts consider surgical removal of the cyst to be the only effective method in the treatment of endometrioma.
Disease prevention
In order to prevent the development of endometrioma , it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor. It is also necessary to monitor your menstrual cycle and, if alarming symptoms appear, undergo an ultrasound examination .
Doctors also recommend pregnancy after surgery to remove endometrioma as the best means of prevention . Since during pregnancy the cause of the disease itself disappears, if pregnancy is excluded, then taking hormonal medications .
Conclusion
Many women pay little attention to the alarming symptoms that their body gives them. Some people argue that it’s because they’re busy, who think they’ll get sick and stop.
But as we see with this disease, if left untreated, very serious consequences can occur. Therefore, it is necessary to find time to go to the clinic, as well as undergo regular examinations.
Dear women, take care of yourself, take care of your body and be healthy.
Did you find apk for android? You can find new Free Android Games and apps.
Source: https://endometrioz.su/endometrioidnye-kisty-yaichnikov/