Herpes simplex virus is an infectious disease. The main manifestation of the disease is vesicular rashes filled with serous fluid. Periodically they appear on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of an infected person. Herpes simplex cannot be cured; the damage is lifelong. Pathology is classified into two types - HSV-1 and HSV-2.
General information
According to WHO, 90% of the world's population is infected with herpes.
The course of the disease in most cases occurs without any symptoms; a person may not suspect that he is a carrier and spreader of the infection. The disease sometimes appears unexpectedly.
Many people discover unpleasant, painful rashes on the lip during ARVI, after hypothermia, severe stress, that is, after a sharp weakening of the body’s defense system.
The herpes simplex virus most often affects women. It can appear as rashes not only on the lips, but also on the skin around the eyes, directly on the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, in the genital area of men and women, and it also affects the nervous system. The recurrent virus is observed on the wings of the nose, cheeks, lips, ears and forehead.
In total, there are more than 80 types of unclassified herpes in humans and animals. The most common of these is the human herpes simplex virus, which is what most people encounter.
There are two types of pathology:
- Labile herpes (HSV-1) manifests itself as rashes on the eyes (mucous membranes), eyelids, lips, skin, and oral cavity.
- Genital (HSV-2) – the genital area of a man and a woman.
Both types of herpes virus are related by DNA similarity and differ in antigenic properties.
Causes of pathology
The herpes simplex virus affects anyone. Factors that provoke pathology are common and cause a reaction in 90% of the world's population.
The virus enters the active stage under the following conditions:
- Lack of vitamins.
- Unbalanced nutrition, strict diet, exhaustion of the body.
- Hypothermia, overheating.
- Diseases of internal organs, primarily chronic.
- Decreased immunity.
- Diseases of the reproductive system, venereal diseases.
- Stress, prolonged depression, overwork.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse, frequent change of sexual partners.
- Viral, bacterial infections, injuries.
- Taking hormonal drugs for a long period of time.
Since the manifestations of herpes infections of the first and second types are similar, to determine the type of lesion, an analysis is required for antibodies produced by the immune system.
Routes of infection
Regardless of the type of virus, it is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person and that is why it is so common. It is almost impossible to avoid or protect yourself from infection.
Main distribution routes:
- Contact – use of general hygiene supplies (towels, razors, tweezers, toothbrushes, etc.), household items, dishes, etc.
- Airborne - during conversation, coughing, sneezing.
- Sexual – unprotected sexual contact.
Any form of sexual contact is a direct threat of infection with the first and second type of virus at the same time. In this case, the carrier of the virus may not know that he is infected.
HSV-2 (genital herpes) occurs with virtually no symptoms, but a person actively infects everyone with whom he comes in contact. The virus penetrates the nervous tissue, settles there and remains forever.
The patient periodically experiences symptoms due to nervous stress, exhaustion of the nervous system, or hypothermia. Manifestations are noticeable for 10 days, after which they fade away, but the virus does not disappear anywhere.
A small amount of the virus is always present in the saliva of a sick person, and this is quite enough to infect others.
To do this, it is enough to use a poorly washed cup from which the patient drank. Viral herpes remains active in the external environment for 24 hours.
The virus is also transmitted through microcracks in the skin, during labor, and during organ transplantation.
The herpes simplex virus is resistant to temperature changes and does not lose viability at -70 or +50 degrees Celsius. Doctors strongly advise that if even small blistering rashes are detected, seek diagnosis and further consultation. Such a prudent step will help protect against global complications.
Scientists at the University of Manchester after a series of analyzes came to the conclusion that the herpes simplex virus can lead to Alzheimer's disease. After conducting numerous tests and studies, they found that 70% of Alzheimer's patients were infected with HSV-1 or HSV-2, and many had antibodies to both types of virus.
Herpes simplex virus type 1
Infection occurs mainly through contact (saliva, kisses). Primary infection occurs in childhood (from six months to 2 years). In the standard course of the disease, it does not cause symptoms or manifests itself in the form of stomatitis, rashes on the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth or eyes.
After the acute phase subsides, the virus migrates through the nerve endings to the nerve ganglia and settles there forever. There are no conditions for the virus to multiply in nerve cells, but it is periodically released through the salivary glands or skin rashes, causing a surge in the disease.
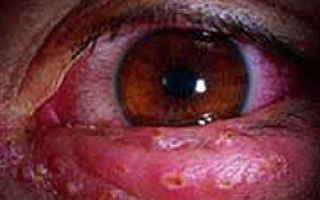
A typical manifestation of the lesion is the appearance on the skin of a group of local blisters up to 2 mm in size. In the affected areas, the skin swells and changes color (reddens). Harbingers of upcoming rashes are a strong burning sensation and itching - this is a reaction of nerve endings affected by herpes.
After a short period of time, the blisters mature and burst, and in their place inflamed ulcers form, which gradually heal. Typically, periodic exacerbations appear in the same places, most often on the lips. The constancy of the localization indicates in which nerve plexus the “den” of the infection is located.
The full cycle of exacerbation of the disease, from the first manifestation to the extinction of symptoms, is 10 or 14 days.
Herpes simplex virus type 2
HSV-2 is called genital herpes, due to the fact that its manifestations most often affect the human genitals. Transmission of the infection occurs through any form of sexual intercourse and usually does not cause any symptoms or noticeable manifestations. Once in the body, the virus immediately moves to the nearest nerve node, in this particular case to the sacral region.
About 15% of affected people experience symptoms. Primary infection with herpes simplex virus type 2 manifests itself on the mucous membrane of men (penis) and women (vulva, cervix, vagina).
Upon visual examination, characteristic rashes are observed - vesicles, swelling and redness of the tissues. An exacerbation is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and pain in the areas where ulcers form.
Some patients may experience increased body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes in the groin.
The acute phase of viral herpes type 2 lasts about 3 weeks. The relapse rate can reach up to 20 cases per year. Up to 75% of patients affected by this type of pathology experience an exacerbation of the disease.
Cervical herpes in women in most cases occurs without any symptoms or manifestations. Today, scientists are increasingly coming to the conclusion that the classification of viruses according to the location of the lesion is arbitrary.
The HSV-1 virus no less actively affects the genital area, and HSV-2 is isolated when diagnosing labile herpes.
Types of diagnostics
There are several types of tests that detect herpes simplex virus:
- Virological – detection of a virus in the human body.
- Detection of herpes antigens.
- Cytomorphological analysis.
- Immunity assessment.
Currently, two groups of diagnostic methods are used:
- Virus isolation and identification.
- Detection of HSV antibodies in blood serum.
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for herpes simplex virus) is the most popular and promising type of diagnosis. The study identifies specific antibodies to the virus produced by the immune system of the sick person.
The specialist’s task is to determine the quantitative assessment of blood immunoglobulins of two types IgG and IgM (markers). Antibodies are the immune system’s response to the invasion of foreign agents; if the test is positive, then a diagnosis of “herpes simplex virus” is made.
Decoding of analyzes, a few examples:
- Detected IgM antibodies indicate recent infection or exacerbation of pathology.
- The detected IgG antibodies speak in favor of a long period of pathology (at least 2 weeks).
- If a herpes simplex virus is detected, IgG antibodies are considered a sign of intense immunity, which indicates a long, acute course of the disease.
- Negative indicators for the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies indicate stable immunity and the “dormant” state of the virus.
Treatment
The presence of the simple herpes virus HSV-1, as well as HSV-2, forces a person to always remain on guard, expecting a relapse of the disease at any time. Pathology does not deprive one of the ability to work, but it brings relative troubles. Timely preventive measures and stopping the exacerbation of the disease help to quickly cope with a relapse and avoid complications.
It is impossible to cure the herpes simplex virus; medicine does not have any means to cope with the disease. The set of measures to overcome symptoms includes the use of medications, ointments for external application and traditional medicine recipes.
Almost all patients experience several relapses and can almost always predict when the acute phase will begin. It is preceded by pain, itching at the site of the appearance of future painful blisters and, possibly, an increase in temperature.
Before herpes breaks out on the face or other part of the body, many people familiar with the manifestations of the lesion treat the skin with antiviral ointments. Preventive measures allow you to localize the rash and prevent its further spread, which can involve large areas of skin.
Therapy for the HSV-1 virus is carried out at home, strictly following the recommendations of the attending physician. Hospitalization is indicated in rare cases.
Treatment of genital herpes virus is carried out in several stages:
- At the first stage, in case of exacerbation, the patient takes antiherperic medications. Treatment is supplemented by taking immunomodulators, interferons, and natural antioxidants.
- The second stage includes the use of immunomodulators, probiotics, and prebiotics to restore normal microflora.
- The third step is vaccination to stimulate cellular immunity.
- At the last stage, inflammation is sanitized, cellular immunity to herpes is strengthened and developed.
Drugs
Effective and frequently prescribed medications include the following groups of drugs, classified according to the main active ingredient in their composition:
- Acyclovir – “Zovirax”, “Acyclovir”, “Herperax”. This group of drugs shows high efficiency and is prescribed most often. Used to control the herpes simplex viruses HSV-1 and HSV-2. The main advantage is a good reaction of the body, an almost complete absence of side effects, and an affordable cost.
- Valacyclovir – “Valacyclovir” or “Valtrex”. When taken orally, it is well absorbed, but can cause headaches.
- Famciclovir – “Famciclovir-teva”, as well as “Famvir”. The drugs are effective for genital and labile herpes and practically do not cause side complications. The only drawback many consider is the high cost.
- Penciclovir - the drugs "Pencivir" and "Fenistil" are prescribed in the later stages of the disease. They show effectiveness with long-term use, are affordable, and do not cause harmful side effects. Preparations containing panciclovir are contraindicated in children.
- Allostatin – “Allomedin” increases skin immunity and reactivates herpes on the face. It is considered most effective when used in the initial stages of the disease.
Virus in children
The herpes simplex virus can appear in a child in the first three years of life. Most children under 6 months do not get sick - they are protected by IgG antibodies.
Defeat occurs if the mother has no antibodies in her blood, which is passed on to the child. This happens extremely rarely. If the incredible does happen, then the baby has a severe course of the disease.
By the age of three, the immune system of most children produces antibodies; their high level is reached by the age of 7.
There are a number of dangers when a pregnant woman is infected with the herpes virus - fetal pathology may develop in the early stages or a miscarriage may occur. If the pregnancy is resolved by childbirth, the newborn may exhibit the following disorders:
- Rashes.
- Incomplete brain development.
- Eye damage.
- Delayed physiological and mental development.
Maternal antibodies to the herpes simplex virus reliably protect the child from the disease during intrauterine development and during breastfeeding.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to avoid herpes, but you should adhere to certain rules so as not to cause an exacerbation of the disease.
Experts recommend the following measures:
- Use only personal hygiene products and do not share them with anyone.
- Avoid contact with a person who has obvious signs of herpes.
- Do not finish someone's food or drink.
- Follow the rules of safe sex and maintain a consistent partnership. Completely avoid contact with a person who has been diagnosed with genital herpes.
- During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system by taking additional doses of vitamins C and B.
- Lubricate the rash areas with vitamin E of oil consistency.
- To strengthen the immune system, take tinctures of eleutherococcus, ginseng root or echinacea in courses.
- Avoid certain foods – chocolate, peanuts, raisins, beer. Give preference to plant foods and water.
- It is recommended to walk in the fresh air more often and engage in accessible sports.
- If you have a cold, be sure to take treatment until complete recovery. Avoid hypothermia, loss of strength, get enough sleep.
- If possible, strengthen the immune system by hardening.
Doctors say with full confidence that it is not possible to cure herpes; even the nature of the virus is not fully understood. You can only deactivate it for a long time to avoid relapses and complications.
Experts insist that at the first manifestations of the lesion it is necessary to undergo diagnostics, determine the type of virus and receive advice on the use of medications and further behavior.
Source: https://www.syl.ru/article/378255/virus-prostogo-gerpesa-tipyi-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnostika-i-lechenie
What are the features of the herpes virus in adults and children
The herpes virus in most clinical cases affects the skin, mucous membrane of the eyes and genitals. You can become infected with herpes through direct contact with an infected person and through household means (using hygiene products of a virus carrier).
The herpes virus in most clinical cases affects the skin, mucous membrane of the eyes and genitals.
What is herpes?
We are talking about an intracellular parasite (herpesvirus), which is integrated into the DNA of human nerve cells, which promotes the replication of viral DNA. Therefore, the disease is incurable.
Herpes simplex virus is the most common viral infection, affecting about 90% of the world's population, but the clinical picture of the disease is observed in only 25% of those infected:
- Herpes type 1 affects the lips, nose, chin, phalanges and nail folds (herpetic panaritium). People involved in contact sports (wrestling, rugby) experience Herpes Gladiatorum (vesicles in the ears and neck).
- Herpes type 2 causes an inflammatory process in the genital area and rectum.
After the initial episode of the disease, HSV remains in a latent stage in the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves, which provide skin sensitivity. During a relapse, the virus reaches various areas of the skin or mucous membrane of organs through the processes of nerve cells, where it multiplies. The disease is characterized by the appearance of a blistering rash.
The incubation period lasts from 2 to 7 days. External signs of the disease disappear within 7-21 days.
There is a chronic form of herpes with varying rates of relapses throughout the year (depending on the presence of provoking factors). If a person experiences repeated exacerbations more than 6 times a year against the background of a short remission, then we are talking about a monotonous course of a viral disease.
Kinds
There are several types of herpes:
- Labial and genital forms.
- Chickenpox and herpes zoster (herpes zoster type 3).
- Epstein-Barr virus (herpes type 4). The human lymphatic system is affected, and infectious mononucleosis develops.
- Cytomegalovirus (herpes type 5). In children, a viral infection has mild symptomatic signs of influenza.
- Roseola in children under 2 years of age is pseudorubella (herpes type 6).
- Herpes types 7 and 8 have been little studied. But they can provoke the development of cancerous tumors.
Shingles is caused by the herpes virus type 3. It manifests itself in the form of rashes with different localizations throughout the body, and is caused by neuralgic lesions of those body systems where it manifests itself.
Symptoms
Symptomatic manifestations depend on the type of herpes infection. A characteristic rash occurs on various parts of the body with chickenpox. In the genital form, damage to the genitals and buttocks in women, as well as the groin area in men, is observed. Blisters on the lips appear with herpes type 1.
Human herpes virus (HHV) can occur in a mild form, and may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. But these symptoms in most cases are characteristic of the primary episode of infection.
Symptomatic manifestations depend on the type of herpes infection.
Psychosomatics herpes
Signs of herpes type 2
Read more about herpes by blood - read here.
A description of the clinical picture of a viral infection requires test results to confirm the diagnosis.
What does it look like
The pathogenesis of a viral infection is as follows:
- At the initial stage, there may be a deterioration in health. A person feels pain and burning in the areas of future rashes. But the first signs cannot always be detected.
- Blistering rashes with serous contents appear, which is accompanied by severe itching sensations. After a few days, the blisters open, forming erosions (ulcers), which then become covered with a crust. With proper treatment, the scab disappears without leaving scars on the skin.
- Herpes goes deep into the nerve ganglia, becoming more active when favorable conditions occur.
At the initial stage, there may be a deterioration in health. A person feels pain and burning in the areas of future rashes.
Causes
The causative agent of a viral infection has the following etiology:
- Infection with herpes type 2 occurs during sexual intercourse, even if partners use latex contraceptives (you can become infected by contact with an unprotected skin surface). Herpes on the lips is transmitted mainly by kissing. Chickenpox and herpes on the nose can be contracted through airborne transmission.
- There is transmission of infection from mother to child during intrauterine development or the process of delivery.
The occurrence of repeated exacerbation is due to a number of factors:
- Weakened immunity.
- Systematic stress exposure.
- Frequent colds.
- Hypothermia or excessive sun exposure.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- A group of blisters on the skin in the genital area appears if your sexual partner has an incubation period for herpes. A large number of virions in vaginal secretions or semen causes a recurrence of a viral infection in a loved one. With herpes on the lips, during oral-genital contact, activation of herpes in the genital area can occur.
- After kissing a person who has the initial stage of development of the labial type of the virus, blisters appear on the lips.
After kissing a person who has the initial stage of development of the labial type of the virus, blisters appear on the lips.
Treatment of herpes
Therapeutic effects are carried out using medications and traditional medicine.
Only a doctor determines the exact dosage, frequency and time interval for taking medications.
How to determine
Diagnostics includes the following procedure:
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test to determine the predisposition to infection, the possibility of re-exacerbation and the primary episode of herpes.
- Blood test using PCR method to identify the type of herpes infection.
- In a scraping of the affected area of the epithelium, stained according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, multinucleated cells with intracellular inclusions are found.
Drug treatment
The diagnosis involves treatment with drugs in tablets and in the form of ointments (creams):
- Acyclovir (Gerpevir, Zovirax) is used orally for herpes, and Acyclovir ointment is used for external treatment of vesicles. The simultaneous use of ointment and tablets is recommended.
- Valaciclovir is a highly effective agent for inhibiting the growth of viral cells.
- Penciclovir is used in case of individual intolerance to acyclovir (active substance).
Sometimes your doctor may prescribe intravenous injections.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods are actively used in combination with medications.
- Calendula tincture for external treatment of ulcers and oral administration.
- Garlic (pasty consistency) for application to affected areas of the skin. Do not use for treating mucous membranes with genital herpes.
- A white wine-based tincture of licorice root helps fight herpes on the lips.
- Kalanchoe juice has antiviral properties. To eliminate the rash, simply cut a leaf of the plant and apply it to the affected area.
Traditional medicine methods are actively used in combination with medications.
Prevention
Prevention is of great importance in preventing infection with a viral infection:
- Lead an active lifestyle. Stagnant processes in the pelvic area provoke activation of type 2 viral infection.
- Avoid promiscuity.
- Do not use other people's hygiene products.
- Eat more vegetables and seafood.
- Dress appropriately for the weather. Don't get too cold.
- Consult your doctor regarding herpes vaccinations, as... The vaccine is an effective way to get rid of frequent relapses.
Complications
If treatment is ignored or the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, the following complications develop:
- The appearance of erosions in the digestive organs. Constant dysbiosis in the intestines.
- Herpetic keratitis.
- Extensive lesions.
- Inflammation of the brain (herpetic encephalitis) against the background of an increase in the intensity of symptomatic manifestations of meningitis. The localization of virions was recorded mainly in the temporal lobes.
- Neuritis. Bell's palsy can be caused by reactivation of herpes type 1.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary tract (ulcers in the mucous membrane of the anterior urethra).
- Cervicitis of herpetic etiology (discomfort during sexual intercourse).
- Infertility and malignant neoplasms in the uterine cavity.
- Pneumonia in people with immunodeficiency.
- Herpetic sycosis: damage to hair follicles both during primary activation and as a result of recurrent viral infection.
- Possible death.
- Herpetic esophagitis is characterized by painful or difficult swallowing. It often occurs against the background of immunodeficiencies (for example, HIV/AIDS) and in the post-transplant period.
If treatment is ignored or the doctor's recommendations are not followed, infertility and malignant neoplasms in the uterine cavity may occur.
Peculiarities
Herpes virus infection has a number of properties:
- Rarely transmitted through household objects.
- Viral DNA is localized in β-amyloid plaques, which is characteristic of Alzheimer's syndrome.
- Even during the period when the crust falls off, there is a risk of infection upon contact with the affected area.
- The virus dies at a temperature of +50°C, but excessive exposure to direct sunlight can provoke an exacerbation.
- It is impossible to get rid of the virus forever, so preventive measures are required.
- After infection, the body begins to synthesize antibodies to HHV, preventing the spread of infection. In case of infection with the HSV-1 virus, such seroconversion (production of antibodies) will protect the body from other infectious processes caused by this virus: herpes type 2, herpetic keratitis and felon.
- Herpes is not able to penetrate the healthy stratum corneum of the skin, which is due to the lack of specific receptors on it.
- The female condom provides effective protection because... During sexual intercourse, there is no contact between the labia and the skin in the man’s groin area.
- Those infected with the genital form have a high risk of contracting HIV through unprotected sexual intercourse with an HIV-positive partner (especially during periods of exacerbation of herpes infection).
In adults
Common herpes is localized in the nerve plexuses of the sacral region or in the ganglia of the trigeminal nerve when it is in an inactive phase.
When infected with chickenpox (chickenpox), the body produces antibodies to the virus. But in old age, a person may experience symptoms of herpes zoster in conditions of weakened immunity. It is impossible to become infected with this type of infection.
In children
Viral infection in children requires immediate treatment. It has the following features:
- In most cases, symptoms of chickenpox and herpes type 6 are observed.
- The development of the inflammatory process may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature, vomiting, and muscle weakness.
- It is necessary to observe the exact dosage of drugs (take into account weight) during treatment of children under 3 years of age in order to avoid the development of complications.
During pregnancy
If a blister pops up on the lips, then there is no threat to intrauterine development either during primary infection or during repeated exacerbation.
With a characteristic rash in the genital area, abnormalities in the development of the child’s brain and spontaneous abortion are possible if the virus is activated for the first time in a woman.
Drug treatment is allowed in the 3rd trimester. Additionally, ozone therapy is used.
Your doctor may prescribe immunoglobulin for intravenous administration.
Source: https://oherpese.ru/vopros-otvet/virus-gerpesa
Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex - herpes simplex or herpes zoster has been known to mankind since ancient times, and the name “herpes” is of Greek origin - “crawl”, “sneak”, which fully corresponds to the clinical manifestations of diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Due to the typical clinical picture, diagnosing herpes simplex is a fairly simple task. In doubtful cases, a study of the discharge of herpetic vesicles is carried out. Treatment of herpes simplex is reduced to local or systemic administration of antiherpetic drugs based on acyclovir, and, if necessary, immunomodulatory therapy is carried out.
Herpes simplex - herpes simplex or herpes zoster has been known to mankind since ancient times, and the name “herpes” is of Greek origin - “crawl”, “sneak”, which fully corresponds to the clinical manifestations of diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus are quite common, and some complications of the infection are fatal. Data from the US Centers for Disease Control record about half a million cases of herpes infection per year, which suggests that between 2 and 20 million people are carriers of herpes infections.
Americans. In England, the incidence of genital herpes infection is rising above other sexually transmitted infections. In Scandinavian countries, herpes simplex is found in approximately 8% of women who consult a venereologist.
In our country there are no statistical data on the incidence of herpes, but herpes infection is widespread, as indicated by data from private examinations of carriers of the herpes simplex virus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zQNs9l4A31A
Recurrence of herpetic infection occurs in the event of reactivation of the virus, this is possible after hypothermia, overheating, with reduced immunity, in particular, herpetic infection is a specific complication of HIV infection.
Rashes caused by herpes virus serotype 1 are usually localized in the nasolabial area, the virus also manifests itself as keratoconjunctivitis, and rashes caused by HSV-2 are localized in the genital area. But, taking into account the characteristics of sexual behavior, the localization of the rash may be exactly the opposite.
Therefore, herpes requires serological studies to establish the serotype.
Herpes simplex
The group of herpes viruses includes 4 viruses similar in morphology: HSV (herpes simplex), varicella-zoster - the causative virus of herpes zoster and chickenpox, Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus; In 1962, it was discovered that the herpes simplex virus has two serotypes - serotype 1 and serotype 2.
Serological studies confirm that by the end of the 18th month of life, almost every person has been in contact with AIV-1, and the entry gate is usually the respiratory tract.
After which the virus penetrates the cells of the trigeminal ganglion, but during its life it may never cause clinical manifestations of infection.
The first contact with HSV-2 usually occurs during puberty at the beginning of sexual relations. Moreover, after external manifestations, which may not exist, the virus also becomes inactive and can persist in the cells of the sacral ganglion for a long time.
Herpes simplex, especially the second type, has oncogenic properties, which is of great importance, given the prevalence of the infection.
The incidence rate of herpes infection is approximately the same in all age groups and is equally common regardless of gender.
Clinical manifestations depend on the location and size of the lesion, as well as on the general condition of the immune system.
When the process is localized, blisters on areas of the skin that are not subject to maceration and friction shrink into a yellowish-gray crust, which disappears on its own after 5-7 days. And in place of the bubble, a pigmented area remains, which after some time acquires a normal color.
On the mucous membranes, as well as in those areas that are subject to maceration or friction, the bubbles open, resulting in the formation of polycyclic erosions with a bright red bottom.
The rashes are accompanied by burning, pain and a tingling sensation; if there are a lot of rashes, swelling of nearby tissues occurs.
The general condition of the patient with infection caused by the herpes simplex virus does not suffer, but in some cases chills, muscle pain and low-grade fever may occur. In general, the process lasts 10-14 days; when a secondary infection occurs, the duration of the disease increases.
The herpes simplex virus can cause herpetic stomatitis, the clinical manifestations of which are lesions of the mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, cheeks, gums and palate. Small groups of small bubbles appear on the swollen and hyperemic mucous membrane.
The bubbles open in the first few hours, leaving erosions that, due to fusion, have finely scalloped outlines. After 2-4 days, the erosions are covered with a delicate fibrous film and then epithelialized.
Herpetic stomatitis, not complicated by other infections, lasts 6-14 days, the general condition of the patient is satisfactory, but pain in the oral cavity and hypersalivation are noted.
In children of primary and preschool age, the herpes virus most often causes acute aphthous stomatitis. During the short prodromal period, general malaise, weakness, loss of appetite and a slight increase in body temperature are noted. The oral mucosa is sharply swollen and hyperemic, and aphthoid-like rashes are localized everywhere. Unlike simple stomatitis, the rashes have the form of aphthae with an area of necrosis in the center and a pronounced inflammatory rim along the periphery, the diameter of individual rashes is up to 1 cm. As the process progresses, the aphthae merge and form extensive erosive and ulcerative areas with uneven edges. There is hypersalivation, loss of appetite, fever and severe pain.
In some patients, relapses of herpes infection are possible depending on seasonality or without connection with the time of year; with reduced immunity, relapses can occur several times a month. Clinical manifestations of recurrent herpes depend on the location and general condition of the patient, but do not differ from the manifestations of herpes simplex.
The basis of the pathogenesis of recurrent herpes are predisposing factors: hypothermia or overheating of the body, common and colds, previous infectious diseases, as well as all diseases that weaken cellular immunity. In women, there is a connection between the periods of the menstrual cycle and exacerbations of recurrent herpes infection.
Diagnosis of diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus is not difficult, and in typical cases, clinical manifestations allow an accurate diagnosis to be made. But when localized in the genital area, herpetic ulcers may resemble chancroid.
Erosion caused by the herpes virus has a polycyclic outline and there is a tendency to merge fine-vesicular elements; there is no infiltration specific to chancre, on the basis of this their differentiation occurs. Herpes simplex, unlike syphilis, is acute and in most cases is recurrent.
In doubtful cases, they resort to laboratory diagnostics and test the erosion discharge for the presence of treponema pallidum.
Herpes, localized on the oral mucosa and occurring as stomatitis, should be differentiated from pemphigus vulgaris and from exudative erythema multiforme, which has a seasonal course and recurs in spring and autumn. Diagnosis of herpetic stomatitis is based on clinical manifestations.
Stomatitis caused by the herpes simplex virus is characterized by swelling and hyperemia of the oral mucosa, the appearance of large blisters prone to fusion. The blisters open within a few hours, and in their place there remain erosions with a scalloped edge, covered with a fibrous film on top.
If the red border of the lips is affected, then the exudate from serous quickly turns into bloody, and the rashes shrink into single bloody crusts. There is loss of appetite, hypersalivation and pain when eating.
Rashes with pemphigus are usually located singly on the mucous membrane, which is not prone to swelling, epithelization and formation of a fibrous film also do not occur, acantholytic cells are found in smears from the eroded surface, and Nikolsky’s symptom is positive, which is not observed during infection with the herpes virus.
If confirmation of the diagnosis of the presence of the herpes virus is required, then in the first few days from the onset of the disease, cytological studies are most informative. The material is taken by scraping and stained according to Romanovsky-Giemsa; after staining, giant multinucleated cells with basophilic cytoplasm are clearly visible.
The nuclei inside the cells are arranged crowded together, forming layers, and outwardly resemble a single conglomerate. If unclear staining occurs, then the nuclei may not have clear outlines, which does not make it difficult to confirm the diagnosis of herpes simplex.
Additionally, a PCR test for the herpes simplex virus, an immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) and a test for antiherpetic antibodies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are carried out.
Treatment of recurrent herpes involves immunorehabilitation of patients, this helps to achieve a reduction in relapses or stable remission. Herpes simplex does not tolerate monotherapy, since it is inappropriate; it is used only to treat the acute phase of the disease.
If you use such therapy as the only method of treatment, then the constant use of drugs such as acyclovir and valacyclovir, the use of ointments resemble a vicious circle from which it is impossible to escape, and stressful situations only aggravate the patient’s condition.
Complex treatment of infection caused by the herpes simplex virus can quickly stop the process and lead to stable remission. In the initial phase of relapse, a course of suppressor drugs is prescribed, for example acyclovir, valacyclovir. Taking these drugs for 5-7 days dramatically reduces the number of herpes viruses in the body.
After this, immunotherapeutic drugs are prescribed, in the form of courses of recombinant alpha interferons and/or immunomodulators. The duration of the course depends on the severity of the infection and the state of the patient’s immune system. In severe cases, alpha interferon is taken for 10 days or more.
After 1-2 months after stopping the process, it is advisable to use a herpetic vaccine, which allows you to achieve stable remission.
The effectiveness of vaccination depends on the state of immunity, the prescribed regimen and the frequency of administration of the drug.
The vaccine is administered intradermally with the formation of a specific “orange peel” at the injection site.
But the lack of timely revaccination significantly reduces the effectiveness of the entire multi-month course of treatment, so revaccination against the herpes simplex virus should be carried out without violating the deadlines.
Independent use of the inactivated herpes vaccine should be excluded, since, despite its simplicity, the procedure requires certain conditions and knowledge of medical personnel, and the instructions for use do not contain all the necessary information. Negative opinions about the vaccine are based on the fact that it slightly increases the likelihood of tumor development, but persistent infection caused by the herpes simplex virus can cause more serious damage to the immune system.
The vaccine contains inactivated HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses, which, like ordinary serotypes of herpes simplex, can transform, which, according to some studies, can induce cervical cancer in isolated cases.
But the vaccine and the virus present in the body have the same ability to induce the development of oncological processes, and therefore, for patients who have herpes, vaccination does not pose an additional risk of developing induced cancer. To prevent the formation of tumors, a reliable way is to use prophylactic specific anticancer vaccines.
Physiotherapeutic methods in the treatment of herpes simplex include ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy, OKUV, infrared irradiation, etc.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_dermatologia/herpes_simplex
Herpes simplex virus - causes, symptoms and treatment
Herpes simplex virus is a viral pathology characterized by the appearance on the skin and mucous membranes of characteristic blisters with a serous filling.
There are two serotypes of this virus: 1 and 2.
Once settled in a person’s body, this pathogen remains with him forever, so tests for igg and igm make it possible to determine antibodies to the virus and understand whether a person has it in the body.
Online consultation on the disease “Herpes simplex virus”.
Ask a question to the specialists for free: Dermatologist, Infectious disease specialist.
A positive test result for igg antibodies indicates that the pathogen is active, a negative result indicates that it is in the latent phase. Actually, even without analysis, a person can understand that a virus has appeared in his body when the disease manifests itself with pronounced symptoms.
The only problem is that a large number of people are asymptomatic carriers of the virus, that is, they have it in their bodies, but do not manifest themselves in any way.
People who do not have symptoms are also infectious to others, so testing for Igg antibodies should be done periodically, especially during pregnancy, when there is a risk of infection of the baby in the womb.
Peculiarities
Herpes simplex virus 1 is the most common and manifests itself with characteristic rashes on the lips, near the nose, on the cheeks and other parts of the face. Type 2 virus often leads to rashes on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Very often, this type of pathology is asymptomatic, although a person continues to infect others through sexual contact with them.
As mentioned above, it is impossible to cure this disease, but the body is able to produce antibodies, due to which the pathogen is kept under the control of the immune system for a long time.
When the immune defense weakens, viral rashes are the first sign of this - if there is a type 1 virus in the body, they appear on the lips (mainly), and with a type 2 virus - on the genitals.
Symptoms and stages
If an antibody test shows that IgM is detected in a person’s body, this indicates that the pathogen has not yet been activated and does not pose a threat to the person and the people around him.
But it is present in the body, and if favorable circumstances are created, it will manifest itself.
When an antibody test shows the presence of Igg, this means that the virus is active and the person poses a danger to others and requires treatment.
Herpes symptoms
The symptoms of the pathogen type 1 virus are specific, and they are difficult to confuse with the symptoms of another pathology. The disease manifests itself as rashes that look like small blisters with liquid on the hyperemic area of the skin or mucous membranes.
Depending on the stage of the disease, symptoms may vary. So, the first stage is characterized by the appearance of redness in a certain area and a feeling of itching.
If you begin to treat herpes at this stage, the likelihood of its development decreases sharply and the disease usually subsides.
The second stage is the appearance of small bubbles filled with transparent contents, which become cloudy over time. Itching at the site of the rash persists.
Stage three is characterized by ulceration of the vesicles, with the release of exudate and the formation of an erosive surface. During this period, a person is most contagious to others. An antibody test during this period shows the presence of Igg in the blood.
The last, fourth stage, is characterized by the formation of crusts, which, if their integrity is violated, can bleed and cause pain.
With a mild course of the pathology, there is usually no disturbance in the general condition, but with a severe form of the disease, a person may complain of:
- temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- enlargement of lymph nodes located near the site of the lesion;
- strong painful sensations.
If we talk about herpes simplex virus type 2 (genital), then its manifestations are similar to type 1 virus, with the only difference being that blisters form on the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs.
Genital herpes is divided into primary and secondary. They speak of primary when the disease first manifests itself - its course is more severe and prolonged than when it reoccurs.
Secondary genital herpes is a relapse of the pathology, occurring either with mild symptoms or asymptomatically. In a blood test, antibodies to the causative agent of herpes simplex type 2 also show the amount of igg or igm, which indicates the active phase of the disease or inactive.
Herpes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman can also become infected with herpes simplex type 1 or 2.
In adults, the herpes simplex virus rarely causes severe illness, but the fetus in the womb may develop various deformities as a result of its exposure.
In addition, it can cause severe congenital pathologies in newborns. Therefore, during pregnancy, women are first of all examined for antibodies to igg and igm.
The genital variety of the pathogen during pregnancy is a more dangerous form than the type 1 virus, since it causes severe disorders in the fetus three times more often. In particular, in the early stages of pregnancy, it can cause miscarriage and death of the fetus in the womb. If the child does not die in the mother’s womb, he may subsequently develop pathologies such as:
- convulsions;
- underdevelopment of the brain;
- mental retardation and other disorders.
When a woman becomes infected with this virus late in pregnancy, the baby may become infected during childbirth. In particular, he may develop encephalitis, develop skin rashes, and sometimes develop disseminated infection, in which the infection spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing the death of the baby.
Tests can be carried out several times throughout the entire period of gestation.
If they show: igm antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 are negative, and igg antibodies are negative, it means that at the moment the woman is healthy and her baby is not in danger.
In cases where the test for igg antibodies gives a positive result, it is necessary to undergo antiviral treatment, since this means that the pathogen is currently activated in the woman’s body and can threaten the life and health of her child.
Treatment
How to avoid getting herpes
As already mentioned, treatment does not completely destroy the herpes simplex virus in the body, but makes it possible to deactivate it.
The most common drug, which is effective against 90% of people with this disease, is Acyclovir and its generics.
This drug is effective against viruses types 1 and 2, is low cost and has virtually no side effects.
In Western countries, doctors are increasingly prescribing the drug Valacyclovir to patients with this pathology, which is more effective, but more expensive. Also, treatment of this disease can be carried out with the help of drugs such as Panavir, Flavozid, Proteflazid.
Treatment with traditional methods has a good effect. In particular, effective remedies in the fight against rashes on the lips and mucous membranes are garlic and celandine juice, which can be used to lubricate the rashes, which promotes their rapid healing.
Treatment with traditional medicine can be different, because there are many recipes for how to treat the disease - some remedies are used externally, others are taken orally.
But even diligent comprehensive treatment with medications and folk remedies will not remove the virus from the body, so it is very important to strengthen the immune system, which will suppress the virus, preventing it from manifesting itself.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/infektsii-parazity/1743-virus-prostogo-gerpesa-simptomy