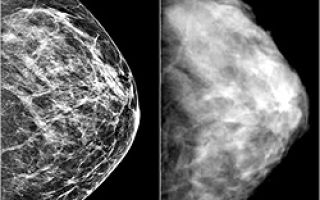
Mastopathy is the most common female disease, which is characterized by pathological changes in the tissue of the mammary glands. These changes cause the development of compactions of different types, which can be localized in different places of the chest. There are two main types of mastopathy – diffuse and nodular.
Quite a large number of women suffer from one or another type of mastopathy
Main types of pathology
Diffuse mastopathy is determined by the presence of compactions that appear in various places of the gland. This type of disease is considered its initial stage. Mastopathy is progressive in nature and often lasts for a long period at one level, and then, under a number of unfavorable circumstances, it can make a breakthrough in development.
The next stage of the disease is nodular mastopathy, which manifests itself as connective tissue nodes simultaneously in two mammary glands or one of them. Characterized by the appearance of individual or multiple nodes of different sizes. This subtype is considered a more dangerous type of mastopathy of the mammary gland due to the possibility of the nodes degenerating into a malignant formation.
Nodular mastopathy, which is more diffuse, is at risk of malignancy
Common causes of the disease
The types of disease described above are divided into several subtypes - fibrous, cystic and mixed, combining both subtypes. Each of them has different symptoms.
More often than others, the fibrocystic form of mastopathy is recorded, because, as the connective tissue grows, it creates fibrous adhesions together with cysts - cavities of fibrous tissue in which fluid is located.
For all types of mastopathy, several common causes of their occurrence can be named. This:
- genetic predisposition (burdened heredity);
- lack of regular sex life, bad habits;
Emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere contribute to the development of mastopathy
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- frequent stress and overexertion;
- injury to the mammary glands;
- abortions (increase the risk of mastopathy by 7 times), late births;
- existing concomitant diseases of the reproductive organs;
- Excessive exposure to the sun without a bra.
Separately, the fibrous or cystic form is found quite rarely. Most often they talk about diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of fibrous or cystic components, due to the fact that each form contains cysts and fibrous formations in different proportions.
In isolated form, any form of mastopathy is almost never diagnosed
Diffuse mastopathy and its subtypes
Diffuse mastopathy affects the mammary glands completely and often becomes a harbinger of nodular mastopathy.
The following symptoms correspond to this type of disease:
- swelling and increased sensitivity of the breast;
- pain of varying intensity in the mammary glands;
- the appearance of lumps in the chest, determined by palpation;
- the appearance of discharge from the nipples - transparent or greenish-brown.
By the appearance of discharge from the nipples one can judge the form of mastopathy and the stage of its progression
Diffuse mastopathy is divided into several types based on the nature of the damage to the mammary glands. She may be:
- fibrous, which is characterized by predominant changes in the connective tissue of the gland;
- fibrocystic – a mixed form of the disease, during the development of which cysts appear simultaneously with the active growth of connective tissue;
- cystic - characterized by the predominant presence of small cysts.
The most dangerous form of the disease is considered to be mixed type mastopathy.
With a mixed form of mastopathy, a woman may experience severe pain
It has to be treated long and hard, because with this type of mastopathy the soft tissue of the mammary glands is severely affected. Its symptoms can be either very pronounced or, on the contrary, not manifest themselves in any way, without creating the slightest discomfort for the woman’s well-being.
Fibrous mastopathy
For this subtype of mastopathy, characteristic features are the appearance of lumpy lumps in the breasts, itching of the nipples and possible discharge of clear fluid.
Grayish-green discharge from the nipples indicates an inflammatory process or tumor formation. Pain may occur. At the initial stage they are weak and aching, and at the later stage they are strong, radiating to the shoulder and neck.
The seals are soft and move easily across the chest.
Often the fibrous form occurs in girls 20–30 years old. It usually occurs due to changes in hormonal balance or due to poor heredity.
Fibrous mastopathy is often observed at a young age
Doctors recommend that such patients follow a diet that excludes alcoholic beverages, coffee and tea. These drinks contain substances that increase stress hormones, which leads to the formation of lumps. The diet should contain foods high in iodine, and meat foods should be included in the menu to a minimum.
Another type of such mastopathy is fibroadenoma, identified by a round, mobile formation in the chest area. With adenoma, lobules of the gland grow. It often occurs in women in early pregnancy, developing due to hormonal imbalance.
Changes in hormonal levels can cause the development of fibroadenoma in pregnant women
Fibroadenoma has a local or diffuse form. In the first case, all the lobules are large in size and the seals are located in one area; in the second, the seals have a different appearance and grow unevenly, without precise boundaries.
Cystic mastopathy
Small round lumps of different sizes in the mammary glands are considered the main sign of the cystic type of disease. The number of cysts can vary from one to many. This form develops due to hormonal disorders (decrease in progesterone and increase in estrogen levels in the body), breast trauma, heredity, and previous abortions.
Abortions and spontaneous miscarriages can provoke the development of mastopathy
A cyst is a dense formation surrounded by connective tissue, the cavity of which is filled with fluid. Small cystic mastopathy is not detected by palpation, but medium-sized cystic lumps can be more easily diagnosed by conventional palpation.
Characteristic signs of cystic mastopathy are sensations of pain and heaviness in the chest. When the inflammatory process occurs, the temperature rises, discharge from the nipples is noted, and the tissues in the affected area of the chest turn red. Enlargement of the lymph nodes under the arms may occur, accompanied by pain.
The group of axillary lymph nodes is the most often responsive to inflammatory processes in mastopathy
Fibrocystic mastopathy
All types of mastopathy pose an equal degree of danger to women. However, the most common and, at the same time, dangerous type of this disease, currently diagnosed most often, is its fibrocystic form, which is also called mixed.
It is more difficult to carry out effective treatment than other subspecies. Doctors explain this point simply - as a result of the changes that affect the mammary gland in the mixed form of the disease, all its tissues are affected.
All types of breast tissue are involved in the pathological process during FCM
This type of pathology is considered the most dangerous to health, because it is characterized by simultaneous cystic growth of formations with damage to the glandular connective tissue.
Women have to deal with varying degrees of such mastopathy, which can be minor, moderate or pronounced. The diagnosis depends on which component predominates in this pathology - fatty, glandular or connective.
This pathological process is observed in many female representatives. It usually occurs in women who have crossed the age of 30, but most often mixed mastopathy appears at the onset of menopause.
Women in menopause are at risk for the development of a mixed form of mastopathy
Nodular mastopathy
The main characteristic sign of this type of disease is considered to be partial disruption of the mammary gland tissue. Pathology is a formation in the form of nodes that have clear boundaries that are not connected to the surrounding tissues. This is a focal disease, in which damage may occur on the left side, right side, or involving the area of both breasts.
Nodular mastopathy has two types - proliferative and non-proliferative forms.
Formations in this disease appear due to improper cell division in the glands, accompanied by their proliferation. As a result, active growth of soft breast tissue is observed.
The proliferative form of nodular mastopathy is dangerous due to the possibility of malignancy - degeneration into a malignant formation
More serious complications can occur with proliferative mastopathy, which must be treated urgently to avoid complications.
In some cases, nodes are removed surgically while preserving the volume of the breasts as much as possible. This happens if there are many nodes or they are large in size.
The removed tissues must be sent for histological examination to exclude oncology.
If nodular mastopathy is detected in a timely manner, then treatment quickly produces a positive effect, significantly reducing the risk or completely eliminating the transition of mastopathy to malignancy.
Another complication of the nodular form is fibroadenoma, which can only be eliminated through surgery. This type of pathology most often occurs in women aged 30 to 50 years.
Nodular mastopathy is fraught with complications for which only surgical treatment is indicated
Preventive measures
Regardless of what types of mastopathy there are and their subtypes, following simple recommendations will significantly reduce the risk for women of developing any form of the disease. Prevention measures include:
- annual examination by a gynecologist (after the onset of sexual activity) and a mammologist (if indicated up to 30 years of age, after – once a year for each woman);
- complete cessation of alcohol and smoking;
- adherence to diet and proper nutrition;
- regular sex;
- minimizing stressful situations;
- selection of suitable underwear.
The mammography procedure will help identify mastopathy at an early stage of its development.
Due to the fact that mastopathy of the mammary glands is classified according to a complex system, which involves many types and their varieties, the method of treatment, necessary medications and frequency of monitoring are selected by the doctor based on examination data, laboratory tests, and the results of diagnostic studies.
With timely seeking help and proper treatment, getting rid of mastopathy occurs in a fairly short time.
All women need to know what the signs of mastopathy are in order to start treatment on time.
It is important to understand that with any negative changes in the functioning of internal organs, there is an increase in glandular tissue in the female breast, which reacts more than others to the processes occurring in the body.
Therefore, it is necessary to cure all diseases of your body in a timely manner, preventing them from affecting such a sensitive female organ as the breast.
Healthy women with strong immune systems are less likely to develop mastopathy
The growth of tumor-like formations is greatly influenced by the state of the patient’s immune system. Regardless of which form of this disease is diagnosed, a quick cure is possible in women who have a strong immune system.
A positive outcome of the disease is also associated with the speed of visiting doctors. The sooner a woman pays attention to suspicious symptoms and visits a gynecologist or mammologist, without trying to treat herself, the greater the opportunity to slow down the development of the disease or completely get rid of it.
You will learn from the video who is at risk for mastopathy and what to do if it is detected:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/mastopatiya/vidy-mastopatii-molochnyx-zhelez.html
Types of mastopathy
Most often, mastopathy is observed in women after 35 years of age. This disease also occurs at younger ages.
In women who have a history of gynecological and endocrine diseases, mastopathy develops in 70-90% of cases.
The development of the disease directly depends on neurohumoral regulation.
Everyone knows that the growth and development of the mammary gland directly depends on hormones. The most important are estrogen, prolactin and progesterone.
If their ratio is normal, the mammary glands are healthy. Mastopathy develops due to imbalance of hormones.
In this article we will look at what mastopathy is, what it is like, as well as its main methods of treatment.
The essence of pathology
Mastopathy is a pathology that is accompanied by changes in the tissue of the mammary gland. Fine-grained lumps form in the breasts, which most often cause pain.
Despite the fact that mastopathy is a benign disease, it can transform into oncology, and therefore requires a very careful attitude.
Mastopathy is a collective term that unites a whole group of breast pathologies. Since 1984, all pathologies of the mammary glands, which are accompanied by tissue changes due to hormonal imbalance, are commonly called mastopathy.
The main function of the mammary gland is to produce breast milk to feed the baby. It consists of connective, glandular and adipose tissue. The shape and size of the breast depends on the ratio of these tissues.
Every month, cyclic processes occur in the mammary glands, which are subject to hormonal regulation. If the correct concentration of hormones is disrupted, namely with a high estrogen content, the tissue in the mammary gland begins to change - the glandular tissue is converted into adipose or connective tissue.
This process can occur unevenly, which leads to the formation of dense tumors in the female breast.
Associated symptoms
The most common clinical signs of mastopathy are the following:
- pain in the mammary glands , which can be periodic or constant, with increased pain noted before the onset of menstruation, and after its end the pain may subside or even disappear completely;
- nipple discharge . The color of the discharge can be clear, white, yellowish, greenish or ichorous. Bloody discharge is considered the most dangerous;
- feeling of fullness of the mammary gland;
- swelling of the glands , and as a result - an increase in breast size;
- the presence of dense neoplasms in the gland, which a woman can palpate on her own. The lumps are painful, their size can vary - from very small to several cm.
Currently, medicine distinguishes the following types of mastopathy:
- involutive – growth of the subcutaneous fat layer. The development of pathology is noted in the deep layers of the mammary gland. The upper layers are significantly less involved in this process, since they contain a significant fibrous and glandular layer. The essence of the pathology is that glandular tissue is gradually replaced by adipose tissue, and thinning of the skin occurs;
- proliferative - gland tissue grows as a result of active cell division. In turn, this form of the disease is divided into epithelial, myoepithelial and fibroepithelial forms;
- dishormonal - involutive form most often occurs in women after 40 years, when natural changes occur in the structure of the mammary glands. Dishormonal mastopathy is changes in the mammary glands associated with hormonal imbalance.
The types of dishormonal mastopathy should be considered in more detail.
Diffuse
Diffuse mastopathy is a process that affects the entire mammary gland, and is often a harbinger of nodular mastopathy.
This form of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- breast swelling;
- increased sensitivity of the mammary glands;
- pain;
- presence of seals;
- nipple discharge.
Diffuse mastopathy, according to the nature of the damage to the glands, is divided into the following types:
- fibrous – changes in the connective tissue of the gland predominate. This pathology is observed in women under 30 years of age; the causes may be heredity and hormonal imbalance. A type of fibrous mastopathy is fibroadenoma - a round, mobile neoplasm in the mammary gland; in this form, the lobules of the mammary gland grow. Often develops in women carrying a baby;
- fibrocystic – a mixed form of pathology, which is accompanied by the growth of connective tissue and the presence of cystic neoplasms. In most cases, it is diagnosed after 35-40 years. The disease is characterized by a combination of symptoms of fibrous and cystic forms;
- cystic - this type of pathology is characterized by the presence of small cystic formations. Cysts are small connective tissue compactions with liquid contents. Small cystic mastopathy cannot be palpated; a characteristic sign is pain and heaviness in the mammary gland. As the inflammatory process develops, the tissues in the affected area turn red and the overall temperature rises.
Also read about the types of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Nodal
With nodular mastopathy, a characteristic feature is partial disruption of breast tissue.
The pathology itself consists of nodular formations that have regular and clear boundaries and do not connect with surrounding tissues. This is a focal disease that can be expressed in right-sided or left-sided lesions.
Nodular mastopathy can be proliferative or non-proliferative.
The reason for the formation of nodes is improper cell division and their pathological proliferation. The soft tissue of the mammary gland is actively growing.
The proliferative form can lead to serious complications, so nodular mastopathy must be treated very carefully. In some cases, surgical treatment is required; during the operation, the removed tissue is necessarily sent for a biopsy to exclude an oncological process.
What is the danger of the disease?
Any form of mastopathy is dangerous for the following reasons:
- Breast diseases often signal problems in the health of a woman’s reproductive system. Most often the problem lies in the ovaries. Their diseases, like the actual diseases of other organs of the reproductive system, are dangerous for a woman’s reproductive function;
- Often mastopathy develops simultaneously with disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine or nervous system. These diseases can lead to unpredictable consequences;
- The greatest danger of pathology is its transition into a precancerous and then into a cancerous state.
Can fibrocystic mastopathy develop into cancer? Read here.
In some cases, there is a retraction of the nipple, or lumpy skin of the mammary gland, which also does not have the best effect on the psychological state of the woman.
Basic treatment methods
- Of course, the selection of optimal therapy should be made by a competent doctor.
- Mastopathy can be treated conservatively or surgically.
- Which method is preferable depends on many factors:
- type of pathology;
- patient's age;
- the presence of concomitant ailments;
- degree of damage and so on.
- What should be the treatment for fibrocystic mastopathy, read in this article.
- Conservative treatment consists of taking hormonal drugs.
- These may be oral contraceptives or other hormonal drugs, which the doctor selects according to the patient’s age.
- Antietrogens are prescribed, which will reduce the concentration of estrogen in a woman’s body, and therefore eliminate the cause of mastopathy.
- Progestogens are also prescribed, which also normalize the balance of hormones, but there are a lot of contraindications for taking them, which a competent specialist will definitely take into account.
Non-hormonal treatment is possible, which is based on taking homeopathic medicines. This treatment is more effective in the initial stages of the disease, as well as if for some reason hormonal treatment is contraindicated for the patient.
The woman is also prescribed topical ointments and gels, analgesics to relieve pain, immunomodulators and vitamins to restore the body’s protective function.
In some cases, the prescription of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is required, which are especially relevant in the presence of severe pain.
Hepatoprotectors are necessary to maintain liver function and protect it from toxins. These drugs are prescribed for mastopathy due to the fact that, as a result of hormonal imbalance, the liver is also negatively affected.
- alternative medicine methods - hirudotherapy and treatment with herbal decoctions that have an antitumor effect.
- It is recommended to use sedatives that will suppress increased nervousness and mental disorders, which quite often occur in women with hormonal imbalance.
- Diuretics are prescribed if mastopathy leads to swelling of the mammary glands; as a rule, these are light diuretics - herbal teas.
- As for surgery, it can be performed in three ways:
- removal of the neoplasm itself, while the breast tissue remains intact;
- sectoral resection - removal of the tumor along with part of the damaged gland;
- radical resection – the mammary gland is completely removed.
There is a new development for the removal of benign tumors - laser ablation, but this intervention is not indicated for all patients.
Conclusion and conclusions
To prevent the development of mastopathy, it must be treated at the very beginning of its development. It is very important that the treatment is carried out by a competent specialist who has experience.
All types of mastopathy are treated in the same way - hormone therapy, non-hormonal treatment or surgery. As for the treatment features for each type of pathology, the doctor determines them in accordance with the test results individually for each patient.
Due to the fact that the classification of mastopathy is carried out according to a rather complex system, which involves many types and subtypes of the disease, treatment of different types may differ not in principles, but in the dosage of funds.
The potential risk of degeneration of a benign disease into a malignant process obliges us to take a responsible approach to regular breast self-palpation, timely visits to a mammologist and quality treatment.
Source: https://zhenskoe-zdorovye.com/mammologija/mastopatiya/vidy-mas
Mastopathy
Mastopathy is a pathological fibrocystic change in the breast tissue, characterized by the appearance of dense, often painful, fine-grained formations. Worrying about engorgement, soreness of the gland, more pronounced before menstruation, serous, sometimes bloody discharge from the nipple. Has a tendency to relapse and is a cancer risk factor. Diagnosis of mastopathy requires mammography, ultrasound of the mammary glands, and, if necessary, diaphanoscopy, MRI of the mammary glands, pneumocystography, and puncture biopsy. Treatment of mastopathy is carried out using conservative methods. If there is a danger of malignancy of nodular mastopathy, surgical removal of the node is performed.
Mastopathy is a concept that combines a group of diseases of the mammary glands, characterized by the development of pathological changes in the gland tissue with a violation of the ratio of epithelial and connective tissue components.
According to the WHO nosological classification of 1984, mastopathy is understood as fibrocystic disease of the mammary glands.
The incidence of mastopathy of various etiologies in young women ranges from 30-45% and increases noticeably after 40-45 years.
Mastopathy is a benign change in gland tissue that is directly dependent on neurohumoral regulation. This means that the factors for the development of mastopathy are both pathologies associated with disturbances in the state of nervous regulation (stress, neuroses, depression), and a disorder of hormonal balance and internal homeostasis of the body.
Mastopathy
There is currently no complete understanding of the causes and mechanisms of development of mastopathy, but there is every reason to assert that hormonal status plays a significant role in the occurrence of this disease.
Factors contributing to the development of mastopathy: early menopause, menstrual irregularities (hormonal dysfunctions, polycystic ovary syndrome, improper use of hormonal contraceptives), prolonged absence of childbirth, numerous (more than three) abortions, irregular sex life (or lack thereof), diseases of the genital organs , lactation for less than three months, endocrine pathologies (hypo- and hyperthyroidism, dysfunction of hypothalamic and pituitary regulation, functioning of the adrenal glands, liver, pancreas), hereditary predisposition.
There is an assumption that the most significant pathogenetic factor in the development of mastopathy is progesterone deficiency with an excess of estrogen.
In this case, there is an increase in proliferation (reproduction) of epithelial cells and connective tissue cellular elements. In addition, the production of prolactin plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of mastopathy.
Prolactinemia increases the sensitivity of breast tissue to estrogen.
The most common classification of mastopathy in clinical practice distinguishes three forms: mastalgia (mastoplasia or mastodynia), diffuse fibroadenomatosis and localized fibroadenomatosis. Mastalgia is characterized by a predominance of severe pain and is an indication for the prescription of analgesics.
Diffuse adenomatosis is the development of diffuse compactions and cysts in the gland tissue. It is divided into two types: fibrous mastopathy, when connective tissue seals are predominantly formed in the gland tissue, and fibrocystic mastopathy, when in the gland, in addition to foci of fibrosis, cysts (cavities filled with liquid) are formed in the gland.
With localized fibroadenomatosis, pathological changes are detected in a limited area of the gland (segment, quadrant) and do not spread throughout the parenchyma of the organ. Detection of a localized formation in the mammary gland is an indication for a biopsy to exclude a malignant tumor.
The predominance of the fibrous component is detected by touch as a compaction; cystic changes in the first stages may not be detected at all by palpation (duct microcysts). Pain in the mammary glands, as a rule, is dull, aching or pulling.
Its occurrence is associated with compression of nerve endings in glandular tissue by fibrous growths, as well as their partial sclerosis.
The intensity of the pain syndrome depends on the severity of the pathology; most often, the occurrence and intensification of pain is associated with the menstrual cycle (before menstruation, at the peak of estrogen production, the pain intensifies). Sometimes there is irradiation of pain into the shoulder blade or arm.
In 10-15% of women, there are no complaints of pain, although upon examination pathological changes of a significant degree are detected.
This is associated with different levels of pain sensitivity in women and the individual branching of the nervous system of the mammary glands.
About 10% of mastopathy is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits. Sometimes palpation of the lymph nodes is moderately painful.
An increase in the volume of the mammary gland, their periodic engorgement (in the second period of the menstrual cycle) is associated with the formation of venous stagnation in the vascular network of the glands and swelling of the connective tissue.
The glands can increase by 15%. This is characterized by a feeling of discomfort and pain during palpation (increased breast sensitivity). The combination of these symptoms is called premenstrual syndrome.
Sometimes there is discharge from the nipples of varying degrees of abundance and of varying nature. They can only be detected when pressing on the nipple, and can be quite pronounced.
The consistency of the discharge is usually transparent or whitish, and may have a greenish or reddish-brown color. The greatest danger is bloody discharge, as it can be a sign of the development of a malignant process.
The appearance of any discharge from the nipples, regardless of its nature, is a reason to contact a mammologist.
You also need to be careful about detecting a node (or several). Palpation of a dense, limited nodular formation may be a sign of localized nodular mastopathy, or it may be developing breast cancer. When nodes in the mammary gland that are suspicious from the point of view of malignancy are identified, a biopsy is always prescribed.
One of the most significant elements of timely detection of pathologies and neoplasms in the mammary glands is self-examination (self-palpation of the mammary glands). To identify formations, determine their shape, size, quantity, as well as to identify diffuse pathological changes in the gland tissue, instrumental diagnostic methods are used.
Biocontrast mammography is an X-ray examination of the mammary glands. Mammography is optimally performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. A chest photograph is taken in two projections: frontal and lateral. This study is one of the most informative and specific.
In addition, ultrasound of the mammary glands is currently used. As a rule, fibrocystic changes in glandular tissue affect the echogenicity of its structures and can be identified and studied quite qualitatively using this technique.
MRI of the breast marks areas of increased and decreased temperature of the gland tissue. The diaphanoscopy technique involves transilluminating the mammary gland using a light source. In this case, the neoplasm in its thickness will be noted as a darker spot. Using ductography, the system of the milk ducts is examined.
A contrast agent is injected into the mammary gland through the nipple, after which an x-ray is taken. The image visualizes the ductal system; areas of deficient filling with contrast agent may be signs of neoplasms. Pneumocystography is performed under ultrasound control.
Air is injected into the cyst cavity using a thin needle, which allows the walls to be straightened and carefully examined for wall formations.
When a nodular formation is detected, a breast biopsy is performed - a tissue sample is extracted using puncture with a thin needle for histological examination.
To identify the etiological factors of mastopathy, methods of studying hormonal status are used.
Colposcopy and cytological examination of vaginal epithelial cells allows us to draw a conclusion about the total hormonal background, since the shape and structure of the cells directly depend on the action of sex hormones.
They directly determine the content of hormones in the blood: progesterone and estrogens, follicle-stimulating, luteinizing hormones, as well as thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenal hormones. Sometimes a test is performed for the presence of autoantibodies to thyroid cells to detect autoimmune thyroiditis.
To determine the general hormonal state of the body, studies of the organs of the endocrine system are carried out to identify possible pathologies (ultrasound of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, liver, pancreas; radiography of the sella turcica, CT scan of the pituitary gland). To exclude immune and metabolic pathologies, an immunogram is done and a biochemical blood test is performed.
In the treatment of mastopathy, correction of the hormonal balance of the body plays a significant role. When choosing treatment tactics, consultation with a gynecologist and endocrinologist is necessary. These specialists jointly perform a thorough analysis of the endocrine system and prescribe medications that correspond to the identified pathologies.
In cases of severe estrogenism (and significant pain), medications that reduce the effect of these hormones on the mammary gland (tamoxifen, toremifene citrate) may be prescribed.
To normalize the menstrual cycle, oral contraceptives are used (chosen according to hormonal status). To treat functional disorders of the thyroid gland, agents that regulate the production of thyroid hormones are used.
Vitamin complexes help improve liver function and normalize metabolic processes.
Among other things, topical progesterone preparations are used (act directly on the gland tissue, helping to reduce the proliferation of connective tissue and epithelial cells, relieving swelling), and homeopathic remedies.
Patients suffering from mastopathy are advised to limit the consumption of coffee and strong tea, stop smoking, and enrich their diet with fruits, vegetables, and foods high in fiber and vitamins.
If a malignant tumor is suspected, the node is surgically removed; in other cases, conservative treatment is limited.
As a rule, mastopathy is not prone to complications and malignancy. With proper correction of the hormonal state, the prognosis is positive, but hormonal imbalances can provoke relapses.
Many factors contributing to the development of mastopathy make it difficult to develop a unified and consistent prevention scheme.
However, the most significant factors should be avoided: stressful situations (as a preventive measure, it is recommended to take medicinal sedatives of natural origin - valerian, motherwort), creating a psychologically comfortable environment, and a positive way of thinking.
Proper balanced nutrition without excess calories, prevention of excess weight and obesity, but without indulgence in mono-diets and dubious weight loss methods, help maintain internal homeostasis and the proper functioning of the neurohumoral regulatory system. One of the dietary components that negatively affects the hormonal status of women is caffeine. Women should limit and, if possible, completely eliminate caffeine from their diet and in no case abuse strong coffee on an empty stomach.
Older women using oral contraceptives should stop smoking. Limiting the consumption of alcoholic beverages will also be useful in terms of preventing breast pathologies. A significant factor in maintaining a woman’s health is regular sex life and physical activity.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_mammology/mastopatia
Mastopathy as a dyshormonal disease
Mastopathy is a series of breast diseases that are characterized by the development of single or multiple benign neoplasms in its parenchyma. In some cases, this diagnosis can be made without the presence of a tumor.
Today, there are approximately 50 different nosologies that potentially fit the above definition. That is why the classification of mastopathy is very multifaceted and there are several working versions that are successfully used by doctors all over the world. It all depends on the specific situation and need.
Breast mastopathy is a dyshormonal disorder in the patient’s body, which leads to histological changes in breast tissue and the appearance of characteristic symptoms. Therefore, it would be fair to use the term “hormonal mastopathy” for almost all types of this disease.
Clinical classification
Now in the world there are several recognized ways to differentiate the disease according to various characteristics. One of the most common among practicing doctors remains the classification of mastopathy according to the severity of clinical manifestations. According to it, there are three main forms of damage to the mammary glands:
- Mastalgia (mastodynia) is a variant of the disease, which is characterized by the appearance of painful sensations in the parenchyma of the breast in a state of calm and upon palpation. This remains the leading symptom of the pathology. In addition, changes in the appearance, structure and shape of the mammary gland (swelling, hardening, increased venous pattern) may be detected.
- Diffuse form of mastopathy. It is characterized by the massive formation of various compactions and cysts in the breast tissue. In turn, it is divided into 2 subspecies:
- Fibrous. The main reason for this dyshormonal disease is the presence of neoplasms with a predominance of connective tissue and fibrous component in the glands. The pathological process is interstitial in nature with damage to fibrous cords and fibers.
- Fibrocystic. Progression of the disease is observed with additional formation of cavities (cysts), which are filled with serous fluid. This form is relatively easy to diagnose thanks to modern methods of examining the patient.
- Localized mastopathy (focal fibroadenomatosis). One of the types of breast disease, which is characterized by the presence of a benign neoplasm (mostly single), which is shaped like a cake and remains “mobile”. On palpation, pain is noted in the affected area. The consistency of the tumor is elastic. When clear boundaries and increased density of this element are determined, we can talk about the presence of a cyst. Focal mastopathy requires clear differentiation from breast cancer.
One of the forms of localized mastopathy remains fibroadenoma or “breast mouse”. It manifests itself mainly in adolescence (puberty). Upon palpation, a round, elastic neoplasm is detected, which has smooth and even boundaries and often does not cause pain.
Classification according to ICD-10
According to it, scientists and doctors distinguish the following types of mastopathy:
- N60 – benign type of breast dysplasia (including the fibrocystic form of the disease).
- N60.0 – single (solitary) breast cyst.
- N60.1 – diffuse form of cystic mastopathy.
- N60.2 – breast fibroadenosis.
- N60.3 – fibrous sclerosis of the mammary gland.
- N60.4 – ectasia of the milk ducts of the breast.
- N60.8 – other benign forms of mammary dysplasia.
- N60.9 – unspecified type of benign breast dysplasia.
This classification provides the possibility of total unification of all diagnoses and mutual understanding between medical staff around the world.
Thanks to the availability of standard ciphers, a doctor in India can easily understand his colleague from the USA or Russia.
However, as practice shows, in everyday healing this type of differentiation of diseases is not particularly popular. It is used when patients are discharged or transferred to another facility.
Clinical and radiological classification
In 1984, the World Health Organization (WHO) proposed the following definition of the term “mastopathy” - a complex of pathological processes that are characterized by the progression and regression of changes in the structure of the parenchyma of the mammary glands. As a result, there is the formation of inadequate relationships between the epithelial and connective tissue components with the development of fibrous and cystic neoplasms in the parenchyma of the organ.
Women with fibrocystic mastopathy are at risk for breast cancer
According to this definition, in 1985, the USSR Ministry of Health proposed a clinical and radiological classification of the disease, which is actively used in modern medical practice. It is based on the results of radiation studies and the clinical picture of the disease and proposes a division of the disease into the following forms:
- Diffuse. It is characterized by multiple neoplasms in the parenchyma of the gland and provides for additional differentiation into the following subtypes:
- Glandular mastopathy. Another name for the pathology is adenosis.
- Fibroadenomatosis. A variant of the disease that develops with a predominance of the fibrous component.
- Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component.
- Mixed form, which includes characteristics of all previous types of pathology. The second name is fibrocystic mastopathy.
- Sclerosing adenosis.
- Nodular or focal mastopathy.
- Benign neoplasms and tumor-like processes:
- Cyst.
- Adenoma.
- Fibroadenoma.
- Intraductal papilloma.
Characteristics of diffuse types of breast lesions:
- Glandular mastopathy is a borderline condition between normal and pathological. It most often occurs in women aged 20-30 years and is manifested by hyperplasia of the glandular elements (lobules) of the mammary glands.
- Fibroadenomatosis is manifested by a significant change in the internal structure of the parenchyma of the gland. There is a significant replacement of glandular components with connective tissue. It occurs more often in women over 40.
- Mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component is characterized by the formation of chambers of different sizes with liquid contents. Most often this is serous matter, sometimes fatty deposits. The cause of the pathology is a violation of the excretory function of the milk ducts with their subsequent fibrosis. The process is basically two-way. The size of the lesions can vary from a few millimeters to 4-5 centimeters.
- Mixed forms of mastopathy are characterized by the presence of all the pathological elements described above. The degree of manifestation of certain disorders is determined by the individual course of the disease in each patient.
Focal mastopathy (nodular) is characterized by the presence of one (rarely several) areas of compaction of the gland parenchyma with clear edges and regular shape. The surface may be granular, lobed or smooth.
Source: http://grudi.pro/zabolevaniya/mastopathy/klassifikaciya-mastopatii.html
62. Mastopathy. Classification, diagnosis, treatment
one
of the most common diseases
of women: the incidence is 30-43%, and among
women suffering from various
gynecological diseases - 58%. The frequency
of mastopathy reaches a maximum at 45 years of age.
According to
the WHO definition (1984), mastopathy
is
a fibrous-knstotic
disease characterized by a spectrum of
proliferative and regressive changes
in gland tissue with an abnormal ratio
of epithelial and connective tissue
components.
In
etiology, a huge role is given to
the state of
the hypothalamic-hypophyseal system.
progesterone deficiency conditions ( in
which excess estrogen causes
proliferation of all gland tissues),
less
influence from liver diseases (Diseases of the hepatobiliary
initiate the development of chronic hyperestrogenism
utilization of estrogens in the liver).
Thyroid hormones (thyroxine,
triiodothyronine) play an important role in
the morphogenesis and functional
differentiation of
mammary epithelial cells.
In 64% of patients with various
forms of mastopathy, pathology
of the thyroid gland was detected.
-
Classification.
-
1. Diffuse
fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM): - 1) with a predominance
of the glandular component (adenosis); - 2) with a predominance
of the fibrous component; - 3) with a predominance
of the cystic component; - 4)
mixed form I -
2. Nodular
fibrocystic mastopathy
Diffuse
and nodular FCM can have both proliferating
and non-proliferating forms.
With proliferation in the epithelium, papillomas develop
.
There is
a special form of mammary gland pathology
in the premenstrual period : mastodynia
or mastalgia -
cyclic
engorgement of the gland, caused by
venous stagnation and swelling of the stroma;
the mammary gland increases in volume
by more than 15%,
Clinic. The main
pain
is
pain, which usually intensifies in
the premenstrual period, sometimes from
the second half of the menstrual cycle.
The pain may be local and
radiate to the arm or shoulder blade.
Women also note painful
lumps in the gland.
There are three clinical phases of mastopathy:
-
1 -
age 20-30 years, the menstrual cycle
is regular, but often shortened to
21-24 days;
a week before mens engorgement, tenderness of the mammary gland appears
, - 2-30-40
years the pain is constant, lasts
2-3 weeks until mens
individual
painful compacted lobules - 3 – age over
40-45 years, pain is less intense and
cystic formations
are palpable a brownish-green secretion is released when pressed. - 10-15% of women
have no pain, but there are changes
Treatment.
Women in
whom FCM was discovered accidentally as
a concomitant pathology without significant
complaints do not require special treatment.
Such patients must be examined (
ultrasound and/or mammography
puncture) and further observation can be continued
a gynecologist or surgeon at least once
Women
with moderate cyclic or constant
form of mastodynia and diffuse
fibrocystic changes
in the structure of the mammary gland are treated
with conservative therapy using
both hormonal therapy and
non-hormonal treatment methods.
Most often this applies to young, practically
healthy women.
1.Methods of
non-hormonal therapy
correction
. limiting products containing
coffee, tea, chocolate, cocoa, cola) or completely
Both
FCM and breast cancer are
associated with sluggish bowel movements,
chronic constipation, altered
intestinal microflora and insufficient
fiber in the daily
diet.
In this case, reabsorption
already excreted in bile occurs from the intestine
-> consumption of food rich
in fiber and adequate
fluid intake (at least 1.5-2 liters per day).
Since
recycling
estrogen
occurs in the liver, any
dietary disturbances that impede or limit
the normal functioning of the liver (cholestasis,
high-fat foods, alcohol, other
hepatotoxic substances) over time
can affect the clearance of
estrogen in the body.
In turn, to facilitate and normalize
liver function, additional intake
of vitamins B
(especially
Bb), A
C and B is desirable - as food additives or even in therapeutic
Diuretics
. Cyclic
mastopathy, as one of the manifestations
of premenstrual syndrome, especially
if it is accompanied by swelling of the hands
and feet shortly before menstruation, can
be treated with mild diaphoretics.
-
NSAIDs
for pain -
Medicines
that improve blood circulation Ascorutin - (eat
chokeberries, cherries, raspberries,
citrus fruits)
Calming
agents. The mammary
glands are a very sensitive
organ to psycho-emotional stress.
(tincture of motherwort, valerian, etc.
).
-
Choosing
a bra. don't
ignore, don't wear small -
2Hormonal
therapy - Hormone therapy
is aimed at reducing the stimulating
effect of estrogens on the mammary
glands -
Antiestrogens.
(tamoxifen,
toremifene) block estrogen receptors
in target tissues
contraception
. Properly
selected and used oral
contraception provides constant
suppression of steroidogenesis and ovulation,
suppression of the synthesis of ovarian
androgens, as well as estrogen receptors
in the endometrium, equalization of excessive fluctuations
long-term protection against the development of ovarian
Gestagens
inhibit functional gonpophyseal-ovarian
connections and reduce
the proliferation-stimulating effect of estrogens on
breast tissue.
Androgens
(danazol)
as estrogen antagonists are used
to treat mastopathy.
The action of danazol is based on its ability to inhibit
the synthesis of gonadotropic hormone
inhibitors
. These
drugs (bromocriptine) are prescribed only
to patients with hyperprolactinemia.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues significantly
reduce circulating levels
of estrogens and testosterone.
Conservative therapy for FCM requires long courses (3-6
months). However, already 1 year after the end of
treatment, a relapse of the disease occurs in 60% of cases
.
3. Surgical
sectoral
resection of the mammary gland with urgent
histological examination of the node.
In cases where cytological
examination reveals proliferating
the treatment of choice is simple mastectomy
This form of mastopathy
should be considered as an obligate
precancer.
?.
Pelvic pain
syndrome Causes. Diagnostics. Treatment.
- —
Pain in the pelvis, abdominal wall,
below the navel, lower back, may not have
a cyclic pattern - a connection with the menstrual
cycle, and leads to a deterioration
in the functional state of the woman. -
Classification1) Acute
and Chronic.2) Cyclic and Non-cyclic -
Causes of
acute pelvic pain1) Cyclic
pain: ovulation;
primary or secondary algodismenorrhea
2) Non-cyclic
pain: ectopic
pregnancy; termination of intrauterine
pregnancy;
ischemic pain; rupture of space-occupying formations; inflammation
of the internal genital organs; acute
abdominal aortic
aneurysm of mesenteric circulation, etc. -
Differential
diagnosis: * Ovulation - hemorrhagic
syndrome is not very pronounced, but there may be
hemodynamic disorders -
*Apoplexy
of the ovary -
rupture of the corpus luteum in the luteal phase,
blood loss is often insignificant; * Rupture
of a benign tumor -
peritonitis clinical picture Myoma moderate
bleeding; * Acute
salpingitis -
acute onset and acute pain syndrome,
the infection quickly spreads to
the pelvis and abdominal cavity, the pain
intensifies with movement;* Tuboovarian
abscess is
a bilateral process, pronounced,
prolonged pain, fever.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome pain in
the pelvis, abdominal wall below the navel,
lower back, which lasts 6 months or
more
Gynecological
reasons: chronic.
inflammatory diseases of the pelvis
(subacute salpingoophoritis, chlamydial
salpingitis, tuberculous salpingitis,
chronic
endometritis); adhesions in the pelvis
; fibroids, circulatory disorders
in myomatous nodes; endosalpingiosis;
ovarian cysts; ovulatory
pain; pelvic varicose disease
(“congestive syndrome”); impaired
outflow of menstrual blood with malformations
; cancer of the internal genital organs
, etc. .
Urological
causes:
bladder
cancer urinary tract infection ; interstitial cystitis; radiation
cystitis;
urolithiasis; ureterocele , etc.
-
Gastroenterological
causes:
colon
cancer chronic obstruction; colitis; constipation; diverticulitis;
Crohn's disease; - Hernias; IBS, etc.
-
Musculo-ligamentous,
bone and neurological
causes: myofascial
pain (myofascial syndrome) of the anterior
abdominal wall, pelvic floor, other
pelvic muscles and fibromyalgia, accompanied by
spasm or neuralgia, etc. -
Other
causes: psychogenic
pain (stress, emotional problems -
depression); porphyria; mesenteric adenitis
(inflammatory lesion of the
mesenteric lymph nodes), etc. -
Diagnostics: Diagnosis
of gynecological diseases, the most
common causes of chronic syndrome. pelvic pain - Exclusion
of extragenital pathology that
can cause pain:
urological, muscular and neurological,
gastroenterological
Methods:
1. History
2. Examination 3. manual examination 4. Ultrasound
5. X-ray 6. MRI 7. Laparoscopy
8. Laboratory
- Treatment
-
Medication : 1) In the
absence of obvious gynecological
pathology - oral contraceptives
and/or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs (COX-2 selective);
2) Antidepressants if there are signs of depression.
3) Manual therapy 4) Reflexology -
Indications
for surgical treatment: 1) fibroids
2) hydrosalpinx 3) cysts in the area of
the uterine appendages and other space-occupying formations
in the pelvic area (malignant
tumors, purulent-inflammatory
formations);
4) prolapse (drooping) of the genitals, etc. - Laparoscopy
- in the absence of a positive effect
from conservative therapy, the possible
causes of chronic pelvic pain
are eliminated, and in the absence of pathology
, the uterosacral ligaments are intersected
or a presacral
neurectomy is performed.
Source: https://studfile.net/preview/6024460/page:22/