HPV is a human papillomavirus, which 8 out of 10 people have, and the risk of becoming infected is very high. Women are more susceptible to this problem.
According to statistics, almost all representatives of the fair sex become infected before the age of 50. HPV type 45 can cause cervical cancer, which is dangerous for women. The level of oncogenicity of this species is high.
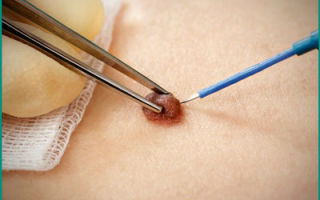
Therefore, if you have flat or genital warts on your body, you should immediately undergo a diagnosis.
HPV type 45 is especially dangerous for women
Details about the pathology and routes of transmission
There are more than 100 varieties of human papillomavirus, most of which are harmless. In this case, warts may not appear if the person has a high level of defenses. But even with the formation of growths, the likelihood of spontaneous expression over time is enormous.
However, about 30 subtypes are responsible for urogenital infections in men and women. Some strains of the virus cause the development of genital warts. In medicine they are called condylomata acuminata. If HPV type 45 is diagnosed in women, how dangerous the species is can be determined by the following list of the body’s reaction to its development:
- proliferation of genital warts in the genital area, regardless of the patient’s gender;
- in women, growths form on the walls of the vagina;
Condylomas appear in the patient's genital area
- damage to the anal area;
- penetration into internal organs;
- rapid growth and frequent itching;
- bleeding;
- degeneration into cancer cells.
During the examination, you can hear about HPV type 45 DNA in women, which leads to an acceleration of the problem. Yes, the virus changes its genetic code. This fact triggers a rapid process of cell division and proliferation of the formation over a large area. And such a lesion can be diagnosed using the PCR or Digen test method.
The virus multiplies quickly in the body
HPV type 45 manifests itself equally in men as in women. It is easy to become infected during sexual contact. The risk of degeneration into cancer is somewhat lower due to high stress resistance, so pathology rarely develops against the background of a depressive state or hormonal imbalance.
The physiological feature of the male genital organs facilitates diagnosis, because they are not hidden deep in the body, and all changes and rashes can be seen immediately.
Methods of infection with papillomavirus type 45:
- an act of love that occurred without a protective device;
- being in places of public use (nail salons, saunas, baths);
The virus is transmitted sexually
- household contact with an infected person;
- the presence of microtraumas on the genitals;
- infection in a medical facility due to the negligence of health workers and lack of personal hygiene.
Laryngeal papillomas in children born by cesarean section indicate the possibility of infection of the child in the womb (placenta). Another source of pathology is infected family members.
Risks and dangers of the disease
This is a highly oncogenic genotype of the virus, when infected, there is a high probability of developing cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva or anus in women.
Changes caused by the HPV virus can complicate pregnancy, as large warts or cancer develop as a result of the infection.
Doctors say that human papillomavirus type 45 in women more often provokes miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy.
Infection can cause miscarriage
Before conceiving a child, it is worth taking a test for the presence of HPV and other urogenital infections. If such a pathology exists, you need to start treatment before and during pregnancy (the drugs used can harm the baby). Carrying a fetus in combination with HPV type 45 or the presence of warts in the past becomes a threat to mother and child. In this case, it is better to inform your gynecologist about this.
The specialist can immediately plan a cesarean section, since the passage of the fetus through the birth canal infects it with the HPV virus, which is fraught with various complications.
Men are diagnosed with cancer of the anus or penis. Genital papillomas affect the inner side of the foreskin and form on the skin of the scrotum and groin. The growth will be soft and whitish, gray or pinkish in color. The papilloma is elongated or thread-like.
In men, warts affect the penis
Another type of penis lesion is a small flat discoloration with a broad base. Anal condyloma is more often diagnosed in men than in women. Homosexuals suffer from this pathology. People with weakened immune systems find it difficult to get rid of a viral infection.
Untreated phimosis is considered a factor in the development of penile cancer, but it can also occur in men who do not take care of personal hygiene. Cancer is more common in uncircumcised patients, while the procedure performed in infancy reduces the likelihood of the disease. Neoplastic lesions occur on the glans and foreskin and are less commonly observed elsewhere on the penis.
Over time, erosions and ulcers may appear. The disease is chronic, and in the absence of proper treatment it causes significant destruction of the penis.
Cancer infiltration towards the urethra causes pathology in the urination process, including retention. In the early stages of the disease, it is effectively treated with cryotherapy and laser techniques.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a common cause of organ amputation.
Pathology disrupts the urination process
Clinical picture
Within 2-3 weeks or months after infection, condylomata acuminata occurs around the labia and cervix in women or on the scrotum and anus in men. These are single or confluent growths that look like cauliflower. They increase in size and may cause pain during intercourse or prevent urination.
Genital warts occur on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, resulting from a secondary infection resulting from lesions on the skin or as a result of anal intercourse.
In men with the development of anal cancer, the following is observed:
- bleeding;
- soreness;
If the anus is affected, men may experience anal discharge
Lymph nodes around the anus or groin become enlarged. Oncology of the penis in men is manifested by the following changes:
- the color and thickness of the skin differs;
- the genital organ thickens;
- wounds appear, which are accompanied by pain and bleeding.
With the development of cancer, the penis thickens
This disease in some cases is asymptomatic. The incubation period of papillomavirus ranges from 6 weeks to 8 months.
Development of the disease by stages
Usually, having become infected after an act of love, a person does not feel any changes in his body. And at this time, the pathology develops, going through several stages.
Viral agents penetrate the mucous membrane, microtraumas on the skin and begin to fight immune cells. With a low level of protective forces, victory goes to the HPV strain.
The further action is to penetrate healthy cells and penetrate into the structure of the basal layer of the epithelial system of the cervix.
This is how the virus integrates into chromosomes and disrupts their functionality. All this leads to rapid and uncontrolled division of infected cells, from which the papilloma body develops. This is the first stage when the growths are just forming.
Women develop cervical dysplasia
At the second stage, cervical dysplasia occurs, which leads to the formation of the last step - the development of cancer. There are usually no symptoms, which makes diagnosing the pathology difficult. Only in some cases there may be bleeding during the act of love.
The immediate process of dysplasia can be characterized by 3 stages:
- Easy. The epithelium is affected by 1/3, but in most cases the pathology disappears on its own. The patient is under medical supervision at all times.
- Average. The lesion increases by 2/3, but this is noticeable only in some places, and not over the entire area. The patient will be prescribed an immediate course of therapy.
- Heavy. Surface damage is 2/3. Urgent course of treatment.
There are 3 stages of cervical dysplasia
Diagnostic measures
Cytological examination often identifies changes caused by early-stage human papillomaviruses. The procedure is painless and lasts a moment. It is recommended to do the analysis once a year (but at least once every 3 years).
Cytological testing is not specific for HPV viruses, so the result of such a test does not clearly indicate the presence or absence of infection. For women over 30 years of age, a molecular test is used, which more reliably identifies HPV and, in combination with cytology, confirms the pathology.
Detection of papilloma in men is not as easy as in women. The only way to detect the virus is to test HPV DNA. To perform testing, the doctor must take the material for examination.
Diagnosis is carried out by cytological examination
It is important not to wash your genitals 12 hours before the test.
Course of therapy
If HPV 45 is diagnosed, only a doctor will tell you how to treat it and with what medications. You should not expect results from traditional medicine; you need to carry out complex therapy.
There are no antiviral drugs to treat HPV type 45, but there are many symptomatic treatments for genital warts, precancerous lesions and cervical cancer.
In some cases this is enough, but there is no guarantee that the changes will not appear again.
At the first stage of mild damage, doctors prescribe immunostimulants, vitamin complexes and traditional methods of therapy. The second stage of moderate level of damage requires restorative drugs. At the last stage, a complex of therapeutic measures is used:
Viferon helps strengthen the immune system
- taking Viferon;
- antiviral Isoprinosine;
- insertion of suppositories or tampons to eliminate HPV;
- hardware techniques.
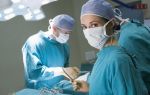
Sometimes it is necessary to perform a freezing procedure or treat the pathology with the classical method of surgical excision. Laser manipulation, radio wave therapy, and removal of the cervix or entire organ according to indications are popular. Consultation with a gynecologist, urologist or dermatovenerologist is necessary.
In advanced cases, the cervix is removed
ethnoscience
To remove warts, various herbal remedies are recommended that are applied to the skin. Be sure to use Vaseline ointment around the papilloma, after which a clean bandage is applied. This therapy must be repeated every day until the growths disappear.
In the morning and evening, you can apply dandelion juice to the wart or rub it with a clove of raw garlic or onion 2 times a day. Banana peel compresses will help get rid of papilloma if you do them 2-3 times a day. You can take propolis tincture 15-20 drops per day.
An antiseptic is useful. Thus, iodine dries out neoplasm tissue and is often used in the fight against papillomatosis. But it should be remembered that the drug cannot be used on the face and mucous membranes.
The growths are treated with iodine
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer and constantly maintain normal body health, it is necessary to get vaccinated against HPV. The procedure is carried out in 3 stages: the second 2 months after the first, and the third - after the next 4.
The vaccine is prescribed by a family doctor or pediatrician. Doctors especially recommend vaccinating girls who have not practiced sexual intercourse (since the age of 12), but the procedure is also useful for adult women who are sexually active and not infected with HPV. A gynecologist gives a referral for manipulation.
You can reduce your risk of getting HPV by limiting the number of sexual partners you have. Correct use of condoms reduces the likelihood of infection, but complete protection with these products is not yet guaranteed. It is recommended to regularly test for HPV type 45 DNA in women, which clearly confirms the presence of infection at the earliest stages.
The doctor will tell you in the video what danger HPV poses:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/vpch-45.html
HPV type 45 in women
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the common name for a group of viruses that has more than 100 different types. It is the second most common viral infection of the female genital area, as it is found in approximately 70% of the population.
HPV penetrates into human cells and exists there in 2 forms: benign and malignant. In the first version, it lives outside the human chromosome, in the second, it is integrated into the genome and causes tissue degeneration. The incubation period can last from several weeks to several years.
Depending on the level of danger, all types of HPV can be divided into three groups:
- non-oncogenic;
- low oncogenic risk;
- highly oncogenic.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The disease does not manifest itself in any way until the immune system is severely weakened. On the body, HPV manifests itself by the appearance of papillomas and condylomas. If these tumors are not treated and removed, the virus will continue to spread throughout the body.
Genital warts are flesh-colored
The following factors can activate type 45 strain:
- acute and chronic diseases that reduce immunity;
- stress, depression, constant fatigue and excessive irritability;
- the period before, during and after pregnancy;
- bad habits (alcohol, nicotine and drugs);
- low physical activity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- promiscuous unprotected sexual intercourse (including without penetration, but with close contact of mucous membranes).
HPV infection often occurs through sexual contact or close contact with a carrier of the virus. Moreover, the disease can remain in a latent state for many years (more than 15 years) and does not manifest itself in any way until the immune system is greatly reduced.
In order not to create an environment for the virus that is acceptable for its development, you need to follow some rules:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Treat all diseases immediately after symptoms are detected.
- Regularly, for preventive purposes, visit a gynecologist, take tests and undergo a full examination.
- Use contraception.
- Remove warts and papillomas only with the permission of a specialist.
If the virus does enter a woman’s body, she may experience the following symptoms:
- condylomas on the genitals;
- increased proliferation of epithelial cells in the perineum;
- unusually heavy vaginal discharge;
- itching;
- pain during urination or sexual intercourse;
- formation of growths in the vagina.
The virus is often detected against the background of sexually transmitted diseases (herpes, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, etc.) and the shape of the tumors resembles a rash with flat growths. But the appearance of genital warts can also mean infection with HPV type 45.
Danger of HPV type 45
The disease progresses as follows:
- The virus is latent and does not affect healthy tissue until favorable conditions are created for the activation of the disease.
- HPV type 45 develops and acquires characteristic symptoms (skin formations).
- The viral DNA combines with the cellular DNA, affecting the structure of the cells. This is how koilocytosis occurs.
- Cells mutate and become malignant. An invasive cancerous condition develops.
Diagnostics
If symptoms appear on the skin, the woman is advised to visit a dermatologist and gynecologist as soon as possible. After examining the patient, doctors may prescribe the following series of studies:
- Colposcopy (examination of the vagina and part of the cervix using a colposcope);
- cytological and histological analysis;
- biopsy (a piece of skin formation is taken for examination).
Colposcopy of the cervix
Indications for these studies may include erosions, metaplasia of the cervix, internal and external condylomas on the genitals, dysplasia, cancer of the uterus or its cervix. If during these studies HPV type 45 is detected, additional tests will be prescribed.
The polymerase chain reaction will determine the presence of viral DNA, and the Digen test will accurately tell you about its type and volume. The latest study is able to effectively identify strains with high oncogenicity. A Papanicolaou smear (PAP test) from the cervical canal is also taken for examination. It allows you to identify the oncological process.
This procedure is carried out 2 days after colposcopy.
After confirmation of HPV type 45, a dermatovenerologist, gynecologist or urologist prescribes the most appropriate treatment for the patient
It often happens that a person’s immune system returns to normal and independently suppresses this infection.
Treatment
Unfortunately, scientists have not yet invented a remedy that can specifically combat the human papillomavirus. To treat the disease, the doctor may prescribe the woman surgical removal of papillomas, anti-inflammatory drug treatment and drugs that strengthen the immune system. The latter are necessary to ensure that the disease does not return after some time.
Specialized creams that can be prescribed by a doctor can also destroy tumors on the genitals. Among the most famous remedies are Bonafton and Condilin.
Drug therapy is the basis of treatment for type 45 strain. All infected women undergo it without fail. The most famous drugs are: Interferon, Cycloferon, Groprinosin.
And for grade 1 cervical dysplasia, women are prescribed vaginal suppositories Viferon and Panavir.
Herbal medicine (tea with lemon balm, St. John's wort, Echinacea tincture, etc.) is also included in the general range of therapy methods.
Radio wave removal of papillomas
To remove papillomas from the surface of the skin, laser, cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen), radio wave method (Surgitron device) and electric knife (with a large radius of damage) are used. The method of their removal is selected taking into account the location of the formations, their size and the individual characteristics of the patient.
With stage 1-2 dysplasia, surgery allows you to completely get rid of the disease while preserving the woman’s reproductive function. But over the next years she will be forced to take immunostimulating drugs. If dysplasia has reached stage 3, then the operation will most likely lead to infertility.
HPV of high oncogenic risk in women
When healthy cells in the uterus become cancerous, the organ must be removed.
ethnoscience
Some traditional medicine recipes have a long history and have miraculous effects, but before using them you will have to obtain the approval of your doctor.
The most popular remedies are castor or tea tree oil. To use them, you need to dilute the medicine with water in a 1:1 ratio, and apply bandages soaked in it to the affected area.
Another equally popular remedy is tar soap, which dries out papillomas. Over time, all unpleasant formations begin to disappear. It is enough just to regularly wash the affected areas with it.
And vinegar mixed with petroleum jelly, onion juice and wheat flour is applied as medicinal compresses at night.
HPV type 45 in pregnant women
Pregnancy greatly suppresses a woman's immune system. Therefore, the occurrence of papillomas during this period is not at all uncommon. To prevent the appearance of type 45 strain during pregnancy, you need to take all tests before planning it.
If a pregnant woman is aware of the infection, then she should inform the gynecologist about this, then it will be possible to keep the disease under control throughout the entire period and during lactation.
First of all, the expectant mother must exclude any possibility of infection of the fetus. Therefore, in the last trimester, a pregnant woman needs to undergo a course of drug therapy. The safest means for carrying it out are: Prodigiozan, Poludan and Cycloferon.
Until the moment of planned conception, you need to be attentive to your health and treat all diseases associated with the development of the strain.
Prevention of HPV type 45
To prevent this virus from entering the body, the following rules and measures must be followed:
- Vaccination with Gardasil and Cervarix from 9 to 25 years of age. According to experts, regular vaccinations can protect the body from all types of papillomavirus for more than 15 years. Moreover, resistance and resistance to various viruses directly depends on the duration of administration of the drug to the patient. The earlier a woman starts getting vaccinated, the lower her risk of infection.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and eliminate all bad habits.
- Protect yourself and avoid promiscuity.
- Play sports or go for walks at an intense pace at least several times a week.
- Try to avoid stressful situations and do not forget about rest.
- Take vitamin complexes and immunostimulants.
- Treat diseases and regularly undergo a full medical examination.
Conclusion
A woman should take much more careful care of her health than a man. After all, it is the weaker half of humanity that is more susceptible to HPV type 45.
Untimely and incorrect treatment of this disease can lead to a number of serious complications, including oncology.
The best prevention of this problem is a healthy and active lifestyle, with the exception of promiscuity.
Source: https://papillomus.ru/virus-vpch/vpch-45-tipa-u-zhenshhin/
What is HPV type 45 in women and men - how to live and what to do?
In a wide range of different strains of human papillomaviruses, it is necessary to identify type 45, which is defined as an infection of high oncogenic risk.
What does it mean?
When viral agents are introduced into the female body, healthy epidermal cells begin to rapidly divide, which causes the appearance of genital warts in the vagina, cervix, and external genitalia.
Prolonged course of the disease in the absence of adequate treatment can lead to the development of malignant tumors of the cervix.
Of course, it may take more than one month from the appearance of growths to the development of cancer, but it is still not recommended to delay treatment.
Taking appropriate measures against the background of the appearance of the first signs of HPV type 45 invasion will help eliminate serious consequences and preserve not only health, but also life.
What it is
So, HPV type 45 in women - what is it, what is the danger of this strain of viral infection, how to prevent infection, what treatment methods are effective if there is an invasion? Papillomavirus type 45 is one of the rarely detected.
Infection with it is fraught with the appearance of growths on the internal and external genital organs, on the mucous membranes of the mouth, as well as the development of malignant neoplasms.
A characteristic feature of HPV type 45 is a high oncogenic risk. Infection with viral agents of this type can lead to the development of cancer. It should be noted that women are especially susceptible to infection and such severe consequences.
Video
Human papillomavirus treatment
How does infection occur?
HPV type 45 is an invasive disease. The main route of infection is considered to be parenteral, that is, through contact of mucous membranes, skin, and biological fluids. There is also a possibility of infection of the fetus during the process of natural delivery.
It should be noted that almost all types of HPV are extremely contagious; infection can occur not only through close tactile contact, for example, during sexual intercourse, but also through household items, hygiene, and when visiting public places. This rule is not relevant for HPV type 45; in this case, infection is possible only through the parenteral route.
Reasons for development
Symptoms of HPV type 45 infection do not appear immediately. The appearance of the first clinical signs usually occurs against the background of provoking factors, which include the following:
- Decreased immunity, as well as the tone and resistance of the body.
- The presence of diseases of the reproductive or digestive systems, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms. A particularly common factor that provokes the appearance of papillomas is gynecological diseases.
- Hormonal imbalances, which occur especially often during the gestation period, as well as during menopause.
- The presence of bad habits, which include smoking, alcohol, eating heavy, fatty, spicy foods.
- Low level of physical activity.
- Having a lot of extra pounds.
Some strains of viruses can remain in the infected person’s body in an anabiotic state throughout their life, that is, without manifesting themselves in any way. In such situations, self-healing is quite possible, that is, suppression of the activity of viral agents by the body’s defenses. However, for HPV type 45 this rule is not relevant.
Characteristic symptoms
The following clinical manifestations are characteristic of HPV type 45:
- The main symptom is the appearance of numerous growths in the perineal area. In this case, genital warts can appear on mucous tissues and skin.
- Severe itching, burning, and painful sensations appear. discomfort can increase significantly during sexual intercourse or during urination.
- Thick, uncharacteristic discharge may appear, often with an unpleasant odor.
To prevent the degeneration of genital warts, the appearance of which is provoked by oncogenic HPV, it is important to promptly consult a doctor who will help you choose the best option for removing papillomas, as well as a general antiviral therapy regimen.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to diagnose papillomavirus type 45, a comprehensive examination is used, including a physical examination, instrumental, and laboratory research methods.
At the initial stages of treatment, the patient’s complaints are taken into account, anamnesis is collected, colposcopic and histological diagnostics are carried out, the task of which is to determine pathological changes in tissues.
Also, diagnosis of the disease includes additional methods aimed at identifying the virus, determining the viral load, and the HPV strain. The most common ones include the polymerase chain reaction and the Daijin test.
Also, these methods make it possible to determine the sensitivity of viral agents to the effects of drugs, which is especially important for selecting the most appropriate individual treatment regimen.
Treatment options
Treatment for HPV type 45 is complex. The use of individual methods will not allow you to obtain positive results. Removal of genital warts is practiced through the use of invasive methods or medications.
It is also necessary to take restorative and antiviral drugs, which is necessary to suppress the activity of HPV type 45.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy for HPV genotype 45 is a mandatory and fundamental method of treatment. To suppress viral activity, increase immune strength, and general tone of the body, a woman may be prescribed the following drugs: viferon, interferon, groprinosin.
To remove external clinical manifestations of the virus, the patient may be recommended to use topical medications such as supercelandine, bonafton, condiline.
Regular application of these products to the growths will help quickly eliminate them, as well as improve overall well-being.
Destructive methods
With a large number of pathogenic tumors, the use of invasive methods for removing pathological growths is required.
To eliminate condylomas from mucous tissues, as well as the skin of the genital organs, gentle methods such as laser therapy, cryodestruction, and electrocoagulation can be used.
Surgical intervention is performed only if there is no positive dynamics after drug therapy.
Traditional medicine methods
Against the background of the detection of HPV type 45, neglecting traditional methods of treatment in favor of traditional therapy is dangerous to health and life.
The low effectiveness of home-made medications will help to somewhat reduce the symptomatic manifestations of the invasion, but will not completely suppress the activity of HPV type 45.
However, judicious use of folk remedies will help alleviate the patient’s condition. The following methods are most effective:
- To remove pathological tumors, it is recommended to regularly treat them with an ointment made from tar or ordinary laundry soap. Preparing such a product is quite simple: you need to grate a small amount of soap and mix it with water to form a thick paste. Apply the resulting medicine to papillomas several times a day.
- To eliminate growths on mucous tissues, it is recommended to use a more gentle remedy: tea tree oil should be thoroughly mixed with water in a one-to-one percentage ratio. Treat neoplasms regularly with the resulting medicine.
When carrying out treatment for HPV type 45, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene: be sure to perform washing procedures after each visit to the toilet, change underwear and bed linen, and use only personal household items. The following rules will help prevent repeated self-infection.
We should also talk about ways to prevent viral diseases.
The only effective method is vaccination.
The use of this method will not only reduce the likelihood of infection, but also reduce the risk of developing malignant tumors.
Source: https://papilom-net.ru/vpch/vpch-45-tipa
Features of the manifestation of HPV type 45 in women
HPV type 45 is considered one of the most dangerous strains due to the high risk of developing cancer. Infection occurs during sexual intercourse or through the birth canal.
After entering the body, the virus remains in the latent phase until favorable conditions are created. The appearance of papillomas on the skin means a transition to the active stage.
The patient will need to see a doctor to eliminate the formations and increase the body’s natural defenses.
HPV type 45: what a woman should be afraid of
HPV type 45 in women is considered one of the most dangerous oncogenic strains, but many still do not know what it is. The virus belongs to the Alphapapillomavirus 7 species. In terms of the risk of cancer development, it is assigned a high level. Once in the body, HPV remains in a latent state until suitable conditions are created.
When the body's natural defenses decrease or hormonal imbalance occurs, the virus enters the active phase. As a result, growths appear on the skin. If left untreated, the disease can cause cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer.
The presence of papillomavirus in the body usually becomes known when visible manifestations are detected. The risk group is represented by girls and women from 18 to 30 years old. The virus is especially dangerous for minors due to the immaturity of the reproductive system.
Spread of the virus
According to statistics, 90% of men and women who are sexually active suffer from HPV of various genotypes. Condoms reduce the risk of infection, but not by 100%. The virus is quite capable of entering the human body through unprotected areas of the skin. In addition to the sexual route, there are other ways of spreading the disease:
- passage of the child through the birth canal;
- contact with the oral mucosa;
- transmission of infection through underwear or towels.
The risk of contracting the virus increases among frequent visitors to swimming pools, beauty salons and other public places. No less important is how many sexual partners a woman has had, since a promiscuous intimate life is one of the main reasons for the spread of infection.
Symptoms of infection
The problem with virtually all types of HPV is an asymptomatic course. Women learn about the disease mainly during a preventive examination or before planning a pregnancy. In rare cases, the virus manifests itself with the following clinical picture:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of genital warts in the genital area and anus;
- vaginal discharge characterized by an unpleasant odor;
- discomfort during urination or sexual intercourse.
Any deviations from the norm should be a reason to go to the hospital. The woman will be prescribed special tests and will need to be examined by a gynecologist.
The hidden danger of HPV 45 for women
Women can live with papillomavirus for many years and not realize the presence of infection in the body.
Attention! The danger of HPV type 45 is the high chance of developing cervical dysplasia against the background of a secretive course. The disease is characterized by the degeneration of healthy cells into atypical ones.
Without treatment, pathological changes will progress. Over the years, the risk of developing malignant tumors will increase many times.
Reasons for the progression of papillomavirus
A strong immune system is quite capable of coping with HPV. If self-elimination does not occur, the surviving virus will enter the latent phase. The activation trigger may be the following reasons:
- weak immune system;
- endocrine disruptions;
- development of other infections in the body;
- genetic predisposition to cancer;
- frequent exposure to stressful situations;
- physical inactivity;
- development of gynecological diseases;
- bad habits;
- early entry into sexual activity;
- pregnancy;
- violation of metabolic processes.
If you are at risk, a woman should monitor her health. It is recommended to follow the rules of prevention and be examined annually.
Different stages of virus development in the female body
The papillomavirus, once in the body, goes through 4 stages of development. At the final stage, the patient is diagnosed with cancer. Details are given in the table:
StageDescription| 1 | HPV is inactive at first. Healthy cells are not affected and do not show symptoms indicating the presence of infection in the body. The disease is detected only by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. The duration of the stage depends on the circumstances. Under the influence of trigger factors, the virus can be activated. |
| 2 | HPV at stage 2 is actively developing. The patient's epidermal cell division accelerates, which leads to the formation of papillomas. You can find out about the virus using the PCR method and using cytological or histological examination. |
| 3 | At the third stage, the virus begins to actively interact with cells, changing their structure. Scientifically, the process is called koilocytosis. |
| 4 | The final stage is characterized by active integration of viral DNA. The patient's cells mutate. As a result, cancer develops. |
The entire process from infection to oncology takes approximately 20 years. In the allotted time, the disease can be stopped. When malignant tumors appear, the prognosis for recovery worsens significantly.
Diagnostics
There is a need to be tested for HPV if external growths are detected, the presence of erosion or dysplasia of the cervix. It is enough for a woman to contact a gynecologist. To begin with, the doctor will perform a calposcopy, take a smear for cytological analysis and take a biopsy of the mucous membrane and cervix. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient will be recommended to undergo additional examinations:
- PCR testing recognizes most types of HPV. Vaginal discharge is analyzed. The results obtained help to understand whether there is DNA of the virus in the body. It is impossible to see the extent of cell damage using the polymerase chain reaction.
- The Digen test highly accurately indicates the presence of HPV in the body or refutes the diagnosis. A scraping from the vagina is taken for analysis. As a result, the virus stamp and its quantity will become known.
You can do a rapid test at home. It is enough to buy a special device, study the instructions and remember the rules for collecting material. The result obtained will roughly reflect the situation and should prompt the woman to go to the hospital.
Treatment of HPV 45
There is no need to treat HPV type 45 in the absence of external manifestations. There is a high probability that the body will fight the virus itself. To monitor the condition, you will need to regularly see a gynecologist and undergo examinations.
If condylomas or warts are detected, complex treatment is prescribed:
- removal of growths;
- taking antiviral drugs;
- using techniques to strengthen the immune system.
Papillomavirus in a pregnant woman is one of the reasons for a cesarean section, since there is a risk of infection of the child. Expectant mothers will definitely need to consult a specialist in order to prescribe safe medications that cannot harm the fetus. If dysplasia or erosion of the cervix is detected, additional drugs are introduced into the treatment regimen.
Conservative way
Drug therapy is aimed at fighting the virus and increasing the body's natural defenses. Drugs are prescribed based on the stage of development of the disease, the presence of other pathologies and the age of the patient.
Examples of effective treatments are presented in the list:
- Preparations for general strengthening of the body and suppression of viral activity:
- "Lykopid";
- "Immunal";
- "Galavit";
- "Imudon."
- Means to combat the virus and prevent relapses:
- "Acyclovir";
- "Panavir";
- "Vivorax";
- Imiquimod.
- Complex drugs:
- "Viferon";
- "Altevir";
- "Genferon";
- "Interal P".
Folk remedies can be used to supplement the treatment regimen. They rarely cause adverse reactions and are good at increasing the effectiveness of medications. According to patient reviews, it is best to use tinctures and decoctions based on chaga and echinacea.
Removal of papillomas
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser therapy;
- use of radio waves;
- surgical removal;
- influence of drugs.
The method is selected depending on the situation. If oncology is suspected, excision with a scalpel is required. After removal of condyloma, it is recommended to undergo a course of drug treatment in order to reduce the likelihood of relapses.
HPV 45 vaccine and other prevention measures
In order to prevent cancer due to exposure to oncogenic strains of viruses, various vaccines have been developed. Now the introduction of Gardasil and Cervarix is relevant. The preparations contain particles of killed HPV.
Parental consent is required. As an additional protective measure, you must follow the rules of prevention:
- exercise;
- Healthy food;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- try to avoid stress;
- regularly take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators;
- enter into intimate relationships with one partner;
- use condoms.
Prevention rules will help strengthen the immune system and reduce the likelihood of infection. If HPV has already entered the body, then the strengthened natural defense will prevent the virus from entering the active stage.
Papillomavirus type 45 is dangerous for women. The infection can lead to dysplasia and uterine cancer over a long period of time. Medicines with immunomodulatory and antiviral effects are used as treatment. Visible growths are removed surgically, using medications or other methods. It is necessary to combine a course of therapy with compliance with the rules of prevention.
Source: https://UroMir.ru/zppp/hpv/vpch-45-tipa-u-zhenshhin-chto-jeto.html