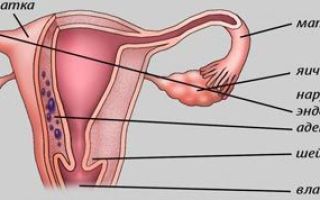
Uterine adenomyosis is a disease characterized by the spread of tissue similar in structure to the endometrium (uterine mucosa) into the thickness of the uterine muscle.
Adenomyosis causes considerable damage to the uterus, as a result, the endometrium grows and affects the nearby layers of the organ. This problem does not apply to malignant tumors, but only if detected and treated in a timely manner.
How to treat this disease, how serious is it and what consequences can it have for a woman?
What is uterine adenomyosis
Adenomyosis of the uterus is a special case of endometriosis, a systemic benign disease in which endometrial cells begin to multiply outside the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. The term “adenomyosis” literally means glandular degeneration of muscle tissue (“adeno” - gland, “myo” - muscle tissue, suffix “oz” - degenerative changes).
Under normal conditions, endometrial cells, in accordance with their name, are located exclusively in the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium. When they spread beyond the uterine cavity, a pathological condition occurs - endometriosis.
Causes
There is still no consensus on the causes and mechanisms of the development of endometriosis. There are several hypotheses for etiopathogenetic variants of the disease. However, none of them separately explains the entire essence of the pathological processes occurring during endometriosis of the uterus.
In fact, the main, leading cause of the development of adenomyosis is still hormonal imbalance. It is this factor that is primary and underlies the pathogenesis of this pathology.
Other reasons:
- operations such as cesarean section, curettage, fibroid removal, and so on;
- abortions;
- age-related changes. This pathology is in most cases diagnosed in women after 30-45 years of age;
- genetic predisposition;
- excessively frequent visits to the solarium, constant exposure to the sun without protection;
- excess body weight.
Uterine adenomyosis can be diagnosed in young women who have never experienced such manipulations. In this group of patients, the disease develops due to congenital pathologies or insufficient dilatation of the cervix during menstruation.
In addition to the above points, it is worth paying attention to the fact that any uterine surgical interventions or curettage significantly increase the risk of adenomyosis. First of all, these include abortions, mechanical injuries, medical intervention after a miscarriage, etc.
Symptoms and photos of uterine adenomyosis
Now you know what kind of disease this is, but the worst thing about uterine adenomyosis is its predominantly asymptomatic course. The first symptoms may appear already at the third stage, at which conservative treatment is already difficult.
In the photo you can see adenomyosis of the uterus
The most typical symptoms and signs of adenomyosis are:
- pain in the pelvic area before menstruation, during it, and also a few days later;
- dark brown discharge from the genital tract some time before and after menstruation;
- various disorders of the menstrual cycle (as a rule, its reduction);
- change in the size and shape of the uterus (this symptom is established during a special examination);
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
- deterioration of general condition, frequent headaches, migraines, decreased performance, apathy, depression, sudden mood changes, decreased performance.
Adenomyosis of the uterus is largely characterized by an asymptomatic course of the pathological process, which can last for many years and even decades.
Forms of the disease
The following forms of uterine adenomyosis are distinguished:
| Form | Description and symptoms |
| Focal | With focal adenomyosis, characteristic foci of endometrial penetration into other internal structures of the uterus are clearly visible. Quite often, a combination of nodular and diffuse forms of this pathology is diagnosed - combined adenomyosis of the uterus. |
| Nodal | Nodular and diffuse nodular endometriosis of the uterus is a consequence of severe diseases of the reproductive, endocrine and digestive systems. These include:
The main symptom of the nodular form is menstrual irregularity. The cycle becomes shorter, and menstruation becomes more abundant and longer due to the appearance of spotting 2-3 days before the start of menstruation and for several days after its end. |
| Diffuse | Diffuse adenomyosis is considered one of the types of endometriosis. Sometimes the disease does not reveal itself in any way, but is diagnosed by chance on an ultrasound. In most cases there are no symptoms. In all other cases, the following occurs:
|
| Mixed | This form is a kind of combination of the previous two. With it, there are both nodes and blind pockets of the endometrium. Mixed adenomyosis is more common than others and is the most difficult to treat. |
Adenomyosis: 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees
The intensity with which certain symptoms of the disease appear is associated with the severity of adenomyosis. The classification of adenomyosis by degree of prevalence is not international, but it is quite convenient and is carried out in practice. There are four stages in total, which vary depending on the spread of the endometrium:
- Cell proliferation is limited to the internal space of the uterus and does not extend beyond its lining.
- At the second stage, uneven compaction and growth of the endometrium is diagnosed in the muscle layer of the organ.
- Third degree: involvement of more than half or all of the muscular wall of the uterus.
- At stage 4, growing through the serous layer, endometrial tissue migrates outside the uterus
Before and after menstruation, mucous discharge with a sharp, unpleasant odor may be observed. This suggests that the development of internal endometriosis reaches the 2nd or 3rd degree.
The severity of the abnormal process depends on the depth of the lesion. Mild cases of adenomyosis occur in many women. In this case, the endometrium grows no further than the submucosal layer.
Possible consequences for women
Adenomyosis of the uterus has 2 development paths - favorable and critical. Timely detection and timely treatment of the disease ends generally well for the woman, with preservation of reproductive function and restoration of hormonal levels.
The growth of the endometrium outside the internal space of the uterus leads to the fact that the mucous membrane of the organ is disrupted, becoming thinner and more fragile.
She is unable to receive and hold a fertilized egg. If left untreated, infertility may develop over time.
The disease is the result of hormonal imbalances that make it difficult to conceive a child.
This is why it is very important to visit a gynecologist regularly; endometriosis of the uterine body detected at an early stage is successfully treated, after which pregnancy is quite possible.
Pregnancy with adenomyosis
Infertility is one of the common consequences of the presence of endometrial cells in the muscular layer of the uterus. For some, this manifests itself as the inability to conceive, while others cannot bear a child. In some cases, women suffer from blocked fallopian tubes, which prevents the egg from connecting with the sperm.
In a healthy woman, in the second phase of the cycle, the size of the endometrium increases in anticipation of pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, then endometrial cells are rejected and come out along with menstruation. With adenomyosis, such release from the muscle tissue of the uterus does not occur, which causes hemorrhage and severe inflammation of the organ.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine adenomyosis? Pregnancy with adenomyosis is possible if complex treatment is carried out aimed at restoring reproductive function. The effectiveness of therapeutic intervention depends on the duration of the disease. If adenomyosis has bothered a woman for no more than 3 years, most likely the treatment result will be positive.
Diagnostics
It is possible to presumably diagnose uterine adenomyosis on the basis of characteristic complaints and as a result of a gynecological examination. Additional examination methods can be used to clarify the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, where changes in the shape and size of the uterus are clearly visible. Is it possible to see signs of uterine adenomyosis in women on an ultrasound? During an ultrasound, you can see on the screen the growth of the layers of the uterus, both uniform and uneven, and sharp protrusions or irregularities similar to myometrium may also be visible.
- The most accurate results (about 90%) are provided by transvaginal ultrasound scanning, which, like a gynecological examination, is performed on the eve of menstruation.
- For a detailed examination of the endometrium, hysteroscopy is prescribed. With its help, the doctor studies the nature and extent of damage to the uterine cavity, which makes it possible to determine the further course of treatment.
- Laboratory tests of smears for flora are also required.
- conducting the necessary comprehensive studies of other internal organs and systems - endocrine, genitourinary, respiratory, nutritional, cardiovascular;
- endometrial biopsy;
- MRI;
- bimanual gynecological examination.
Treatment of uterine adenomyosis
Treatment is based on the use of medications (conservative treatment), surgical intervention, and alternative medicine techniques.
When choosing a method and volume of therapy, the following must be taken into account:
- the patient’s age, her desire to have children, neuropsychiatric status;
- all characteristics of the pathological process;
- the combination of adenomyosis with the process of inflammation, whether there are cicatricial and adhesive changes, as well as the presence of hyperplasia and destruction in the uterus.
Drugs
When treated with medications, patients are prescribed hormone therapy, this should stop the menstrual cycle, so to speak, creating menopause. Treatment with hormones takes a very long time, from 3 to 5 months. The cycle can be completely normalized only after six months, after completing the medication.
Hormonal drugs for pathology:
- gestagens - drugs to restore reproductive function;
- oral contraceptives;
- antiestrogens;
- drugs analogues of gonadoliberin;
- antigonadotropins.
Removing the inflammatory process. To do this, use various gels, suppositories, and douching solutions. Medicines can be produced on the basis of medicinal herbs. Also, to relieve the inflammatory process, antibiotic-based drugs are often used, which makes it possible to get rid of fungal formations, infections, etc.
Surgical intervention (operation)
The operation is shown:
- with adenomyosis grades 3 and 4;
- when adenomysoa is combined with fibroids and atypical endometrial hyperplasia;
- in case of nodular form (in women with infertility, conservative organ-preserving operations are performed);
- with persistent anemia;
- if conservative treatment is ineffective.
In recent years, hardware methods have been used in the treatment of adenomyosis by cauterizing inflammatory foci of the endometrium in the body of the uterus using a laser.
If the patient is contraindicated from conventional hormonal therapy, the issue of drug treatment of adenomyosis is not discussed; surgery becomes the method of choice.
Recommended Diet
There is no special diet recommended by doctors for the treatment of uterine adenomyosis. Therefore, the best diet would be to exclude fatty and spicy foods, excessive amounts of sweets and baked goods. It is better to replace these products with fresh vegetables and fruits, nuts.
Try to include omega-3 fatty acids in your diet, which are involved in many important metabolic processes that occur in the body. Healthy fatty acids are found in foods such as:
- Fatty fish and fish oil.
- Walnuts and walnut oil.
- Pumpkin seeds.
- Vegetable oils.
For this disease, it is very beneficial to eat a lot of dark green leafy vegetables.
How to treat adenomyosis with folk remedies
Experts say that most medicinal herbs can improve the patient’s condition. Decoctions have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, regenerating and hemostatic effects.
Collection of herbs for douching No. 1
To cope with the problem, you can use douching. To prepare a medicinal composition, you need to mix the following herbs in equal parts:
- eucalyptus;
- bergenia root;
- mistletoe;
- bedstraw;
- cottonweed;
- celandine;
- peony;
- calendula;
- Oak bark;
- yarrow.
The collection of herbs should be poured with boiling water and left to infuse. Then the composition should be filtered through a double layer of gauze and used for douching.
Herbal collection No. 2
It is good to use a collection of mistletoe, peony, cudweed, oak bark, calendula, yarrow flowers, celandine and nettle. Crushed dry plants are mixed in the same quantities, poured with hot water, wrapped and left to stand for up to 5 hours. Next, the herb is filtered through gauze folded several times and syringed while warm several times a day.
Nettle decoction
Nettle decoction four times a day. To prepare the drink, you need to pour two teaspoons of the collection with a glass of boiling water, let the medicine brew and cool, then strain and take a couple of tablespoons several times a day. This infusion relieves inflammation and stops heavy menstrual bleeding.
Prevention
- Prevention of uterine adenomyosis mainly comes down to regular visits to a gynecologist. A specialist can correctly interpret such symptoms in a timely manner and prescribe appropriate treatment.
- Undergoing pelvic ultrasound 1-2 times a year.
- Gynecologists believe that stress and constant overwork have a strong impact on women's health and can undoubtedly lead to the development of adenomyosis.
To prevent the onset of the disease, a woman needs to: rest more, take relaxing baths, attend a massage, and be in a calm and comfortable environment more often.
- Keeping the body clean. Girls who ignore the rules of personal hygiene from an early age are more prone to this type of disease.
And also those who engage in sexual relations in childhood and adolescence.
Taking care of your health is the main way to prevent not only adenomyosis, but also other equally dangerous diseases.
Source: http://www.zdoroviyvopros.ru/ginekologiya/adenomioz-matki/
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a disease in which the inner lining (endometrium) grows into the muscle tissue of the uterus. It is a type of endometriosis. It manifests itself as long, heavy menstruation, bleeding and brownish discharge during the intermenstrual period, severe PMS, pain during menstruation and during sex. Adenomyosis usually develops in patients of childbearing age and subsides after the onset of menopause. Diagnosed on the basis of a gynecological examination, the results of instrumental and laboratory tests. Treatment is conservative, surgical or combined.
Adenomyosis is the growth of the endometrium into the underlying layers of the uterus. Usually affects women of reproductive age, most often occurring after 27-30 years. Sometimes it is congenital. It fades away on its own after menopause.
It is the third most common gynecological disease after adnexitis and uterine fibroids and is often combined with the latter.
Currently, gynecologists note an increase in the incidence of adenomyosis, which may be due to both an increase in the number of immune disorders and improved diagnostic methods.
Patients with adenomyosis often suffer from infertility, however, the direct connection between the disease and the inability to conceive and bear a child has not yet been precisely established; many experts believe that the cause of infertility is not adenomyosis, but concomitant endometriosis.
Regular heavy bleeding can cause anemia. Severe PMS and intense pain during menstruation negatively affect the patient’s psychological state and can cause the development of neurosis.
Treatment of adenomyosis is carried out by specialists in the field of gynecology.
Adenomyosis
The reasons for the development of this pathology have not yet been precisely clarified. It has been established that adenomyosis is a hormone-dependent disease. The development of the disease is facilitated by impaired immunity and damage to the thin layer of connective tissue that separates the endometrium and myometrium and prevents the growth of the endometrium deep into the uterine wall.
Damage to the separation plate is possible during abortion, diagnostic curettage, use of an intrauterine device, inflammatory diseases, childbirth (especially complicated ones), operations and dysfunctional uterine bleeding (especially after operations or during treatment with hormonal drugs).
Other risk factors for the development of adenomyosis associated with the activity of the female reproductive system include too early or too late the onset of menstruation, late onset of sexual activity, taking oral contraceptives, hormonal therapy and obesity, which entails an increase in the amount of estrogen in the body. Risk factors for adenomyosis associated with immune disorders include poor environmental conditions, allergic diseases and frequent infectious diseases.
Some chronic diseases (diseases of the digestive system, hypertension), excessive or insufficient physical activity also have a negative impact on the state of the immune system and the general reactivity of the body.
Unfavorable heredity plays a certain role in the development of adenomyosis. The risk of this pathology increases if you have close relatives suffering from adenomyosis, endometriosis and tumors of the female genital organs.
Congenital adenomyosis is possible due to disturbances in intrauterine development of the fetus.
Adenomyosis is a type of endometriosis, a disease in which endometrial cells multiply outside the lining of the uterus (in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, digestive, respiratory or urinary systems). Cell spread occurs by contact, lymphogenous or hematogenous route. Endometriosis is not a tumor disease, since heterotopically located cells retain their normal structure.
However, the disease can cause a number of complications. All cells of the inner lining of the uterus, regardless of their location, undergo cyclic changes under the influence of sex hormones. They multiply intensively and then are rejected during menstruation.
This entails the formation of cysts, inflammation of surrounding tissues and the development of adhesions.
The frequency of the combination of internal and external endometriosis is unknown, but experts suggest that most patients with uterine adenomyosis have heterotopic foci of endometrial cells in various organs.
Taking into account the morphological picture, four forms of adenomyosis are distinguished:
- Focal adenomyosis . Endometrial cells invade the underlying tissues, forming separate foci.
- Nodular adenomyosis . Endometrial cells are located in the myometrium in the form of nodes (adenomyomas), shaped like fibroids. The nodes, as a rule, are multiple, contain cavities filled with blood, and are surrounded by dense connective tissue formed as a result of inflammation.
- Diffuse adenomyosis . Endometrial cells invade the myometrium without forming clearly visible foci or nodes.
- Mixed diffuse nodular adenomyosis . It is a combination of nodular and diffuse adenomyosis.
Taking into account the depth of penetration of endometrial cells, four degrees of adenomyosis are distinguished:
- 1st degree - only the submucosal layer of the uterus is affected.
- 2nd degree – no more than half the depth of the muscular layer of the uterus is affected.
- Grade 3 – more than half the depth of the muscular layer of the uterus is affected.
- Grade 4 – the entire muscle layer is affected, with possible spread to neighboring organs and tissues.
The most characteristic sign of adenomyosis is long (over 7 days), painful and very heavy menstruation. Clots are often detected in the blood.
Brownish spotting is possible 2-3 days before menstruation and 2-3 days after it ends. Intermenstrual uterine bleeding and brownish discharge in the middle of the cycle are sometimes observed.
Patients with adenomyosis often suffer from severe premenstrual syndrome.
Another typical symptom of adenomyosis is pain. Pain usually occurs several days before the start of menstruation and stops 2-3 days after it begins. Features of the pain syndrome are determined by the localization and prevalence of the pathological process.
The most severe pain occurs with damage to the isthmus and widespread adenomyosis of the uterus, complicated by multiple adhesions. When localized in the area of the isthmus, the pain can radiate to the perineum; when located in the area of the angle of the uterus, it can radiate to the left or right groin area.
Many patients complain of pain during sexual intercourse, which intensifies on the eve of menstruation.
Clinical manifestations of the disease may not correspond to the severity and extent of the process. Grade 1 adenomyosis is usually asymptomatic.
In grades 2 and 3, both an asymptomatic or low-symptomatic course and severe clinical symptoms can be observed.
Grade 4 adenomyosis is usually accompanied by pain caused by widespread adhesions; the severity of other symptoms may vary.
During a gynecological examination, changes in the shape and size of the uterus are revealed. With diffuse adenomyosis, the uterus becomes spherical and increases in size on the eve of menstruation; with a widespread process, the size of the organ can correspond to 8-10 weeks of pregnancy.
With nodular adenomyosis, tuberosity of the uterus or tumor-like formations in the walls of the organ are detected.
When adenomyosis and fibroids are combined, the size of the uterus corresponds to the size of the fibroids, the organ does not shrink after menstruation, and other symptoms of adenomyosis usually remain unchanged.
More than half of patients with adenomyosis suffer from infertility, which is caused by adhesions in the fallopian tubes, preventing the penetration of the egg into the uterine cavity, disturbances in the structure of the endometrium, complicating the implantation of the egg, as well as the accompanying inflammatory process, increased myometrial tone and other factors that increase the likelihood of spontaneous abortion . Patients may have a history of no pregnancy with regular sexual activity or multiple miscarriages.
Heavy menstruation with adenomyosis often entails the development of iron deficiency anemia, which can manifest itself as weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin and mucous membranes, frequent colds, dizziness, fainting and presyncope. Severe PMS, long menstruation, constant pain during menstruation and deterioration of general condition due to anemia reduce the patient's resistance to psychological stress and can provoke the development of neuroses.
The diagnosis of adenomyosis is established on the basis of anamnesis, the patient’s complaints, examination data on a chair and the results of instrumental studies. A gynecological examination is carried out on the eve of menstruation.
The presence of an enlarged spherical uterus or tubercles or nodes in the uterine area in combination with painful, prolonged, heavy menstruation, pain during sexual intercourse and signs of anemia is the basis for a preliminary diagnosis of adenomyosis.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. The most accurate results (about 90%) are provided by transvaginal ultrasound scanning, which, like a gynecological examination, is performed on the eve of menstruation.
Adenomyosis is evidenced by the enlargement and spherical shape of the organ, varying wall thickness and cystic formations larger than 3 mm that appear in the uterine wall shortly before menstruation. With diffuse adenomyosis, the effectiveness of ultrasound is reduced.
The most effective diagnostic method for this form of the disease is hysteroscopy.
Hysteroscopy is also used to exclude other diseases, including fibroids and uterine polyposis, endometrial hyperplasia and malignant neoplasms.
In addition, in the process of differential diagnosis of adenomyosis, MRI is used, during which it is possible to detect thickening of the uterine wall, disturbances in the structure of the myometrium and foci of endometrial penetration into the myometrium, as well as assess the density and structure of the nodes.
Instrumental diagnostic methods for adenomyosis are complemented by laboratory tests (blood and urine tests, hormone tests), which make it possible to diagnose anemia, inflammatory processes and hormonal imbalances.
Treatment of adenomyosis can be conservative, surgical or combined. Treatment tactics are determined taking into account the form of adenomyosis, the prevalence of the process, the age and health status of the patient, and her desire to preserve reproductive function.
Conservative therapy
Initially, conservative therapy is carried out. Patients are prescribed hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, immunomodulators and agents to maintain liver function. Anemia is treated. In the presence of neurosis, patients with adenomyosis are referred to psychotherapy, tranquilizers and antidepressants are used.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical interventions are performed. Surgeries for adenomyosis can be radical (panhysterectomy, hysterectomy, supravaginal amputation of the uterus) or organ-preserving (endocoagulation of endometriosis foci).
Indications for endocoagulation in adenomyosis are endometrial hyperplasia, suppuration, the presence of adhesions that prevent the egg from entering the uterine cavity, lack of effect when treated with hormonal drugs for 3 months and contraindications to hormonal therapy.
Indications for hysterectomy include progression of adenomyosis in patients over 40 years of age, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and organ-preserving surgical interventions, diffuse adenomyosis of grade 3 or nodular adenomyosis in combination with uterine fibroids, and the threat of malignancy.
Therapy during pregnancy
If adenomyosis is detected in a woman planning a pregnancy, she is recommended to attempt conception no earlier than six months after undergoing a course of conservative treatment or endocoagulation. During the first trimester, the patient is prescribed gestagens.
The need for hormonal therapy in the second and third trimester of pregnancy is determined taking into account the result of a blood test for progesterone levels. Pregnancy is a physiological menopause, accompanied by profound changes in hormonal levels and has a positive effect on the course of the disease, reducing the rate of proliferation of heterotopic endometrial cells.
Adenomyosis is a chronic disease with a high probability of relapse. After conservative therapy and organ-preserving surgical interventions during the first year, relapses of adenomyosis are detected in every fifth woman of reproductive age.
Within five years, recurrence is observed in more than 70% of patients. In premenopausal patients, the prognosis for adenomyosis is more favorable, which is due to the gradual decline of ovarian function. After panhysterectomy, relapses are impossible.
During menopause, spontaneous recovery occurs.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/adenomyosis
Adenomyosis of the uterus: causes, symptoms and treatment of adenomyosis
The gynecological disease uterine adenomyosis is a common problem, a pathology that has a benign course and a high tendency to develop relapses. According to statistics, the pathology occurs mainly in women of mature age.
The main method of treatment is conservative or surgical (with preservation of organs), however, over the next 5 years, in most patients, symptoms of the disease appear again.
Therefore, a woman needs regular examination by a gynecologist.
Relapses are excluded if the affected organ is completely removed, however, in this case, the operation leads to loss of reproductive function and significant hormonal disruptions.
Characteristics of the pathology
Adenomyosis is a malignant disease of the uterus, in which pathological growth of the connective tissue of the organ occurs into the muscles of the uterus. In this case, the pathological process occurs only in certain areas and is accompanied by severe inflammation, hormonal imbalances and the menstrual cycle.
The reproductive function of the female body also suffers. If there is a lack of therapy and treatment, problems with conceiving and bearing a child in the future may occur. The uterus has a complex structure; the walls of the organ consist of 3 layers. This is the endometrium, which includes the basal and functional layer, the myometrium, consisting of muscle tissue, and the perimeter, which is the serous membrane of the organ.
Stages and forms of adenomyosis
Depending on how deeply the connective tissue grows, there are 4 stages of pathology development:
- The first stage is characterized by superficial damage to the myometrium;
- At the second stage, the connective tissue grows more deeply, reaching the middle layers of the organ;
- With third-degree adenomyosis, the structure of the serous tissue is disrupted;
- The terminal stage is characterized by irreversible processes that damage all layers of the uterine wall.
Types of adenomyosis
- Nodular form, characterized by the formation of multiple nodules, the cavity of which is filled with menstrual blood.
The nodules are dense, surrounded by a special capsule, which consists of connective tissue;
- Focal form accompanied by the formation of separate, larger foci of epithelial growth into muscle tissue.
The pathology is typical for representatives of the older generation;
- Diffuse form characterized by multiple foci of damage to muscle tissue located throughout the entire area of the organ.
The pathology has a severe course and a pronounced clinical picture;
- Mixed form , which is characterized by various manifestations.
Enlarged spleen - symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Causes of uterine adenomyosis
The following provoking factors lead to the growth of connective tissue of the uterus and the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- Burdened heredity;
- Hormonal imbalances in the body (for example, with endocrine diseases, long-term use of hormonal medications, during menopause);
- Traumatic injuries to the uterus during surgical operations, artificial termination of pregnancy (cleaning, curettage);
- Complicated labor (protracted, or, conversely, rapid);
- Inflammatory processes affecting the organs of the female genitourinary system;
- Frequent stress, chronic fatigue;
- Local exposure to negative temperatures (hypothermia);
- Long-term disruption of the immune system.
Symptoms of uterine adenomyosis
The main symptoms of adenomyosis are:
- Irregular menstruation (menstruation is accompanied by heavy discharge and its duration increases);
- In the intervals between menstruation, a woman often develops a specific red-brown spotting;
- Changes in the size of the uterus. The organ enlarges significantly, especially a few days before the onset of menstruation;
- Acute pain syndrome. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen and is poorly relieved even with the use of painkillers;
- As a result of large blood loss during menstruation, a woman experiences signs of anemia, such as weakness, pallor, and attacks of dizziness;
- Disruption of the body’s natural defenses, and, as a consequence, frequent infectious diseases;
- Breathing disorders, shortness of breath, which develops even in the absence of intense physical activity (this symptom is characteristic of a severe form of the disease).
These symptoms do not always appear. So, if the pathology is at the initial stage of its development, there may be no clinical signs; the only warning sign in this case will be painful menstruation (which is not particularly uncommon in healthy women), and minor discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Methods for diagnosing uterine adenomyosis
It is quite difficult to identify pathology at the initial stage of development, since in most cases it is asymptomatic. However, as time passes, characteristic signs appear that indicate a problem.
Varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster
To obtain more accurate diagnostic results, it is not enough just to evaluate the totality of the manifestations of the disease; it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- Gynecological examination of the patient using special instruments;
- Colposcopy to detect changes in the cervix;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs to assess the condition of their tissues;
- A smear to determine microflora disorders in the vaginal area;
- Examination of other internal organs for differential diagnosis (excluding diseases accompanied by similar symptoms).
Methods for treating uterine adenomyosis
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the doctor. In this case, it is important to take into account numerous nuances, such as the patient’s age, the characteristics of her body and state of health, the location and extent of damage, and the stage of formation of the pathological process.
Most often, conservative methods of therapy are used, involving drug treatment. The patient is prescribed the following groups of medications:
- Hormonal drugs to restore normal hormonal levels;
- NSAIDs to eliminate the inflammatory process in the uterus;
- Sedatives if stress is the cause of the pathology;
- Vitamin complexes and immunostimulants to restore the functioning of the immune system and generally strengthen the body;
- Hepatoprotectors to prevent the development of complications;
- Iron-containing products to eliminate the manifestations of anemia.
In addition, physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed. The most effective methods are treatment with currents, ultrasound, cryotherapy, and cauterization of overgrown connective tissue.
Surgical treatment of adenomyosis
In severe cases of pathology, when conservative treatment does not give a positive result, surgery is prescribed. Surgery involves partial removal of the organ (only the affected areas are removed), or complete removal of the uterus. Depending on how the organ is accessed, the following types of operations are distinguished:
- Laparotomy (the most dangerous and invasive method), when access to the uterus is through incisions;
- Laparoscopy with access through small punctures;
- Vaginal surgery – access is provided through the vagina.
Unfortunately, many women visit a gynecologist only when certain problems arise. This is not true, because many diseases at the very beginning of their development are asymptomatic. And the sooner treatment for such pathologies begins, the more favorable the outcome will be.
Facial skin care in different phases of the menstrual cycle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ToQYW4nB99U
Source: https://healthhacks.ru/adenomioz-matki-simptomy-prichiny-lechenie/
Drugs for uterine adenomyosis - modern treatment of uterine adenomyosis with safe means in Moscow
April 24, 2017 59674 0
Adenomyosis is a form of endometriosis. The main difference between this form is that the endometrium, breaking through the protective layer of the uterus, grows into its muscle layers. In this case, the uterus, as a protective reaction, forms muscle seals around the implanted endometrium to prevent further growth.
Let's take a closer look at the structure of the uterus to understand what adenomyosis is. The uterus itself consists of several layers - the myometrium, that is, the muscular layer of the uterus and the endometrium, the mucous layer covering the inside of the uterus. It is the rejection of the endometrium, at the end of each cycle, that is accompanied by bleeding. The endometrium itself is two-layered, i.e.
it consists of a main layer - the basal layer, which serves as the basis for the growth of new endometrium, and the functional layer, this layer exfoliates monthly. The functional layer consists of one layer of cells resembling the shape of a cylinder; between them are cells that produce mucus - glandular cells.
In pathology, it is the functional layer that grows into the muscular body of the uterus, “breaking through” the basal layer.
Please note that this text was prepared without the support of our Expert Council.
1
Causes of adenomyosis development
Today there is no one theory that fully answers the question of why adenomyosis appears. Each of the theories put forward can partially explain its appearance, but does not completely answer all the questions. Here are the most common theories about the causes of adenomyosis:
- Implantation - this theory explains the appearance of endometriosis due to a sharp reflux of blood into the pelvic organs and peritoneum, but if this can explain endometriosis, then the appearance of adenomyosis is difficult to explain.
- Metaplasia of the coelomic epithelium - this theory explains the appearance of adenomyosis by the fact that not all embryonic tissue undergoes regression before menstruation; it is this tissue that is introduced into the myometrium.
- Induction - this theory largely coincides with the previous one and assumes the possibility of the appearance of adenomyotic foci under the influence of unfavorable external factors.
The second or third theory may partially explain the appearance of adenomyosis in young patients, but evidence for these theories has not yet been provided. In addition to the theories described above, there are others - hormonal (lack of prostaglandins), genetic and others, but they still remain theories.
In addition, there are a number of factors that can increase the risk of adenomyosis. These include:
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
- Abortions and curettages.
- Intrauterine interventions.
- Injuries, including birth injuries.
- Disturbed hormonal levels.
- Genetic predisposition.
2
Types of adenomyosis
- Adenomyosis of the uterine body is divided into nodular, focal and diffuse. There are four stages of development of this pathology:
- I - the endometrium grows to the myometrium;
- II - the endometrium penetrates to the middle of the muscular layer of the uterus;
- III - the endometrium reaches the serous layer;
- IV - the endometrium penetrates the peritoneum.
3
Main symptoms of adenomyosis
- Pain during menstruation or algodismenorrhea is the most common symptom. It is especially worth paying attention if it appears in teenagers. Pain appears due to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues and the local inflammatory process, as well as due to the accumulation of blood.
- Cycle disruption is another symptom of adenomyosis.
Most often it manifests itself in the form of bleeding. Brown discharge is possible before and after menstruation, but menstruation itself may last longer and with heavier bleeding than usual.
- Infertility is usually not so much a consequence of adenomyosis as a combination of several factors.
When the process spreads to the entire uterine cavity, active adhesions are possible, and if adenomyosis is accompanied by other diseases, such as endometriosis, fibroids and others, then the chance of getting pregnant is sharply reduced. Adenomyosis itself cannot become an obstacle to pregnancy with proper treatment and prevention.
- Miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion, is also a consequence of a combination of several pathological conditions.
4
Course of adenomyosis
Without proper monitoring and treatment, adenomyosis progresses in most patients. Thus, in the absence of treatment for six months, the disease progresses in 45% of patients, and improvement is observed in 30%.
If the disease is neglected for a longer period of time, for example for a year, deterioration is already noticed in 65% of patients, and improvement in only 25%. The condition of adenomyosis can stabilize and even improve during pregnancy.
5
Diagnosis of adenomyosis
When making a diagnosis of adenomyosis, anamnesis is of no small importance. The patient's complaints about an irregular cycle, painful periods, brown discharge before and after menstruation, pain during intercourse - all of these are indirect indicators of the presence of adenomyosis. In addition, adenomyosis can be determined by:
- In terms of the size and structure of the uterus - the size of the uterus, depending on the stage and development of adenomyosis, can be either enlarged up to 5-8 weeks of pregnancy, or normal. The body of the uterus is often compacted and, in some cases, lumpy. When palpated before menstruation, the patient may feel pain. Pain and tightness of the cervix are also possible. The uterus itself may lose normal mobility.
- With an ultrasound examination, it is much easier to diagnose adenomyosis, especially if a vaginal examination is performed. With this type of diagnosis, the accuracy of the diagnosis will be 90%. It is better to perform an ultrasound on days 22-25 of the cycle.
An ultrasound examination may show the following signs of adenomyosis:
- increased echogenicity of the myometrium;
- increased size of the uterus;
- the presence of small inclusions with a diameter of 0.2 to 0.6 mm. In this case, an experienced doctor will be able to distinguish an adenomyotic node from a myomatous one by the absence of a capsule in it and by its clear shape.
- MRI is not used so often, but with this method it is possible to assess the condition of the myometrium and the presence of adenomyotic foci in them.
- Hysteroscopy. The most effective and informative diagnostic method. Allows you to accurately determine the condition of the myometrium and more accurately determine the stage of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment. The disadvantage of this method is that the patient must be put under anesthesia. The hysteroscopic classification of adenomyosis looks like this:
- At the first stage, small lesions are visible, but the walls of the uterus are not changed.
- In the second stage, adenomyotic “movements” are observed, the uterus does not stretch well and has uneven walls.
- At the third stage, “bulges” of varying sizes appear in the uterine cavity, without clear contours. The presence of adenomyotic “passages” on the protrusions is possible, but not necessary.
- Collection of uterine material for histological examination - diagnostic curettage. This method can accurately confirm or refute the presence of adenomyosis in the uterine cavity. Most often, I prescribe this method to women over 40 years of age who complain of brown discharge between periods. The method allows not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to exclude the oncological component.
6
Uterine adenomyosis treatment and medications
Since the development of adenomyosis directly depends on the level of estrogen in a woman’s body, treatment is primarily aimed at suppressing estrogen.
Confirmation of the effectiveness of this method is the improvement of the clinical picture during pregnancy and immediately after it - when the woman’s body produces a minimum amount of estrogens.
Foci of adenomyosis immediately respond to altered hormone levels in a similar way to normal endometrium.
Drugs prescribed for uterine adenomyosis:
- Oral contraceptives - can simulate pregnancy and cause amenorrhea and Oral contraceptives - they simulate pregnancy, cause amenorrhea and loss of the myometrial membrane and adenomyotic lesions. Often, when treated with contraceptives, the foci of adenomyosis completely disappear. Any contraceptives that contain ethinyl estradiol in doses of at least 0.03 mg can be used to treat adenomyosis. Contraceptives are taken either in a continuous mode or 63+7, where a hormonal contraceptive is taken for 63 days, and a break is taken for seven days. Treatment should last at least six months, usually the treatment period is 6-12 months, depending on the stage of the disease. Studies show that after a course of treatment with contraceptives, pregnancy occurred immediately after the course of treatment in 50% of women, pain and bleeding stopped in 70-85% of women. The relapse rate was about 18%.
- Progestogens are quite effective in the treatment of adenomyosis, and they already have a low cost. Thanks to their action, foci of adenomyosis atrophy. The following drugs are used in treatment:
- Medroxyprogesterone is most often used in the treatment of adenomyosis, since this drug is the most studied. The approximate daily dose is 30 mg; in case of discharge, the dose may be increased.
- Dydrogesterone - used 2-3 times a day, 10 mg.
These drugs have a number of side effects, the main ones being weight gain and nausea. In some cases, bleeding is possible, in which a short course of estrogen is recommended.
- Androgens. The most commonly used is danazol. It causes amenorrhea and prevents the growth of foci of adenomyosis and the appearance of new ones. Can cause long-term remission in adenomyosis. Used in doses of 600 to 800 mg per day. Start taking 200 mg. 2 times a day, gradually increasing the dose to 800 mg. The drug is taken until the clinical manifestations of adenomyosis begin to disappear. However, it should be noted that this drug has a number of side effects: acne, decreased libido, weight gain. Contraindicated for liver diseases as it can destroy liver cells.
- Analogues of GnRH such as: goserelin, histrelin, leuprolelin, buserilin, nafarelin and others. When prescribing this drug, mandatory monitoring of its level in the blood is carried out, due to the fact that it can cause osteoporosis. Other side effects include decreased libido and atrophic vaginitis. To prevent the occurrence of osteoporosis, it is necessary to prescribe the drug in combination with progestogens and estrogens.
- The Mirena spiral is installed for a period of 5 years. Thanks to it, adenomyosis stabilizes and stops regressing, and the symptoms gradually disappear.
Please note that all information in this article is for reference only and in no way encourages self-medication. Only a doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
7
Other treatments for adenomyosis
Embolization of the uterine arteries is a fairly effective method in some cases, especially when adenomyosis nodes are well supplied with blood. In other cases, this method is ineffective.
Removal of the uterus is indicated only in particularly severe cases and is a last resort, often unjustified.
Surgical removal of adenomyosis nodes is possible only with a small number and minimal size.
8
Prevention of adenomyosis
Timely and annual visits to the doctor are the best prevention of such a disease. Women should also try to avoid abortions and use modern methods of contraception to avoid unwanted pregnancies.
Bibliography
- Sidorova I.S. Uterine fibroids (modern aspects of etiology, pathogenesis, classification and prevention). In the book: Uterine fibroids. Ed. I.S. Sidorova. M: MIA 2003; 5-66.
- Androutopoulos G., Dekavalas G. Recent advances in the treatment of uterine fibroids. Translation from English N. D. Firsova (2018).
- Savitsky G. A., Ivanova R. D., Svechnikova F. A. The role of local hyperhormonemia in the pathogenesis of the growth rate of tumor nodes in uterine fibroids // Obstetrics and Gynecology. – 1983. – T. 4. – P. 13-16.
Source: https://www.mioma.ru/preparaty-dlya-lecheniya-adenomioza-matki-sovremennyj-vzglyad-na-lechenie-patologii.html
Treatment of uterine adenomyosis: basic methods and medications
- The occurrence of uterine diseases is associated with many factors - poor lifestyle, stress, neglect of one’s own health.
- Adenomyosis is one such disease that occurs in women of all ages.
- We will tell you what medications help with adenomyosis, whether hormones and folk remedies help with therapy, what is the treatment regimen for the disease.
Is it possible and how to cure the disease?
Is there a cure for uterine adenomyosis? Doctors consider the disease to be completely incurable, but self-healing occurs in approximately 30% of cases .
Medications can be used to stop the development of the endometrial growth process and regression of the disease.
To make a woman feel better and relieve unpleasant symptoms, the following methods are used:
- surgical - with partial removal of endometrial foci or complete removal of the uterus;
- drug treatment of adenomyosis of the uterine body: taking hormonal drugs is the most common method. The drug is selected individually depending on the characteristics of the woman’s body and the stage of development of the process.
The gynecologist will tell you how and how to treat uterine adenomyosis, with what medications:
How the disease is treated depending on the stage
The treatment regimen for the disease is selected based on the stage of the disease and the advanced stage of the process.
Stage 1 (damage to the mucous membrane up to the myometrium) - a course of treatment of adenomyosis with oral contraceptives (Zhanine, Logest, Jess) is prescribed.
The course of treatment for grade 1 adenomyosis is from 3 to 6 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman. As a side effect, the absence of menstruation is noted.
- Stage 2 (damage to the mucous membrane up to the middle of the myometrium) - the treatment regimen for grade 2 adenomyosis is practically no different from that prescribed for the first stage.
- In addition to contraceptives, women are prescribed painkillers (No-Shpa) and Epigen-type ointments.
- Stage 3 (damage to the mucous membrane to the serous layer) - an ultrasound examination is prescribed to identify lesions.
The first step in the treatment of grade 3 adenomyosis is the prescription of hormonal drugs that normalize the functioning of the ovaries. Additionally, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are taken.
- If therapy does not produce any results within 6 months, it is proposed to perform surgery to remove endometrial lesions.
- Stage 4 (endometrial nodes move into the abdominal cavity) - at this stage, the only treatment method is surgery to remove the nodes.
- If the lesions are extensive, the organ is removed completely, and the cervix may be removed.
Drugs used
What drugs are used to treat uterine adenomyosis? Therapy for the disease can be carried out with hormones or more radical methods.
In this case, you can combine treatment with hormonal pills, massage and douching .
Hormonal
To treat uterine adenomyosis with hormones, the following medications are prescribed:
- Visanne - tablets containing the active substance - dienogest, which allows you to normalize the functioning of the ovaries and stabilize the production of estrogen hormones. The course of treatment is 6 months. In this case, you need to take 1 tablet per day;
- Depo Provera is an anti-estrogen injection. Thanks to the drug, hormones are produced without affecting the uterus, and menstruation and manifestations of the disease completely stop. The course of treatment is 3 months. It is necessary to administer 1 injection every 7 days;
- Duphaston is a progestogen tablet that reduces estrogen production and normalizes ovarian function. When taking them, menstruation becomes scanty, and the endometrium cannot grow. To treat uterine adenomyosis, Duphaston tablets should be taken from the 5th or 16th day of the cycle;
- Janine - tablets that also help normalize the production of estrogen. The course of taking tablets is at least six months, 1 tablet per day.
But there are other drugs.
In addition, you cannot take several types of hormonal pills at once to treat adenomyosis!
Non-hormonal
Non-hormonal drugs are used when therapy with other drugs is contraindicated or the disease is diagnosed at an early stage.
Your doctor may prescribe the following medications to treat adenomyosis without hormones:
- Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory drug used for pain;
- Epigen ointment - allows you to increase the natural immunity of the uterine mucosa. It is necessary to use the drug at least 2 times a day for approximately 14 days.
Other methods
Electrocoagulation - in this case, removal of tumor foci by exposing tissue to high-frequency current.
In this case, pathological tissues are destroyed almost without a trace. Most often, only one procedure is required, which is performed under local anesthesia.
Embolization - the essence of the method is to stop the supply of blood to foci of pathological tissue.
To do this, a catheter is inserted into the uterine artery through a small puncture in the groin area, through which a special drug is delivered to the artery to block it. The procedure is almost painless; only local anesthesia is required.
Ablation - during the procedure, the upper layer of the uterine lining (endometrium), which is the cause of the disease, is removed.
A probe is inserted through the vagina into the uterine cavity to remove the endometrium. Ablation methods - laser, radiofrequency, cryodestruction, microwave, etc.
Operation
Surgery for adenomyosis is a last resort and is prescribed only in emergency cases:
- severe uterine bleeding, which is difficult to treat even when taking hormonal drugs;
- if concomitant diseases arise with adenomyosis, for example, large uterine fibroids;
- if the disease has progressed to stage 3-4, and the endometrial nodes have grown outside the uterus.
The operation is performed in a hospital under general anesthesia . In this case, depending on the degree of damage to the uterus, either the foci of the disease themselves or the entire organ can be removed.
After surgery, a fairly long recovery period is required.
Folk recipes
If the disease is in its initial stage, and the woman is not bothered by the severe symptoms of its manifestation, you can resort to traditional medicine.
- Propolis . Propolis helps restore natural immunity, has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. To do this, a piece of propolis must be crushed, mixed with honey and heated in a water bath for 10 minutes. The mixture can be taken as food in a tablespoon 1-2 times a day.
- Celandine . A plant with anti-inflammatory properties helps reduce the severity of symptoms and get rid of the negative manifestations of the disease. To prepare the infusion you need 2 tbsp. l. Pour a glass of boiling water over the celandine and leave for at least 3 hours. Strain the decoction and take a tablespoon 3 times a day.
- Beetroot juice helps restore immunity, normalize hormonal levels, and restore the lining of the uterus. For results to appear as early as possible, it is important to take ½ glass of juice daily for 2 weeks.
- Douching - infusions of chamomile, calendula, nettle or celandine are suitable for douching. To prepare the solution, 2 tbsp. any selected plant is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 2-3 hours. The liquid is filtered and used for douching.
Features of therapy for different forms of the disease
Forms of adenomyosis:
- diffuse - in this case, endometrial tissue grows quite deeply into the muscular layer of the uterus. In some cases, diffuse adenomyosis caused the formation of fistulas in the uterine body;
- nodular - pseudoendometrial cells penetrate into the muscular layer of the uterus, creating passages there. In the resulting voids, rapid growth of pathological cells begins;
- diffuse-nodular.
Diffuse
With diffuse adenomyosis, surgical removal of individual lesions is practically not used due to their large number and the nature of their growth.
The only gentle method is hormonal therapy . In addition, you can resort to traditional methods and massage.
If the described methods do not help, and the disease progresses, a decision is made to remove the uterus.
Foci of endometrial growth can extend beyond the uterus, affecting nearby organs!
Nodal
Treatment of nodular adenomyosis of the uterus begins with the prescription of hormonal drugs.
The form of treatment and dosage of the drug is chosen by the attending physician. Nodular adenomyosis is the most dangerous form of the disease.
Diffuse nodular
Treatment of this form is not much different from therapy with the methods described. Hormone therapy is the very first step that the doctor resorts to.
- Only after this, looking at the results, can you move on to more radical techniques, for example, installing the Mirena spiral .
- Diffuse nodular adenomyosis is more common than other forms.
- Although adenomyosis is a benign disease , it requires close and constant monitoring by specialists until the onset of menopause.
If left untreated, the process quickly becomes malignant . Endometrial lesions can spread to nearby organs, forming metastases.
Source: https://beautyladi.ru/lechenie-adenomioza-matki/