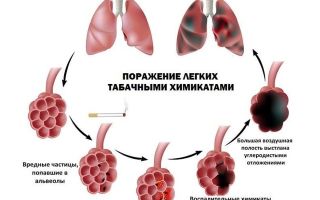
Often when visiting a doctor, a patient complains of pain in the chest. What could this be connected with, and why do my lungs hurt when I cough?
Difficulty breathing, elevated body temperature, general discomfort and cough may indicate problems with the breathing apparatus.
There are more than 20 pulmonary pathologies that are directly related to these symptoms.
Why do my lungs hurt when I cough? To answer this question, you need to establish the symptomatic signs and causes of various diseases of the pulmonary system, as well as decide on methods of treating them.
Bronchitis
A dry and severe cough, the lungs hurt, the body temperature stays within 37-38ºС - all signs of an acute respiratory disease. A more detailed medical examination of the respiratory system determines the involvement of the bronchi in the inflammatory process.
This pathology of the respiratory tract is diagnosed as bronchitis. According to ICD-10, disease of the bronchopulmonary system has 2 forms:
- Chronic bronchitis is a type of diffuse damage to the mucous membrane of the bronchial tree. The form of the disease may have the following symptomatic signs: wet cough, sore lungs, no fever.
- Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bronchi and trachea. As a rule, this type of damage to the tracheobronchial tree lasts about 2 weeks and may have accompanying symptoms of influenza or a cold. Main symptoms: lungs hurt from the back when coughing, low-grade body temperature, rapid heartbeat, increased blood pressure. A prolonged process of acute irritation of the respiratory tract can lead to complications and provoke bronchial asthma.
Important! Any form of bronchopulmonary damage requires a thorough medical examination and adequate treatment.
If chronic bronchitis refers to a nonspecific type of inflammation of the respiratory system and the causative factor of the disease is caused by external irritants (smoking, environmental exposure, chemical irritants), then the acute form of bronchitis has all the signs of a recurrent respiratory infection.
Anti-inflammatory therapy in the treatment of acute bronchitis is more justified. Traditional drug treatment involves the use of dosage forms belonging to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory group. These include all pharmacological drugs with expectorant and antitussive effects.
No less effective is treatment with traditional medicine, which, together with medications prescribed by a doctor, gives a positive dynamics of recovery. A patient with a strong cough during a bronchopulmonary attack is advised to drink plenty of warm fluids. Traditional methods of folk treatment:
- tea with raspberries or honey;
- warm milk with soda and butter;
- heated mineral water;
- linden decoction.
A warm castor oil compress is another great cough remedy. If you have a severe cough during bronchitis and your lungs hurt, what should you do in this case? There are several effective methods of treatment at home using traditional medicine:
- Herbal collection No. 1. You can prepare a diaphoretic, antipyretic and expectorant using coltsfoot herb and mint leaves. Brew 3 tbsp. dry raw materials in 500 ml of boiling water. Take 200 ml every 2 hours.
- Herbal collection No. 2. Lungwort and black elderberry blossom (1 tablespoon each) are poured into 1000 ml of boiling water, after infusing for 3 hours, the medicine for bronchial disease is ready. In addition to the expectorant effect, the drug helps reduce swelling in the bronchi and eliminate pain in the lungs when coughing.
- Herbal mixture No. 3. With a severe coughing attack, eucalyptus and medicinal marshmallow root are very helpful. The prepared product has an expectorant, anti-inflammatory and enveloping effect. You need to take 1 tbsp. components and pour 500 ml of boiling water. Take 100-150 ml 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
Prevention of bronchitis will be the normalization of thermal regulation of the body, hardening, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards, complete cessation of smoking as a provoking factor of inflammation of the bronchial tract.
Pneumonia
Can your lungs hurt without coughing? Unfortunately yes. Pneumonia or pneumonia may be asymptomatic at the initial stage. The person feels a slight tingling in the pulmonary area, but there is no fever or cough.
When inflammation of the lung tissue enters a more severe phase, dangerous symptoms of acute inflammation begin to appear. A classic manifestation of pneumonia is the patient’s complaint that when coughing, the back hurts in the area of the lungs.
In this case, the infection process is actively developing, which will be confirmed by an x-ray examination of the lungs and a biochemical analysis of sputum released during coughing. If antibacterial therapy is not prescribed in a timely manner, the prognosis of the disease is not comforting - death is possible.
Data from the World Health Organization indicates that about 8 million cases result in death, and this with an annual average of 450 million people suffering from acute inflammation of the lung tissue.
Symptomatic signs that are determined when diagnosing the disease:
- when coughing, the left lung or the right side of the sternum hurts;
- weak physical activity of a person;
- pain in the thoracic diaphragm when moving;
- unhealthy appearance (pallor, general malaise);
- shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat;
- low-grade fever.
There are also other symptomatic signs that depend on the type and degree of damage to the lung alveoli.
Important! In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization is necessary to provide qualified antibacterial care.
Treatment of pneumonia with folk remedies is possible only after the doctor’s approval, but subject to compliance with all treatment instructions. At the initial stage of the disease, the so-called catarrhal syndrome is determined, which is caused by the destruction and subsequent separation of the alveolar and bronchial epithelium.
Catarrhal respiratory syndrome can be eliminated using traditional methods of treatment:
- Wash, peel and chop 20 g of horseradish root. After pouring the medicinal raw material with 80% alcohol and leaving it for 20-30 minutes, you can begin treatment. The cough will disappear after 15-20 minutes of inhalation.
- 1 tbsp. medicinal elecampane pour 200 ml of water and boil over low heat, then let it brew for 4-5 hours. Take 50 ml 3-4 times a day an hour before meals. The remedy will reduce cough and relieve pain in the lungs.
- A wet cough due to pneumonia can be eliminated as follows: mix 1 tbsp. plantain and natural honey. Take daily before meals.
Silicosis
Can your lungs hurt from coughing? Pneumoconiosis is a group of occupational diseases caused by damage to lung tissue from industrial dust. The most common and severe type of pneumoconiosis is silicosis.
This type of lung damage is observed in people whose professional activities have long been associated with the mining, coal or engineering industries. Dust of free silicon dioxide, falling on the connective lung tissues, forms characteristic nodular connections, which help reduce the processing of oxygen by the lungs.
At the initial stage of the disease, a person feels a lack of air during physical activity, accompanied by pain of an unspecified nature in the diaphragm.
Symptoms of a severe form of silicosis are accompanied by the following signs:
- shortness of breath similar to bronchial asthma;
- the presence of a dry hacking cough;
- respiratory failure;
- scattered wheezing in the chest;
- hemoptysis;
- tachycardia;
- facial cyanosis.
Occupational silicosis may be aggravated by a number of other diseases of the respiratory system:
- bacterial pneumonia;
- spontaneous pneumothorax;
- lung cancer;
- bronchial asthma.
In 30% of cases, severe silicosis can develop into pulmonary tuberculosis.
To date, there are no radical treatments for the disease. When a confirmatory diagnosis is established, it is recommended to stop contact with dust.
Further treatment consists of therapeutic and preventive measures based on fortified and protein nutrition, therapeutic exercises of the respiratory tract and other actions aimed at inhibiting the progression of fibrous abnormalities in the lung tissues. Recommendations for treating silicosis at home:
- Spa treatment;
- alkaline and salt inhalations;
- dietary nutrition;
- milk.
On a note! Unfortunately, all fibrotic processes in the tissue structure of the lungs in silicosis are irreversible and cannot be completely cured.
Pain in the right lung: causes
If your right lung hurts when you cough, this may indicate existing problems in the body related to the respiratory system.
As a rule, such painful attacks intensify with sharp turns, deep breaths, and sudden changes in body position.
What are the causes of unilateral chest inflammation? The most likely diagnosis may be right-sided dry (fibrinous) or exudative (effusion) pleurisy.
Clinical symptoms of fibrinous pleurisy:
- unilateral pain when breathing and coughing;
- sweating;
- shallow rapid breathing.
With right-sided dry pleurisy, inflammation of the right pleural lobes occurs, followed by the formation of fibrin, a non-globular high-molecular organic substance, on their surface.
With exudative pleurisy, symptomatic signs of the disease are manifested by the following symptoms:
- a feeling of heaviness in the right half of the thoracic diaphragm;
- dry cough;
- dyspnea;
- skin cyanosis;
- venous cervical swelling.
A patient with exudative right-sided pleurisy constantly complains of pain in the lung when coughing. There is an accumulation of pathological effusion (effusion) in the pleural cavity, which entails paroxysmal pain in the affected area.
The disease is treated with complex therapy, which is based on eliminating symptomatic manifestations, pain relief and accelerating the resorption of fibrinogen.
The scheme of complex effects on pleurisy is similar to the treatment of tuberculosis, in which appropriate pharmacological drugs are prescribed: Ethambutol, Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Streptomycin.
There are effective traditional home treatments:
- Mix the juice of 1 onion with bee honey in equal proportions. Take the resulting mixture 1 tbsp. at least 3 times a day. This folk remedy has an antimicrobial effect on the pleural cavity.
- The juice of 4 lemons is mixed with chopped horseradish in a proportional ratio of 2:1. It is recommended to take the remedy on an empty stomach or before bedtime. The purpose of this treatment is to prevent the resorption of exudate.
- A herbal mixture based on mint, sage, anise, elecampane and licorice root, taken in equal proportions, is poured into 300 ml of boiled water. After one day of exposure, the medicine is ready for use. Take ½ glass 3 times a day.
Important! Prevention of pulmonary diseases comes down to compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards, proper regulation of body temperature and complete cessation of smoking.
Source: https://antirodinka.ru/chto-delat-kogda-bolyat-legkie-pri-kashle
Why Coughing Causes Pain in the Lungs
Pain in the lungs during coughing is a common companion to diseases of the respiratory system. At the same time, diseases of other organs can also cause discomfort. There is only one thing that is alarming: lung tissue cannot hurt.
This is due to the peculiarities of their innervation. There are no nerve endings in the lungs that would signal pain to the central nervous system.
What then hurts? We are most likely talking about sensitive neurons located in the near-pulmonary tissues, which react to the cough reflex with irritation.
However, the question requires consideration: why do the lungs hurt when inhaling or when coughing and what diseases provoke the unpleasant symptom?
Pain in the lungs and bronchi when coughing
Medical practice includes more than 20 pathologies that cause pain symptoms. Therefore, if coughing causes pain in the lungs, you should consult a doctor for a detailed diagnosis and clarification of the diagnosis. It will not be possible to independently determine the reason why it hurts to cough, especially in the absence of other symptoms.
The anatomical features of the human structure “surrounded” the lungs with other important systems, which, with the development of pathological processes in them, radiate pain to the respiratory system. It can be:
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
- cardiovascular problems
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- neurological diseases
Note! The intensity of pain is always a signal for urgent hospitalization!
The most common causes of pain in the lungs are pathologies of the respiratory system. But to correctly differentiate the disease, pay attention to the following manifestations:
- pain intensity
- when it appears (during breathing and coughing)
- presence of shortness of breath
- nature and localization (right, left lung) of pain syndrome
- Is there a reaction to taking analgesics?
The following signs indicate a life-threatening condition of the patient:
- with a strong cough, a sharp, stabbing and acute pain syndrome occurs in the lung tissue
- When coughing, thick, viscous mucus is coughed up
- there is a cough with bloody sputum
- difficulty breathing
At the same time, the following symptoms are often added to the described symptoms: vertigo, shortness of breath, weakness, chills, fever, numbness of the hands, abdominal pain. This symptomatic picture serves as a signal to immediately call an ambulance.
Symptoms
It has already been said above that pain in the lungs is one of the manifestations of a possible pathology, but based on one symptom alone, it is not possible to identify the problem. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, other symptoms of a particular respiratory system disease are taken into account. Let's look at them:
- Pleurisy. Symptomatically, the pathologies are expressed in an increase in temperature, localization of pain on only one side (on the side or at the bottom of the lung), a dry, debilitating cough, and general weakness.
- Pneumonia. Characteristic signs: fever, cough with bloody sputum, sweating, tingling and burning in the chest, difficulty breathing.
- Pneumothorax. Accompanied by sharp stabbing pain when breathing and coughing, decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, malaise and pale skin.
- Malignant tumors in the lungs that make breathing difficult and cause severe pain when breathing and coughing.
- Bronchitis and tracheitis. Depending on the severity of the pathology, symptoms may vary, but the main signs are as follows: general weakness, fever, “barking” dry cough, causing discomfort in the lungs
- Pulmonary infarction. Accompanied by acute pain, shortness of breath, blue extremities, coughing up blood, high fever, and fainting.
- Tuberculosis is characterized by a wet cough with copious sputum discharge, chest pain, weight loss, and pallor.
- Silicosis. Symptoms for differentiation are: hemoptysis, shortness of breath, respiratory failure, tachycardia, dry cough.
- Pulmonary abscess. The manifestation is similar to pneumonia, the difference is the course and nature of the disease.
- Viral infections of the upper respiratory tract (ARI, ARVI). Pain in the lungs manifests itself as a dysfunction of the muscular corset due to a frequent cough reflex.
Less often we can talk about pain symptoms due to diseases of other organs.
Causes of pain in the lungs when coughing
Why else can your lungs hurt when you cough? In addition to diseases of the upper respiratory tract, pain in the lungs when coughing is provoked by the following reasons:
- injuries of the bony corset of the chest
- inflammatory processes in muscles and nerves (neuralgia and myositis) and accompanying pathologies
- malignant neoplasms with secondary lesions (metastases)
- osteochondrosis
- gastroesophageal and peptic ulcer diseases
- arthritis, arthrosis and rheumatism
To identify the original source of discomfort, make an appointment with a therapist. For a correct diagnosis, he will draw up an anamnesis based on symptoms and the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Diagnostics
Popular methods for diagnosing pathologies of the upper respiratory tract and other systems are:
- general examination of the patient
- blood test (general and biochemistry)
- sputum examination
- radiography
- fluorography
- CT and MRI
- fibrobronchoscopy
- echocardiography
- spirometry
- lung biopsy
- Ultrasound of the chest organs
- pleural puncture
Such methods allow you to most accurately determine the cause of unilateral and bilateral pain in the lung.
Treatment
The very concept of “pain treatment” is not correct from a medical point of view. The therapeutic treatment regimen is prescribed based on the root cause that provoked the pain. Upon receipt of the final diagnosis, the following medications may be included in the list of medications:
- antibiotics
- antihistamines
- antiviral drugs
- mucolytic and bronchodilators
- chemotherapy course
- analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs
Note! The choice of medication, its dosage and duration of use is made only by a doctor. Self-treatment is dangerous to the life and health of the patient!
Additional therapeutic methods are: traditional medicine methods, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, inhalations. Depending on the disease, the degree and severity of its course, in some cases surgical intervention is indicated.
Treatment with folk remedies
To relieve pain symptoms, traditional medicine methods are often used, but subject to prior consultation with your doctor.
Review of popular tools:
- Honey with onions. The juice of one onion is mixed with 2-3 tablespoons of honey and taken three times a day.
- Mix the medium horseradish root with the juice of 3 lemons and take a teaspoon of the mixture before bed.
- Almond oil is useful for consumption. Dosage: 1 teaspoon three times a day.
- Herbal decoctions based on: licorice, fireweed, elecampane, elecampane, mint, anise, and sage help relieve discomfort in the chest. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water and taken a third at a time throughout the day.
Better than any treatment is disease prevention. To avoid manifestations of pain in the lungs, you need to maintain a thermal regime, give up bad habits, enrich your diet with healthy vegetables and fruits, and consult a doctor in time if you are sick.
Why Coughing Causes Pain in the Lungs Link to main publication
Source: https://kashlya-net.ru/kashel/bolyat-legkie-pri-kashle
Lungs hurt when coughing: without fever, what to do
- Often the symptom is associated with disorders of the nervous system or gastrointestinal tract.
- Discomfort is caused by the pleura, bronchi, and trachea.
Loading …
Use search
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
↑
During the examination, the specialist pays attention to:
- nature of pain;
- localization;
- intensity;
- accompanying symptoms.
Experts identify two groups of reasons for the appearance of unpleasant sensations. The first includes diseases of the respiratory system.
The second includes pathologies of other organs:
- Pleurisy. Characterized by a strong paroxysmal cough. The pain is localized in the lower chest.
- Pneumonia. Main symptoms: difficulty breathing, sweating, fever, sputum discharge.
- Pneumothorax. In the acute phase, it begins to hurt with every breath and when coughing. Blood pressure decreases, skin tone changes.
- Malignant formations. Associated with difficulty breathing.
- Bronchitis and tracheitis. Characterized by weakness, dry cough, chest discomfort.
- Pulmonary infarction. Manifests itself in the form of shortness of breath, bluish skin, cough with bloody discharge.
- Tuberculosis. Signs include a strong wet cough and pain in the chest area.
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections. Unpleasant sensations arise as a result of dysfunction of the chest muscles.
Other reasons include:
- chest injury;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- malignant neoplasms with metastases;
- osteochondrosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism.
A mild cough may occur as a result of insufficient air humidity or increased dust content in the room.
The primary diagnosis is carried out by a general practitioner. He gives a referral for consultation with a specialist and additional research.
↑
https://gidpain.ru/bolit/legkie-kashle.html
Effective treatments
The treatment regimen and the speed of symptom relief directly depend on the diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Therapy is carried out in several areas:
- When body temperature rises, antipyretics are prescribed. Required for pleurisy, bronchitis, pneumonia.
- In case of bacterial infection, antibiotics are used.
- To reduce pain and relieve muscle spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed.
- If osteochondrosis or neuralgia is detected, anti-inflammatory therapy is used.
- For pneumothorax, surgery is performed to remove air from the pleural cavity.
For chest injuries, patients are prescribed bed rest and maximum rest. Traditional methods can be used to prevent pulmonary cough.
↑
Help from relatives during treatment
In case of pain, relatives can provide the patient with all possible assistance. It consists of normalizing your diet and lifestyle.
Prevention methods include:
- to give up smoking;
- annual fluorography;
- diet;
- maintaining indoor air humidity;
- physical exercise.
Relatives help the patient follow the doctor’s instructions and also monitor his general condition. If it worsens, contact a medical facility.
Unpleasant sensations in the chest require examination and diagnosis. Timely examination and prescription of competent therapy helps to exclude the development of complications.
↑
How can the lungs hurt in general: in front, behind, on different sides, at the tops of the lungs
The lungs hurt - this is how patients often describe their sensations at a doctor’s appointment. In fact, the paired organs of the respiratory system are devoid of sensory nerve endings. Constant or short-term pain indicates a developing pathology of nearby internal organs.
Her response is pain - a signal about disturbances in the functioning of the body. But it is felt not in the affected organ, but in the lungs.
What does the doctor suspect first, based on the location of the pain:
- in front - various disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- behind - slowly but persistently progressing osteochondrosis in the cervical, cervicothoracic or thoracic spine;
- from different sides - the formation of an intervertebral hernia, exacerbation of the pathology of one of the organs of the digestive tract;
- from above - chronic damage to the upper respiratory tract, problems with the myocardium, bronchial asthma;
- from below - disorders in the functioning of the gallbladder or small intestine, destruction of the cartilage lining of one of the lumbar intervertebral discs.
If the discomfort is mild, then the disease has just begun to develop until it spreads to healthy, nearby tissues.
Sharp, piercing, shooting pains indicate serious health problems. You cannot put off visiting a doctor, as this is a characteristic sign of angina pectoris and coronary heart disease.
A dry, unproductive cough indicates chronic bronchitis or insufficient blood supply to the brain due to a vertebral artery compressed by an osteophyte. And cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle warns of severe cardiovascular pathology or respiratory infection.
↑
What can cause a man's lungs to hurt?
Often, discomfort in any particular part of the body is explained not only by pathological, but also by natural causes. For example, drinking alcohol, smoking for a long time, preferring fatty foods rich in spices and herbs. But not in the case of the lungs.
Unpleasant sensations in them should not occur even after increased physical activity - hard work or intense sports training.
The factors that provoke deterioration in physical condition in men are the same as in women. But there are diseases that are more often diagnosed in the stronger sex.
↑
Enlarged spleen
Aching, dull, seemingly distant pain under the lower ribs is a nonspecific clinical manifestation of an enlarged spleen. The process occurring in it can be both inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic.
Men are usually more physically active, which is why they are more likely to get injured. Enlargement of the spleen, sensitive to external damage, is observed after falls, directed blows, and bruises.
A rapidly developing disease also leads to it:
- mononucleosis is an acute infection of viral origin that affects the reticuloendothelial system;
- lymphoma is an oncological disease that affects lymphocytes (immune cells);
- leukemia is a clonal malignant disorder of hematopoiesis;
- purulent abscess - inflammation of tissues with their melting and the formation of a cavity with purulent exudate.
It is damage to the spleen that is recognized by a person as pain in the lower part of the pulmonary lobes. It is not complicated by coughing or wheezing, but a feeling of lack of air when inhaling is quite possible.
↑
Lower respiratory tract diseases
Associated symptoms help to recognize them:
- pneumonia, tuberculosis - shortness of breath, bluish skin, weakness, fatigue, weight loss;
- abscess pneumonia - cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, pale, moist skin, neurotic conditions.
Sharp weight loss is observed when a malignant or benign neoplasm forms in the pulmonary structural elements. The veins in the neck become swollen, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and when you cough, sputum mixed with blood comes out.
↑
Other common causes
In men, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels are more often diagnosed, the common symptom of which is pain in the upper pulmonary lobes. If it is acute, then there is a threat not only to health, but also to life. This is typical for a pre-infarction, pre-stroke condition, or recurrent angina.
What else could explain the pronounced discomfort:
- Gastrointestinal disorders. As a result of indigestion of food, putrefactive and fermentative processes develop. Due to the commonality of innervation, it seems that even the liver and heart hurt.
- Taking pharmacological drugs. Some medications have side effects - shortness of breath, dry cough, sore throat, discomfort when trying to breathe in more air. This is typical for glucocorticosteroids, systemic antimycotics, and cytostatics.
Men who lead a sedentary lifestyle are more likely than women to suffer from cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis. His clinical picture includes pain in the area of the right or left respiratory organ. Localization depends on the location of the bone growth that is pinching the artery that supplies the brain.
↑
What can cause a woman's lungs to hurt?
Reflected discomfort sensations are more typical for the weaker sex. Women are more emotional, susceptible to neurotic and depressive states, and cope with stress worse.
They often misinterpret the pain and intensify it many times due to self-hypnosis. But you should definitely see a doctor. After all, there are certain pathologies that manifest themselves as pain in the lower respiratory tract, found mainly in women.
↑
Malignant neoplasms
Although smoking is more common among men, lung cancer is slightly more common in women. In them, it first manifests itself as a sore throat, a desire to constantly cough up, and a burning sensation in the bronchi.
Gradually, the cough turns from dry, unproductive to wet. When coughing, thick yellowish mucus with blood streaks is released.
Malignant tumors manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- sudden weight loss due to suppressed appetite, impaired absorption of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals;
- inability to swallow food well;
- shortness of breath even after minor physical exertion;
- fever, chills, cold sweat;
- temperature fluctuations above subfebrile values (37.1-38.0 degrees Celsius);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
It should be noted that such signs, as well as pain in the lower lobes of the respiratory system, are characteristic of the formation of a tumor in the liver. The growing tumor puts more and more pressure on the nerve roots, so the intensity of the manifestations steadily increases.
↑
Lesions of the urinary organs
The female urethra is wider and shorter than the male urethra, which predisposes to the development of infectious processes.
In what cases does this happen:
- pyelonephritis - nonspecific infectious kidney damage caused by various bacteria;
- glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory pathology of the kidneys, which is characterized by inappropriate behavior of the immune system in relation to the cells of the renal glomeruli;
- renal failure is a syndrome of decreased functional activity of the kidneys, leading to a disorder of water, electrolyte, and nitrogen metabolism.
- hydronephrosis is a persistent increase in urine pressure in the urinary system, causing atrophy of the renal structures.
When a stone passes from the ureter, acute pain radiates and is felt even in the cardiac zone. Serious damage to the nephrons, glomeruli, and cones is indicated by thickening of urine, changes in its color, and odor.
Urination is significantly disrupted, appearance deteriorates (hair falls out, nails split) due to inadequate removal of toxic substances.
↑
What does temperature indicate when there is pain in the lungs?
High temperature is the body’s response to the invasion of viruses or microbes. During the process of reproduction, they release the products of their vital activity into the surrounding space. They are very harmful, therefore, after spreading throughout the body, its general intoxication develops.
It is typical for the following respiratory tract infections:
- bronchitis;
- tracheitis;
- sinusitis;
- bronchiolitis;
- dry pleurisy;
- exudative pleurisy in the initial stages of development;
- pneumonia.
The inflammatory mediators prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and bradykinins produced by the immune system rush into the bronchi and parenchyma to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Inflammatory processes develop with fever, chills, fever, and general malaise. In young children and people with immunodeficiency conditions, even gastrointestinal disorders occur - nausea, diarrhea, flatulence.
↑
What does dull or cutting pain mean?
In most cases, aching or dull discomfort indicates a developing pathology. They can intensify with changes in body position, hypothermia, and increased physical activity. If you seek medical help at this stage, you will be able to avoid surgical interventions and avoid disability.
Sometimes the disease proceeds silently at a rapid pace without any worrying symptoms. A person does not take remote mild pain seriously and does not consult a doctor.
A sharp, acute pain syndrome indicates the rapid course of an inflammatory or destructive-degenerative process. Medical intervention is required urgently. Otherwise, health problems will soon arise, including irreversible ones.
↑
What does pain in the lungs at night mean?
At night, the course of biochemical reactions slows down somewhat, including those aimed at restoring detected damage. So, the intensity of the symptoms increases slightly.
- lesions of the spinal column;
- intervertebral hernia;
- myositis;
- osteochondrosis of any localization;
- respiratory, intestinal infections.
They are also characteristic of recent injuries to the spine or ribs. If a person does not attach due importance to them and does not go to the emergency room, then the fusion of cartilage, bones, ligaments, muscles, and tendons occurs incorrectly. Subsequently, pain during sleep becomes constant.
↑
Medicines for lung pain
To confirm the primary diagnosis, a number of instrumental and laboratory studies are carried out. After identifying the cause of the patient’s poor physical condition, etiotropic and pathogenetic treatment begins, aimed at eliminating it.
Three groups of drugs are used directly to eliminate pain:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Nimesulide, Ketorol, Diclofenac are universal, have an analgesic, decongestant, antipyretic effect;
- antispasmodics No-shpa, Drotaverine are used to relieve pain in internal organs, as they relax smooth muscle muscles;
- narcotic analgesics Tramal, Tramadol are prescribed for renal colic, severe injuries, and cancer.
Painkillers are used in the form of tablets, dragees, and injection solutions. Sweet syrups and suspensions are intended especially for children.
↑
When to call an ambulance
A sharp deterioration in health requires an urgent call to the ambulance team. Especially burning in the heart, shortness of breath, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle against the background of increased sweating, panic attacks, fear. These are signs of exacerbation of angina pectoris, as well as pre-stroke and pre-infarction conditions.
A high temperature in a child, especially accompanied by vomiting, leads to rapid dehydration. If a newborn’s body loses more than 10% of fluid, then the likelihood of death is high. The doctor arrives to administer rehydration solutions and admit the child to the hospital.
Source: https://GidPain.ru/bolit/legkie-kashle.html
Pain in the lungs when coughing - the main causes and the correct approach to treatment
Pain in the chest is a serious, dangerous symptom. For any etiology of this phenomenon, it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo treatment. But in order to understand what disease causes the lungs to hurt when coughing, it is necessary to recognize all the reasons for the formation of the symptom and be able to differentiate them.
The main causes of pain in the lungs
Even an experienced specialist without additional examinations will not be able to determine where the discomfort is coming from, from the lungs or other organs of the chest cavity. It is impossible to distinguish only by the nature of the symptom what worries the patient: pneumonia or myocardial infarction, especially in older people.
The reasons for the emergence of the clinic can be divided into two groups:
- Coming from the respiratory system.
- Other.
More often, the etiological factor for the appearance of pain is infections of the lungs, bronchi, and pleura.
The diseases are presented below:
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Pleurisy.
- Tuberculosis.
- Lung cancer.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Silicosis.
- Pneumothorax.
Lung pain without cough is usually caused by extrapulmonary causes. But there are exceptions, for example, diseases of the cardiovascular system can occur with a cough.
Other sources are as follows:
- Stable angina pectoris, myocardial infarction.
- Neuralgia.
- Osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia.
To understand why the lungs hurt with or without coughing, you should analyze the nature of the symptom.
Pain in the lungs – sharp or mild
During the diagnostic search, the degree of symptom intensity plays an important role. Sharp pain is characteristic of acute diseases or a period of exacerbation of a long-term illness. For example, pneumonia, pleurisy, acute bronchitis, pneumothorax, neuralgia, heart attack or angina pectoris provoke acute pain of various localizations.
Important! If, after a traumatic injury to the lung area, sharp pain appears, you should contact an ambulance, as this may be a pneumothorax, which leads to collapse of the lung.
Weak, aching and pulling is a characteristic of a chronic, sluggish process. It can be caused by limited pleurisy, tuberculosis, lung cancer, silicosis, and bronchial asthma.
Osteochondrosis and hernias cause mild pain, but if a nerve root is pinched, a severe pain attack will begin.
Pain in the lungs when inhaling
The pleura, ribs, and intercostal muscles are involved during breathing. When you inhale, tension occurs in the diaphragm and muscles, as a result of which the volume of the chest increases, the lungs stretch, drawing in air.
Pain can occur due to a rib injury, for example, a fracture, when, when a muscle is strained, the surrounding tissues are injured by a piece of bone. Pinched and inflamed nerves also cause discomfort when taking a deep breath. The listed reasons cause pain in the lungs without fever and cough.
The inflammatory process of the pleural layers provokes pain during the act of breathing.
Pain in the lungs when coughing
Respiratory tract infections cause pain in the lungs when coughing, but at the same time, the patient is worried about fever and other signs of intoxication.
Without fever and inflammation, the lungs hurt when coughing due to the following processes:
- Chronic bronchitis due to smoking, cough with brown or yellow sputum.
- Silicosis is accompanied by a nonproductive cough.
- Bronchial asthma occurs with cough, discharge of mucous, viscous sputum.
- Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, which occurs with stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
- Pneumothorax provokes severe chest pain, fear of death, and dry cough.
During respiratory infections, laryngitis and other diseases accompanied by severe attacks, the lungs hurt after coughing.
Pain in left lung, pain in right lung
A localized symptom can occur both with infections and with other processes. A clinical picture that is more pronounced on the left indicates heart problems. In this case, the pain radiates to the arm and ear on the left.
Pleurisy, focal pneumonia, lung abscess, tuberculosis, cancer are unilateral. In this case, the left or right side will lag behind the healthy side when inhaling, and wheezing or weakening breathing may be heard above the surface of the lungs.
A sharp one-sided symptom indicates pneumothorax, rupture of the cyst.
Lung pain and fever
If the temperature rises when coughing, then the patient has one of the acute inflammatory processes: pneumonia, pleurisy, tracheitis, bronchitis. In this case, the thermometer mark can rise to 39-40 °C.
Diseases are accompanied by symptoms of intoxication:
- Weakness, fatigue, drowsiness.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Pain in the eyes, muscles, joints.
- Dry mucous membranes.
- Pallor.
Lung cancer and tuberculosis are accompanied by low-grade fever, which the patient may not even notice.
Diseases accompanied by pain in the lungs
The cause of the development of the symptom is identified by the accompanying clinic, since painful sensations in the chest are not a pathognomonic sign, so a diagnosis is never made based on it.
All diseases can be divided into life-threatening and non-life-threatening. For example, respiratory infection, tracheitis, bronchitis are not life-threatening conditions. Pneumonia, pleurisy, tuberculosis, heart disease, cancer, silicosis must be treated under the mandatory supervision of a doctor, tests, and x-rays.
Respiratory infections
Viral infections affect the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchi. As a result, inflammation develops, which is accompanied by a dry cough, swelling, and soreness.
Coughing attacks can be very strong, so after them the chest will hurt due to overstrain of the intercostal muscles.
A viral infection is characterized by fever and a significantly pronounced intoxication syndrome. The disease usually goes away in 5-7 days.
If sputum appears, a bacterial infection may be suspected.
Bronchitis
With inflammation of the bronchi, in addition to lung pain, the following symptoms are observed:
- The cough at the onset of the disease is dry, and at its height it is wet with purulent sputum.
- Increased body temperature up to 38-39°C.
- Wheezing of varying sonority.
Bronchitis is caused by viruses, bacteria, smoking, and occupational hazards.
Tracheitis
Damage to the trachea occurs with the appearance of a dry, painful cough. Attacks occur when inhaling cold or hot air, laughing, or talking. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes wet. The patient is worried about fever and chest pain.
If the patient has a sore throat, a hoarse voice, or spasms during breathing, then tracheitis occurs together with laryngitis.
Bronchial asthma
Pain occurs after an attack of bronchospasm, which develops after inhalation of an allergen, physical activity, or exposure to other trigger factors.
The disease is accompanied by bronchospasm, resulting in impaired exhalation. After using drugs to stop the attack, viscous sputum begins to be discharged.
Pleurisy
The process is characterized by the presence of fluid between the layers of the pleura or dry inflammation. The patient is bothered by a dry cough, as the pleural receptors are irritated, increased body temperature, and pain when breathing. Alleviation of the condition occurs when the patient is on the affected side, as the excursion of the chest is limited.
Pneumothorax
Air in the pleural cavity leads to lung collapse, as a result of which gas exchange is disrupted and shortness of breath develops. Pain and cough receptors are irritated. Symptoms worsen when inhaling air. Patients experience fear of death and are pale in appearance.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Usually, with angina pectoris or myocardial infarction, the patient has an extensive history of pathology of the heart and blood vessels. The pain may occur with coughing, gurgling during breathing, and the discharge of foamy, pink sputum. Symptoms indicate acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
With chronic cardiac asthma, patients may experience lung pain without fever or severe cough. Symptoms will include coughing and shortness of breath, which improves while sitting and worsens while lying down.
Tuberculosis
The infection occurs with prolonged low-grade fever, coughing, night sweats, pain, and intoxication. If tuberculosis becomes open, a productive cough and deterioration in general condition may appear. The disease is characterized by cavities - cavities formed by the collapse of lung tissue. In this case, hemoptysis and copious sputum will be observed.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Lung pain.
- Cough with purulent sputum.
- Increasing the number of breathing movements.
- Fever.
- Intoxication.
The diagnosis is made only after radiographic examination.
A complication of inflammation is an abscess - a cavity filled with pus. When the abscess breaks through, coughing up a mouth full of phlegm occurs, all symptoms of intoxication subside, and pain is relieved.
Cancerous tumors
Lung cancer takes a long time to grow, but it also causes symptoms to appear late. The most alarming symptoms:
- Chest tenderness, usually one-sided.
- Coughing or dry cough.
- Hemoptysis or pulmonary hemorrhage.
- Low-grade fever.
- Leukocytosis, anemia, thrombocytopenia.
- Losing weight by 5 or more kg in recent months.
- Enlarged lymph nodes supra-, subclavian, axillary.
- Neurological symptoms.
Cancer is more common in long-term smokers, predominantly men.
Silicosis
The disease is characterized by the accumulation of silica dust in the lungs, which leads to the following symptoms:
- Lack of air, suffocation, shortness of breath.
- Nonproductive cough.
- Chest pain.
Patients may be bothered by coughing up sputum if bronchial inflammation is associated.
Diagnostics
A chest x-ray is taken to determine the cause of the pain. This study is a screening study and often puts an end to it, as it can exclude or confirm the following diseases:
- Pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis.
- Lung cancer.
- Pleurisy.
- Pneumothorax.
- Broken or cracked ribs.
- Silicosis.
When taking an x-ray of the spine, osteochondrosis and hernia may be suspected.
If the patient has a complicated cardiovascular history, advanced age, or an established diagnosis of coronary heart disease, then an electrocardiogram is taken to rule out myocardial infarction.
Bronchial asthma is differentiated from chronic bronchitis using a spirogram.
Auxiliary diagnostic methods are:
- Examination of sputum if she coughs up.
- Ultrasound scanning of the pleural sinuses and heart.
- CT – computed tomography.
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging.
Important! It is necessary to provide the doctor with a history of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, lungs and other organs, as this will facilitate the diagnostic search for the cause of pain.
What to do and how to treat if your lungs hurt from coughing?
Any infection with thoracalgia should be treated with antibacterial drugs if the symptom is sharp and severe. The severity of the attacks indicates the intensity of the inflammation.
Tracheitis, bronchitis and uncomplicated pneumonia are treated on an outpatient basis with tablets. Severe pneumonia, tuberculosis, and pleurisy necessarily require hospitalization.
It is allowed to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during this process to reduce pain and reduce temperature.
Root pinching, intercostal neuralgia, injuries, and fractures are also treated with painkillers. COX-2 inhibitors are prescribed, which do not affect the gastric mucosa.
Nitrates are used to reduce heart pain. In case of a heart attack, narcotic analgesics are administered, as in advanced stages of lung cancer.
Puncture of the pleural cavity with pumping out fluid and air will help reduce pain with pneumothorax and effusion pleurisy.
Treating lung pain at home with folk recipes is unacceptable. The exception is discomfort after prolonged attacks due to a respiratory infection, which can be relieved by inhalation, humidification, and taking expectorant syrup.
Important! If there is pain in the lungs in pregnant women and children, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, especially with accompanying fever and intoxication. Pneumonia in these population groups is severe.
Which doctor should I contact for pain in the lungs?
In case of acute pain, which occurs with a cough, fever or without them, you need to contact an ambulance. Doctors will guess the cause and take you to the necessary hospital. In case of inflammatory processes, this will be a therapeutic or infectious diseases department. For pneumothorax – surgical. Due to injury or fracture of a rib – traumatic.
Tuberculosis is treated by a phthisiatrician, cancer by an oncologist, silicosis by an occupational pathologist, osteochondrosis and intercostal neuralgia by a neurologist. A cardiologist deals with diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and a cardioreanimatologist deals with myocardial infarction.
Important! For mild, aching pain in the lungs, it is better to consult a local physician or general practitioner.
What tests can doctors order for pain in the lungs?
Clinical blood and urine tests are standard. Tests help determine the level of leukocytes, on the basis of which the inflammatory process can be judged or not. With any infection there will be a moderate increase in white blood cells. In lung cancer, pronounced leukocytosis and a decrease in hemoglobin levels are observed. Specific tumor markers: CEA, NSE, Cyfra-21-1.
- Urinalysis is not specific for identifying the cause of pain.
- A biochemical study is carried out to determine the level of troponins - proteins that increase during myocardial infarction.
- Cytological, bacterial diagnosis of sputum will help with the identification of tuberculosis, pneumonia, and cancer.
Prevention of lung diseases
The following measures will help prevent chest pain:
- To give up smoking.
- Annual fluorography.
- A diet with a high content of plant foods, with a reduced intake of fat and salt.
- Air humidification.
- Rinsing the nose and throat with saline solutions during infections.
- Mandatory compliance with the doctor's recommendations.
- Walks in the open air.
- Drink enough water, up to 2 liters per day.
- Relief of high blood pressure.
- Regular charging for at least 30 minutes per day.
Conclusion
Discomfort in the lower respiratory tract requires additional examination, precise determination of the cause of the pathology and the choice of adequate therapy. Timely consultation with a doctor helps prevent a decrease in quality of life, disability, and sometimes death. In this regard, doctors do not recommend treatment at home if symptoms are present.
Source: https://MyKashel.ru/lechenie/bolyat-legkie-pri-kashle.html