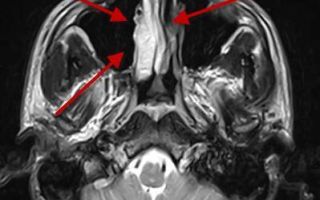
Nasal diseases are characterized by different etiologies. An infection or inflammatory process often develops in the paranasal sinuses of the respiratory organ.
Using MRI diagnostics, pathologies of deeply localized, tortuous sinuses that are inaccessible for viewing by X-ray are identified.
What are the sinuses
The nasal cavity forms a single communicating system together with the paranasal sinuses.
The latter are the cavities of the main and facial cranial zones. On the inside they are covered with an epithelial membrane.
- The basic function of the structures is to warm, cleanse and humidify the air entering the nose.
- The sinuses act as shock absorbers of the skull and take part in the process of voice formation.
- There are four types of anatomical structures:
- maxillary (maxillary);
- frontal;
- main;
- lattice.
In children under 7-8 years of age, the frontal sinuses are not yet developed and for this reason are considered absent.
Essence of the procedure
MRI of the nose is prescribed to examine the sinuses (sinuses). During the diagnostic process, the equipment reproduces several images of the local zone, which are used to study its structure.
If it is necessary to study the vascular system, a contrast agent is used.
This drug makes the bloodstream more visible on high-quality images. This method is justified in case of suspected tumor processes.
- MRI diagnostics of the nasal sinuses is carried out using a tomograph - a complex apparatus that is a volumetric magnetic cylinder.
- Once the patient is inside the equipment tunnel, the tomograph ring begins to move—the process of processing magnetic impulses coming from body tissues begins.
- The software translates them into images that are displayed on the computer screen.
MRI
When is MRI diagnostics necessary?
The paranasal sinuses are examined using magnetic resonance imaging for the following indications:
- chronic form of rhinitis;
- periodic pain in the frontal region;
- the patient's inability to breathe through his nose;
- suspicion of a neoplasm in the paranasal sinuses;
- frequent nosebleeds.
The procedure is indicated in cases where the patient has congenital or acquired defects in the nasal area.
MRI for sinusitis and sinusitis is not a basic diagnostic method; in this case, X-ray and CT are used. This approach is justified only if the allergic nature of the pathologies is suspected.
List of contraindications for MRI
The limitations to magnetic tomography include the following circumstances:
- metal objects (bullets, fragments, implants, clips) and other medical devices (the presence of insulin pumps, pacemakers, etc.);
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- the patient’s body weight is more than 120 kg (the use of specialized equipment is not excluded);
- pathologies that do not allow the patient to remain motionless inside the tomograph.
Claustrophobia can also make the examination difficult. In such cases, anesthesia is used.
Contraindications to contrast scanning include an allergic reaction to the drug and renal failure.
Preparatory stage
If you plan to diagnose the nose and nasopharynx without using a contrast agent, special preparation for the procedure is not required.
Immediately before scanning, you will need to remove metal items (glasses, watches, jewelry, etc.). It is recommended to visit the toilet.
In case of contrast MRI, you should refrain from eating and drinking 6-8 hours before the scan.
Patients with neurotic disorders are recommended to take sedatives several days before diagnosis.
Features of MRI examination
MRI of the paranasal sinuses is performed using a conventional tomograph. However, the process uses a special program for detailed scanning.
The patient is placed on a movable equipment table, which is subsequently moved into the tomograph tunnel.
The patient must remain motionless inside the device. Diagnostic time is 15-20 minutes.
If a contrast agent is used, the procedure is extended to 60 minutes. There is no discomfort during the examination.
The only thing that can confuse the patient is the noise of the equipment. If necessary, the patient is given earplugs or headphones.
After scanning is completed, the results are analyzed. This process takes no more than an hour.
What does an MRI of the nose show?
The table below shows pathologies that can be diagnosed during an MRI examination:
Disease Explanation| Cystic formations on the mucosa | Cysts in the maxillary sinuses are visualized on MRI images as hypertensive, homogeneous and round structures in bone tissue |
| Inflammation of the sinuses or nearby tissues | with sinusitis, there is heterogeneous thickening of the wall of the maxillary sinuses (one) with or without fluid |
| Tumor processes | The image shows round or oval neoplasms with a vague outline |
| Polyps | MRI demonstrates accumulation of glandular or lymphoid tissue |
| Anomalies in bone structure, injuries (fractures, cracks) | the doctor notes a bone defect, displacement of fragments, deformation of the sinuses, hematomas |
Cyst
MRI or CT
What to choose as an alternative to MRI or CT? If we consider the methods according to their information content, in this regard the procedures are almost at the same level.
However, when the privilege is to assess bone structures, preference should be given to computed tomography (before this, radiography is usually used).
When dealing with soft tissues, vessels, MRI is more likely to be prescribed.
The advantage of this technique is the absence of radiation exposure to the body. For this reason, in some cases, magnetic tomography turns out to be the most suitable (when examining small children, pregnant women, etc.).
However, the financial aspect also becomes important in this regard: the cost of MRI is 2 times higher.
The choice of a specific diagnostic method largely depends on the doctor’s opinion.
CT is a harmful diagnostic method
Question of price
MRI, in comparison with other diagnostic methods, is a rather expensive technique. The average cost of the procedure in the country is 2500-3000 rubles.
If you plan to use a contrast agent, you will have to pay 2000-3000 rubles more.
The price tag for medical services varies depending on the region, clinic, and equipment used.
MRI of the nasal sinuses is an informative diagnostic method when it is necessary to identify pathologies of the local area in the early stages of their development.
- Among the diseases likely diagnosed during tomography are: cysts, neoplasms, injuries, structural anomalies, inflammation.
- The procedure is contraindicated for persons with metal objects and electronic devices in the body, and for pregnant women (in the 1st trimester).
For detailed diagnosis, MRI with contrast is indicated. This procedure is prohibited for patients with an allergy to the contrast component, pregnant women and patients with renal failure.
- No preparation for scanning is required, the duration of the diagnosis is from 15 to 60 minutes.
- X-rays and computed tomography are considered as alternative methods for studying the sinuses.
Source: https://osnimke.ru/golova-i-sheya/mrt-pazuh-nosa.html
MRI of the sinuses: what does it show and how is it done? price
The study is quite highly informative and painless, despite the fact that there is active debate regarding the appropriateness of use, the choice of management protocols and its advantages over CT.
However, it is difficult to overestimate the capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging, especially in comparison with x-ray diagnostic methods.
What are the sinuses: where are they located?
As is known, the nasal cavity communicates directly and forms a single functional system with the paranasal sinuses.
They are depressions (or cavities) in the main and facial parts of the skull, lined from the inside with an epithelial membrane.
Their function is to cleanse, warm and humidify the inhaled air.
In addition, they participate in the formation of the voice and play the role of a shock absorber in various skull injuries.
At the same time, the sinuses often serve as entry points for various pathogenic microorganisms, pus and atypical cells, which subsequently easily spread to other structures of the skull and brain.
In adults, there are four types of paranasal sinuses:
- maxillary (are paired);
- two frontal;
- main;
- lattice
The maxillary, also called the maxillary, is located in the substance of the maxillary bone and communicates with the nasal cavity.
It is noteworthy that the upper wall of the formation contains the canal of the infraorbital nerve. This structure increases the risk of developing both intracranial and intraorbital inflammatory complications in case of damage to these sinuses.
- The frontals, according to their name, are localized in the thickness of the frontal paired bones and consist of four walls.
- In this case, the lower and cerebral walls can serve as a place for the spread of infection into the orbit or substance of the brain.
- The location of the main sinus is the body of the sphenoid bone, located posterior to the ethmoid labyrinth.
- Of importance, the upper wall of the formation is the bottom for the sella turcica, on which the pituitary gland (an organ of neuroendocrine regulation), the optic chiasm and the olfactory pathways “sit”.
- The ethmoid labyrinth is located in the bone of the same name and is of great clinical significance due to the fact that it has connections with many canals of the facial part of the skull.
to the content?
Indications for the procedure: grounds for such a diagnosis
MRI of the nose and paranasal sinuses is not a routine examination method, since during its passage a person experiences a certain radiation load.
Source: nasmorkam.net
Indications for the procedure:
- Prolonged pain localized in the sinuses (forehead, brow ridges, above the upper jaw, etc.), signs of pathological changes on radiography or during direct rhinoscopy.
- Prolonged headaches of unspecified origin, frequent nosebleeds.
- Purulent or other abnormal discharge from the nasal passages that does not fit into the picture of an acute respiratory infection or other respiratory infection.
- Signs of a birth defect, injury to the nasal cavity and sinuses.
- Loss of smell, sudden deterioration of vision (when more common causes are excluded), causeless congestion and allergic rhinitis resistant to specific treatment.
- If you suspect sinusitis, polyposis or cysts in the sinuses, a neoplastic process.
to the content?
Advantages and disadvantages of the MRI procedure: when is a CT scan needed?
It is not always necessary to blindly prescribe MRI of the paranasal sinuses, since some pathology is better “seen” by x-rays or computed tomography.
If you make a comparison between CT and MRI, it is quite difficult to determine which is better. Each method has its own disadvantages and advantages.
In addition, as a result of magnetic tomography, a more detailed image of soft tissues is obtained, and the device itself is able to change the image contrast and examination plane without changing the patient’s position. Consequently, magnetic resonance diagnostics is most often used when a tumor process, the presence of polyps or cystic formations is suspected.
In case of injury to the facial skull, it is preferable to prescribe a CT scan, since it allows for excellent visualization of the bones.
It is also worth noting that when performing an MRI with contrast, the patient is injected intravenously with a substance that does not contain radioactive iodine, to which allergies often develop and which is often used in computed tomography.
The advantages of the X-ray method include the speed of the procedure (about 5-7 minutes), the absence of contraindications in the presence of metal objects in the body (pacemakers, etc.) and the cost - CT is cheaper.
The mechanism of action of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
The machine's built-in magnetic coil and its pulsating waves read the magnetic field created by tissues containing large amounts of water, and then takes a picture of the paranasal sinuses.
The device itself can scan in different planes specified by the doctor, creating a multi-planar image.
to the content?
Preparation for MRI of the paranasal sinuses
When an MRI of the maxillary sinuses or other paranasal structures is prescribed, the attending physician must consult the patient about the specifics of preparation.
First of all, you must follow safety precautions and some recommendations:
- Remove all metal objects (earrings, rings, watches, piercings);
- Wear loose clothing without metal inserts.
- If you have mild claustrophobia or other mental disorders, it is advisable to start taking sedatives 1-2 days before the test.
- If the procedure involves the introduction of a contrast agent, it is advisable to refrain from eating a few hours before the start.
- People prone to allergies are prescribed antihistamines.
Thus, there are no significant rules for preparation, but the patient should be aware of the important nuances and technique. to the content?
MRI of the sinuses: how is the examination done?
After removing all unnecessary items, the patient goes to a special diagnostic room with a tomograph.
The nurse helps him lie down comfortably on the extendable table and advises him on further actions.
At this stage, it is important to lie with your eyes closed and not make any movements.
While rotating, the cylindrical camera makes many slices of the human body in different planes, while creating loud and unpleasant sounds that should not be frightened.
Typically, the examination takes from 20 to 40 minutes, and the nurse notifies you when it is completed. The conclusion is issued either on the day of the procedure in a couple of hours, or you are asked to pick it up the next day.
The price for MRI of the sinuses ranges from RUB 1,600.00 to RUB 4,980.00
to the content?
What does MRI of the sinuses show: interpretation
Many people wonder whether the study will show sinusitis or a tumor. Therefore, consider the pathology visible using magnetic resonance imaging:
1
These formations can be single- or multi-chamber. Cysts in the maxillary sinuses on MRI (T2 mode) are visualized as hyperdense, homogeneous and round structures in the thickness of the bone.
2
Inflammatory lesions of the sinuses or adjacent tissues. With sinusitis, the image will show heterogeneous thickening of the wall of the maxillary sinus (or both), sometimes with a level of fluid, which is often represented by pus.
3
Neoplastic processes. With MRI, tumors, as a rule, are differentiated already in the early stages and represent a round or oval formation with unclear contours.
4
Polyps are multiple benign formations consisting of lymphoid or glandular tissue on a stalk. Polyps of the maxillary sinus are clearly visualized on the tomograph screen.
5
Anomalies of the bone structure of the nasal cavity and sinuses, injuries - cracks, fractures, etc. The description of a fracture includes: a bone defect and deformation of the sinus, displacement of bone fragments, and quite often the formation of a hematoma (hypodense round formation).
MRI of the sinuses during pregnancy
Pregnant women are not recommended to undergo magnetic tomography, as the field it creates may have a detrimental effect on the fetus.
If the procedure is absolutely necessary, then it is recommended to wait until the end of the first trimester, when the development of the embryo is most active and susceptible to the influence of external factors.
[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
to content ?
In what cases is examination contraindicated?
Contraindications to this diagnosis are as follows:
- pregnant and nursing women;
- for a closed tomograph – children under seven years of age;
- persons whose weight exceeds 120 kg;
- patients with pacemakers, fixed prostheses, pins, etc.;
- people suffering from claustrophobia;
- persons who are unconscious or under the influence of drugs/alcohol.
to the content?
Video MRI of the sinuses
Share with friends
Source: https://nasmorkam.net/mrt-pazux-nosa-chto-pokazyvaet/
MRI of the paranasal sinuses for sinusitis and other diseases: what magnetic resonance imaging of the paranasal sinuses shows
Magnetic resonance imaging is a method for studying the tissues of the human body, based on the reflection of electromagnetic pulses from them.
The accuracy of the images obtained with this diagnostic procedure is far superior to X-rays. MRI of the sinuses is rarely prescribed, but for a number of diseases it cannot be avoided.
The essence of the procedure
The purpose of the procedure is to examine the sinuses (sinuses). During the scanning process, the device takes many pictures of a given area, which allows you to study its structure in detail.
If there is a need to improve the accuracy of vascular imaging, contrast is administered intravenously to the patient. This is a specific liquid that makes the bloodstream more visible in the pictures. The use of contrast is recommended if any neoplasms in the examined area are suspected.
Mechanism of action of the tomograph
A tomograph is a complex device consisting of magnets, gradient coils, a radio pulse generator and receiver, a power source, a Faraday cage, a data processing system and a cooling unit. To conduct the study, the patient is placed on a special retractable table in a narrow tunnel inside the device.
After switching on, the device processes magnetic pulses reflected from body tissues. Using a computer program, he converts them into images and displays them on the screen. In this case, the organ under study is viewed in various projections and planes. The thickness of the sections depends on the research objectives and can start from 0.8 mm.
Indications and contraindications
MRI of the nose and paranasal sinuses is performed for the following indications:
- chronic rhinitis, loss of smell;
- pain in the frontal region that occurs regularly;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses;
- suspicion of a neoplasm in the area of the paranasal sinuses;
- recurrent nosebleeds.
In addition, a magnetic resonance imaging study is performed if the patient has congenital or acquired defects in the structure of the nasal cartilage and bones due to trauma. MRI for sinusitis and sinusitis is not the main diagnostic method, but can be used if the doctor suspects the allergic nature of the disease.
Contraindications to magnetic tomography:
- metal plates, vascular clips or fragments in the body;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- weight exceeding 150 kg (this limitation applies to most tomograph models);
- a disease that does not allow a person to remain motionless, for example, Parkinson's disease;
- The patient has a pacemaker, hearing aid, or insulin pump.
Intolerance to confined spaces makes research difficult. However, in such patients, MRI can be performed using medicated sleep. Scanning with the introduction of contrast cannot be used to diagnose patients who are allergic to the components of the staining composition or have severe liver and kidney dysfunction.
Is preparation necessary?
No preparatory procedures are required before MRI of the sinuses and nasopharynx without contrast. It is advisable to take with you a medical card or extracts from your medical history, if any.
It is recommended to remove metal jewelry, piercings, earrings, hair clips, and watches in advance. Clothing should be comfortable, without metal elements. Immediately before the examination, you should visit the toilet so that the need does not arise during the scan.
If an MRI with contrast is scheduled, you should stop eating and drinking 6 hours before the procedure. People with mild claustrophobia are advised to take sedatives for 1-2 days before the procedure.
How is the procedure performed?
MRI of the sinuses lasts on average from 10 to 20 minutes; when using contrast, the duration of the study can increase to 1 hour. At this time, the patient is in a horizontal position inside the device (in a cylindrical tunnel with a diameter of about 60 cm), the head can be fixed with a special device. He should remain still, as movement degrades the quality of the pictures.
The procedure is accompanied by rhythmic noise (tapping, crackling) that occurs when the tomograph is operating. The doctor is in an adjacent room, monitoring the operation of the program and observing the patient through glass. If during the examination the patient feels unwell and wants to interrupt it, just press the device with a button, which is placed in the hand before the scan begins.
The MRI result can be obtained after the specialist describes the images and prepares a conclusion. The waiting time for an answer depends on the workload of the clinic at the moment; it usually varies from 1-2 hours to a day. At the patient’s request, the images can be printed, recorded on disk or other media.
What does it show?
What does MRI of the paranasal sinuses show? The study can reveal infectious lesions of bone tissue, deviations in the structure of soft tissues, accumulation of fluid in cavities, tumors, cysts, polyps, structural anomalies, and consequences of injuries.
Thickening of the walls of the maxillary sinus in the photographs indicates an inflammatory process in this area. If a tumor is detected, MRI with contrast allows you to clarify the extent of its spread.
Price
MRI of the nasal sinuses costs on average from 2,400 to 2,900 rubles. The introduction of contrast increases the price by another 2-3 thousand rubles. Prices may vary depending on the region of residence and the specific medical institution.
MRI or CT?
Patients often have a question: which diagnostic method is better, MRI or CT (computed tomography)? If we consider the methods from the point of view of information content, their reliability is almost identical. But in cases where it is necessary to show the condition of bone tissue, CT is still preferable.
The advantage of MRI is the absence of radiation, which affects the patient’s body during CT scanning. For this reason, many people prefer magnetic tomography. But the financial issue is also important - the cost of MRI is approximately 1.5 times higher. In any case, the decisive factor in choosing a diagnostic method should be the opinion of the doctor referring the patient for examination.
MRI of the paranasal sinuses is a safe and informative procedure. With its help, you can examine in detail the structure of the sinuses, exclude or identify inflammation, neoplasms and other anomalies.
Yana Semich,
specially for Moylor.ru
Source: https://moylor.ru/nos/mrt-pazuh/
MRI of the sinuses - the main imaging function
MRI of the sinuses is an imaging function performed using magnetic resonance imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic procedure needed to detect pathologies of ENT organs.
The use of the method in otolaryngology is widespread. The complex structure and interaction of organs makes visual diagnosis difficult. MRI is used to determine the cause and location of the disease.
Based on what the examination shows, it becomes easier to find the root cause of the pathology, make a diagnosis, and determine treatment tactics.
Advantages
An informative, short-time computer diagnostic method allows you to make an MRI of the paranasal and paranasal sinuses or nasopharynx.
The examination quickly reveals the pathology, exact location, size, character. A diagnostic search carried out with the maximum degree of reliability speeds up and simplifies the determination of treatment tactics for complex diseases of the ENT organs.
Magnetic resonance imaging method and laryngology
The paranasal space is a complex and highly functional structure. Anatomically, it contains 4 pairs of sinuses, ethmoid labyrinths in close proximity to the brain and frontal lobes.
In a pathological state, diseases arise in it that cannot be detected either by analysis of mucous secretions, or by examination, or even by radiographic examination. Magnetic resonance imaging of the nasal sinuses shows pathological changes, determine the dislocation, size, and degree of danger that they pose in their development.
Examination of the nasal area makes it possible to assess the condition of the sinuses (sinuses), intranasal structures, and a separate display of each element of a complex structure.
The effect of this diagnostic method is not limited; it is contraindicated only for people with metal prosthetic elements. The operation of diagnostic equipment is based on a high-power constant magnetic field, which causes existing limitations.
Special devices that create local magnetic fields, high-power fields, and radio frequency radiation help obtain an image of the organ located in the scanner (tomograph).
Computer-analyzed signals located in a constant magnetic field make it possible to obtain, after appropriate processing, images of the desired parts of the nasal region.
Attention! Magnetic resonance imaging is not a diagnosis, but a way to obtain the information necessary for a doctor to determine the nature of the pathology. The conclusion is drawn based on the results of the study.
Indications
Complaints of discomfort in the sinus area during x-ray examination often show sinusitis. If the x-ray does not give any obvious cause for concern, and pathological symptoms are present, a magnetic resonance examination is prescribed.
Sometimes tomography of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed.
Information! Read here about whether X-rays are harmful for infants and how they are done
Indications
The reasons for this are the following symptoms:
- headaches of unknown etiology, in the forehead;
- negative sensations in the paranasal space;
- loss of smell, accompanied by nasal discharge;
- discomfort when swallowing, not accompanied by inflammation;
- noise in ears;
- injuries sustained in this area.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the sinuses shows diseases that are not detected by x-rays. This method allows you to diagnose a much more extensive list of pathologies. It indicates infectious processes of the mucous membranes, inflammation of the joints, soft tissues and cavities, cerebral hernia, metastases, and the consequences of poorly treated sinus injuries.
Attention! The need for research is obvious if there are negative symptoms that are not confirmed either visually or by x-ray.
Sinuses and thorough examination
Magnetic resonance imaging of the nasopharynx allows you to assess the condition of the structure, mucous membranes, features of the individual anatomical structure, and existing developmental anomalies. Using MRI of the nasopharynx, you can see the condition of deep-lying tissues that are not accessible to visualization.
Examination of soft tissues helps to detect polyps, cysts, tumors located in soft tissues. If a CT scan allows you to see only darkening in the image with sinusitis, an MRI will show the distribution, type, and identify the root cause. New growths can be measured using tomography and their relationship with nearby organs can be determined.
In some cases, an MRI of the sinuses is prescribed, but not everyone knows what such a study shows. A tomographic examination of the paranasal sinuses will show inflammatory processes, osteopathic disorders, chronic diseases, tumors, polyps. The result is evaluated after decoding the information received.
He will confirm or refute suspicions of a cyst or polyps, and reveal:
- sinusitis of various degrees;
- will indicate congenital and acquired structural anomalies;
- will provide reliable information about allergic reactions;
- localizes neoplasms;
- will clarify the extent of their spread, the presence or absence of metastases.
For sinusitis, magnetic resonance imaging will reveal the presence of intraorbital and intracranial complications and will help in differentiated diagnosis of etiology and existing inflammation.
Intraocular complications of sinusitis result in an abscess, or phlegmon, intracranial complications – meningitis, or encephalitis, abscesses, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus. For cysts and tumors, MRI distinguishes between inflamed tissue (zone of reactive inflammation) and the tumor itself.
Which is better - computed tomography or MRI of the sinuses?
It is difficult to answer the question of which is better - tomography or CT scan of the sinuses. Using magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor sees the surgical area, predicts the likelihood of the outcome, and sees possible complications.
CT and X-ray do not differentiate in this case. The introduction of a contrast agent allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels and nerves. These studies help to differentiate neoplasms into benign and malignant, which gives a preliminary prognosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging helps in the diagnostic process. This is a progressive, safe, informative examination. Examination of the sinuses, due to the short reach by other means, is urgently necessary for treatment.
Source: https://aboutrentgen.ru/mrt/mrt-pazuh-nosa
What will an MRI of the sinuses show?
Have you had ARVI, but your runny nose still won’t go away? Do you continue to have headaches, does your forehead or paranasal area hurt when you press it?
Our readers probably remember that these symptoms are possible with sinusitis - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Read more about sinusitis, diagnosis and treatment here
How can MRI help in their study and what other ailments can be detected using magnetic resonance imaging of the nasal sinuses? Vladimir Aleksandrovich Mikolaichuk, a radiologist at MRT Expert Lipetsk LLC, told us about this.
- Vladimir Aleksandrovich, before talking about the features of magnetic resonance imaging of the paranasal sinuses, let's answer the question - what are sinuses?
The sinuses (or, otherwise, sinuses) are cavities in the bones of the skull, normally filled with air and communicating with the nasal cavity. There are 4 types of sinuses in total: 3 paired (maxillary, or maxillary; frontal; cells of the ethmoid labyrinth) and 1 unpaired (sphenoid).
Their main functions: warming the inhaled air, participating in the formation of voice timbre, reducing the mass of the skull, and sensing atmospheric pressure.
- Are the sinuses and turbinates the same thing or not?
No, these are different entities. If the sinuses are cavities, then the conchae are convoluted bony structures. Most often there are 3 pairs of nasal conchae: lower, middle and upper. Occasionally, the so-called superior (or highest) nasal concha is encountered.
The turbinates divide the nasal cavity into nasal passages through which air moves.
Their surface is covered with a mucous membrane, consisting, among other things, of different types of cells - for example, secreting mucus, perceiving odors.
The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity also contains a rich network of blood vessels, which helps warm the inhaled air and also traps microparticles entering from the outside, including microorganisms.
- For what diseases is MRI of the nasal sinuses prescribed?
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the sinuses, as well as the nose, are quite extensive. Mainly, these are inflammatory processes of the sinuses - sinusitis (sinusitis), both acute and chronic; various neoplasms, including polyps, cysts. During the examination, it is possible to detect a curvature of the nasal septum, turbinates, and an enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil.
You can find out the cost of MRI of the nose and paranasal sinuses and sign up for the study here.
- Is this type of study performed with or without contrast?
In the vast majority of cases, MRI of the sinuses is performed without contrast. A contrast study is performed if there are any volumetric formations in them: in this case, the neoplasm begins to accumulate a contrast agent, and its boundaries and distribution can be seen more clearly.
Why is contrast used in MRI?
- Is there an alternative to MRI of the nose and paranasal sinuses? When is magnetic resonance imaging used and when is CT scan used?
Computed tomography, in fact, is this worthy alternative. Moreover, in relation to the paranasal sinuses, CT is the reference research method.
It is, in particular, prescribed to patients who are planning to undergo surgery.
With CT, bone formations, topographic relationships of various structures (including nerves, large vessels), and anatomical variations in the structure of the sinuses are better visible.
Magnetic resonance imaging is more preferable when so-called rhinogenic complications occur, when the pathological process spreads to the membranes of the brain or to the brain itself (for example, with the development of meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscess). It is also advisable when the process is in the soft tissues of the face. In addition, MRI is used for dynamic monitoring, for example, after surgery.
- You can find out the cost of a CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses and sign up for the study here.
- ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
- - Vladimir Aleksandrovich, in order to do a magnetic resonance imaging of the nose, do you need a doctor’s referral or can the patient make an independent decision about undergoing diagnostics?
- You can undergo examination with or without a referral.
- How is MRI of the nasal sinuses performed and is preparation required for the study?
The person is placed on the MRI machine table and a series of pictures are taken. The duration of the study is about 8-10 minutes. No special preparation is required. However, it is highly advisable to refrain from using vasoconstrictor drops (such as naphthyzine, etc.) 5-6, or better yet, 12 hours before the procedure, since they, by relieving swelling of the mucous membrane, can reduce the information content of the study.
- You might be interested:
- When is a nosebleed a reason to make an appointment with an ENT doctor?
- Your nose is stuffy, but you don’t have any drops on hand?
- What is ARVI?
- For reference:
- Mikolaichuk Vladimir Alexandrovich
- Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of the Ryazan State Medical University in 2014.
- In 2015, he completed an internship in the specialty “Ophthalmology”.
- In 2017, he underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Radiology”.
- Currently working as a radiologist at MRI Expert Lipetsk LLC.
Source: https://www.mrtexpert.ru/articles/518
MRI of the sinuses: what does it show and when is it prescribed?
MRI of the paranasal sinuses is the highest quality examination of the facial part of the head.
With the help of this medical device, it is possible to detect the slightest changes in the paranasal area, thereby identifying various diseases, if any, at the initial stage.
What kind of procedure is this, how is it carried out and for what symptoms is it prescribed? We will try to answer these and related questions in this article.
What is MRI?
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a special medical equipment that can be used to thoroughly and safely examine internal organs or human tissues. The operation of this device is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic nuclear resonance.
During an MRI study, a person is placed in a “scanner” where a relationship occurs between magnetic radiation and the nuclei of hydrogen atoms located in the body’s tissues.
Electromagnetic waves at constantly high power excite protons, thereby provoking them to produce signals that are collected in the equipment receiver.
Thus, having collected all the data, the scanner processes all the information received and produces an image of the problematic parts of the body.
When is an MRI prescribed?
An MRI of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed by a specialist only if absolutely necessary. This is due to the fact that during the procedure the person is still exposed to a small dose of radiation. Therefore, this examination technique is prescribed only in such cases as:
- Suspicion of congenital defects of the nasal cavity.
- Unreasonable loss of charm and decreased vision.
- Pain in the frontal and paranasal parts of the face.
- Suspicion of cancer.
- Purulent and bloody discharge from the nose, without the characteristic symptoms of acute respiratory infections and other respiratory infections.
- When sinusitis and rhinitis cannot be treated.
- Suspicion of a foreign body in the nasal cavity.
There are cases when tomography is prescribed to patients who experience tinnitus and nasal congestion for no reason.
In what cases is MRI not prescribed for patients?
Due to the fact that electromagnetic resonance is used during tomography of the nose and paranasal sinuses, this examination has individual limitations. Thus, MRI should not be prescribed to people with the following symptoms:
- Age of children up to 7 years.
- The presence in the body of metal prostheses or implanted objects that cannot be removed.
- Pregnant women.
- Mothers who are breastfeeding.
Also, this examination is not recommended for people who use hearing aids or use cardiac stimulators.
Preparing for an MRI exam
If the attending physician prescribes an MRI, he must explain to his patient how to prepare for this procedure. So, according to his recommendation, when contrasting, you should refuse to eat 6 hours before the examination technique. Refusal from water should be 3 hours before diagnosis.
All subsequent preparation is based on safety precautions and involves the following actions:
- Remove all accessories and jewelry.
- Wear loose, light clothing, without metal objects.
If MRI is prescribed for children, the child must be prepared for the confined space of the “scanner”, explaining that he is not in danger, since the parents will be nearby.
Carrying out MRI diagnostics
After preparation, the patient is taken to a special room where the tomograph is located. All subsequent tangential actions occur in this order:
- The patient wears special clothing that will prevent the influence of electromagnetic waves.
- Sitting on the couch, the patient's arms are extended along the body, and the head is secured on the headrest.
- Contrast is injected into the patient's vein through a catheter.
- The patient, together with the couch, moves in and closes himself in the “scanner”.
The timing of the examination usually depends on the diagnosis. On average it is about 20 minutes. During this time, specialists are in another room, observing how the resonance tomograph scans the area of pathology.
Upon completion of the examination, the doctor gives the diagnostic result to the patient immediately or the next day.
It is worth paying attention: When receiving a photograph in your hands, you should not pay attention to its image.
Sometimes, at first glance, terrifying images do not mean the presence of pathology. Therefore, in order not to upset yourself prematurely, it is better to find out what the picture shows in a specialist’s office.
What does an MRI show?
After the patient receives the results of the study, he needs to visit a specialist who sent him for an MRI of the sinus region of the nose. After carefully studying the images, the doctor will be able to identify the following pathologies:
- congenital anomalies of the paranasal part of the face;
- the presence of polyps and cysts in the nasal cavity;
- chronic diseases;
- osteomyelitis;
- injuries from external factors;
- sinusitis and sinusitis;
- inflammation of the soft tissues of the nose.
It will also be possible to identify oncological tumors of both malignant and benign types.
Pros and cons of MRI diagnostics
During the study and scanning of the sinus spaces of the paranasal region, MRI, unlike an X-ray machine, produces less radiation on the human body. In this regard, tomography can be performed every 2–3 months, which is very convenient for monitoring treatment results. In addition, the advantages of computer diagnostics MRI include the following indicators:
- The ability to determine the exact dimensions of the sinuses and nasal septum.
- Clear visualization of tumors and demyelinating pathologies.
- The three-dimensional image of the image allows you to examine in detail the necessary part of the nasal cavity.
- Absence of associated negative factors when scanning the bone parts of the face.
- Such MRI indicators of the nose make it possible to correctly identify the diagnosis at the initial stage or as it progresses.
- Despite such positive qualities, magnetic resonance imaging also has its negative aspects.
- The disadvantages of this diagnosis include:
- When an MRI of a child's sinuses is performed, he usually behaves restlessly. Excessive movements and sobs negatively affect an accurate diagnosis.
- The procedure is quite expensive, so not every patient can afford it.
In addition, as already shown above, metal objects inside a person also pose limitations when using this diagnostic method.
Based on the presented data, it is clear that magnetic resonance imaging is a fairly effective diagnostic tool for identifying diseases of the nasal cavity.
If you follow the recommendations of the specialist in preparing the study and the rules for conducting it, it will be possible to achieve an accurate diagnosis in a short time.
After all, the earlier a pathology is detected, the easier it is to treat and further prevent.
Author of the article: Yulia Kalashnik
Source: https://VipLor.ru/nos/mrt-pazuh