Peyronie's disease (ICD code 48.6) is diagnosed when foci of fibrosis are detected in the tunica albuginea of the penis (fibroplastic induration). These formations cause deformation of the organ, which manifests itself during an erection.
In a number of sources, the pathology is known as “penile fibromatosis”. The disease is rare and occurs mainly in men aged 35 to 70 years. It almost never occurs in young men.
Peyronie's disease not only distorts the appearance of the penis, but is also accompanied by pain during erection, depriving a man of intimate life.
Symptoms and stages of development
Peyronie's disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of compactions (plaques) and fibrin strands under the skin of the penis, a decrease in its turgor (elasticity);
- pain during erection, increasing during friction. The symptom is caused by the pressure of the seals on the blood-filled corpora cavernosa;
- gradually increasing degree of deformation of the erect penis. There are three types of curvature: dorsal (up), ventral (down), lateral (sideways).
In the acute form of Peyronie's disease, pain and a pronounced change in the shape of the penis occur already at the initial stage, which lasts from 6 to 18 months, then the pain subsides and the chronic phase begins.
In most cases, the pathology develops slowly. For a long time, the only symptom is barely palpable single or multiple lumps under the skin of the penis. A dull pain may come and go periodically. As the disease progresses, the intensity of pain symptoms increases; the curvature of the penis during erection can reach 60-90 degrees.
Complications
Although Peyronie's disease is not fraught with the development of life-threatening complications, without diagnosis and treatment this pathology makes intimate life impossible. Infertility, relationship breakdown, severe depression and neuroses - this is an incomplete list of negative consequences.
From the moment the plaque originates until the completion of its formation, approximately one and a half years pass. The disease tends to progress. Pathology resolves spontaneously only in 13% of cases.
A big mistake is trying to self-medicate with medications, physical influence or injections.
This can lead to new compactions, hematomas, suppuration, and stricture (narrowing) of the urethral canal.
Reasons for development
Injury to the shaft of the penis leads to ruptures and displacement of collagen fibers, damage to blood vessels, and the formation of hematomas.
Normally, tissue regeneration occurs without consequences, but in some cases, fibroblast cells are activated, producing fibrin in large quantities.
Gradually, the inflamed area is replaced by scar tissue, which over time “matures,” calcifies and becomes hard (osteogenic degeneration).
Injuries are considered the most common cause of onset of the disease. In 70% of patients with Peyronie's disease, damage to the penis occurred during sexual intercourse when the partner was on top.
A significant part of specialists in the field of urology are inclined to the autoimmune origin of the disease, believing that the cause of scar formation is an attack of one’s own immunity on the tissue of the tunica albuginea. This pathology is not systemic in nature, like lupus or arthritis.
Classification and methods of treatment of hypogonadism in men
According to the genetic theory, fibrous deformities develop due to a congenital disorder of the processes of collagen protein synthesis.
Peyronie's disease can also be diagnosed in newborns if the urethral canal is too short or there is hypoplasia of the tunica albuginea. There are no pronounced plaques in such cases, but neoplasms of connective tissue are found in the cavernous bodies.
The main risk factors for the disease:
- age. The older the man, the less elastic the penis, and therefore the risk of injury increases significantly;
- disturbances in the processes of development and regeneration of connective tissue (Dupuytren's contracture);
- diabetes;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- collagenoses;
- dyslipidemia;
- shortened urethra;
- deficiency of vitamin E or testosterone.
Peyronie's disease can be provoked by long-term use of a number of drugs:
- beta blockers;
- drugs for the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies;
- medications that raise blood pressure.
Alcoholism and smoking have an extremely negative effect on the elasticity of blood vessels and skin, and therefore are also included in the list of factors that provoke pathology.
Early diagnosis of Peyronie's disease significantly simplifies and speeds up the course of treatment, providing more opportunities for quick and painless correction of the shape of the penis. Examination methods used:
- inspection and palpation. At this stage, the doctor can already draw conclusions about the nature of the tumors;
- Ultrasound of the penis;
- radiography;
- cavernosography.
If necessary, an MRI of the pelvis is prescribed. It is important to distinguish a fibrous plaque from a malignant tumor, as well as the consequences of tuberculosis or syphilis.
Treatment
Each man has his own characteristics of the disease.
If plaques can be palpated, but their presence is not accompanied by pain and intimate discomfort, then a wait-and-see approach is chosen, since all treatment methods can subsequently provoke erectile dysfunction.
If the disease progresses, conservative methods - physical and drug therapy - are started. Treatment of Peyronie's disease with surgical methods is carried out in the presence of direct indications or due to the ineffectiveness of previous correction options.
Medicines
Conservative treatment of pathology is aimed at relieving pain and reducing the size of fibrous formations.
The following drugs are injected:
- steroids. It is advisable to use it during the first year and a half of the disease, while the plaque is just forming. Hormonal drugs are not popular due to their low effectiveness;
- Collagenase is an enzyme that helps soften fibrous formations by breaking down the peptide bonds of collagen. It is inserted directly into the plaque perpendicular to the shaft of the penis. A positive effect in the form of reducing the curvature of the penis is achieved in 65% of cases. The course of treatment is about 1.5 months, injections are given twice a week. In case of overdose, side effects are possible: hemorrhages and the appearance of new scars due to the decomposition of capillaries;
- interferon. The effectiveness of the drug in Peyronie's disease is still being studied;
- verapamil. Prescribed for injection into acute and chronic non-calcified plaques. Has a direct antifibrotic effect.
Classification and methods of treatment of hypogonadism in men
Oral medications:
- vitamin E. Can slightly reduce pain and slightly smooth out the deformation of the penis;
- colchicine Slows down the production of collagen and activates collagenase, has an anti-inflammatory effect. One of the side effects from taking pills is diarrhea;
- tamoxifen. It has antitumor and antiestrogenic properties. Deactivates T-lymphocytes and macrophages;
- potassium paraaminobenzoate (potaba). Slows down fibrin formation;
- pentoxifylline. Increases the level of nitric oxide and improves blood microcirculation, due to which not only the development of deformation slows down, but in some cases its regression is observed;
- propional L-carnitine. With regular use, it can reduce pain and the degree of curvature of the penis.
The course of treatment usually consists of a combination of different types of medications and vitamins.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an effective complement to drug treatment. The following methods are used:
- extracorporeal shock wave therapy (shock wave therapy). It has almost no effect on the degree of curvature of the penis, but relieves pain well;
- extension (traction) of the penis using a special device - an extender;
- iontophoresis with dexamethasone, verapamil, lidocaine. Relieves pain and reduces the size of formations;
- massage using heparin ointment to improve hemodynamics in the penis.
Of the conservative methods, injections of verapamil, interferon and traction are considered the most effective. The feasibility of other treatment methods requires additional research and confirmation.
Conservative therapy is advisable in the first 18 months of development of the pathology. A positive result can be achieved in 50-60% of cases.
Surgery is recognized by doctors as the fastest and most effective method of treating Peyronie's disease. It is used only for fully formed plaques. Absolute indications are calcification of formations, significant curvature of the penis (more than 45 degrees), erectile dysfunction throughout the year.
There are 3 types of operations possible:
- Nesbit plication, in which folds are formed by suturing the tunica albuginea opposite the plaque. It is carried out in cases where the penis is longer than average (after the operation there will be a shortening of 15. -2 cm) and the angle of its curvature is no more than 45 degrees. In case of severe curvature, the tunica albuginea on the side opposite to the seal is excised and the tissue is sutured;
- plastic. The plaque is dissected with a linear incision into which an autograft is placed - a segment of the saphenous vein (autovenous patch taken from the leg above the ankle, or from the deep dorsal vein of the penis), a piece of skin (dermal flap) taken from the testicle or in the area of the pelvic bones. The use of a pericardial graft eliminates the need for a donor incision;
- penis prosthesis used for severe erectile dysfunction.
Causes and treatment of redness on the head and foreskin of the penis in men
All manipulations are performed under general anesthesia.
Having sex is not allowed earlier than 1.5 months after surgery. Failure to follow the doctor's recommendations in the postoperative period can lead to suture ruptures, hematomas, displacement and rejection of implants. But spontaneous erections without physical force are beneficial because they help straighten the penis.
Recurrence of curvature is likely within a month. The reason is the reduction in the area of the transplanted flap. The situation usually resolves on its own within 3-6 months. In some cases, the penis is bent in the other direction. If the patient retained the ability to have a normal erection, the result of the operation is positive in 90% of cases.
Traditional methods
Occasionally it is possible to get rid of Peyronie's disease using traditional methods. It should be noted that treatment at home should be carried out after diagnosis and under the supervision of a specialist.
A decoction of chestnuts and honey is used as an adjuvant. Recipe: 20 g of nuts are poured into a glass of water, boiled for 15 minutes. Then the broth is filtered and taken 1/3 cup per day. Honey is added to soften the bitter taste.
The original method of treating Peyronie's disease is hirudotherapy. Substances that leeches secrete into the wound promote the dissolution of collagen. It is not recommended to use this method on your own.
At home, you can prepare an external remedy based on dried leeches: mix ¼ cup of the raw material with heparin ointment, a glass of honey and two tablespoons of dimexide solution. Gently rub into the skin of the penis at night.
The mixture should be stored in the refrigerator.
Prevention
Since Peyronie's disease is provoked mainly by injuries, the most effective preventive measure would be careful handling of the penis:
- in sex, it is better to avoid positions where the girl is on top, especially for men at pre-retirement and retirement age;
- exclude sexual contacts while under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- choose underpants and trousers that do not compress the genitals.
If any lumps are detected in the penis, a man should not wait for its shape to become distorted and self-medicate. Timely consultation with a urologist will preserve erectile function and eliminate the need for surgery.
Source: https://potencia.online/zabolevaniya/bolezn-pejroni/
Peyronie's disease
Treatment of Peyronie's disease in men, causes and first symptoms Peyronie's disease is a non-life-threatening deformation of the male genital organ when it is in a state of erection.
This pathology was described back in 1743 by a surgeon from France, Francois de la Peyronie.
This doctor, after whom the disease was named, described the clinical picture in great detail, namely the inclination of the erect penis in relation to the central axis, the angle of which could reach 90 degrees.
When palpated, a lump could be felt, and patients felt pain.
The compaction was caused by inflammatory processes and the deposition of fibrous plaques under the skin of the penis, as a result of which blood microcirculation was disrupted and microhematomas were formed.
Subsequently, the elasticity and extensibility of the tunica albuginea was impaired, which then led to visible curvatures at the site of compaction formation.
What it is?
Peyronie's disease is a curvature of the penis due to the growth of the fibrous membrane, where plaques form, or benign neoplasms in the body of the penis.
Causes of Peyronie's disease
Today, none of the world's scientists can name the exact cause of Peyronie's disease. However, microtraumatization of the penis is considered the main risk factor in the development of such a pathology.
It is believed that with constant irritation of the head and body of the penis, inflammation of the latter develops. As a result of this, the activity of fibroblasts is activated and connective tissue degeneration of the tunica albuginea occurs. After this, the skin and tissue of the penis cease to be soft and elastic, but, on the contrary, become hard and immobile.
If the inflammatory process continues against the background of active formation of connective tissue, then the so-called remodeling of the latter occurs.
In other words, the connective tissue begins to change its own configuration and curvature of the penis occurs.
In addition, systemic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, erectile dysfunction, arterial hypertension and lipid metabolism disorders can increase the risk of developing Peyronie's disease.
The attitude of scientists towards smoking and alcoholism in the development of Peyronie's disease is ambiguous. While some believe that these factors lead to this disease, others completely refute such information.
The role of a hereditary factor in the genesis of the disease cannot be excluded. At a minimum, this is evidenced by Dupuytren's contracture, which occurs in more than half of patients with Peyronie's pathology. [adsense1]
Classification
Peyronie's disease is classified according to stage, cause and degree of deformity.
Taking into account the cause of occurrence, the following are distinguished:
- acquired form – developed as a result of hormonal imbalance or injury;
- congenital – formed as a result of intrauterine disorders.
According to the degree of progression, Peyronie's disease is divided into:
- pain – severe pain is observed at rest and during erection;
- functional - apart from pain, with the disease it is impossible to lead a normal sex life.
According to the degree of deformation, the disease is divided into several types:
- dorsal – the penis is directed upward;
- ventral – the genital organ is tilted down;
- lateral - the penis is directed to the side.
Peyronie's disease is not a disease that poses a threat to human life, but has a high social significance, since it has a direct impact on sexual communication, and, therefore, the quality of life of men of active working age.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Peyronie's disease in men (see photo) sometimes make themselves felt gradually, sometimes they appear quickly and unexpectedly acutely. The main signs of the disease are:
- Painful erection;
- Curvature of the erect penis;
- The presence of lumps under the skin of the penis.
In some cases, the painful symptoms of Peyronie's disease are mild or go away over time. Sometimes the appearance of plaques does not lead to deformation of the genital organ.
Some patients experience a decrease in sexual desires or short duration of sexual intercourse.
If you have at least one symptom of Peyronie's disease, you should consult a doctor, since in its advanced state it often leads to impotence. [adsense2]
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis is made based on the results of an external examination and palpation of the penis. The diagnosis can be confirmed after X-ray or ultrasound of the penis, which determines the size and structure of fibrous plaques.
Clinically, the disease manifests itself as curvature of the penis and pain during erection, up to the impossibility of sexual intercourse. About 30% of patients suffer from erectile dysfunction.
Complications
Although this disease is not life-threatening, if left untreated it can lead to sexual dissatisfaction, painful erections and irreversible functional impairment.
The course of the disease is also complicated by the danger of psychotraumatization of patients who are seriously experiencing their “illness.”
With a small percentage of penis deviation, this cannot yet be called a disease. Peyronie's disease is accompanied by a significant increase in fibrous tissue, leading to the formation of compactions - this can ultimately lead to the inability to perform sexual intercourse (dysfunction).
How is Peyronie's disease treated in men?
Treatment of pathology is prescribed individually to each patient, after analyzing all the results of the study.
There are several methods of therapy:
- surgery;
- local treatment;
- medicinal;
- shock wave therapy;
- folk remedies.
The first step is to resort to drug treatment. It involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs orally or injecting them into the penis. Additionally, physiotherapy is used. [adsen]
Conservative treatment
It consists of the internal use of oral medications, local injection into the affected areas, physiotherapy and remote shock wave therapy.
The commonly used oral medications are colchicine, procarbazine, vitamin E, pentoxifylline, and potassium aminobenzoate.
Previously, glucocorticoids were used to treat the disease, but they were found to be ineffective and are no longer prescribed.
To administer medications directly into the plaque, the following are used:
- steroid hormones;
- Collagenase (prescribed for penile curvatures of no more than 30°);
- Verapamil is a calcium channel antagonist (effectively reduces plaque area and stiffness).
However, the use of local injections, although much more effective than systemic treatment with medications, carries a hidden threat. After injections, additional injuries to the tunica albuginea may occur, leading to new inflammatory processes, increased plaque or neoplasms.
Physiotherapeutic treatment includes procedures such as:
- magnetic therapy;
- diadynamic currents;
- laser therapy;
- mud therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- shock wave therapy.
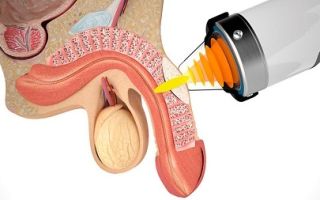
With shock wave therapy, a special device generates a series of pulses, which the specialist directs through a nozzle directly to the plaque. As a result, the seals on the tunica albuginea soften and the penis straightens. This technique is used for penile curvatures of no more than 45°.
Operation
For Peyronie's disease, surgical treatment is more effective, since it allows one to simultaneously correct the curvature and remove compacted nodes. The surgical procedure is determined in each case of Paironi's disease individually.
So, if the curvature of the penis is less than 45 degrees, and its length is sufficient, then plication, when the defect is corrected by applying folds on the opposite side, is most preferable. The tissue is sutured with non-absorbable suture material, the penis loses some length, but the likelihood of complications is minimal. [adsense3]
If the length of the penis is sufficient and the curvature is more than 45 degrees, the tunica albuginea is excised in the form of ellipses, and the side opposite the curvature is sutured with non-absorbable suture material.
If the length of the penis is insufficient or if the patient refuses the above methods, they resort to dissection or excision of the plaque, followed by the use of plastic surgery.
A defect in the tunica albuginea is eliminated using the tunica vaginalis of the testicle, a skin flap, or synthetic materials.
If Peyronie's Disease occurs with erectile dysfunction, then the optimal solution is penile prosthesis or dildo implantation. This allows you to eliminate problems with erection and correct the curvature of the penis.
Treatment with folk remedies
For Peyronie's disease, it is better to adhere to traditional methods of treatment, since traditional medicine may not only not help the patient, but also worsen his condition.
As a rule, traditional healers use local compresses and lotions, which only intensify the processes of inflammation and exudation in the body of the penis. This is accompanied by the progression of Peyronie's disease. Thus, the use of folk remedies during such a disease is unacceptable.
Prevention
Disease prevention measures are designed mainly for men over 35, but young people should also adhere to them, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition.
First, you need to eliminate all risk factors, such as injuries during sex. Choose only comfortable positions and do not make love after drinking alcohol or drugs. Wear comfortable underwear that does not compress the genitals.
Since some systemic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, can provoke Peyronie's disease, they need to be treated promptly.
Source: https://p-87.ru/m/bolezn-pejroni/
Peyronie's disease
Peyronie's disease is a pathology characteristic only of the male half of humanity.
The disease is characterized by pain during erection, which occurs against the background of fibrous changes in the tunica albuginea. The disease is rare, and it is more common in males aged between forty and sixty years.
In some cases, such a disorder can negatively affect conception, but this is only present in cases where the sexual organ is curved to such an extent that it cannot enter the female genitalia.
That is why it is necessary to seek the help of specialists when the first symptoms occur (the presence of a small lump that is easy to detect by touch, pain during sexual intercourse, deformation with each erection).
The basis of treatment is surgery. There is a lot of controversy among specialists about the effectiveness of therapy carried out with folk remedies at home.
What it is?
Peyronie's disease is a disease in which the male penis becomes curved due to progressive fibrous changes in the tunica albuginea of the penis. The disease is named after the French surgeon Francois Peyronie, who described it in 1743. Most often it affects men aged 30 to 60-65 years.
Reasons for development
To date, the causes that lead to the disease have not been fully identified, however, there are etiological factors that contribute to the pathology:
- genital injuries;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- closed fracture of the penis;
- decreased elasticity of the tissues of the genital organ;
- inflammation of connective tissue - collagenosis;
- some abnormalities of the immune system;
- inflammatory process in the urethra;
- taking certain medications;
- metabolic disease;
- narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, characteristic of atherosclerosis;
- increased levels of serotonin in the body;
- connective tissue diseases;
- lack of calcium and vitamin E;
- arterial hypertension;
- bad habits;
- cardiac ischemia.
In extremely rare cases, the disease may be congenital. For example, with a pathology in the structure of the tunica albuginea, or with an abnormally short urethra. The difference between congenital and acquired is that in the first case there are no plaques. The deformity develops against the background of cords in the cavernous bodies.
Minor deformities are not a serious disease and do not require surgical intervention.
Classification
Based on etiology, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Acquired form - characterized by a gradual loss of elasticity and proliferation of connective tissue of the penis, leading to distortion of the shape and the occurrence of pain;
- The congenital form is often caused by a genetic factor and finds its manifestations in the compaction of the cavernous body of the genital organ.
In addition, there are three categories of Peyronie's disease, depending on the degree of curvature of the penis and the size of the fibrous formation:
- Category 1 – penile curvature up to 30 degrees, fibrous plaque size up to 2 cm;
- category 2 – curvature angle from 30 to 60 degrees, fibrous plaque size from 2 to 4 cm;
- Category 3 – the appearance of a strong inclination angle of 60 degrees, the size of the fibrous plaque is from 4 cm.
Associated symptoms
Symptoms of Peyronie's disease (see photo):
- Erectile dysfunction – deterioration of erection (penis does not grow to the required size and does not harden).
- Curvature of the penis. This sign is noticeable visually.
- Pain syndrome. At the moment of erection, the patient experiences pain, which ultimately makes sexual intercourse very painful.
- Functional reduction of the male penis. This is the result of a curvature of the organ.
- Curvature of the penis (towards the abdomen, or scrotum, or to the side).
- Sometimes the skin where the plaque is located may become stretched.
- Increased sensitivity of the penis, observed even during a relaxed state.
- The presence of a plaque that looks like a compaction under the skin of the penis and sometimes reaches a large size - up to 3 cm, which negatively affects local blood circulation.
- Irregular shape of the penis. In some cases, when there are several plaques, the penis takes an irregular shape in the form of a bottle neck, an hourglass, etc.
GLOBAL
Complications
Despite the fact that Peyronie's disease has a simple cure, the consequences relate to both the psychological sphere and the general health of the patient:
- impaired erection due to pain, as well as a number of psychological reasons (emotional stress, sexual dissatisfaction, problems in intimate relationships);
- infertility;
- impotence;
- shortening of the penis;
- psychological disorders.
With timely treatment, these negative consequences, as a rule, are temporary and superficial. The moral support of a partner is of great importance for overcoming negative consequences and successful rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
Fibroplastic induration of the penis (Peyronie's disease) is determined by specialists quite quickly and easily.
Plaques leave no room for doubt, and in principle, it is necessary to determine the form of the disease and the possibility of carrying out therapy or prescribing surgery.
Some doctors ask you to bring a photo of an erect penis to determine how many degrees it bends when aroused. We list what other methods are used in diagnosis:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the penis - to assess how blood circulation occurs in the area of the manifested compaction. This is how the acute form of the disease is revealed;
- MRI diagnostics is a layer-by-layer image of organ tissue. An even more accurate way to assess blood flow;
- Cavernosography - an x-ray after filling the cavernous bodies with radiopaque liquid;
- Biopsy – removal of a microscopic piece of tissue for subsequent laboratory testing;
- Doppler ultrasound is a test similar to ultrasound to assess the condition of blood vessels in the penis.
An appointment for examination can be given by a urologist or andrologist, after a previously collected medical history and palpation of the penis.
Drug treatment
Treatment algorithm for patients with Peyronie's disease, which is at an early stage of development:
- Reducing pain.
- Relieving inflammation.
- Plaque resorption.
- Stopping the progression of the disease.
Treatment should last at least six months.
At this time, medications such as:
- Interferons.
- Vitamin E.
- Drugs from the NSAID group.
- Colchicine.
- Tamoxifen, etc.
Experts do not recommend injecting any drugs directly into the plaque itself. The fact is that even minor damage to the integrity of the genital organ can increase fibrosis. However, sometimes it is not possible to do without injections.
For this purpose, drugs such as:
- Steroids. They are used only if a person has been sick for no more than 1.5 years and his plaque has not completely formed. Hormones are rarely used because they do not achieve the desired effect.
- Enzymes (collagenase). This remedy allows you to soften scar tissue, as it breaks the peptide bonds of collagen. The drug is injected into the plaque perpendicular to the penis. In 65% of cases, it is possible to reduce the curvature. Treatment lasts 6 weeks. Injections are given 2 times every 7 days. The procedure must be performed by a professional, since an overdose of the enzyme is dangerous due to hemorrhages and the appearance of new areas of fibrosis.
- Interferon. To date, there is no precise data on the effectiveness of this drug.
- Verapamil. This drug is injected into calcified plaques and areas of fibrosis during an acute inflammatory process. It helps dissolve such areas.
For oral administration, the following medications are recommended:
- Vitamin E. It slightly reduces the deformation of the organ and helps reduce the intensity of pain.
- Colchicine. The drug prevents the production of collagen and activates its own collagenase, and also helps reduce pain and inflammation. However, during use, many patients begin to suffer from loose stools.
- Tamoxifen. This drug has an antiestrogenic and antitumor effect. Thanks to its intake, T-lymphocytes and macrophages die.
- Potaba. This drug aims to slow down the production of fibrin.
- Pentoxifylline. In a patient receiving this drug, the blood supply to the organ improves, and the content of nitric oxide in the blood increases. This stops the progression of the disease and even promotes its reverse development.
- Propionyl L-carotene. This drug helps reduce the degree of deformation and reduces the intensity of pain.
In addition to the use of medications, a man may be recommended physiotherapeutic effects on the diseased organ:
- Magnetotherapy.
- Use of diadynamic currents.
- Laser treatment.
- Treatment with mud.
- Electrophoresis.
- UVT. In this case, a special device is used, which is a source of impulses. The doctor directs them directly to the area of fibrosis. This allows you to soften the plaque and straighten the penis. To be able to implement UVT, the curvature should not be more than 45 degrees.
It is important to remember that it is prohibited to use any drug yourself! This can cause serious complications and health problems.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is more effective, as it allows one to simultaneously correct the curvature and remove compacted nodes. The surgical procedure is determined in each case of Paironi's disease individually.
So, if the curvature of the penis is less than 45 degrees, and its length is sufficient, then plication, when the defect is corrected by applying folds on the opposite side, is most preferable.
The tissue is sutured with non-absorbable suture material, the penis loses some length, but the likelihood of complications is minimal.
If the length of the penis is sufficient and the curvature is more than 45 degrees, the tunica albuginea is excised in the form of ellipses, and the side opposite the curvature is sutured with non-absorbable suture material.
If the length of the penis is insufficient or if the patient refuses the above methods, they resort to dissection or excision of the plaque, followed by the use of plastic surgery.
A defect in the tunica albuginea is eliminated using the tunica vaginalis of the testicle, a skin flap, or synthetic materials.
If Peyronie's Disease occurs with erectile dysfunction, then the optimal solution is penile prosthesis or dildo implantation. This allows you to eliminate problems with erection and correct the curvature of the penis.
Folk remedies
- Horse chestnut. In order to prepare the decoction, you will need 20 g of chestnuts (fruit). First chop them, and then add a glass of boiling water and immediately put on the fire. Boil for a quarter of an hour. When it cools down, pass through a sieve or cheesecloth and take a quarter glass before meals. Treatment takes three months.
- Herbal infusion. Mix in equal parts (100 g each) primrose, sage, initial cap, oregano, flaxseed and burdock root. Place the mixture in a thermos (2 large spoons) and add a glass of boiling water. Leave to infuse overnight. In the morning, strain and take half a glass four times a day before meals (at least half an hour before).
It is important to prepare new infusions every day so that they are fresh.
- Leech ointment. Measure out a quarter cup of dried leeches and grind them into powder. Mix with heparin ointment (15 g), demixide (2 large spoons) and a glass of white honey. Then rub it into your penis every day (once). Start healing when the moon wanes.
- Therapeutic baths. Pour three packs of sage into a bucket of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for half an hour, then strain. Meanwhile, fill the bathtub with water and pour the strained infusion into it. But don’t get carried away, such procedures can be carried out no more often than once every two days and only for 15 minutes. As soon as you finish the procedure, go to bed.
A greater effect occurs if baths are used simultaneously with decoctions.
Since the disease develops rather slowly, there is a misconception that when the first signs appear, it is best to use traditional medicine in order to avoid medical intervention.
But it is important to remember that only surgery is the only sure way to treat Peyronie’s disease in men.
Prevention
Prevention measures for Peyronie's disease:
- do not have sex while under the influence of drugs or alcohol to avoid injury to the penis;
- between the ages of 30 and 60, undergo annual preventive examinations;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- control body weight;
- monitor the pressure level;
- wear comfortable underwear;
- exercise regularly.
If any disorders of the reproductive system occur, you must immediately contact a urologist to diagnose and begin treatment.
Source: https://doctor-365.net/bolezn-pejroni/
Peyronie's disease: causes, signs, symptoms, treatment
Peyronie's disease is a pathology characteristic only of the male half of humanity. The disease is characterized by pain during erection, which occurs against the background of fibrous changes in the tunica albuginea. The disease is rare, and it is more common in males aged between forty and sixty years.
Online consultation on the disease “Peyronie’s disease”.
Ask a question to the specialists for free: Urologist.
The main cause is considered to be the formation of plaques in the membrane, as well as benign neoplasms on the penis or urethra. Since such a disorder tends to progress, it can reach an extreme degree - the complete impossibility of sexual intercourse.
In some cases, such a disorder can negatively affect conception, but this is only present in cases where the sexual organ is curved to such an extent that it cannot enter the female genitalia.
That is why it is necessary to seek the help of specialists when the first symptoms occur (the presence of a small lump that is easy to detect by touch, pain during sexual intercourse, deformation with each erection). The basis of treatment is surgery.
There is a lot of controversy among specialists about the effectiveness of therapy carried out with folk remedies at home.
Etiology
The causes of Peyronie's disease are not fully understood, but there are a number of etiological factors that contribute to this anomaly:
- a wide range of injuries to the genital organ, for example, during sexual intercourse, from a blow or an accidental fall on a hard surface;
- microtraumas that are invisible to the eye and not accompanied by pain. They often occur during sexual intercourse;
- closed fracture of the penis, in which the integrity of the skin is not violated, but hemorrhage occurs;
- some abnormalities on the part of the immune system, when the body begins to attack itself;
- diabetes;
- taking certain medications;
- the presence of narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which is characteristic of a disease such as atherosclerosis;
- a wide range of connective tissue diseases;
- gout – an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood;
- deficiency of vitamin E and calcium in the body;
- the use of certain drugs aimed at treating impotence;
- increased levels of serotonin in the body;
- the man's age. As the body ages, tissues lose their elasticity and are more susceptible to injury.
Very rarely, such a disease is congenital, for example, with pathologies in the structure of the tunica albuginea or with an abnormally short urethra.
The main difference between a congenital and an acquired disease is the absence of plaques, and the deformation develops against the background of cords in the cavernous bodies.
However, minor deformations are not a serious problem and do not require surgery. Globally, approximately three percent of the male population suffers from congenital Peyronie's disease.
Varieties
Peyronie's disease
According to the degree of deformation, this disease is divided into several types:
- dorsal – the genital organ is directed upward;
- ventral – the penis is tilted down;
- lateral - the penis will “look” to the side.
Depending on the stage of its progression, Peyronie's disease is divided into:
- pain – men complain of severe pain not only during an erection, but also at rest. Only in isolated cases does the manifestation of pain not bother men, and the reason for contacting a doctor is a well-palpable plaque. Often its size does not exceed two centimeters;
- functional - in addition to causing pain, such an illness leads to the inability to lead a normal sexual life.
Symptoms
In addition to painful sensations of varying intensity during sexual intercourse, the symptoms of this disorder are:
- significant curvature in one direction or another;
- decreased erection - during the period of arousal, the sexual organ does not enlarge and does not fully harden;
- the formation of a compacted area under the skin of the organ;
- change in size - the decrease is not associated with a decrease in length, but is caused by the curvature of the penis.
At the initial stage of the disease, a person may not feel any symptoms at all. This phase lasts from six to eighteen months. The earlier the disorder is identified, the more effective conservative therapy will be.
In most cases, it happens that even after expressing the signs, a man is in no hurry to see a doctor, but makes attempts to independently eliminate the discomfort using traditional medicine.
This should not be done under any circumstances, since they will not bring results, but will only aggravate the course of the disease.
Complications
Due to a delay in seeking help from a specialist, every male suffering from Peyronie’s disease may experience the development of the following consequences:
- impotence;
- male infertility;
- prolonged depression;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse and erection. With this disease, this is not only an unpleasant symptom, but also an undesirable complication, often from treatment with folk remedies;
- shortening the size of the genital organ is a complication after surgery.
Diagnostics
When making a final diagnosis of Peyronie's disease, the specialist uses data obtained during:
- collecting thorough information about the time of onset of the first symptoms of the disease and previous illnesses of both the patient and his immediate family. This is done to identify the cause of the expression or confirmation of a hereditary factor;
- patients completing specially designed tests aimed at determining the quality of sexual life;
- direct examination by a urologist of the genital organ in a state of erection. This process will be accelerated if the patient himself brings a photo of the penis in different projections;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the penis - is carried out to assess blood circulation in the area of the seal;
- MRI of the genital organ - this technique makes it possible to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the tissues of this organ. This is the most informative diagnostic method, allowing you to determine the location of the plaque and its volume;
- cavernosography - introducing a special contrast agent into the internal structures of the penis and performing radiography;
- additional consultation with a specialist such as a urologist-andrologist.
After receiving all the research results, the doctor prescribes the most effective way to treat Peyronie's disease. Before choosing a tactic, the patient must be informed that he should not attempt independent therapy with folk remedies.
Treatment
Treatment of Peyronie's disease is carried out individually, depending on the degree of curvature and the manifestation of pain. There are several methods of therapy:
- Surgery is the most effective way to eliminate the disease. The basis is several measures - eliminating the plaque and creating special folds from the membranes of the penis on the opposite side of the lesion, thanks to which it is possible to achieve its alignment. In some situations, penile prosthetics or dildo implantation may be necessary;
- the use of medications is carried out in several cases when it is impossible to carry out medical intervention or in the early stages of the disease. Vitamin E is often prescribed, substances that reduce the likelihood of plaque formation and promote their resorption. But in this case, there is a high probability of relapse of Peyronie's disease. The prescription of medications that reduce the content of fibrinogen, cell division and collagen, anti-inflammatory substances, as well as drugs that reduce the activity of the immune system is also indicated;
- introduction of medicinal substances directly into the places of formation of compactions;
- physiotherapy - electrophoresis and the use of laser radiation.
Since the disease develops rather slowly, there is a misconception that when the first signs appear, it is best to use traditional medicine in order to avoid medical intervention. But it is important to remember that surgery is the only way to treat Peyronie’s disease.
Prevention
Preventive measures for this disorder are the following rules:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- Never make love while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Because the highest probability of injuring the penis is in such conditions;
- rationalization of diet and quality of nutrition. Eat food enriched with vitamins and nutrients;
- strictly monitor blood pressure levels;
- exercise regularly;
- exercise control over body weight;
- undergo preventive examinations in the clinic for diabetes mellitus, as well as for men aged thirty to sixty years.
In addition, it is necessary to promptly contact a urologist if any disorders of the reproductive system occur. Never self-medicate with folk remedies.
Impotence (overlapping symptoms: 2 out of 6)
Impotence (erectile dysfunction) determines the relevance for a man of such violations of his sexual functions in which he is unable to complete sexual intercourse.
Impotence, the symptoms of which indicate an inability to maintain an erection at the level required for sexual intercourse or an inability to achieve ejaculation, or a combination of both conditions, can be characterized by either a complete inability to achieve ejaculation or an erection, or a short duration of maintaining an erection.
... Penile cancer (matching symptoms: 2 of 6)
Penile cancer is a malignant tumor that is localized on the male reproductive organ. This type of cancer causes metastases and can lead to the death of the patient. It is a rare cancer of the genitourinary system, most often found in men over 60 years of age.
... Adenocarcinoma of the uterus (overlapping symptoms: 1 of 6)
Uterine adenocarcinoma is an oncological process that leads to the development of malignant neoplasms in the female reproductive system.
A characteristic feature of this disease is damage to the upper layer of the uterus - the endometrium. A tumor formed from abnormal cellular structures of glandular tissue is asymptomatic in the first stages.
There are no restrictions regarding age. However, women aged 40–60 years are at risk.
... Bacterial vaginitis (overlapping symptoms: 1 of 6)
Bacterial vaginitis (syn. bacterial colpitis) is an inflammatory disease that affects the organs of the female reproductive system, which occupies one of the leading places in gynecology. It is worth noting that pathology often develops during the period of pregnancy.
... Reiter's disease (overlapping symptoms: 1 of 6)
Reiter's disease belongs to the category of diseases of a rheumatic nature. The pathology is characterized by combined damage to the urogenital tract, the membranes of the eyes and joints. Infectious and inflammatory changes can develop both simultaneously and sequentially.
…
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/muzhskie-zabolevaniya/1826-bolezn-peyroni-simptomy