According to the World Health Organization, there are currently more than half a million cases of cervical cancer reported annually. About 250 thousand women die from this disease due to too late diagnosis and ineffective treatment. The human papillomavirus is one of the most dangerous oncogenic viruses that provokes the development of malignant tumors.
What it is?
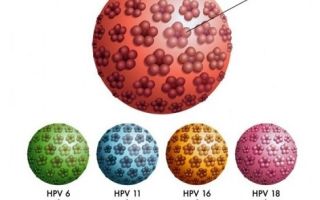
HPV is the name for a unified family of viruses that includes more than 100 different species. All these strains are divided according to the degree of oncogenic risk. About 13 strains lead to various types of cancer. After recovering from the virus, a person can become infected again.
Types of virus
According to statistics, more than half of the Russian population are carriers of different types of the virus, which shows the enormous prevalence of the virus. But this does not mean that HPV becomes a fatal diagnosis for everyone. Many types of papillomavirus do not affect human health in any way and only cause aesthetic defects in the form of papillomas and warts.
There are strains of the virus in which the development of cancer is almost impossible, the so-called low-oncogenic risk HPV. Types of the intermediate oncogenic type are also widespread, and these two categories include most varieties of papillomavirus.
There are significantly fewer types of viruses that provoke the occurrence of malignant tumors. This includes types 31, 33, 6, 11, 16 and 18. The last two pose a greater threat to women.
Today, with the help of numerous studies, a connection has been reliably established between the development of cervical cancer and infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV. In 70% of cases, the appearance of malignant neoplasms is associated with the destructive effects of infection.
Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women.
Already in the first two years after the virus enters the body, 15-30% of women experience changes in the cervical area, and a precancerous condition occurs. During the same time, such changes occur in only 2% of women not infected with HPV.
Types 16 and 18 are dangerous due to the complete absence of external manifestations. Only appropriate tests can indicate the presence of papillomavirus, while the infection itself is asymptomatic. Even with a routine examination by a gynecologist, it is impossible to detect infection with these types of viruses. This manifestation of the virus is called the latent form and without treatment can lead to the development of cancer.
Transfer methods
The most common route of transmission is unprotected sex with HPV carriers . The risk of contracting the virus in the first three years after first sexual intercourse is 46%. That is why those women and girls who can only have one sexual partner are added to groups traditionally at risk, for example, prostitutes. In particular, a high percentage of infections occurs among adolescents. Infection can occur through any type of sexual contact, including anal and oral.
Another method of infection is infection of newborns passing through the birth canal. If the expectant mother is a carrier of HPV, the child has a high chance of catching the virus during natural childbirth.
Subsequently, such children may develop laryngeal papillomatosis, a viral disease characterized by the appearance of papillomas in the larynx.
Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to treat the infection, if present.
HPV type 45 in women
The contact and household route of infection is also known This can occur through small skin wounds through close contact.
For example, when using common hygiene items, visiting the gym or swimming pool. However, this route of transmission cannot lead to infection with a highly oncogenic type of HPV.
But this way it is quite possible to become infected with skin warts.
How does infection occur?
Manifestations of HPV
- Warts. Dense growths with an uneven surface and color from gray to black. Appear after infection with low-oncogenic types of the virus. They do not threaten human life and health, but cause cosmetic problems. They are most often localized in the area of the hands and feet, but can also appear on the surface of the entire skin. There are also plantar warts, which become thicker and rougher when walking. Their characteristic difference is the appearance of blood when the top is cut off.
- Genital warts. They are benign neoplasms located on the skin and genitals. There are growths that are flesh-colored, pink or brown. Their characteristic feature is rapid spread. They can occur in the cervix, but it is also possible that the urethra, rectum and anus are affected. Condylomas cause discomfort in the form of itching and burning. At an early stage, single growths most often appear. At later stages, condylomas show the ability to merge. They do not pose a risk of degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
- Flat condylomas. More dangerous in terms of the development of cancer. The likelihood of cancer increases as new growths appear. This type of condylomas is usually located on the vaginal mucosa.
- Bowenoid papulosis. A viral disease considered precancerous. A characteristic feature is a rash in the genital area. Pigmented papules also appear - smooth brown formations. Papules often appear together with condylomas and warts. The components of the rash can lead to various types of cancer that are dangerous for women.
- Cervical cancer. For every woman, there is a risk that the virus will degenerate into a chronic form, and the precancerous condition may ultimately develop into cancer. If you don't treat the virus, it will just be a matter of time. In women with good immunity, such processes occur within 15 years. For those whose bodies suffer from weakened immunity, for example, HIV-positive women, this will take only 5 years.
Diagnosis of the disease
It often happens that a woman can discover problems in the body after a routine visit to the gynecologist, where a smear is taken from her. To identify the causes of possible diseases, the doctor has to conduct a number of additional studies and tests.
So, the procedure for diagnosing the disease should be as follows:
- An initial external examination by a doctor, during which a smear is taken to determine the state of the vaginal microflora, the level of leukocytes and identify diseases.
- If the test results are unsatisfactory, as indicated by an increased level of leukocytes, the gynecologist prescribes additional tests for STDs, which necessarily include several strains of HPV. In particular, PCR analysis is used to help determine not only the presence of the virus in the body, but also its types. Together with the PRC, a quantitative test is performed to diagnose the level of virus concentration. This indicator, as well as the number of tumors, influence the possibility of oncology.
- When the result shows one or more types of HPV, the woman is scheduled for colposcopy. This is a procedure for examining the cervix using a colposcope, a device designed for multiple magnification. In this way, a detailed examination of the cervix, vagina and vulva is carried out. Using colposcopy, you can assess how much the virus has affected the condition of the cervix, identify lesions, and view the presence of precancerous changes and genital warts. Typically, the gynecologist performs an extended colposcopy using chemicals to identify atypical lesions.
- When HPV is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed according to the type of virus and its manifestations.
Causes of papillomas on the human body
Treatment of papillomavirus
Another direction is aimed at eliminating the consequences of infection: removing existing papillomas and condylomas. There are several ways to do this:
- Surgical intervention. It is an operation to cut off tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantages of this method are not only possible consequences in the form of scars, but also the risk of blood loss. In addition, this method does not guarantee the removal of all papillomavirus cells.
- Electrocoagulation. The most common method of removing papillomas and warts due to its low cost and availability. It is carried out using high-frequency current, which acts specifically on the growths. Like the previous method, it leaves marks on the body from removed papillomas. It also does not guarantee the absence of relapses.
- Laser destruction. One of the most modern methods of removing papillomas. For this, a laser beam is used, which completely removes papilloma cells, affecting atypical tissues. This method is considered the most reliable and safe. It does not leave undesirable consequences in the form of scars and immediately seals the vessels to prevent bleeding.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is carried out using liquid nitrogen, which is applied to a special applicator. Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, the growth gradually disappears. However, with this method it is possible to get burns, which will ultimately result in an unwanted scar. This is due to the deep effect of the substance on the skin.
HPV prevention
Prevention of this disease comes down to a few simple rules:
- Using condoms as a means of contraception during sexual intercourse. This point is especially important, since sexual transmission of infection is the most common.
- Examination by a gynecologist. Women need to be examined by a doctor and have a smear every six months to know about the condition of their body.
- Maintaining immunity. It is the immune system that gives the main resistance to papillomavirus, and good immunity can suppress its manifestations even before the infection develops.
About what oncogenic HPV is in women and what it can lead to, watch our video:
Source: https://papillomus.ru/virus-vpch/vpch-vysokogo-onkogennogo-riska-u-zhenshhin/
General information about type 35 human papillomavirus in women
There are 150 types of pathogenic HPVs. Some of them are potentially dangerous, while others do not pose serious problems. But doctors assure that absolutely all papillomas can be removed.
One of the terrible types of infection is HPV type 35 in women; not all patients know what it is and how to diagnose it correctly. Pathology in 97% of cases leads to precancerous changes and cervical cancer.
The latter disease is considered the second most common malignant tumor among women. 230,000 people die each year and the number of new cases is estimated at 470,000.
Each type of virus is dangerous in its own way, but some are especially
Methods of infection
Genital warts are usually found on the genitals, although they can be found in the mouth or near the anus. Their formation in women is the result of a secondary infection that occurs due to damage around the vulva. The condyle at the anus is formed after anal intercourse.
Although genital warts are mainly diagnosed in sexually active people, the formations also develop in prepubescent children. The cause of infection is the infected mother.
Another source of infection may be sick family members. For example, dad is infected with HPV 35: in men, growths form on the head or scrotum of the genital organ, as well as in the anus.
The infection occurs as a result of non-compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene and infection of children. Particularly dangerous are frequent changes of sexual partners or acts with several at once. Thus, patients who engage in anal intercourse suffer from pathologies.
The situation is aggravated by the lack of contraception, although it cannot guarantee accurate protection.
HPV type 35 DNA appears in the baby's genital area already at birth in case of infection from the mother.
Infection occurs when hygiene rules are not followed
The transmission mechanism itself has not been fully studied, but the normal HPV level is up to 3 Lg. Sometimes one of the sexual partners is not infected with the virus. Therefore, pathology can be transmitted so imperceptibly that a person does not realize there is a problem for years.
The incubation period takes only a few weeks, but in the absence of favorable conditions it extends to 8-10 years.
Details about the features
A characteristic feature of HPV is the absence of symptoms in the latent phase. Until visible damage appears, the disease does not show symptoms, although it is transmitted to a sexual partner.
Purulent discharge and itching are also characteristic of other diseases, but with HPV 35 they appear only in the presence of obvious, visible warts or precancerous changes. Coexisting infections enhance the changes.
Main risks
The first phase of papillomavirus type 35 in women is the period from infection to the first manifestations. Pathogens are detected only by virological tests. At this stage, both cytology and colposcopy are unchanged.
The risks of negative consequences are higher for people who are promiscuous
The dormant form lasts for several months or years. The last evolutionary phase of HPV infection is considered to be the clinical stage, during which the appearance of benign proliferative lesions is observed. Usually these are condylomas, cervical or vaginal formations of the cervix. Feedback from patients about the condition is the same: the symptoms exist, they cause a lot of discomfort.
For HPV type 35 to cause cancer, many concomitant factors are required: decreased cellular immunity, smoking, lack of beneficial microelements, pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives.
Patients who are sexually active early and have contact with multiple partners have a high risk of developing sexually transmitted diseases: HIV, herpes, chlamydia. All of them, together with nonspecific inflammation, are independent factors favoring CIN and cancer processes.
The HPV virus is not a threat to fetal development
Condylomata acuminata in women looks like soft growths located on the labia and perineum. They can affect the vaginal epithelium, urethra, anus and cervix. It happens that small discolorations combine with each other to create multiple lesions. This is a rare disease of the genital mucosa caused by the human papillomavirus.
The precancerous condition is explained by the risk of the rod passing into squamous cell carcinoma or the vulva. Skin changes have flat spots, several millimeters in diameter. They are pink or slightly brown in color and have a smooth surface, sometimes prone to sticking together.
In men, the lesion is mainly located on the heads, and in women on the labia, inguinal folds and anal area. In some cases, the changes disappear spontaneously, while in other patients the pathology is characterized by a complex and long-term course. In women, dysplastic lesions are found in 75%.
Bowen disease and the HPV virus are diagnosed together. In this case, the tumor is located only under the basement membrane of the epidermis. But the lack of treatment leads to deeper damage, and sometimes the pathology metastasizes to the lymph nodes or bones. In women, these areas are flat, red or dark brown, distinct and itchy.
The worst thing is the degeneration of cells into cancerous ones.
Bowen disease is mainly diagnosed in women over 60 years of age. In older patients, it is recommended to completely excise the vulva.
In younger people with smaller areas of infected skin or mucous membranes, 5-fluorouracil cream or cryotherapy is used. In case of failure, surgical treatment is used.
In men, small changes are treated with freezing or with 5-fluorouricyl cream. Large areas are removed surgically or with a laser.
Kairat erythroplasia is a squamous cell carcinoma resembling Bowen's disease. Rarely found on the vulva in women. In most cases, the pathological condition is caused by HPV.
Vulvar cancer is a rare problem. According to indicators, it accounts for 3 to 5% of all malignant tumors of the genital organs in women. Vaginal cancers often occur in scars and on skin irritated by long-term inflammation. Pathology also develops through infection with the human papillomavirus.
Vulvar cancer is located on the labia majora, in close proximity to the clitoris, vestibule of the vagina and perineal skin around the urethra.
One of the common symptoms is itching, which requires differentiation from other diseases that cause the same symptom in this area.
The diagnosis of vulvar cancer in its extended form usually does not give reason to doubt the correctness of the diagnosis.
HPV-35 is most often mentioned in the context of oncology of female organs. And this is correct, because almost 100% of cases of such a disease are regenerated by the virus. This fact is confirmed by the results of genetic testing of HPV DNA in women affected by severe disease.
Timely diagnosis of the problem will protect you from cancer
Clinical manifestations
HPV has about 200 serotypes, some of which have outstanding oncogenic potential, so infection can lead to the development of cancer. Among the population aged 19-45 years, about 80% have had contact with any type of virus. What allows it to spread is the often asymptomatic nature of the infection.
HPV type 35 in women manifests itself in the form of single or confluent formations. After a few weeks or months, condylomata acuminata appears. It increases in size and in extreme cases causes pain during intercourse or prevents urination.
Any changes to genital warts should be removed. Usually the procedure is performed using a laser or cryotherapy, because the formations are contagious and potentially dangerous for the patient’s other half.
The most serious consequences are oncogenic types of HPV, especially 16, 18, 31, 35 and 44. Most often, pathologies are asymptomatic. Infection with a viral genotype is not synonymous with cancer, but significantly increases the risk. A concomitant disease provokes the development of oncology.
Be alert to any signs of HPV
The following conditions are considered important irritating factors:
- onset of sexual activity at an early age;
- frequent change of partners without using condoms;
- oral hormonal contraception, multiple births;
- smoking.
Diagnostic measures
Long-term stay in the body and active development of HPV-35 leads to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in women of varying severity and pancreatic cancer.
According to the results of most epidemiological studies, the most common type of infection in patients with cancer is HPV type 35. One of the methods for reducing cancer mortality is early detection (screening) and regularly repeated PAP tests, which make it possible to determine the initial changes in stage before the formation of invasive cancer.
However, a condition for success is the widespread and regular encouragement of women to conduct research. A valuable additional method is considered to be the prevention of chronicity of the virus through protective vaccinations, which will lead to a reduction in the incidence of cervical cancer.
Regular examinations will allow you to timely identify the problem and avoid negative consequences.
Treatment Options
In early periods, when symptoms are not typical, caution is recommended. Therefore, if the patient notices the following signs, you should definitely consult a doctor:
- 1 or more nodules located near the vulva;
- itching;
- bleeding.
HPV-35 infection quickly forms metastases to surrounding lymph nodes. That's why it's so important to consult your doctor about any warning signs in the genital area.
Changes caused by exposure to the HPV virus often go into remission. If the lesion does not resolve after treatment, surgery should be performed. In the case of highly dispersed dysplastic formations, the main surgical procedure is cervical conization. The uterus is excised only if there are other instructions for performing manipulations, except for highly dispersed dysplastic lesions.
For women who wish to have children, doctors perform surgical procedures that allow them to preserve the uterus and the possibility of procreation. Topical chemical solutions are used to remove genital warts.
The effectiveness of this type of medicine varies, and relapses are common. Another method of treating condyloma is cryostimulation or laser evaporation of lesions, which gives a positive result and allows the patient to be cured forever.
The growths are often removed mechanically
Preventive measures
Although the risk of HPV infection cannot be eliminated, it can be reduced. The process of avoiding casual sexual contact remains an important principle. Of course, using condoms reduces the risk of HPV infection, but does not provide 100% protection. It is important to educate young people not to become sexually active too early.
Prevention requires a healthy diet, adherence to a therapeutic diet containing large amounts of vitamins and quitting smoking. In addition, remember about regular colposcopy and cytological tests. Vaccines are available for some types of HPV, although their effectiveness is still uncertain, so they are not used instead of these methods.
Vaccines against papillomavirus contain virus-like particles produced by genetic recombination. Doctors have 3 medicinal liquids for injection: 2-valent (4 and 9).
All of them protect against the most oncogenic types of viruses 16, 18, 35. The drugs are used as protection against precancerous pathologies, as well as against genital warts.
According to statistics, over the course of 10 years, patients who received preventive vaccination against HPV noted a 90% decrease in infection with types 6, 11, 16, 18 and 35, as well as a 90% decrease in the incidence of genital warts.
In addition, the incidence of high-grade cervical pathologies decreased by 85%.
You can protect yourself with vaccination
HPV vaccines are safe and well tolerated. More than 270 million doses of the substance have been administered. There are several side effects:
- pain at the injection site;
- redness;
- itching;
- edema;
- fatigue;
- headache and muscle pain.
Vaccination is not carried out for children under 9 years of age, for pregnant women, or for patients who are allergic to any substance in the medication. There are no studies on the use of the vaccine in immunocompromised people.
Preventive actions boil down to giving up risky sexual behavior and eliminating more associated factors. An HPV DNA test is also recommended. It is necessary to work with the younger generation, because they need to be taught the rules of intimacy and safety during sex. You will also have to give up frequent changes of partner and anal contact.
The steps to take when detecting HPV will be discussed in the video:
Source: http://bolezni.com/stati-o-boleznyah/papilloma/vpch-tridcat-pjatogo-tipa.html
Papillomavirus type 35: features, danger and treatment methods
Home-HPV
HPV type 35 is one of the strains that belongs to the oncogenic risk category. The human papillomavirus provokes the development of benign growths on the surface of the skin.
What is HPV type 35 and its features
There are about 170 types of human papillomavirus, the 16th strain is most often identified.
Manifestations of HPV are typical for all types; only a specialist doctor (dermatologist, dermato-oncologist, gynecologist, urologist, oncologist) can determine the danger of a malignant process and the level.
A type of papillomavirus, strain hpv 35, provokes the development of condylomas, genital warts, which have a high level of oncogenicity.
It is found in cancer of the cervix and labia, cancer of the penis, malignant tumors of the vagina and anal area.
When it enters the body, papillomavirus type 35 provokes the growth of cells in the epidermal layer of the skin.
When diagnosing oncological processes of the reproductive organs in women and men, in 60% of cases exactly type 35 is detected. The development of easily traumatic polyps on the mucous membranes of the anogenital area is often provoked. Such growths bleed, form long-term non-healing wounds, and stimulate the aggression of cancer cells inside the body.
A prerequisite for the development of lesions from HPV is a weakened immune system of the body.
How dangerous is the type for men and women?
Under the influence of the formation of papillomas of the HPV 35 genotype, men and women may experience various characteristic manifestations, complications of the reproductive sphere, damage to the external skin, internal organs:
| In men | Among women |
| In men, the HPV 35 strain increases the risk of developing a complication of papillomatous growths - bowenoid papulosis. The disease affects the entire anogenital area, the normal process of urination is disrupted, libido decreases up to impotence, neuroses and psychological discomfort appear (depression, stress, psychosomatic disorders). | In women, the formation of giant papillomas of the genital area is often provoked, which, when fused, form characteristic warts in the form of a cauliflower inflorescence, a bunch of broccoli, or a chicken scallop. The formations are easily injured during sexual intercourse and grow quickly. |
| Infection in men can spread to the mucous membrane of the urethra. The danger of the appearance of filamentous papillomas in the urethra is the risk of provoking urethritis, cystitis, and prostatitis if the infection spreads. Therapy requires surgical intervention with the complex effect of immunostimulating agents. | A secondary infection often occurs, which causes foul-smelling vaginal discharge. |
| With the development of pathology in men, more often than in women, the intestines are retracted: the process of defecation is disrupted, papillomas appear in the anus, on the rectal mucosa. Due to constant traumatization by feces, malignancy is virtually inevitable. | The female population is prone to developing oral condylomas when infected with HPV 35 (loose mucous membrane, oral types of sexual contact). Oral papillomas are injured when chewing food or brushing teeth. |
Causes and symptoms of HPV 35
The main etiological factors of occurrence, triggers of the disease:
- Transmission of HPV from a sexual partner in the presence of warts on the skin of the anogenital area in a carrier partner and microtraumas on the mucous membranes and skin in a healthy partner, even during protected sexual intercourse.
- Skin injuries in adults and children during everyday contact with a carrier of the disease. There may be sharing of towels, razors, bed or underwear, visiting public bathing places (baths, showers, swimming pool).
- Transmission of HPV when a child passes through the birth canal from a carrier mother, during breastfeeding. The first signs of the development of papillomatosis appear by the age of 1-2 years of the baby’s life.
There are a number of factors in the presence of which HPV is activated and the body’s immune defense is suppressed:
- hormonal disruptions (puberty, pregnancy, lactation, menopause, taking oral contraceptives, treatment with corticosteroid drugs, pathological disorders of the endocrine glands);
- infectious diseases of a protracted nature with massive antibiotic therapy (pneumonia, bronchitis, influenza), autoimmune pathologies (scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout) with the use of hormonal drugs to suppress the symptoms of the disease;
- smoking, drug addiction and alcohol abuse;
- having promiscuous sex life;
- frequent exposure to stress, depressive disorders;
- lack of normal nutrition, vitamin deficiency, exhaustion of the body.
The clinical picture of the consequences of activation of the HPV 35 strain in the body includes the following symptoms:
- development of warts in children and adults. They can have different localizations (face, neck, torso, limbs, intimate area), be from light pink to black in color, differ in a convex shape or voluminous growths in the anogenital area;
- genital warts are typical for adults and older people and develop on the genitals. They can be punctate or, when several cutaneous elements merge, they form into a pedunculated condyloma fungoides;
- flat condylomas rarely develop when type 35 is activated. The danger of such formations is that the roots grow into the deep dermal layers; this type of papillomas is oncogenic.
Common manifestations of papillomatosis, regardless of location, include: itching when rubbing with clothing, pain, swelling, hyperthermia of surrounding tissues during the growth of papillomas.
Methods for diagnosing the virus
The diagnostic complex consists of a number of studies and tests to determine the HPV 35 strain. The examination regimen is prescribed by the doctor after examining the skin lesion:
- genotyping of the virus with determination of DNA identity using polymerase chain reaction (taking biomaterial from the papilloma for analysis);
- a general blood test to determine disorders in the body (anemia, bacterial or viral infection, the presence of inflammatory reactions, the norm of leukocytes, lymphocytes is determined to determine the functioning of the immune system);
- examination of the genital organs, mucous membranes of the mouth (frequent localization) and the skin of the body;
- cytological scraping from the cervix, smear from the urethral canal;
- positive digest test;
- histological examination of papilloma biopsy to identify cancer cells.
Treatment methods for HPV type 35
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
If HPV strain 35 is detected, treatment should include complex treatment with antiviral drugs and surgical removal of external manifestations using hardware techniques. Elimination with folk remedies or cauterization with pharmaceutical preparations (supercelandine, condiline, verrucacid) is unacceptable due to the high risk of injury to the formation.
Taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs helps the body cope with the aggression of strain 35 and prevent relapses.
Oral administration and intravenous administration of drugs are used: interferon, viferon, genaferon, proteflazid, immunoflazid.
Removal of condylomas using surgical intervention includes the following techniques:
- surgical excision of growths and affected tissues, used for large papillomas, combined with antiviral medications;
- laser coagulation allows you to quickly and painlessly eliminate all condylomas; inconvenience is caused by hard-to-reach condylomas on the genitals and the risk of burns to the genital mucosa;
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen (freezing apparatus) allows you to get rid of warts most effectively in several sessions, even with deep localization;
- radiosurgical method with the creation of a radioactive field for the destruction of papilloma. A new, effective method for removing formations.
The selection of an elimination method and further therapy to suppress the activity of HPV 35 in the body is prescribed by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Life prognosis and prevention of degeneration
There is no specific prevention for strain 35. To prevent infection and prevent the activation of the virus, you must follow the following rules:
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, do not use public items;
- support the body's defenses;
- carry out sanitation of chronic foci of infection;
- undergo preventive examinations with a therapist once a year.
With timely diagnosis and the appointment of an adequate treatment regimen, the prognosis is favorable, cure occurs in most cases. With the development of an oncogenic process, degeneration into a malignant formation, treatment is carried out by an oncologist with chemotherapy drugs that suppress the body’s immune forces.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Link to main publication
Didn't find suitable advice?
Ask your doctor a question or see all questions...
Article rating:
(1
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/hpv/35-tipa
11 types of papillomavirus (HPV) of high oncogenic risk - list
The human papillomavirus is classified as one of the most common infectious pathologies.
According to statistics, more than 70% of the average population of the planet are carriers of various HPV genotypes. Most of them do not pose a health hazard and can remain latent in the body throughout life.
But there are also dangerous strains of pathogenic microorganisms classified as high oncogenic risk HPV.
Infection with viruses of this type without proper timely treatment can lead to the occurrence of malignant tumors, the appearance of a massive number of condylomas and warts. How to prevent infection and identify a dangerous virus in a timely manner? Let's talk about this further.
What is HPV
The term “HPV” is used to define a broad group of viruses, which includes pathogens that cause the formation of growths and warts on the skin and mucous membranes. About thirteen genotypes of this family are viruses of high oncogenic risk.
What does it mean? Infection of the body with the given strains of pathogenic flora can cause the transformation of condylomas on the genital organs and skin growths into malignant tumors, that is, lead to the development of oncological diseases.
Symptoms of HPV of high oncogenic risk may not appear immediately, but after a long period of time after infection.
In some cases, the incubation stage can take about ten years. This is due to the fact that active reproduction of viral microorganisms occurs more often against the background of a decrease in immune strength or the development of chronic diseases in an infected person.
Types
Despite the fact that the incidence rate of the population with various types of HPV is incredibly high, only certain types of viruses can lead to the degeneration of epithelial cells and the development of cancerous tumors. For example, strains 11, 6, 13, 18, 39 are classified as low oncogenic risk HPV group. If diagnosed and treated quickly, the likelihood of developing cancer is minimal.
It should be noted that these strains lead to the appearance of genital warts on the mucous tissues and skin of the genital organs, which can grow and enlarge. In the absence of therapy, there is a high risk of condylomas transforming into an oncological tumor or the appearance of malignant papillomas.
The most dangerous are oncogenic types of HPV - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 51,56, 59,66, 68. Infection with these genotypes of viruses can lead to the development of a number of oncological diseases, the most common of which are: cervical cancer , the occurrence of malignant neoplasms affecting the mucous membranes of the genital organs and large intestine.
Video
High oncogenic risk papillomavirus
Oncogenic classification
In the field of practical medicine, the types of human papillomaviruses are divided into three groups, each of which includes pathogenic microorganisms that, to one degree or another, influence the possibility of the formation of malignant tumors. There are three groups in total, oncogenic HPV is included in the second and third.
First group
The first group does not include oncogenic type HPV; this category combines strains from 1 to 5, infection of the body with which threatens the appearance of growths and papillomas, but does not lead to an increased risk of malignant tumors.
Second
The second group also does not include highly oncogenic types of HPV; this category includes viruses whose infection can cause the development of cancer only in the presence of favorable circumstances, including reduced immunity and chronic diseases. The second group includes HPV strains 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
Third
The third group combines genotypes of viruses with high oncogenic activity: 16, 18, 33, 31, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 59, 68. The presence of the above strains of pathogenic microorganisms in the human body can lead to the appearance of genital warts, and also the development of cancer of the bladder, uterus, and colon.
It should be noted that the growth of malignant tumors can be caused not only by the presence of a virus in the body, but also by combined factors, for example, chronic diseases, low resistance of the body, and others.
Why are types 16 and 18 dangerous?
The most dangerous types of HPV are strains numbered 16 and 18. The presence of these types of viral microorganisms in the body in seven out of ten cases leads to the development of cervical cancer in representatives of the fair half of humanity. For men, this type of HPV is also dangerous and can cause cancer of the bladder or colon.
The considerable danger of high-carcinogenic risk HPV 16 and 18 also lies in the absence of clinical manifestations characteristic of most strains.
It is impossible to determine infection even with standard medical diagnostic procedures and tests.
To identify the above types of HPV, the use of highly targeted research methods, carried out only in a laboratory setting, is required.
Diagnostics
For timely detection of the virus, it is recommended to diagnose the disease at least once every three years. Informative and reliable methods for identifying oncogenic type HPV are:
- Polymerase chain reaction. One of the most reliable methods by which not only the presence of pathogenic flora is determined, but also the strain of the virus.
- Daijin test. One of the innovative and expensive diagnostic methods, which is currently used only in large medical centers. It is the most informative, allows you to determine the number of viral microorganisms in the blood, strain, oncogenic risks.
- Dad - test. It is also a fairly reliable method for detecting oncogenic HPV, used primarily for diagnosing infectious diseases in women.
- ELISA. This method allows you to determine the level of viral load on the body, strain and oncogenic risks of infection. In addition, the method is one of the few on the basis of which it is possible to create a complete picture of the disease and determine the duration of infection, that is, the presence of HPV in the body.
Often, for additional diagnostics, the genotyping method is used, which makes it possible to determine the identity of the pathogenic flora. More often, this method is relevant if there is a suspicion of oncogenic type HPV infection.
Treatment of high oncogenic risk HPV
Unfortunately, there is no universal and effective antiviral medicine, the use of which would get rid of the virus, in modern medicine.
Treatment methods for HPV of high oncogenic risk are based on an integrated approach and include the use of local agents, oral medications, and, if necessary, invasive methods aimed at removing existing tumors.
As a rule, standard treatment regimens for oncogenic HPV include the use of the following drugs and methods:
- When a large number of neoplasms appear on the skin and mucous tissues, destructive treatment of papillomas is carried out, that is, removal of the growths. According to the number and size of tumors, the following methods can be used: cryodestruction or treatment with liquid nitrogen, laser therapy, electrocoagulation, radio wave therapy, surgical removal.
- In the presence of small growths, it is permissible to use conservative methods, which involve the use of antiviral creams and ointments. The following are most effective: Condilin, Solcoderm, Acyclovir, Panavir, and regular oxolinic ointment.
- Therapy aimed at increasing local immunity is mandatory, including the use of the following drugs intended for oral administration: Immunomax, Allokin - Alpha.
Important! When oncogenic HPV is detected, it is strictly not recommended to use a variety of folk remedies for treatment.
Using home remedies may backfire and spread the infection.
You should know that infection with an oncogenic papilloma virus is not a death sentence.
The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood leads to the development of cancer only under favorable conditions, including reduced immunity and lack of therapy.
Conducting timely treatment, agreed with a specialist, will reduce the risk of malignant tumors to a minimum.
Source: https://papilom-net.ru/vpch/vpch-vysokogo-onkogennogo-riska
Signs of HPV type 35 in women: what kind of virus it is and how to treat it
For many years, the human papillomavirus has remained one of the sexually transmitted diseases that cannot be completely cured - the virus does not die from exposure to antibacterial drugs.
In addition, diagnosing this disease is very difficult - there are practically no symptoms, and general tests do not detect the microorganism. The main danger of this is that the lack of proper treatment can lead to the development of cervical cancer, as well as infertility.
Is it possible to avoid infection, how do doctors identify pathology, and is it possible to reduce the risk of complications?
Peculiarities
The virus spreads very quickly, there are many ways of infection. According to WHO statistics, about 60% of the world's population is infected with this disease. Moreover, this figure is growing every year.
The reason for this is that people are increasingly engaging in unprotected sexual contacts with untrusted partners.
Since the main route of transmission of infection is sexual, the disease is easily transmitted from one person to another, as a result of which more and more carriers appear.
There are other ways of transmitting HPV type 35:
- household - due to the use of someone else's bedding or underwear;
- social - as a result of visiting places such as swimming pools, public restrooms, solariums;
- generic - the virus is transmitted during the birth of a child from the mother.
In addition, there is a risk of self-infection, for example, if a person transfers microorganisms from dirty hands to his genitals.
HPV 35 penetrates into cells, quickly multiplying there and parasitizing. At the same time, it changes the DNA structure of the affected cells. It is this circumstance that contributes to the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
At risk are those people who suffer from immune problems: smokers, alcoholics, patients leading a sedentary lifestyle. The likelihood of the disease also increases if there is no proper treatment for other infectious pathologies.
Symptoms
The subtlety is that HPV of any type practically does not manifest itself in the form of symptoms. This complicates diagnosis, because the disease can only be detected through tests done in a clinical setting. However, there are pharmacy tests for HPV, but their accuracy is minimal. This leads to the fact that collecting anamnesis during a visit to the doctor practically does not bring any results.
The only symptom that almost always appears is genital warts. But they are not always located on the surface of the body; in most cases, their location is in the internal genital organs, for example, the walls of the vagina.
And there is little sense in visually studying them, because it is impossible to identify the exact strain based on this characteristic, and the treatment strategy depends on this.
Human papillomavirus type 16 is one of the most dangerous strains. According to some statistics, it affects 60 to 70% of women around the world. You can learn about symptoms that are very difficult to notice, as well as how to treat this disease.
In women, HPV 35 is expressed by the following symptoms:
- painful sensations are felt in the lower abdomen, and sometimes in the lower back;
- urination is accompanied by pain;
- sexual intercourse brings more discomfort than pleasure;
- sexual desire is lost;
- urine contains bloody impurities;
- unusual purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor appears.
In advanced stages of the disease, constant weakness and drowsiness occur. Sometimes they are accompanied by nausea and dizziness. This occurs due to inflammatory processes during the degeneration of neoplasms into malignant ones.
Men experience other signs of HPV 35:
- condylomas on the head of the penis;
- purulent discharge from the urinary tract;
- pain when urinating;
- weak potency.
Since this virus poses much less danger to men than to women, other symptoms occur very rarely.
Condylomas can occur not only in the genital area, but also in the anus. This usually causes great discomfort.
Diagnostics
Despite the “sluggish” symptoms, detecting the virus in a person is quite simple. There are a number of tests that can not only detect the causative agent of the disease, but also determine its DNA, which is necessary to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics, and also find out how dangerous the disease is in each specific case:
- PCR diagnostics. This method allows you to determine the extent of infection in the body. The accuracy of the method is quite high, but errors are common - it is not always possible to determine the exact strain of HPV.
- Sowing. The biomaterial taken from the patient is “grown” in an artificial nutrient medium. The method requires a decent amount of time, but its accuracy is close to 100%. In addition, culture can accurately determine the type of virus and assess its sensitivity to drugs.
- Visual gynecological examination. Allows you to detect the presence of condylomas on the genital organs. The accuracy is minimal - this examination does not determine the type of HPV; it is impossible to prescribe treatment based on the results of this examination.
- Biopsy. It is prescribed rarely and only if it is necessary to establish the nature of the neoplasm. This is done in the last stages of illness, when the occurrence of cancer becomes quite real.
A complete blood test can theoretically detect HPV 35, although this happens extremely rarely. As a rule, it reveals only concomitant inflammatory processes that accompany the disease in question.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely remove the virus from the body; you can only weaken it by stopping the development of the disease. Therapy must be comprehensive, otherwise there will be no result. Treatment includes:
- Taking antibiotics. Doctors usually prescribe Panavir, Epigen and Isoprinosine.
- Strengthening the immune system. A very important component, since the body’s own defenses fight the virus more effectively than any antibiotics. For this, drugs such as Immunal, Reaferon, Polyoxidonium are suitable. Please note that these products also work as antiviral drugs.
- Removal of condylomas and papillomas. This must be done, but only in a clinical setting. Both the classic surgical method and more “advanced” methods are used, for example, cryodestruction, chemotherapy, electrocoagulation.
The use of folk remedies is allowed only to increase the level of immune protection. They cannot stop the development of the disease, much less remove the virus from the body.
Consequences and danger
HPV 35 is an oncogenic virus. It promotes the development of cancer. While men are relatively safe, women are at great risk. Without treatment, the emergence of malignant tumors is a matter of time.
This happens due to the fact that microorganisms change the DNA structure of the affected cells, “forcing” them to actively reproduce.
As a rule, the process of developing a cancerous tumor takes at least 5 years from the moment of infection, and then in the complete absence of any therapy.
In addition, HPV 35 causes:
- infertility;
- impotence;
- weakening of sexual treatment.
This can all be treated, but it is much easier to prevent the development of HPV than to deal with complications. To do this, it is enough to follow the rules of personal hygiene and avoid casual sex.
By watching this video, you can learn about the papilloma virus, as well as its manifestations, what treatment methods are available and how you can protect yourself from this disease.
Source: https://myvenerolog.com/spisok-boleznej/virusnye-infektsii/papillomavirus-cheloveka-vpch/vpch-35-tipa-u-zhenshhin-chto-eto.html