When they talk about STDs, they talk about sexually transmitted diseases.
This means that they are already associated with sex, and the main way of their spread is sexual.
- Sexual contacts with persons with STDs are extremely undesirable.
- After all, even protected sexual contacts do not provide a one hundred percent guarantee (for various reasons) against infection.
- If a person has an STD, then, for health reasons, sex is contraindicated for him, even if he does not infect anyone.
- All the body's strength must be spent fighting infectious agents.
- Sex during an STD is unnecessary emotional and physical stress.
STDs during oral sex
- You can also get an STI during oral sex.
- On the contrary, it is believed that oral sex is very dangerous in terms of the possibility of infection.
- He is not always protected.
- In addition, in the oral cavity there are very often microtraumas, which means the gates for infectious agents are always open.
- Although barrier methods are used to protect against infection - condoms for blowjobs and a latex napkin for cunnilingus.
- Most often, oral sex causes infection with syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, genital herpes, HPV, mycoplasmosis and hepatitis B.
- You can also become infected with HIV.
- It is necessary to avoid any sexual contact, including oral, if the sexual partner experiences rashes, abscesses and ulcers on the genitals of the sexual partner.
- Oral sex is dangerous for laryngeal cancer.
STDs during anal sex
- During anal sex you can also become infected, for example, with HIV infection.
- The rectum has many microtraumatic injuries.
- Anal sex risks chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, hepatitis A, B and C, and syphilis.
- The means of protection against infection are condoms, which are coated with a special lubricant.
- There is no special lubricant inside the rectum, like in the vagina, so it is injured more often.
- That's why there are so many STDs among homosexual men who engage in anal sex.
- In terms of contagiousness, the least of the troubles come from kissing, although they also lead to herpes.
- It must be remembered that both anal and oral sex are quite dangerous due to the spread of STDs and it is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible.
Does a condom protect against STDs?
The degree of protection a condom provides against STDs is not ideal and ranges from ninety-two to ninety-five percent.
- The most common reasons for the ineffectiveness of condoms are their violation of integrity and the end of the warranty period for use.
- But hepatitis B and C, herpes and the human papillomavirus (HPV) can also be contracted through the porous holes in the rubber of a condom.
- The highly contagious form of syphilis can also be obtained by rubbing bodies against each other.
- Nowadays, women use oil-containing substances for intimate hygiene.
- And they increase the permeability of condoms for various infectious agents.
- Therefore, the best prevention of STDs is to have a permanent healthy sexual partner.
Which STDs are sex with a condom contagious?
In addition to the listed STDs, the condom does not protect well against tropical STDs (donovanosis, chancroid and lymphogranuloma venereum), scabies, lice pubis and molluscum contagiosum.
A condom, moreover, may be of poor quality and break during sexual intercourse, thereby making protected sexual intercourse unprotected.
When is sex possible after STD treatment?
To prevent re-infection to partners, during positive tests for STIs, you should not enter into intimate relationships.
When the test results are negative, sexual life can be resumed in two weeks.
The main thing is to reliably cure STDs so that sex with a partner brings only joy and confidence.
Preventing STDs after sex
To prevent STDs, certain rules must be strictly followed:
- maintain intimate hygiene
- contraception
- apply bactericidal agents topically
- regularly visit gynecologists or urologists, depending on gender
- timely and qualified treatment of identified diseases
- abstain from promiscuity
- vaccinate against HPV and hepatitis B
- To prevent STDs, it is necessary to use condoms, spermicides and antiseptics.
- Emergency preventive measures include taking certain antibiotics in a pronounced dosage.
- They are treated prophylactically, for example, with Safocid tablets.
Preventive treatment after sex with a partner with an STD
If you had sex with a partner who may have an STD, then preventative treatment is necessary.
- The regimens for such treatment correspond to the treatment regimens for uncomplicated acute STDs.
- Preventive treatment does not replace the use of a condom.
- Such treatment is often not carried out and is only applicable in emergency cases.
How to find out during sex whether your partner has an STD or not?
- Very often, STDs are asymptomatic, so no one can say for sure that a person does not have an STI in the body.
- Only a series of necessary tests will help determine whether there is a pathogen in the body or not.
- Only the presence of such symptoms for women always indicates an STD: the presence of copious discharge from the vagina, urethra and pain in the lower third of the abdomen and when emptying the bladder.
- Men are characterized by discharge from the penis and pain in the scrotum.
And also painful urination.
It’s bad when a partner tries to hide such symptoms.
What signs after sex will indicate an STD in a partner?
- Well, firstly, if an STD causes inflammation in the genitals, then sexual intercourse itself will be painful and unpleasant.
- Moreover, both for women and for men.
- There are no specific signs of STDs.
- Each disease has its own symptoms, and sometimes STDs also have an asymptomatic course.
- Therefore, it is better not to engage in sexual relations with unfamiliar people.
- And if such a relationship does occur, then it is necessary to use a condom.
How to find out before sex whether your partner has an STD?
- It is impossible to know this before sex.
- Moreover, if the partner hides his symptoms of the disease.
- But, if the partner is frank, then he will note:
- presence of itching and burning in the genitals
- hyperemia of the genitals and (or) perianal area
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
- presence of discharge, often with an unpleasant “fishy” odor
These symptoms are added to the above symptoms.
You can’t delay, you need to contact specialists as soon as possible.
How quickly is STD transmitted through sexual contact?
- It doesn't matter how long sexual intercourse lasts.
- If there are microtraumas, then this fact significantly increases the possibility of contracting an STI, regardless of its duration.
- And there are almost always microtraumas in the mouth, vagina and rectum.
- It is much more important whether sexual intercourse is protected or not.
- A condom is a necessary component of sex with a partner who has not been tested for STDs.
- If sexual intercourse is unprotected, then the chances of getting infected immediately increase many times over.
- You need to remember this and not use a stopwatch to time the duration of sexual intercourse.
What is the probability of getting an STD in one sexual act?
- During unprotected sexual intercourse, there is always the possibility of becoming infected, even if the sexual intercourse was only once.
- Naturally, this probability increases with repeated sexual intercourse.
- STDs appear not only on the organs of the genitourinary system, but also on the throat, rectum, eyes and other organs.
- They concentrate in these organs and can cause infection.
- But still, the main route of infection is sexual contact.
- The contagiousness of STIs depends on direct sexual contact, since STD pathogens do not live long outside the human body.
- What is the duration of contagious sexual contact?
- The duration of sexual contact does not affect infectiousness.
- But if sperm is released, this increases the likelihood of contracting an STD.
- Therefore, completed sexual intercourse is much more contagious than incomplete sexual intercourse.
- I have already said that there is no need to track the duration of sexual intercourse.
- The main thing is not to engage in casual unprotected sexual intercourse.
- And if this happens, then do not panic and be sure to do all the necessary control tests.
- Especially if you have a regular sexual partner.
- And if the presence of an STD is confirmed, inform him about it, no matter how difficult it is.
- He has the right to know about it.
Is it possible to get an STD through vaginal mucus through stroking, petting, rimming, etc.?
- As I already said, the presence of microtraumas and the pathogen in the biomaterial is important for infection.
- You can become infected through vaginal mucus only if it gets into microtraumas in the mouth, penis or rectum.
- When stroking, too, if it is stroking the genitals, but there are no microtraumas on the hands, it means that the infectious pathogen will not enter the bloodstream.
- Petting, rimming and the like are dangerous because there are almost always certain microtraumas in the mouth.
- And through them the entrance gates of infection open.
- Therefore, all of the above types of caresses are not as harmless as is commonly thought.
- And you need to treat them with caution.
- Mucus from the vagina got onto the penis, but there was no sex.
- Is it contagious?
- I have already said that if there are no microtraumas on the penis, then the infection will not penetrate the body through it.
- Is it vaginal mucus or something else like that?
- It must be remembered that:
- not every symptom indicates an STD, sometimes it is simply an allergic reaction to barrier protection in the form of condoms, to the use of vaginal suppositories and all kinds of pills
- intimate hygiene products increase dryness and increased vulnerability of the mucous membranes of the genitals
- premenopausal and menopausal periods are characterized by dryness and itching of the genitals
- narrowing of the foreskin causes pain and dryness of the head of the skin of the penis and the appearance of cracks on it
- itching and rashes on the genitals are characterized by neurodermatitis, eczema, LP and other diseases, not just STDs
And the presence of dryness and microtraumas increase the likelihood of getting a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
What tests to do after sex with someone with an STD?
After sex, even protected sex, with strangers, you should always do tests to clarify the diagnosis of an STD.
For STIs, smears are taken and serological tests are performed for diagnosis, such as ELISA and PIF.
- Conduct cultural studies and PCR diagnostic method.
- Each method has its own indications for use, advantages and disadvantages.
- You just need to choose them correctly.
- When should they be done?
- Do not immediately run away after sex with a suspected STD, but a period of at least seven days must pass.
- And then submit the biomaterial for analysis.
- To perform serological tests (ELISA and PIF), it is necessary to pass at least four to six weeks after sexual contact.
- During this time, specific antibodies should appear in the blood, the presence of which will indicate the presence of an infectious agent.
- Therefore, to obtain reliable results, it is necessary to wait the correct period of time after sexual intercourse.
Which doctor should I contact if I suspect an STD?
If you suspect an STD, you must undergo examination by a dermatovenerologist.
- After examination and passing the necessary tests, the need for treatment may arise.
- You definitely need to go through it.
- When examining a dermatovenerologist, you should not hesitate to ask him in detail about all the points regarding STDs in order to quickly deal with it and not develop complications of the disease.
- Especially, many are interested in the possibility of re-infection, the degree of contagiousness of single sexual contacts and questions regarding planned pregnancy.
- Having received comprehensive answers to all your questions, you can get psychological support, which is also very important.
- For diagnosis, treatment and prevention of STDs after sex, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Source: http://www.venerologia.ru/seks-pri-zppp
Is it possible to have sex with HPV, the consequences of intimate life
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common infections and is highly contagious.
Detection of HPV involves not only completing a course of appropriate therapy for the case. The carrier of the virus must exercise certain caution, which also applies to sexual activity.
Routes of transmission
Sex with HPV is not the only option for transmitting the infection to a partner.
It is known that infection occurs through direct and indirect interactions, for example as a result of:
- kiss.
- Other types of sex (anal, oral).
- Everyday situations.
- Using the same hygiene items that contain HPV (toothbrush, razor, etc.).
Risk factors include the following:
- stressful situations.
- History of viral pathologies.
- Long-term use of corticosteroid drugs and antibiotics as a method of therapy.
- The presence of a focus of infection in the human body in a chronic form.
If immunity is reduced, a person can become infected with papillomavirus, even by using a cup of an HPV carrier. Experts believe that exposure to the virus provokes the development of cancer on the organs of the partners’ genital systems.
Video
HPV
Is it possible to have sex if you have HPV?
Therapy for HPV should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. The specialist will tell you whether the virus carrier can have sex or whether it is better to postpone any sexual contacts.
It is important to understand that this is not only about the usual version of intimacy. The human papillomavirus can be transmitted through oral sex, especially if the partner has an immunodeficiency.
Sexual life during treatment
There is no clear answer to the question of whether it is possible to have sex during treatment for HPV. If infection occurs through sexual contact, unprotected intimacy is quite capable of triggering re-infection.
According to experts, it is better for a patient with HPV to abstain from sexual intercourse for the entire duration of treatment.
This approach is based on a treatment regimen that consists of two stages:
- getting rid of the virus with appropriate drugs.
- Direct removal of warts on the skin and mucous membranes.
If an HPV carrier has papillomas, he can infect his partner during any type of intimate intimacy.
Pain during sex after genital wart removal
Removal of genital warts does not mean an immediate return to sexual activity. The patient should wait some time, giving the immune system a chance to recover. Only the attending physician can specify the period of abstinence based on data from laboratory tests.
If growths are found on a person’s skin or mucous membranes, this requires them to undergo appropriate tests. The results will allow the specialist to determine the type of viral infection and assess the possible risks to the body. After therapy and removal of warts, a repeat examination is necessary to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Removal of vaginal papillomas (condylomas) involves the absence of intimacy for several weeks. If you do not wait the prescribed time, the resulting wounds will not have time to recover, which will subsequently cause pain during sexual intercourse.
After removal of papillomas, sex is allowed as soon as the analysis confirms a decrease in HPV activity. In addition, the patient and his partner must have good immunity.
How reliable is the protection of a condom?
When having sex with a carrier of the virus, you should not rely on condoms for everything. This is explained by the fact that no contraception guarantees absolute protection against infection. In addition, transmission of the virus does not only occur through direct penetration. The attending physician should tell the patient how to protect himself against HPV.
It is possible to determine that the human papillomavirus is in the active stage by the appearance of new growths. This state of affairs requires special caution from both the carrier of the virus and his partner. If existing growths are damaged in the process, there is a risk of re-infection and worsening the situation.
Depending on the location of the warts, the use of a barrier contraceptive (condoms) does not always help avoid actual contact with the growths. The presence of any damage to the skin or mucous membrane of a healthy partner is an excellent opportunity for transmitting the causative agent of the virus to him.
Please note: oral sex, if it affects the affected areas, can also contribute to HPV infection.
Using condoms if both partners have the virus does not affect the course of the infection. You can have sex with a regular partner after removal of papillomas without contraception.
How to prevent complications?
Radical methods for removing papillomas will help to avoid complications and significantly improve the patient’s quality of life.
These include the following methods:
- exposure to electric current. The use of electrocoagulation allows you to resume sexual activity a couple of weeks after surgery. The technique copes well with genital warts.
- Laser exposure. The results are slightly worse than after other methods; healing takes longer. Sexual activity is allowed after 12-14 days.
- Radiosurgery. This method of removing tumors using radiation therapy is considered universal. It takes 14-21 days for the wound to heal.
- Cryodestruction. The essence of the method is to freeze papillomas. It is allowed to resume intimate life after about a month.
- Conventional surgery. You can have sex after the wound has healed.
If chemical treatment is used to remove warts, there is a high probability of recurrence of the pathology.
What is prohibited?
Experts have established a number of absolute contraindications, on the basis of which people with HPV should completely avoid having sex with their partners.
These factors include:
- the presence of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes, which are an indicator of the active stage of the process.
- Results of laboratory tests that confirm the activity of the human papillomavirus.
- Physical discomfort caused by growths (burning, itching, redness and irritation).
- Pain that occurs during sexual intercourse.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Injury to papillomas, bleeding in places where warts form.
Therapy involves careful selection of medications, as well as the choice of a technique for a more radical effect. You can resume sexual activity only after removing the papillomas and completing a course of drug treatment.
Precautionary measures
To protect your body from HPV and at the same time maintain the level of your sex life, you need to adhere to some preventive measures.
Here they are:
- reduce the number of sexual partners, eliminate promiscuity.
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse. They help reduce the risk of transmission of the virus, but are not completely safe.
- Minimize contact with the area affected by warts.
- Along with your partner, be regularly examined and take the necessary tests.
Please note: engaging in other types of sex (oral or anal) does not eliminate the risk of transmitting infection. This is due to the presence of the causative agent of the virus in all biological fluids produced by the human body.
Sexual contact with an HPV carrier who has no external manifestations of the virus is permissible if his partner has good immunity. In addition, it is recommended to use not only contraceptives, but also local antiseptics, which will reduce the likelihood of infection.
It is important not to damage the papillomas, otherwise inflammation can be provoked.
Source: https://papilom-net.ru/vpch/seks-pri-papillomah
Sex when human papillomavirus is detected
The question of whether it is possible to have sex with HPV worries every adult who has been diagnosed with this disease. The relevance of the problem is undeniable, since the virus has become widespread in recent decades.
Transmission of papillomavirus from one person to another occurs through direct and indirect contact and sexual intercourse. The appearance of genital warts on the body causes discomfort and many problems.
As experts note, the virus contributes to the development of cancerous tumors on the female and male reproductive organs. It is for this reason that everyone should make sure that sex with HPV is protected.
Sexual transmission of the virus and genital warts
The virus, which is transmitted through intimate intimacy, contributes to the development of the cancer process and the appearance of anogenital warts. Infection occurs when unprotected sex occurs. However, the course of the disease in some cases may be asymptomatic. The activation of the virus occurs against the background of a decrease in the level of the body’s natural defenses.
In turn, condylomas, which are formations on the mucous membranes, are localized on the organs of the reproductive system and in the anal area. The risk of infection will be much higher in the following groups of people:
- Persons suffering from diseases that affect the reduction of immune defense. Examples of such pathologies include HIV and diabetes.
- People who are promiscuous.
- A person can become infected, which is much more likely if he begins sexual activity early.
- Patients with other sexually transmitted diseases have a much higher chance of contracting the virus.
- A couple who engages in anal sex is susceptible to infection.
- Couples who refuse to use a condom during sexual intercourse.
- The virus is easily transmitted from partner to partner if the couple practices unprotected oral sex.
- Women who have had an artificial termination of pregnancy at least once during their life.
As practice shows, the appearance of genital warts can most often be observed on the genitals.
Sex if you have papillomavirus
Until today, medicine has not been able to find a cure for the human papillomavirus. Therefore, when treating HPV, all efforts will be aimed at maintaining the patient’s immune system and eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
However, in case of condylomas in one of the partners, the only means of protection is barrier contraception. As the results of medical research show:
- using a condom for papillomas in one of the partners allows the healthy partner to protect themselves from infection in 2 out of 3 cases;
- If you do not protect yourself during sexual intercourse, the risk of infection increases to 90%.
As a rule, patients seek medical help when the growths that appear cause significant discomfort during sex.
As for the possibility of having sex during the treatment of the virus, in order to achieve the desired result of therapy, intimate relations during the treatment period are absolutely excluded.
It is not prohibited to have sex if there is papillomavirus in the body. The only exception is the treatment period.
In other cases, the decision about whether or not to enter into an intimate relationship always remains with the person.
In this case, it is only important not to forget that active sexual life with HPV causes many problems. This is due to the fact that it will not be possible to completely get rid of the virus.
Treatment will only strengthen the immune system and eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Therefore, there is always a possibility that the disease will return again. And the patient will be forced to seek medical help again. In addition, in the case of regular intimate life, the growths formed on the body will be subject to constant injury.
The repeated process of damage to papillomas will lead to their bleeding, development of the inflammatory process and suppuration.
All this will cause significant discomfort not only during intimacy, but also in everyday life.
Therefore, when making a decision, you need to weigh all the pros and cons and think about the consequences. After all, every person must take responsibility for their health and life.
Source: https://venerologia03.ru/papillomavirus/seks-i-vpch.html
HPV: how is it transmitted, infection through a condom
Human papillomavirus is a fairly common infection. About 90% of women experience this phenomenon during their lifetime. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that for many years, being in the body, it does not manifest itself in any way.
Symptoms become noticeable only in the middle and advanced stages. As a result, pathologies of the genital organs develop in a “quiet” way. Among them there are both benign formations and oncologies.
To avoid infection, you need to know how HPV is transmitted.
General understanding of HPV and its types
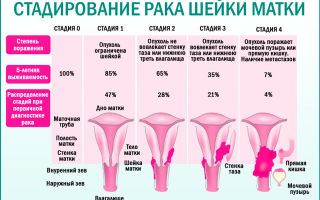
HPV infects epithelial cells and transforms their structure. As a result of increased division, papilloma is formed (Latin papilla - “nipple” and Gr. oma - “tumor”). The group associated with the development of cervical cancer consists of fourteen types (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68). These are species with a high oncogenic risk.
If a man is a carrier of one of the listed viruses, he has a high probability of “getting” a malignant pathology of the genital organs. There is a low-oncology group (6 and 11). All kinds of warts and genital warts are common signs of infection with these infections.
Respiratory papillomatosis, caused by formations in the respiratory tract, is also a consequence of low-oncorisk viruses.
Methods for introducing human papillomavirus into the body
Almost all men and women deal with HPV at one time or another. Researchers - epidemiologists from the Bronx - came to the conclusion that the vast majority of infected people are able to “overcome” the virus on their own within two years. (This time period is due to the natural progression of the infection.)
The main route of transmission is sexual. Taking into account individual characteristics, the time frame for getting rid of the disease may vary among sexual partners. It often happens that one person is diagnosed with papillomavirus, while the other is healthy.
Stable immunity is not formed after infection, so re-infection is possible.
Main route of infection
It is important to have an understanding of how human papillomavirus is transmitted. The main way HPV spreads is through sexual contact. Most often, the “carrier” is a man. This fact is associated with the peculiarity of the development of the virus in representatives of the stronger sex.
The male body takes longer to get rid of infection. At the same time, the carrier for a long time can be one hundred percent confident in his “heroic” health and not undergo treatment. It has been noticed: the “wider the circle” of intimate partners, the greater the radius of transmission of microbes. Then the domino effect kicks in.
The high risk of serious consequences is characteristic primarily of women.
Different types of intimate relationships and degree of risk
Is it possible to have sex with HPV – a question that worries many patients. The type of intimate relationship does not affect the risk of infection.
Attention! Genital, oral, anal sexual contact with a suspected carrier of the virus will equally lead to infection. There is a chance of getting sick even after a one-time sexual kiss.
Small wounds on the oral mucosa do not always cause discomfort and therefore may not be noticed by a person. It is through them, with the help of saliva, that the insidious strain is transmitted from one to another.
Barrier contraception: will it help or not?
Many people wonder if HPV is transmitted through a condom. Alas, barrier methods of protection cannot guarantee good health.
If a person belongs to a “risk group” (early onset of intimate relationships, frequent changes of sexual partners, the presence of sexually transmitted diseases, HIV), then condoms will not save. Virus molecules are able to penetrate through the microscopic pores of the barrier protection.
To avoid the exchange of various “sores”, doctors recommend “Miramistin”. An important condition is to take it in the first two hours after unprotected sex.
Domestic infection
Methods of transmitting HPV through the use of household items (towels, clothing, for example) are much less common. You can catch the infection when visiting “mass” places:
- Germs and viruses love a moist environment, so they can be “found” in public baths, saunas, showers and swimming pools. Experienced regulars recommend cleaning all surfaces and items of use with soap and water before use.
- But in a hairdressing salon or barbershop, no one will let you wash your tools yourself. Therefore, we have to rely on the conscientious implementation of sanitary standards by local employees.
- There is also a certain risk when visiting beauty salons. At the same time, the “sword of Dodocles” hangs not only over the clients, but also over the staff - no one wants to get sick.
- During minor medical procedures (donating blood for analysis, caries treatment), there is a very small percentage of risk. But it does exist.
No one is immune from the disease. To protect yourself as much as possible and not turn into a paranoid social phobe, experts recommend timely vaccination.
Transmission of the virus from mother to fetus during pregnancy and childbirth
In order not to worry unnecessarily when carrying a child, before planning conception, you need to undergo a medical examination. Pregnancy itself is a factor that provokes an exacerbation of HPV.
Behavior of HPV in the body
During the penetration of the papilloma virus into the cells of the body, a healthy structure is transformed. For a long period the disease does not manifest itself in any way. The person’s well-being does not change. Subsequently, various stages of dysplasia occur (pre-cancer form). In the “advanced” stage, mutated DNA changes tissue, which can result in cancer.
“Sleeping” virus and the reasons for its “awakening”
Having penetrated the epidermis, the virus “attracts” cells of the immune system. In most cases, defenses win. From the moment it enters the body, the infection is “frozen” and remains in incubation mode for a long time (sometimes years).
The disease “wait” for suitable conditions, and then a “breakthrough” occurs. A weakened immune system can increase the likelihood of the disease occurring. Long-term illnesses, regular stress, physical overexertion are factors that can provoke a “surge.”
Hormonal changes in women due to pregnancy or menopause also contribute to the manifestation of a hidden disease.
Stages of progression and symptoms
The main task of every infected person is not to miss the visible symptoms. Exacerbation of HPV goes through three periods of development:
- First stage. Small flesh-colored lumps appear on the human body. The area of distribution is the entire body (from head to heels).
- Second stage: the growths move to a new level - papillomas, the diameter of which is about 7 mm.
- Third "stage". Inflammation and bleeding of condylomas appear.
The external manifestation of papillomavirus indicates the “height” of the disease.
Consequences of HPV for men and women
The manifestation of HPV and its consequences do not occur equally in patients of different sexes. For men, papillomavirus poses less of a threat. However, this disease can cause significant damage to men's health. The table lists the consequences of infection and the corresponding symptoms.
Name of diagnosis Characteristic symptoms| Condylomatosis | It begins with the appearance of small formations (on the penis, urinary tract, anus, scrotum, rectum). As a result of rapid growth, the compactions turn into genital warts. Often individual growths are united in groups resembling a cockscomb. All this is accompanied by itching and discharge. |
| Bowenoid papulosis | It appears in the form of various rashes of brown, purple, pink hue. Location: penis. The disease is classified as precancerous. People of reproductive age mainly suffer. |
| Bowen's disease | A single scaly plaque with uneven edges. Under the top layer there is a wet surface. The lesion is always growing and can reach ten centimeters in diameter. The opinions of experts vary: some consider this manifestation to be pre-cancer, others define it as full-fledged skin cancer of the penis. |
At any moment, growths can turn into a malignant state, so postponing a visit to the doctor is akin to a crime.
You should know how HPV is transmitted to women. This mainly occurs through sexual intercourse with an infected man. Let's take a closer look at the features of the development of HPV in the female body. The appearance of warts and papillomas brings a lot of trouble for the fair sex.
Causing pain, the formations have a negative impact on a woman’s self-esteem, worsening her appearance. In this case, the risk of transition of benign growths to the oncological stage increases. The “culprit” for this is the hormone estrogen.
Anything can provoke irreversible processes: trauma to papillomas, exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Of particular danger is the development of cervical cancer. Most often, the patient does not feel visible discomfort until the very later stages. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular gynecological examinations.
Having discovered obvious manifestations of HPV on the internal tissues of the genital organs, the doctor registers the visitor.
An intermediate step between infection with an oncogenic virus, its activation and the development of oncology are atypical changes in the epithelium, called cervical dysplasia. At the initial stage, this pathology is treatable.
Preventive measures
Many people who have already contracted the unpleasant disease want to know how to avoid infecting their partner with HPV. According to WHO recommendations, to prevent the emergence of the virus and its consequences, a set of measures is required. “Recruitment” is a multidisciplinary, lifelong intervention and includes the following components:
- Vaccination against HPV. Mostly girls aged 9-13 years are vaccinated.
- Educating individual communities and groups on safe sex issues. Particular attention is paid to adolescents, who are given new arguments in favor of delaying the onset of sexual activity.
- Distribution of barrier contraceptives among sexually active people.
- Information campaign for life without bad habits. Nicotine use is one of the important risk factors in the development of a number of oncologies.
- Practicing male circumcision.
Elena Malysheva believes that adults should be screened for precancerous conditions. Currently, there are three methods of initial examination: Pap test and liquid-based cytology; visual inspection using acetic acid; tests for high-risk HPV types.
Conclusion
Human papillomavirus is the most oncogenic. It is present in almost every body and is responsible for the appearance of moles, warts, and age spots on the body, which can turn into melanoma at any time. Skin cancer is currently an incurable disease.
Source: https://UroMir.ru/zppp/hpv/vpch-kak-peredaetsja.html
Is HPV transmitted from woman to man through sexual contact and how to avoid infection?
The papilloma virus affects all areas of human life. If there are formations in the anogenital area, patients are interested in whether it is possible to have sex with HPV. It is important to know the route of transmission of the virus and the mechanism of its development.
Routes of transmission of HPV
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease transmitted sexually with a high degree of contagiousness. The disease can be transmitted in three ways:
- Through everyday contact. Infection can occur through the common use of hygiene equipment, dishes, clothes, and shoes. You can catch HPV in public bathing areas where you can walk barefoot.
- The mother can transmit the virus to the child if at the time of birth the expectant mother has condylomas of the intimate area. As soon as the baby begins to pass through the birth canal, he comes into contact with the growths.
- Genital papilloma is transmitted through intimate contact. The most common method of infection with an infectious pathogen.
During sexual contact, the mucous membrane of the anus is most susceptible to damage. In second place is the female vagina.
The least sensitive to microtraumas are the male genital organ and the oral cavity. For these reasons, infection is likely during anal sex, traditional for women.
Oral contact (blowjob) is among the safest. HPV is also transmitted through condoms.
Transmission of infection from one person to another does not mean 100% development of the disease. The main role is played by the immunity status of the sexual partner. A stable immune system will not allow the infection to activate. Some people are unaware of the presence of HPV in their own body. The manifestation of papilloma virus symptoms occurs when the immune defense is weakened.
Mechanism of transmission of the virus from woman to man
The transmission process is the same for both sexes. The human papillomavirus is transmitted to a partner during sexual intercourse through microscopic injuries caused by friction.
The virus cells are so small that they can easily penetrate minor scratches or cracks. The pathogen settles in the body. Sometimes the incubation period can take several years. Weakening of the immune defense can cause the infection to “exit” to the outside. The condition is provoked by:
- acute infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiencies;
- a woman is pregnant;
- diseases of the immune system;
- stress, nervous breakdowns.
Depending on how the infection occurred, the growths are localized. The formation of condylomas is inherent in the anal, genital and oral areas. There are two types of condylomas - pointed and broad.
The first are elongated growths, on a thin stalk, which are prone to fusion.
The second - flat plaques, are caused by Treponema pallidum - the causative agent of syphilis, which indicates the development of secondary manifestations of the disease.
The resulting growths contain the highest concentration of viral cells. If the growth is damaged, the infection spreads to healthy areas. In the same way, HPV passes from one sexual partner to another.
Oncogenic types pose a danger to humans, especially 16 and 18. In women, these strains are found in cervical cancer. In men, malignant processes of the prostate, head of the penis, and rectum may appear.
With extensive papillomatosis, patients are faced with problems of the urethra, women with gynecological pathologies, men with urology.
Does a condom protect against HPV?
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Condoms are an effective means of protection against most sexually transmitted diseases. To penetrate the body, the virus only needs microscopic damage to the skin, which is invisible to the eye.
Synthetic materials are not an obstacle for him either. It is not recommended to consider barrier contraception as a way to protect the body from HPV.
Even a high-quality condom is not able to protect against the transmission of the disease.
HPV can be transmitted through a condom. It is important to realize that the presence of the virus in the body is serious, and complications may develop in the partner. Intimate papilloma is always transmitted sexually.
Many sources claim that sex with a condom is safe, but these statements are incorrect. The presence of condylomas on the genitals, groin, anus, and oral cavity is a significant barrier to sexual intercourse.
Those who doubt whether to have sex during active manifestations of infection need to deal with two questions.
Is an infected person with warts on the genitals ready for sexual intercourse in order to deliberately infect a partner? The risk that a previously healthy person will exhibit the same symptoms of the disease is not guaranteed. But it is not excluded.
If both partners are carriers of the papilloma virus, and both have growths on the genitals (or other area), sex with a condom is quite acceptable.
Things are different if HPV is detected in the body, but there are no external manifestations of the disease. This indicates the passive presence of the pathogen or the active activity of the immune system. Taking into account that a person with this diagnosis will begin timely treatment, preventing the warts from coming out, sexual relations are allowed.
Is it possible to infect a partner after treatment?
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection is a process that includes a set of measures. In severe cases of the disease, the patient is prescribed a course of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs and removal of condylomas.
Drug therapy includes the use of Interferon, Viferon, Cycloferon, Allokin Alpha. The products have a complex composition that simultaneously helps to suppress the activity of the pathogen and normalize the body’s natural defenses.
You can treat the external manifestations of the disease using destructive chemicals, keratolytics, or hardware influence.
After removing the growths, to prevent bacterial infections, it is recommended to treat the wounds with antiseptic solutions and use Miramistin.
Correctly selected treatment helps to completely neutralize the infection. The virus enters a latent state, in which it is unable to reproduce and cause symptoms of the disease. After treatment, the person becomes non-infectious to others.
To confirm the fact of effective treatment, it is advisable to undergo repeated diagnostics - be examined by a doctor and take tests.
HPV does not apply to diseases, after which long-lasting immunity is developed. The disease can be cured, but the virus remains in the body. A person who has undergone therapy will not infect a partner during intimacy. The main condition for a person who has suffered the active phase of papillomavirus is not to allow the infection to reactivate.
To do this, it is recommended to pay attention to the state of immunity, avoid stress, hypothermia, and treat infectious diseases. Women need to visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year so that the doctor can notice the appearance of new formations in time.
Patients who have had a strain that causes cancer have been identified in their bodies should be careful.
Precautions to avoid getting infected
The papilloma virus is so common that becoming infected with it is not particularly difficult. Following certain recommendations will reduce the likelihood of disease transmission:
- use exclusively personal hygiene items;
- check compliance with sanitary standards during salon procedures and gynecological examinations;
- do not walk barefoot in public places;
- exclude contact with papillomas in another person.
The main recommendation for people who are sexually active is to have a regular lover. Based on the fact that HPV is transmitted from partner to partner through a condom, only this condition can guarantee safety.
Another way to avoid infection is vaccination. There are 3 HPV vaccines. Quadvalent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 types. 9-valent Gardasil - from 16, 18, 6, 11 and 5 highly carcinogenic strains. Cervarix - from types 16 and 18. Vaccination occurs in 3 stages, after which the vaccination can be considered complete.
HPV is transmitted to a partner. It is important for people suffering from this disease to understand that they can easily become infected with papillomavirus. To avoid such a situation, it is necessary to identify the development of infection and begin treatment.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Source: https://VashaDerma.ru/hpv/seks
Is it possible to have sex if you have HPV?
Human papillomavirus infection is the most common chronic viral disease that affects the mucous membranes of various organs and systems, including the genital area.
The virus is constantly in the cells, and then what about sexual activity, which is almost always prohibited in case of STIs and sexually transmitted diseases. Is it possible to have sex if you have HPV?
Several factors affect the ability to lead a sexual life with human papillomavirus infection:
- The presence of active manifestations of HPV on the genitals: condylomas, erosions, ulcers, papillomas. With this course of the disease, of course, sexual intercourse is prohibited until the symptoms are eliminated.
- The presence or absence of this infection in both partners. If both sexual partners are already infected with the same types of HPV, then sexual contact does not carry a risk in terms of transmitting the virus, since it already exists.
- The presence of a latent human papillomavirus infection in one of the partners, which has no manifestations, but is determined during an HPV test, and its absence in the other partner. In this case, it is better to plan sexual activity after treatment for HPV and receiving negative control tests for the human papillomavirus. Vaccination of a healthy partner can also protect in this case.
- Is it possible to have sex with HPV if your partner has already been treated? In this case, the decision is made by the healthy partner. The likelihood of complete elimination of the virus from the body is very low. The result of therapy is almost always a decrease in its activity and transfer to a dormant form, which is not detected by PCR analysis and has no clinical manifestations. That is, there is always the possibility of HPV activation and its transmission to a sexual partner. That is, there is a risk of infection even after high-quality treatment.
- Is it possible to have sex with HPV with a condom? If there is no contact between unprotected areas of the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs of a healthy and sick person, then the contact can be considered relatively safe, provided that the condom does not fly off or break.
When deciding whether it is possible to have sex if you have HPV, you are always guided by two components: the risk of infecting a healthy partner and the negative consequences for someone already infected. The dangers of contact with HPV-infected people for healthy people have already been described above.
If the patient has condylomas or erosions on the genitals, or other manifestations of papillomavirus infection, then sexual activity is prohibited. It can worsen the course of the disease. The rashes are injured during the act, begin to bleed, bacterial flora penetrates into their damaged areas, suppuration, ulceration, and abscess formation of the genitals occur.
The papilloma virus also spreads throughout the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix in women, along the head of the penis and foreskin in men, and penetrates into the urethra with the growth of intraurethral condylomas.
Active reproduction of HPV of high carcinogenic risk in the cervical canal and prostate in men can cause cancer of these organs.
Is it possible to have sex with HPV in each specific case of the disease? A venereologist or gynecologist who treats papillomavirus infection in a given patient will answer. This decision is made on the basis of clinical examination data, laboratory diagnostic results and previous therapy.
Source: https://www.academy-health.ru/napravleniya/venerolog/udalenie-papillomi/sex.html
Questions about HPV
Is it possible to plan a pregnancy while being treated for human papillomavirus infection (HPV)? How to get rid of condylomas forever? What is high-risk papillomavirus? Doctors from Art-Med medical clinics answer questions about human papillomavirus infection.
HPV was first discovered 2 years ago. Types 31, 35, 39, 59, was treated with Isoprinosine, Panavir, Genferon. I thought everything would go away forever, that’s what the doctor assured me. Recently I decided to get checked again, nothing bothered me, they found type 51.53, and my partner had 18, how can this be? Why do we have different types?
This condition is possible. It is unlikely to be completely cured of HPV, but treatment is necessary. Contact a gynecologist and an immunologist for joint treatment. Different types of viruses and partners are a common situation, since diagnosing inactive viruses is difficult.
I am 19 years old and have been sexually active for a year. HPV 16 was recently discovered, but there are no external signs. Colposcopy also did not give results. The doctor intimidated me with the threat of cancer and prescribed Allokin Alpha. What should you do in this situation, because it is often written that HPV goes away on its own. And what should your partner do?
Carriage of HPV is asymptomatic. Manifestations of highly oncogenic strains, which include type 16, are destructive processes in the tissues of the cervix, followed by the development of precancer. Despite the aggressiveness of type 16, at a young age it is possible to independently eliminate the virus from the body due to a powerful immune response.
After 30 years, as a rule, this does not happen. The instructions for Allokin-alpha indicate that its action is aimed at activating the synthesis of endogenous interferons, that is, stimulating one’s own immunity. Allokin Alpha does not affect the life cycle of HPV, therefore it does not guarantee 100% cure.
In this regard, only you can decide whether to use this drug or not.
I have HPV 16, six months later the first genital wart came out, it was removed, now all the labia are covered, I go to the gynecologist and constantly have it removed, I have been undergoing treatment for 5 months. I donated blood, histology and other tests - everything is normal, except for genital warts. During this time, doctors prescribed treatment, and now I still need 6 Immunomax injections and take Promisan dietary supplement for 3 months. Is it worth doing this already? I am 21 years old.
Considering that your HPV showed up not only in tests, but also clinically (in the form of genital warts), treatment is indicated for you. Taking into account the relapsing course, it is necessary to study in detail the use of drugs with their dosages and the course of the disease. If necessary, a consultation with an immunologist is possible.
Can you get HPV through oral sex?
It is possible - with any contact.
I was treated for HPV and received negative results. After 9 months I went for a second test and found HPV 16.18. The doctor said that it reappeared due to decreased immunity; indeed, when I arrived I had a fever and runny nose. Is there a chance that after I am cured, the virus will go away again or will it appear after every cold and I will be forced to drink a mountain of pills, do IVs and injections?
Human papillomavirus infection is usually lifelong. This is written in detail in articles on our website.
I have HPV types 16 and 53, but there are no external signs (papillomas and thuribles, no itching, no burning). Now I will undergo treatment. Could I have infected the young man if we took precautions? Could I transmit the virus through oral sex? And, if I transmitted it, what is the likelihood that after a course of treatment, this virus can be transmitted back to me through protected sexual intercourse and oral sex, in particular, kissing? Is it possible to have sex during treatment?
There is no reliable protection against HPV infection. This is usually a lifelong infection. Read more about this in the “Medical Publications” section.
Source: https://www.art-med.ru/faq/r107/p1