Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a contagious and unpleasant disease. To alleviate the symptoms and speed up the patient’s recovery, the doctor prescribes the necessary medications and outlines a treatment regimen, taking into account one or another form of the disease. Read about all this in our article.
Which doctor should I contact?
When the first signs of illness appear, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist . If an eye doctor is not available, the sick person should consult with a primary care physician. The doctor will examine the patient and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the ophthalmologist interviews the patient, performs a visual examination and conducts additional research methods. These include:
Therapy
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is known to ophthalmologists for its high complications. This is why it is so important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Duration
With adequate therapy in adults, the disease resolves within 10–14 days . It usually resolves without the development of serious complications.
In advanced cases, it takes longer - about 20-30 days.
Basic Rules
Depending on the type of illness, the doctor selects an individual treatment regimen for the patient.
Catarrhal
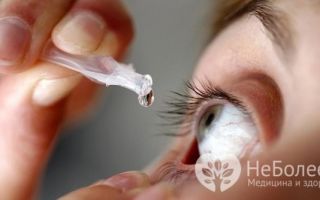
It is characterized by a mild course and absence of complications. In this form, antiviral drops are used - Interferon, Ophthalmoferon, Poludan. The frequency and duration of instillation is determined by the treating ophthalmologist.
The doctor may prescribe antibacterial drops to prevent the secondary addition of bacteria. Sulfacyl Sodium, Vigamox, Tsipromed are used for these purposes.
It is useful to wash the eyes with antiseptic solutions - Furacilin, herbal decoctions. If the disease occurs with severe swelling of the conjunctiva, antihistamines are prescribed - Cetrin, Claritin. They reduce and eliminate itching and burning in the eye.
Follicular
This form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is characterized by the formation of multiple blisters on the mucous membrane of the eyelids. It has a tendency to chronic inflammation.
In addition to antiviral drugs, the ophthalmologist may recommend tear substitutes - Hilo-chest, Systane, Hyphen. These medications will reduce the unpleasant manifestations of the disease - the feeling of sand in the eye.
The ophthalmologist prescribes NSAIDs (Diclof, Diclofenac) . Drops reduce pain, discomfort, and fight inflammation. He also recommends antibacterial drops and antihistamines.
Membranous
For the filmy form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, the main treatment is removal of the films. For these purposes, the doctor uses tweezers, with which he picks them up and removes them from the conjunctiva of the eyelids. This procedure avoids development.
The doctor also uses antiviral drugs (Ophthalmoferon, Poludan, Interferon), antibacterial agents (Vigamox, Tobrex).
Additionally, the ophthalmologist prescribes glucocorticoids - Dexamethasone. The active substance exhibits anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and.
The ophthalmologist may prescribe combination drops. They also contain an antibiotic. Such drugs include Maxitrol, Tobradex.
Acute
The main drugs used in this form:
- antiviral agents;
- antibacterial drops;
- tear substitutes;
- ;
- .
Chronic
Rinse with antiseptic solutions: chamomile decoction, Furacilin. Antibiotics and antiviral agents are instilled into the conjunctival cavity. Instillation of tear substitutes is also required, since dry eye syndrome develops in the chronic form.
The doctor prescribes hormonal drops (Dexamethasone), NSAIDs (Diclo-f). They help cope with the inflammatory process and accelerate remission. To increase the body's resistance, immunostimulants are well suited - Timalin, Timogen, Immunal, echinacea tincture.
Medications
The ophthalmologist selects a treatment regimen, including various forms of medications.
Drops
They have a local effect. The drugs are instilled into the conjunctival sac several times a day. The doctor prescribes:
Did the drops help you in the treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis?
- Antiviral drops. The patient can purchase ready-made forms at the pharmacy (Poludan, Oftalmoferon) or dilute the drug himself (Interferon).
- Antibacterial drops. Albucid, Tobrex, Vigamox, Ofloxacin are used. The recommended course of treatment is 5–10 days. The duration of instillation is determined by the attending physician, based on the clinical picture of the disease.
- Tear substitutes. Prescribed to eliminate the sensation of a foreign object in the eye and discomfort. An ophthalmologist can prescribe Oftagel, Hilo-chest, Artelak Balance, Visin Pure Tear. The drugs have different levels of viscosity, so they must be prescribed by the attending physician.
- NSAIDs (Diclofenac). Medicines are used to eliminate unpleasant symptoms (pain and discomfort in the eyes).
- Glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone). When applied topically, the drops exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antiexudative effects.
- Combined drops (Tobradex, Maxitrol). They include a hormonal component and an antibiotic.
Ointments
A similar form of medication is placed behind the lower eyelid. Typically, an ophthalmologist prescribes the following ointments:
- Antibacterial. The doctor may prescribe Tetracycline ointment, Oftocipro, Ofloxacin. They are necessary when a secondary infection occurs.
- Antiviral (Oxolinic ointment). Adenoviral conjunctivitis most often develops against the background of catarrhal symptoms of the ENT organs. The ointment is applied to the nasal mucosa.
Solutions
Suitable for these purposes:
- antiseptic solutions (Furacilin). To prepare medications, you need to dissolve a medication tablet in a glass of warm boiled water. Treat the mucous membrane of the eye with the resulting product;
- herbal decoctions of chamomile and sage. 1 tbsp. l. one of the plants is poured with 200 ml of boiling water. Let it brew and then strain. Treat the conjunctiva or apply cotton compresses soaked in the decoction.
Pills
Oral medications can be prescribed for various purposes:
- Antiviral (Anaferon, Ergoferon, Cycloferon). The doctor prescribes them for concomitant infections of the ENT organs. They promote the production of immune cells and quickly cope with viral inflammation.
- Antihistamines (Claritin, Suprastin, Loratadine). The drugs block the production of other substances. Thanks to their action, the patient is relieved of symptoms such as itching, burning, and swelling of the conjunctiva.
Review of folk remedies
If a patient develops adenoviral conjunctivitis, he can use alternative medicine recipes. There are many ways to alleviate the patient’s condition and speed up his recovery.
Folk remedies should not be used as the main treatment. It is advisable to consult a doctor before use.
| Product name | How to use |
| Honey | Prepare the product and warm boiled water. Mix them in a ratio of 1:2. Dip a cotton pad in the solution and apply the lotion to your eyes. |
| Honey and milk | Take half a teaspoon of honey and 100 ml of milk. Bring the mixture to a boil. Cool slightly and use the product as a lotion. |
| Honey and fish oil | Honey is mixed with fish oil in equal proportions. The resulting mass is placed behind the lower eyelid 4–5 times a day. |
| Yarrow or thyme | Prepare 1 tbsp. l. crushed yarrow or thyme. Pour 200 ml of hot water into the raw material. Leave to brew for 20 minutes. At the end of the time, strain the drink. Rinse your eyes with the decoction 3-4 times a day. |
| Dill | Finely chop the dill. 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials. Cook in a water bath for about 5 minutes. Then let it brew for half an hour and strain. Rinse eyes 3-4 times a day. |
| Eyebright grass | Add 1 liter of boiling water to 50 g of eyebright herb. Leave to brew for 2–3 hours. Then rinse your eyes with the product or make a lotion out of it. |
| Althaea officinalis | Prepare 2 tbsp. l. marshmallow officinalis. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the plant. Leave for half an hour. Make eye lotions. |
| Kalanchoe juice | Squeeze juice from Kalanchoe. Then dilute it with water in a 1:1 ratio. Soak a cotton pad in the solution and apply compresses to the eyes 3 times a day. |
Prevention
The disease is characterized by a transition to a chronic form, as well as the development of complications. To prevent the onset of adenoviral conjunctivitis, simple preventive measures should be followed .
These include:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap after every time you go outside.
- Regularly ventilate the room at home or at work.
- If you have a cold, use disposable handkerchiefs. Do not use them on your eyes and try not to touch them with your hands.
- Isolate patients in case of isolated diseases or introduce quarantine in case of outbreaks of infection.
- In the autumn-spring period, take vitamins and immunomodulators.
Source: https://kakorel.com/bolezni/zabolevaniya-konyunktivy/konyunktivit/raznovidnosti/virusnyj/lechenie-adenovirusnogo.html
The danger of adenoviral conjunctivitis: treatment, prevention and symptoms
21.06.2018
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a type of viral form of infectious inflammation of the conjunctiva. It is often accompanied by typical symptoms of ARVI, which is why it is also called pharyngo-conjunctival fever.
Once on the mucous membrane of the organs of vision, the virus begins to multiply, causing unpleasant symptoms. To ensure that the symptoms go away as quickly as possible and without consequences, find out how to deal with this disease correctly.
What is a disease?
The pathological condition causes damage to the mucous membrane of the eye. This is a viral conjunctivitis caused by a specific group of viruses called adenoviruses. Certain strains of the virus cause acute inflammation of the eyes, also accompanied by symptoms of general infectious intoxication of the body, including increased body temperature.
The adenoviral form is contagious and is transmitted in two ways:
- Contact-household: a person touches his eyes with unwashed hands, causing infection (especially typical for children).
- Airborne: from person to person when sneezing, coughing.
The incubation period lasts from 3 to 10 days. Treatment of adenoviral eye infection in adults and children is aimed at suppressing the replication of the virus and eliminating discomfort. For this purpose, a number of modern medications and hygiene procedures are used.
Forms of the disease
With adenovirus infection, conjunctivitis is acute. According to its course, acute adenoviral conjunctivitis is divided into several forms:
- Catarrhal form: uncomplicated, passes quickly (usually within a week), symptoms are not too pronounced, can occur without fever.
- Film conjunctivitis: the course is more severe, characterized by the formation of films on the conjunctiva. The general symptoms are more severe, the illness lasts longer than a week, the temperature can rise to 38 - 39 degrees. Membranous conjunctivitis is observed in 25% of cases.
- Follicular form: expressed by rashes on the eyelids. Translucent bubbles with pathological fluid form, especially in the fold area and in the corner of the eye.
Causes of the disease
In addition to the main one – the virus entering the mucous membrane – there are also indirect causes of the development of the disease that contribute to infection:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- contact with an infected person;
- general hypothermia of the body;
- decreased immunity;
- swimming in bodies of water where the water does not meet sanitary standards.
In children's groups, adenovirus infection often causes epidemic outbreaks, since children are often careless with hygiene and are in direct contact with each other for a long time in kindergarten or school. Spending at least half the day in one small room with other members of a group or class, it is easy to get infected from each other, which is what happens in such cases, especially with kids.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis has characteristic symptoms. The disease begins with the following symptoms:
- general malaise;
- increased body temperature;
- runny nose, cough;
- headache, weakness;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
These are the first signs with which adenoviral conjunctivitis begins. After a day or two, visual symptoms appear:
- mucous discharge;
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- vascular network on the cornea;
- burning, sometimes itching;
- feeling of sand in the eyes;
- lacrimation and photophobia;
- if it is membranous conjunctivitis, then gray-white films form on the mucous membrane.
Diagnosis should be carried out by an ophthalmologist. The diagnosis is confirmed after examining a smear from the conjunctiva, the result of which shows the presence of one of the strains of adenovirus infection in the patient’s biomaterial. After this, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
How to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis?
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis is complicated by the fact that there is no specific drug that acts specifically on this virus. However, doctors have effective antiviral agents in their arsenal that have a suppressive effect on many groups of viruses. Therefore, treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults and children mainly consists of the following:
- prescription of antiviral drops and ointments;
- washing sore eyes;
- Artificial tear drops to relieve symptoms;
- Sometimes antibacterial drugs are prescribed to prevent secondary infection.
With an integrated approach, these treatment methods give excellent results: the severity of symptoms decreases, the duration of adenoviral conjunctivitis is reduced.
Effective medicines
In pharmacies you can find a wide selection of drugs to combat adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- Drops for treating the adenoviral form most often contain interferon, a natural substance that prevents the virus from multiplying in the body. Among them are Tebrofen, Laferon and others.
- To relieve the symptoms of irritation, moisturizing drops are used: Artificial tears, Systane, Hyphene.
- If antimicrobial drops are used to prevent or treat an associated bacterial infection, then Tobrex, Albucid, Floxal are usually prescribed.
- At night, it is recommended to use antiviral eye ointments (Bonafton, Florenal), and if necessary, the doctor will also prescribe an antibacterial one (with tetracycline or erythromycin).
Remember that the choice of treatment tactics always remains with the doctor who made the diagnosis. Self-selection of medications can lead to complications instead of relief. If symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis appear, first make an appointment with your doctor. Follow his instructions exactly to avoid unpleasant consequences and recover as soon as possible.
Proper hygiene of sore eyes
A very important component of treatment is hygiene: before instilling drops or applying ointment, the eyes must be cleared of mucous discharge. This is done using a clean cotton swab, new for each eye. If there are films, remove them first.
If the films that form on the mucous membrane during the film form of conjunctivitis are not removed in a timely manner, the subsequent appearance of wounds and scars on the cornea is possible.
As a solution for washing, you can use decoctions of medicinal plants - chamomile, calendula, sage. Washing with a solution of furatsilin, which has a pronounced antiseptic effect, is effective. The eye is washed with gentle movements from the outer corner to the inner, towards the nose.
After the eyes are cleared of mucus and films, you can begin instilling drops and applying ointments.
Complications and prognosis
The adenoviral form of conjunctival inflammation can lead to a number of complications if it is not treated or treated incorrectly. Among these consequences:
- The addition of a secondary bacterial infection with the development of bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Violation of the production of natural tear fluid - dry eye syndrome.
- The development of keratitis - inflammation of the cornea.
- Complications from other organs: otitis (ear inflammation), tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils).
- In order to avoid these troubles, consult a doctor promptly if symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis appear and strictly follow all instructions for effective treatment.
- After recovery, pay attention to general strengthening procedures and prevention of adenoviral conjunctivitis and its other forms to prevent re-infection. We invite you to watch an interesting video from Dr. Evdokimenko about increasing immunity:
-
Prevention
Prevention of adenoviral conjunctivitis is as follows:
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene: your own face towel, regular hand washing.
- Avoid touching your eyes with dirty hands.
- Do not swim in dirty waters.
- Avoid contact with infected people.
- Strengthen the immune system: hardening, walking in the fresh air, proper nutrition, adherence to work and rest schedules.
- Regular ventilation and wet cleaning of premises.
Preventive measures, if everyone begins to follow them, will help not only protect themselves from infection, but also prevent adenovirus epidemics.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a common disease that spreads especially easily in groups among children. With timely and adequate treatment prescribed by a specialized specialist, adenoviral conjunctivitis goes away quickly and without consequences.
An ophthalmologist will tell you about adenoviral conjunctivitis in the video:
Share your experience with adenovirus infection and tell other readers of the article exactly how you managed to defeat it. Repost on social networks and save the article in your bookmarks. All the best.
The danger of adenoviral conjunctivitis: treatment, prevention and symptoms Link to main publication
Source: https://ozrenieglaz.ru/bolezni/konyunktivit/adenovirusnyj
Proper treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults and children
Home › Conjunctivitis › Correct treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults and children
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is an infectious disease that is transmitted from person to person. The disease begins in one eye, causing redness, discomfort, a feeling of pain, profuse lacrimation, and swelling. After 1-2 days, the second eye is affected. Severe headaches may occur. To prevent the spread of infection, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What is adenoviral conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is an acute infection of the eye. The disease may be accompanied by fever, nasopharyngitis, and characteristic symptoms (itching, swelling, increased lacrimation, discharge from the affected eye).
This form of conjunctivitis can be diagnosed by conducting a bacteriological examination and PCR scraping. Therapy for adenoviral conjunctivitis includes antiviral and antibacterial drugs. Relapses of adenoviral conjunctivitis are rare.
Causes of the disease
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is considered a highly contagious infection, that is, the disease is contagious. Outbreaks of the disease occur in the autumn-spring period (mainly in children's groups).
This form of conjunctivitis is caused by different types of adenovirus. Despite the fact that eye damage from viruses seems to be a simple disease to many, without timely treatment it can lead to serious complications.
Drops for bacterial conjunctivitis.
During an outbreak of the disease, the causative agents of conjunctivitis are adenoviruses 3, 7a and 11 serotypes. Sporadic cases are caused predominantly by adenoviruses types 4, 6, 7 and 10. Adenoviruses enter the body through airborne droplets or contact. The infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the eye through coughing, sneezing and dirty hands.
Risk factors:
- contact with an infected person;
- ARVI;
- mechanical damage to the eye;
- hypothermia;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- swimming in a polluted pool or pond;
- insufficient care of contact lenses;
- corneal surgery;
- stress.
Symptoms of eye damage from adenoviruses
The development of the disease can be triggered by contact with a patient, hypothermia, respiratory disease, eye injury, or surgery. From the moment of infection to the first symptoms, 5-7 days pass.
The first symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis include fever, headaches, severe signs of pharyngitis and rhinitis, and dyspeptic disorders. Sometimes submandibular lymphadenitis develops. Later, signs of conjunctivitis appear. The disease first affects one eye and gradually spreads to the second.
Local symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- swelling;
- redness (in all parts of the conjunctiva);
- discomfort;
- scanty discharge (mucous or mucopurulent);
- itching and burning;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- blepharospasm.
Forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
The catarrhal form of conjunctivitis is mild. There is minor local inflammation with mild redness and a moderate amount of discharge. Catarrhal form is easy to cure; as a rule, the disease goes away within a week. Complications from the cornea are usually not observed.
The follicular form is accompanied by blistering rashes on the mucous membrane of the eye. Follicles are small and large, dotted, translucent. In mild cases, the rash is localized in the corners of the eyelids, but usually covers the entire mucous membrane. The conjunctiva becomes loose and infiltrated.
Despite the fact that follicular rashes resemble the first stage of trachoma, doctors rarely make the wrong diagnosis. This is due to the fact that with trachoma there are no symptoms of nasopharyngitis and fever, and the rash collects on the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid.
The filmy form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is observed in 25% of patients. A thin grayish-white film forms on the mucous membrane. In mild cases, the film is removed with a cotton swab, but in severe cases, a dense overlay is formed, which is fused to the conjunctiva. After removing the film, the mucous membrane may even bleed.
With membranous conjunctivitis, body temperature rises to 38-39°C and lasts for 3-10 days. Due to the similarity of symptoms, eye damage may be confused with diphtheria.
Sometimes with membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis, subconjunctival hemorrhages and infiltrates occur. These phenomena completely disappear after treatment, sometimes scarring of the mucous membrane is noted as a complication.
It is also possible that bacterial or toxic-allergic conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome, keratitis, otitis, tonsillitis and adenoiditis can be associated.
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is often diagnosed in young children and middle-aged adults. Depending on the severity, the disease can last 1-3 weeks. The infection enters the eyes from dirty hands, household items, or through airborne droplets. The latter route of transmission is observed quite rarely, but the danger cannot be excluded.
When a patient presents with symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis, the ophthalmologist should find out the presence of contacts with patients. Examination reveals symptoms of conjunctivitis, catarrhal changes in the upper respiratory tract and lymphadenitis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes serological, virological and cytological tests. At an early stage, adenoviral conjunctivitis can be detected using immunofluorescence testing. It allows you to find specific viral antigens in a smear.
Cytological examination of a smear for adenoviral conjunctivitis shows destruction of the epithelium, breakdown of chromatin, vacuolization, hypertrophy of the nucleoli and formation of a nuclear membrane. The cytogram contains cells predominantly of the mononuclear type.
The polymer chain reaction is more informative; it detects adenovirus DNA in conjunctival scrapings. The complement fixation test and enzyme immunoassay detect antibodies in the blood serum. With adenoviral conjunctivitis, antibody titers increase fourfold or more.
Treatment methods
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis must be comprehensive, since not only the mucous membrane of the eye is involved, but also the ENT organs. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is treated on an outpatient basis, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs.
It is recommended to use drops of interferon and deoxyribonuclease: 6-8 times a day in the first week and 2-3 times in the second. The use of antiviral ointments (tebrofenovaya, bonaftone, adimalovaya, florenalovaya, rhiodoxolovaya) is effective.
To prevent secondary infection, antibacterial drops and ointments are prescribed. Antihistamines are taken until complete recovery. To prevent xerophthalmia, it is recommended to use artificial tear substitutes.
What is prescribed for children with conjunctivitis:
- Antihistamines. Helps relieve swelling of the mucous membrane. Children are prescribed Zyrtec, Fenistil, Zodak. In severe cases, it is allowed to use Suprastin.
- Antiviral. Fight against conjunctivitis pathogens. Young patients are allowed to use antiviral drops Poludan, Tobrex, Oftalmoferon, Aktipol. In the first days you need to instill up to 8 times, reducing the dosage as you recover. Antiviral drops are prescribed for 8-10 days.
- Immunomodulatory. Help strengthen the immune system.
- Antibacterial drugs. Children can be prescribed universal Albucid drops.
- Preparations for the treatment of respiratory organs. To prevent recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to simultaneously treat the respiratory system. Children are prescribed vasoconstrictors (Nazol-Baby). After the vasoconstrictor drug, the nose is washed and antibacterial drops (Albucid, Isofra, Dioxidin, Polydexa) are instilled.
In case of severe damage, children are prescribed antiviral ointments. First, the mucous membrane is treated with a mixture of chamomile, tea or furatsilin, then the ointment is applied along the edges of the lower eyelid. You can use tebrofen ointment, Florenal, Bonafton. Sometimes doctors prescribe ointments with antibiotics (erythromycin, tetracycline). Ointments are used for 10-20 days.
Precautionary measures
Within 14 days after infection, the patient is a carrier of the infection, so precautions must be taken. If the disease is severe, the person may be dangerous to others for even longer.
To make it easier for a patient with adenoviral conjunctivitis to cope with the disease and not expose loved ones to danger, certain rules must be followed.
The patient is placed in a separate room, since adenoviruses are easily transmitted from person to person. It is necessary to minimize close contacts with family and especially with children.
The room should be ventilated and the windows should be darkened so as not to irritate the sensitive mucous membranes of the eyes.
Toilet items, hygiene products, bedding and dishes must be individual. A person caring for a patient must wash their hands thoroughly before and after each manipulation. This not only protects family members from adenoviruses, but also the patient himself from additional infections.
All medications and instruments for their use should be used by only one patient. All wipes and cotton swabs can only be used once. Handkerchiefs and pipettes must be sterilized. Family members can further strengthen the immune system.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis, the prognosis is favorable. Complete clinical recovery occurs in 2-4 weeks. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is dangerous due to severe complications, so at the first symptoms you should consult a doctor.
Timely treatment with antibacterial drugs allows you to get rid of symptoms in 4-7 days. Mild forms of conjunctivitis can be cured even without medications by following the rules of personal hygiene. Treatment for severe eye damage can last for months.
To prevent eye damage, you need to strengthen your immune system in every possible way and take vitamins. During the flu season, immunomodulatory drugs are recommended to be taken even by healthy people. It is important to pay attention to personal hygiene and cleaning, as well as regularly ventilate areas at home and at work. You need to wash your hands after every time you go outside or have contact with animals and people.
If ENT diseases develop, it is necessary to undergo treatment to the end. Redness of the eyes is a reason to rinse the mucous membrane with a weak solution of chamomile, manganese or furatsilin. If the redness does not disappear, you should consult a doctor.
Since outbreaks of adenoviral conjunctivitis are not uncommon in groups, it is necessary to immediately isolate the infected. It is recommended to ventilate and wet clean the premises.
Complications of adenoviral conjunctivitis
If characteristic symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is treated by an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist). Treatment of the disease cannot be delayed, as it can become chronic and bacterial conjunctivitis will appear. Complications develop when viruses infect other structures of the eyeball.
Most often, inflammation affects the cornea. Point opacities occur, visual acuity decreases. Depending on the severity of adenoviral conjunctivitis and the state of the immune system, these complications can develop within 1-12 months. Without treatment, corneal opacities will last a lifetime and may develop as a cataract in the future. Irreversible vision loss is possible.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis requires attention. Eye damage can be treated quickly and easily, but if the doctor’s recommendations are ignored, severe complications may develop. Therefore, you should not self-medicate if symptoms of conjunctivitis occur.
Source: https://BeregiZrenie.ru/konyuktivit/adenovirusnyj-konyunktivit/
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis (pharyngo-conjunctival fever) is an infectious and inflammatory disease caused by adenoviruses and occurring with signs of damage to the conjunctiva (swelling of the eyelids, discharge from the eyes, burning, pain), symptoms of nasopharyngitis and increased body temperature. Outbreaks of the disease are most often recorded during the cold season among children attending organized groups.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Causes and risk factors
Sporadic cases of adenoviral conjunctivitis are most often caused by adenovirus types IV, VI, VII and X. Epidemic cases are usually caused by adenoviruses III, VIIa and XI types.
The infection is transmitted through household contact or airborne droplets. When sneezing, coughing or through dirty hands, the adenovirus enters the mucous membrane of the eyeball.
Risk factors that increase the risk of developing adenoviral conjunctivitis are:
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- injuries of the organ of vision (including surgical ones);
- non-compliance with the rules of wearing and caring for contact lenses;
- swimming in public pools and open reservoirs.
From the moment of infection until the first symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis appear, 2 to 10 days pass (in most cases, the incubation period is 5–7 days). During their life activity, adenoviruses lead to the destruction of epithelial cells, which is characterized by nucleolar hypertrophy, chromatin breakdown, and vacuolization.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical course, three forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- membranous.
The first two forms of the disease can be observed in patients of any age, and the latter occurs mainly in children.
In most cases, adenoviral conjunctivitis ends in complete recovery after 15–30 days.
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
The first symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are:
Headache, lacrimation, fever are the main symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
After a few days, the body temperature decreases, and then it rises again. At this moment, patients begin to show signs of damage to the conjunctiva, first in one and then in the other eye:
- redness and swelling of the eyelids;
- itching;
- burning;
- foreign body sensation;
- mild blepharospasm;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- light discharge of a mucous or mucopurulent nature.
Hyperemia (redness) of the conjunctiva covers all its parts, and also extends to the lower and semilunar fold, the lacrimal caruncle.
The catarrhal form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is characterized by mild symptoms of local inflammation. The amount of discharge is insignificant, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes is moderate. The duration of the disease does not exceed a week. Complications from the cornea do not develop.
With follicular adenoviral conjunctivitis, follicles (small vesicles) 1-2 mm in size, filled with translucent gelatinous contents, appear on the mucous membrane of the eyes. They can cover the entire surface of the mucous membrane or concentrate in the corners of the eyelids.
Attention! Photo of shocking content. To view, click on the link. Adenoviral conjunctivitis in children in 25% of cases is presented in a membranous form. The disease is characterized by the appearance of thin, delicate films of a grayish-white color on the conjunctiva.
In most cases, they can be easily removed with a cotton swab, but sometimes they take the form of dense fibrous deposits adhered to the mucous membrane. In this case, they are difficult to remove; after removal, the areas of the conjunctiva under them bleed.
In some patients, infiltrates and hemorrhages form in the subconjunctival space. After recovery, they completely resolve.
With membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis in children and most adults, the general condition suffers: body temperature rises to 38.5–39.5 ° C, general malaise, weakness, and headache appear. The duration of the febrile period ranges from 3 to 10 days.
- 16 causes of bleeding in the eyes
- 10 interesting facts about eyes and vision
- 6 eye changes that indicate disease
Diagnostics
It is possible to assume pharyngo-conjunctival fever in a patient if there is a history indicating contact with a patient suffering from this disease. During the examination, attention is paid to the combination of signs of conjunctivitis with regional lymphadenopathy and inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out by virological, cytological and serological research methods. For early diagnosis of the disease, an immunofluorescent method is used, which makes it possible to detect specific viral antigens in the mucous membrane of the eye.
Adenovirus DNA can be detected in scrapings from the conjunctiva using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is highly informative.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation reaction (FFR) allow us to determine the content of antibodies to adenoviruses in blood serum.
For adenoviral conjunctivitis, the diagnostic criterion is an increase in the concentration of antibodies by at least 4 times.
ELISA for adenoviral conjunctivitis reveals an increase in antibodies to adenoviruses by more than 4 times
To isolate and identify adenoviruses in cell culture, a virological study of discharge from the conjunctiva is performed.
Sporadic cases of adenoviral conjunctivitis are most often caused by adenovirus types IV, VI, VII and X. Epidemic cases are usually caused by adenoviruses III, VIIa and XI types.
In the follicular form of adenoviral conjunctivitis, differential diagnosis is carried out with trachoma. With trachoma, the follicles are localized in the upper eyelid, and in addition, the disease is not accompanied by fever and symptoms of nasopharyngitis. The filmy form of adenoviral conjunctivitis is in some cases mistaken for ocular diphtheria.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
Therapy for adenoviral conjunctivitis is carried out on an outpatient basis. In the first week of the disease, antiviral drugs are instilled into the conjunctival sac 6–8 times a day. In the second week, the frequency of their use is reduced to 2-3 times a day. Ointments with an antiviral effect can also be used, which are placed behind the eyelids 3-4 times a day.
In order to prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, the use of eye drops and ointments with antibiotics or sulfonamides is indicated.
Antiviral eye drops are prescribed to treat adenoviral conjunctivitis.
During the course of treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis, patients are prescribed antihistamines.
To prevent the development of xerophthalmia (dry eye syndrome), patients are recommended to instill moisturizing artificial tear eye drops several times a day.
Possible consequences and complications
Delayed or inadequate treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis can cause complications:
Forecast
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable, with complete recovery after 15–30 days. If a patient develops dry eye syndrome, it becomes necessary to use moisturizing eye drops for a long time.
Prevention
- Prevention of infection with adenoviral conjunctivitis includes timely isolation of sick children from an organized group, regular wet cleaning, ventilation of premises, as well as careful adherence to personal hygiene rules.
- Swimming pools require careful monitoring of chlorination and water compliance with current sanitary standards.
- To prevent iatrogenic infection of patients with adenovirus infection, it is necessary to thoroughly sterilize and disinfect medical instruments (eye sticks, pipettes), and carry out routine and general cleaning in the ophthalmology office using disinfectants and subsequent quartz treatment.
- Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Source: https://www.neboleem.net/adenovirusnyj-konjunktivit.php
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is an acute infection of the mucous membrane of the eyes caused by adenoviruses. Adenoviral conjunctivitis occurs with fever, symptoms of nasopharyngitis, local symptoms (swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, lacrimation, burning, pain, itching, discharge from the eyes). Diagnosis of adenoviral conjunctivitis is carried out by an ophthalmologist, taking into account the data of a bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva and PCR scraping. Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis includes instillation of antiviral and antibacterial drugs and eye ointments.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis (pharyngo-conjunctival fever) is a highly contagious infection caused by adenoviruses and occurring with inflammatory damage to the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract (
pharyngitis
), increased body temperature. IN
ophthalmology
Epidemic outbreaks of adenoviral conjunctivitis are usually recorded in the autumn-spring period, mainly in organized children's groups.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
The causative agents of adenoviral conjunctivitis during epidemic outbreaks are adenoviruses of serotypes 3, 7a, 11; in sporadic cases – adenoviruses 4, 6, 7, 10 types. The modes of transmission of adenoviral conjunctivitis are airborne or contact.
Adenovirus enters the mucous membrane of the eyes by sneezing, coughing, or direct infection from contaminated hands. From the moment of infection to the appearance of clinical symptoms, 3 to 10 days pass (on average 5-7 days).
Increased risk factors are:
- contact with a patient with adenoviral conjunctivitis;
- hypothermia, ARVI;
- violation of hygiene;
- swimming in contaminated ponds and pools;
- eye injuries;
- non-compliance with the rules of wearing and caring for contact lenses;
- surgical treatment of corneal pathology;
- stress.
A cytological examination of a smear in patients with adenoviral conjunctivitis reveals destruction of epithelial cells, characterized by vacuolization, chromatin disintegration, nucleolar hypertrophy, and the formation of a nuclear membrane. The cytogram is dominated by mononuclear cells.
According to the characteristics of the clinical course, catarrhal, follicular and membranous forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are distinguished.
Catarrhal and follicular adenoviral conjunctivitis can occur at different ages; membranous conjunctivitis develops mainly in children. The clinic manifests itself 5-8 days after infection.
At the beginning of the disease, there is an increase in body temperature with pronounced symptoms of pharyngitis and rhinitis, headache, and dyspeptic disorders; submandibular lymphadenitis develops.
During the second wave of fever, signs of conjunctivitis appear, first in the area of one eye, and after 2-3 days - in the other eye.
Local symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis are characterized by swelling and redness of the eyelids, light mucous or mucopurulent discharge, foreign body sensation, itching and burning, lacrimation, photophobia, and moderate blepharospasm.
Hyperemia is expressed in all parts of the conjunctiva, extending to the lacrimal caruncle, semilunar and lower transitional fold.
Catarrhal form
Occurs with minor symptoms of local inflammation: slight redness of the eye mucosa, moderate amount of discharge. The course of catarrhal adenoviral conjunctivitis is mild, the duration of the disease is about one week. Usually there are no complications from the cornea.
Follicular form
It is characterized by the presence of vesicular rashes (follicles) on the mucous membrane of the eye.
Follicles can be small, pinpoint or large, translucent and gelatinous; located in the corners of the eyelids or covering the entire infiltrated and loosened mucous membrane, especially in the area of the transitional fold.
The follicular reaction superficially resembles the initial stage of trachoma, however, there are usually no diagnostic errors, since with trachoma there are no symptoms of nasopharyngitis or fever, and the rash is localized in the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid.
Membranous form
Occurs in a quarter of cases. It occurs with the formation of thin grayish-white films covering the mucous membrane of the eye.
Usually the films are delicate and can be easily removed with a cotton swab; but sometimes dense fibrinous deposits may form, adherent to the conjunctiva, which are difficult to remove from the inflamed mucosa. After removing the films, the exposed mucosa may bleed.
Sometimes pinpoint subconjunctival hemorrhages and infiltrates are detected, which completely resolve after recovery.
The outcome of membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis is often mucosal scarring. With membranous adenoviral conjunctivitis, the general condition suffers: a high fever develops (up to 38°C–39°C), which can last from 3 to 10 days. The filmy form of adenoviral conjunctivitis can be mistaken for diphtheria.
If adenoviral conjunctivitis is suspected, the ophthalmologist determines whether there is a history of contact with a patient with pharyngo-conjunctival fever. On examination, symptoms of conjunctivitis are revealed in combination with catarrhal changes in the upper respiratory tract and regional lymphadenopathy.
To isolate adenovirus, laboratory serological, cytological, and virological methods are used. Early diagnosis of adenoviral conjunctivitis is carried out using the immunofluorescence method, which allows the detection of specific viral antigens in a smear from the mucous membrane of the eye.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which detects adenovirus DNA in a conjunctival scraping, is informative.
Antibodies to adenoviruses in blood serum are detected using the complement fixation test (CFR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The diagnostic criterion for adenoviral conjunctivitis is an increase in antibody titer by 4 or more times.
In order to isolate and identify adenovirus in cell culture, a bacteriological examination of a smear from the conjunctiva is carried out.
Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis is carried out on an outpatient basis using antiviral agents.
Local instillations of interferon and deoxyribonuclease in drops are prescribed 6-8 times a day in the first week of the disease and 2-3 times a day during the second week.
Placing ointments behind the eyelids (tebrofenova, florenal, bonaftone, rhiodoxol, adimaleva) is also used as antiviral therapy.
To prevent secondary infection, it is advisable to use antibacterial eye drops and ointments. Until complete clinical recovery in adenoviral conjunctivitis, antihistamines are indicated. To prevent the development of xerophthalmia, artificial tear substitutes (for example, carbomer) are used.
The prognosis for adenoviral conjunctivitis is favorable: usually the disease ends in complete clinical recovery after 2-4 weeks. When dry eye syndrome develops, long-term use of tear substitutes is required.
Prevention of outbreaks of adenoviral conjunctivitis in groups consists of timely isolation of sick people, ventilation and wet cleaning of premises, and personal hygiene.
In the ophthalmologist's office, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect and sterilize instruments (pipettes, eye sticks), clean them using disinfectants, and quartz.
In swimming pools, it is necessary to control the water chlorination regime in accordance with current standards.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/ophthalmology/adenoviral-conjunctivitis