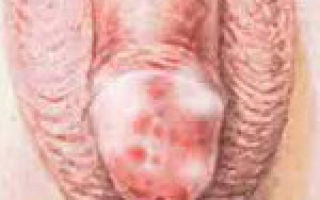
Due to their anatomical characteristics, the male external genitalia are constantly in contact with the environment. The skin of the glans penis and the inner layer of the foreskin are relatively sensitive to aggressive factors and are relatively easily inflamed. Balanitis is an inflammation of the skin of the glans penis. Posthitis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the foreskin. Since, in the presence of the foreskin, its inner layer always comes into contact with the head, the inflammation spreads to both elements. Consequently, posthitis and balanitis in the vast majority of cases develop simultaneously and are combined under one term - balanoposthitis. Of course, this disease can only develop in uncircumcised men, since otherwise there is no foreskin.
Types and symptoms of balanoposthitis
The disease is divided into many types depending on what caused its development. When describing each subtype of the disease, its most characteristic clinical manifestations will also be indicated.
Simple catarrhal balanoposthitis
It is one of the most common subtypes that doctors most often have to deal with.
A patient develops such balanoposthitis after contact with various irritants (chemical, mechanical). Often the cause of the development of the disease is a man’s failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene.
Gradually, smegma accumulates under the foreskin, which is a good breeding ground for bacteria and fungi.
The man develops the following symptoms:
- pain in the area of the head of the penis;
- the foreskin turns red and swells;
- purulent contents accumulate between the head and foreskin;
- phimosis, urinary retention - all this threatens the patient in the absence of timely treatment.
Candidal balanoposthitis (erosive)
Not only women can get candidiasis. Relatively often, this disease also affects men. In most cases, urogenital candidiasis manifests itself in the form of balanoposthitis.
- The head of the penis and the inner layer of the foreskin swell and become bright red.
- Sometimes separately located bright spots appear on the head.
- Due to the activity of fungi, a cheesy discharge is constantly present on the head, which has a rather unpleasant odor and provokes itching and burning.
- In the absence of radical and timely treatment, red spots can progress to the stage of erosion or even ulcers, which are located on the skin of the head or foreskin.
Chronic balanoposthitis
This variant of the course of the disease develops in cases of balanoposthitis that are caused by pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases, the herpes virus, and are a consequence of the progression of diabetes mellitus. The form is dangerous because there is a high probability of developing urethritis and prostatitis.
The infection travels up the urinary tract and can reach the kidneys (pyelonephritis) because it has enough time to do so. In cases where the pathogen penetrates the vas deferens, inflammation of the epididymis can develop, and in the most severe cases, cause infertility.
- The glans penis of a man is characterized by some dryness, slight redness and soreness - this is the main manifestation of chronic balanoposthitis.
- In some cases, the symptoms are so minor that the man does not even suspect anything about the ongoing process.
Acute balanoposthitis
Acute balanoposthitis is provoked by staphylococcal or streptococcal microflora. It is characterized by the following manifestations:
- it all starts with minor painful sensations in the area of the head of the penis and foreskin, over time all this intensifies;
- the skin of the head turns red, swells somewhat, and the patient begins to experience severe itching.
If it is not treated in a timely manner, the disease is likely to progress to the chronic stage.
Recurrent balanoposthitis
This form is characterized by alternating periods of remission and relapse. In those times when the disease recedes, the patient does not worry about anything, and he does not go to the doctors. Periodically, exacerbations occur, and all the symptoms return. The symptoms are similar to those that develop in the acute form, but are slightly less pronounced. It turns out that a man always has a risk of developing complications of the disease.
Acute purulent balanoposthitis
This form of the disease is provoked by pyogenic microflora: staphylococci, streptococci, yeast fungi. The likelihood of developing this form especially increases in patients with diabetes, since bacteria can develop under better conditions.
- Deep lesions of a purulent-necrotic nature appear on the head of the penis and the inner layer of the foreskin.
- The head of the penis is swollen and has a bright red color, which indicates an active inflammatory process.
Ulcerative balanoposthitis
If you do not seek treatment in a timely manner, the disease may progress from milder stages to an ulcerative form.
- Numerous small ulcers appear on the surface of the inflamed head. In this case, even simple walking causes discomfort to a person, urination is painful, and sexual intercourse is impossible.
- Violation of the integrity of the skin makes the body defenseless against many harmful factors. As a result, microorganisms are more likely to penetrate inside and cause inflammation of the lymph nodes of the groin area.
Traumatic balanitis and balanoposthitis
In most cases, the cause of the development of this form is not an injury received as a result of a blow or any accident. Wearing underwear that is too tight is the main reason for the development of the disease.
If the laundry is not rinsed thoroughly enough after washing, large amounts of detergent may remain on it, which, upon contact, will cause a minor burn to the skin of the penis and provoke traumatic balanoposthitis.
- Redness and swelling of the glans penis can be observed both on the entire surface and locally, at the site of application of the unfavorable factor.
- If the impact was significant, then the shaft of the penis, where the skin is less sensitive and better protected, may also change.
Keir's erythroplasia and Zoon's balanitis
These are two outwardly similar diseases with radically different prognoses. Zun's balanitis has a benign prognosis, but erythroplasia is a disease with a malignant course that requires immediate treatment with radical methods, since in the most severe case the patient's life may be in danger.
- It all looks like atrophy of the skin on the head of the penis. Pink plaques gradually appear that do not merge with each other.
- If we are talking about a very advanced case, then vegetation, erosion and ulcers can be found on the head.
- What is noteworthy is that the patient is practically not bothered by anything except the changed appearance of the penis.
Adhesive balanoposthitis
As a result of this disease, the head of the penis cannot be exposed when emerging from the foreskin. In this case, all tissues swell, become red and painful. Most often, this balanoposthitis develops in children, since their foreskin fits the head more tightly, and many still have physiological phimosis.
For this form of the disease, doctors very often offer a surgical treatment method - circumcision (circumcision of the foreskin).
Allergic balanoposthitis
Like all other allergic diseases, it manifests itself after the skin of the foreskin and the head of the penis comes into contact with an allergen.
Most often, allergies to the external genitalia are provoked by: latex condoms, other contraceptives, personal hygiene products with a large number of chemical additives, flavors and dyes.
It is relatively rare that the penis is affected when an allergen gets ingested.
Symptoms of allergic balanoposthitis:
- severe itching;
- allergic rash;
- swelling of the glans and foreskin of the penis;
- blisters and minor erosions.
Nonspecific balanoposthitis
It develops in most cases in patients with diabetes or alcohol abusers. A characteristic feature is that at the beginning of the disease, inflammation of the head is slightly expressed, but subsequently the process becomes so activated that phimosis develops.
Liquid pus is discharged from the patient's preputial sac (the space between the head and the foreskin). Doctors always strive to cure the patient before exposure of the head becomes impossible.
Otherwise, it is more difficult to observe the rules of personal hygiene and diagnose the disease.
Gangrenous balanoposthitis
With this form of the disease, a large number of foci of suppuration form on the affected skin. The general condition of the patient in this case is also an order of magnitude more severe than in other forms. The inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, and the body temperature reaches quite high numbers.
Gangrene of the head progresses very quickly, which necessitates timely treatment. Otherwise, bleeding may develop in the early period, and deformation of the penis may develop in the later period due to the proliferation of connective tissue.
In the most severe cases, complete destruction of the head is possible.
Irrital balanoposthitis
According to the mechanism of development, the form is close to traumatic. Inflammatory phenomena in patients occur in response to constant and regular irritation of the skin of the head of the foreskin:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- very frequent masturbation;
- excessive use of skincare products;
- lack of natural lubrication in the sexual partner;
- congenital narrowness of the flesh, etc.
Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
It all starts with a visit to the venereologist. The doctor conducts a general and local examination of the patient, collects a thorough history and listens to complaints.
Many patients believe that this is not all that important and do not treat this part of the diagnosis with due responsibility.
In fact, patients are advised to prepare in advance for a visit to the doctor, think about hygiene and remember all the factors that could cause the disease or increase the likelihood of its development.
It is absolutely impossible to hide important facts from a doctor, even if it is embarrassing to talk about them. The doctor will not tell everyone around about them, because he observes medical confidentiality. A hidden fact can lead doctors down the wrong path, and in the end the patient himself and his body will suffer. In addition to increasing the risk of side effects, you may end up taking a lot of unnecessary medications.
- General clinical blood test - where doctors can detect changes indicating inflammatory phenomena in the body.
- A smear from the affected surface allows you to remove part of the pathological material, and subsequently doctors can deal with it in different ways:
- - examination under a microscope, which sometimes allows us to determine the type of pathogen;
- - sowing the resulting material onto a nutrient medium - subsequently a colony of microbes grows there, and doctors can easily determine its type;
- — special nutrient media allow you to test the sensitivity of microbes to antibiotics, which allows you to immediately prescribe the most appropriate treatment.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a modern diagnostic method that allows you to identify the causative agent of the disease with the highest accuracy, even from a small fragment of its genetic material, which is present in abundance in the discharge from the affected skin.
- Determining blood sugar levels can confirm the presence of diabetes in a patient, which predisposes to the development of certain forms of balanoposthitis.
- Testing for sexually transmitted diseases.
- If a malignant process is suspected - cytological and histological examination.
- An allergy test is most informative if the likely cause of inflammation is a hypersensitivity reaction.
Treatment of balanoposthitis
The tactics of doctors depend on what caused the development of the disease in each specific case.
- First of all, the patient must carefully observe all the rules of personal hygiene. Often the disease develops due to the fact that a man does not pay due attention to this aspect. As a result, smegma accumulates under the foreskin, and bacteria begin to multiply there.
- Antibacterial drugs are used by doctors in cases where it is proven that the cause of inflammation is microorganisms. Ideally, doctors should conduct tests to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to the drugs used.
- Antifungal substances are relevant for candidiasis balanoposthitis.
- Removing the foreskin is a fairly effective measure that doctors sometimes have to resort to. This operation is especially often performed in case of recurrent balanoposthitis, an adhesive form of the disease, when the likelihood of complications is high, and inflammation continues to arise between the foreskin and the head of the penis.
- If the etiology of the disease is allergic, then limiting contact with the allergen is the most effective and mandatory condition for cure.
- Elimination of phimosis - this measure is often necessary for young children, who often have physiological phimosis. Modern drugs allow you to open the head conservatively, using special ointments and performing exercises. Doctors can perform surgery, which also eliminates phimosis.
- During the treatment period, the man uses a special device (silicone retractor ring), which moves the foreskin back and fixes it there. Due to this, the head is cleaned faster and a kind of bag in which everything was previously collected is eliminated.
If you want to treat balanoposthitis with folk remedies, you should first discuss all the details with your doctor. If he approves this measure, it is important to remember: folk remedies should complement basic methods, and not replace them completely. Only in this case will it be possible to achieve a good result.
Source: https://bezboleznej.ru/balanopostit
Symptoms and causes of balanoposthitis (balanitis) in men: do not miss the onset of the disease!
Of all the infectious diseases that can worsen periodically or become chronic, balanoposthitis can be noted - an infectious disease that can be sexually transmitted.
When a man experiences a process characteristic of inflammation on the head of the penis, the disease is called balanitis; when it is accompanied by a process that is fraught with inflammation of the foreskin, fasting occurs; if the patient simultaneously has signs of both processes, the disease is called balanoposthitis.
Hide content
The first signs of balanoposthitis in men
This disease is characterized by an acute form - both the beginning of the process and its course.
Signs of incipient balanoposthitis are swelling and unusual redness of the foreskin and glans penis, tingling during urination, as well as upon completion of sexual intercourse.
If a patient has the following symptoms in addition to changes in the appearance of the head of the penis, then we can talk about the presence of balanoposthitis in a man:
- the appearance of erosive spots and ulcers on the penis;
- specific discharge with pus and odor from the genitals;
- itching, burning, discomfort. At the same time, personal hygiene procedures do not bring relief;
- enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes, as well as their soreness;
- swelling in the place where inflammation is caused;
- the same processes described also affect the inner part - the lining - of the penis;
- the man's movements become more constrained.
If immediate treatment is not started, the disease progresses and more serious symptoms are added to the already received symptoms, aggravating the patient’s condition:
- feeling of weakness, malaise, possible increase in body temperature;
- the discharge takes on a greenish color and becomes thicker;
- the mucous membrane begins to peel off even in the absence of movement;
- urination accompanied by severe pain.
If balanoposthitis is observed in a man for the first time, then usually it does not require a lot of time and effort to treat it.
If this disease occurs with periodic frequency, again and again causing anxiety to the patient, then the disease has acquired a chronic form. In this case, the disease can be triggered by a slight infection on the man’s penis.
Balanoposthitis tends to occur in a person at any age - both in children from infants to teenagers, and in elderly and even very old men.
In order for the doctor to be able to accurately determine the presence of balanoposthitis in a patient, it is necessary to prescribe some tests:
- blood test - both general and biochemical;
- urine examination using a general analysis;
- examination of secretions for bacteria;
- analysis for the presence of syphilis and HIV.
Additionally, the urinary tract can be examined using ultrasound to ensure confidence in the diagnosis. The doctor may also for the same purpose. Balanoposthitis is treated with ointments or surgery, depending on the form of the pathology. In some cases, home treatments are used, but a visit to the doctor is still necessary.
What are the causes of balanoposthitis in men?
Since this disease is infectious in nature, the pathogens that provoke it can be:
- microflora consisting of nonspecific bacteria - streptococci, anaerobic cocci;
- pathogens capable of sexual transmission;
- various viruses, not excluding human papillomavirus;
- presence of fungi.
The reasons that can cause the appearance of balanitis or balanoposthitis in a man can be either trivial - minor irritation when using a condom, followed by swelling, or more serious - fungi and bacteria that provoked the infection, and subsequently the disease itself.
The most common provocateurs of this unpleasant situation may be:
- use of personal intimate hygiene products that can cause allergies, itching and burning sensation;
- injury to the penis or injury to it;
- a developing infection of the penis that occurs when fungi or bacteria enter and spread to the skin around the penis in the presence of wounds and cracks;
- ignoring personal hygiene, both daily and after sexual intercourse;
- frequent washing of the genital organ, resulting in thinning of the skin and the appearance of dryness, which becomes prone to injury during sexual intercourse;
- diabetes mellitus, if present in a man, can provoke the appearance of balanoposthitis regardless of his age;
- if the head does not open completely due to phimosis, this situation also contributes to the appearance of balanitis;
- psoriasis can provoke this disease;
- balanoposthitis tends to occur as a complication of sexually transmitted infectious diseases (gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, etc.);
- frequently changing sexual partner;
- cold or hypothermia;
- kidney diseases.
The acute form of balanoposthitis can be divided into the following subtypes of this disease: simple; erosive; gangrenous .
The simple form is characterized by swelling and softening of the inner covering of the foreskin and head of the penis. Subsequently, erosive lesions of different sizes appear, accompanied by discharge with pus, as well as itching and burning.
The erosive form is characterized by the formation of dead skin that is white and separated by areas that turn into erosive spots with clearly defined edges.
The gangrenous form brings with it general weakness with accompanying fever. The inflamed head of the penis and foreskin are covered with deep purulent-necrotic ulcers of various sizes, which take a very long time to heal. In this regard, the development of phimosis is provoked.
The chronic form is divided into indurative (wrinkling of the head of the penis and its foreskin), ulcerative-hypertrophic, which lasts a long time with fewer symptoms.
The overwhelming majority are cases with a severe course of this disease, especially if the patient has an ulcerative or gangrenous form.
If the above parts of the penis are affected superficially - erosively, then the disease is easier.
In some cases, the patient may experience increased sexual excitability . This occurs due to the involvement of sensitive receptors at the initial stage of the disease.
The chronic form of balanoposthitis is characteristic of patients who have suffered from sexually transmitted diseases, in the presence of diabetes mellitus, herpes, mycosis, and other infectious diseases.
also be horny . It occurs infrequently, mainly in older men.
A characteristic sign of this type of balanoposthitis is the appearance on the head of the penis of a loose warty elevation, pink in color, and an ulcer in the form of a crater in its structure.
If the causative agent of gonorrhea, gonococcus, which usually accompanies acute gonorrhea, enters the body, then gonococcal balanoposthitis may occur .
The disease is characterized by copious amounts of discharge from the urethra. It is characterized by a catarrhal and erosive circular character.
Find out all about phimosis in boys: in what cases is it treated?
Problems conceiving, perhaps you just need to know how to treat aspermia? Here you will find a lot of useful information.
This page: https://man-up.ru/bolezni/andrologiya/fimoz/operatsiya-pri-fim.html describes the main methods of performing surgery for phimosis.
Men with diabetes are most susceptible to candidal balanoposthitis. Balanoposthitis also occurs as a complication after undergoing treatment for a disease with a course of antibiotics.
Phimosis can also become a provocateur of candidiasis balanoposthitis.
It is possible that a woman can become infected with this type of disease if her sexual partner is simply a carrier of the fungus. Once the fungus gets to a man, it poses a danger to him.
Symptoms of this disease can be reddened, swollen head of the penis and foreskin, and its irritation. The presence of red spots on the head of different sizes.
The main symptom of candidal balanoposthitis is the appearance of cheesy white discharge . There is also itching, burning, discomfort and an unpleasant odor.
To prevent the occurrence of balanoposthitis in various forms and types, a man must strictly observe personal hygiene, use personal protective equipment, promptly treat phimosis, if any, and also regularly visit a urologist.
You should also not delay visiting a doctor if you detect initial signs of an inflammatory process on the penis. If the factors accompanying the disease occur regularly, there is a need for examination of the partner.
Source: https://man-up.ru/bolezni/andrologiya/balanopostit/simptomy-i-prichiny-balan.html
Balanoposthitis - causes, signs, symptoms and treatment
Balanoposthitis is a fairly common inflammatory disease of the skin of the penis. According to statistics, every year 11% of men on Earth suffer from this disease.
Balanoposthitis in men, according to ICD-10 (international classification of diseases), is a double disease, as it involves an inflammatory process in both the head and the inner layer of the foreskin.
Online consultation on the disease “Balanoposthitis”.
Ask a question to the specialists for free: Urologist.
Causes of the disease
Acute balanoposthitis develops due to the following factors:
- mechanical damage to the penis;
- washing the foreskin with medications;
- increased concentration of salts in urea;
- uncontrolled use of various medications that lead to irritation of the skin of the head of the penis;
- an infection located in the genital tract, which got there from other organs or from an infected partner.
The reasons that cause the appearance of the disease determine the nature of its course. For example, balanoposthitis in men can be characterized by both the appearance of irritation and erosions on the skin.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of balanoposthitis are:
- burning and itching sensation in the penis area. It is the most common reason for visiting a doctor;
- redness and swelling of the foreskin;
- the appearance of foreign secretions that have an unpleasant odor and purulent nature;
- the presence of detachments of the upper tissue (erosion);
- growth of lymph nodes;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- high body temperature;
- phimosis (cessation of opening of the glans penis, which occurs due to the presence of edema).
If there is no timely treatment for balanoposthitis, then the process of tissue death in the penis area will soon begin.
Characteristic signs of the disease include:
- the appearance of edema;
- hyperemia (flush of blood) to the head of the penis;
- the appearance of spots with defined boundaries of different shapes, sizes and scarlet colors;
- burning and itching, which intensifies during urination and sexual intercourse;
- increased libido, which causes inflammation of the receptors on the head of the penis;
- curdled or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- cracks in the foreskin;
- fibrosis of the penis.
Symptoms and complications of balanoposthitis
Candidiasis balanoposthitis in men is a common type of disease that is caused by the yeast type Candida fungus. Typically, men need to be treated for balanoposthitis and balanitis at the same time. Most often the disease occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus. Rare cases suggest the development of the disease against the background of phimosis existing from birth or too long foreskin.
If the patient is diagnosed accordingly, then, in addition to taking medications (antibiotics, antifungal agents), it is necessary to follow a certain diet. The patient will need to completely exclude sweet, spicy or pickled foods from the diet. The consumption of alcoholic beverages is also strictly prohibited.
If a patient is diagnosed with a candida variety of the disease, he is also advised to abstain from sexual activity during treatment.
If the disease is caused by phimosis, then doctors must dissect the flesh of the penis, and in some cases the patient is also circumcised.
If phimosis is absent, then only conservative methods (broad-spectrum drugs) are used for treatment.
It is worth remembering that neglecting to see a doctor can cause inflammation of not only the penis, but also the lymph nodes in the groin, which will lead to the formation of gangrene, and in some cases, death. Therefore, a man should always remember the importance of maintaining genital hygiene.
Types and forms of the disease
The disease, depending on its occurrence and form of progression (according to ICD-10), is divided into:
- acute balanoposthitis. Has more pronounced symptoms and is characterized by faster progression;
- chronic balanoposthitis. It may have phases of remission and relapse, while the symptoms are less pronounced.
The main forms of balanoposthitis include:
- ordinary. Accompanied by inflammation, which over time contributes to the appearance of erosive wounds from which pus is released;
- gangrenous. This type is often complicated by the presence of phimosis. With gangrenous balanoposthitis, the resulting ulcers take a very long time to heal;
- erosive. A large amount of purulent discharge contributes to the appearance of erosive areas that are white in color. Also, characteristic erosive wounds with defined boundaries appear on the head of the penis.
Chronic balanoposthitis is presented in the following forms:
- candidal balanoposthitis. This type of disease affects men much less frequently than women due to the anatomical features of the location of the genital organs. Candidiasis balanoposthitis in males can be triggered by a weakened immune system. In this case, the foreskin is affected, on which a characteristic white coating forms. If it is removed, ulcers and redness may appear in its place. The patient complains of burning or itching during sexual intercourse or when urinating. Candidiasis balanoposthitis is contagious and is transmitted from an infected partner to a healthy one. Therefore, this disease should be treated in two partners at once;
- allergic balanoposthitis. The patient complains of symptoms typical of the disease (pain, itching, inflammation of the tissues of the foreskin). A characteristic sign is the appearance of blisters or spots. Such chronic balanoposthitis can be caused by the patient having an allergy to latex (a common cause of the development of pathology), eating foods with allergens, as well as the use of local contraceptives;
- circinar balanoposthitis. With this type, spots with clear boundaries form on the head of the penis. They usually arise due to the presence of chlamydial-type diseases or are one of the signs of Reiter's syndrome. Inflammation occurs on the penis. If left untreated, white or gray spots form on the surface of the penis. As a result, tissue necrosis develops. This type of disease is characterized by the appearance of ulcers that are gangrene-like;
- anaerobic balanoposthitis. It is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the prepuncial sac. Anaerobic balanoposthitis is usually provoked by gram-negative microorganisms and can occur in the form of erosion. A mild form of the disease has the following symptoms: the presence of a sticky coating on the head, as well as an unpleasant fishy odor. Anaerobic balanoposthitis requires specific treatment from a qualified specialist;
- ulcerative balanoposthitis. It is characterized by the appearance of a large number of ulcers from which pus is released. The disease is caused by fungi, staphylococci and other pathogenic microorganisms. The patient complains of swelling and a burning sensation on the head of the penis. In addition, the patient may be bothered by pain in the groin and general weakness of the body.
Complications that may arise from the disease include, in addition to phimosis, decreased sensitivity on the head of the penis. This is caused by the fact that the receptors atrophy during the inflammatory process.
If the infection gets into the urinary canal, it will also cause urethritis.
The most serious complication is paraphimosis, in which the head of the penis is pinched due to the fact that the foreskin begins to scar.
Diagnostics
A urologist makes a diagnosis to the patient. When a disease is detected, he prescribes the patient to undergo several tests, such as:
- taking material for bacterial culture. It is taken from the affected areas of the foreskin;
- conducting a potassium hydroxide test if the doctor suspects that the patient is developing a fungal type of illness;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to clarify the cause of the development of the pathological process.
It is noted that the disease is quite rarely caused by diseases that are sexually transmitted.
At the same time, chronic infection reduces the human body’s resistance to other diseases, which increases the likelihood of developing an illness caused by nonspecific flora.
In addition to the urologist, the patient will also be referred to an allergist and dermatovenerologist. He may be prescribed tests to detect diabetes mellitus, since the latter is a common cause of pathology.
Treatment of the disease
A treatment plan for the disease is developed by a specialist only after preliminary diagnosis. It is the results of tests and analyzes that can provide the most complete information about the patient’s health status. Treatment of balanoposthitis involves:
- conservative methods. Antifungal drugs are used to treat the fungal form of the disease. If hormonal levels or metabolism are disturbed, then treatment is adjusted taking into account this problem, since reduced immunity will not contribute to achieving the desired effect during treatment. To overcome the pathology, a man is prescribed Mikosist, Fluconazole or other similar drugs that are prescribed to him by a doctor. Ointments are also used, which are a convenient and inexpensive way to relieve symptoms. Most often, specialists prescribe xeroform or prednisolone ointments. If there is deep damage to the tissues of the penis, doctors must prescribe antibiotics;
- surgical intervention. It is carried out if a severe stage of the disease has developed, which is often accompanied by phimosis. To cure the patient, doctors resort to cutting the foreskin, which has been narrowed as a result of inflammation. Also, in some cases, circumcision of the foreskin is required;
- unconventional methods. These include the use of folk remedies, such as compresses, as well as baths with the addition of herbal tinctures.
Circumcision of the foreskin
For various forms of the disease, a urologist may prescribe:
- medications that are aimed at eliminating inflammation, removing the causative agent of infection and reducing symptoms;
- corticosteroids, combination drugs such as Levomekol or Triderm;
- medications that increase the body’s resistance to various pathogens;
- antifungal agents (for yeast-type balanitis), such as Nizoral or Clotrimazole;
- antibiotics if the patient is diagnosed with an anaerobic type of disease.
Self-medication can be dangerous to the health and even life of the patient, so folk remedies can only be considered as an auxiliary treatment that alleviates symptoms, but not as the main one.
In addition, treatment of balanoposthitis at home should be carried out only with the permission of the attending physician and under his constant supervision.
If the doctor has approved the use of certain treatments at home, they can be used, but very carefully.
First of all, when treating a disease at home, you need to remember the need to wash the glans penis. This can be done under running water with the addition of regular soap. Often this is enough to reduce the symptoms.
If balanoposthitis does not go away, then the head of the penis is additionally treated with antiseptic agents after each wash. You should not use iodine or potassium permanganate for washing at home - they will only cause dryness in the already inflamed tissue.
Among the traditional methods of treatment, the following are the most popular ways to alleviate the symptoms of pathology:
- black currant leaves. They are brewed in boiling water. The resulting decoction should be taken several times before meals to improve the general condition. In addition, in parallel with the decoction, it is recommended to eat fresh currant berries;
- To cure urethritis that appears as a result of illness, you need to pour milk over the parsley and then put it in the oven at low temperature. After a slight boiling of the milk, the resulting parsley decoction should be drunk every hour, a tablespoon;
- For inflammatory processes of the foreskin, a tincture of water paint is used. One spoon of this herb is poured into a glass of hot water and then infused. You need to drink the decoction 20 minutes before meals;
- If the patient has candidal inflammation, then the calendula flowers must be filled with olive oil. The resulting mixture is covered with a lid and left warm for 3 weeks. After this, you need to strain the olive oil and anoint the affected tissues with it.
Prevention
Urologists advise as preventive measures:
- maintain hygiene of the genital organs, in particular the foreskin;
- eliminate the pathogen locally (use antiseptics, herbal tinctures);
- carry out antiviral or antibacterial therapy. It is prescribed for each patient individually;
- exclude casual sex;
- use contraceptives, having first checked whether there are any allergies to certain drugs;
- do not eat allergens.
Source: https://SimptoMer.ru/bolezni/muzhskie-zabolevaniya/1019-balanopostit-simptomy
Balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis is an inflammation of the glans penis and prepuce. Symptoms include pain, swelling, rashes, and accumulation of secretions in the preputial sac. The diagnosis is established during a physical examination; to determine the cause, laboratory diagnostics are performed: microscopy of a smear from the urethra, bacterial culture for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics, PCR tests for STIs. A skin biopsy is performed in the absence of positive dynamics during therapy to exclude a neoplastic process. Treatment depends on the pathogenetic factor, it can be conservative (antibiotics, antihistamines, corticosteroids), in case of tumor pathology and in the absence of effect - surgical.
Balanoposthitis most often develops in boys aged 1 to 5 years and in men with high-risk sexual behavior (polygamous relationships, homosexuality, penile-anal contacts).
Experts say that 30-50% of men experience inflammation of the head of the penis and prepuce, expressed to one degree or another, at least once; this pathology accounts for 11% of all visits to the urologist. Most cases respond to conservative therapy.
Balanoposthitis of candidal etiology is especially difficult in people with decompensated diabetes mellitus, AIDS, and severe hypovitaminosis. The recurrent course is often provoked by cicatricial phimosis, which requires hospitalization in the clinical urology department and surgery.
A certain role belongs to immunosuppressive disorders of any origin (taking antibiotics or hormones, chemoradiotherapy, concomitant severe generalized infection).
Inadequate hygiene leads to the proliferation of microflora in the smegma, which initiates inflammation. In older men, balanoposthitis develops due to sclerotic processes between the head and the skin of the prepuce in the absence of sexual life.
The condition is caused by many diverse etiological factors:
- Specific diseases . Neisser's gonococci, Trichomonas, and chlamydia are the most frequently detected pathogens in genital infections. In 35-50% there is a combined composition of microflora. Urogenital candidiasis is complicated in 90% by inflammation of the head and prepuce. Also, an inflammatory reaction in this area is diagnosed against the background of herpes, HPV and donovanosis.
- Nonspecific diseases . In a child, inflammation of the genitals can develop due to childhood infections, acute respiratory viral infections, and sore throat. In adults, the cause of balanoposthitis is chronic diseases of the genitourinary system: prostatitis, urethritis, orchiepididymitis. Staphylococcus aureus and group B streptococci are the most commonly isolated bacteria. Recurrent balanoposthitis occurs in all patients with cicatricial changes in the prepuce.
- Traumatization . Violation of the integrity of the skin as a result of a bite, pinching of a trouser zipper, tearing of the frenulum during sexual intercourse or aggressive masturbation are the entry points for infection. Microflora can spread from the urethra during catheterization or bougienage. Secondary inflammation occurs after urological operations. Sometimes balanoposthitis is provoked by a smegmolith stone formed in the prepuce due to the thickening of infected smegma.
- Dermatological pathology . In men who are forced to use condoms or diapers due to incontinence, contact dermatitis and secondary balanoposthitis develop on the head of the phallus and the foreskin due to constant irritation by urine. Psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, etc. are accompanied by inflammatory changes in the genitals. Bowen's disease and Queyre's erythroplasia, both predictors of penile cancer, have similar presentations.
Agents that cause balanoposthitis are divided into infectious (pathogenic, opportunistic microorganisms) and non-infectious (trauma, burns, contact with chemicals, etc.).
In the genital area, the circulatory and lymphatic networks are extremely developed, which is manifested by pronounced exudation during inflammation, up to the development of phimosis and paraphimosis.
Increased temperature and humidity in the prepuce, the alkaline reaction of smegma (and in diabetes mellitus also glucose) contribute to the increased reproduction of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms and viruses.
Violation of hygiene rules, as well as frequent contact with aggressive environments, lead to the realization of pathogenic properties in conditional pathogens or to the predominance of pathogenic microflora over conditionally pathogenic ones. In children, balanoposthitis often develops after severe retraction of the foreskin due to phimosis, prolonged exposure to diapers, or the generalization of any infectious disease.
Balanoposthitis can be primary or accompany any pathological process (DM, tumor). According to the type of pathogen, specific and nonspecific balanoposthitis is distinguished, according to the nature of the course - acute or chronic, complicated or uncomplicated. Experts use a classification that takes into account the predominance of clinical manifestations, on the basis of which the following forms are distinguished:
- Simple catarrhal . The inflammatory process is slightly expressed; there are areas of hyperemia on the head of the penis and foreskin. This form is typical for men with latent STIs, for older patients with a burdened premorbid background (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular failure).
- Papular . Hyperemia is moderate, but nodular elements are visualized. This type of balanoposthitis is associated with lichen planus, psoriasis, and Queyra's erythroplasia.
- Scleroatrophic . It occurs in older people; upon examination, you can see cracks, erosions, areas of sclerosis and atrophy with a slight background hyperemia. Cicatricial phimosis is typical.
- Verrucous and vegetative. The appearance of growths and vegetations is preceded by human papillomavirus infection, urogenital tuberculosis, etc. Hyperemia is moderate.
- Granulomatous. It is typical for patients with severe immunosuppression as a result of the progression of opportunistic infections, for example, generalized urogenital candidiasis. Granulomatous growths accompany chronic recurrent balanoposthitis.
- Vesicular . Redness of the skin and the appearance of vesicles are preceded by severe itching. A typical example is herpetic rashes accompanied by reactive balanoposthitis.
- Pustular . Hyperemia is variable (from slight redness to pronounced), multiple pustules are visualized (for example, balanoposthitis against the background of donovanosis).
- Bullous . The appearance of blisters on the hyperemic skin indicates the toxic-allergic nature of the disease. The size of the blisters varies; without treatment and with continued contact with the provoking agent, erosions form.
- Erosive and erosive-ulcerative . It occurs in a number of pathologies: syphilis, Vincent's disease, tuberculosis.
- Gangrenous . Accompanies chancroid, and can also precede the fulminant form of Fournier’s gangrene. The most severe type of balanoposthitis with probable self-amputation of the penis and the development of fatal complications.
Clinical manifestations are variable and depend on the pathogen, the severity of the process, and concomitant pathology. The nature of skin rashes varies.
Common to all types is swelling, hyperemia (of varying severity), pain, limited mobility of the foreskin, and in dermatological pathology - itching.
The most favorable catarrhal form manifests itself clearly: patients complain of excruciating itching, severe pain in the affected area, burning sensation when urinating, swelling of the skin of the prepuce and glans.
With fungal balanoposthitis, as the infection progresses, deep cracks appear; due to increasing infiltration, the foreskin does not move. The discharge is whitish, with a kefir smell; films may be present on the surface of the inner layer of flesh and the head; after their removal, a bleeding wound remains.
Herpetic balanoposthitis is manifested by characteristic transparent vesicles, their contents gradually become cloudy, and the element itself resolves with the formation of a yellow-brown crust.
The temperature may rise, the general condition may suffer: weakness, chills, loss of appetite. In some patients, regional lymph nodes become enlarged.
The severity of the pain syndrome is due to the involvement of nervous tissue in the process, where the virus persists.
The more weakened the immune reactions are, the higher the likelihood of the vesicular form transforming into erosive-ulcerative and gangrenous inflammation.
In the gangrenous form, the general condition is severe, which can be explained by intoxication and fever, the genital organ is sharply enlarged in size, pus and ichor ooze from the tissues.
Tachycardia and a drop in pressure may be present, which is a predictor (harbinger) of possible bacteriotoxic shock.
Chronic balanoposthitis has mild symptoms: episodic hyperemia, no pronounced discharge from the prepuce, discomfort intensifies after sexual intercourse or physical activity.
Consumption of spicy foods and alcohol aggravates adverse symptoms.
Chronicization of the process often leads to atrophy; the skin of the genitals is dry, wrinkled, thin, easily injured and periodically bleeds.
Complications include phimosis (if balanoposthitis is primary), frequent relapses of infectious and inflammatory processes of the urinary tract, and impaired sexual function. The likelihood of developing penile cancer is higher in patients with phimosis and balanoposthitis.
Cases of the formation of smegmolites (stones from smegma) in the prepuce are described. In children, the infection often spreads to the upper urinary tract (pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis). With the gangrenous type, self-amputation of the penis may occur.
Against the background of weakened immunity, fungal septicemia and bacteriotoxic shock develop.
The etiological factor of inflammation of the head and skin of the preputial sac requires clarification. A morphological study is justified if balanoposthitis does not go away with persistent treatment.
Instrumental diagnosis is not required, with the exception of a penile neoplasm with reactive inflammation.
Laboratory diagnostics is aimed at a comprehensive examination, including the identification of diseases that support balanoposthitis (DM, AIDS, atherosclerotic processes, circulatory disorders). The diagnostic algorithm includes:
- History taking and examination . A urologist establishes a connection between inflammation and the causative factor: trauma, unprotected sexual intercourse, taking antibiotics, using spermicides, etc. In 30%, the provoking factor cannot be determined. During the examination, the nature of the rash and the condition of the regional lymph nodes are assessed.
- Lab tests. Initially, smear microscopy is performed. If the number of leukocytes and bacteria increases, further examination is indicated: PCR analysis for STIs, inoculation of biomaterial on nutrient media. Testing for HIV and syphilis is carried out. If there is information about the patient's travel to endemic areas, testing for donovanosis is justified. If genital tuberculosis is suspected, consultation with a phthisiourologist and special tests are recommended.
Therapeutic measures depend on the cause, with priority given to treatment of the underlying disease. The patient is explained the need for personal hygiene. With venereal genesis, both partners receive drugs.
Men with allergies should avoid irritants (fragrant soaps, gels, cosmetic sprays). During sexual intercourse, if there is insufficient hydration, you can use a neutral lubricant.
Treatment options for balanoposthitis include:
- Systemic medication . Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to suppress secondary infections, antihistamines and corticosteroids are prescribed for itching and allergic manifestations. For herpes and HPV infections, antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are used. Antifungal drugs are used in combination with hormone therapy for candidiasis against a background of weakened immunity, and for generalization of lesions.
- Local . Hormonal, antibacterial and antifungal drugs can be used topically in the form of creams, ointments, and sprays. Irrigation with antiseptic solutions helps relieve symptoms of bacterial infections. Children are prescribed warm baths with decoctions of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Operational . Complicated balanoposthitis occurring against the background of dermatological diseases, accompanying cancer and precancerous pathologies, with cicatricial phimosis is an indication for surgical treatment - circumcision (circumcision). If the cause of inflammation is phimosis with a narrow ring of the foreskin, preputioplasty may be performed. If there is a concomitant tumor of the penis, the extent of the operation depends on the type of tumor and stage.
The prognosis for primary uncomplicated balanoposthitis is favorable, for secondary balanoposthitis it depends on the concomitant pathology. If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical treatment always relieves unpleasant symptoms.
Prevention involves following the rules of intimate hygiene, avoiding casual sex without a condom, and undergoing regular preventive examinations by a urologist.
Boys' genitals need careful care: diapers should be changed in a timely manner, diaper rash should be prevented, and there should be no attempt to roughly move the head of the penis in case of physiological phimosis.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_urology/balanoposthitis