- And although hydrocele is not a dangerous or serious disease, it is difficult to get rid of.
- You can try both the standard surgical method recommended by doctors and others, which in some cases also lead to results.
- These include drug therapy, physiotherapy and traditional medicine.
- And sometimes complex treatment may be required, using all these types of treatment.
What is hydrocele
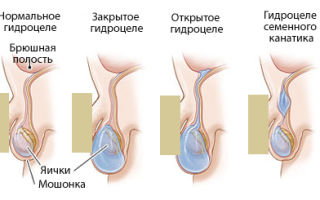
Dropsy is a membrane that consists of epithelial tissue. It may be covered by skin if it is on the surface of the body. In this case, dropsy is internal. Hydrocele is an accumulation of serous fluid inside the testicles. Dropsy can progress or remain unchanged for a long time, at the same size.
Types and causes of the disease
The main classification is the division into congenital and acquired types.
The disease appears either in the womb or during adulthood. Sometimes the formation of clusters is not characterized by external causes and occurs even in healthy adult men.
The main cause of congenital dropsy is when the testicles descend in the womb, the place that was formed as a result of their movement must be overgrown. However, sometimes this does not happen. Dropsy develops in the resulting pocket. This process usually occurs around the ninth month of pregnancy.
Symptoms, examinations and diagnosis
The main symptoms of hydrocele:
- Swelling of the genital area . Sometimes swelling occurs and then disappears without any particular reason. If we are talking about dropsy, then the problem will manifest itself at night. During the day, the fluid is distributed throughout the abdominal cavity, releasing the channels. Therefore, the increase may not be observed for some time, but later it appears again.
- Pain . Pain sensations appear in the scrotum area, which are expressed slightly. Rather, it is characterized by severe discomfort, especially when pressing on the problem area.
- Dropsy is often accompanied by an inflammatory process . It is characterized by the presence of severe redness. When the skin and internal cavities become inflamed, the pain becomes more pronounced and brings a lot of discomfort. Inflammatory processes in dropsy need to be removed, this requires visiting a doctor and prescribing adequate therapy.
- If the dropsy is not red, but is very painful, we may be talking about a previous injury . This caused fluid accumulation and swelling.
- If dropsy is accompanied by an increase in temperature, we are talking about the development of a concomitant infection . In this case, there is a feeling of heaviness in the groin.
As part of its implementation, the organs are illuminated with a special device, with the help of which it is possible to extract light with the necessary indicators.
Ultrasound (ultrasound) examination is also prescribed. It will help to establish with high accuracy how dropsy occurs, where exactly it is concentrated, and what its size is.
- Other methods are also used for diagnosis, which depend on the doctor’s suspicions of the development of other diseases, since in some cases edema forms as a result of abnormal deviations.
- Video: “What is testicular hydrocele”
How to cure dropsy without surgery
The method of treating dropsy depends on the characteristics of the disease. If we are talking about a newborn, then dropsy may go away on its own . In this case, the attending pediatrician should give recommendations.
In some cases, in babies, part of the intestine gets into the lumen that has formed. When a child begins to eat solid foods, it can cause serious difficulties characterized by severe pain.
This situation is very dangerous and parents and doctors will have several hours to correct the situation as it can be fatal.
Medicines
Medicines for dropsy (hydrocele) are also used. The need for their appointment should be determined by certain features. So, dropsy is always accompanied by some kind of disturbance in the functioning of the genital organs due to bacterial load.
This is explained by the fact that the contents press on healthy tissues, friction occurs constantly, and blood circulation worsens. This causes the development of a pathogenic environment. If you do nothing, inflammation may appear.
Also, in addition to antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
They help cope with swelling, especially when the disease is infectious. Anti-inflammatory drugs generally alleviate the condition with a complex course of the disease and a gradual increase in dropsy.
Physiotherapy
With the help of physiotherapy, it is possible to achieve relief of the syndrome if the dropsy is not in the active phase of development . If it is constantly growing, procedures are prescribed that can slow down and subsequently completely stop the increase in the problem area for subsequent fight against the disease.
Traditional methods
Instead of tea, you can use a decoction of watermelon seeds - this remedy will help improve blood circulation, help get rid of swelling, and remove excess fluid from the body. This drink will become a natural anti-inflammatory agent.
Onion juice also helps a lot . You can take one onion, chop it finely, add a few tablespoons of sugar. After a few hours, when a sufficient amount of juice has formed, you need to drink it (2-3 tablespoons).
Black radish juice with honey will also help . First, you need to take a third of a glass, and divide this intake into two times. Next, gradually, you need to increase the volume of drink consumed. Maximum - drink two glasses a day (again, divide by two - morning and evening, regardless of meals).
- You can drink half a glass of pumpkin juice
- Video: “Treatment of hydrocele”
How is the treatment carried out?
Non-surgical treatment does not involve only taking medications orally, and traditional medicine is not always sufficient. If dropsy does not grow, if there is no inflammation, you can limit yourself to these methods. But in cases where the situation does not change, we have to act more radically.
Thus, sclerotherapy is one of the most popular ways to solve the problem , but this technique does not always help to completely get rid of the disease. With the help of certain manipulations, which are carried out under local anesthesia, everything unnecessary is pumped out from the cavity where the fluid has accumulated.
The effect can be maintained for six months, but the advantage is that during this time a person has every chance to improve his health through the use of traditional methods and think about what to do next.
Also, in some cases, the operation simply cannot be performed . This usually occurs for medical reasons or in older people. Then periodic sclerotherapy becomes the solution. Once every six months, the patient visits the doctor and undergoes appropriate manipulations.
You must understand that the operation still gives a longer lasting effect, in addition, it allows you to get rid of both the disease and its consequences once and for all. In this case, the liquid is not simply pumped out, but a channel leading into the pocket is sutured, where the contents accumulate.
That is, after such manipulation and completion of the recovery course, the patient no longer waits for dropsy to appear again and for everything to happen again.
Bottom line
- Dropsy appears in men of different ages ; it can be congenital or acquired.
- Symptoms of dropsy are pain, heaviness in the scrotum, redness, swelling, difficulty moving, increased body temperature, and general malaise.
- Diagnostics includes an external examination by a doctor, diaphanoscopy, and ultrasound examination.
- Treatment is carried out with the help of surgery , but in addition to it, it is possible to prescribe antibacterial, anti-inflammatory therapy, the use of traditional methods, physiotherapy, including sports.
- An effective method of non-surgical solution to the problem is sclerotherapy.
- Sclerotherapy does not always help get rid of dropsy - the effect can last for about six months, and then, if the canals are not sewn up, the fluid again accumulates in the pockets and either repeated sclerosis or surgery is required.
Source: https://kakbyk.com/bolezni/patologii-moshonki/bezoperatsionnoe-lechenie-vodyanki-yaichka.html
Hydrocele of the testicle - symptoms, treatment, causes of the disease, first signs
The process of diagnosing this disease has never caused any particular difficulties for doctors. As already mentioned, urologists and surgeons diagnose this problem in men. Diagnosis is based on the patient's complaints and medical history.
The patient is asked whether he or she has previously had a groin injury or acute and chronic diseases associated with the external genitalia. Have there been any surgical interventions in the scrotum area?
Having all this information, the doctor will be able to accurately determine the diagnosis, after which a full medical examination will be carried out.
The first thing the doctor will pay attention to will be a greatly enlarged scrotum, or the entire organ. How much the organ will be enlarged depends on factors such as the duration of the disease and its possible causes.
During palpation, the doctor determines the pear-shaped testicles, which are dense, elastic and fluctuating in consistency. If the formation in the testicles is shaped like an hourglass, this indicates that fluid from the testicles is flowing through the inguinal canal.
In this case, the skin usually remains the same as usual; it can be easily folded into several folds. The palpation procedure will not cause discomfort to the patient if we are talking about a chronic form of the disease.
But in an acute form of hydrocele, pain sensations of varying degrees will occur in different areas of palpation.
If there is little fluid in the membranes, the testicle can be felt in the lower part of the scrotum. In the case of an excessive degree of increase in the size of the scrotum, the testicle cannot be felt, or it is inaccessible.
Procedures for diagnosing hydrocele
In order to confirm this diagnosis, two procedures are used: ultrasound of hydrocele and diaphanoscopy.
Diaphanoscopy is the fastest method of determination and uses the natural properties of light. If there is liquid between the layers, the light passing through the scrotum will be uniform, but if there is a hernia inside the scrotum, the light will no longer be able to pass through.
Ultrasound of the scrotum can detect the disease with higher reliability. With its help, you can determine the volume of fluid inside and the possible cause of the hydrocele (whether it is a tumor or an infectious inflammation). This method can distinguish dropsy from varicocele, hernia, orchitis, epididymitis and tumor of the spermatic cord.
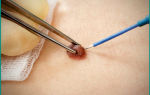
In case of difficulties in identifying the causes that led to this type of formation, puncture of the hydrocele is used. A puncture is made and a fluid sample is taken from the scrotum for subsequent analysis and diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of hydrocele is not an easy task and depends on a large number of factors and issues such as: congenital or acquired hydrocele (including primary or secondary), the person’s age, and whether there are complications (especially in cases where the hydrocele is large) ).
Treatment of testicular hydrocele without surgery is possible only for symptomatic hydrocele, which can form as a result of trauma, inflammatory diseases of the testicle and its appendages, as well as testicular torsion and hedatidity in children.
For symptomatic (secondary) testicular hydrocele, treatment of the underlying pathology such as orchitis, orchiepididymitis or a tumor process is indicated.
In this case, a course of antibiotics is prescribed - for orchitis and orchiepididymitis, fluoroquinolones (ofloxacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin) and macrolides (azithromycin) are used. The goal is not only to kill bacteria, but also to prevent the development of purulent complications.
In addition, it is necessary to wear a suspensor and constant rest. After eliminating the underlying cause, the fluid, as a rule, resolves itself into the surrounding tissues. However, in some cases, such treatment may not be sufficient and surgical treatment will be necessary.
Sometimes testicular hydrocele is diagnosed in a newborn. Treatment in this case is carried out using the methods described below, however, they try to postpone surgical intervention until the age of two, while monitoring the dynamics with a urologist (or andrologist).
An important point is the need to remove fluid from the cavity, which can be achieved by puncture of the hydrocele. After the fluid has been evacuated, sclerosing drugs can be injected into the cavity. But such an operation is not a radical treatment and is currently rarely used.
This is explained by the fact that after such punctures (although they are less traumatic), relapses and/or complications often occur, and repeated removal of the hydrocele is required.
Therefore, indications for such procedures are either a person’s refusal to undergo radical surgery, or severe general condition and concomitant diseases.
The main method of treating hydrocele is surgical operations, which are radical in nature. They can be open or laparoscopic. Due to frequent complications and relapses, laparoscopic surgery is not widely used. Hydrocele of the testicle during open surgery recurs in only 2% of cases, which is a fairly good indicator.
There are many described surgical techniques and modifications in the treatment of hydrocele, the main of which are:
- Winkelmann operation – used quite often;
- Lord's operation, or plication of the testicular membranes, is the most effective way to treat acquired hydrocele.
- Bergmann's operation is most often indicated when testicular hydrocele occurs in a child over 12 years of age.
- Ross operation is indicated for communicating hydrocele of the testicle.
Winkelmann's operation is an operation to remove hydrocele of the testicle, which is performed in three stages: first, the cavity of the hydrocele is opened, at the second stage, the testicular membranes are everted, and then the resulting edges of the membranes are sutured behind the epididymis. This eliminates the cavity in which the fluid was located, and brings the testicle’s own membrane into contact with the fleshy membrane, which will allow the fluid to be absorbed.
Lord's operation (or plication of the testicular membranes) is the most effective surgical procedure for the treatment of hydrops in men. Treatment for such an operation is reduced to minimal damage to the scrotal tissue, which has a beneficial effect on recovery.
After the incision, the surgeon separates the tunica vaginalis from the surrounding tissues by everting it and collects it into the parietal layer with several sutures (plication). In total, about 7 such sutures are placed around the perimeter of the testicle and the testicle is immersed under the fleshy membrane. Finally, the scrotum must be placed in an elastic suspension.
Removal of hydrocele in a child during such an operation also begins with a transverse incision, but in the area of the external inguinal ring, and when ligating the vaginal process of the peritoneum, only the proximal end is ligated.
Bergmann's operation is used for large-sized hydroceles, in particular for sclerotic and dense testicular membranes.
During this operation, part of the membrane is removed (part of the inner layer is resected, leaving about 1 cm from the testicle) and then what remains is stitched. It is very important to carry out adequate hemostasis.
After surgery for hydrocele, it is necessary to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy and cold is applied to the operated area in the first hours.
The Ross operation for testicular hydrocele requires good qualifications of the operating surgeon, adequate technology and careful handling of the elements of the spermatic cord. After an incision has been made in the area of the inguinal ring, the spermatic cord is isolated and the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum is ligated in the area of the internal inguinal ring. A so-called “window” is formed in the testicular membranes.
The performance of a particular operation depends on the form of the hydrocele, the preference of the surgeon and the presence of complications, therefore the approach to surgical intervention is strictly individual.
In the post- and preoperative period, the patient often has a question: “What kind of panties should be worn when hydrocele is detected?” There is only one answer: comfortable, elastic and not tight, so that they do not squeeze the scrotum.
Rehabilitation after surgery for hydrocele
The postoperative period in 95% of cases proceeds well, the movement of children is not limited, and in some clinics a person after the operation can be sent home within 5-6 hours after the operation. When performing surgery in children, it is recommended:
- If there is some discomfort, the child may be advised to use anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen.
- Limit physical activity (including outdoor games) and do not injure the scrotum.
- Parents need to supervise their child so that he does not touch, scratch or wet the postoperative wound.
Prevention of testicular hydrocele consists of treating inflammatory diseases of the scrotal organs, avoiding traumatic injuries and timely consultation with a doctor. Avoid hypothermia of the scrotum, which will contribute to the development of inflammation.
Parents need to examine the genital organs of newborns in the first 2 years of life and pay attention to deviations in the size of the scrotum.
In order to prevent hydrocele, adult patients are recommended to avoid sexually transmitted infections, and if detected, treat them promptly.
Medicines
Hydrocele of the testicle is a common disease. As a rule, surgery is used to eliminate it. But sometimes doctors limit themselves to drug therapy. The main thing in this case is the competent selection of drugs.
Medicines for hydrocele in the inoperable phase
If dropsy is acquired, then medications are selected based on the nature of the disease - infectious or traumatic. In these cases, testicular hydrocele plays the role of a symptom, and medications should be aimed at combating the underlying disease.
If hydrocele is infectious
Infectious testicular hydrocele can be caused by orchitis, epididymitis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. In this case, the following may be prescribed as drug therapy:
- to eliminate pain - painkillers (Analgin, Baralgin, Ketorol);
- to combat edema - anti-inflammatory (Aponil, Ketoprofen);
- to fight infection - antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin, Cefotaxime).
The course of treatment can last from one to several weeks, depending on the nature of the underlying disease - the source of infection.
If hydrocele is traumatic
Injuries, bruises, and blows to the groin area can also lead to various diseases, the treatment of which will require drug therapy. Among the most common is testicular torsion. In this case, the medications should restore normal blood circulation in the groin area, impaired by injury. The drugs are used both during and after surgery:
- novocaine solution, which is injected into the spermatic cord - to improve microcirculation;
- sodium chloride solution for compresses - to improve blood circulation;
- sodium heparin intramuscularly and novocaine blockade - during the postoperative recovery period to prevent thrombus formation;
- acetylsalicylic acid - to prevent toxic substances from penetrating the seminiferous tubules.
Also, testicular hydrocele can be caused by heart failure. Then the doctor prescribes drugs that are aimed at improving the functioning of the heart muscle - Furosemide, Torasemide.
Medicines for hydrocele in the postoperative period
Drug support will consolidate the result of the operation. Its task is to neutralize swelling and pain. Such support can be of three types:
- pain reliever (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol) – if after the surgeon’s intervention the patient feels painful discomfort;
- antiseptic (Betadine, Chlorhexedine) - to prevent infection. For the same purposes, the baby will need antiseptics during each diaper change;
- antibacterial - to relieve possible inflammation.
Important: treatment of hydrocele with medications should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. All medications must be taken as prescribed by specialists. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Folk remedies
Alternative treatment for hydrocele
In most cases, traditional treatment for hydrocele is not used, but instead, modern advanced surgical intervention is used. However, if hydrocele in men is not advanced and does not progress, folk remedies can be used to treat it.
It should be borne in mind that such folk treatment should not be carried out without prior consultation with the attending physician.
If you try to treat hydrocele on your own, this can only worsen the current situation, complicate intimate life and even deprive you of the opportunity to have offspring.
The use of herbs, plants and vegetables in the fight against hydrocele
Dropsy of the testicles can be treated well using a pea compress. For newborns, such treatment is very effective and popular. For this you will need dry peas, clean drinking water and a small piece of cotton cloth.
Place the peas in a saucepan and allow them to swell, then bring to a boil and cook for about fifteen minutes. As soon as this decoction has cooled, soak a cloth in it and apply it to the swollen testicle for twenty to thirty minutes. This kind of compress can quickly remove swelling.
You need to repeat the procedure twice a day until the swelling is completely gone. Store in a cool place and warm to room temperature before use.
Another effective remedy is ordinary parsley. For the recipe you will need parsley leaves and fresh unpasteurized milk. Mix parsley and milk in a saucepan and then boil.
The contents are then cooled and filtered. The resulting mixture should be drunk twenty to thirty milliliters every hour. The portion made should be enough for a day of treatment; the next day you need to make a new portion.
Mixtures of medicinal herbs can also be used to treat hydrocele. Take dried clover and coltsfoot in the amount of one tablespoon and pour boiling water. Leave for about thirty minutes.
Then strain through cheesecloth and consume the resulting tincture several times a day. This mixture has natural decongestant properties, removing excess fluid from the body.
Continue the course until complete recovery.
To get rid of hydrocele, you can use a mixture of baby cream and calendula ointment in equal proportions. Apply the product to the swollen scrotum, then covering it with a bandage and thick underwear. The cream must be applied daily until the swelling disappears completely.
The following method is especially popular among men. White grape wine is mixed with agrimony herbs, the mixture is boiled for about five minutes, then cooled and filtered using a strainer. Gauze soaked in this mixture is applied to the swollen testicles for thirty minutes. Repeat the procedure twice a day. Such a compress will be able to remove the fluid accumulated in the testicles.
Also, some people in a similar situation use a spell for hydrocele, which must be read a certain number of times. Naturally, there is no reliable information whether it is possible, in principle, to “talk” hydrocele of the testicle with a similar method.
If after a few days of treatment with folk remedies you do not find any improvement, you should immediately go to a specialist doctor and consult with him about your problem.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Source: https://yellmed.ru/bolezni/vodyanka-yaichka
Hydrocele of the testicle (hydrocele): causes and treatment
Dropsy of the left or right testicles in men is an increased amount of serous fluid in the organ capsule. Its accumulation occurs constantly; normally its volume does not exceed several milliliters.
An increase in its quantity occurs when the balance between its production and lymphatic drainage is disturbed. The volume of liquid when dropsy occurs varies between 20-200 ml. If left untreated for a long time, its amount can reach several liters.
The disease is accompanied by obvious discomfort that appears due to the enlargement of the scrotum. The remaining symptoms are determined by the origin of the dropsy. With a slight increase in the volume of serous fluid, hydrocele can be asymptomatic.
What it is?
Hydrocele of the testicles, or hydrocele, is a disease accompanied by the accumulation of serous fluid between the layers of the visceral and parietal tunic of the testicle. The volume of liquid varies widely and ranges from 20 to 200 ml, in some cases up to 3 liters. Both children and adults suffer from this pathology.
In childhood, congenital hydrocele is diagnosed - this is a physiological condition characteristic of the vast majority of newborns, developing in connection with the intrauterine descent of the testicles into the scrotum. In adult men, this disease is acquired - this is what will be discussed in our article.
Classification
Doctors classify hydrocele of the testicles according to the cause of the disease and the severity of the pathological process.
According to the origin of dropsy, experts divide it into congenital and acquired.
The congenital type of the disease is associated with impaired fetal development and can either communicate with the abdominal cavity (impaired formation of abdominal tissues) or be isolated (excessive fluid production).
The testicle, during the development of the fetus, descends from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum through the inguinal canal along with the peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity).
During the first months of life, if the passage into the abdominal cavity is preserved, fluid from the cavity flows into the testicular membranes through the “unclosed” canal. Up to 1.5-2 years, the pathology does not require treatment.
Acquired ones are a complication of other diseases and, according to the causative factor, are divided into several types:
- post-traumatic;
- inflammatory;
- lymphostatic (difficulty in the outflow of lymph from the scrotum);
- iatrogenic (post-operative);
- idiopathic (imbalance between the fluid secreted and absorbed by the testicular membrane).
Based on the nature of the process, doctors separately identify acute dropsy (cyst) of the testicular membranes.
The side of the disease distinguishes between lesions of the left testicle, lesions of the right testicle and bilateral hydrocele.
Reasons for development
The causes of development vary depending on the type of disease. The congenital or primary type appears under the influence of the following factors:
- intrauterine development disorders;
- threat of miscarriage;
- aborted fetus;
- birth injuries;
- high intra-abdominal pressure;
- hispopadia.
Causes of secondary testicular hydrocele in men:
- testicular torsion;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- sexual infections;
- genital injuries, including injuries resulting from sports – cycling, wrestling, weightlifting;
- previous surgical interventions;
- severe course of viral and infectious diseases - sore throat, influenza;
- tumors of the genital organs;
- heart failure;
- liver dysfunction.
Several reasons can simultaneously contribute to the development of pathology - and the chance of rapid progression of hydrocele increases significantly.
Clinical picture
Symptoms during the development of the disease in question are of low intensity. In very rare cases, the accumulation of fluid in the scrotum is spasmodic in nature - for example, if there are acute inflammatory diseases or the patient is in the early postoperative period.
Pronounced symptoms appear only when the testicle is too large - they can reach more than 10 cm in diameter. And then the patient will complain about:
- difficulty urinating;
- inability to walk normally;
- constant feeling of heaviness in the scrotum;
- discomfort, in rare cases – pain, during sex;
- high density of the scrotum;
- clear perception of a splash of liquid in the scrotum upon palpation of the testicles;
- inability to determine the contour of the testicle.
If hydrocele in men is accompanied by a severe infectious disease, then the accumulated exudate in the saccular space of the scrotum becomes purulent. This condition is classified in medicine as a complication of testicular hydrocele and is called pyocele. With this development of the disease, the following symptoms will be noted:
- increase in body temperature to critical levels;
- the patient’s general well-being sharply deteriorates - weakness, drowsiness, dizziness appear;
- the inflammatory process spreads to nearby tissues.
In the absence of adequate treatment, pyocele can lead to the following problems:
- reproductive dysfunction - compression of the blood vessels located in the scrotum occurs, which leads to testicular atrophy;
- hematocele - accumulation of exudate with blood in the saccular space, against the background of vascular injury;
- rupture of the testicular membranes - due to overstretching of their walls by accumulated fluid;
- progression of scrotal hernia.
Complications
Hydrocele of the testicles can cause various types of complications in men. Right-sided and left-sided hydrocele, if left untreated, can result in complications such as:
- Inguinal hernia. In the presence of the disease, the canal that connects the peritoneum with the vaginal membrane expands. As a result, part of the intestine may enter this channel. Another problem is that with a hydrocele, part of the bladder may also prolapse into the affected area.
The hernia itself is dangerous because it can be strangulated. A man may suspect that he has an inguinal hernia due to acute pain that will radiate to the groin.
- Change in testicle size. During the course of the disease, fluid often accumulates in the scrotum, causing them to increase in size;
- Difficulty walking. As the size of the testicles increases, it becomes uncomfortable for a man to walk. The skin in the folds begins to chafe and calluses appear. Due to the fact that the urinary tract is pinched, problems with urination begin. Since the patency of the spermatic cord is impaired, difficulties also begin to arise with sexual intercourse;
- Rupture of hydrocele of the testicle. Quite a dangerous complication. A man may notice this consequence by reducing the size of the genital organs.
Diagnostics
The preliminary stage of the disease is determined by examination, palpation of the scrotum and testing, the purpose of which is to identify the condition of the veins. The vessels may be swollen but not visible, or dilated and bulging. In many men, venous pathology is visible visually when the patient strains his abdominal muscles. Urine tests reveal kidney function in cases of testicular hydrocele.
The doctor clarifies the data obtained by performing an ultrasound, which helps determine whether the patient has venous hypertension. Ultrasound scanning together with Doppler sonography makes it possible to determine the state of blood circulation in the testicles and kidneys.
Healthy men do not experience venous reflux (reverse blood flow when the valves are damaged). By analyzing the seminal fluid, one can judge the viability of sperm.
The disease dropsy is determined only by a doctor; independent prescriptions are excluded.
How to treat hydrocele?
The main method of treating dropsy is surgical , with the exception of children under the age of one and a half years who have been diagnosed with congenital dropsy.
If, after reaching this age, fusion of the vaginal process of the peritoneum has not occurred, it is ligated.
Sometimes they practice elimination of dropsy through puncture, however, in most cases, the disease relapses.
If hydrocele is a consequence of the presence of other diseases (gonorrhea, inflammatory process, etc.), then the first thing to do is treat the root causes of hydrocele.
Operation
The main types of surgical intervention for hydrocele:
- Winkelmann operation - one of the membranes of the testicle is cut and stitched in such a way that the accumulation of fluid becomes impossible;
- Operation according to Bergman - part of the membrane is completely removed, the rest is stitched. In this case, you cannot do without antibacterial therapy and wearing a special bandage;
- Operation according to Lord's method - dissection of the testicular membranes allows you to free it from excess fluid. Next, the shell is slightly corrugated, which is a more gentle method and does not lead to surgical dislocation or damage to the testicle itself.
What type of dissection will be used is decided by the surgeon during the operation, since there are indications for each method, and the condition of the testicle must be appropriate. Sometimes doctors do a simple puncture, that is, they pump out the fluid. However, such a measure is always temporary, since the cause of fluid accumulation is not eliminated.
Relapses after surgical treatment are rare - no more than 5% of the total number of patients.
Doctors include postoperative complications:
- High standing testicle - repeated surgery is required to lower and fix it.
- Hematocele is an accumulation of blood between the membranes, requiring puncture and determination of the causes of bleeding.
- Pyocele is an infection and accumulation of pus that requires a course of antibiotic therapy.
- Dehiscence of postoperative sutures (complex therapy required).
- Poor tolerance to anesthesia.
- Testicular atrophy due to impaired blood supply. Changes in the appearance of the scrotum and its deformation.
Reviews from people
Some reviews from men who have experienced testicular hydrocele from personal experience:
- Kirill, 24 years old: I had testicular hydrocele as a child, from birth. At first they said it was an inguinal hernia, but then it turned out that it was dropsy. The doctors told my parents that I had to wait until I was 3 years old. This dropsy went away for me even earlier, by the age of two. I recently got married, had a daughter, nothing bothers me!
- Alexey, 27 years old: a year ago I was playing football and received a strong blow to the groin. In the evening, my temperature rose, my scrotum became swollen, and I had to call an ambulance. The doctor said it was hydrocele. They offered to undergo surgery, but I refused. A couple of days later it got even worse. Then I agreed and regretted that I had not done it right away. I feel great now.
- Vladimir, 34 years old: About five years ago I caught trepak. When the pain became unbearable, my friends advised me to take antibiotics. I felt better, but then my scrotum became so swollen that I still had to go to the doctor. It turned out to be hydrocele. They gave me punctures, but the benefit from them is temporary - only surgery will help. I experienced it myself, it’s better not to delay it.
Prevention
Prevention consists of preventing inflammatory diseases and injuries of the genitourinary system, timely treatment of genital infections and monitoring one’s health. 55% of acute epididymitis and inflammation of the epididymis are caused by undiagnosed and untreated chlamydia.
If you have pain, redness, or swelling of the scrotum, you should contact a urologist-andrologist.
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, the prognosis of acquired hydrocele is favorable - it goes away either on its own or after surgical intervention.
When large hydroceles are removed, relapses of the disease are possible. There have been no cases of death of patients as a result of surgical treatment of hydrocele.
Source: https://p-87.ru/health/vodyanka-yaichka/
Treatment of hydrocele
Hydrocele of the testicular membranes (hydrocele) is a pathological condition manifested by the content of serous substance between the parietal and visceral layers of the testicular membrane.
Manifested by an increase in its size, it often may not cause other inconveniences. It is observed mainly in children, but also occurs in adult men.
Accordingly, dropsy is distinguished between congenital and acquired.
With the normal development of the genitourinary system, the laying of the testicle occurs in the abdominal cavity, from where the formed testicle, with the participation of the Gunther's ligament and hormones characteristic of the male body, moves into the scrotum surrounded by the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum. It is its lumen that should close before the baby is born, but this does not always happen, which causes the occurrence of a hydrocele or even an inguinal hernia.
Congenital dropsy is observed in boys whose embryonic development contained such a disorder as cleft processus vaginalis of the peritoneum, where fluid accumulates. Such a hydrocele is usually called communicating.
It is also possible to develop a non-communicating hydrocele, manifested by the formation of closed cavities along the spermatic cord, which occurs with partial obliteration of the processus vaginalis.
The open lumen becomes a path for free penetration of fluid from the abdominal cavity into the membranes of the testicle, and if the appendage is overgrown at different levels of the inguinal canal and testicle, then the conditions are created for the occurrence of a testicular cyst, spermatic cord, or both at the same time.
Separately, it is worth noting that the tunica vaginalis of the testicle has the function of producing a special fluid to lubricate the testicle and its free movement within the scrotum; when the balance between its production and reabsorption is disturbed, another reason for the formation of dropsy arises. As the child grows, it is possible both to complete the obliteration of the vaginal process and to increase the absorption properties of its membranes, and this leads to self-healing in a significant proportion of children.
Acquired dropsy also comes in two types. It can develop at any age. This is idiopathic - which develops, for example, due to age-related changes and is manifested by sclerotic changes in the vaginal membrane, obliteration of lymphatic vessels and, accordingly, difficulty in the outflow of fluid and its accumulation between the parietal and visceral membranes of the testicle.
The second type of acquired dropsy is called symptomatic or reactive and is usually a consequence of an acute inflammatory process, trauma or tumors of the testicle, surgical interventions on the genitals, as well as heart failure.
Reactive dropsy, unlike idiopathic dropsy, certainly contains a background disease, the treatment of which causes its resorption.
The mechanism for the formation of this kind of pathology is due to the compaction of the testicular membranes, disruption of lymphatic outflow and suppression of blood microcirculation. The consequence is a slow, and sometimes rapid, accumulation of fluid between the membranes, the development of dropsy without pain or other discomfort.
The causes of testicular hydrocele depend entirely on its type, that is, on whether it is congenital or acquired.
Causes of congenital dropsy:
- non-closure of the lumen of the vaginal process after its descent together with the testicle into the scrotum in the prenatal period;
- concentration of fluid from the peritoneal cavity in the patent lumen, its circulation from the hydrocele into the abdominal cavity, if the processus vaginalis remains connected to it;
- imperfection of the lymphatic apparatus of the groin area in newborns and infants, which prevents the normal absorption of fluid produced by the cells of the inner lining of the peritoneal appendage, even if it is blind and not connected to the peritoneum.
Causes of acquired dropsy:
- inflammatory diseases of the scrotum;
- testicular torsion;
- injuries of the scrotum and perineum;
- disturbances of lymphatic drainage from the scrotum.
Assessing the clinical course of hydrocele , we can distinguish two of its forms - acute and chronic.
The acute form is more typical of the symptomatic acquired form, observed, for example, with orchitis, epididymitis, and colds.
It manifests itself as a rapid increase in the volume of the scrotum (sometimes to the size of a goose egg and even a baby’s head), its surface is smooth, a fluid of dense elastic consistency is detected in the scrotum to the touch, palpation is not accompanied by pain, but fluctuation is likely.
It is usually not possible to palpate the testicle itself. In general, it is accompanied by symptoms typical of inflammation of the scrotum - high body temperature, pain in the testicle and epididymis, hyperemia and swelling of the scrotum.
The chronic form is characterized by an asymptomatic course. It can develop from a congenital form of hydrocele, as well as from an acute acquired one. Possible symptoms include:
- increased volume of the scrotum;
- nagging pain along the spermatic cord;
- discomfort during physical activity, such as walking or sexual intercourse, urination;
- maceration of the skin due to urine entering during urination;
- in advanced stages, the penis can be retracted under the skin of the scrotum stretched over the dropsy.
Hydrocele in certain cases may be accompanied by hematocele and pyocele, that is, accumulation, respectively, of blood and pus in the membranes of the testicle. Hematocele becomes a consequence of injury, hemorrhagic diathesis, or unsuccessful puncture of the hydrocele. Pyocele is characteristic of orchitis, epididymitis, and other consequences of penetrating infection (for example, testicular or epididymal abscess).
Treatment of hydrocele of the testicle is determined by its form. The range of measures considered by the doctor is so wide that it can consist of simple observation of the patient (if it is a congenital pathology, it can self-heal) and surgical intervention (the indication for which is an advanced chronic process).
Targeted treatment of congenital hydrocele in children may involve excision and ligation of the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum.
Treatment of symptomatic dropsy, that is, developed against the background of an underlying disease, involves treatment of the background pathology, after which the dropsy naturally resolves.
Treatment of idiopathic hydrocele can be carried out by puncture of the hydrocele. Afterwards, sclerosing substances are introduced, but the risk of complications still remains, although the method is not radical. Sclerotherapy is indicated only when the severity of the patient’s general condition does not allow surgical treatment.
The surgical method is used for chronic forms of hydrocele. This is mainly the Winkelmann operation:
- opening of the hydrocele cavity of the shell;
- everting the cavity and suturing its edges behind the epididymis;
- the ability of the inner surface of the testicular membrane to absorb transudate is ensured by contact with its fleshy membrane.
For sclerotic, thickened membranes, their resection is performed, that is, Bergmann's operation:
- opening of the hydrocele cavity of the shell;
- excision of the testicular membrane.
There are no differences between the two methods for the patient’s health, and therefore the decision about which operation will be performed is made by the surgeon during the surgical intervention itself after gaining direct access to the membranes.
Frequent complications of operations include inflammation of the testicle, which is associated with its mechanical irritation during surgery, bleeding or hematoma of the scrotum. To prevent these complications after surgery, drainages are often installed and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
In this case, doctors make a favorable prognosis, except in the case where the size of the hydrocele was large or the long course of the disease provoked testicular atrophy and impaired spermatogenesis.
The congenital form of hydrocele is usually not associated with any diseases; moreover, it can heal itself as the child’s body grows. However, medical supervision is advisable, since the risk of complications cannot be completely excluded.
Acquired hydrocele develops against the background of an underlying disease, which is predominantly:
- orchitis is an inflammatory process localized in the male gonads and paired gonads;
- testicular torsion is a dangerous condition manifested in the cessation of blood supply to the testicle due to twisting of the spermatic cord around its axis and thereby closing the lumen of the veins and arteries; the cause may be an injury to the groin area or sudden muscle contraction;
- heart failure is a complex disorder characterized by a decrease in the contractility of the heart muscle and, consequently, its inability to pump a sufficient amount of blood; among other ways to compensate for this disorder, the body uses the ability to retain liquid and salt; accumulation of fluid can also be localized in the scrotum area;
- Epididymitis is an inflammatory process localized in the appendages of the male gonads, often combined with inflammation of the glands themselves and the same hydrocele.
Complications of testicular hydrocele in the absence of timely and adequate treatment include testicular atrophy and spermatogenesis disorders.
Treatment of hydrocele at home is rarely used. Conservative therapy is appropriate in this case for the treatment of symptomatic hydrocele, or more precisely, for the treatment of its underlying cause.
In other cases, if after examining the patient the doctor does not see the need for urgent therapy or surgery, then the patient is released until the next appointment. If manipulations and operations are prescribed, they are carried out in a medical institution.
At home, it is possible to take medications during the postoperative period, carefully observe hygiene and other medical recommendations.
Drugs used in the treatment of hydrocele are from the category of those used to treat the disease that provoked hydrocele.
If the hydrocele in its nature does not contain another pathology, such as inflammation of the genital organs or heart failure, then sclerotic substances are used as part of sclerotherapy, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents after surgery.
Folk remedies for the treatment of hydrocele can be used only after consultation with a professional doctor, unless objections are raised to this.
Among the popular and effective recipes are the following:
- agrimony - place 100 grams of agrimony herb in an enamel bowl, pour in a liter of grape wine, bring to a boil over low heat, cover with a lid, let stand for 5 minutes; remove from heat and leave covered for half an hour, strain; use for compresses;
- coltsfoot and sweet clover - combine coltsfoot grass and medicinal clover inflorescences in equal proportions; 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and leave for 30 minutes; use 3-4 tsp. 5 times a day;
- chamomile - rinse the raw chamomile herb thoroughly and pass through a meat grinder; apply to the scrotum 3-4 times a day;
- peas and beer - pour 50 grams of peas into ½ liter of beer, after an hour put on low heat, boil for 15 minutes, cool; use for compresses in combination with a linen cloth flap.
Diagnosis of hydrocele begins with collecting anamnesis and familiarization with the patient’s complaints (probably a combination with other diseases). Initial examination shows:
- enlargement of the scrotum,
- delimitation of the upper part of the hydrocele from the external opening of the inguinal canal
- mobility of the skin over the hydrocele,
- smooth surface of the skin above the hydrocele,
- the bag itself will have a dense or soft elastic consistency,
- fluctuation.
Percussion produces a dull sound. The hydrocele is usually not retracted into the inguinal canal.
Other examination methods include:
- diaphanoscopy - transillumination of the scrotum with an intense and directed light beam; the passage of the light beam through the liquid provides the scrotum with a uniform, intense pink color; thus, suspicions of a tumor or hernia are excluded, in which light will not pass through the scrotum;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum - allows you to identify a testicular tumor in the presence of symptomatic hydrocele of the testicular membranes; with hydrocele, on echograms the testicle is determined as an echo-positive formation of a homogeneous structure, surrounded by an echo-negative zone, that is, hydrocele.
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Source: https://www.eurolab.ua/treatment/166/
Hydrocele of the testicle
Hydrocele of the testicle - what kind of disease is it?
A disease in which a liquid substance begins to accumulate in the scrotum, which should not normally be present, is called hydrocele or hydrocele.
This disease is more common in younger people, but it also occurs in adult men, especially as a complication after surgery. The disease leads to a noticeable enlargement of the ovary.
This is not a fatal disease, but it can constantly progress, which will seriously complicate a man’s life in the later stages. This type of tumor is the most common type of benign tumor today.
Hydrocele of the testicle according to ICD 10
Hydrocele of the testicle in ICD 10 is classified as a disease of the genital organs. The International Classification of Diseases identifies several different types of hydrocele, although the essence of the disease does not change. The difference is influenced by the time of formation. Hydrocele ICD 10 code N43 includes several diseases at once.
This is the dropsy of the testicle itself, as well as its vaginal membrane and spermatic cord. If all these are acquired diseases that developed as they grew older and were caused by some extraneous factors, then they belong to this code. According to ICD 10, congenital hydrocele has a different designation – P83.5.
This is the same disease, but which developed during the development of the fetus in the womb.
The main classification includes several types of manifestations of the disease. They are associated with various forms of manifestation. The ICD code for hydrocele of the testicle can be of the following types:
- Infectious form of hydrocele – N43.1;
- Other forms of hydrocele – N43.2;
- The specified form of hydrocele and spermatocele (they belong to the same type according to the ICD) is N43.3.
The congenital form is classified into another sphere, since it is more characterized by the location of dropsy between the membranes of the testicles. Otherwise, it is not much different from the usual manifestation after birth. The congenital form is detected almost immediately after the baby is born.
The probability of developing this disease is no more than 10% of boys. One of the features of this form is that it can go away on its own without surgery in the first year of life. This variety is also called physiological. It is caused by poor development of the lymph nodes of the testicular membrane.
Over time, as they grow older, they can develop and the disease goes away on its own.
Treatment of hydrocele according to ICD 10
Now doctors do not see any other way to treat the disease other than surgery. Conservative methods for the treatment of dropsy, which would help get rid of the disease, are not used.
Treatment of hydrocele without surgery is possible only when a reactive process occurs. It may appear after infection or inflammation occurs.
As with many other diseases, the first stage is best treated, and the further the progress, the more difficult it is. The first stage is precisely associated with those few methods of conservative treatment that can help.
But it is at the beginning of its onset that dropsy is most difficult to detect. After the onset of the second stage and beyond, all folk methods, in the form of compresses, taking medications and other methods become simply auxiliary.
Source: https://zabolevaniya-yaichek.ru/perekrut-gidatid-yaichka-i-ego-pridatka.html
Treatment of hydrocele of testicular membranes
Any changes in the size of the genital organs should alert its owner. An increase in the size of the scrotum on one or both sides is a reason to check whether it is a hydrocele? It doesn’t hurt, it doesn’t tug, it doesn’t interfere with small accumulations of fluid, but it can grow to enormous sizes, collecting a liter or more of fluid.
In our everyday life, it is more common to call this disease hydrocele of the testicles - a pathological accumulation of fluid in the inner lining of the testicle. The liquid comes in droplets and gradually accumulates. Men of all age groups, from infants to the elderly, are susceptible to this disease.
Depending on the moment of occurrence, hydrocele can be congenital or acquired. If one testicle is affected - unilateral, two - bilateral.
The process is sluggish - a chronic disease, and if accompanied by pain and fever - an acute course of the disease.
A clear sign is an increase in the size of one or two testicles. As the size increases, the structure of the skin changes, it becomes taut and smooth, although its mobility is not impaired.
There is discomfort when walking, sexual intercourse.
It is urgent to visit a urologist in St. Petersburg; the appearance of pain in the groin and an increase in body temperature indicate the onset of the inflammatory process.
Acquired hydrocele can result from:
- inflammatory processes in the testicle and its appendages;
- diseases of the lymphatic system in the pelvic area and groin;
- traumatic injuries;
- as a consequence of a severe form of cardiovascular failure;
- complications after surgery.
In any case, this disease requires systematic observation by a doctor, especially at a young age, so as not to be treated for infertility later.
Any disease, if left untreated, becomes chronic, the pathological process continues, and an exacerbation can begin at any time.
A sharp enlargement of the scrotum, redness, increased body temperature, and difficulty urinating are the main signs of an incipient pyocele, a purulent process inside the membrane of the testicle.
Complications should not be allowed; finding time to visit a urologist in an excellent medical center is not difficult.
Another complication may be hemorrhage into the cavity of the dropsy - hematocele. No one is immune from falls and injuries. Don't risk your health, complications can lead to the inability to become a father.
A highly qualified urologist can easily identify a hydrocele as a result of visual examination and palpation of the patient’s scrotum. If it is necessary to clarify the amount of accumulated fluid, the size and condition of the testicle, ultrasound diagnostics is prescribed. In complex, advanced cases, additional examination and examination of the contents of the dropsy using a puncture is required.
Do not try to diagnose yourself at home, as this may have consequences for your reproductive organ.
Treatment of hydrocele in men is possible only with the help of surgery; this disease cannot be treated with medications.
If there is a large amount of fluid in the membrane and it is impossible to urgently perform an operation, the patient’s condition is alleviated with the help of a puncture. To do this, a puncture is made with a special syringe, and the liquid is pumped out.
This procedure is effective, but after six months the fluid is collected again. They resort to it if surgery is contraindicated for the patient due to health reasons.
As a result of a review of existing methods of treating hydrocele, the most used can be identified:
1. Bergmann's operation - used for large accumulations of fluid and the presence of seals. An incision is made on the anterior side of the scrotum, then all the inner membranes of the testicle are dissected step by step, the fluid is pumped out, and the last membrane surrounding the testicle is excised. After the gradual stitching of all the membranes, a small drainage tube is left for the healing period.
2. Winkelmann operation - using a puncture, all fluid is pumped out from the membrane, the scrotum and all membranes are dissected from the front, as a result of a thorough examination, the damaged membranes are removed, and the remaining ones are stitched inside out. The operation is effective, but the process changes the appearance of the scrotum.
3. Lord's operation - after dissection of the membranes, a special channel (corrugation) is created to drain the fluid, the testicle is not taken out and the membranes are not removed, minimal trauma to tissues and blood vessels, the testicle remains in its native environment.
4. Ross operation – performed for congenital pathology of hydrocele. The dissection is made in the groin area; the difficulty lies in strict adherence to the technique.
Dissection must be carried out very carefully so as not to damage the inguinal nerve, testicular vessels, or vas deferens. The peritoneal process is removed and ligated at the internal inguinal ring.
At the same time, a lumen is formed for normal fluid outflow. The operation is effective for communicating forms of dropsy.
The modern method of sclerotherapy is increasingly used for the treatment of hydrocele abroad. After removing the liquid, a sclerosant is introduced between the membranes, a special substance that acts as an antiseptic and at the same time promotes the fusion of the membranes. As a result, the liquid stops accumulating.
Any operation is aimed at eliminating the causes of hydrocele and its consequences; the type is selected individually by a practicing surgeon, performed under general or local anesthesia and allows you to completely get rid of an unpleasant and dangerous disease. The seams are aesthetic and almost invisible. You just need to trust the doctor.
To prevent hydrocele from developing to incredible proportions, it is necessary to promptly respond to the first signs of the disease and visit a urologist. Particular attention should be paid to the problem at an early age by parents, when children are not yet able to assess the situation and make a decision.
Treat your body with care - avoid hypothermia, inflammatory processes and, of course, injuries - this is how you can avoid acquired disease.
Every man wants to become a father, so why not take care of this from a young age?
Source: https://ecosafety.ru/ru/gidrocele_(vodyanka_obolochek_yaichka)/