An ovarian corpus luteum cyst is a tumor-like structure that is formed as a result of natural processes - the maturation and opening of the dominant follicle.
In the normal state, the formation is not a pathology, has no pronounced symptoms and goes away on its own in several cycles. If the cystic corpus luteum has not resolved, then it must be treated. Complications may even require surgical intervention, but these cases are rare.
It is impossible to say for sure how quickly the cyst resolves. The average period of regression (reverse development) is 1-6 months.
Content
- What is an ovarian corpus luteum cyst?
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Signs on ultrasound
- How to treat
- Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary and menstruation
- The nature of menstruation and discharge
- Feel
- Duphaston for corpus luteum cyst
- Can a cyst in an ovary burst?
- Symptoms of a cyst rupture
- Surgical treatment of complications
What does a corpus luteum cyst mean?
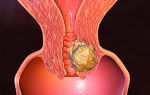
A corpus luteum cyst is a formation that forms at the site of an ovulated follicle. The parietal contents got their name because of their special color. Inside the yellow body contains a reddish liquid.
If a tumor has formed, this means that ovulation has occurred. A luteal cyst is a functional neoplasm and is usually asymptomatic. If anxiety occurs, a woman is prescribed treatment, which includes hormonal medications.
Cyst regression is a condition in which it gradually decreases and disappears. After ovulation, the corpus luteum functions for 10-14 days. Normally its dimensions are 15-20 mm. If the volume of the luteal sac is larger, then they speak of a cystic formation.
Corpus luteum cyst: causes of occurrence
A luteal cyst differs from endometrioid and dermoid cysts in that it is functional and has different mechanisms of formation. The causes of a large corpus luteum are:
- hormonal imbalance;
- puberty in a teenage girl;
- taking hormonal drugs that stimulate ovulation (Clostilbegit, after an injection of hCG, IVF);
- termination of pregnancy, including medication (after an early abortion);
- treatment with oral contraceptives, as well as gonadotropin-releasing hormones (after discontinuation of Buserelin, Diferelin, Zoladex);
- infections and acute inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- emotional instability;
- bad habits;
- playing sports;
- dieting, anorexia or obesity.
Corpus luteum cysts have natural causes. This distinguishes it from pathological ovarian tumors, including follicular cysts. A woman's ovaries form a dominant follicle every month that releases an egg. At this site the formation of the luteal body occurs.
A follicular cyst, on the other hand, is formed due to an overgrown follicle that did not open at the right time. The causes of hemorrhage into the luteal cavity and the formation of a hemorrhagic cystic body can be increased physical activity or rough sexual contact.
In this case, the patient requires immediate treatment.
Corpus luteum cyst: symptoms and signs
Often, an ovarian corpus luteum cyst does not cause symptoms in women. A delay in the next menstruation may indirectly indicate the formation of a tumor. The cause of cycle disruption can be determined using ultrasound. In rare cases, the luteal capsule can be confused with pathological cysts. MRI will help differentiate the problem in this case.
In practice, the large corpus luteum is discovered incidentally during ultrasound or diagnostic laparoscopy. Sometimes the tumor may be accompanied by such manifestations as:
These signs can also be a symptom of other pathological processes. Therefore, you should undergo an examination and, if necessary, treatment.
Corpus luteum cyst: signs by ultrasound
The reference point for diagnosing corpus luteum cysts is ultrasound of the ovaries. Based on ECHO signs, the diagnosis is confirmed or refuted.
During the procedure, the specialist receives a photo of the gonad with a parietal formation on the screen. It looks like a slight elevation on one side.
Also, the luteal body can be bilateral or even located in both ovaries (after double ovulation). Echo signs are signs of a corpus luteum cyst on ultrasound:
- the neoplasm has a round, regular shape;
- its walls are characterized by heterogeneous thickness;
- inside the capsule contains polymorphic tissue;
- ovarian tissue is determined along the periphery;
- physiological signs of the corpus luteum are present;
- conducts sound waves well;
- a large amount of vascular tissue is present;
- the size ranges from 2 to 4 cm.
It is quite easy to confuse a luteal cyst with an endometrioid cyst. However, the latter usually grows and can be two-chambered. If it does not go away after menstruation and does not even decrease in volume, the need for removal should be considered. Endometrioid cysts are always dangerous due to their consequences, are accompanied by infertility and can only be treated surgically.
Corpus luteum cyst: treatment
Since in most cases there are no symptoms of a large luteal formation, specific therapy is not performed in women. The tumor resolves on its own after menstruation, gradually decreasing in size.
If a woman has complaints, then a corpus luteum cyst requires mandatory treatment. The method for carrying it out will depend on how many days the delay is, whether there is a positive pregnancy test and what description of the ultrasound was received.
Often, a large luteal body appears during pregnancy. If this happens, the woman is not prescribed therapy. By the beginning of the second trimester, the body will get rid of it on its own. It is recommended to remain calm and avoid sexual activity to prevent apoplexy or the formation of a retention tumor.
Is it possible to get pregnant with a corpus luteum cyst?
If the test is negative and pregnancy is excluded, the patient is prescribed drug therapy. Before treating the tumor, it is necessary to take tests: hormones, tumor markers (CA-125) and find out why a large luteal body appears.
If there is no effect from the medications, it is recommended to remove the capsule using laparoscopy. If the patient has no complaints, then before treating a luteal or ovarian cyst, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach for 3-6 months.
Corpus luteum cyst and delayed menstruation
If a woman is diagnosed with a corpus luteum cyst, then most likely she has a delay in menstruation. For treatment it is necessary to induce menstruation. For this purpose, drugs containing progesterone are used: Utrozhestan, Duphaston, Prajisan and others. How the corpus luteum cyst resolves during menstruation is monitored by ultrasound.
If a tumor occurs monthly, it is recommended to carry out hormonal therapy with oral contraceptives or use Norkolut. Conception in this case will be impossible, but periods will become regular and painless.
After stopping the medications, pregnancy will occur fairly quickly.
To increase the likelihood of conception, it is recommended to track favorable days: keep a schedule, measure BT (basal temperature), observe the nature of the discharge, and also use vitamins.
The nature of menstruation
Menstruation with a corpus luteum cyst may occur later than expected and be unusual. During the bleeding process, a large volume of endometrium is released in the form of mucous clots. In the first days, your stomach may hurt.
Scanty discharge should alert a woman and force her to see a doctor. Menstrual bleeding against the background of a corpus luteum cyst can be prolonged and last up to 7 days.
If it does not go away after a week, and its rate does not decrease in the first 4 days, hemorrhage should be excluded.
Feel
If you are worried about pain due to a corpus luteum cyst, your gynecologist will tell you how to treat it. Symptomatic painkillers are usually prescribed: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesulide. If the cyst gives a fever, then they will also be effective. Pain relief using folk remedies is performed by applying a heating pad. However, this method is not allowed for all women and has contraindications.
Duphaston for corpus luteum cyst
Treatment of corpus luteum cyst with Duphaston is very popular. This drug is prescribed to patients to induce menstruation. The medicine produces progesterone, as a result of which it creates the illusion of the second phase of the cycle for the ovaries and uterus.
After its discontinuation, menstrual bleeding begins within a few days, and the cyst, as a rule, gradually regresses. Treatment with Duphaston is carried out for 1-2 weeks, the drug must be taken daily. The dosage is determined individually for each patient.
Do not be afraid to gain weight from Duphaston. The dosage of the medication is too small and the period of its use is short.
Can a corpus luteum cyst burst?
If a corpus luteum cyst bursts, signs of rupture will be clearly visible. Apoplexy is the first way a tumor is dangerous.
This condition is accompanied by bleeding and can be fatal. The causes of this condition are intense physical activity and sex.
There are cases when, with a large luteal body, even doing yoga was prohibited, since there was a high risk of rupture.
Rupture of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
Rupture of a corpus luteum cyst is manifested by symptoms:
- acute constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness like fainting;
- decreased blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- loss of consciousness;
- blue discoloration of the umbilical area on the abdomen.
If there are signs that the cyst has burst, the patient requires immediate medical attention. Treatment of this complication is exclusively surgical. It is unacceptable to try to treat a ruptured cyst on an outpatient basis or use folk remedies.
Treatment of rupture
If intra-abdominal bleeding or hemorrhage into a cyst is confirmed, then surgery is necessary. In most cases, laparoscopy is performed, which involves reduction of the cyst capsule.
The manipulation is performed under anesthesia and does not take much time. The removed segments are necessarily sent for histology.
The sooner the operation is performed, the greater the likelihood of saving the ovary.
After treatment, it is important to determine why the cyst is forming. If the cause is a hormonal imbalance or an inflammatory process, it is necessary to undergo additional examination and eliminate the cause. To prevent the formation of adhesions, Longidaza is prescribed, and antibacterial therapy is also carried out. You can return to your normal lifestyle after surgery within 2-4 weeks.
Current video
What is an ovarian corpus luteum cyst?
Recommended materials:
- Endometrioid cyst of the right ovary: causes, symptoms, treatment and photos
- Can there be 2 ovulations in one cycle?
- Could thrush be the first sign of pregnancy?
- Pain during intercourse during ovulation
- How do the ovaries ovulate: do they take turns or does ovulation occur in only one?
- What is the corpus luteum in the ovary
- Ovulation: what is it and when does it happen?
- Can breasts hurt during ovulation?
Source: https://stanumamoy.com.ua/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika/
Causes and treatment of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary is a problem that occurs during a woman’s reproductive period. This disease is functional in nature and leads to dysfunction of the ovaries.
The ovaries are a pair of glandular organs located in the pelvic cavity. The ovaries produce the most important sex hormones necessary for the regulation of the menstrual cycle, as well as affecting the functioning of vital human organs.
Estrogens are involved in the processes of emergence of secondary sexual characteristics, the formation of mammary glands, and play a vital function in the regulation of menstruation.
This hormone has an important effect on the skeletal system, protecting against osteoporosis. The effect on the cardiovascular and nervous system consists of a protective effect on the vascular link.
In the ovaries, the maturation of the egg occurs - the cell necessary for fertilization and pregnancy.
Ovarian function gradually declines after age 35 and practically stops with the onset of natural aging—menopause.
The menstrual cycle lasts on average 28 days, but there may be slight fluctuations, both down and up.
There are two phases - follicular and luteal
Under the influence of external hormones in the middle of the cycle, the follicle ruptures and the female reproductive cell is released.
This process is called ovulation. The presence of normal ovulation is a prerequisite for the occurrence of a future pregnancy.
In place of the burst follicle, under the influence of the luteinizing hormone of the pituitary gland, a corpus luteum appears - a temporary gland that secretes progesterone.
Progesterone is a steroid hormone that supports and “protects” pregnancy by reducing uterine contractility.
Under the influence of progesterone, lactation is inhibited. Outside the reproductive system, a positive effect of this hormone on the nervous system and skin condition has been noted.
In cases where conception does not occur, the corpus luteum helps start the next menstruation. This gland received its name in connection with its color, which, in turn, is formed due to the specific luteal pigment.
Typically, the luteal phase lasts 14 days and is genetically determined. With the onset of menstruation, the cycle is renewed.
So, what is a corpus luteum cyst?
A corpus luteum cyst is an ovarian formation that occurs at the site of a ruptured follicle after ovulation. The tumor itself is usually small in size, but can reach sizes of up to 6-7 cm.
In the cavity of the cyst, fluid of serous or hemorrhagic origin, and often completely mixed, accumulates.
Causes
The causes of a corpus luteum cyst of the right or left ovary are not fully understood.
At the moment, one of the main factors is the disruption of blood supply and outflow of lymphatic fluid against the background of a failure in the hormonal regulation of menstrual function. Blood and lymph flow into the corpus luteum, forming a specific cavity.
The formation of a cyst can be triggered by intense physical activity, sexual intercourse, taking hot baths during the period of ovulation, as well as frequent inflammatory formations of the appendages.
Insufficient intake of important microelements from food, in particular with mono-diets, can also underlie dysregulation of the menstrual cycle and lead to the formation of functional cysts.
Symptoms
Often, corpus luteum cysts are asymptomatic. In rare cases, there is a slight delay in menstruation, which goes away naturally.
But if the blood circulation of a sufficiently large vessel feeding the tumor is disrupted, pain in the lower abdomen of varying intensity and a disturbance in the general condition may occur.
If the formation is large, irritation of the pelvic peritoneum receptors may occur, leading to aching pain, as well as compression of nearby organs. Some patients complain of discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this disease includes:
- Mandatory manual inspection on the chair . The doctor can determine by touch the approximate size of the formation, as well as possible swelling of the surrounding tissue. When pressing on the affected area, a woman may feel sensitivity and even severe pain. The doctor will also check for pain with slight displacement of the appendages relative to the uterus and with palpation of the vaginal walls.
- After the examination, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed, in which the doctor can accurately identify the location of the tumor, its size, and also conduct a study of the blood flow of the vessels feeding the formation. This method is called Doppler blood flow measurement. As a rule, all corpus luteum cysts have pronounced blood flow. This fact can also be used for differential diagnosis.
- In rare cases where the diagnosis is not obvious, diagnostic laparoscopy . It is worth noting that this method is used for complications of the cyst, which will be discussed further.
Main signs of complications
Before we talk about the main signs of complications, let's understand what consequences can arise in principle.
Apoplexy—rupture of an ovarian mass—is the most common complication. In this case, the tumor shell ruptures and the contents spill into the pelvic cavity.
If the cyst is large, it may twist, thereby cutting off the blood supply to the ovary and fallopian tube.
The main complaints of patients in such cases are severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness as a result of a drop in blood pressure and painful shock.
All complications require immediate hospitalization in order to resolve the issue of surgical treatment.
Differential diagnosis
Given the existence of other types of cysts, differential diagnosis is often necessary. This is a method that allows you to determine the correct type of tumor by comparing the symptoms and diagnostic picture of different tumors.
For differential diagnosis the following are used:
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, allowing to suggest the structure of the tumor;
- Laboratory methods should include the identification of specific tumor markers CA-125 and HE4, indicating a possible malignant nature. A general blood test will help determine the presence of an inflammatory process.
Treatment
In most cases, no specific treatment is required. Formations of the corpus luteum undergo reverse development within one to three cycles. In other cases, specific therapy is necessary.
Treatment of ovarian corpus luteum cyst is divided into conservative and surgical:
1) Drug (conservative) therapy. Represents the prescription of combined oral contraceptives in a continuous mode until the formation disappears.
As a rule, this takes two to three months. Another type of hormonal treatment is the administration of gestagens in the second phase of menstruation in a cyclic manner.
One of the most common drugs in this category is Duphaston.
Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics are used to relieve tissue swelling and reduce pain.
During treatment, intense physical activity, sexual activity, and visits to baths and saunas should be avoided. You should also not take hot baths, as exposure to temperature can lead to a deterioration in the blood supply to the tumor.
2) Surgery. The question of surgical intervention arises in cases where the cyst does not regress despite comprehensive drug therapy. The main method in this case is laparoscopy. In a large operating room, special manipulators are used to enucleate the formation and suturing the ovarian tissue.
You should know that in emergency cases when complications develop, the surgeon will give preference to the abdominal method - laparotomy.
To improve the course of postoperative therapy, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy for the lower abdomen. Magnetotherapy, electro- and phonophoresis are recognized as the most effective physiotherapeutic methods.
These methods are based on the positive influence of physical forces. The regeneration of damaged tissues is accelerated and inflammatory reactions are reduced.
The pain syndrome becomes less intense. Radon therapeutic baths are also successfully used by physiotherapists.
Cyst and pregnancy
Corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy is essentially one of the subtypes of this formation.
Cysts can reach very large sizes and threaten to cause a very dangerous complication during pregnancy - rupture or necrosis of the tissue of both the tumor itself and the entire ovary.
However, most often the cysts are of medium size and must be dynamically observed using ultrasound. As a rule, such formations resolve by the 16th week of pregnancy and do not require specific treatment.
The question of surgical treatment arises quite rarely and requires a thorough analysis of all the pros and cons.
Prevention
- The basis for the prevention of any hormone-dependent formation is the normalization of the menstrual cycle.
- If the cyst has regressed over a long period of time and caused complaints in women, it is advisable to prescribe combined oral contraceptives to reduce the own activity of the ovaries and give them a rest.
- It should also be remembered that the basis of any prevention is a healthy lifestyle, adequate physical activity, and timely detection of any inflammatory diseases.
- Each woman should be dynamically observed by a gynecologist and periodically undergo screening ultrasound examinations.
Source: https://mymatka.ru/kista/zheltoe-telo-yaichnika
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary
An ovarian corpus luteum cyst is a functional retention formation of ovarian tissue that forms in the place of a non-regressed corpus luteum. The ovarian corpus luteum cyst is practically asymptomatic; in rare cases, it is accompanied by slight pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities, complicated course. Diagnostics includes examination by a gynecologist, ultrasound, Doppler sonography, and laparoscopy. An ovarian corpus luteum cyst can regress on its own within 3 menstrual cycles; in case of complications, cystectomy, resection or removal of the ovary is indicated.
The corpus luteum is a cyclically formed gland in the ovary, which appears at the site of the ovulated Graafian vesicle (follicle) and produces the hormone progesterone. The name of the gland was given by the lipochrome pigment present in its cells and giving them a yellowish color. The corpus luteum develops in the ovary during the second (luteal) phase of the menstrual cycle.
In the flowering stage, the corpus luteum reaches a size of 1.5-2 cm and one pole rises above the surface of the ovary. In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum at the end of the luteal phase undergoes involutive development and stops producing progesterone.
When pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum does not disappear, it continues to grow and function for another 2-3 months and is called the corpus luteum of pregnancy.
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary
An ovarian luteal cyst is formed from a corpus luteum that has not undergone regression, in which, due to circulatory disorders, fluid of a serous or hemorrhagic nature accumulates.
The size of an ovarian corpus luteum cyst is usually no more than 6-8 cm. An ovarian corpus luteum cyst occurs in 2-5% of women of reproductive age after the establishment of a two-phase menstrual cycle.
Clinical gynecology differentiates corpus luteum cysts that develop outside of pregnancy (from an atretic follicle), as well as corpus luteum cysts that arise during pregnancy.
The corpus luteum cyst of the ovary is often unilateral, single-cavitary; has a capsule lined from the inside with granular luteal cells, filled with reddish-yellow contents.
The spontaneous disappearance of the ovarian corpus luteum cyst occurs within 2-3 menstrual cycles or in the second trimester of pregnancy.
The reasons for the formation of ovarian corpus luteum cysts are not completely clear.
It is believed that the formation of a corpus luteum cyst is caused by hormonal imbalance and impaired blood circulation and lymph drainage in the ovarian tissues.
The risk of luteal cyst formation increases while taking drugs to stimulate ovulation in case of infertility or preparation for IVF (for example, clomiphene citrate) and emergency contraception.
The possibility of the formation of a cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary under the influence of heavy physical and mental stress, harmful production conditions, malnutrition (mono-diet), frequent oophoritis and salpingo-oophoritis, and abortion cannot be ruled out. All these factors can lead to endocrine imbalance, and, consequently, the formation of an ovarian corpus luteum cyst.
Symptoms of an ovarian corpus luteum cyst are mild. Often luteal cysts develop within 2-3 months, after which they spontaneously and suddenly undergo involution.
An ovarian corpus luteum cyst detected during pregnancy does not pose a threat to the woman and the fetus.
On the contrary, the absence of the corpus luteum of pregnancy in the early stages can cause spontaneous abortion due to hormonal deficiency.
Reverse development of ovarian corpus luteum cysts during pregnancy also most often occurs spontaneously by 18-20 weeks. gestation: by this time, the formed placenta completely takes over the hormone-producing functions of the corpus luteum.
Sometimes an ovarian corpus luteum cyst can cause slight pain, a feeling of heaviness, fullness, and discomfort in the abdomen on the developmental side. A luteal cyst that produces progesterone can cause delayed menstruation or, conversely, prolonged menstruation due to uneven shedding of the endometrium. Luteal ovarian cysts never become malignant.
Most often, symptoms develop with a complicated course of the ovarian corpus luteum cyst - torsion of the pedicle, hemorrhage into its cavity, or ovarian apoplexy.
In all these cases, a clinical picture of an acute abdomen is observed - cramping acute pain of a diffuse nature, vomiting, tension and sharp pain in the abdomen, positive peritoneal symptoms, gas and stool retention, disappearance of peristaltic noises, intoxication, etc.
Diagnosis of an ovarian corpus luteum cyst is carried out taking into account anamnesis, complaints, gynecological examination data, ultrasound, and laparoscopy. Vaginal examination reveals a tight elastic formation on the side of the uterus or behind it, which has limited mobility and sensitivity to palpation.
Echoscopically, a corpus luteum cyst is defined as an anechoic, homogeneous, round formation, 4 to 8 cm in diameter, with smooth, clear contours, sometimes with a fine suspension inside.
To accurately recognize a luteal cyst, a dynamic ultrasound is performed in the first (follicular) phase of the menstrual cycle.
Carrying out color Dopplerography (CDC) is aimed at excluding vascularization of the internal structures of the cyst and differentiating retention formation from true ovarian tumors.
As with other identified ovarian tumors and cysts, a study of the CA-125 tumor marker is indicated. To exclude or confirm pregnancy, a determination of human chorionic gonadotropin and a pregnancy test are performed.
In cases where it is difficult to differentiate a corpus luteum cyst from other neoplasms (ovarian cystoma, theca lutein ovarian cysts with chorionepithelioma and hydatidiform mole, etc.
) and ectopic pregnancy, diagnostic laparoscopy is required.
Patients with a small and clinically silent ovarian corpus luteum cyst are advised to observe a gynecologist, ultrasonic dynamic control and color circulation during 2-3 menstrual cycles. During this period, the cyst may undergo regression and completely disappear.
Symptomatic and recurrent ovarian corpus luteum cysts can also resolve under the influence of conservative anti-inflammatory therapy, selection and prescription of hormonal contraceptives, balneotherapy (therapeutic baths and vaginal irrigation), peloid therapy, laser therapy, SMT phoresis, electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis, magnetic therapy. During the period of treatment for ovarian corpus luteum cysts, physical activity and sexual activity are limited in order to avoid torsion or rupture of the tumor-like formation. If the luteal cyst does not resolve within 4-6 weeks, the issue of its surgical removal is decided.
Planned intervention for a corpus luteum cyst is most often limited to laparoscopic enucleation of the cyst within the unchanged ovarian tissue and suturing its wall or resection of the ovary. In case of complications (necrotic changes in ovarian tissue, bleeding, etc.), emergency laparotomy with oophorectomy is indicated.
Prevention of the formation of functional ovarian cysts is facilitated by timely and complete treatment of inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system, as well as correction of disturbed hormonal balance.
Observation by a gynecologist-endocrinologist and ultrasound control when identifying an ovarian corpus luteum cyst allows you to take the necessary measures in a timely manner and prevent complications. An ovarian corpus luteum cyst does not pose a threat to a developing pregnancy.
With spontaneous regression or planned removal of the ovarian corpus luteum cyst, the prognosis is favorable.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/corpus-luteum-cyst
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary: causes, symptoms, conservative and alternative treatments
An ovarian corpus luteum cyst is a benign neoplasm in the form of a capsule with liquid contents.
The corpus luteum (temporary gland), in which the hormone progesterone is produced, appears during ovulation. As a result of poor circulation in the gland, a cavity is formed in which fluid accumulates.
In some cases, the cystic capsule may fill with blood - this is due to a ruptured blood vessel.
Features of a corpus luteum cyst
The menstrual cycle of a healthy woman is a 2-phase period:
- Follicular phase;
- Luteal.
During the menstrual cycle, processes occur in the uterus and ovaries that create the conditions for fertilization and pregnancy.
During the onset of the follicular phase, every month, a gland develops in the ovary, which is called the corpus luteum. This gland produces progesterone, a hormone that ensures a normal, healthy pregnancy without complications.
The color of the gland is determined by the presence of a special pigment. The temporary gland can reach a maximum size of 2 cm. If fertilization does not occur, the gland involutes (returns to its previous form) and resolves, and hormone production stops. In case of pregnancy, the iron increases, progesterone is synthesized in large volumes.
Hormonal disruptions, dysfunction, structural changes in the reproductive organs lead to the fact that the temporary gland does not disappear. Blood circulation is disrupted, fluid accumulates, resulting in the formation of a cystic formation. The maximum size of the cyst can reach 8 cm.
In some cases, the tumor formation eliminates itself, its complete disappearance is observed within several months. The cyst in the expectant mother may disappear after the formation of the placenta (16th week of pregnancy).
Causes of formation of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
The reasons for the formation of cystic cavities of the temporary gland are not fully understood. The dominant factor provoking the occurrence of formations is hormonal imbalance. Other reasons include:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- Problems with lymphatic drainage and blood circulation in the ovaries;
- Infectious lesions, inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs;
- Endocrine diseases: diabetes mellitus, adrenal gland pathologies;
- Functional disorders, pathological changes in the structure of the thyroid gland;
- Hereditary factor;
- Weight disorders: overweight or underweight;
- Taking emergency contraceptives (Postinor), ovulation stimulants (Clostilbegit) - which cause a sharp hormonal “jump”;
- Early menstruation in girls;
- Disorders caused by mono-diets (eating one product);
- Instability of psycho-emotional state: depression, nervous breakdowns, increased emotionality (including positive);
- Ectopic pregnancy, abortions, miscarriages;
- Inadequate physical activity causing overexertion.
Symptoms of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
Cystic formation can develop asymptomatically, in some cases it is manifested by a feeling of fullness, heaviness in the abdomen, mild pain and discomfort. There may be a delay in menstruation due to a corpus luteum cyst, or a prolonged period of menstruation.
Severe symptoms appear in the complicated course of tumor formation:
- Complete or partial torsion of the ovarian pedicle. This complication causes compression of the nerves and blood vessels of the organ, disrupting nutrition and blood circulation in the organ. The corpus luteum cyst is very painful, the pain syndrome is of an acute, stabbing nature. The condition is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, general weakness, attacks of dizziness, and nausea. In some cases, there is an increase in temperature and disruption of the intestines (constipation). The pathological condition occurs as a result of the growth of the cyst to a large size exceeding 5 cm. Twisting of the organ pedicle requires immediate surgery;
- Menstruation disorders. In most cases, the disorder manifests itself as delayed menstruation. The condition occurs due to the active influence of progesterone synthesized by the gland. Activation of the hormone leads to later rejection of the mucous membrane in the uterine cavity, which provokes a delay in menstruation. The duration of the delay, with the development of a hollow formation, can reach up to 2 weeks;
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst of the corpus luteum occurs infrequently. It manifests itself with severe symptoms: a sharp pain permeates the lower abdomen, which does not subside when the body position changes. Accompanying symptoms are nausea and vomiting, attacks of dizziness, lightheadedness, severe weakness, and cold sweat. The temperature does not rise.
Emergency surgical intervention is required if, when the cyst ruptures, bleeding occurs into the pelvic cavity or peritoneum. The main manifestations of the condition: shock, weakness, lethargy. Blood pressure drops sharply, heart rate increases, and the skin turns pale.
Diagnosis of ovarian corpus luteum cyst
- Gynecological examination. Diagnosis begins with a consultation with a doctor. In most cases, patient complaints are absent or relate to moderate pain in the pelvic area and delayed menstruation. However, women note the presence of brown, brown discharge with a corpus luteum cyst, the amount of which can vary (from insignificant and spotting to heavy).
The small size of most cysts does not allow them to be detected by palpation. Cystic formations of the temporary gland are similar to manifestations of oophoritis and ectopic pregnancy, so additional examinations are required for an accurate diagnosis.
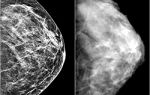
- Ultrasound examination. The method is one of the most accurate and informative.
The study allows us to identify the formation, its size and internal structure. The cystic node is visualized as a round-shaped formation with a pronounced capsule, which has clear boundaries. On ultrasound, a corpus luteum cyst is determined down to the smallest structural features, and the contents of the capsule are revealed in detail.
The fluid that fills the cyst cavity does not transmit ultrasound rays. Areas with liquid content are visualized during ultrasound examination as darkening. The presence of exclusively dark areas in the formation indicates the development of a “simple” cyst - its capsule contains liquid without impurities.
If there are light and dark areas in the area, the formation is considered “complex” and indicates that in addition to liquid, the capsule contains dense blood clots.
In cases where the diagnosis of cyst formation is inaccurate, additional examinations are necessary for differentiation:
- Doppler ultrasound allows you to distinguish between an ovarian tumor and its cyst (the manifestations of which are similar). Color Dopplerography is based on the study of blood flow in organ tissues. The visualization appears as areas of different colors. In a temporary gland cyst, blood flow is not visualized;
- A tumor is differentiated from a cyst by testing the blood for an oncological marker (CA-125), which is not detected during the development of benign formations (cysts);
- Pregnancy tests, since the neoplasm does not exclude the possibility of fertilization;
- Laparoscopy used for diagnosis and treatment. During the examination, hemoglobin levels are determined and assessed;
- Hormone tests (LH, FSH, testosterone, estradiol). Identifying the nature of hormonal disorders helps to establish the cause of the development of the formation and allows you to prescribe adequate therapy.
Treatment of corpus luteum cyst in the ovary
For small tumors, wait-and-see tactics are used. The doctor monitors their development over 3 menstrual cycles.
An ultrasound scan is performed every month to track changes in the size and capsular contents of the formation. In most cases, during this period, the tumors disappear.
In situations where watchful waiting is ineffective and uncomplicated cystic nodes develop, classical therapy is prescribed.
Classical therapy combines:
- Hormone therapy. In most cases, for the treatment of corpus luteum cysts of the right ovary or left organ, new generation oral contraceptives are prescribed (Yarina, Jess). They restore normal hormonal levels, which helps eliminate the cyst;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs help eliminate the source of inflammation and pain (Ketorol, Diclofenac);
- Physiotherapeutic procedures combining: radon baths, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, laser exposure;
- Diet therapy and exercise therapy. The developed diet will help adjust weight, restore metabolic processes, and strengthen the immune system. Complexes of therapeutic exercises will enhance metabolism, normalize hormone synthesis, and accelerate blood circulation in the reproductive system.
At the end of the classical treatment course, a follow-up examination is carried out to determine further actions. If there is no regression after 1-1.5 months of classical therapy, surgical intervention is prescribed, the purpose of which is to remove the cyst and preserve the organ.
In most cases, the following surgical methods are used:
- The cyst is excised, healthy organ tissue is preserved. The cyst and capsule are removed. After a certain time after the operation, the ovary is completely restored and functions normally;
- In some cases, surgical treatment of a corpus luteum cyst of the left ovary, like the right one, involves removing the tumor along with nearby tissues. After such an operation, the functioning of the organ is partially restored.
Traditional medicine methods are used as an auxiliary treatment area. Some of them are particularly effective.
Borovaya uterus, Rhodiola, wintergreen - a triple “blow” to the cyst
One of the most effective ways to combat cystic formations (and many other diseases) of the temporary gland is the alternate use of these herbs.
Plant properties
- Ortilia (hog queen). The plant is used to treat infertility and has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antitumor and resorption effect. Borovaya uterus helps get rid of many gynecological diseases: cysts, fibroids, polyps, uterine bleeding, erosive lesions. Effective for fibroadenoma, mastopathy;
- Rhodiola quadruple (Red Brush). It is used to eliminate tumor formations (cysts, fibroids), has the ability to restore hormonal imbalances and normalize the functioning of the woman’s reproductive system;
- Wintergreen will help relieve swelling and has a strong absorbable effect.
Recipe
A tablespoon of dry raw materials is poured with boiling water (1 cup). The decoction is infused for 20 minutes, taken orally three times a day, before meals (a third of a glass).
Reception scheme
During the first week of treatment, a decoction of ortilia is taken, in the second - Rhodiola, in the third - wintergreen.
Burdock juice
This method of eliminating cysts is one of the most effective (the juice of the plant has a strong absorbent effect). Using a juicer, the juice of the plant is extracted; you can use a paste of leaves by passing them through a meat grinder.
The juice or pulp from the leaves is cooled and taken orally (30 ml) before meals for a month. Freshly prepared mixture or juice is stored in the refrigerator for no more than 3 days.
Herbal decoctions and tinctures
Herbal mixture of 5 ingredients. Used in equal quantities: viburnum bark, chamomile, motherwort, rowan berries, Rhodiola rosea root. Pour 15 grams of the mixture with half a liter of boiling water and leave for 12 hours. Take 50-100 ml orally before meals. The course of treatment is several months.
Collection of 4 components. Leaves of nettle, mint, and currant are mixed in equal proportions; wormwood, rose hips, jasmine, thyme. 30 grams of herbal mixture are poured into 1 liter of hot boiled water and left overnight. Take 100-120 ml 30 minutes before meals three times a day. Course – 3 months.
Raisin tincture. Preparation: 30 grams of raisins are poured with 500 ml of vodka. The product is infused for 2 weeks in a dry and dark place. The tincture is taken orally, 15 ml, three times a day, before meals. Course=30 days.
Peony. Recipe: 50 grams of plant roots are poured with 500 ml of vodka. The container containing the product is tightly closed and placed in a dark place for several weeks (3-4). After the required infusion period has passed, the product is filtered. 5 ml. tinctures are diluted in 1/3 glass, taken three times a day. Course = 1 month.
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary during pregnancy
Regardless of the location of the formation: a cystic structure in the organ on the left, a luteal cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary, this does not pose a danger during pregnancy.
The development of a node during pregnancy does not threaten either the mother or the fetus. All that is required is regular ultrasound examination to monitor the growth of the formation.
In cases where the size of the cyst formation is large (more than 5 cm), the pathology occurs with complications, laparoscopy may be prescribed.
In most cases, a formation in the left organ, a cyst of the corpus luteum of the right ovary, during pregnancy dissolves by itself by 16-20 weeks, after the formation of the placenta.
Prevention and prognosis for ovarian corpus luteum cyst
The timely elimination of disorders, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the pelvic organs will help prevent benign formations of the temporary gland.
Cyst formation can be prevented by timely treatment of endocrine diseases, correcting and leveling the hormonal balance in the body. Strengthening immune forces helps to activate the body's defense against any pathologies and diseases.
You need to get proper rest, engage in adequate physical activity, adhere to a complete and balanced diet, and stabilize your emotional state.
When a neoplasm is detected in the ovary, constant medical monitoring is necessary, first a wait-and-see approach, then, if the formation does not resolve on its own, conservative therapy. The prognosis is favorable with regression of the node and surgical excision of the tumor.
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary: causes, symptoms, conservative and alternative treatments Link to main publication
Source: https://prorak.info/kista/kista-zheltogo-tela-yaichnika/
Why does an ovarian corpus luteum cyst form?
The corpus luteum is a temporary secretion gland.
It is formed at the site of the follicle, functions in the second half of the female cycle and produces the hormone progesterone.
If fertilization does not occur, it disappears. But sometimes the temporary secretion gland does not regress - a cyst of the corpus luteum of the right or left ovary begins to form from it.
What is a corpus luteum cyst?
Benign ovarian formations developing from the body of the temporary gland are called corpus luteum cysts, or luteal cysts.
Stages of formation
- Every month, a mature egg is released through the rupture of the follicle, traveling through the fallopian tubes to the uterus.
- The granular cells of the follicle begin to rapidly divide, accumulate yellowish pigments and turn into a temporary gland.
- In the absence of pregnancy, it gradually atrophies, but if conception has occurred, it continues to function and ensure the release of progesterone.
- The gland functions for 3-4 months, ensuring the development of the embryo until the placenta is formed, then it begins to regress.
- If reverse development does not occur, the shell of the gland accumulates serous fluid and blood - a capsule is formed, the size of which can increase to 6-8 centimeters.
If the cyst is small and begins to shrink and regress, the pathology occurs with virtually no symptoms.
A corpus luteum cyst in the right ovary develops more often than a cyst in the left ovary.
This is due to the fact that the right appendage has more blood capillaries, so more blood or serous fluid accumulates in the cystic formation of the right ovary.
Causes
The exact reasons for the formation of cysts are still unknown to doctors, but it is believed that their appearance may be caused by hormonal disorders.
There are known factors that provoke the occurrence of pathology of the luteal body:
- taking certain contraceptives that can cause hormonal imbalance;
- sharp fluctuations in weight, impaired nutrition;
- mental and nervous overstrain, constant stress;
- inflammation of the appendages, ovarian abnormalities;
- frequent terminations of pregnancy - abortions.
Treatment of borderline ovarian tumor - is it cancer or not?
Symptoms
- Pain with a yellow ovarian cyst is rare, but sometimes there is minor pain, similar to mild intestinal colic or premenstrual symptoms.
- On ultrasound you can see that the signs of luteal formation disappear on their own within 2-3 months.
- As a rule, a corpus luteum cyst hurts when its stem is twisted, which leads to poor circulation, hemorrhagic hemorrhages in the ovary, and necrotic processes.
A cyst can hurt more severely when it degenerates into a malignant neoplasm.
An advanced disease sometimes leads to rupture of the gland, entry of its contents into the abdominal cavity, and the development of peritonitis.
Symptoms such as sharp, persistent pain, severe bleeding, repeated vomiting if peritonitis is suspected require immediate surgical treatment of the ovary.
Diagnostics
- The diagnosis is made based on a study of the anamnesis, the patient’s complaints, visual and palpation gynecological examination, ultrasound, and analysis of tumor markers.
- With manual vaginal palpation, a compaction with limited mobility and pain sensitivity is determined on the side or behind the uterus.
- Ultrasound scanning is prescribed at the first stage of the menstrual cycle and determines the size, position, and internal structure of the pathological formation.
- Differential diagnosis is carried out if:
- true (special tests) or ectopic pregnancy (ultrasound);
- ovarian tumor (color Doppler sonography, tumor markers CA-125);
- hormonal dysfunction (blood tests for follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, testosterone, estradiol);
- the presence of neoplasms of unknown etiology (laparoscopy).
Treatment methods
Treatment of a small, uncomplicated yellow cyst involves monitoring its development.
If within two to four cycles the formation cannot resolve on its own, drug treatment is recommended:
- anti-inflammatory, painkillers (Diclofenac);
- hormonal dosage forms that normalize hormone levels;
- progesterone-containing agents that inhibit the functioning and rapid growth of tumors.
Physiotherapy
Cysts can be treated using physiotherapeutic procedures, although some doctors question their effectiveness.
Physiotherapy uses laser treatment, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, and radon baths. Acupuncture has become widespread.
Attention! Thermal procedures: visits to the sauna, steam room, hot baths, mud therapy are prohibited for patients with pathologies of the female organs.
Surgical intervention
Necrotic changes in ovarian tissue, extensive bleeding, and perforations require treatment by laparotomy.
Laparotomy is a common traumatic surgical operation that provides access to the uterus and appendages. Resection and removal of the affected ovary are performed under general anesthesia.
Laparoscopy
Multiple or single uncomplicated formations that are not amenable to drug treatment are removed laparoscopically.
Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic intervention used as a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for pathology of the luteal body.
Under general or local anesthesia, the surgeon removes the contents and sutures the resulting cavity. After the wound heals, ovarian function is restored.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine does not replace drug or surgical treatment, but only complements them. You can treat a cyst with such folk recipes as:
- compresses (1:10) of ordinary table salt, which are placed on the lower abdomen overnight;
- decoctions from the shells of pine nuts or partitions of walnuts;
- infusions of spruce or pine needles, medicinal herbs (shepherd's purse, wormwood, string, yarrow, nettle, chamomile).
Caution: Never self-medicate. Look for good specialists in the field of traditional medicine, consult with your doctors. Self-medication is fraught with complications.
Complications
In most cases, these temporary secretion glands do not pose a health hazard and disappear on their own over time. But sometimes the course of the disease becomes more complicated:
Such situations require surgical intervention. And the sooner the patient receives medical assistance, the higher the likelihood of maintaining reproductive function.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable if you consult a gynecologist early: timely medication or surgical treatment reduces the likelihood of complications.
Prevention
To maintain women's reproductive health, you need to:
- regularly undergo preventive examinations by a gynecologist 1-2 times a year;
- promptly treat hormonal disorders, inflammatory or infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- choose sufficiently reliable means to prevent unwanted pregnancy, avoid abortion.
Causes of enlarged ovaries in a woman - symptoms of inflammation
Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary during pregnancy
Experts believe that if you have a cyst, it is possible to get pregnant, but it is better to plan the birth of a child a month after treatment. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the formation disappears on its own.
But if for some reason it continues to grow, it is removed in a laparoscopic manner that is safe for the fetus and mother.
Cyst rupture
Breaks are rare. A provoking factor for rupture or rupture of a cyst can be heavy pregnancy, overly active sexual intercourse, excessive physical activity, or nervous shock.
Symptoms: sharp burning pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the perineum, rectum, nausea, vomiting.
Blood pressure may increase, chills and fainting may appear. If these signs occur, you should immediately call 103 and call an ambulance.
Treatment of cyst rupture
Treatment is carried out only in inpatient settings. Gynecologists determine the degree of blood loss and choose a treatment method:
- mild degree - with minor blood loss, drug treatment is sufficient;
- moderate severity - laparoscopic surgery;
- severe degree - laparotomy (abdominal surgery) and massive infusion (intravenous administration of drugs) therapy to restore blood loss.
Despite the fact that a cyst of the temporary gland of the left or right ovary is considered a relatively harmless disease, you cannot be careless about your health.
To preserve reproductive function, after diagnosis, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations and be sure to undergo additional preventive gynecological examinations.
Source: https://endometriy.com/yaichniki/kista-zheltogo-tela