Brain tomography is the most accurate and popular examination method. It provides the most objective understanding of the state of brain tissue, adjacent soft tissue and skull bones. In this article, we will talk about how the tomography procedure is carried out, what it means when doctors prescribe a CT scan, are there any contraindications, it will also be useful to know how to prepare for a computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain.
When is a CT scan of the brain indicated?
The slightest disturbances in brain function may serve as an indication for undergoing a computer diagnostic procedure. Brain tomography has a whole list of symptoms, and if found, it is prescribed to the patient.
Seemingly harmless conditions can have irreversible consequences. Therefore, if there is any suspicion of illness, the doctor will refer you for a tomography.
In a situation where there is even the slightest likelihood of illness, it is better to play it safe in order to save a life, especially since the technical level of diagnostics allows this to be done. So what are the indications for a brain CT scan?
List of symptoms for which it is advisable to undergo a tomography
If you have been tormented by the same symptoms for a long period of time, this is already a reason to get examined. A CT scan of the head is needed if:
- Severe or persistent headaches do not go away, and the cause is impossible to understand.
- If double vision occurs in the eyes, you feel dizzy, all this is accompanied by nausea, possibly vomiting. These are alarming symptoms, if they are supplemented by periodic fainting, then you cannot waste an hour, you should find medical help as soon as possible to undergo an X-ray examination on a computer.
- Emergency examination requires brain injury, edema, hematoma, foreign objects entering the skull, or the neck through the wound cavity. In this case, the tomograph will show all deviations that could arise.
- Often, not only tomography of the brain is required, but also of the cervical vessels.
- Any hint of the onset of a stroke requires an urgent understanding of the disease picture. Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke are completely different diseases that are treated in different ways.
- If the patient has a previously documented condition that predisposes to stroke, arterial diagnosis is mandatory.
- If there is a suspicion of thrombosis or atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head, a visual examination will resolve the doubts.
- If a patient’s hearing has deteriorated or their vision has sharply decreased, a CT scan is also indispensable.
- Computed tomography of the head is performed on those individuals whose behavior has changed, inappropriate reactions, or mental or thinking disorders have appeared.
- A rare but possible problem is parasites inside the head. To see them, as well as to measure the cystic blisters formed by them, you need a computer picture of what is happening.
- The preoperative period on the face is necessarily accompanied by scanning. This includes the implantation of dentures.
- A CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck is done in the presence of cancerous tumors to clarify the situation with the stage of the disease. Next, repeated studies are performed to check the results of the operation and oncology therapy.
- Foci of inflammation in the head area, abscesses, require examination on a tomograph.
- Under the watchful eye of a tomograph, a brain biopsy is also performed.
Contraindications for CT
There are also limitations and strict contraindications for computer examination, since it is based on X-ray radiation. When should you not undergo a tomography?
- If a woman is carrying a child, then before undergoing radiation, she needs to make sure that the baby will not be harmed. Therefore, during pregnancy it is better to refuse tomography, so as not to harm the baby during its perinatal period of life.
- Diagnosis is not done during breastfeeding either. The problem is that CT with contrast does not reflect well on the composition of human milk. You should not give your baby breast milk for two days after the procedure.
- Those who have iodine intolerance, including seafood intolerance, should refuse a CT scan or perform it without a contrast agent. The contrast agent contains iodine, which can cause allergies.
- In addition, CT with contrast is prohibited if renal failure is severe.
In this case, it will be difficult for the body to get rid of the foreign drug in the bloodstream. Overweight people cannot undergo a CT scan of the head and neck, but the newest models can support weights of up to 200 kilograms. - Due to the need to do head tomography while still, it is impossible to examine a person who does not control his behavior. If his condition is accompanied by spontaneous movements, twitching, and other uncontrolled actions, diagnosis cannot be made.
Contraindications, although minor, are very important and cannot be ignored, otherwise the computer test will cause harm instead of promoting treatment.
Preparing for a tomography test
CT scan of the brain vessels and neck vessels can be performed without preparation, especially if there is an urgent case. If possible, the patient should relax and balance his emotions. If it is possible to prepare in advance, then you should exclude overwork and stressful situations the day before the diagnosis.
Preparing for a CT scan takes only a few minutes. You should get rid of metal objects (hairpins, hairpins, jewelry made of any metal, watches, removable dentures).
If you are planning to prepare for a CT scan of the brain, then you need to have a referral from a doctor, a passport, a medical history, and a medical card with you. Be sure to discuss any allergic reactions you have with your doctor before you begin the test procedure. It will be important to know about your chronic diseases.
When tomography of cerebral vessels is planned with contrast, how to prepare in this case? Fast the day before the procedure. You should not drink a few hours before your diagnostic visit.
How is a CT scan done?
How is a CT scan of the brain done? What sensations can you expect? Do you experience any pain or discomfort during the CT scan? The patient lies on his back, trying to find a comfortable position on the mobile table. After this, the table is rolled into the tomographic scanner tunnel. The doctor performs the procedure from the next room. For convenience and safety, a connection is established between the doctor and the patient thanks to a microphone built into the scanner. When the examination begins, a ring equipped with an X-ray tube and many sensitive sensors begins to rotate around the patient. The X-ray beam moves in a circle through a person, which allows you to take layer-by-layer frames. The program arranges the captured data in the form of a continuous image. In addition to the beam, the table on which the patient is located also moves. All these possibilities will be shown to the diagnostic doctor on the monitor of images of each part of the head.
The procedure does not provide any sensations to the patient at all. You can only hear the noise of the installation's engines.
If a CT scan of a child’s brain is performed, the doctor fixes his head with special straps. This is necessary for the immobility of the research object. Otherwise, you can get a blurry picture, that is, spoil the results of the examination. Computed tomography of the brain of a child under one year old can be replaced by ultrasound examination methods.
The doctor sees the scan transcripts on his monitor. They look like sections of different tissues and organs.
A contrast enhancer is used to view the results more clearly. This is especially often done if there is a suspicion of a tumor. After all, the tumor has a better blood supply, and therefore more actively accumulates the contrast agent. Due to this, it stands out more clearly. Clear boundaries of a tumor, for example, can help determine its nature, location, and histological features.
The contrast agent is iodine in diluted form. Used for images of the head and neck, as well as the spinal column. In the presence of iodine, the transcripts can be examined in more detail, with more details. How is the procedure performed if the administration of a contrast solution is indicated? The contrast agent is administered intravenously, otherwise the procedure is no different.
Is contrast agent harmful? If a computed tomography scan of the brain itself does not cause any discomfort, then the use of contrast can give some sensations:
- Feeling hot;
- Nausea;
- Metallic taste on tongue;
- Itching on the skin, rash, Quincke's edema.
The contrast is not harmful unless the patient is allergic to iodine. The entire procedure lasts a maximum of 15 minutes.
Angiography of cervical and head vessels
Along with abnormalities of the soft and bone tissues of the head, there are many problems with blood vessels. Any CT scan can be supplemented with angiography of cerebral vessels. This is a very accurate and comprehensive method for obtaining information about the structure and changes of blood vessels.
What can an angiogram “see”:
- Stenosis or narrowing of the vessel;
- Pathological connections between veins and arteries (fistulas), which should not exist;
- Aneurysms;
- Atherosclerotic changes and other anomalies.
How are the results interpreted?
After completing a CT scan of the brain, the doctor will not immediately release the results. It always takes some time to understand the data received and analyze it.
As a rule, this takes up to half an hour, sometimes a little longer.
But after this, the images will be handed over to the patient to be provided at the place of his treatment, for example, to the doctor who sent him for testing.
The patient is immediately informed of those transcripts that require urgent treatment, then the diagnostician can draw your attention to certain results. The patient is sent for a consultation with the necessary specialist (oncologist, ENT, neurosurgeon, dentist, therapist, and so on).
Along with a printout of the x-rays selected by the doctor, the patient also receives a statement with the radiologist’s report. You also receive a disk with a fully recorded CT scan of the brain or neck and software that allows you to read it.
Evaluating the result
What does a brain CT scan show? If all indicators are normal, the tomogram frames show that the bones are intact, the vessels have their usual sizes and shapes, there are no shadows, neoplasms or foreign bodies, there are no fluid accumulations or bleeding.
Any deviations are considered abnormal: aneurysms, changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain, altered bone structures, bleeding, swelling, hematomas, tumors, and other deviations. All of them characterize the presence of a particular disease.
Is it possible to replace CT with another research method?
If a person has contraindications to a CT scan of the brain, what can be offered instead of this procedure? Modern clinics are equipped with alternative options that are gentler on the brain than computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging also allows you to visualize brain structures and check for abnormalities; MRI can replace the usual computed tomography. MRI works using a magnetic field and better shows those tissues that contain fluid.
- X-rays are prescribed when a simple problem is being examined. X-ray can detect foreign bodies, violations of the integrity of the skull, but is not able to detect hemorrhages.
- Neurosonography is used for babies and newborns; it is performed using ultrasound through an open fontanel. Computed tomography of the brain for children with an overgrown fontanel replaces neurosonography.
The advantage of CT is that this method is more reliable than others in providing data on fluid accumulations, such as hemorrhages, as well as solid structures such as bones. Is CT scanning harmful? The radiation dose that the patient receives during the examination is acceptable and within the normal range.
Brain tomography (CT) Link to main publication
Source: https://CheckUpAdviser.ru/kt-scan/golovi-i-shei/kt-golovnogo-mozga
Features of CT angiography of cerebral vessels
Computed tomography (CT) is a modern way of studying the structure of an object using x-rays. Radiation, when passing through tissues of different densities, is attenuated to varying degrees; this attenuation is recorded and processed by a computer.
CT angiography of cerebral vessels examines the shape, condition of the arteries, veins, capillaries of the head, blood flow, the presence of deformations, structural abnormalities (narrowings, malformations, aneurysms), atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, tumors, hematomas, and consequences of injuries.
Computed angiography provides the doctor with a three-dimensional model with a series of layer-by-layer images-sections of the vascular system of the brain. In terms of information content, such research surpasses all other research methods.
Indications and contraindications
X-ray studies have their own indications and contraindications. CT angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck is prescribed in the following cases:
- severe headaches - constant or acute;
- persistent increase in pressure;
- convulsive syndrome;
- stroke - angiography helps to assess the consequences;
- disorders of the blood clotting system or taking anticoagulants;
- frequent dizziness or fainting;
- head injuries;
- pain or discomfort in the neck;
- memory impairment, ability to concentrate, decreased cognitive function;
- inability to use MRI;
- examination before brain surgery;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms;
- the presence of all other symptoms indicating an acute or chronic disorder of the blood supply to the brain;
- suspected cerebral edema.
Contraindications to the study:
- irradiation of pregnant and lactating women is unacceptable - exposure to X-rays can lead to disturbances in fetal development, and it is even more unacceptable to use radioactive iodine preparations;
- children's age (up to 14 years);
- impaired renal and liver function;
- heart failure;
- myeloma leukemia;
- allergy to contrast;
- claustrophobia;
- scanning with contrast – in the presence of endocrine disorders (thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus), with increased sensitivity to iodine;
- for patients weighing over 150-200 kg (depending on equipment modification). Tomographs are designed for patients with a certain body weight;
- Tomography creates a radiation dose to the body (2 mSv), so a CT scan of the head can be performed no more than three times a year, with breaks of at least two months.
For health reasons, the study is carried out if there are contraindications.
How to prepare properly
No special preparation is required before performing a CT scan. If possible, you should stop taking medications 12 hours before the procedure.
If it is impossible to refuse medications, you must notify the doctor about undergoing drug therapy, indicate the frequency and dose of medications.
If oral administration of a contrast agent is planned (for example, during simultaneous abdominal tomography), you should not drink or eat food for 4-5 hours before the scan.
Before the procedure, you must remove metal objects (buckles, hairpins, watches), and electronic gadgets.
How to get a referral for diagnostics
A referral for a computed tomography scan of the cerebral vessels is issued by the attending physician. Most often this is a neurologist, oncologist, angiosurgeon, or neurosurgeon.
The examination is expensive and involves radiation, so the doctor must weigh the pros/cons of prescribing tomographic angiography.
Typically, diagnosis is carried out in cases where it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, in preparation for brain surgery.
How is the procedure performed?
The examination for the patient is quite simple. You only need to lie still during the procedure. The patient is placed on a sliding table, the body is fixed with bolsters, the head with clamps. For small children, patients with claustrophobia, and mental disorders, sedatives, even anesthesia, can be used.
If necessary, contrast is injected into the vein. After administration of a contrast agent, you may experience a cold sensation or a metallic taste in your mouth.
If the patient experiences a headache, nausea, or difficulty breathing, it is necessary to immediately inform the doctor.
The table with the patient slides into the tomograph. During a CT scan of cerebral vessels, the staff is in the next room. You can communicate with doctors via special audio communication. The tomograph makes quite a noticeable noise (since its outer part rotates).
It is very important not to move during the entire procedure - then the computer model and sections will be of high quality and reliable.
At the end of the procedure, the table is pulled out, and the patient waits for the examination results to be deciphered.
Using Contrast
When using contrast, clearer images of all structures of the studied part of the body are obtained; more differentiated resolution and a more accurate model can be obtained. CT with contrast reveals the smallest structures, including capillaries. Pictures using contrast are more informative.
Radioactive iodine preparations are usually used for contrast. The composition can be administered intravenously or orally. Oral contrast is taken before examining the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract - stomach, intestines.
The intravenous route of contrast administration is ideal for visualizing the vascular system. With this method, it is much more accurate to determine the shape of internal organs and identify abnormalities: neoplasms, pathologies of arteries, veins, capillaries, hematomas, tissue damage due to injuries.
In oncology, the use of contrast helps to find a tumor and examine its histological structure in the image. The use of contrast in CT is indispensable for a full diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
When conducting multi-slice computed tomography, contrast is injected into a vein using a special injector with a precisely specified delivery rate of the drug. Scanning is carried out several times at precisely calculated intervals. With MSCT, it is possible to accurately differentiate arteries, veins, and capillaries. This method is indispensable for angiography of blood vessels, especially the head.
The radiation exposure from radioactive iodine is negligible - much less than the radiation from a tomograph. Therefore, contrast can be used several times a year - contrast does not pose any particular harm to the patient. The contrast agent is quickly and completely eliminated from the body.
How long does it last?
Tomography is performed relatively quickly - in 5-10 minutes, on some devices - less than a minute. The examination using contrast takes 20-30 minutes.
Possible side effects
CT scan has virtually no complications. Panic attacks are possible in patients with claustrophobia. A complication may be an allergic reaction to the contrast. There are side effects to the use of iodine preparations in patients with hyperthyroidism or renal failure (if a CT scan was performed urgently for health reasons).
Irradiation at a dose of 2 mSv is safe; a conditionally dangerous dose of radiation can accumulate only when the study is performed more than 10 times a year. But even cancer patients are not irradiated this way.
Interpretation of results
Based on the measurement results, the computer builds a three-dimensional virtual model of the vascular system. Changes in tissue density are visualized as dark and light areas.
The doctor receives the results of the study in the form of layer-by-layer x-ray sections taken at a frequency of 0.5-1 mm. The doctor compares the patient's visible vascular system with the norm and analyzes deviations.
With CT, the speed of blood flow is measured, the presence of foreign structures, neoplasms, vascular pathologies, hemorrhages, and so on is determined.
How long does decryption take?
Transcription usually lasts from 15 minutes to an hour and a quarter. In exceptional cases, if there is a need to consult several specialists - up to 24 hours. The patient receives photographs and a conclusion; it is possible to copy information in electronic form.
What diseases can it detect?
Using CT angiography, you can identify many pathologies and diseases of the skull and its contents, including cerebral vessels:
- fractures and cracks of the skull;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- bleeding and hematomas;
- abscesses;
- meningitis, encephalitis and their complications;
- hydrocephalus, microcephaly and the like;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- cysts, neoplasms;
- atherosclerosis, the presence of plaques in blood vessels;
- acute and chronic coronary disorders;
- vascular spasms;
- blockage of blood vessels with plaques or blood clots;
- strokes and their type (hemorrhagic or ischemic);
- aneurysms, vasoconstriction, excessive tortuosity;
- swelling of the brain.
Pros and cons of the method
The biggest advantage of using CT is the ability to quickly scan if a patient's life is suspected to be at risk. CT machines are available in all major hospitals and traumatologies, and the study can be carried out in any acute and dangerous patient conditions: injuries, infectious diseases, suspected stroke, convulsive conditions, cerebral edema, and so on.
- The second advantage is that computed tomography can be used in the presence of insulin pumps, pacemakers, stents, implants, pins, endoprostheses, and tattoos.
- For health reasons, CT scans of cerebral vessels can be performed even on children.
- The disadvantages of the method are radiation exposure, high cost, and somewhat limited distribution of tomographs.
- The cost of conventional CT angiography of cerebral vessels is from 4,300 rubles, with the use of a contrast agent – from 7,400 rubles.
Alternative Research Methods
The most modern type of tomography is multislice (multilayer) computed tomography. MSCT devices have several rows of detectors; X-ray radiation comes in a volumetric beam. If spiral SCT is used, then angiography of cerebral vessels is much more informative. MSCT has many advantages:
- double the scanning speed;
- increased contrast and resolution;
- reduction of radiation exposure by a third;
- reduction in the size of visible structures.
The most informative alternative research method is magnetic resonance imaging. But MRI cannot be performed in the presence of pacemakers, insulin pumps, vascular clips, metal pins and plates, tattoos made with metal-containing dyes, and so on.
- There is also a method of x-ray angiography - ordinary x-rays in two projections with contrast.
- Ultrasound is used to examine large vessels.
-
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/kt/osobennosti-provedeniya-kt-angiografii-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga
CT scan of brain vessels
Brief description of the procedure
Duration: 10-35 minutes
Necessity of using a contrast agent: as prescribed by a doctor
Necessity of preparation for the study: no
Presence of contraindications: yes
Restrictions: available
Time to prepare a report: up to 1 hour
Children: over 14 years old
The resulting images can be two- or three-plane, and they can be viewed on a monitor or recorded on external media for more detailed study and storage of the obtained data.
To conduct a CT scan of the brain vessels, no special preparatory measures are required. The study is carried out as prescribed by a doctor if he suspects a certain group of diseases.
For what symptoms can a CT scan of the brain vessels be recommended?
A CT scan of the brain vessels may be prescribed if the patient has:
- vomiting, nausea;
- headaches of unknown origin;
- loss of consciousness, dizziness;
- other neurological symptoms that indicate a violation of cerebral blood supply;
- recent traumatic brain injury;
- after recently suffering a stroke.
What abnormalities does a CT scan of the head vessels show?
CT angiography of cerebral vessels is an informative x-ray technique for assessing the functional and anatomical state of the blood vessels in this area. The method makes it possible to examine vessels with a diameter of up to 1 mm in various planes and projections, identify disturbances in the blood supply to the brain and its structures, and also reconstruct the obtained data into a spatial model indicating venous and arterial blood flow.
The images visualize areas of impaired blood circulation, occlusion, stenosis, aneurysm and other disorders. Based on the data obtained, the state of the lumen of the vessel, blood flow speed and other indicators of the functioning of the bloodstream are assessed.
CT scan of brain vessels shows the following changes:
- atherosclerosis of the arteries with secondary cerebral ischemia;
- vascular malformations, for example, arteriovenous malformations;
- vasculitis and other inflammatory processes;
- hemorrhages into the cranial cavity and other damage to the bloodstream due to traumatic brain injuries;
- angiopathy of various origins;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- micro-strokes;
- thrombosis of the venous sinus, artery or vein;
- embolism;
- foci of infarction or ischemia;
- disorders of the ventricular system of the brain;
- in case of oncological formations - vessel compression syndrome, germination of malignant formations into the vessel;
- protrusion (aneurysm) of vascular walls;
- looping, kinks, narrowing of the lumen and other changes in blood vessels.
In patients with ischemic stroke, CT is used to assess the degree of cerebral vascular occlusion and monitor the effectiveness of thrombolysis. In case of diagnosed meningioma, the technique makes it possible to evaluate the sinuses of the dura mater.
Also, CT of the vessels of the head is performed in patients with contraindications to MRI of this area, in preparation for operations, to monitor the effectiveness of prescribed therapy, and in cases where other research methods were ineffective or provided ambiguous data.
Note that due to the relationship between the cerebral and cervical vessels, a comprehensive study is often performed - CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck.
Features of the study
CT scans of the head vessels are performed using multispiral devices and only with intravenous injection of a radiocontrast agent into the patient’s blood, which allows blood vessels to be clearly marked in the images. Since this substance contains iodine, such diagnostics have a number of contraindications - it is not performed on patients:
- with an allergy to the components of the contrast agent;
- with renal or liver failure;
- for multiple myeloma, thyroid pathologies;
- with severe forms of diabetes;
- when the serum creatinine level is above 130 µM/l.
There is no preliminary preparation for the study - the day before you do not need to take special medications, for example, urografin, or refuse to take medications or food. Note that some medical centers perform CT scans of cerebral vessels on an empty stomach, so this preparation point must be clarified at the clinic when registering for the study.
Since an iodine-containing drug is injected into the blood during a CT scan of blood vessels, patients with kidney pathologies must undergo a blood test for urea and creatinine before diagnosis.
The duration of a CT scan of brain vessels takes on average 20-30 minutes.
Alternative methods for diagnosing cerebral vascular disorders
The main alternative methods for diagnosing pathologies in cerebral vessels are ultrasound, angiography and MRI.
Duplex ultrasound scanning has no restrictions and can be performed on pregnant women and young children. The method makes it possible to assess the functional indicators of the blood supply to the brain, but is inferior in information content to CT and MRI, since the capabilities of ultrasound examination are limited due to the screening of ultrasound by the bone tissue of the skull.
Unlike CT, MRI of the vessels of the head does not carry radiation exposure and informatively diagnoses most pathologies in this area without the introduction of contrast, and shows the condition of the adjacent soft tissues of the brain. However, the method is less effective for traumatic brain injuries and damage to the bone structures of the head.
Classic angiography diagnoses disorders in all vessels of the head, but is an invasive examination method; in addition, it exposes the body to radiation and has limitations due to the need to administer a contrast agent.
Source: https://MRT-catalog.ru/kt/kt-golovnogo-mozga/kt-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga
CT angiography of cerebral vessels
Brain diseases are quite common and can lead to disastrous consequences. A thorough diagnosis of the structures and vessels of the organ reveals various features and pathologies.
Performing CT angiography of cerebral vessels helps to obtain the necessary information about blood circulation and diagnose plaques.
The method differentiates pathology at the earliest stage, which facilitates the start of timely treatment and eliminates delays in therapy.
Features and essence of the procedure
A modern tomographic device takes layer-by-layer images of the vascular branch in different projections.
The method provides data on the blood supply to the brain and the condition of the cranial structures. The vessel is scanned, and the equipment determines its parameters. The method has been used for a century to diagnose the body. The rays produced by the tomograph pass through soft tissues and blood vessels. The method is based on an X-ray of the head using a contrast agent. Creating a digital image from the received signals makes it possible to identify the pathology of the entire vascular branch. CT scanning of blood vessels and capillaries of the brain with contrast is prescribed for tumors and other pathologies.
Blood flows from the carotid and vertebral arteries. Carrying out contrast allows you to improve the display and makes the picture clearer. The drug is injected into the carotid artery during examination of the brain.
The study reveals disturbances in arterial or venous circulation, shows the phases of general circulation of the brain and vascular defects. Differentiation is especially necessary when identifying a brain tumor.
MSCT (CT) of head and neck vessels is used in adults and children. This is a safe research method that completely scans the vessel and detects changes. Angiography is a combination of computed tomography and a standard examination.
Main types of procedure
Each type of procedure has its own nuances and differences. There are several types of research. The brain vessel is scanned with contrast. This angiography is called puncture angiography. The drug is administered using a special thin needle.
Contrast can also be administered using a catheter.
The type of research is selected taking into account the area being studied. During general angiography, the catheter is placed on the abdominal or thoracic aorta. In a selective study, the drug is injected into a cerebral vessel. There is also superselective angiography, when the medicine is injected into the main arteries. The choice of catheter location depends on the area being examined. A CT scan with general angiography of the cerebral vessels is prescribed to identify the blood supply to the affected area.
Among the types of research:
- Venography.
- Arteriography.
- With contrast.
Traditional visualization of the cerebral vessel comes down to sequential computer images. A clear series of sections is subjected to 3D processing. This allows you to obtain an accurate tomographic picture. The vascular bed can also be scanned using MR angiography.
Each individual type of CT has its own characteristics and nuances. The required research option is selected by the doctor.
Benefits of the procedure
Scanning is used to plan subsequent surgery. CT helps to perform the operation accurately and without errors.
The device provides a unique opportunity to create an accurate 3D model of the identified tumor, determines the stage of vascularization and the type of cancer.
Based on the data received, surgeons preliminarily think through the entire course of the operation, all its stages. CT scan of brain vessels reduces the risks of pathological complications.
Advantages of CT:
- Absence of risks that are present in the standard version of angiography.
- Low x-ray load on the human body.
- Very high information content.
- No distortion, greater accuracy of the information and images obtained.
- Insignificant time period of the session.
- The most informative and high-quality research.
- Possibility of identifying the early stage of pathology and morphological features of the vessel.
A CT scan of brain vessels with contrast is performed to identify the speed of blood flow and the characteristics of the blood supply to the organ. It identifies various disorders of cerebral circulation, the cause of dizziness and fainting.
Indications and contraindications for angiography
The reason for prescribing tomography is the ability to obtain very accurate images of the vascular trunk in various projections. It is especially necessary to undergo research in a pre-stroke and pre-infarction state.
CT scan of cerebral vessels is indicated in the following situations:
- hematomas;
- injuries;
- hemorrhage;
- soft tissue rupture;
- impaired blood circulation;
- anomalies;
- malignant tumor;
- benign neoplasms.
The use of tomography also has its limitations. Foci of pathology cannot be scanned during pregnancy and lactation. Contraindications also include:
- allergy to iodine-containing medication;
- poor kidney function;
- heart diseases;
- hyperkinesis;
- claustrophobia;
- severe obesity.
Preparatory processes
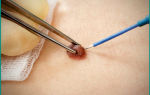
Before the session, a test is carried out to determine the level of exposure to medications that contain iodine. The nurse takes the minimum amount of contrast component used during the session and slowly injects the product into the vessel.
The patient is monitored. The appearance of swelling, migraine, cough, shortness of breath, redness of the skin indicates the beginning of a negative response from the body. When an allergy begins, the doctor cancels the procedure with contrast.
An MR examination without contrast is prescribed.
Additional tests are performed before scanning the blood vessels of the brain. It is required to consult a therapist and cardiologist. The blood is also examined for general chemical parameters and the degree of coagulation. It is important to examine the body’s urine and blood and take an ECG.
A CT scan session is a minimally invasive and safe procedure. However, during the event there are certain risks of bleeding. A range of tests helps to collect the necessary information about the general condition of the patient’s body for further research of the brain.
In order for the scanning of cerebral vessels to be error-free, it is necessary to follow certain preparation rules:
- Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids the day before. This measure allows you to quickly remove the contrast agent much faster.
- On the eve of the session, completely abstain from eating. This measure avoids provoking gag reflexes.
- You should not drink or eat before the scan.
- You should not apply makeup to your face or wear jewelry or items containing precious metals. Cosmetic decorative products contain microparticles of metals that can distort the results of the procedure.
- You also need to remove all metal objects and removable dentures, glasses, watches, and belts with plaques.
- Before the session begins, the patient's clothes are removed. A spacious disposable gown is put on.
Progress of the procedure
Before starting, the nurse administers a contrast agent. If you have an allergy to iodine, you must report it. A substance can be tested for an allergic reaction first.
The patient is placed on a retractable tomograph couch. The body is secured with special straps. During the session you cannot move your limbs and head. Remaining completely still is the basic rule of the procedure. The area of the couch where the patient's brain is located is placed under the X-ray source. You cannot move during the procedure, otherwise the picture will be blurred and will not work.
Scanning of the brain vessels takes place within half an hour. During the procedure, the doctor’s commands are received into the intercom.
Features of the procedure with contrast
An angiographic study provides the doctor with a detailed study of blood flow. The total depth of the blood vessels, features of blood circulation and the development of pathologies are determined. The contrast allows you to clearly visualize the vessels and show all deviations in the channel. Before prescribing a study, all main types of procedures are taken into account, among which the desired method is selected.
How does the drug work? As soon as the product enters the bloodstream, it instantly stains the lumen of all blood vessels. Visualization of desired organic areas is enhanced.
Gradually, the coloring substance spreads throughout the body, immediately stains a large number of brain vessels, and then accumulates in soft tissues.
The coloring medication is excreted within 12 hours by the kidneys, urine and feces.
Proper contrasting does not have any negative effect in the body. The image obtained in the process is quite informative.
This examination reveals the slightest changes in blood vessels and pathology of the brain.
Using computed tomography and drug administration, the condition of the vessels of the back, cerebral arteries, and cerebral vessels is checked, and the development of an aortic aneurysm is excluded.
Modern medicine has come a long way. Many dangerous diseases are detected during the procedure; angiography is considered very informative. Almost all pathologies of the vascular system are revealed by CT scan of brain vessels.
Coloring the lumen allows you to identify:
- blockage of blood vessels;
- finding a blood clot;
- blood clot size;
- aneurysm;
- plaque;
- atherosclerotic changes;
- consequences of skull trauma.
Possible side effects
The session proceeds without any unpleasant discomfort for the person. There are no painful sensations during the procedure. A slight warmth is felt from the introduced contrast. The only negative is the constant presence of the body without moving to explore the required place. This may cause tingling in the limbs and other unwanted reactions during the session.
Basically, side effects are always associated with the development of an allergic reaction to the administered iodine-containing drug. The skin may turn red and your heart rate may increase. Any fear before the procedure sometimes results in shortness of breath. In some cases, there is a feeling of lack of air.
If you experience any unpleasant sensations or feel unwell, you should definitely tell your doctor about the discomfort. For this purpose, a special intercom is used, built into the tomograph capsule. It is through him that the patient communicates with the diagnostician.
The doctor is located in another room during the procedure and is separated from the patient by glass. However, he hears the patient through the intercom.
The examination does not take much time. Some modern devices have new technologies that can significantly reduce session time.
Before scanning a cerebral vessel, the indications for angiography are taken into account. The patient needs to know the specifics of the session; the doctor introduces them to them before starting the study.
A CT scan is prescribed for a detailed study of the vessels and tissues of the brain.
Source: https://mrtdom.ru/diagnostika-kt/kt-golovy/kt-angiografiya-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga
CT scan of brain vessels
CT (computed tomography) of cerebral vessels is a diagnostic study in medicine, which is the most effective and accurate method for diagnosing the condition of the brain, pathologies developing in it, disorders of its activity, and so on.
The content of the article:
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels has been widely used in medicine not so long ago, but in a relatively short period it has become one of the most effective diagnostic procedures that allows timely detection of disorders in the activity of the human brain. It is worth immediately noting that CT of brain vessels is also one of the most expensive techniques.
Computed tomography of human brain vessels can be prescribed for both adults and children due to the patient’s head injury or suspicion of it, the likelihood of detecting pathology, disease, inflammatory foci in the brain, and so on.
Indications for CT scan of cerebral vessels
Computed tomography of the cerebral vessels, as mentioned above, is prescribed by a specialist in case of suspicion of any disturbances in the functioning of the organ caused by a wide variety of factors.
First of all, this is a previous injury, especially accompanied by the appearance of hematomas or bleeding. CT allows for timely detection of any irreversible processes resulting from this.
It is necessary to turn to the CT technique of cerebral vessels even if a specialist detects any signs of various neoplasms.
For patients who have complaints of constant or regularly recurring headaches, computed tomography is mandatory.
Also, indications for CT scanning include patient complaints of periodic fainting and dizziness.
It is worth noting that in this case, the technique of spiral scanning of cerebral vessels is used: in this way, the specialist is able to promptly identify possible vascular deformation, aneurysm, and the risk of stroke.
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels is also widely used in the field of maxillofacial surgery: if any operation is necessary, for example, reconstruction of the skull bones, a tomogram image is of great benefit.
Treatment of tumors, neoplasms, cysts, as well as altered blood vessels is not complete without a specialist ordering a tomography of the brain vessels. Convulsions, noticeable asymmetry of facial features, impaired speech function, and swallowing functions are also indications for spiral and multispiral CT.
If we talk directly about diseases that can be successfully and timely diagnosed using CT of brain vessels, then the list of such can include:
- neoplasms, cysts and tumors;
- epidural hematomas, hygromas;
- fractures, cracks and other injuries to the bones of the skull;
- encephalitis, hydrocephalus, encephalopathy;
- neuroinfections;
- toxoplasmosis.
Contraindications for CT scanning of cerebral vessels
Before talking about contraindications for this procedure, it is worth saying that, even despite minimal radiation exposure, it cannot be called completely harmless. Therefore, most contraindications are associated with this factor.
Pregnancy and lactation period strictly do not allow the procedure. The procedure is not recommended for children under 14 years of age due to the risk of exposure to strong radiation, however, in case of urgent need, a CT scan of the brain vessels is still performed.
If we talk directly about CT scanning using contrast, then in this case allergic reactions to the constituent elements of the injected substance will be contraindications.
People suffering from asthma, diseases of the thyroid gland, cardiovascular system, renal and pulmonary failure, and so on should not conduct the study.
CT scanning is strictly prohibited for patients with leukemia or multiple myeloma.
- For a patient whose body weight exceeds 120 kg, tomography of the brain vessels cannot be performed due to the fact that such a patient will not be able to fit into the tomograph.
- The procedure is strictly prohibited for those who have implanted metal elements or foreign bodies.
- It is worth noting that due to the wide list of contraindications for performing CT scans of the brain vessels, this procedure cannot be called completely safe.
Multislice CT of brain vessels
As mentioned above, multislice tomography is often used directly to diagnose cerebral vessels. This type has its own distinctive features, being safer, but no less effective.
Its main advantage is that, while producing a much lower level of radiation, it produces images of fairly high quality.
It is multislice tomography that is allowed to be performed on pregnant, lactating women and young children.
Preparation for CT scan of brain vessels
It is worth noting that the classic version of a CT scan of the brain does not imply any specific preparatory measures. In the case where there is a need for contrast tomography, certain requirements, on the contrary, exist.
For example, 4-5 hours before the scheduled procedure, the patient should refuse to eat.
If a CT scan with the introduction of contrast is prescribed in case of urgent need for a patient with an allergic reaction to it, then before the procedure he must undergo a preliminary examination by a specialist, and during the examination there must be an anesthesiologist in the office in case of an unforeseen situation.
In the event of the same urgent need for a CT scan in a patient with diabetes, he should temporarily stop taking medications if his health condition allows it.
The procedure for performing a CT scan of brain vessels
Before the examination, the patient is required to remove all metal objects, jewelry, and watches. Then he needs to undress.
In this form, the patient is placed on a table on which he is pushed into the tomograph chamber.
The patient does not experience any unpleasant sensations or discomfort during the procedure, however, for those who suffer from claustrophobia, CT with its specific characteristics can cause a panic attack.
A CT scan using a contrast agent is different in that during the administration of the drug the patient feels a metallic taste in the mouth, alternating sensations of hot and cold, nausea and headaches. If, after administration of the substance, the patient develops a rash, itching, or cough, an antihistamine should be taken immediately: all this indicates an allergic reaction to the contrast.
On our resource you can find more detailed information on the issue of performing CT scans of cerebral vessels in diagnostic clinics in Moscow.
Source: https://www.mosmedportal.ru/article/kt-sosudov-golovnogo-mozga/
How is a CT scan of the brain performed and what does it show?
To make a correct diagnosis, patient complaints alone are not enough, especially when it comes to such a complex and “delicate” organ as the brain.
The doctor always prescribes diagnostic procedures that will help determine what the problem is.
And computed tomography of the brain and its vessels is today considered one of the most accurate and informative diagnostic methods.
CT scan of the brain: what does the study show?
Computed tomography (CT) is an x-ray diagnostic method. During the procedure, the tomograph takes a series of layer-by-layer X-ray images in different planes. After this, the image is processed by a computer.
One of the options for this examination is with contrast. In this case, before the procedure, the patient is injected with a special substance (usually iodine-based), which does not transmit x-rays and is therefore very clearly visible in the image.
Spreading throughout the vessels and tissues, the contrast allows you to see their boundaries more clearly.
CT scan, with or without contrast, provides comprehensive information about the condition of the bone structures and soft tissues of the head. The photographs clearly show the bones of the skull, blood vessels and paranasal sinuses.
In addition to injuries, CT scan of the head makes it possible to detect acute cerebral circulatory disorders, blood clots in the veins of the brain, hematomas, aneurysms and hemorrhages, enlarged brain cavities in patients with hydrocephalus, neoplasms, meningitis and its complications.
When is the study scheduled?
A CT scan of the brain is often used to determine the causes of regular headaches, general weakness, seizures, dizziness and fainting, and confusion.
The study is also often prescribed in cases of sharp deterioration in vision and hearing - such symptoms may indicate pathological processes in the brain.
It is also prescribed after traumatic brain injuries, especially those accompanied by loss of consciousness and neurological symptoms. CT scan helps to detect cerebrospinal fluid leaks and skull fractures, cerebral edema and the presence of hemorrhages.
By the way, Computed tomography is an alternative to magnetic resonance imaging. This type of examination has a number of advantages over MRI - it is better suited for diagnosing traumatic changes and fresh hemorrhages in the first day after injury. In addition, CT is prescribed in cases where MRI is not possible - for example, if the patient has metal implants.
Contraindications for CT diagnostics
Computed tomography has become so widespread not only because of its information content, but also because this method has practically no contraindications.
As a rule, CT is not prescribed to pregnant women, since X-ray radiation can negatively affect the fetus, as well as to patients whose weight exceeds 130 kg - the latter limitation is due to the design features of the device.
CT with contrast has slightly more contraindications. This type of examination is not recommended for people with severe kidney or liver impairment, some forms of diabetes mellitus, or allergies to contrast agent components. Relative contraindications are mental illness and claustrophobia, but sedatives solve this problem.
Do you need any preparation for the procedure?
For the patient, a CT scan of the brain is a painless and simple procedure that does not require any special preparation. It is enough to remove all metal objects - earrings, piercings, dentures, hearing aids, glasses - and change into comfortable, loose clothes.
How is a CT scan of the brain done?
After preparation, the patient is placed in the tomograph. It looks like a tunnel, inside which a special movable table moves. The patient lies down on it, his head is fixed with straps - this is necessary to maintain complete immobility, because even one accidental movement will not have the best effect on the quality of the image.
The table slides into the machine, and from that moment the patient can only wait for the tomograph to finish working. The doctor is in the next room at this time, but can maintain contact with the patient using a microphone.
The main inconvenience is the need to lie still, but no unpleasant sensations arise during the examination. When undergoing a CT scan with contrast, some patients report a feeling of warmth throughout the body and a metallic taste in the mouth. This is how our body reacts to iodine preparations, which is the norm.
The entire procedure takes 30-60 minutes, with most of this time spent on preparation, and the scan is a relatively quick affair.
A CT scan of the brain is sometimes prescribed for children. The procedure for examining the brain of children is no different from an “adult” CT scan. Unless babies who are unable to remain still for a long time are given anesthesia - it is harmless and its effect ends very quickly, immediately after the procedure is completed.
Is CT scanning harmful?
Of course, during the examination the patient receives a small dose of radiation (1-2 mSv), but it is much less than the maximum permissible effective dose of radiation (150 mSv per year).
A CT scan is prescribed by a doctor, and when making such a decision, he takes into account all factors: the patient’s age, his state of health, the number of recent X-ray examinations. In emergency situations where life and death are at stake, CT scans can be ordered as often as necessary.
The harm from such an examination is not commensurate with the consequences that a brain pathology that is not detected in time will cause to a person.
Evaluation of tomography results
Usually you don’t have to wait long for the results of a brain CT scan. This is especially true for private medical centers, where the flow of visitors is less - there the results are given to the patient in an hour and a half after the examination.
The results of a brain CT scan are black and white images and a report from a radiologist. If you wish, you can ask a specialist to record the results on a disk or other media.
With normal values, the images show that all the bones of the skull, blood vessels and brain are of normal size, there are no foreign bodies or neoplasms, and there are no shadows indicating fluid accumulation or bleeding.
Neoplasms, bleeding, foreign bodies, violation of the integrity of bone structures, changes in the size of bones and blood vessels, damage to nerve fibers, fluid accumulations, aneurysms, enlargement or expansion of the ventricles of the brain, as well as its swelling are considered deviations from the norm.
CT is one of the fastest diagnostic methods. In critical situations, when the doctor needs to make a diagnostic decision here and now, the method has no competitors. However, even in less dramatic cases, computed tomography is extremely informative.
Source: https://www.eg.ru/digest/protsedura-kt-golovnogo-mozga.html