The adrenal glands are small glands located at the top of the kidneys. They take part in the reproduction of hormones in the body, play an important role in the production of adrenaline, and also take part in coordinating the metabolic process. Diseases of these glands affect the general condition of the body and can even lead to disability.
At the moment, the most effective way to diagnose the disease is a CT scan of the adrenal glands. Computed tomography of the adrenal glands is a computer diagnostic that allows you to obtain the most accurate information about the presence or absence of diseases.
The scanning results produce a three-dimensional image, which allows specialists to identify even the smallest deviations in the functioning of organs.
Symptoms for which a CT scan of the adrenal glands is prescribed
The most common cause of adrenal disease is hormonal imbalance. Certain symptoms appear depending on which hormone is malfunctioning.
With a lack of aldosterone in the body, blood pressure decreases and the number of potassium particles in the blood increases.
If, in parallel with this, there is a failure in the body’s production of cortisol, there is a possibility of developing adrenal insufficiency.
This disease is very dangerous and complex, which can be fatal. The main symptoms are low blood pressure and rapid heartbeat.
Lack of androgens in boys can lead to abnormal development of the genital organs, and in girls it can lead to delayed puberty.
The initial symptoms of adrenal disease appear gradually and are characterized by:
- rapid fatigue;
- muscle weakness;
- poor sleep;
- increased irritability;
- nausea and vomiting;
- anorexia;
- hyperpigmentation of exposed parts of the body.
Most often, such signs are perceived as simple overwork of the body, but practice shows that such symptoms can subsequently progress and lead to more severe diseases.
The examination process
The scan is performed with a computer tomograph, which is a special device and has the shape of a ring. The installation, rotating around the couch on which the patient lies, emits X-rays that penetrate the desired organ in a spiral. It is for this reason that CT is also called spiral tomography.
Modern tomographs make it possible to examine the required organ in just one rotation of the installation, since they have several X-ray emitters at once. Studies carried out on such devices are called multislice computed tomography.
The use of MCT to study organs with a developed circulatory system, such as the adrenal glands, is carried out with contrast (a special substance).
This substance is administered intravenously either in the office while preparing the patient, or using an automatic device during the procedure itself.
In the body, such a substance flows through all the veins and arteries, which gives the most accurate pictures, down to millimeter-sized formations. The average duration of the procedure with a conventional tomograph is 10 minutes, with a multispiral installation a couple of minutes.
What does a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
Based on the results of a CT scan of the adrenal glands, the doctor can determine their location, shape, density and changes. If a neoplasm is present, a specialist can easily identify its type and rate of development.
- When examined using CT, a disease such as adenoma is detected in 99% of cases.
- Cysts and lipomas, as well as adenomas, appear as clear areas with a homogeneous composition.
- Hematomas are distinguished by heterogeneous areas and with ragged outlines.
CT is most effective in diagnosing malignant tumors. They appear as large areas with blurred contours and high density. Often with such diseases, enlarged lymph nodes occur.
There are only a couple of factors that can interfere with the study - the presence of metal implants and the movement of the patient during the procedure.
Preparing for a CT scan of the adrenal glands
Before the procedure, the patient should not eat or drink for six hours. If the patient has an increased content of gases in the intestines, then preparation consists of taking gas-removing drugs. In case of constipation, a cleansing enema is used.
If you are planning a procedure using contrast, you should take Urografin a day before the procedure. This drug is sold at any pharmacy. The ampoule with the solution is diluted in two liters of water. The first liter of solution must be drunk a day before the procedure, the second liter before the study itself.
Contraindications for carrying out
There are contraindications in which CT scanning of the adrenal glands is not possible or advisable. The use of CT is limited during pregnancy if an X-ray contrast examination using barium was carried out in the coming days.
CT scanning is not possible if the patient has an allergic reaction to iodine-containing drugs or has serious kidney disease.
Benefits of the procedure
Pathologies are detected using ultrasound, but this method has a rather low diagnostic ability in identifying the early stages of diseases.
MRI allows you to diagnose diseases at approximately the same level as CT, but this research method has a number of important disadvantages in relation to CT:
- lasts much longer;
- there are a large number of contraindications;
- the cost is significantly higher.
Modern tomographs and their capabilities allow doctors to detect the smallest changes in the adrenal glands and identify the disease in the early stages, which makes it possible to undergo treatment without surgery.
Computed tomography is the optimal choice for determining pathologies in the adrenal glands, even in the early stages of the disease.
Source: https://DiagnostLab.ru/kt/zhivota-i-taza/kt-nadpochechnikov.html
Modern diagnostic method - CT scan of the adrenal glands
Pathology of the adrenal glands affects the condition of the entire body and can lead to disability. An effective diagnostic method is CT scan of the adrenal glands. This procedure is carried out using X-rays, which are combined in a machine with computer technology. The images produced by the scanner are of higher quality than standard x-rays.
What it is
The adrenal glands are paired retroperitoneal endocrine organs. They are thin, inverted V-shaped soft tissue structures with flat or concave edges. They are located on the upper poles of the right and left kidneys. The vertical length of each gland is from 2 to 4 cm. Their tips have an axial cross-section of about 0.4 cm.
The job of these paired organs is to maintain hormone balance. One of the hormones produced by the adrenal glands is cortisol. Its excess or deficiency determines: increased weight around the waist, poor sleep, blood sugar levels, menstrual irregularities, increased thirst, blood pressure, as well as the appearance of a number of infections.
The adrenal glands are the body’s shield from a stressful situation. When they are healthy and perform their functions normally, a person does not feel tired or irritated.
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands is one of the main visual test methods for assessing their functioning. To detect small lesions and correctly measure voltage, scanning a thin section of the adrenal gland is required.
X-rays do not have a clear image of soft tissues or blood vessels, so doctors ask patients to take pictures of sections of the organ using a tomograph.
Indications and contraindications
Adrenal health is of utmost importance. If the organs responsible for hormonal changes, such as the testicles in men and ovaries in women, are removed, then the person lives without them. After excision of the adrenal glands, the likelihood of death, without permanent medical intervention, is high.
It is advisable to conduct an ultrasound examination before doing a CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Reasons for a CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands:
- diagnosing tumors, growths or lumps;
- determining the location of the tumor, the stage of its development;
- detection of cysts;
- establishing the exact location of the injury after an accident;
- determining the extent of the disease outside the organ and the presence of metastases;
- the presence of endocrine diseases such as Cushing's and Conn's syndromes.
CT scanning is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. Children under 12 years of age can undergo the procedure only if there is an urgent medical need. Doctors do not recommend scanning a patient more than once a year.
If a person has an allergy to iodine, this must be reported before diagnosis. In this case, CT can be replaced by an MRI procedure.
People with severe bronchial asthma and hyperthyroidism are also contraindicated for examination with a contrast agent.
CT scan of the adrenal glands: preparation
It is advisable to scan on an empty stomach. On the eve of the procedure, you should abstain from alcohol and do not consume products with a gas-forming effect.
Diabetics should eat a light breakfast or lunch 3 hours before the procedure. If a CT scan is performed with contrast, then after scanning you should not take hypoglycemic drugs for 48 hours.
In preparation for the examination, the patient will be given comfortable clothing if his costume is too restrictive. They will ask you to remove all metal objects and jewelry.
How they do it
CT scan is performed on an outpatient basis. The scanner is a large donut-shaped machine. During the test, the subject lies down on a table that is connected to a scanner. The machine sends pulses of X-ray radiation through its body. Each pulse lasts no more than a second, and during this period a picture, or a thin section of the organ being scanned, is taken.
CT scans can show three-dimensional images of internal organs. Sometimes these pictures are compared to a loaf of bread. By examining and removing each piece of the sliced loaf, you can see its entire interior from one crust to the other. The specialist will look at each fragment or draw up an overall picture.
One part of the machine can make different angles to better view the area being examined.
All photos are saved on the computer. If you wish, you can order a disc with pictures, but to view them at home, you must have a special program installed on your computer.
You should remain still during the procedure. Sometimes the doctor asks you to hold your breath while examining the organs.
Possible risks
If X-ray examinations are performed repeatedly, there may be risks associated with the development of radiation sickness. This also applies to those patients undergoing radiation treatment. In this case, you can ask your doctor about the amount of radiation received during the procedures.
If we consider a CT scan with contrast, then renal failure may become an obstacle to the examination. Preserved renal function is required to remove the contrast agent from the body. It is assessed using serum creatinine parameters. Serum creatinine 1.5 mg is a contraindication to the use of CT.
Patients taking antidiabetic medications are at increased risk when undergoing a procedure with contrast. They may develop a state of metabolic acidosis or changes in blood pH levels.
CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast
Scans are often performed using a contrast agent, which is infused intravenously or offered to the person being examined as a drink. It helps the radiologist get a better look at the organs inside the body. Sometimes it is necessary to conduct a double contrast examination, in which the substance is administered both intravenously and orally.
During the procedure with contrast, unpleasant sensations may occur, such as a salty or metallic taste in the mouth, short-term headache, and nausea. These phenomena are considered normal and pass quickly. If rapid heartbeat, sweating, or numbness in the extremities begins, you should consult a doctor conducting an examination.
Sometimes contrast agents cause side effects several hours after the procedure, such as pain, redness, or swelling. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor. This often indicates the presence of an infection in the body.
CT photographs can be taken both before and after contrast is applied.
It is not advisable for people with diseased kidneys to drink contrast medications. If there is a problem with constipation, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with the help of an enema before the procedure.
Decoding the received data
All received images are interpreted by a radiologist for pathology and changes in the adrenal glands. This may take from 20 minutes to 1 hour. The description indicates deviations from the norm in the adrenal glands, if any, for example:
- The size of the adrenal glands is noted. Normally, they should be between 2.4 and 2.6 cm, the right organ is always slightly larger than the left.
- Healthy organs have clear borders. Their contours must be differentiated from the surrounding tissues.
- CT scan determines the density of the adrenal glands. Increased density and heterogeneity of the tissue structure may indicate the presence of hyperplasia. Sometimes penetration of adrenal tissue into nearby organs is visible. This indicates the presence of metastases.
- During the scan, signs of calcium deposits may be visible, which indicate the previous development of tuberculosis.
Deviations from the norm seen in the photographs cannot serve as a diagnosis of the disease, it is only a prognosis. The final diagnosis will be made by the doctor after collecting all the necessary tests.
Alternative research methods
Of the inexpensive examination methods, the most informative is ultrasound.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is used as a way to clarify the diagnosis after ultrasound and CT. With this device, soft tissues are clearly visible, and signs of benign and malignant neoplasms are clearly visible.
MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) is a painless procedure that allows you to see volumetric changes in the adrenal glands. This device is less sensitive to the patient’s movements and does not produce residual radiation. The pictures obtained with its help are the most informative.
Source: https://iDiagnost.ru/kt/sovremennyj-metod-diagnostirovaniya-kt-nadpochechnikov
CT scan of the adrenal glands with or without contrast, what does it show?
Computed tomography or CT scan of the adrenal glands is a method for diagnosing pathologies associated with disturbances in the secretion of aldosterone, cortisol, catecholamines and other adrenal hormones. The cause of the disease may be endocrine disorders, hereditary diseases or tumors.
Tomography is a safe, non-invasive (bloodless) outpatient procedure (to get a CT scan of the adrenal glands, you must visit a medical facility) and does not require hospitalization or complex medical procedures.
The method is based on the use of X-rays and computer data processing algorithms.
Indications and contraindications for computed tomography of the adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are a paired organ of the endocrine system, responsible for the secretion of vital biologically active substances (hormones).
It is located, as the name implies, above the tips of the kidneys, in close proximity to them.
Hormones secreted by the adrenal glands are responsible for the regulation of all types of metabolism, blood pressure, stress reactions, and participate in the synthesis of sex hormones.
Dysfunction of the adrenal glands leads to the occurrence of various endocrine pathologies. Often the cause of endocrine disorder is benign or malignant tumors of this organ.
Indications for computed tomography of the adrenal glands
Computed tomography is used to diagnose the following pathologies of the adrenal glands:
- Benign and malignant tumors;
- Addison's disease (adrenal cortex insufficiency);
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- Congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex;
- Increased secretion of aldosterone, Cohn syndrome:
- Decreased secretion of aldosterone;
- Necrosis, hemorrhages in the adrenal tissue.
A CT scan of the adrenal glands is necessary if the patient has the following complaints:
- Stretch marks on the skin of the body, arms, thighs;
- Skin hyperpigmentation;
- Excessive hair growth, menstrual irregularities in women;
- Anxiety, persistent depression;
- Severe weakness, fatigue, worsening over time to the point of inability to maintain an upright body position;
- Darkening (pigmentation) of the gums, inner surface of the cheeks;
- Extremely high blood pressure, tachycardia.
Incidentalomas are asymptomatic benign or malignant tumors of the adrenal glands that are discovered incidentally during an examination for another reason (for example, during a CT scan of the kidneys in patients with urolithiasis). Detected in 1.3% of cases during CT scanning of the abdominal organs.
Contraindications to computed tomography of the adrenal glands
Computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands is an x-ray diagnostic method that uses x-rays to obtain images. In most cases, this does not become an obstacle to the examination. The exception is the use of computed tomography in pregnant women and pediatric patients.
Pregnancy is the main contraindication for CT scanning. The reason is the negative impact of X-ray radiation on the developing fetus. Using this method can lead to the formation of malformations, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. The exception is when computed tomography is used for health reasons.
The child's body is also sensitive to the negative effects of x-rays due to the higher radiation exposure.
It is not recommended to use computed tomography in cases where a safer diagnostic method can be used.
The use of CT is allowed if there are clear indications for examination, in patients over 5 years of age, only with a referral from the attending physician.
Adrenal CT scan with contrast
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands can be performed using contrast enhancement. This is a special technique that involves the intravenous administration of iodine-containing contrast agents (Ultravist). Since iodine is able to block X-rays, the use of contrast allows for better detection of pathologies leading to local accumulation of the drug. Most often these are benign or malignant neoplasms rich in blood vessels. This technique is especially relevant when diagnosing diseases of the adrenal glands, due to the small size of the organ and susceptibility to the occurrence of hormonally active tumors.
CT scanning of the adrenal glands with contrast is contraindicated in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- Allergic reactions/individual iodine intolerance;
- Diseases of the urinary system, accompanied by impaired renal function and an increase in the level of creatinine in the blood: the use of contrast agents in this group of patients poses a danger to health and life due to the ability to provoke acute renal failure. For this reason, before performing a CT scan with contrast, it is necessary to do a blood test for creatinine. A high level of creatinine in the blood is a sign of hidden renal dysfunction;
- Taking metformin, a drug used to treat diabetes. Metformin (Glucophage) is a hypoglycemic drug that can provoke complications of diabetes mellitus (ketoacidosis) when administered simultaneously with iodine-containing contrast agents. In order to reduce the risk, it is necessary to stop taking metformin 2 days before CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast. Resumption of treatment is possible 2 days after the examination.
CT scan of the adrenal glands - preparation for the examination
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands is performed on an empty stomach. Avoid eating 4-5 hours before the examination.
It is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol the day before (higher risk of contrast side effects).
To reduce the risk of side effects and speed up the clearance of the contrast agent, it is necessary to maintain a positive fluid balance. Increase your water and fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
Before a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, you can take a light breakfast, but you should not overeat - a full or completely empty stomach provokes nausea when the contrast drug is administered.
How is a CT scan of the adrenal glands done?
Computed tomography is a simple and painless procedure. A special device is used for this - a tomograph, which has the form of a ring with a hole - the Gantry aperture - in the center.
During the examination, the patient lies on a table passing through the aperture.
Along the inner radius of the aperture, behind a plastic casing, there is an X-ray source and detectors rotating around the patient's body.
The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes, including positioning the patient. When contrast is used, another 15 minutes are spent preparing the patient for intravenous administration of contrast, administering the drug, and repeating a series of images against the background of contrast enhancement.
After completing the procedure, you must wait for the study results to be deciphered (from 20 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the number of patients and complexity). The photographs themselves are provided on a CD. The written opinion of the radiologist and the images must be handed over to the doctor who referred the patient for examination.
What does a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
A series of CT scans of the adrenal glands in the form of virtual slices less than 1 mm thick are used to assess the condition of each gland. Attention is drawn to the size of the organ, the ratio of the thickness of the cortex and the medulla. Tissue density, gland contours, and the presence of more or less dense areas are assessed. The presence of areas of necrosis, bleeding, deposition of calcium salts, and neoplasms is determined. The extent of pathological changes is assessed. After the administration of contrast, the accumulation of the drug in gland tissues and neoplasms is studied; the rate of removal of the contrast can help identify the tumor. Determine the signs characteristic of a particular disease.
Which is better, MRI or CT scan of the adrenal glands?
Both computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are well-proven methods for diagnosing adrenal diseases, with their own advantages and disadvantages.
However, computed tomography is used more often than MRI due to its lower cost (the price of computed tomography of the adrenal glands and kidneys is half the cost of MRI) and availability, with the same specificity and sensitivity.
Magnetic resonance imaging does not have the main disadvantage of CT - radiation exposure. It is preferable to use MRI when conducting examinations in children and women. However, the higher cost may be a barrier for the patient.
To solve the problem of choice, clarify prices, choose a clinic for CT scanning of the adrenal glands in St. Petersburg, find out about discounts and promotions - use the VSEMRT.RU diagnostic registration center. Just call [GetPhone] and make an appointment for a test.
Source: https://vsemrt.ru/kt/vnutrennih-organov/nadpochechnikov/
Adrenal CT
Computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands is one of the most informative methods for studying this organ. It is not always easy to suspect its pathology, however, if there are indications, CT scans of the adrenal glands are successfully used in endocrinology and surgery.
In St. Petersburg, the Magnit medical center uses the latest technology of multislice computed tomography (MSCT).
The modern Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 device allows you to perform CT scans of the kidneys and adrenal glands with minimal radiation and the most accurate results, making it possible to identify the earliest morphological changes in these organs and conduct detailed diagnostics.
What will a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
The adrenal glands are paired endocrine glands that are located above the upper lobes of the kidneys.
They are part of the human endocrine system and produce biologically active substances (hormones) necessary for normal life: they participate in mineral metabolism, ensure the body’s resistance to stress, regulate the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and also affect libido and fertility. Even minimal changes in the structure or functioning of the adrenal glands can greatly worsen a person’s condition and lead to diseases of other organs and systems.
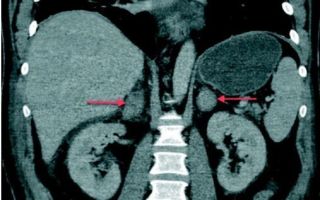
- Adrenal glands on CT (indicated by arrows)
- During the examination, the organ is examined layer by layer and the slightest deviations from the norm become visible to the specialist.
- In the photographs you can see:
- structure and size of the adrenal glands (with the possibility of diagnosing nodular or diffuse hyperplasia of the organ), kidneys, nearby lymph nodes;
- the presence of an adenoma (benign formation), lipoma, cyst, hematoma;
- malignant neoplasms and involvement of regional lymph nodes in the pathological process.
When using a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, the vessels of the organ are clearly visible, and one can easily distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one. First of all, the diagnostician will be interested in the size of the adrenal glands.
If the size of the glands exceeds the established limits, this is a reason for a more thorough study.
If a tumor is detected during a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, it will be necessary to identify the nature of the tumor, its density and structure; for this, the scan is supplemented with contrast enhancement.
Indications for CT scan of the adrenal glands
CT allows you to quickly examine the adrenal glands for the presence of a pathological process. More often, this type of diagnosis is prescribed as a clarifying method if the presence of tumors is suspected, but other reasons for the malfunction of this gland are also possible. A doctor will suspect adrenal pathology if a person experiences the following symptoms:
- sudden fluctuations in body weight for no apparent reason;
- increased sweating;
- excessive growth of body hair;
- the appearance of bronze spots or depigmentation of areas of the skin;
- in women, the voice becomes rough, and in men, the mammary glands grow;
- muscle weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- blood pressure surges;
- infertility (can also be a consequence of a malfunction of the pituitary-adrenal system).
Enlargement of both adrenal glands according to CT data (indicated by arrows)
As a result of a CT scan of the adrenal glands, the following diseases can be diagnosed:
- benign and malignant tumors;
- adrenal cysts;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- Addison's disease;
- primary hyper- and hypoaldosteronism;
- hemorrhage in the adrenal cortex (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome);
- congenital anomalies of organ development.
How is an adrenal CT scan performed?
Computed tomography is one of the methods of radiological diagnostics. It allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the required organ and study its structure in the smallest detail. The study helps to diagnose the disease in the initial stages and begin the treatment process on time.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient is asked to remove all metal products. The patient is then placed on the tomograph table. To ensure that there are no motion artifacts during scanning, a special roller system is used to make it easier for the patient to maintain correct positioning.
The doctor and his assistant are in the next room during a CT scan of the adrenal glands, while specialists carefully monitor the patient’s condition. Then the doctor gives a command, and the patient stops breathing for a short period of time. Using X-rays, multiple layer-by-layer images are taken.
A contrast agent allows you to get a clearer picture. It contains iodine, which may trigger an immune response in certain groups of people. Therefore, when a contrast agent is administered, the patient is closely monitored.
For most of the population, iodine-containing drugs are harmless and are quickly eliminated from the body.
After taking pictures, the data is processed on a computer using special software. Next, the research results are printed out, and all digital data is recorded on a CD.
In what situations is a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast required?
The study will almost always be performed with contrast, since without it the adrenal glands are not clearly visible on the images, and the information content of the method is conditionally equivalent to ultrasound.
Iodine-containing preparations are used as a contrast.
The enhancing substance helps to distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one if it is present, as well as to determine the extent of involvement of surrounding tissues in the case of oncology.
Hemorrhage into the tissue of both adrenal glands
Important! Patients are accepted for CT scans with contrast in our clinic only if they have a test - CREATININE! If necessary, you can submit this indicator on site using the express method for an additional fee or bring your own result (good for 10 days).
After a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, you may experience a slight metallic taste in the mouth.
Contraindications
Adrenal CT has a number of contraindications, and the use of a contrast agent expands this list:
- pregnancy;
- the patient’s weight is more than 150 kg or the waist circumference is more than 150 cm;
- children under 5 years of age (up to 12 years of age in contrast studies);
- allergic reactions to iodine preparations (with contrast);
- diabetes mellitus, provided it is treated with metformin;
- severe kidney disease.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to inform the doctor about all the drugs that the patient took the day before or takes constantly, since their interaction with the contrast agent can lead to an unpredictable reaction of the body. If a breastfeeding mother is being examined, then after a CT scan she must pump her breast twice before feeding her baby.
It is important to ensure that the patient does not have contraindications. To exclude a possible allergic reaction to contrast, before making a diagnosis, our specialists carefully study the patient’s medical history. Thus, the development of possible complications after a CT scan of the adrenal glands becomes extremely unlikely.
What preparation is needed before an adrenal CT scan?
CT scanning of the adrenal glands is a completely safe and virtually painless procedure. Thanks to the latest Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 device, the radiation load on the body will be minimal.
Some preparation for performing an adrenal CT scan is necessary, but it is not at all complicated. First of all, you need to stop eating 4 hours before the scheduled test.
Immediately before performing a CT scan of the adrenal glands, it is necessary to remove all metal objects, since their presence may distort the results of the study.
No further special preparation is required for the examination.
It is better to take with you all previous studies in this area and a referral from your attending physician, if available.
Adrenal CT results
After a CT scan of the adrenal glands, the best specialists at the Magnit Medical Center will interpret the images. All doctors working in our clinic have valid certificates and at least 7 years of experience in this industry.
Source: https://spb24mrt.ru/kt-info/nadpochechnikov-chto-pokazyvaet
Features of CT scanning of the adrenal glands and examination results
Computed tomography is the “gold standard” in identifying a tumor process in the adrenal glands. CT scan can detect a volumetric neoplasm with a size of 0.5 cm or more. Spiral tomography helps not only to identify tissue proliferation (hyperplasia), but also its shape - nodular or diffuse. For even greater accuracy of the study, a contrast agent is injected intravenously.
As a result of the diagnosis, you can evaluate:
- size, shape of the gland;
- contours, structure, density of the volumetric process (tumors, cysts);
- degree of hyperplasia;
- the presence of calcium salt deposits, focal destruction (necrosis), hemorrhage;
- enlarged lymph nodes, which helps in the diagnosis of malignant tumors.
CT and MRI can detect diseases with the same degree of probability . Their sensitivity for tumors approaches 100%. At the same time, “silent”, asymptomatic space-occupying processes – incidentalomas – are also found.
Traditional CT
Due to lower cost, CT is more often used , and MRI is recommended if there are contraindications to X-ray diagnostics. A contrast agent is always used.
Indications for tomography:
- arterial hypertension resistant to traditional therapy;
- crisis increases in blood pressure with a feeling of fear, increased heartbeat, sweating, trembling of hands, having a sudden beginning and end;
- signs of hyperandrogenism (excess of male sex hormones in women);
- early puberty in children;
- premature loss of testicular or ovarian function;
- enlargement of the mammary glands in men, sexual weakness, decrease in the size of the testicles;
- symptoms of excess cortisol - obesity, purple stretch marks, moon face, hypertension, diabetes, fatigue, osteoporosis;
- detection of increased levels of steroid hormones in the blood (cortisol, testosterone, estrogens), high or low levels of corticotropin;
- hypertension, muscle weakness, decreased potassium in the blood, changes in the fundus, thirst, excessive urine output;
- preoperative examination if tumor removal is necessary;
- guiding the needle during fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the adrenal gland to enter the tumor tissue.
Contraindications to CT:
- pregnancy;
- recent diagnosis of the digestive organs with barium contrast or the use of medications with bismuth;
- high motor activity, mental agitation, inability to maintain a stationary body position;
- contrast intolerance, allergy to iodine, decompensation of diabetes mellitus, reduced filtration capacity of the kidneys.
Preparation for the examination includes:
- you must refrain from eating for 4 hours;
- to eliminate the risk of developing an allergic reaction, patients are prescribed a trial administration of a drug that will be used in the study of the adrenal glands;
- If blood tests for hormones or ultrasound of the adrenal glands have previously been performed, then their results should be taken with you.
The risks of the diagnosis are insignificant , however, patients may experience hot flashes, burning or itching of the skin, and a metallic taste in the mouth after intravenous administration of contrast. The phenomena are temporary and usually do not require additional treatment.
How to do a CT scan with and without contrast:
- Before the examination, the patient must remove all metal objects and exclude metal on clothing in the scanning area.
- The patient is placed on a couch that is connected to a scanning device.
- When contrast enhancement is used, Omnipaque or Ultravist is administered intravenously before scanning. Otherwise, all stages of the procedure are similar to native CT (without contrast). During the diagnostic period, it is important to remain motionless.
When the tomograph's beam tube moves, tissue is examined layer-by-layer in the form of images - tomograms. They are processed by a computer program and produces the final image. The result can be printed or recorded on media.
The entire procedure usually takes about half an hour . Upon completion, the patient needs to drink as much plain water as possible, avoid eating salty and spicy foods, so as not to create additional stress on the kidneys, and remove the contrast agent from the body as soon as possible.
When describing a tomogram of a healthy person, the adrenal glands look like this:
- shape - the left one looks like the letter V, the right one is usually linear;
- size – not increased;
- structure – homogeneous;
- outlines – smooth and clear;
- perinephric tissue (perinephric) – no changes;
- lymph nodes are of normal size and structure;
- contrast accumulation is uniform.
When examining the adrenal gland, neoplasms of the adjacent renal tissue may also be detected . Their distinctive features:
- boundaries are unclear;
- density is reduced;
- the structure is heterogeneous;
- there are areas of calcium deposition, hemorrhage, and decay (necrosis).
- When contrast is administered, a local enhancement of the vascular pattern is noted.
Tomography can also detect a cavity (kidney cyst), stone, abnormal organ structure, abscess.
Right adrenal cyst
An adenoma, cyst, or hematoma of the adrenal gland has the shape of an oval or circle, the contour is clear and even, the structure is either homogeneous or moderately heterogeneous.
The cyst is characterized by a clearly visible thin capsule and the same (low) density of the contents. There may be pockets of calcium deposits in the walls.
After the administration of contrast, the adenoma becomes clearly visible, and the cysts do not change their symptoms.
The hematoma has a capsule, but its contents look heterogeneous - these are areas of coagulated blood. The boundaries of the hemorrhage are clear, but uneven.
Lipoma is a hormonally inactive tumor shaped like a ball with an even structure. There is also slight heterogeneity due to fat inclusions. There is complete delineation of the neoplasm from the adrenal tissue; the glands are not deformed.
Pheochromocytoma has a heterogeneous structure, smooth outlines, and a clearly visible capsule that separates it from the unchanged adrenal tissue. After contrast administration, intensive absorption is observed due to the developed vascular network.
Signs that are characteristic of malignant tumors include:
- large size;
- focal inclusions of different densities;
- blurred outline;
- zones of calcium deposition, destruction;
- increased density;
- enlargement of neighboring lymph nodes.
Read more in our article about CT scanning of the adrenal glands.
What does a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
This examination method is recognized as the “gold standard” for detecting a tumor process in the adrenal glands. This is due to the fact that the adrenal glands are adjacent to fatty tissue, and the right one is adjacent to a dense organ - the liver. This anatomical location allows the glands to have a natural distinction from surrounding tissues and makes it easier to recognize their size and structural features.
CT scan can detect a volumetric neoplasm with a size of 0.5 cm or more. Spiral tomography helps not only to identify tissue proliferation (hyperplasia), but also its shape - nodular or diffuse. For even greater accuracy of the study, a contrast agent is injected intravenously.
As a result of the diagnosis, you can evaluate:
- size, shape of the gland;
- contours, structure, density of the volumetric process (tumors, cysts);
- degree of hyperplasia;
- the presence of calcium salt deposits, focal destruction (necrosis), hemorrhage;
- enlarged lymph nodes, which helps in the differential diagnosis of malignant tumors.
We recommend reading the article about diagnosing adrenal adenoma. From it you will learn about the primary diagnosis of adrenal adenoma, what tests are taken, and detailed examination methods.
And here is more information about MRI of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Which is better - CT or MRI
Imaging performed using X-ray scanning (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect diseases with the same degree of probability. Their sensitivity for tumors approaches 100%. At the same time, “silent, asymptomatic space-occupying processes—incidentalomas”—are also found.
Due to lower cost, CT is more often used, and MRI is recommended if there are contraindications to X-ray diagnostics. Both of these types of tomography are combined with contrast enhancement in order to specifically examine the tumor.
Although there are criteria by which the likelihood of a malignant process can be determined, in practice there are often cases when the type of tumor is confirmed only during surgery after histological analysis of the tissue.
Watch the video about which is better than CT or MRI when diagnosing the adrenal glands:
Indications for tomography
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- arterial hypertension resistant to traditional therapy;
- crisis increases in blood pressure with a feeling of fear, increased heartbeat, sweating, trembling of hands, having a sudden beginning and end;
- signs of hyperandrogenism (excess of male sex hormones in women) - increased hair growth on the limbs and face, acne, lack of menstruation, infertility, rough voice;
- early puberty in children;
- premature loss of testicular or ovarian function;
- enlargement of the mammary glands in men, sexual weakness, decrease in the size of the testicles;
- symptoms of excess cortisol - obesity, purple stretch marks, moon face, hypertension, diabetes, fatigue, osteoporosis;
- detection of increased levels of steroid hormones in the blood (cortisol, testosterone, estrogens), high or low levels of corticotropin;
- hypertension, muscle weakness, decreased potassium in the blood, changes in the fundus, thirst, excessive urine output;
- preoperative examination if it is necessary to remove the tumor (to determine the method of surgical intervention and its volume);
- guiding the needle during fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the adrenal gland to enter the tumor tissue.
Contraindications
The study is not carried out if:
- pregnancy;
- recent diagnosis of the digestive organs with barium contrast or the use of medications with bismuth (they may interfere with the visibility of tissues);
- high motor activity, mental agitation, inability to maintain a stationary body position (as an exception, sedatives and muscle relaxants that relax muscles can be administered);
- intolerance to contrast, allergy to iodine, decompensation of diabetes mellitus, reduced filtration capacity of the kidneys.
Preparing for the examination
If it is necessary to undergo a procedure with the introduction of a contrast agent, you must refrain from eating for 4 hours. To eliminate the risk of developing an allergic reaction, patients are prescribed a trial administration of the drug that will be used in the study of the adrenal glands,
It is recommended to warn the doctor performing the CT scan about iodine intolerance, medications, and the presence of food allergies. If you have previously had blood tests for hormones or an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands, you should take the results with you.
The risks of the diagnosis are insignificant, however, patients may experience hot flashes, burning or itching of the skin, and a metallic taste in the mouth after receiving intravenous contrast. These phenomena are temporary and usually do not require additional treatment.
How is a CT scan done with and without contrast?
Before the examination, the patient must remove all metal objects; there should also be no metal elements on clothing in the scanning area.
The essence of tomography is to pass X-rays through the body and process the resulting data using special equipment. The patient is placed on a couch that is connected to a scanning device.
When contrast enhancement is used, the patient is given intravenous Omnipaque or Ultravist before scanning. Otherwise, all stages of the procedure are similar to native CT (without contrast). During the diagnostic period, it is important to remain motionless.
When the beam tube of the tomograph moves, a layer-by-layer examination of tissue occurs in the form of images - tomograms. They are processed by a computer program and produces the final image. The result can be printed or recorded on media.
The entire procedure usually takes about half an hour. Upon completion, the patient needs to drink as much plain water as possible, avoid eating salty and spicy foods, so as not to create additional stress on the kidneys and remove the contrast agent from the body as soon as possible
Norm and formations of the adrenal glands, kidneys, which reveal
Depending on the detected abnormalities, the doctor can presumably make a conclusion about the existing pathology.
Norm
When describing a tomogram of a healthy person, the adrenal glands have the following characteristics:
- shape - the left one looks like the letter V, the right one is usually linear;
- size – not increased;
- structure – homogeneous;
- outlines – smooth and clear;
- perinephric tissue (perinephric) – no changes;
- lymph nodes are of normal size and structure;
- contrast accumulation is uniform.
Kidney tumor
When examining the adrenal gland, neoplasms of the adjacent renal tissue may also be detected.
Their distinctive features:
- boundaries are unclear;
- density is reduced;
- the structure is heterogeneous;
- there are areas of calcium deposition, hemorrhage, and decay (necrosis).
- When contrast is administered, a local enhancement of the vascular pattern is noted.
Adrenal tumor
Tomography can also detect a cavity (kidney cyst), stone, abnormal organ structure, or abscess.
Adenoma, cyst, hematoma of the adrenal gland
The formation has the shape of an oval or circle, the contour is clear and even, the structure is either homogeneous or moderately heterogeneous. The cyst is characterized by a clearly visible thin capsule and the same (low) density of the contents. There may be pockets of calcium deposits in the walls.
After the administration of contrast, the adenoma becomes clearly visible, and the cysts do not change their symptoms.
A hematoma, like a cyst, has a capsule, but its contents look heterogeneous, since there are areas of coagulated blood in the cavity. The boundaries of the hemorrhage are clear, but uneven.
Adrenal hematoma (white arrow)
Lipoma
A hormonally inactive tumor has the shape of a ball with a smooth structure. There is also slight heterogeneity due to fat inclusions. There is complete delineation of the neoplasm from the adrenal tissue; the glands are not deformed.
Pheochromocytoma
The medulla on the tomogram is indistinguishable from the cortex. The tumors found have a heterogeneous structure, smooth outlines, and a clearly visible capsule that separates the pheochromocytoma from the unchanged adrenal gland tissue. After contrast administration, intensive absorption is observed due to the developed vascular network.
Phochromocytoma of the adrenal gland
Adrenal cancer
Signs that are characteristic of malignant tumors include:
- large size;
- focal inclusions of different densities;
- blurred outline;
- zones of calcium deposition, destruction;
- increased density;
- enlargement of neighboring lymph nodes.
We recommend reading the article on how to test your adrenal glands. From it you will learn about warning signs, when it is necessary to check the adrenal glands, which doctor examines women and men, a child, how to check the structure of the adrenal cortex, what diseases can be detected in women, men, and children.
And here is more information about adrenal hyperplasia.
Computed tomography is highly accurate in identifying tumors in the adrenal glands. It is necessary for choosing surgical tactics. To clarify the size and spread of the tumor process, additional contrast is used.
On a tomogram of the glands, you can see the size, location, contours of the neoplasm, examine its density and structure, and also evaluate the condition of the kidneys and lymph nodes. The degree of malignancy of the tumor cannot always be determined before surgery.
Source: https://endokrinolog.online/kt-nadpochechnikov/