A breast cyst is a common pathology, which is a capsule with liquid contents in the ducts of the mammary gland. In this article we will talk about the types, causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment of breast cysts.
Many women today are interested in issues related to breast disease. This is especially true for one of the most common ailments - breast cysts. According to medical statistics, women who do not have children most often experience this disease.
What is a breast cyst
A breast cyst is understood as a single or multiple pathology of cavity formation, in the ducts of which something similar to a capsule with liquid contents is formed.
In medicine, breast cysts are usually classified because they differ in size, shape and structure.
What are the types of breast cysts?
An atypical cyst is a benign neoplasm that grows inside the cavity due to the absence of walls. Often forms in the dilated duct of the gland. May recur and become inflamed. In addition, the cavity may contain benign and malignant papillomatous formations.
A fibrous cyst is a neoplasm that plays a significant role in the occurrence of cancer in the mammary gland. A distinctive feature of a cyst is an increase in connective tissue, which leads to the appearance of cavities in which fluid accumulates. This fluid then begins to come out of the nipples.
A fatty cyst is a benign neoplasm with smooth walls, filled with milk. Formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland during pregnancy or lactation.
A solitary cyst is a benign neoplasm in which the fluid can be of different colors. This breast cyst resembles a dense capsule. Affects only one breast.
Multilocular cyst - separate small tumors form in the breast, which eventually combine into one cyst.
A ductal cyst is a benign formation that appears in women in adulthood. Ductal cystic formation is considered a precancerous condition.
Causes of breast cysts
Why do cysts appear in the mammary glands? There are a lot of reasons. Here are the most common causes of breast cysts:
- hormonal disbalance;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- traumatic injuries of the mammary glands;
- previous breast surgery;
- UV - radiation;
- frequent worries and severe stress;
- thyroid gland;
- inflammation of the mammary gland (mastitis);
- violation of hormonal function of the ovaries;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- intellectual loads;
- neuropsychic stress;
- sensitivity to problems;
- abortions;
- weight gain;
- diabetes;
- poor nutrition;
- degenerative disease of the thoracic spine;
- biliary dyskinesia.
Watch a video with a doctor about the causes of breast cysts.
Any type of breast cyst can manifest as painful sensations before menstruation. Women do not pay attention to such pain because they associate it with premenstrual syndrome.
Symptoms of a breast cyst
If the size of the cyst is insignificant, then it can proceed without any changes. Complaints appear only when a breast cyst is palpated during palpation.
Symptoms:
- feeling of constant burning and heaviness
- headache
- in the second phase of menstruation, pain in the mammary glands increases;
- a dense formation appears in the chest;
- discomfort in the lower part of the abdominal cavity;
- discharge of fluid from the nipples;
- nervousness;
- the shape of the breast is distorted;/li>
- unevenness is felt when palpating the area near the cyst.
If inflammation occurs in the breast cyst, the following symptoms appear:
- severe pain in the place where the cyst is located;
- redness;
- swelling;
- temperature;
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- decreased performance.
A woman can examine and palpate her breasts herself, and if any suspicious lumps are detected, contact a specialist. How to do this, read the article breast self-examination.
Is a breast cyst dangerous?
Why is a cyst in the mammary gland dangerous? Doctors believe that a cyst located in the chest does not pose a threat to a woman’s health, but still one should not remain indifferent to this disease. The tumor very rarely develops into breast cancer. But there is always a risk of inflammation and suppuration, leading either to the development of purulent mastitis or to the appearance of a cancerous tumor.
Signs of development of an oncological process in the mammary gland:
- hardening of the skin on the affected area and pulling it inward;
- damage to epithelial tissue of the skin;
- redness of the nipples and the appearance of fluid from them;
- formation of a “lemon” peel;
- breast deformation;
- in the place where the lesion occurs, the nipple begins to retract;
- when feeling the mammary gland, a knot is very clearly visible under the fingers;
- asymmetry of the mammary glands is clearly expressed.
In order to respond to the slightest changes in a timely manner, it is necessary to conduct an independent examination of the mammary glands after the end of your period.
If during an independent examination any changes were found, then there is no need to panic. First of all, you need to contact your gynecologist at the antenatal clinic, who will give you a referral to a mammologist-oncologist. There is no point in waiting for your assumptions to be confirmed in reality.
Does a cyst turn into cancer?
A breast cyst does not pose any danger to a woman’s life.
Of course, it adversely affects life itself due to several reasons, but this disease is rarely classified as a pathology that degenerates into oncology.
Despite this, its nodular forms are quite capable of prompting the development of a malignant tumor, since a breast cyst is a background for the development of oncology.
Faced with such an illness, women begin to panic, but this should not be done. You just need to consult a doctor in a timely manner and start treatment.
Diagnosis of breast cyst
In order to diagnose a “breast cyst,” the doctor first examines the breasts and prescribes diagnostic tests for the woman:
- Mammography - x-ray of the mammary glands. This procedure reveals the location of the cyst, then the shape and size. Next, the location for puncturing the wall of the cystic formation is determined. All women (over 45 years old) should have a mammogram, since it is during this period that there is a high risk of developing cancer.
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to examine and accurately describe the tumor. In addition, MRI can detect subtle changes in the tissue that surrounds the cyst.
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands - studies the shape, size of the cyst and reveals the presence of parietal formations inside the cyst. With ultrasound, the elastography method is used, thanks to which the elasticity of the tissues of the studied material is assessed. An ultrasound scan is recommended for women under 30 years of age.
- Cytological analysis - biological material is taken from the neoplasm. With the help of such an analysis, the doctor will find out whether the cyst is malignant or not.
- Doppler studies - during such diagnostics, specialists can identify a breast cyst with a smooth wall of the same thickness. If the contents of the capsule are homogeneous and there is no constant movement of blood, then this indicates the benign nature of such a neoplasm.
- Pneumocystography - provides detailed information about the walls of the cyst capsule. The essence of this study is that air is introduced into the cavity in order to study the walls of the cyst.
The final diagnosis is made after a biopsy (lifetime sampling of cells from the body).
Do I need to treat a breast cyst?
To the question of whether it is necessary to treat a breast cyst, there can be only one answer - it is necessary.
How to treat a breast cyst? Basic methods of treating breast cysts
Treatment methods for breast cysts can be divided into several ways: conservative therapy, surgery and folk remedies.
Conservative treatment
If a breast cyst is detected in the early stages and its size does not exceed 0.5 mm, then the doctor will not remove such a tumor. A woman should be checked every year not only by a gynecologist, endocrinologist and immunologist, but also by a mammologist who will select the correct conservative therapy.
The following can help make the cyst disappear:
- modern medications (help restore hormonal balance in the body);
- puncture (a small puncture is made, the liquid is pumped out and a special solution is injected, thanks to which the capsule disappears);
- aspiration (liquid is drawn out from the tumor cavity using a thin tube).
Surgical intervention. Surgery to remove a breast cyst
When therapy does not bring results, the specialist prescribes surgical removal of the breast cyst. Surgery is also necessary if taking medications does not bring the desired effect or it turns out that the cyst may be malignant.
The operation takes place under general anesthesia. The surgeon cuts out the cystic formation and the part of the tissue that surrounds it from the breast.
When the operation comes to an end, the doctor applies a neat suture, which after the recovery period becomes almost invisible.
Treatment of breast cysts with folk remedies
Sometimes treatment of breast cysts with folk remedies gives excellent results. This method of treatment involves the use of only natural products. Before using your grandmother’s recipes, you need to consult with a specialist so that there are no serious consequences in the future.
Prevention of breast cysts
The best prevention of cystic formation is an annual visit to a mammologist. The specialist will prescribe an examination that will help to detect and prevent the development of breast cysts in the early stages. In addition, he will teach self-examination techniques.
If a woman monitors her health, then she should conduct an independent examination of the mammary glands once every 30 days after the end of her period.
For the purpose of prevention, you should follow simple rules:
- limit consumption of tea, coffee and dark chocolate,
- reduce the amount of salt in the food you eat,
- Wear a comfortable, supportive bra.
A cyst in an advanced form poses a danger not only to a woman’s health, but also to her life. Therefore, it is worth finding out in advance all the details about this disease: what a benign formation is, what its symptoms are and what causes contribute to its appearance.
As for the treatment of breast cysts, this should be decided after a thorough examination. True, most often this disease does not require treatment, but observation.
Source: https://www.mammologia.ru/zabolevanija/kista/
Breast cyst. Diagnostics. Treatment. Removal
Breast cyst
A cyst is a connective tissue cavity filled with serous exudate. The pathology develops against the background of fibrocystic mastopathy, the cause of which is hormonal imbalance.
An increase in serum concentrations of prolactin and estrogen leads to an increase in the diameter of the mammary gland ducts and the accumulation of liquid secretions in them.
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, several types of cysts are distinguished.
Atypical breast cyst
An atypical cyst is an accumulation of liquid exudate in areas of expansion of the mammary duct. The tumor is a fibrous capsule with numerous growths protruding into the pathological cavity. The reasons for its occurrence are:
- recurrent cysts in the breast;
- papillomatous neoplasms;
- frequent inflammation of the mammary ducts.
Important! An atypical cyst can transform into a low-quality tumor and provoke the development of cancer.
Fibrous cyst of the breast
Fibrous cyst (Schimmelbusch disease) is a dangerous disease that often accompanies the development of cancer. There are proliferative and non-proliferative forms of pathology, the manifestations of which are:
- increased chest pain on the eve of menstrual bleeding;
- discharge of liquid secretion from the nipples;
- presence of cluster-shaped tumors in the breast.
Inflammation of a breast cyst
Septic inflammation in tumors leads to the transformation of serous exudate into purulent. The causes of infection of the contents of pathological cavities in the chest can be:
- infectious diseases;
- decreased body resistance;
- stagnation of milk during lactation;
- often hypothermia of the chest;
- hypovitaminosis.
Breast cyst pain
The occurrence of discomfort is directly related to the increase in the size of pathological cavities. The intensity of pain increases on the eve of menstrual bleeding and during exacerbation of chronic diseases. Discomfortable sensations are characterized by nagging and aching pains that can radiate to the subscapular region or shoulder.
Breast cyst mastopathy
Violation of the structure of the mammary glands occurs due to hormonal imbalance and endocrine diseases. Depending on the morphological changes in tissues and the tendency of tumors to become malignant, several types of cysts are distinguished:
- true;
- pseudocysts;
- multiple;
- solitary;
- fibrous;
- typical;
- atypical;
- multi-chamber.
Fibrocystic mastopathy is diagnosed in approximately 45-50% of women of reproductive age. All of them develop against the background of endocrine disorders and gynecological diseases.
Diagnostics
- mammography;
- pneumocystography;
- echogram;
- Breast MRI;
- biopsy;
- Breast ultrasound;
- laboratory analysis of aspirate.
After the pathology is detected, the examination is continued to determine the reasons for its development. During the diagnostic process, consultation with doctors of related specializations is possible - endocrinologist, surgeon, gynecologist, etc.
Recommendations! To diagnose the disease at an early stage, visit a mammologist annually, including undergoing an ultrasound of the mammary glands.
Causes of breast cysts
The functional state of the mammary glands depends on the content of steroid hormones in the blood, which are produced by the thymus gland, ovaries, pituitary gland, etc. Any endocrine disorders entail the development of gynecological diseases, and therefore pathological changes occur in the mammary glands. Hormonal imbalance and mastopathy can be provoked by:
- endometriosis;
- inflammation of the gonads;
- frequent abortions;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands;
- liver failure;
- early menarche;
- refusal of breastfeeding;
- taking oral contraceptives.
Signs and symptoms of breast cysts
Breast tenderness is the first sign of the formation of a cyst in the mammary duct. As its size increases, patients experience the following symptoms:
- increase in breast volume;
- liquid discharge from the nipples;
- compactions on palpation;
- inverted nipples;
- increased pain during menstruation.
Breast cyst cancer
Cystic neoplasms in the breast are signs of the development of mastopathy, which in turn can cause low-quality tumors in the ducts of the mammary glands.
Most often, cancer is diagnosed in patients with fibrous and atypical cysts.
The development of cancer can be prevented through timely medical or surgical treatment of the pathology.
Treatment
Small cysts without growth dynamics are treated conservatively. The therapy is similar to the treatment of diffuse forms of mastopathy. In cases where a large breast cyst is detected, punctures are performed and a treatment regimen is drawn up based on the results obtained.
In case of repeated recurrence of the cyst or detection of intracystic growths, surgical treatment is performed in the scope of sectoral resection of the mammary gland.
Important! Only a mammologist can draw up the correct treatment plan for a cyst based on the results of ultrasound, MRI, mammography and tissue biopsy.
Removal of a breast cyst
Surgical intervention is resorted to only in case of rapid progression of the tumor and infection of its contents. Cysts are removed using sectoral tissue resection. During the procedure, the surgeon excises not only the fibrous membrane of the tumor, but also the surrounding tissue.
The method of surgical intervention directly depends on the form of the disease, the location of the cysts, their number and the cause of development. Indications for surgical treatment are:
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- frequent recurrence of pathology;
- septic inflammation of the cyst contents;
- multilocular benign tumors;
- large cysts (more than 1.5 cm).
Currently, the following surgical techniques are used to remove pathological cavities:
- puncture - a puncture of the tumor with subsequent pumping out of its liquid contents;
- laparoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention that involves removing not only the contents of the cyst, but also its capsule;
- laser resection – destruction of tissue of cystic formations by exposing them to a beam of laser light.
Laparoscopy
Despite its safety, this is a fairly serious surgical procedure. The laparoscopy procedure is performed under general anesthesia of the patient. However, unlike standard surgery with dissection (laparotomy), laparoscopy is a low-traumatic and gentle procedure.
During laparoscopy, intervention in the woman’s body is minimal, therefore the likelihood of adhesions forming after laparoscopy is much lower than after laparotomy. Blood loss during laparoscopy is minimal. The patient's stay in the hospital after laparoscopy is short.
In our clinic it is kept to a minimum.
Laser resection
The interstitial laser treatment technique is one of the minimally invasive methods for removing nodular formations. In terms of its effectiveness, it is not inferior to surgery, but causes complications much less often. Tumors are removed using a laser beam that has a destructive effect on pathological tissue.
After the operation, there is a risk of disruption of the symmetry of the mammary glands, so upon completion of the procedure, the doctor applies cosmetic sutures.
2-3 days after removal of the cyst, a drainage tube is placed in the operated area, through which exudate is removed from the glands.
In case of re-formation of cystic tumors, a decision is made to repeat the operation along with removal of the axillary lymph nodes and mammary gland.
Conclusion
Breast cysts are benign tumors prone to malignancy. The cause of its occurrence is most often hormonal disorders and gynecological diseases. Treatment involves taking medications that affect the patient’s hormonal levels or surgical removal of tumors if they reach large sizes.
Source: https://klinika.k31.ru/napravleniya/mammologija/kista-molochnoy-zhelezy/
Breast cyst: effective treatment with folk remedies
Cystic formations are cavities filled with liquid secretion. They belong to benign tumors. A breast cyst forms in the ducts of the breast. The doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment, including medications and folk remedies. The choice of drugs and methods of therapy is influenced by the form of the disease and the reasons that led to hormonal imbalance.
Causes
Cysts appear when the ducts in the mammary gland pathologically expand, a fibrous capsule is formed, in the cavity of which secretions accumulate. Cysts are mainly formed from benign cells . Malignant neoplasms occur rarely.
Cysts vary in size, shape, and structure. Single and multiple tumors form in the mammary gland. When the capsules merge with each other, a multi-chamber formation appears. In this case, the woman is diagnosed with polycystic breast disease.
There are two types of neoplasms:
- typical tumor (the surface of the walls is even, smooth)
- atypical cyst (growths form on the surface of the walls, protruding into the capsule cavity).
Hormonal imbalance is the key reason causing cystic formations. The disease is caused by:
- excess amount of female sex hormones;
- deficiency of hormones produced by other glands;
- uncontrolled use of contraceptives containing hormones.
Hormonal imbalance can be caused by the following reasons:
- chest injuries;
- hormone replacement therapy;
- thermal procedures that activate the production of estrogen;
- prolonged exposure to the sun: ultraviolet irradiation provokes the synthesis of estrogens;
- impaired functioning of the thyroid gland;
- nervous and emotional tension: stress increases the production of testosterone, prolactin, cortisol;
- mastitis;
- failure of the ovaries;
- breast surgery;
- childbirth;
- abortions;
- poor nutrition, impaired metabolism.
The risk group includes nulliparous women from the age group of 35-55 years.
Symptoms
Cystic formations affect one breast or both at once. If their size is excessively large, the mammary gland becomes deformed. Large capsules lead to changes in the skin. Redness appears on it, which is replaced by cyanosis. If the cyst connects to the duct, abnormal discharge will ooze from the nipple. In this case, the woman complains of pain and discomfort in the chest.
A cyst in the mammary gland is not a dangerous phenomenon. But if infectious agents penetrate the capsule, a purulent process occurs. Inflammation that breaks out in the cyst causes the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- hyperemia (blood vessels become overfilled with blood, congestion occurs);
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits.
Multiple small cysts do not cause much discomfort. The disease is asymptomatic. It is detected during mammography. With the appearance and growth of cystic capsules, the structure of the mammary gland changes.
Large cysts put pressure on nearby tissues. Pain is the main symptom of extensive lesions. Soreness increases before menstruation. It can spread beyond the breast, extending into the sternum, which indicates severe inflammation and suppuration.
Changes in hormonal levels lead to an increase in gland tissue. A clear sign that appears during menstrual bleeding is thickening. Nodules are detected by palpation of the chest.
With large cysts, the entire period of the menstrual cycle is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- persistent pain;
- discomfort in the chest;
- unbearable burning sensation.
Conservative therapy
Treatment for a cyst in the breast is prescribed by a doctor. It is prohibited to get rid of tumor formations on your own, even if their size is small .
Conservative treatment methods are used when the size of the cyst is less than 0.5 mm. In this case, it is not advisable to perform the operation. Small cystic neoplasms are treated as follows:
- Medicines are prescribed that help the nodules resolve.
- They do a puncture. The pathological exudate is pumped out through a small incision, and a solution capable of dissolving it is injected into the capsule.
- Hormone therapy is carried out. After prolonged treatment, hormonal balance is restored.
If therapy is unsuccessful, the breast cyst is removed surgically. Surgery is resorted to when the neoplasm is malignant.
Traditional medicine methods are used in conjunction with medications. The treatment regimen is drawn up by the attending physician. He prescribes remedies that can:
- suppress hormone production;
- get rid of problems that cause hormonal imbalance;
- improve metabolism.
Treatment using traditional medicine methods
In addition to traditional treatment, the doctor will recommend suitable traditional methods of recovery. At home, treatment of breast cysts is carried out with folk remedies for external and internal use.
Herbal preparations contain phytohormones that can maintain the balance of prolactin and estrogen. They suppress the synthesis of hormones that are in excess.
Folk remedies eliminate hormonal imbalances, strengthen the immune system, stop the development of the inflammatory process, and relieve fever. Soothing herbal extracts relieve stress, which triggers the development of cystic formations. Treatment is carried out strictly observing the dosage of medicinal components.
Means for topical treatment
At home, remedies are prepared that can resolve cystic tumors. Compresses and rubbing help to heal:
- Applications with St. John's wort extract. Boil 200 ml of water, pour 20 g of herbs into it. After an hour, filter. Soak a napkin in a warm solution, apply it to the chest, and leave the compress on for 15 minutes.
- A beet compress helps treat a cyst. Take 200 g of beets, grind them to a pasty state, pour 2 tablespoons of 9% vinegar into it, and knead thoroughly. The product is placed on a napkin and secured to the sore chest with a bandage. The compress is applied before bedtime. In the morning, the application is removed and a warm bandage is applied to the chest. Treatment lasts 10 days.
- Application with beets. Take the root vegetable, grind it to a pulpy state, and squeeze out the juice. The paste is applied to the chest, covered with polyethylene, and insulated with a bandage. The compress is applied overnight.
- A compress with honey and beets is an effective way to treat cysts. The beet pulp is mixed with honey (take 2 tablespoons of each). The mass is distributed over the affected area and covered with a cabbage leaf. The procedure is done in the evening, the application is left until the morning. Treatment lasts 30 days.
- Applique with carrots. The carrot pulp is applied to the damaged breast, covered with polyethylene, and secured with an insulating bandage. Do not allow the pulp to dry out. A fresh compress is applied as needed.
- Compresses with cabbage leaves help cure a cyst. The sheet is beaten, greased with butter or honey, and secured to the chest. The dressing is changed twice a day.
- An effective home method is honey cakes. Combine a tablespoon of flour and honey with an egg yolk. Roll out the dough into a thin cake and pin it on your chest. The compress applied in the evening is removed in the morning.
- Chaga oil is an effective folk remedy for the treatment of formations . Pour cold water into the pan, put the mushroom in it, and leave for 6 hours. The swollen chaga is taken out, squeezed out, and crushed. The liquid is heated to 50 degrees, chaga is dipped into it in a ratio of 5:1. Place in a cool place for 48 hours, then filter and put in the refrigerator (shelf life 4 days). Add 4 teaspoons of extract to 10 tablespoons of vegetable oil. Place in a dark place for 24 hours. Rub oil on the affected area several times a day.
- Celandine ointment. The herb is mixed with ghee in equal quantities and thoroughly ground until smooth. The finished product is rubbed into the skin. The chest is insulated with a bandage for 6 hours.
Products for internal use
Preparations for oral administration are prepared at home. The cyst in the initial stage can be eliminated using folk remedies.
- Burdock extract. Boil 200 g of water, pour 10 g of burdock root into it. After 3 hours, filter. Take a tablespoon three times a day, half an hour before meals. Treatment lasts 1.5-2 months. They rest for 10 days. They do a repeat course.
- To cure cysts in the mammary gland, make a walnut tincture. Take a 0.5 liter jar, put the shells of 15 nuts in it, pour vodka under the neck. After 10 days, the extract is filtered. Use it once a day, in the morning on an empty stomach, taking one sip.
- Chaga extract. For a cyst in the chest, prepare a remedy according to the following recipe: add 250 g of chaga to 2 liters of cool water and leave for two hours. The swollen mushroom is pounded, combined with the water in which it was located, and simmered over low heat for 60 minutes. Filter after cooling. A glass of viburnum is poured into the water and left for six hours. Place in a water bath and leave for an hour. Allow to cool, drain the juice. Combine 250 ml of aloe juice and honey, chaga and viburnum berries. The product is diluted with boiling water to make 4 liters of medicine. The extract is kept in the dark for 7 days. Store in the refrigerator. Take 2 tablespoons three times a day, half an hour before meals.
- Chaga suppresses inflammation and tumor development. Extracts from it do not allow tumor cells to divide. 0.5 kg of mushroom is dipped into heated water. After 2 hours, the swollen mushroom is crushed. Boil 3 liters of water, put chaga in it, leave until it cools and put it in the refrigerator. Take the medicine on the fourth day after the end of menstrual bleeding. Drink 100 ml of medication three times a day. Treated before the onset of the next menstruation. The dose is gradually adjusted to 200 ml. Treatment lasts 3 months.
- Chaga tincture. Add 50 g of mushroom to 0.5 liters of vodka. After three weeks, the tincture is filtered. Take 10 ml three times a day half an hour before meals. Treatment lasts 60 days. When treating with chaga, it is forbidden to eat fatty, spicy, smoked, meat broths, drink coffee and tea.
- Boron uterus extract. This herb has an antitumor and absorbable effect, eliminates inflammation . Women use it to eliminate multiple gynecological pathologies. It effectively fights cystic formations in the breast. Boil 250 ml of water, brew a tablespoon of the plant in it, and simmer for 15 minutes. After 4 hours, filter. Drink 15 ml five times a day.
- Tincture from boron uterus. Medical alcohol is diluted to 40% (vodka is not suitable for preparing medicine). Pour 50 g of herbs into 0.5 liters of alcohol. The drug is filtered after 21 days. Take 20 drops three times a day for 3 months.
Breast cysts cannot be cured without medications. Refusal of drug therapy leads to the development of the disease, the formation of new cysts, and the degeneration of benign tumors into cancerous tumors. Only timely treatment prescribed by a doctor helps keep the disease under control and transfers it to a stage of stable remission.
Source: https://FitoOtvet.com/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/kista-molochnoj-zhelezy.html
Breast cyst: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
A breast cyst can be a single or multiple cavity formation in the breast tissue, filled with some kind of fluid. The contents of a cyst in the breast can be blood plasma or pus.
For a long time, such a cyst may not give any symptoms, perhaps only a slight burning sensation and soreness in the mammary gland, which intensifies before menstruation. There is a risk of the cyst degenerating into breast cancer. With its large size, the shape of the gland changes.
Causes of cyst formation
Among the reasons leading to the development of a disease such as a breast cyst, one can note a change in hormonal levels, which shifts towards an increase in estrogen and prolactin. The following reasons can disrupt hormonal levels.
- Psycho-emotional factors. When stress occurs, the body responds by increasing levels of hormones that can help adapt to a stressful situation. In this case, the concentration of the hormones cortisol, prolactin, and testosterone increases. In frequent stressful situations, such hormonal changes in the body can lead to the formation of a breast cyst.
- Increased insolation. This takes into account the effect on the body of both natural and artificial sunlight (solarium). During tanning, the production of estrogen by the ovaries and adipose tissue is stimulated. Therefore, it is possible for a cyst to appear in the chest after prolonged sunbathing (a trip to the sea).
- Prolonged exposure to thermal procedures. Taking shared baths, staying near heating appliances, in a hot shop, etc. leads to stimulation of estrogen production.
- Thyroid dysfunction can also lead to hormonal imbalance.
- Breast contusion.
Breast cysts are a relatively common pathology, but are most common in nulliparous women aged 35 to 55 years.
Provoking factors
Among the provoking factors that lead to the formation of breast cysts against the background of altered hormonal levels, the following can be identified:
- ovarian dysfunction, which can occur in various diseases (for example, polycystic ovary syndrome);
- past mastitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs (endometritis, adnexitis, etc.).
Cyst formation
The mammary gland has about 20 lobes of glandular tissue, each of which, in turn, is divided into small parts. During pregnancy and after childbirth, milk is formed in the glandular tissue, which flows through the ducts into a kind of reservoir located behind the nipple.
If there is an increase in the glandular tissue of certain areas, then they block the ducts of the glands. This causes the gland ducts to dilate and fill with fluid. This is how a cyst can form in the breast.
Types of cysts
All breast cysts that form can be divided into the following types.
1. By size:
- microcysts, which are very small in size, cannot be felt independently, but can only be detected using ultrasound or mammography;
- macrocysts can be detected independently, as they can reach several centimeters in size.
2. By number of cameras:
- a unilocular cyst in the chest consists of one chamber;
- multilocular cyst consisting of several chambers.
Symptoms
If the size of the breast cyst is insignificant, then, as a rule, it does not manifest itself with any symptoms. The appearance of complaints is often observed with the size of the cysts, which can be felt independently.
Therefore, one of the first clinical manifestations will be the discovery in the gland tissue of a rounded formation that has a soft and elastic consistency, immobile and varying degrees of pain.
Also, a cyst in the breast is characterized by a cyclical change in its size, which is associated with the menstrual cycle - before menstruation the cyst increases, and after - its size decreases.
Approximately 5-12 days before the onset of menstruation, engorgement of the mammary glands may occur, and a burning sensation may appear in them. In some cases, these symptoms are permanent and are not associated with the menstrual cycle. With larger breast cysts, visible breast asymmetry may occur.
How does a doctor make such a diagnosis?
The diagnosis of “breast cyst” is made by a doctor only after confirming it using additional research methods.
Therefore, after a palpation examination, during which a breast cyst manifests itself as a formation of a round shape and soft-elastic consistency, the following diagnostic studies may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands. Using this method, you can study the gland cyst in more detail - determine its size and shape, and identify the presence of intracystic parietal formations. It is also possible to perform 3D ultrasound using the elastography method.
- Mammography involves x-ray examination of breast tissue. It can also be used to identify a cyst in the breast, determine its shape and size.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is considered a more accurate diagnostic method and, as a rule, is prescribed in addition to the above research methods.
If during diagnosis a breast cyst with a smooth wall is discovered, which has the same thickness, its contents are homogeneous, and according to Doppler studies there is no peripheral blood flow, then with a high degree of probability they speak of the benign nature of such a formation.
If the cyst contains parietal formations, its contour is uneven, the contents of the cyst are heterogeneous, and atypical hemodynamics are present, then to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy may be required, which is performed under the control of an ultrasound sensor.
Also, as an additional examination for a disease such as a breast cyst, pneumocystography may be prescribed, which will provide detailed information about the walls of the cyst capsule.
This study consists of introducing air into the cavity of the cyst and subsequent ultrasound or x-ray examination of its walls.
Also, an additional diagnostic method can be a blood test for tumor markers.
Cyst treatment
The treatment of a cyst largely depends on its size and the results obtained during additional examination.
Conservative treatment
Such treatment can be prescribed only for small breast cysts (up to 2.5 cm). Also prerequisites are the presence of a thin wall of the cyst in the chest and the complete absence of signs of its malignancy. In this case, the doctor may prescribe therapy to normalize hormonal levels.
Surgery
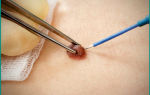
A cyst in the breast is usually treated by a surgeon as follows. In the presence of a single-chamber simple cyst, puncture of the cyst can be performed, followed by pumping out fluid from it. At the end of this procedure, special preparations are introduced into the cyst cavity to promote healing of the cavity.
All these manipulations are carried out under the control of an ultrasonic sensor. After puncturing, regular monitoring by a mammologist and periodic ultrasound examinations are required for timely detection of relapses.
If, according to additional research methods, signs of malignancy of the breast cyst have been identified, then sectoral resection will be required. The same operation can be prescribed in the presence of multi-chamber and multiple cysts.
Source: http://MastopatiiNet.ru/kista-molochnoj-zhelezy/
Breast cyst symptoms and treatment
A cyst is a pathological benign formation, the walls of which are connective tissue, and the internal contents are liquid. The size of cysts can vary from one millimeter to several centimeters. On palpation, it is defined as a compaction with a smooth surface, usually not causing pain.
The cyst can be either single (solitary) or numerous. Not every cyst is detectable by palpation and the patient may have it throughout his life. If the mammologist probed the cyst. Then it is already big and requires the necessary treatment.
Causes of breast cyst formation
The risk group includes women aged 30 to 40 years, as well as nulliparous women.
Doctors identify the following reasons for the onset of pathology:
- Hormonal disorders (probably this is the main reason; the growth of pathology is sometimes influenced by taking oral contraceptives);
- Breast surgery or physical trauma;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Nervous stress (it has long been known that almost all diseases are caused by nervous breakdowns, neuroses);
- Mastopathy.
No one is protected from this disease; if you consult a doctor in time, recovery is about 90%. The likelihood of a cyst degenerating into a malignant formation is low, but patients have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Breast cyst: symptoms and diagnosis of pathology
Let's look at the main symptoms that appear in patients:
- Frequent aching pain in the chest area, which intensifies before the start of the menstrual cycle;
- Feeling of discomfort and chest tightness.
Diagnosis is carried out only in medical institutions. To do this, the mammologist prescribes an ultrasound of the mammary glands and mammography to the patient, as well as palpation of the breast. Some people try to identify a cyst on their own by the type of skin, but unfortunately, this is impossible. The skin on the cyst does not change in any way, only in severely advanced cases.
Treatment of breast cyst
It is not life-threatening, but this is not a reason to delay treatment. Remember, there is a risk of developing cancer or, if internal infection occurs, a purulent process may begin. Treatment usually occurs without surgery.
Treatment with drugs
The mammologist prescribes drug treatment - special drugs to regulate a woman’s hormonal levels. This strengthens the immune system and prevents re-formation. When the hormones return to normal, the cyst should resolve.
Surgical method of treatment
If the first method does not help, then you have to undergo surgery. Initially, a puncture is performed (the cyst is pierced with a very thin needle and fluid is taken from the cavity), then air is pumped into the place of the former fluid to quickly heal the tissues. Less often, alcohol is pumped in for faster fusion.
Treatment of breast cysts with folk remedies
There are several methods of treatment with folk remedies, let's look at each in detail.
Burdock tincture
To prepare the tincture you need 10g. finely chopped burdock root, pour 250 ml of boiling water over it. Then cover tightly, leave for 2 hours and strain. You need to drink the tincture one tablespoon half an hour before meals.
St. John's wort tincture
To prepare, take 50g of dry grass and pour half a liter of boiling water. Then the infusion should stand for 15 minutes. Gauze is moistened in it and applied as a compress to the site of the cyst. After an hour, the procedure is repeated. The course of treatment is at least two weeks.
Beetroot compress
Grate 100 grams of red beets and heat this mass in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then add a tablespoon of vinegar. The compress is applied at night. The course is carried out over two weeks.
White
cabbage
You need a washed cabbage leaf, grease it with butter and apply it to the cyst site overnight. The top of the sheet needs to be wrapped with cloth or a special bra inflated. By morning the pain will subside. For complete recovery, therapy is carried out for three weeks.
Carrot compress
Take 500 g of carrots and grate them until a paste forms. A compress with gruel is applied to the formation in gauze or a fabric bandage. The compress needs to be changed three times a day.
Celandine juice
The cyst site is rubbed generously with celandine juice and left for at least 3 hours. Do the procedure once a day for 10 days.
Sunflower oil
The third medium head of garlic is grated, then 100 ml of sunflower oil is poured into it and left for a day in the refrigerator. Take one teaspoon before meals. Treatment lasts three weeks.
Chaga mushrooms
Take freshly cut chaga mushroom. Finely cut and filled with warm water in a ratio of 1:6. The infusion should stand for at least two days. Take 100 ml before meals for two weeks.
Quite often, traditional methods are effective or are an excellent assistant to traditional treatment. But you cannot self-medicate, but it is better to seek professional help.
Source: http://womansecret.com.ua/kista-molochnoj-zhelezy-simptomy-i-lechenie/