In this article we will consider the following questions:
- what are papillomas;
- what is the reason for their formation.
- where they are more often formed in men and women;
- typical photos of papillomas.
Papillomas are benign neoplasms localized on the skin and mucous membranes. The reason for their formation is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted in various ways. The appearance of the formations depends on the type of virus that caused them.
What diseases are caused by the human papillomavirus?
Scheme of human papillomavirus infection
palm lesion
Transmission routes
Human papillomavirus is transmitted:
- During sexual intercourse, including anal, oral-genital.
- By everyday means. The microorganism can exist on contaminated personal belongings, personal hygiene items, and towels. It easily penetrates through scratches and abrasions on the skin.
- During the birth process from mother to child.
Self-infection is possible if the virus is transferred from one part of the body to another, which usually occurs during shaving and hair removal.
The incubation period (the period from HPV entry into the body until signs of pathology appear) ranges from several weeks to several years.
Papillomas on the body most often appear during illness, pregnancy, alcohol abuse, psycho-emotional stress, hypothermia, accompanied by a decrease in immune defense. The incidence of these formations in men and women is the same.
Human papillomavirus: types
Depending on the risk of oncological pathology on the skin and mucous membranes, papillomaviruses belong to the following groups:
- Low oncogenic risk (HPV types 3, 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 72, 73, 40–44, 51, 61).
- Average oncogenic risk (HPV types 52, 56, 58, 30, 35, 45).
- High risk of developing malignant processes (HPV types 50, 59, 16, 18, 64, 68, 70, 31, 33, 39).
Microorganisms with a low degree of cancer risk cause benign growths on the skin and mucous membranes.
Photo of human papillomavirus
Types of papillomas
They are also called vulgar, ordinary. Such growths are most often caused by HPV types 26–29, 77, 63, 41.
A tingling or burning sensation appears on any part of the body. Later, the growth of a spherical formation is noted, the surface of which gradually becomes rough. At first the tumor is flesh-colored, then darkens. The size of papilloma on the body ranges from 1 mm to cm.
These neoplasms can be single or multiple. In the latter case, the daughter small papillomas are located around the mother one, which is formed first, usually the largest of all.
Their localization is the back of the hands, fingers, spaces between them, the chin area, and the edges of the lips. There are such papillomas on the neck. The child's knees are affected, because children often crawl and become infected through small breaks in the skin.
Simple papilloma
Another one
Plantar
People with these formations are infected with HPV types 1, 2, 4. The growths are similar to dry calluses, but have a number of characteristic differences.
The skin pattern is preserved on calluses, absent on the surface of papillomas, the latter are smooth. The formation caused by papillomavirus is painful, the discomfort intensifies when wearing compressive shoes. Black dots are visible inside the papilloma, which are absent in calluses.
Neoplasms sometimes destroy on their own, which more often occurs in children. Sometimes small bubbles are noticeable around the tumor. The latter turn into new papillomas over time.
This is what plantar papilloma looks like.
Here too
In the photo there is a virus infection on the skin of the foot
Flat papillomas
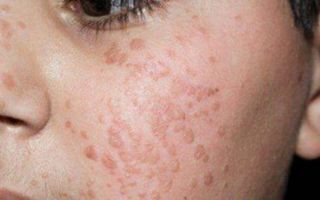
The growths are round, elongated, oval in shape, rising above the skin level by 1–2 millimeters. Flat papillomas are localized around the mouth, on the face, and the upper half of the body. Sometimes papillomas form on the neck.
Flat papillomas on the face in the photo.
This is what they look like up close
Here's another
Another example
These papillomas are found on the labia, cervix in girls, penis in men, in the rectum, near the anus. These formations are located in groups and merge with each other. Flat, flesh-colored papillomas, sometimes slightly darker than the rest of the skin, are formed under the influence of 10, 49, 28 types of papillomavirus.
Filiform
If people notice that small papillomas have appeared on the neck, then most often the growths are thread-like. The second name of the formations is acrochords. The latter are caused by HPV types 2 and 7.
At the initial stage, papillomas on the neck look like small yellowish lumps, then the growths stretch out, harden, and take on an elongated, round, thread-like shape. A distinctive feature of such a papilloma on the neck is a thin stalk.
Most often, acrochords are formed in men and women over 40 years of age. Growths also occur on the skin of the upper eyelids, armpits, mammary glands, and in the intimate area.
This is what threadlike papillomas on the neck look like.
Here they are shown by arrows
The photo shows filiform papillomas
Pointed
These formations are called condylomas and are caused by types 6, 11, 44, 42, 54, 51, 55, 89 of the human papillomavirus in women and men.
Condylomas are small single, multiple flesh-colored growths localized on the female and male genital organs, around the anus. There are papillomas in the vagina, labia minora, and cervix. In men, condylomas are located on the foreskin, glans penis, and inside the urethra.
Individual elements sometimes merge with each other, creating a tumor-like formation that looks like a rooster's comb or cauliflower. Neoplasms are characterized by very rapid growth; a wide lesion can form in a few hours.
A type of pointed papilloma (condyloma).
In the photo there is a condyloma
Condyloma on the skin
The pathology has a relapsing course. It is more severe with concomitant sexually transmitted infections of the urogenital tract (for example, chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis).
Condylomas that form on the cervix, especially inside the cervical canal, are most dangerous during pregnancy. Hormonal changes stimulate rapid growth followed by tissue breakdown and secondary infections.
Damage to the genitals by the human papillomavirus.
Papillomas on the penis in the photo.
Papillomas in the mouth, larynx
Their appearance is associated with the activity of papillomavirus types 6, 7, 11, 72, 73, 57, 32. The formations are rounded formations on a thin or wide base. The mucous membrane around them is pale pink, without any visible pathological changes. The surface of the growths is pale pink, whitish.
Neoplasms can be single, multiple, and painless when palpated. They are located on the floor of the oral cavity, the back surface of the tongue, the hard and soft palate, the mucous membrane of the larynx, the size ranges from 2 mm to 2 cm,
Papillomas on the tongue (photo).
When biting, the growth of the oral mucosa bleeds and darkens as a result of the outpouring of blood into it. The state of health in the presence of such a disease does not worsen, the oral cavity opens freely.
Source: https://vitopharma.ru/zabolevaniya-kozhi/papillomy/chto-takoe-papilloma.html
Papillomatosis photo
Papilloma is a benign tumor localized on the skin, less often on the mucous membranes. The formation of any papillomas occurs after the penetration of HPV, the human papilloma virus, into the body. But you need to know that sometimes several years pass from the moment of infection to the formation of growths on the skin.
Varieties
HPV is a microorganism that has up to hundreds of stamps. Depending on the type of HPV stamp affecting a person, different types of papillomas are formed on the skin. They differ in appearance, growth rate, and location on the body.
The picture shows papillomavirus
Some papillomatous growths are detected on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, in the bladder, in women in the vagina, and in men in the penile area.
Determining the type of papillomas is necessary to select the most effective treatment method and to assess the risk of this tumor degenerating into a malignant one.
Kinds
The human papillomavirus, after its activation in the body, leads to not only changes in the skin and mucous membranes, but also to a number of diseases dangerous to human health. Which path the infection will take depends, first of all, on the type of HPV present in the body.
Papillomas are caused by several types of viruses, and in some cases, their location and external features can suggest the type of HPV.
Simple
Simple papillomas have several other names: vulgar or ordinary. They appear on the body if several types of HPV develop in the body, and more often these are 26-29, 41, 63, 77.
Vulgar papillomas are the most likely formation on the skin from the group of benign ones. The process of papilloma formation begins with a slight burning and tingling sensation in a certain area of the body, then at this place you can notice the growth of a spherical tumor.
Over time, the surface of this uneven formation becomes rough, and the color changes from flesh-colored to darker. The size of a simple papilloma starts from 1 mm and can reach a centimeter in diameter.
The most common location in adults is the fingers, the spaces between the fingers and the back of the palms. Vulgar papillomas are often found in children, and the knee area is a common location for such formations, which is due to the fact that a small child often crawls and becomes infected through the slightest cracks in the skin.
Ordinary papillomas can be single or multiple. In the latter case, the daughter formations grow next to the main one - the mother one.
Plantar
Papillomas on the soles of the feet can appear in people infected with HPV types 1, 2 and 4. These formations can easily be confused with calluses, but there are several signs that specifically indicate plantar papilloma, these are:
- The formation has all the distinctive external characteristics of vulgar papilloma.
- Pain that increases when the papilloma is compressed by tight shoes.
- Lack of skin pattern. On calluses, the skin pattern is preserved, and their surface is quite smooth.
Plantar papillomas can destroy on their own; this is especially common in young children. Often small bubbles form around the first lump, which over time transform into papillomas; this process is referred to in medicine as mosaic papillomatosis.
Flat
Flat papillomas get their name due to the fact that they protrude only slightly, that is, a couple of millimeters, above the skin. Their shape is round, often elongated, oval, the places of growth are the face, the area near the lips, the upper part of the chest, and the external genitalia. In girls and women, they are often diagnosed in the cervix.
The photo shows flat papillomas on the skin of the face
Nearby flat papillomas can merge with each other and then they become very visible on the body. The color of these formations rarely differs from the rest of the skin tone or may be slightly darker.
Filiform
Papillomas that grow on a thin stalk and have an elongated, elongated shape are referred to in medicine as filamentous or acrochords. They are caused by HPV types 7 and 2. At the beginning of the growth of this formation, you can notice a small bump on the skin, which gradually stretches out and hangs down.
Acrochords predominantly grow in people after 40 years of age, regardless of their gender. Most often they are located on the upper eyelids, neck, under the arms and mammary glands, in the groin area. Thread-like formations are prone to injury, since the thin leg can easily be caught by clothing or careless movements.
Pointed
Pointed papillomas or condylomas are papillary formations, they are located both individually and in whole groups. As these papillomas grow, they merge with each other and during this period their surface visually resembles a cockscomb, the color of the formations ranges from flesh-colored to bright pink.
Genital warts are caused only by types of HPV that are sexually transmitted. That is why these papillomas are found on the genitals, in the anus, in the perineum and groin. In men, condylomas often affect the penis or grow inside the urethra. In women, papillary formations involve the vagina and cervix.
Condylomas acuminata grow very quickly, merging and extensive encroachment of healthy tissue is sometimes observed within a few days. This type of skin formation is prone to relapses after treatment. Often, tests can also reveal concomitant infections - mycoplasmosis, chlamydia.
Types
HPV types are usually divided according to the risk of possible oncogenic lesions of the skin and internal organs. Highlight:
- HPV with a high cancer risk, these are the types – 16, 18, 45, 36.
- HPV with an average degree of cancer risk – 31, 35, 33, 58. 51, 52.
- HPV with a low degree of cancer risk (non-oncogenic) – 11, 44, 43, 42, 6.
Features of oncogenic types of papillomavirus and their treatment, in this video:
Non-oncogenic types of the virus most often cause benign growths, that is, papillomas, on the skin.
Squamous
Squamous cell papilloma occurs as a result of the proliferation of squamous epithelium of the skin. It is most often formed in older people and is characterized by slow growth. In younger people, it can form in areas of the body that are subject to constant trauma.
Squamous cell papillomas are both formations on a thin stalk and tumors that have a wide base and a rounded shape. At the beginning of its growth, the papilloma is mobile, its color is whitish, flesh-colored or dark brown, and its size can reach one and a half to two centimeters.
With constant injury, it can become inflamed, as a result of which the cells mutate and can degenerate into cancer and a squamous cell type of cancer occurs.
Inverted
Inverted (transitional cell) papilloma is detected relatively rarely, and it has its own characteristics of occurrence and development, these include:
- Specific localization - this type of papillomas affects only the nose and its paranasal sinuses. The formation often grows in the maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, and ethmoidal labyrinth.
- The lesion is unilateral , that is, the papilloma grows on one side of the nose, but it can be either single or multiple.
- Germination of papilloma into bone structures , which leads to destruction of the walls of the orbit, palate, sinuses, and skull bones.
- Relapse of the disease 5-10 years after effective treatment.
Inverted papilloma leads to severe nasal congestion, the appearance of bloody discharge or nosebleeds.
If the tumor reaches a significant size, then the deformation of the facial skeleton and the displacement on the affected side of the eyeball are visually determined. In 5% of cases, the long-term course of the disease in the absence of adequate therapy leads to the degeneration of papilloma into a cancerous growth.
Localization
Single or multiple papillomas can be found on almost any part of the body. Naturally, growths on the face cause more inconvenience, but papillomas on closed areas of the body are often injured by rough clothing.
Due to the peculiarities of the development of the virus and the structure of the skin, several places with the predominant localization of papillomas are distinguished, these are:
- Natural folds on the body are the armpits, groin area, lower abdomen if you are overweight. In women, the formation of flat and thread-like papillomas often occurs under the mammary glands.
- Hands, skin of the face, neck, back and abdomen. On the face, flat and simple papillomas are often localized near the mouth, near the eyes, and on the eyelids.
- Genital organs : genital warts most often grow on them.
- Internal organs - bladder, stomach, intestines.
- Feet.
Photo of human papillomavirus on the eyelid
Viral growths can also be in the oral cavity, bladder, internal genital organs, and in the ducts of the mammary glands. Papillomas are detected in the esophagus, larynx and trachea. Growths in the throat area lead to a narrowing of the lumen of this channel and then signs of respiratory failure develop.
Papillomas are considered benign formations, but under the influence of negative provoking factors they can degenerate into malignant tumors; this process takes from several months to several years.
How to determine education by symptoms?
Activation of different types of HPV can lead to the appearance of three different benign formations on the skin: warts, genital warts and papillomas.
These formations have both significant differences and some similar characteristics. Comparing the appearance and growth characteristics of growths on the body will help you more likely to independently determine the type of benign growth.
Warts
The appearance of a wart on the body can be determined by some external features of this growth, these include:
- The tumor size is up to 1 cm in diameter.
- Clarity of external boundaries, density on palpation and surface heterogeneity.
- Irregular shape, which is more close to round.
- Color ranges from light gray to almost black.
- Features of the location. Warts occur in people mainly on open areas of the body, especially those that are subject to frequent injury. These are hands and fingers, knees, elbows, scalp.
The virus that causes warts is almost always transmitted through household contact, that is, through handshakes or, less often, through the use of certain things - towels, gloves. Most often diagnosed:
- Vulgar warts - in 70% of cases. Simple warts are also detected in 20% of adolescents and children of primary school age.
- Plantar – detected in 30% of patients with warts.
- The flat type of warts is diagnosed in 4% of patients with this type of papillomas.
“Butcher’s warts” are classified into a separate group; they are detected in people whose specialties are related to the processing of fish or meat.
Papillomas
The virus that causes the growth of papillomas thrives in a humid, warm environment and therefore can easily become infected in baths, saunas, and swimming pools.
At the beginning of their growth, papillomas cause some burning and tingling in the upper layers of the skin, then at this place you can notice the formation of a small lump. Gradually, this growth stretches and lengthens, its dimensions vary from 0.2 mm to 1-1.5 cm in diameter.
The color of papillomas is most often flesh-colored, grayish or yellowish. These tumors grow more often in older people, but often affect the skin of young people. Unlike warts, papillomas prefer to grow on closed areas of the body - under the armpits, mammary glands, in the groin area, on the inner thighs.
Papillomas usually begin to grow during long-term treatment of infectious or somatic diseases, as well as in people with weakened immune systems. A single formation leads to the formation of others and then papillomatosis occurs.
Condylomas
Genital warts appear on the mucous membranes only under the influence of certain types of HPV, which are transmitted in the only way - sexually.
Most often, these growths are localized in the genital area and near the anus, less often in the oropharynx. Condylomas are papillary growths; individual elements can merge with each other and then a tumor appears that resembles a cockscomb.
It is easy to detect condylomas on the external genitalia if you pay close attention to your health. It must be remembered that the mucous membrane is normally always smooth, and the appearance of roughness, bumps, and bumps on it is a reason to seek a diagnosis at a medical institution.
Routes of transmission of HPV
HPV can be transmitted in several ways - sexually, from mother to fetus during childbirth, contact - through cracks and abrasions in the skin.
Contact does not have to be direct; often the virus remains on personal items - towels, razors, washcloths, toothbrushes. It is possible to become infected with HPV in hairdressing salons, beauty salons, and medical institutions - insufficient disinfection of instruments leads to infection with various types of pathogenic microorganisms.
Cause of occurrence
As has already been clarified, the main cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus. Infection with this microorganism occurs unnoticed by humans and sometimes people are completely unaware that they are carriers of the infection.
According to the latest data, HPV of various types is present in the body of a third of the world's population, with the exception of infants and the elderly.
Activation of the virus and, accordingly, the growth of papillomas and the development of other diseases occurs in the following cases:
- With a significant weakening of the immune system.
- Under the influence of harmful factors, which include smoking, alcohol abuse, and taking certain medications.
- Exacerbations of gastrointestinal diseases, influenza.
- With long-term use of oral contraceptives.
It has been noticed that most papillomas on the body occur in people who lead a promiscuous sex life.
Virus in gynecology
The presence of HPV in the body of women is considered extremely dangerous, especially for types 16 and 18.
Against the background of papillomavirus carriage, not only papillomas and cervical erosion occur, but also such a dangerous disease as cervical cancer. Recent studies suggest that in almost one hundred percent of cases of cervical cancer in women, HPV is detected in their body.
The following video will tell you what danger papilloma poses for women:
The virus can be detected through several tests and examinations. Based on them, the doctor selects treatment, and the woman must be constantly examined in order to catch in time the activation of the proliferation of the microorganism, which is the prevention of cancer.
How is it dangerous?
Many people think about the treatment and removal of papillomas only in connection with the occurrence of a cosmetic defect on the skin. But such a change is dangerous only from the aesthetic side; you need to be more careful about another consequence - the degeneration of papilloma into a cancerous formation.
Source: https://rodinkl.ru/papillomy/papillomatoz-foto.html
Papillomatosis of the skin and genital organs: how to effectively remove
This is one of the common infections that, once it enters the body, remains in it forever. The harmful effects and increased activity of HPV are observed only under the influence of provoking factors; otherwise, human papillomavirus predominates in a “dormant form” in the absence of alarming symptoms.
The main cause of dangerous growths on the skin is HPV, which penetrates the patient’s healthy body from the outside. This is not only intimate intimacy without barrier contraception with an infected partner, other routes of transmission of a dangerous infection are also possible. The most common causes of papilloma are detailed below:
- impaired metabolism;
- weakened immune system;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- presence of bad habits;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- promiscuous intimate relationships.
The human papillomavirus, or HPV for short, is responsible for the appearance of papillomas. There are different strains of the virus - oncogenic and non-oncogenic. Oncogenic strains are also called strains of low or high carcinogenic risk.
Infection with the human papillomavirus occurs through household or sexual contact with carriers of the virus. Not everyone in contact gets sick. After sexual contact, the probability of infection is about 70% percent, during domestic contact it is less.
Papillomas grow rapidly when immunity decreases - after long-term illnesses, against the background of constant overwork and lack of sleep, when taking medications that reduce the defenses. Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy and a natural decrease in immunity in a pregnant woman often lead to increased growth of papillomas during this period.
Papillomas are characterized by a slow growth rate, but during pregnancy they not only rapidly increase in size, but also new elements appear.
Tumor growth is usually associated with many reasons, the mutual combination of which leads to the appearance of a tumor. The main factor in papillomatosis is the human papillomavirus, which has more than a hundred varieties.
Benign tumors are more often provoked by so-called non-oncogenic strains of microorganisms and viruses of low oncogenic risk. In other words, malignancy with such a viral infection is unlikely, but still possible.
The presence of condylomas on the genitals reflects the inflammatory process against the background of infection with viruses of types 6 and 11, when the surface epithelial layer grows with the underlying tissue, which looks very much like a tumor.
It is often impossible to distinguish condyloma from papilloma with the naked eye, and this may require examining the lesion under a microscope. The external similarity of condylomas with papillomas, the recurrent nature of the course and the possibility of malignancy make it possible to consider them within the framework of a benign tumor process, and the same methods are used for treatment.
The incubation period lasts up to a year, and if the body is in good condition and the level of immune defense is high, you can count on the fact that the infection will not manifest itself in any way. However, not everyone can boast of excellent health, so sooner or later papillary growths called papillomas appear on the skin.
The ways of spreading infection are varied:
- Contact and household when using shared towels, washcloths, shaving accessories, etc.;
- Sexual, through which genital tract papillomas and condylomas are transmitted;
- From mother to child during childbirth.
It is hardly possible to avoid infection with at least one type of virus, but you should keep in mind the possibility of infection when using common hygiene items, as well as in a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool. There is a risk of infection when visiting a cosmetologist, getting a manicure or pedicure.
Source: https://izlechi-psoriaz.ru/papiloma/papillomatoz-kozhi/