Modern technologies make it possible to diagnose the most complex diseases, carry out treatment, and determine the method of this treatment. Computed tomography is a completely new diagnostic method for many, revealing hidden traumatic injuries, inflammation, pathologies, and destructive processes that occur in the scanning area.
Computed tomography provides a full-fledged opportunity to conduct a thorough analysis of the condition and structure of all structures, in particular, all the sinuses of the nose. High-precision equipment detects and determines pathologies without exposure to X-rays.
Sinuses: description
Significance of the sinuses in the human body
The sinuses are cavities in the bones of the skull, connected to the nasal cavity through small anastomoses. All nasal sinuses are hollow structures, normally filled with air.
It is customary to divide these cavities into 4 groups, 3 of them are paired, and one is the main one:
- The maxillary sinuses are located at the top of the skull and are the largest of the cavities.
- Frontal - in the frontal bone of the skull.
- The ethmoidal labyrinths separate the nose itself from the skull area with a series of ethmoidal cells.
- The sphenoid is the most complex and basic, located in the area of the sphenoid bone.
Each of the sinuses has a mucous coating, which, depending on the condition and the presence of an infectious lesion, begins to increase the production of secretions.
If stagnation occurs, then the development of pathogenic processes begins, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome
- Purulent discharge
- Increased body temperature
- General weakness
- Foul odors from the nasopharynx
CT allows you to informatively and very accurately diagnose the situation, determining the treatment status: medicinal or surgical.
Tomography allows you to identify all formations, determine the content and significance of a possible deviated septum.
CT allows you to observe the dynamics of the condition during therapy. This is an invasive, informative, visual diagnostic study without introducing any technology into the human body. CT scan gives an idea of the condition of the sinuses, cavities, ducts, and tissues.
Computed tomography of the sinuses
Description of the examination method and preparation
This examination does not require special and complex preparation. The only recommended prescription is to refrain from eating food 5-6 hours before the test and from drinking liquids a couple of hours before.
To carry out tomography without errors and errors, it is recommended not to take metal jewelry with you, remove glasses, prostheses (if any), iron objects must be removed, as they can affect the results of the examination.
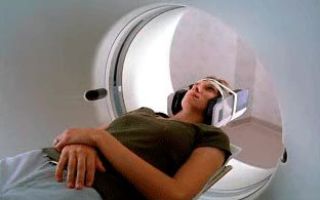
Computed tomography of the sinuses is a painless procedure that involves simple manipulations.
The tomograph itself consists of a machine, a couch and a computer. During scanning, the sinuses are photographed from different angles. The patient is positioned on a couch connected to a tomography machine. It is fixed in the desired position using special belts. This is done in order to avoid interference from involuntary movements.
During the examination, various multiple X-ray tubes, detectors, and scanners “work” around the patient. All of them ensure the accuracy of the resulting image - slice. The research mechanism is such that the sections look like thin slices. If you layer them on top of each other, folding them in 3D, you get a complete three-dimensional image of the entire organ and body.
The duration of the procedure is no more than 10 minutes. During this period, the patient is required to hold his breath several times. Sometimes sedatives are used to calm you down. This approach is required only for seriously ill patients or infants.
Sometimes it is necessary to administer a contrast agent through a vein, which provides better clarity of the image on the screen.
In this case, the injection resembles a pin prick. After administration of the drug, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a spreading warmth throughout the body, and a desire to urinate.
All this passes quickly and has no consequences. While the patient is passing through the tomograph, he is alone in the room, in almost complete darkness.
An exception is when a small child is examined. Then one of the parents holds the baby.
More information about CT scans of the sinuses can be found in the video.
Read: What is computed tomography: types and examination procedure
During operation, a special buzzing sound is produced, accompanied by clicks. This background may irritate some people or put them in a state of stupor.
Using earplugs will help eliminate such an unpleasant moment. The table with the patient slowly passes through the scanner rings. The number of passes through the tomograph depends on the examination and the doctor’s decision. All photographs to be decrypted must be clear and of high quality.
Only this state of affairs will help give an accurate interpretation.
After the CT scan, image analysis is performed. This is done by a radiologist who, if necessary, conducts a conversation with the patient. In cases of need, when the results need clarification, a repeat examination is done with additional angles.
Advantages of the technique
Features of examination of the sinuses using CT
The advantage of tomography over x-rays is the fact that the image is visualized in different projections.
We can name several theses that characterize these advantages:
- Safety
- Reliability of results
- Practical accessibility
- No need to penetrate cavities "In vitro"
- Speed of implementation
- Taking pictures of different types of body tissues
- Painless manipulation
- Minimum exposure
- No side effects
- Minimalism of contraindications
- Tomography results replace biopsy
- Economic perspective
Timely examination allows you to quickly find damage and carry out appropriate treatment.
Indications for examination
Purpose of CT scan of the sinuses
To carry out the procedure, it is necessary to have a referral from the attending physician, in particular, if it concerns the sinuses, the referral is issued by an ENT specialist.
Indications for CT scanning of the sinuses are the following diseases and conditions, including suspicion of their presence:
- Inflammatory process
- Infectious infection
- Assessing the condition of the sinuses
- Swelling of the sinuses
- Injuries
- Tumors and cysts of various etiologies
- Anomalies in the structure and shape of the skull
- Foreign objects
- Headaches of unknown origin
- Suspicion of hemorrhage
- Preparation for operational activities
- Diseases of the tear ducts
- Persistent rhinitis
- Liquororrhea
- Pain in the eye area
- Presence of purulent contents or blood in the sinuses
- Polyps of the nasal passages
- Deviated septum
CT allows you to make a three-dimensional image, where you can examine even small changes and pathologies, identifying any abnormalities and diseases. Often the indication for examination is to monitor the situation after surgery.
Sometimes such an accurate diagnosis is not required; parasinus tomography may not be appropriate for some conditions and diseases. There are cases when a doctor can make a diagnosis based on simpler examination methods. Such cases include sinusitis.
In cases where a more accurate examination is necessary, inflammation of the maxillary sinuses may be included.
For this you will need an MRI. However, when diagnosing various injuries, developmental anomalies, and disorders of the nasal bones, the best method and accurate method is CT examination. Computed tomography allows you to assess the situation not only in the sinuses, but also to examine neighboring areas: tear ducts, congenital anomalies. It is possible to detect abscesses.
Contraindications and restrictions
Possible contraindications to the examination
There is a list of some contraindications for the use of CT in diagnosis.
Such contraindications are:
- High patient weight, exceeding 180 kilograms, because the device is designed for such a limitation.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
- There may be some restrictions in the use of a contrast agent that contains iodine.
Limitations in the use of CT may include:
- Disturbances in the functions of the liver and kidneys.
- Diabetes.
- Critical health condition.
- Thyroid pathologies.
- Myeloma.
- Hypersensitivity and allergy to iodine-containing drugs.
In childhood, computed tomography is prescribed in extreme cases when it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Final actions
- After an examination using tomography, it is deciphered by a radiologist or radiologist with special specialization and qualifications in deciphering tomographic images.
- The extract indicates all the information about the examination, which includes not only the time of the procedure, but also the registration of all identified pathological processes in the nasal and sinus cavities.
- All snapshots taken are provided in the form of images on paper or electronic media.
The results and conclusions are presented to the attending physician, where, in the process of discussing further treatment, subsequent examination, therapeutic actions and possibly surgical intervention are predicted.
The attending physician identifies all hereditary and genetic predispositions, allergies and chronic diseases in the patient. This will eliminate side effects and negative processes in the body due to medications that will need to be used for subsequent treatment of the established disease.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/mrt/kompyuternaya-tomografiya-pazuh-nosa.html
Computed tomography of the nasal sinuses
CT scan of the nasal sinuses is a modern non-invasive diagnostic method that has found wide application in otolaryngological practice. Computed tomography allows you to determine the causes of impaired nasal breathing, recurrent sinusitis, sinusitis, identify the presence of foreign bodies, small formations (polyps), and assess the condition of the bones of the facial skull and sinuses after injuries.
The essence of the method
Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses, CT scan of the paranasal sinuses is a scan of the area under study using x-rays.
Obtaining X-ray images, usually performed in two projections (axial and coronal), when performing a computed tomography scan of the sinuses is based on different tissue densities.
During the examination, the data on the monitor screen is converted into a detailed 3D model. By obtaining layer-by-layer images, CT examination allows you to most accurately visualize the condition of the nasal sinuses on an x-ray.
One of the varieties of the diagnostic method is MSCT - multislice computed tomography. To perform MSCT of the nasal sinuses, more advanced hardware is used.
A holistic three-dimensional image is formed from many images, and it is possible to see a layer-by-layer image of bone and soft tissues in “slices”. The information is analyzed by a doctor to make a final diagnosis.
An ENT CT scan allows you to visualize the patient's nose, ear, and throat areas.
What does a tomogram show?
The study is most often prescribed by an ENT doctor. Indications for CT scan of the nasal sinuses may include:
- prolonged increase in body temperature within 37-37.5 °C. Low-grade fever may indicate a low-grade inflammatory process;
- atypical nasal discharge (greenish, bloody);
- constant headaches;
- suspicion of neoplasms of various nature.
What does a sinus CT scan show:
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- pharyngitis;
- polyps;
- pathologies of the temporal bones, fossae of the lacrimal and nasolacrimal canals;
- liquorrhea;
- malignant neoplasms;
- the presence of anomalies and malformations, for example, a deviated nasal septum;
- traumatic injuries.
CT is an effective and accurate method used to diagnose infectious and inflammatory diseases, including complex forms of sinusitis. Computed tomography of the maxillary sinuses is used to visualize the fluid-filled state of the sinuses and evaluate the thickening of their lining. The study helps to identify:
- degree of progression of the inflammatory process;
- injuries of bone or soft tissue near the maxillary sinuses;
- developmental abnormalities that may cause sinusitis.
A CT examination may be prescribed before endoscopic surgery for sinusitis.
During the examination of the nasal sinuses, the anatomical structures of the nasopharynx fall into the field of view of the tomograph, so CT can be prescribed to assess the condition of the adenoids.
What does a CT scan of the nasopharynx show:
- volumetric formations;
- presence of a foreign body;
- nasopharyngitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx;
- inflammatory processes of various localization within the boundaries of the examination;
- polyposis
Using the images obtained, the doctor evaluates the anatomy of the paranasal sinuses and other organs in this area, makes a diagnosis, and, if necessary, assists the clinician in choosing an effective treatment regimen.
In some cases, computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses may be prescribed in preparation for reconstructive plastic surgery in the facial skeleton.
A common cause of sinusitis is the curvature and spikes of the nasal septum, and deformation of the facial bones. If the patient is bothered by a chronic runny nose, difficulty passing air through the upper respiratory tract, or pain in the paranasal areas, a CT scan of the nasal septum is performed.
Computed tomography is the method of choice when planning septoplasty, a surgical operation to eliminate compensatory and traumatic curvature of the nasal septum.
Contraindications to tomography
In most cases, CT is performed without the injection of contrast material. The first trimester of pregnancy is a contraindication to the procedure.
If a computed tomography scan of the paranasal sinuses requires the administration of contrast, for example, if cancer of the nasal mucosa is suspected, it is necessary to inform the doctor about any allergic reactions to iodine and iodine-containing drugs. Contraindications for contrast studies:
- renal and heart failure;
- multiple myeloma;
- diabetes;
- allergy to iodine;
- thyroid diseases.
Preparation and progress of the procedure
No special preparation is required for a sinus CT scan. If a CT scan with contrast is planned, it is necessary to avoid eating 3-4 hours before the procedure.
To maximize the information content of the study results, before the procedure you should remove things with metal elements or zippers, as well as jewelry, and inform the doctor about the presence of metal dentures and implants.
Patients who are about to undergo the study for the first time are interested in how a CT scan of the sinuses is done. The patient is alone in the room; during the CT scan, the child is allowed to be accompanied by a parent. In this case, the accompanying person is wearing a special protective apron.
The subject takes a lying position, resting his chin. The head is fixed in the desired position. If it is necessary to administer a contrast agent, before the procedure begins, a catheter is installed in the patient's antecubital vein, through which the reagent is administered intravenously.
Before starting the scan, the doctor will ask the patient not to move and to hold their breath for a few seconds. After the doctor’s warning, the tomograph ring or table (depending on the type of tomograph) begins to move smoothly. After the scan with contrast is completed, the patient is recommended to increase the drinking regime in order to speed up the removal of the contrast drug from the body.
Interpretation of tomography results
Detailed examination results with transcripts and conclusions can be obtained a few hours after the procedure. Interpretation of CT scans of the paranasal sinuses is the prerogative of the doctor. The written report describes the anatomical features of the nasal sinuses, identified pathological processes and deviations from the norm.
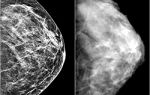
The tomogram clearly shows:
- narrowing of the lumen between the sinuses;
- the presence of minimal swelling of the mucous membranes of the sinuses;
- structural features of the nasal concha;
- accumulation of exudate in the sinuses.
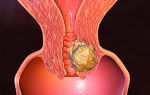
Cavities filled with liquid in combination with defects in bone tissue and formations in the upper jaw may indicate the presence of an odontogenic (arising as a result of tooth disease) cyst of the maxillary sinus.
The altered shape, size and structure of the sinus with reduced airiness and thinning of the membranes of the maxillary sinus makes it possible to detect a rhinogenic cyst of the maxillary sinus.
Polypous pansinusitis on CT looks like heterogeneous polypous thickening of the mucous membrane, complete or partial filling of the maxillary sinus with fluid. Polyps may spread beyond the sinuses, including into the orbit and infratemporal fossa.
Chronic sinusitis is characterized by a decrease in airiness due to the presence of a large amount of exudate, the presence of a horizontal stripe indicating the level of fluid in the cavity, and an increase in the thickness of the mucosa.
The characteristics of the disease determine what a CT scan shows for sinusitis. Acute catarrhal sinusitis looks like a mild shadow caused by thickening of the mucosa, which is localized along the periphery of the sinus.
Computed tomography allows you to assess the thickness of the mucosa in various parts of the sinus, as well as determine the degree of narrowing of the excretory ducts, the density of the fluid in the sinus (for example, pus and blood can be clearly differentiated).
Alternative diagnostic methods
Patients often wonder what the difference is between CT and MRI of the paranasal sinuses, and which of these methods is preferable. The main difference is the difference in the principle of obtaining images.
Computed tomography uses x-rays, and the imaging is based on the varying degrees of absorption of this radiation by tissue. Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to produce images.
Visualization occurs based on the physiological structure of organs and tissues and depends on the number of water molecules in the tissues of the body.
The inclusion of CT or MRI of the paranasal sinuses in the diagnostic scheme is within the competence of the ENT doctor. These modern methods have extensive diagnostic capabilities, but experts say MRI is not the method of choice for studying the sinuses because this area contains many solid structures that are better visualized with CT.
Finally
Today, CT scans of the sinuses can be performed in most major medical centers. When choosing a medical institution, you should focus on the quality of the installed tomograph: the higher its power, the thinner the slice thickness and the higher the information content of the image. The diagnostic method helps to make a timely diagnosis to prescribe adequate treatment.
Video: Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses
[rBlock name=after_video return=1][rBlock name=after_sharing return=1]
[rBlock name=after_text return=1] Megan Washington: Why I live in mortal dread of public speaking Onuka feat. NAONI Orchestra — Megamix — Interval act — 2017 Eurovision Song Contest Grand Final The history of human emotions | Tiffany Watt Smith Alyosha — Sweet People (Ukraine) Live 2010 Eurovision Song Contest
Source: https://reabilitilog.ru/diagnostika/mrt-i-kt/kompyuternaya-tomografiya-nosovyx-pazux.html
computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses: how it is performed and what it shows
CT scanning began to be used to examine the sinuses relatively recently, but doctors and patients have already appreciated the convenience of the procedure. The results of this type of diagnosis are twice as accurate as conventional radiography.
CT does not cause the discomfort that patients experience during rhinoscopy and fibroepipharingoscopy. An examination of the sinuses is prescribed when the patient complains of persistent breathing problems.
In addition, this research method is indicated in the presence of constant or frequently recurring pain in the frontal part of the head, upper jaw and teeth.
Advantages and features of CT scan of the nasal and paranasal sinuses
In comparison with a visual (instrumental) examination of the nasal septum and sinuses, computed tomography of the nose and paranasal sinuses can detect changes in all structures and tissues of the facial part of the skull. Until the 90s, such results were obtained after a complex diagnosis using painful examinations, numerous tests and x-rays.
In comparison with classical radiography, which is effective only in examining the bones of the nose and nearby bone structures, CT of the nasal sinuses allows a detailed examination of the bone structures, cartilage, and mucous membrane.
This method has become widespread in diagnostic practice due to the following advantages:
- the only non-invasive method that allows you to visualize the mucous membranes and bone structures of the paranasal sinuses;
- shows the condition of blood vessels, which is not available when used for diagnostics with a conventional X-ray unit;
- suitable for diagnostics in emergency situations, including determining the causes of nosebleeds and diagnosing injuries;
- unlike magnetic resonance imaging, it is approved for use in the presence of dental implants in the lower and upper jaw;
- Suitable for use as a tool for tracking the position of surgical instruments during biopsy, rhinoantrostomy and other types of interventions.
However, CT scanning of the nose and paranasal sinuses does not cause side effects or complications.
What does a CT scan of the nasal and paranasal sinuses show?
Using computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses, the doctor can examine in detail the structure and current condition of the nasal cavity and the four paranasal sinuses (hereinafter referred to as PNS):
- frontal - located in the frontal bone and shaped like triangles;
- maxillary - located to the right and left of the nasal cavity in the maxillary bone;
- sphenoid - located inside the sphenoid bones of the skull;
- ethmoid labyrinth - located at the junction of the nasal bone with the skull (in the area of the bridge of the nose).
- CT images of the paranasal sinuses clearly show any changes, including inflammatory processes, accumulations of exudate, pus, blood or fluid, disruption of the integrity of bones, cartilage and soft tissues (including mucous membranes, blood vessels and nerves).
- The diagnosis is made based on such parameters of the tissues being examined as their structure, density, degree of mineralization of the tissues and their volume.
- What does a CT scan show:
- any types of sinusitis, including polypous pansinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- sphenoiditis;
- polyps of the paranasal and main nasal sinuses (hereinafter referred to as SNP), as well as the nasopharynx;
- tumors in various parts of the nasal cavity and sinuses, including benign and malignant;
- deformation of the nasal septum and nasal bones, congenital or acquired;
- foreign bodies in the nasal cavity and sinuses.
A standard computed tomography scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses is also prescribed to identify the causes of persistent headaches (migraines) of unknown origin, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge and other unpleasant phenomena.
Indications for CT diagnostics
Direct indications for CT or MRI of the main and paranasal sinuses are symptoms that indicate the presence of diseases of the ENT organs in the acute or chronic stage. They do not always consist of a runny nose and difficulty breathing. Thus, with sinusitis, patients often complain of toothache, headache, and dizziness.
It is important to know! In medicine, there are cases of atypical manifestations of diseases of the paranasal sinuses, which even specialists cannot identify quickly enough. The correct diagnosis in this case is made only after CT scanning.
Doctors recommend undergoing this type of examination in the following cases:
- frequent exacerbation of headaches against the background of normal blood pressure and the absence of diseases that can provoke them;
- prolonged persistence of difficulty breathing, from which vasoconstrictor drugs do not help;
- the appearance of swelling of the nose and “bags” under the eyes, which are not associated with an allergic reaction or poor kidney function;
- discharge of purulent exudate from the nose;
- frequent bleeding from the nose;
- the appearance of a feeling of fullness in the bridge of the nose, in the middle of the forehead or in the cheekbones.
Also, an MRI or CT scan is prescribed in case of injuries in the facial area, when foreign objects enter the nasal passages and further into the sinuses.
Contraindications to CT scan of the nasal sinuses
There are relatively few contraindications for CT scanning of the paranasal sinuses, and all of them are associated with the potential danger of X-ray radiation to the body. First of all, this type of diagnosis is not recommended for pregnant women and women who are breastfeeding a newborn.
Note! It is possible to resort to computed tomography of the maxillary sinuses in pregnant and lactating women only in exceptional cases, when the potential risk is lower than the expected benefit of the procedure.
Other contraindications to CT PPN:
- diabetes mellitus and complex degree of thyroid dysfunction;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- renal failure;
- liver failure.
If it is necessary to use a contrast solution (it is instilled into the nasal passages immediately before the procedure or injected into a vein), such a feature of the patient’s body as an allergy to iodine is also taken into account.
How to prepare for the examination
Unlike the study of other areas, computed tomography of the sinuses does not require special preparation. Before the examination, the patient drinks and eats as usual. On the day of diagnosis, you are allowed to use cosmetics and care products. It is important to remember that it is better not to use cosmetics that contain metals, even if their quantity is very small.
Before the procedure, doctors advise:
- remove piercings from the nose, eyebrows, lips, and in some cases from the ears, as CT scans are done in different projections;
- warn the doctor about the presence of tattoos in the head and face area, which may contain paints with metals;
- inform the doctor about the presence of dental implants or metal braces;
- remove removable dentures made of ferromagnetic alloys from the upper jaw; it is also recommended to remove them during the examination.
If you plan to use a contrast solution, the patient is advised to refrain from eating on the eve of the examination. The first thing to remember when diagnosing sinus diseases in this subtype is that preparations with iodine very often provoke nausea and vomiting.
Sometimes, before a CT scan with contrast, the doctor performs a drug intolerance test.
How is the examination carried out?
You can undergo RCT of the paranasal sinuses only in specially equipped rooms.
Before starting the diagnostic procedure, the patient is taken to a tomograph and asked to remove all jewelry and accessories on the head.
Then he is placed on the couch and, if necessary, a contrast solution is injected into the nasal cavity. This is usually done using a dropper bottle (similar to a regular nasal drop or spray bottle).
Interesting fact! To obtain clear images of certain sinuses, the doctor may place the patient on their side or face down rather than on their back.
Next, the laboratory assistant secures the patient’s head with special fabric straps and leaves the room with the installation. While in an adjacent room, the doctor or laboratory assistant maintains contact with the subject through a speakerphone. You may need to hold your breath briefly during the procedure.
A CT examination of the main and paranasal sinuses lasts no more than half an hour. The average operating time of the installation does not exceed 20 minutes. Already during the procedure, the doctor sees the changes that a CT scan of the bones and soft tissues of the nose and sinuses revealed. At the end of the procedure, the radiologist transmits the images and a preliminary report to the otolaryngologist for diagnosis.
How the result is deciphered
On average, deciphering the results of an X-ray tomogram of the PPN and SPN takes 3-5 hours. At this time, the resulting layer-by-layer images are cleared of noise, digitized, and, if necessary, combined to obtain a 3D image.
We can talk about pathology only if a CT scan in the sinuses reveals:
- thickening or thinning of the mucous membrane and submucosal layer;
- accumulation of fluid in the sinuses;
- change in the volume of the sinuses and their shape;
- formations with or without a stalk on the mucous membrane of the sinuses;
- destruction of bone and/or soft tissue;
- darkened spots with a clear rounded outline;
- change in the shape of the nasal septum;
- cracks in the bones in which the sinuses are located and in the bones of the nose.
Depending on what pathologies a computed tomography scan of the nasal sinuses reveals, the otolaryngologist makes a decision on treatment or involves other specialized specialists: a surgeon, oncologist, etc.
Note! Even if the diagnosis seems unambiguous, the doctor always prescribes an additional examination to differentiate the identified pathology from other diseases.
Precautionary measures
Despite the non-invasiveness of the procedure, doctors treat RCT of PPN with caution. The procedure is not prescribed for children under 14 years of age, since the effect of X-rays on an unformed body has not been sufficiently studied. Particular attention is paid to the problem: how often can a CT scan of the sinuses be done. Here experts are guided by the following principles:
- Use the method only when other types of diagnostics do not allow you to fully examine the PPN and the nasal cavity.
- Use the method no more than once a year, and if necessary, re-examine the patient, resort to MRI of the sinuses or other instrumental methods.
- Take into account the total dose of X-ray radiation that the patient receives during all studies per year in order to prevent the patient from developing radiation sickness.
- Under no circumstances should CT be used if there are contraindications to this type of diagnosis.
Compliance with these measures helps to avoid annoying mistakes and complications that can worsen the patient’s condition and reduce his quality of life.
Computed tomography is a fast and highly accurate method for detecting many ENT diseases and even oncology. It must be used wisely and justifiably. This is the key to the effectiveness of treatment and the absence of complications.
Source: https://DiagnozPro.ru/kt/golova-i-shea/obsledovanie-pazuh-nosa-na-kt
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses (computed tomography): what shows how it is performed, how often can a CT scan of the nose and around the sinuses be done
In what cases is a study prescribed?
When is a computed tomography scan of the nose indicated? Indications for use are the following conditions:
- suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the bones of the nose and sinuses;
- risk of hemorrhage;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- frequent headaches of unknown origin;
- frequent nosebleeds accompanied by increased blood pressure;
- suspicion of the presence of a foreign object in the nasal area;
- chronic nasal diseases;
- malignant tumor, presence of purulent exudate;
- a complication of infectious pathology of neighboring organs, which has spread to the nasal sinuses.
What can a CT scan show?
Computed tomography of the sinuses allows you to see images of layer-by-layer sections of the scanned space. The study shows the contours, density, structure, volume, mineralization of PPN.
- A CT scan of the nose and sinuses will help evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy if the diagnosis was established a long time ago.
- Pathology diagnosed in a timely manner using CT scanning will help to avoid serious consequences and complications.
- So, what does a sinus CT scan show? Using this method, the following diseases can be identified:
- sinusitis at the initial stage and during chronic process;
- neoplasms of the nasal mucosa. The study will also answer the question of whether the tumor is malignant or not;
- sinusitis;
- the cause of regular migraines;
- sphenoiditis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- polyps;
- the cause of the inflammatory process, the treatment of which does not bring effect;
- will help visualize deformation and damage to the nasal bones;
- will show the location of foreign bodies in the sinuses.
Advantages and disadvantages
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses is a highly accurate method for diagnosing pathologies of the nose and its sinuses. A detailed scan helps to understand what stage the pathological process is at and prescribe the most appropriate treatment in this situation.
What are the advantages of CT scanning of the nose and paranasal sinuses? The following advantages of this diagnostic method can be highlighted:
- high-quality images of the sinuses;
- low radiation exposure;
- high research speed;
- absence of negative effects on the body of the subject;
- clear visualization of all nasal formations;
- absence of discomfort and pain during the procedure;
- complexity - based on the scan results, you can assess the condition of bone formations, blood vessels and tear ducts.
But computed tomography of the nose and paranasal sinuses also has disadvantages. They are hidden in contraindications. The study cannot be carried out under the following conditions:
- pregnancy, since CT scans can cause fetal malformations;
- childhood - the child cannot stop moving for a long time. In addition, belts make them afraid;
- allergic reactions to iodine used as a contrast agent. But contrast may not be used in the study;
- lactation period;
- thyroid diseases;
- failure of renal, hepatic, cardiac functions;
- diabetes;
- multiple myeloma.
Is preparation necessary?
Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses does not require preparation if performed without contrast. If contrast is used, the patient should not eat for 6 hours before the study; it is not recommended to drink 3 hours before the procedure. It is also necessary to remove metal objects and dentures.
How is diagnostics carried out?
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses is performed as follows:
- Specialists assess the condition of the subject.
- The essence of the research method and the purpose of its implementation are explained to the patient.
- The patient is put on a suit that will protect the body from exposure to x-ray radiation.
- Next, the patient is placed on his back on the couch. Arms should be extended along the body. The head is fixed in the headrest. You may need to tuck your chin to your chest and look up.
- Contrast is administered if necessary. 50 ml of contrast is usually injected into the cubital vein through a catheter. For a short time, the patient may feel warmth and a specific taste. These sensations pass on their own and quickly.
- The table together with the subject is pushed into the tomograph. Next, the doctor goes into the room where the equipment for recording and processing the device’s signals is located. The specialist has the opportunity to communicate with the patient during the examination using a sound device.
- During a CT scan of the nose, the table moves up or down. This is necessary to register images in different projections.
- The entire examination takes 5-10 minutes. Upon completion, the patient is sent home or to the ward.
Decoding the results
Based on the results of a computed tomography scan of the nose, the doctor evaluates the following parameters:
- how the nasal septum and bones that form the sinuses are located;
- along what paths does the sinuses drain?
- symmetry of the right and left sides of the nose, sinuses. This parameter will help to determine the anatomical location of the bones and, if necessary, carry out surgical correction in the future;
- pneumatization of the sinuses, its degree.
The interpretation of the results of a CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses can be presented in the table:
PathologySigns on CT
Features of the study
What research methods can be combined with?
| Sinusitis | Fluid in the axillary lumens, thickened soft tissues | CT scanning for sinusitis is not one of the main diagnostic methods. Prescribed only in the absence of effect from treatment and to differentiate diseases | X-ray examination of PPN as an additional method |
| Polyps | In the case of a single polyp, a formation is visualized on a stalk, which comes from the shell of the axillary wall. If the polyps are multiple, the shape of the sinus will be changed | It is difficult to detect polyps located in the alveolar bay (formation in the maxillary sinus) | Initially, an X-ray of the PPN is taken. CT scan is prescribed to clarify the data |
| Sinus neoplasms | The bone tissue is destroyed, a formation is visualized in the soft tissues | Difficulties in differentiating benign and malignant formations | If a CT scan fails to differentiate a benign and a malignant tumor, then biopsy material is taken from the altered tissue |
| Odontogenic cysts of the maxillary sinuses | Homogeneous darkening of an intense nature, the upper contour is rounded and clear. The mucous membrane above the cyst may be thickened | There may be a need for differential diagnosis of a polyp in the alveolar bay | This pathology is usually diagnosed using radiographic examination. CT helps to eliminate the shadow of the bones and clarify the size of the cyst. Magnetic resonance imaging may be required to accurately determine the boundaries of the cyst. |
| Rhinogenic cysts of the maxillary sinus | The darkening is homogeneous, round. It is adjacent to the axillary wall. The upper contour is clearly visible | The mucous membrane is not thickened. |
How often can you do the test?
Many people have a question: how often can a CT scan of the sinuses be done, since during this study the patient receives a certain dose of radiation.
The radiation dose received from CT scans ranges from 1 to 5 mSv. It is optimal to scan no more than once every six months. If necessary, this interval can be reduced to 2 months.
With computed tomography, the patient receives more radiation than with x-rays and fluorography.
Which is better: CT or MRI
What is better to do: CT or MRI of the sinuses? Each method has specific indications. This or that study is prescribed based on the suspected disease.
Thus, with CT, bone structures are well visualized, and with MRI, soft tissues are clearly visible. For example, CT is useful for detecting tumors that have penetrated the sinus walls.
CT is also suitable for diagnosing sinusitis and sinusitis, but only MRI of the sinuses can determine their type and detect the cause. Magnetic resonance imaging will also help diagnose mucosal diseases, polyps and labyrinthitis.
These methods can complement each other. Read more about the signs of sinusitis and methods of treating it→
CT scan of the sinuses is a safe and informative study that allows you to diagnose many pathologies due to the high accuracy of the resulting image. Using this method, you can determine the indications for surgery and monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
Vladislava Spiridonova, specialist,
especially for Moylor.ru
Source: https://moylor.ru/nos/kompyuternaya-tomografiya/
CT scan of the sinuses: goals and implementation features
| Computed tomography of the sinuses | |
| Computed tomography of all paranasal sinuses (paranasal sinuses) and the upper jaw (without the lower jaw) - no description | 5000 |
| Computed tomography of the maxillofacial area (both jaws and paranasal sinuses, partially frontal sinus) - no description | 5000 |
| Computed tomography of the maxillofacial area (both jaws and paranasal sinuses, partially frontal sinus) - without description (for children under 14 years old) | 3500 |
| Description of all paranasal sinuses (including maxillary sinuses) | 500 |
The International Center for Health Protection invites you to a safe and non-invasive examination using a computed tomograph. CT scan of the nasal sinuses allows you to study their structure and condition in detail. The study is carried out for the purpose of diagnosing and developing subsequent treatment for sinus diseases. An otolaryngologist usually refers you for examination.
CT scan of the nasal sinuses is a diagnostic procedure performed on a computed tomograph. This equipment combines an X-ray unit and a powerful computer.
Different parts of the human body absorb X-rays differently. The device analyzes this data and displays a three-dimensional image of the area under study.
If necessary, photographs can be printed or recorded on digital media.
What does a CT scan of the sinuses show?
Tomography opens up wide possibilities for diagnostics and allows you to determine:
- condition and size of the nasal sinuses, density of adjacent tissues;
- the presence of abscesses present in complicated sinusitis;
- absence/presence of malignant and benign tumors;
- the presence of damage to bone structures due to facial injuries;
- acquired and congenital disorders of ventilation function;
- the presence of foreign bodies, polyps in the nasal sinuses;
- the presence of foci of inflammation.
Indications and contraindications for CT scan of the sinuses
The study is carried out:
- if you suspect inflammatory processes in the sinuses;
- persistent nasal congestion accompanied by headaches;
- injuries (to exclude cracks and fractures of bones in the sinuses);
- suspected presence of a foreign body;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- suspected polyps, cysts, tumors;
- prolonged headaches and toothaches;
- the presence of purulent inflammation in the lacrimal sac;
- planning operations.
CT scanning of the sinuses is not performed:
- during pregnancy;
- severe pain syndromes, hyperkinesis and other disorders that do not allow a person to remain motionless for a long time;
- the patient's weight is too high for which the tomograph is not designed.
If the study is carried out with contrast, then the following contraindications are added to the above: renal failure, breastfeeding period, allergy to iodine.
Preparing for a CT scan of the sinuses
No special preparation is required for a CT scan of the sinuses. The exception is when performing a procedure with contrast enhancement. As a rule, it is necessary to clarify the presence of neoplasms. Before diagnosis with contrast, the patient may be referred for a blood test for creatinine.
The contrast agent is administered intravenously. To avoid nausea and vomiting, you should not eat or drink 4 hours before the test. If you have an allergy to iodine or seafood (shellfish), tell your doctor in advance. You also need to warn the doctor about the presence of asthma, diabetes, problems with the thyroid gland, and heart.
Procedure for performing a CT scan of the nasal sinuses
Before performing the diagnosis, the patient is asked to remove metal jewelry and leave other metal products outside the office. For example, earrings, chain, glasses, hairpins, removable dentures. If a decision is made about the need for contrast, the drug is injected into the cubital vein.
The patient lies down on a mobile tomograph table. To ensure accurate images, it is important to remain still during the examination. Therefore, the human head is fixed using a system of bolsters and belts.
The patient is placed on the table in the working field of the tomograph, the doctor leaves the office and monitors everything from the adjacent room. During a CT scan of the sinuses, constant two-way communication is maintained. The patient can report changes in health, and the doctor answers his questions.
Operating equipment makes a low noise. The table moves smoothly on its own to take pictures in the required projection. The procedure is absolutely painless and takes about 10 minutes.
CT scanning of the sinuses at the International Center for Health Protection is performed using modern equipment. Experienced doctors quickly and accurately interpret the results. Patients save their time and money due to convenient registration for the procedure on the day of their choice and favorable promotions and discounts.
Source: https://medvedev.ru/diagnostika/drugie-metody-diagnostiki/pazuh-nosa/
Features of CT scan of the nasal sinuses
Sinus CT can provide cross-sectional images of the nasal area. Diagnosing tumors, inflammation, pathologies, injuries, and vascular diseases of the nose is unthinkable in modern medicine without the use of computed tomography. CT allows you to see the smallest bone structures and blood vessels, which can be decisive when prescribing treatment.
What does the study show?
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans can provide important information about the structure and sinuses of the nose.
- Images taken during a CT scan may show fluid-filled sinuses or thickened membranes in these areas.
- Tomography will help the doctor diagnose:
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- acute, chronic infection;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- neoplasm (their size, degree of increase);
- polyps;
- anomalies in the structure of the nasal sinuses.
What are the indications for the procedure?
For the following clinical symptoms, a CT scan of the paranasal sinuses or an MRI is prescribed:
- injuries of the facial bone, nose;
- constant headaches;
- toothache;
- local pain when pressing on the nose;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- recurrent nosebleeds.
Scanning is prescribed to assess the condition of the paranasal sinuses and in preparation for surgery.
A specialist will advise which tomography to choose – computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging – after clarifying the entire picture of the disease.
Difference between CT and MRI when examining the nose
MRI of the sinuses is a method that allows you to obtain a high-quality image of the nasal paranasal sinuses and adjacent soft tissues without x-rays. MRI - a tomograph uses a magnetic field. The electromagnetic energy released is measured and analyzed by a computer. Two or three-dimensional images are obtained.
Unlike an MRI, a CT scan of the nose uses X-rays to produce sectional images from different angles. In this case, cross-sections of the nasal paranasal sinuses can be seen on the screen. The computer groups these images and forms a three-dimensional picture. CT allows you to study bone tissue in more detail.
How to prepare for a CT scan?
No special preparation is required for a CT scan of the sinuses. Wear comfortable, loose clothing for the examination. Anything that contains metal can interfere. Items such as:
- earrings;
- glasses;
- hairpins;
- hairpins;
- chains;
- piercing;
- prostheses.
The listed items must be removed before the procedure begins. Do not forget to remove keys and plastic cards from your pockets.
What do the devices look like and what is the procedure like?
The MRI device is a cylindrical magnet in which a couch is placed. Typically, the patient is asked to lie on their back on a mobile testing table, which is then placed in the tunnel. Modern, improved drugs allow you to examine the desired part of the body without completely immersing yourself under a tomograph.
A CT scanner is a ring with a large hole in the center. The patient lies on his back on a couch that can be moved up or down. An X-ray tube rotates around the body, creating images that are calculated by a computer.
In both cases, the patient must lie still to obtain better images. To do this, he is fastened with seat belts and asked to hold his breath several times. If the patient cannot remain still, a sedative is administered.
During the examination, the patient is alone in the room. The radiologist or assistant monitors the procedure in the next room.
The loud scanning sound and clicking noises disturb some patients. For convenience, earplugs or headphones through which music is played may be provided.
A CT scan of the sinuses is completely painless. Magnetic resonance imaging of the sinuses lasts up to 20 minutes. The CT scan takes approximately 2 minutes.
Use of contrast agent
In some cases, CT scanning requires the administration of an iodine-containing radiocontrast agent. This medication is administered through a vein. It helps the specialist to see the structure and understand the image.
Who evaluates the results and how to get them?
The radiologist evaluates the images and provides a report to the treating physician. The patient may be given copies of images and documents. The doctor receives a conclusion within the next working day. After which the patient can discuss the diagnosis or next steps in therapy with the attending physician.
Contraindications
Before the procedure, the radiologist asks questions to each patient to identify possible contraindications to undergoing computer diagnostics.
- Computed tomography is not performed during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- If the patient has had allergic reactions to contrast agents containing iodine, then the existing intolerance or allergy must be reported.
- Diabetics using metformin should discuss the procedure with their doctor.
- If there are problems with the thyroid gland or limited kidney function, tomography cannot be performed.
MRI is not possible for patients with pacemakers or metal implants.
Benefits and Risks
Computed tomography of the sinuses is the safest way to diagnose diseases of the nasal cavity.
The benefit of the diagnosis is a better bony representation of the nasal system's limitations, while MRI clearly shows soft tissue structure, such as swollen mucosa or inflammatory changes in adjacent soft tissue.
- MRI, unlike CT, provides the ability to obtain images without ionizing radiation.
- But there are also possible risks.
- There are no side effects or negative effects on the body with MRI of the sinuses.
Computed tomography is an X-ray examination combined with radiation exposure. Therefore, you should think carefully when choosing this scan.
Source: https://GorloNosik.ru/diagnostika/kt-nosovyh-pazuh.html