Timely prevention of periodontal disease is necessary to prevent malnutrition of the periodontium (the complex of muscles and bones surrounding the teeth), leading to atrophy of the alveolar bone tissue.
This disease develops gradually and is characterized by a chronic course, in which remissions may occur.
If it is not treated, due to irreversible processes in the tissues, destruction of the dental bed and subsidence of the gums occurs with exposure of the dental neck.
Causes of periodontal disease development
The appearance of periodontal disease is caused by impaired blood supply and a decrease in the rate of metabolic processes in the tissues surrounding the teeth. Such vascular disorders occur in a number of diseases: atherosclerosis, hypertension, pathologies of the thyroid gland, liver, diabetes mellitus, increased acidity of gastric juice, damage to the endocrine system.
Due to deterioration of blood circulation, periodontal tissues experience oxygen starvation and do not receive the required amount of vitamins and microelements. Stagnation of blood in the gums leads to the accumulation of toxic metabolic products in them.
The condition may be complicated by exposure to pathogenic microorganisms that contribute to the occurrence of inflammatory processes and the accumulation of pus.
The sensitivity of bone tissue to adverse factors can aggravate the presence of hormonal imbalances in the body. Most often it occurs during puberty, pregnancy, menstrual irregularities, and the onset of menopause.
An additional factor contributing to the development of periodontal disease is the deposition of tartar. Reproduction of harmful microorganisms in places where it is concentrated causes inflammation, increasing the risk of degenerative changes in tissues.
The following factors can create conditions conducive to the occurrence of periodontal disease:
- neglect of hygiene rules, improper dental care, use of ineffective toothpaste for brushing teeth;
- the influence of certain drugs, in particular those that have an anticonvulsant effect;
- genetic predisposition;
- unbalanced diet, including foods that are harmful to health;
- smoking;
- mechanical damage to oral tissues.
Symptoms and manifestations of periodontal disease
As X-ray studies show, with periodontal disease, the amount of bone marrow decreases, and the bone structure takes on a fine-meshed shape.
Under the influence of dystrophic processes, the height of the interdental septa gradually decreases while maintaining the original dimensions of the cortical plates.
Patients often suffer from cardiovascular diseases, and the endocrine system may be disrupted.
The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- paleness of the gums, including in the absence of inflammation;
- the necks of the teeth become visible due to the subsidence of the gums covering them;
- the appearance of dental damage, the occurrence of which is not caused by caries - abrasion of enamel and dentin, a wedge-shaped defect in the cervical area.
Stages of disease development
During periodontal disease there are 3 stages. They differ in the severity of their manifestations and require the use of various therapeutic methods. If in the initial stage, with timely treatment, it is possible to stop the progression of destructive processes and restore the health of teeth and adjacent tissues, then in the next two stages this is much more difficult to achieve.
Easy stage
Symptoms include swelling of the gums, itching, sometimes bleeding when eating solid foods, and increased sensitivity of the necks of the teeth. At this stage, local and general conservative treatment methods are used:
- It is necessary to brush your teeth to remove tartar deposits.
- To improve blood circulation in the gums, hydromassage is prescribed.
- A finger massage performed by the patient independently can improve the condition.
Middle stage
In the second most severe stage of the disease, the patient feels more pronounced discomfort.
Bleeding of the gums is noted due to inflammation of the periodontal tissues, the teeth begin to gradually loosen, as the ligamentous apparatus that holds them is slowly destroyed.
The color of the gums becomes paler, a slight subsidence of their surface occurs, exposing the necks of the teeth, significantly increasing sensitivity to various types of irritants, for example, cold or hot food.
Severe stage
There is significant exposure of the roots of the teeth - their surface is already open to more than half its length. Due to tissue atrophy, the interdental spaces are widened, the position of the teeth is disturbed - they diverge to the side, resembling the structure of a fan.
If you get cold or hot, severe pain occurs. The teeth are very loose, so they fall out easily. Increased tooth mobility leads to injury and bleeding gums.
The entry of microorganisms into wounds causes an unpleasant odor.
Diagnostic methods
X-rays are used to identify the disease and determine its stage. An X-ray image allows you to obtain data on the degree of damage to bone tissue and the participation of pathogenic microorganisms in the development of periodontal disease. A more modern diagnostic method is radiovisiography, which uses an orthopantomograph.
The images taken with its help help identify the disease and create a treatment program. Panoramic tomography also provides high image quality. They provide the doctor with accurate information about the condition of the periodontium, necessary to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for the disease.
Treatment of periodontal disease, methods used and their success
Periodontal disease is an insidious disease, the treatment of which must begin from the moment the first symptoms appear.
In the later stages, due to the irreversibility of the processes occurring inside the tissues, it is much more difficult to restore the health of the teeth and periodontium. Treatment consists of several stages.
General strengthening measures, which include taking medications containing vitamins and microelements, as well as immunomodulators, can improve immunity. Vitamin C strengthens blood vessels, improving blood circulation.
In the first stages of the disease, tissue restoration can be achieved by complementing drug treatment with physiotherapeutic methods and therapeutic massage.
To eliminate the adverse effects of underlying diseases of the endocrine system, hormonal drugs are prescribed. In the severe stage, the use of surgical methods of therapy is indicated: splinting teeth using a special device.
To partially restore bone tissue, artificial bone can be implanted.
Irradiation of affected areas with a heleneon laser gives good results - its effect improves blood supply to tissues and suppresses the development of pathogenic microflora.
You can consolidate the effect obtained at home with products prepared according to traditional medicine recipes based on the use of medicinal herbs. In the treatment of periodontal disease, an important role is given to the general strengthening of the body and the treatment of underlying diseases.
The patient needs a comprehensive examination with the participation of a therapist, endocrinologist and a number of other specialists.
Massotherapy
Gum massage activates the protective functions of tissues and improves their blood supply.
The use of medicinal preparations (ointments, Methyluracil) or special toothpastes during this procedure provides the periodontium with the substances necessary to reduce the harmful effects of aggressive environmental components.
At home, when performing a finger massage, you can use bee honey. The duration of the procedure is from 3 to 5 minutes. In medical institutions, vibration, vacuum or water massage is performed.
Drug therapy
To eliminate inflammatory processes and increase immunity, Imudon, Levamisole dichloride, and FiBS are prescribed. With the progression of periodontal disease, Ribonuclease and Pentoxyl are used, which accelerate the regeneration processes.
At home, rinsing solutions Polyminerol and Parodontsid are used.
Lubricating the gums with Heparin ointment helps relieve inflammation and pain, while treatment with Traumeel-S gel strengthens the immune defense and accelerates tissue regeneration.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapy normalizes blood circulation in tissues and improves metabolic processes in them. For periodontal disease use:
- electrophoresis;
- short-wave ultraviolet radiation;
- exposure to ultrasound.
These methods effectively eliminate inflammatory phenomena, destroying pathogenic bacteria, improve cellular respiration, dilate capillaries, and increase the supply of oxygen to damaged tissues.
With the help of the “Vector” device, the roots of the teeth are carefully cleaned of tartar, the gums are strengthened, and swelling and pain are eliminated.
Traditional methods of treatment
A good effect is provided by rinsing the mouth with an infusion of calendula and oak bark. Regular rinsing of the mouth with an infusion of walnut leaves helps with loose gums. In severe stages of the disease, it is recommended to use sauerkraut juice, cinquefoil infusion, and horse sorrel decoction.
Oral hygiene
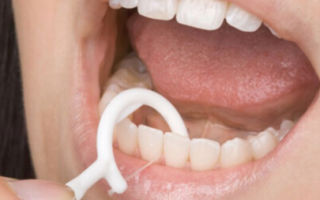
An important factor preventing the occurrence of periodontal disease is careful oral hygiene. After eating, you should use disposable dental floss to clean the dental spaces from food debris.
The use of special flosses that have undergone antiseptic impregnation will destroy microbes that accumulate between the teeth. If you don't have dental floss, you can use sugar-free chewing gum.
The maximum time of its use should not exceed 20 minutes.
You should brush your teeth 2 times a day or, if possible, even more often, after eating food. It is better to choose toothbrushes with polished bristles or those with a rounded surface to avoid damage to the gums and tooth enamel.
The size of the brush should ensure free treatment of any area of the dentition. Harmful microorganisms can accumulate in the bristles, so it is advisable to change the brush every 3 months.
Using an electric brush for cleaning, you can provide micro-massage to the gums, which improves blood circulation in the tissues adjacent to the teeth.
For this hygienic procedure, it is recommended to select toothpastes containing extracts of medicinal herbs that help increase the protective properties of oral tissues, for example, “Forest Balm”.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease consist of creating conditions for the required volume of nutrients to reach the periodontal tissues.
Correcting your diet and including fruits and vegetables will provide the body with a sufficient amount of minerals, vitamins and other useful elements.
If there is a threat of developing periodontal disease, prevention may include taking vitamin-mineral complexes containing all the necessary elements, for example, Multitaba or Carotinoly-M.
Regular consumption of solid foods will help maintain the optimal condition of teeth and gums as a kind of training for their functions - grinding and chewing incoming food.
Foods like apples and carrots naturally massage your gums and remove plaque from the surface of your teeth. You can provide your body with copper by eating cottage cheese, liver, and prunes. Zinc is found in crab meat, legumes, and cheese.
You should limit your consumption of sugar and products containing it - sweets, cakes and other confectionery products.
Folk remedies for preventing periodontal disease
Traditional medicine uses rinsing the mouth with propolis tincture to prevent periodontal disease, dissolving 20 drops of this drug in 200 ml of water. Regular use of propolis strengthens gums well.
Another bee product that improves tissue condition is honey. Its mixture with salt (2:1) should be treated with light rubbing movements on the gums. This product can not be used too often, as it has a rather rough structure.
Do not use a mixture with salt if your gums are bleeding.
A common method of prevention is to rub the gums with a garlic clove. Applications with fir oil give good results. A cotton pad should be soaked in the product and applied to the gum for 15 minutes.
The procedures must be repeated periodically, the course is 15 applications. Chewing sauerkraut and rinsing your mouth with its juice brings considerable benefits.
From time to time, it is recommended to apply finely grated sugar beets to the gums for 30 minutes.
A bad habit such as smoking can lead to periodontal disease. Nicotine contained in tobacco smoke leads to vasoconstriction and decreased immunity, creating favorable conditions for the development of the disease. Quitting smoking will help you avoid cosmetic defects—yellow plaque on your teeth—and prevent atrophy of periodontal tissue.
Periodontal disease: definition, causes, symptoms How I cured periodontal disease. Treatment of periodontal disease with folk remedies! How to treat gum disease at homeHealth (periodontal disease, heart biovalves, broccoli, motion sickness, heat threats) 2011 06 26
Source: https://zubi.pro/bolezni/profilaktika-parodontoza.html
Periodontal disease: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Periodontal disease is a disease of a dystrophic nature, and not an inflammatory one, as is observed in the case of periodontitis. This means that the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms, such as redness, swelling, bleeding, or suppuration. Dystrophy as a term means that tissues do not receive enough nutrients, as a result of which they are destroyed.
Periodontal disease is a generalized disease (appears on the entire upper and lower jaw simultaneously), in the occurrence of which poor quality of oral hygiene plays a significant role. However, the disease is based on more serious disorders in the body:
- diseases of the immune system;
- endocrinological diseases;
- connective tissue diseases;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- hereditary factors.
Poor oral hygiene “triggers” the disease, but is not its only cause. Smokers and people who do not seek help from a dentist in case of inflammatory diseases of the gums and periodontal disease in general are also at risk of developing periodontal disease. Periodontal disease often occurs as a consequence of periodontitis.
Symptoms of periodontal disease : how to determine the disease yourself
Since periodontal disease is non-inflammatory in nature, it is almost impossible to determine the disease in the early stages. Most often, the initial stages are determined in the clinic, when the patient comes for a preventive examination or comes in with another problem that worries him. On an x-ray, the doctor may notice loss of bone tissue or destruction of the interdental bone septa.
If the disease is not detected in the early stages, the following symptoms appear over time:
- The gums become thinner, pale, and itchy;
- The gums “sink”—the neck of the tooth opens, followed by the root;
- Teeth change their natural color, an enamel defect is formed as a result of improper distribution of the chewing load;
- Pathological mobility (looseness) of teeth appears, which can subsequently lead to tooth loss.
Unfortunately, vague symptoms do not allow you to see a doctor in time. First of all, aesthetics suffers, and only then does function, and while there are no significant violations, many patients simply do not pay attention to the symptoms of periodontal disease.
In addition, the process is not always accompanied by pain - in some cases, even opening the root does not lead to reactions to cold and hot. Many people believe that the absence of pain is an indicator that “things are going well.” This is wrong.
In the case of periodontal disease, the longer a person suffers, the higher the likelihood of simply losing teeth.
Treatment of periodontal disease: what the patient faces after examination
Periodontal disease is a disease that occurs due to the confluence of a number of factors. It is not as common as periodontitis. This diagnosis is made only in 5-10% of people who complain of periodontal disease.
Considering that in addition to local factors, general disorders of the body also participate in the development of the disease, treatment of periodontal disease should also be comprehensive.
This means that it will not be possible to deal with periodontal disease in one visit to the clinic.
Depending on the degree of destruction of periodontal tissue, the patient is offered a number of procedures that become more effective in the aggregate:
- Professional teeth cleaning and tartar removal . This will remove additional local irritant that contributes to the development and aggravation of the disease.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis, therapy using ultrasound - improve blood supply to tissues and saturate them with necessary elements.
- Drug treatment . The dentist will recommend contacting specialized specialists (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hematologist), who will help determine the underlying disease that contributes to the development of periodontal disease and write a prescription for the necessary medications. In parallel with this, medications can be used in the dental clinic, depending on the clinical picture (for example, with concomitant periodontitis - anti-inflammatory and antibacterial applications, etc.).
- Additional dental services . Typically, treatment of periodontal disease requires the involvement of other dental specialists in addition to the periodontist. Thus, if teeth are lost, the patient will be offered the services of an orthopedist who will compensate for the defect in the dentition with removable or non-removable structures (crowns, bridges, etc.). To prevent further loosening of the teeth, a splint can be used to secure the mobile teeth in the dentition.
- Surgery . If the bone is significantly destroyed, dental surgeons are involved in the treatment. A bone grafting procedure is performed to preserve the teeth.
The earlier the disease was detected, the more effective the treatment. In the early stages of periodontal disease, the first three steps will be sufficient to stop the process: professional cleaning, stimulation of blood supply to tissues and elimination of the influence of general body problems on the tissues of the oral cavity.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease at home?
Self-medication or the use of traditional methods to treat periodontal disease at home is ineffective and can be hazardous to health. Using medications on your own may make your mouth worse or cause unwanted side effects.
Traditional medicine (the use of infusions and decoctions of herbs with tannins, such as oak bark) can reduce bleeding gums, but will not stop degenerative processes in bone tissue.
That is why visiting a dentist is the only way to get effective help!
However, at home you can contribute to the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment by performing hygiene procedures. Brushing and flossing your teeth, using medicated pastes and antibacterial rinses (as prescribed by your dentist) eliminates pathogenic bacteria that contribute to the development of the pathological process.
Prevention of periodontal disease
To prevent periodontal disease, an integrated approach is also necessary. Preventive measures include:
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- timely preventive visits to the dentist (at least once every six months);
- preventive examinations by general doctors for timely detection of diseases of organs and systems;
- proper diet (eating fresh fruits and vegetables is not only a source of vitamins, hard foods stimulate blood circulation in periodontal tissues);
- rejection of bad habits.
Note that preventive procedures are still necessary after detection and treatment of periodontal disease. The thing is that this disease cannot be cured, only its development can be stopped. Any exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases, suppression of the immune system or imbalance of oral microflora can trigger a resumption of the process.
Source: https://ukrdental.com/forpac/parodontoz-prichiny-simptomy-lechenie-i-profilaktika-zabolevaniya
4 simple ways to prevent periodontal disease that everyone should know
Such procedures do not require special devices , nor do they require a lot of time and effort. However, as a result, these actions will help maintain healthy teeth and gums, as well as a confident, beautiful smile.
Brushing your teeth and choosing a toothbrush
Taking care of your oral cavity should be daily . This condition is the most important point in maintaining the health of the entire oral cavity.
Brushing your teeth should happen at least twice a day : morning and evening. Since during this time a large number of bacteria accumulate in them, the food for which is leftover food.
During hygiene procedures, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the teeth, but also to the gums : clean with a brush. After this, rinse your mouth: make at least ten circular movements throughout your mouth, each time drawing clean water.
Don’t forget also about the inside of your cheeks and tongue, because no less bacteria accumulate on them.
The choice of toothbrush influences to a greater extent not even the teeth, but the condition of the gums . Hard bristles of the brush can injure the gums, which leads to the development of periodontal disease. Therefore, it is better to choose a hygiene item with soft bristles.
It is desirable that there are curves at the ends of each fiber. Remember that cleaning must be combined with a gum massage lasting at least 60 seconds . This manipulation improves blood circulation around the teeth.
The brush needs to be changed 4 times a year . But even when using one brush, it is important to periodically clean it: boil it for several minutes.
Dental floss and chewing gum
Experts advise cleaning your mouth after every meal , but most often it is very difficult to adhere to this recommendation. Then dental floss and chewing gum come to the rescue.
Chewing gum gives the following positive results :
- a person performs the required number of chewing movements, due to which the load on the gums increases and blood circulation in them improves, inflammation decreases;
- cleansing from food debris;
- activation of saliva secretion, which cleanses the entire oral cavity;
- reduction of dental plaque and calculus.
Attention! You need to know moderation in everything, so you can chew gum for no more than 20 minutes . Prolonged chewing will lead to overload of the gums, which can cause the development of gingivitis and periodontitis.
Dental floss (professional name - floss ) is used in cases where it is necessary to clean hard-to-reach areas, especially between the teeth. Using floss is not that difficult, but you need to do it carefully so as not to damage your gums. Because this can lead to infection.
Daily use of floss can help get rid of bad breath, which is caused by food debris between the teeth.
However, remember that you are allowed to use dental floss no more than once a day . And also you can’t brush your teeth with the same section of the floss - it’s not worth saving on your health.
Photo 1. Correct technique for brushing your teeth with dental floss: four simple steps.
Eating solid food
Regular intake of solid foods (apples, carrots) helps maintain healthy teeth and gums. Such techniques are a kind of training for the oral cavity.
Solid products naturally massage the gums and also cleanse the enamel of accumulated plaque.
In addition, vegetables and fruits contain a large number of useful elements that strengthen tissues from the inside.
Prevention of periodontal disease in dental clinics
It is very important for the patient to identify and prevent this disease in the early stages, since in this case all negative processes are still reversible. To detect the disease at the initial stage of development, you need to visit the dentist at least twice a year .
The importance of visiting a professional also lies in the fact that to identify the disease immediately at home.
Therapy will be based on eliminating the causes of the disease. First, the doctor must carry out ultrasonic cleaning of the teeth, since tartar leads to gum atrophy.
- After this, the doctor will move on to treating teeth that can be treated and removing roots that cannot be revived.
- In addition to this , the doctor may prescribe examinations of the whole body to determine the causes of problems with blood vessels and failures in metabolic processes (especially calcium).
- Usually, after the above procedures, the development of periodontal disease stops.
Find out from the video how periodontal disease differs from periodontitis and what are the causes of its occurrence.
To prevent periodontal disease from destroying your gums and teeth, it is necessary to regularly perform preventive procedures.
First of all, this concerns daily hygiene procedures , as well as maintaining proper nutrition and visiting a specialist every six months .
In addition, such prevention will help protect not only from periodontal disease, but also other diseases of the oral cavity.
Source: https://32zuba.guru/parodontoz/profilaktika/
Periodontal disease: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Dental periodontal disease is a serious disease in which the last stage of gum inflammation occurs. This is often the cause of the development of infectious diseases, gastritis, stomach ulcers or cirrhosis of the liver. Even more often, the patient’s teeth simply fall out, and he cannot lead his usual lifestyle or eat his favorite food.
Why does periodontal disease occur?
Ordinary people not connected with medicine often confuse the concepts of “periodontal disease” and “periodontitis”. The first is rare, no more than 8% of all people, mostly elderly. But even among young people, sudden and fleeting development of periodontal disease occurs.
The most commonly cited reasons for this problem are:
-
Insufficient oral care. In particular, poor brushing of teeth, resulting in the formation of plaque.
-
Unstable hormonal levels: pregnancy, puberty, menopause.
-
Weak immunity due to a serious illness.
-
The presence of diseases that primarily affect the immune system: cancer, HIV, diabetes.
-
Bad habits. It has long been known that smoking destroys gum tissue, which means it contributes to the development of periodontal disease.
-
Wrong lifestyle. Insufficient consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables weakens the immune system. Internal organs do not receive enough vitamins and minerals and begin to take them away from the bone tissue of the teeth.
-
Long-term use of certain medications that reduce the normal flow of saliva. It provides gums with protection from external factors, such as eating rough food.
How to recognize periodontal disease
- presence of tartar;
- burning gums;
- discomfort when eating.
Periodontal disease is not accompanied by pain, light pink gums are not visually inflamed, so the patient often postpones a visit to the dentist. In addition, the above symptoms of periodontal disease appear inconsistently.
The main symptom of periodontal disease is exposed tooth roots!
To understand how serious this disease is, it is worth seeing the final stage of periodontal disease development in the photo. A terrifying sight!
Stages of disease development
There are 3 stages of periodontal disease:
- Easy. The patient has no complaints; very rarely there is a reaction to cold or hot food. The presence of periodontal disease can be determined during a dental examination. The mild stage of the disease is best treated.
- Average. The roots of the teeth are exposed by an average of 4-6 mm. The patient begins to experience a burning sensation in the mouth, and there is an acute reaction to eating hot, cold or sour foods.
- Heavy. The roots of the teeth are exposed by 8-10 mm. Chewing food causes severe pain.
Periodontal disease at home: how to treat?
Treatment of periodontal disease at home should not be the only method of solving the problem. This is more of an additional help, but the main one takes place in the dentist’s office and only on his recommendations.
Adviсe:
- Rinse your mouth as often as possible. Pour 20 drops of propolis solution into a glass of warm water. It disinfects and soothes gums. Linden, St. John's wort and oak bark have a similar property.
- Rub your gums. Prepare a mixture of 25 g honey and 5 g salt. Stir until dissolved. Apply to a clean bandage and rub your gums with this product for 5-10 minutes.
- Brush your teeth well twice a day. Do not forget to use dental floss after eating and rinse your mouth with clean water.
- Eat sauerkraut as often as possible and rinse your mouth with its juice.
Treatment of gums with periodontal disease, first of all, should be aimed at strengthening bone tissue. Therefore, the first stage in the fight against the disease is changing your diet. The following should be completely excluded from the menu:
- chocolate and candies;
- carbonated drinks;
- cookies, waffles, gingerbread.
These are solid carbohydrates that create a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria.
Eat lean boiled meat, fatty fish, cottage cheese and any other fermented milk products as often as possible. They contain a lot of protein, which will help restore bone tissue. Don't forget about fresh vegetables, fruits, berries and herbs.
Change your toothbrush. A model with soft, comfortable bristles is suitable. It will not cause mechanical trauma to the gums while brushing your teeth. The paste should be plant-based.
Recipes for strengthening bone tissue:
- Take 20 g of myrrh, add 15 g of chopped mint and raspberry leaves. Dilute a mixture of 80 g of wine alcohol and 25 g of vinegar. Stir and pour into a glass jar. Leave for 3 days in a dark place. Afterwards, rinse your mouth twice a day.
-
Pour 50 g of chopped sage into 100 g of boiling water. Leave covered for an hour. Rinse your mouth thoroughly.
-
Chop fresh plantain leaves and crush well. Soak a clean cotton swab with the resulting juice and wipe the gums with it.
-
Pour 30 g of dried calamus into 0.5 liters of vodka. Leave for a week in a dark place, then strain. Add 3 tbsp. l. mixture into a glass of water and rinse your mouth for 3-6 minutes.
-
6 tbsp. l. Mix crushed pine needles with a liter of boiling water. Bring to a boil, strain and set aside. Rinse your mouth morning and evening.
Modern methods of treating periodontal disease
Treatment of the disease will depend on the degree of neglect of the problem, as well as the number of missing teeth or those that need to be removed. Therefore, first of all, you need to consult a dentist.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination and send you for an x-ray. The image will give an idea of the degree of destruction of bone tissue and inflammation, and the depth of periodontal pockets. After the results, a treatment plan is prescribed.
The next stage is the removal of dental plaque above and below the gums.
The main cause of the inflammatory process during periodontal disease is the presence of a large amount of plaque. Its formation is a consequence of insufficient oral care. Therefore, it is impossible to achieve effective treatment unless the root cause is removed. The optimal way to treat tartar and plaque in modern dentistry is the use of ultrasound.
The next stage of eliminating periodontal disease is therapy aimed at relieving inflammation. As a rule, it lasts about 10 days.
The course consists of rinsing the mouth for an antiseptic effect.
Algorithm:
-
After breakfast, brush your teeth thoroughly for 3-6 minutes.
-
Rinse mouth with chlorexidine (0.05%).
-
Dry the gums using a clean cotton swab.
-
Apply a special gel to the gums.
-
Do not eat for at least 2 hours, drink only clean water.
Such step-by-step treatment is prescribed for mild cases of the disease. If the development of periodontal disease has reached its climax, you will need to take antibiotics (7-10 days). The doctor may prescribe tablets or intramuscular injections.
Medical procedures for the treatment of periodontal disease
Very often, treatment of a disease involves a series of procedures. Which ones?
First of all, splinting. It helps:
- stop further destruction of bone tissue;
- reduce tooth mobility;
- stop tooth decay.
The next procedure that is often used in the fight against periodontal disease is prosthetics. This is possible if the patient has not yet lost his teeth.
Another method of treating periodontal disease is surgery. As is known, the disease provokes the formation of deep periodontal pockets.
They are an excellent environment for the proliferation of bacteria, and this in turn only aggravates the course of the disease. If the degree of periodontal disease is moderate to severe, the pockets can reach a depth of 10 mm.
Their elimination will help stop the development of periodontal disease.
Laser treatment of periodontal disease
The procedure is prescribed and performed by the attending physician after a preliminary examination and x-ray. A laser light guide is inserted into the periodontal pocket, and tissue adhesion begins.
The method is considered one of the latest in modern dentistry. After the procedure is completed, the oral cavity remains sterilely clean, and no infections can enter there. There are several types of rays - diode, neodymium, etc. The attending physician selects the appropriate one in accordance with the treatment plan.
For mild periodontal disease, one procedure is sufficient. For moderate and severe – 2-4 sessions.
Prevention of periodontal disease
Regular visits to the dentist and maintaining a clean mouth are two main conditions for preventing the development of periodontal disease. Reviews about periodontal disease say that someone who brushes their teeth well twice a day and goes to the dentist for examinations every six months cannot, in principle, develop inflammation.
A few final words
The causes and treatment of periodontal disease should be determined by the treating dentist. Identifying and solving the problem yourself is quite problematic. In addition, we should not forget that self-medication often leads to a worsening of the condition.
An experienced dentist will not only successfully treat periodontal disease, but will also tell you about the rules for preventing further development of the disease.
Source: https://dentalgu.ru/statyi/other/parodontoz-prichiny-simptomy-metody-lecheniya/
Periodontal disease: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment in Moscow
Periodontal disease is a lesion of the gum tissue located between the socket and the root of the tooth. An unfavorable course of the disease usually leads to tooth loss.
The disease begins unnoticed and is extremely rarely diagnosed at the initial stage. The pathological process is not visible to either the patient or the dentist. X-ray studies also do not give results.
The affected gums recede over time, exposing the neck of the tooth. The latter begins to loosen, and sensitivity to hot, cold or sweet foods appears. Chewing foods with coarse fibers becomes much more difficult.
As the disease progresses, changes in bone tissue become noticeable on x-ray studies. The disease, in most cases, develops slowly. The period from the initial to the fourth stage can last for several decades.
Periodontal disease should not be confused with periodontitis. These diseases have different courses and symptoms. With periodontitis, the gums bleed, become inflamed, their color changes, and an unpleasant odor appears.
Mucosal tissues with periodontal disease are visually no different from healthy ones, especially in the first stages of the disease.
The formation of gum pockets characteristic of periodontitis is not observed during periodontal disease.
Types of periodontal disease
Based on the nature of treatment of the disease, periodontal disease can be divided into two types:
Since pain, bleeding gums and tissue inflammation are not observed, this division is very arbitrary, and the disease is not acute, in the classical sense. In acute periodontal disease, the disease progresses faster and only a few years may pass from the stage of starting the process of changes in tissues to tooth loss. Acute forms are extremely rare.
The disease is also distinguished by the area affected. Periodontal disease occurs:
- localized;
- generalized.
With a localized type of lesion, the disease affects a small area: from one to several teeth. The pathological process does not spread to the tissues of the rest of the jaw.
With generalized periodontal disease, the upper or lower dentition may be affected, as well as both jaws at once.
Causes of the disease
It is worth noting that periodontal disease is a disease that has not been fully studied. There are a number of reasons that provoke it, but diagnosing what exactly caused the pathological changes in soft and bone tissue can be extremely difficult.
Scientists call heredity one of the reasons for the development of periodontal disease. As practice shows, the risk of developing the disease is much higher in those patients in whose family there are similar cases of damage to the tissues of the oral cavity.
The background to the development of periodontal disease is a violation of metabolic processes and blood supply to the gums. With the likelihood of subsequent development of periodontal disease, it can be caused by:
- disruptions in the functioning of the body associated with hormonal disorders;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as unhealthy diet;
- neurological disorders and diseases;
- presence of bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking);
- lack of minerals and vitamins in the body;
- decreased immunity over a long period of time.
Local factors also matter:
- various bite pathologies;
- incorrectly selected designs to correct the bite;
- mechanical trauma to the periodontium, for example, fractures or bruises.
With periodontal disease, there is always plaque and tartar, but they contribute to the development of the disease together with other factors, without themselves being its cause.
Symptoms of periodontal disease in the mouth
The symptoms of periodontal disease depend on the stage of development of the disease.
- Initial stage. The disease does not manifest itself visually. Neither the patient nor the attending physician can detect it. X-ray studies carried out during this period will also not be able to report the pathological process that has begun in the oral cavity.
- First stage. At the first stage of periodontal disease development, the dentist can see visual changes. During this period, the gums begin to recede a little, but do not yet reach the exposure of the neck. The patient himself may occasionally notice increased tooth sensitivity. At this stage, the teeth are held firmly in their sockets. Most often, these symptoms are detected during professional teeth cleaning. On x-rays you can observe the first changes in bone tissue.
- Second stage. Gum atrophy is progressing. The necks of the teeth are exposed up to the area where the enamel transitions into the cement covering the root. Teeth become increasingly sensitive. Gaps appear between them and increase in size. The teeth are still firmly in the sockets. Periodontal tissues slightly change color. She becomes paler. The photographs clearly demonstrate changes in the ridges of the jaw that hold the tooth.
- Third stage. The gaps in the teeth continue to widen, and receding gums expose more of the tooth root. Teeth react with acute pain to hot, cold, sour and sweet foods. They are noticeably loose. The height of the jaw protrusion holding the tooth is significantly reduced, which is clearly visible on x-rays.
- Fourth stage. Characterized by tooth loss. If they do not fall out on their own, surgical removal is required. They no longer perform their functions, they wobble a lot and interfere with talking and chewing food. At the final stage of the disease, the roots of the teeth are exposed by two-thirds and are held in the jaw exclusively by the apex, which is noticeable during x-ray examination.
It is worth noting that throughout the entire illness there is no redness, bleeding, swelling or soreness of the gums themselves. In fact, the gums and bone tissue adjacent to the periodontium gradually dissolve on their own, and only slight itching may be observed. The pathological process also affects the enamel - it wears away faster than that of healthy teeth.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease
Diagnosis of periodontal disease is carried out comprehensively, and the need for certain research methods is determined by the doctor.
Anamnesis. It is mandatory to interview the patient himself. The specialist must be aware of:
- about the patient’s past history of diseases of the oral cavity and other body systems;
- about the presence of periodontal disease in relatives;
- about the patient’s complaints at a given time.
Examination of the oral cavity. The doctor must conduct an examination of the oral cavity. For an accurate diagnosis, he needs to evaluate:
- position and appearance of the gums (soreness, sensitivity, tint);
- degree of exposure of the neck of the tooth;
- quality of tooth enamel (color, density, sensitivity).
General blood analysis. General clinical study. If periodontal disease is suspected, the main attention is paid to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the blood.
Radiography. X-rays can reveal changes in bone tissue, the width of gaps between teeth, and changes in the boundaries of dental sockets.
Diagnostics using laser and ultrasound may also be required - the blood flow in the periodontium, the oxygen content in it and the condition of the tissues themselves are examined.
Diagnosis of the body . Since periodontal disease is often provoked by diseases of internal organs, consultation with other specialists - a gastroenterologist, oncologist, etc. - may be required.
In this case, the patient is sent to a specific specialist, if there are complaints, or is sent for diagnostics of the whole body.
It will help identify diseases and hidden conditions that the patient is unaware of.
Treatment of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a pathological condition that cannot be completely cured. The course of the disease can be significantly slowed down with proper treatment and compliance with all medical recommendations. Self-medication is strictly not recommended, as this can aggravate the condition of periodontal tissues.
Treatment methods
- taking medications;
- diet;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- orthopedic treatment;
- surgical intervention.
Which one will help in a particular case is determined by the doctor. They can also be combined with each other to give the best result and stabilize the current periodontal condition.
Drug treatment
The initial stage of treatment involves professional teeth cleaning. The specialist must remove the accumulated plaque and tartar from the teeth. Thus, the tissues adjacent to the tooth are cleaned, and the effectiveness of treatment is increased by the use of topical preparations - lotions, rinsing with medicinal solutions.
After this, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed and consultation is conducted on proper oral hygiene at home. Teeth should be brushed thoroughly, removing not only plaque, but also stuck food debris in the spaces between the teeth.
For cleaning during periodontal disease, special pastes are used that have an effect on the periodontium, they help improve blood supply and, thereby, strengthen the tissues adjacent to the tooth.
A specialist can also prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes that improve the condition of the body in general and bone tissue in particular.
Diet food
Reviewing your diet can also help stabilize your gums in many cases. In addition to providing tissue throughout the body, a number of products can cleanse and restore gums and periodontium.
As part of the diet for periodontal disease, the diet must include fiber in the form of vegetables and fruits, legumes, and seafood. They should be prepared correctly: boiled, baked, stewed or eaten raw.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
During physiotherapeutic procedures there is a direct effect on periodontal tissue. This helps improve blood microcirculation and metabolism in the tissues of the oral cavity. Depending on the availability of equipment and the condition of the gums, the following may be prescribed:
- gum massage is carried out both manually and using special massage equipment. Promotes blood flow to affected tissues;
- electrophoresis with calcium gluconate. The procedure is carried out using a special apparatus. Using a low voltage current, calcium preparations are injected deep into the gums. Thus, gums and bone tissue are strengthened, tooth sensitivity is reduced;
- Darsonvalization. The affected areas of the gums are exposed to microcurrents using special equipment. The procedure helps improve the trophism of affected tissues.
Treatment by an orthodontist
If teeth have already begun to become loose, they can be strengthened with plastic splints.
Surgical intervention
The surgical method of treating periodontal disease is very expensive. Destroyed bone tissue and parts of the gums can be restored by suturing grafting materials. The latter are sent by the surgeon under the gum, and if they survive, they contribute to the formation of new bone tissue.
If the treatment is successful, a new alveolar process grows in place of the resorbed tissue, which strengthens the teeth affected by the disease.
To restore gums, stem cells, known for their regenerative properties, are used as a replanting material. Fibroblasts help restore the oral mucosa and strengthen the strength of the periodontium.
They promote the production of collagen and significantly improve the elasticity of soft tissues. Platelets help restore blood supply to the gums and improve metabolism in cells.
They are also responsible for the formation of new small vessels and capillaries.
The last surgical measure for periodontal disease is tooth extraction. Dental restoration is possible thanks to a removable jaw. Dental implants are also used.
Prevention of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, due to the severity of the pathology and the impossibility of curing it completely, is easier to prevent than to treat. Disease prevention is based on general recommendations for strengthening periodontal tissue.
Proper nutrition
A well-designed diet and consumption of properly prepared quality foods helps saturate all tissues and systems of the body with nutrients, minerals and vitamins. If there is a shortage of the latter in the body during the off-season or after protracted illnesses, they can be taken in the form of tablets, but strictly in consultation with a doctor.
Strengthening the gums is facilitated by the presence of moderate amounts of roughage and fiber in the diet.
Proper oral hygiene
When visiting a dentist, you should consult on how to properly care for your oral cavity. It is important to clean teeth and interdental spaces daily from plaque and food debris. By stagnating, they contribute to the development of harmful bacteria and the formation of tartar.
In addition to using a quality toothbrush, you should use dental cleaning aids: dental floss, mouthwash, etc. It is highly advisable to do self-massage of the gums as a preventive measure.
It is also necessary to promptly contact a specialist for professional cleaning and examination of the condition of teeth and gums.
Taking care of your health
The health of the body as a whole is of great importance in the prevention of periodontal disease. Disturbances in its functioning can also lead to pathological processes in the oral cavity. As practice shows, changes and diseases of teeth and gums are the result of problems with internal organs and metabolic disorders.
Source: https://www.polyclin.ru/parodontoz/