A pathological condition characterized by short-term partial or complete cessation of breathing.
Today we’ll talk about sleep apnea. What kind of pathology is this, and how is it dangerous? We will talk about the symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the disease.
What it is
There are many sleep disorders that negatively affect human health and condition. However, there are pathological processes that lead to serious consequences. One such phenomenon is considered to be nocturnal suffocation or apnea.
The period of suffocation lasts no more than a few minutes, since the human brain receives an impulse about oxygen deficiency and the patient awakens. However, the condition brings negative changes.
Nocturnal apnea during sleep occurs during the deep phase. After awakening, the patient does not remember that he experienced a lack of air, but notes a lack of vitality and a clear desire to sleep.
Chronic form:
- impairs sleep quality;
- provokes hormonal imbalance;
- promotes the development of arterial hypertension;
- disables the functions of many body systems.
It often causes metabolic disorders, causing a person to rapidly gain weight.
Without treatment, the risk of diseases of the lungs, heart, brain and blood vessels increases. The reason lies in the constant lack of oxygen.
Against this background, hypoxia is formed, which is aggravated by frequent attacks of apnea.
Kinds
There are several types of pathology.
- By time of attack: partial and complete.
- Depending on the provoking factor: obstructive, mixed and central.
- According to the degree of manifestation and number of attacks per night: mild, moderate, severe.
Causes
- The main cause of the pathology is the increased relaxation of the muscles of the pharyngeal ring, which maintain the tone of the tonsils, tongue and upper palate.
- During excessive relaxation, the muscles close completely or partially and block the windpipe.
- Such provoking factors can cause such a phenomenon as:
- diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract: runny nose, sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.;
- the use of drugs with a sedative effect and sleeping pills;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages or alcohol dependence;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in which blood supply is impaired;
- pathological processes of the central nervous system that cause a false impulse to frequent muscle spasms;
- hereditary predisposition;
- excess body weight - adipose tissue is deposited on the neck and diaphragm, which in both cases leads to increased pressure on the respiratory organs;
- endocrine diseases: diabetes types 1 and 2;
- changes in hormonal levels, for example, during pregnancy or menopause;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the jaw and respiratory tract: deviated septum, large movable muscle (tongue), physiologically enlarged tonsils;
- gender: according to statistics, men are more susceptible to attacks of suffocation than the fair half.
Often the cause of the disease lies in the age characteristics of the patient.
In children
In infancy, the disease manifests itself for the following reasons:
- prematurity;
- underdevelopment of the structure of the bronchi;
- intrauterine infections;
- developmental anomalies;
- anemia;
- hypoglycemia;
- birth injuries.
In preschool children, sleep apnea can be caused by the following disorders:
- adenoid vegetation;
- drug therapy;
- runny nose;
- injuries;
- structural changes.
Causes of sleep apnea in teenagers can include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- psycho-emotional experiences;
- mechanical injuries.
In adults
In men and women, the following factors can trigger attacks of sleep apnea:
- diseases of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system;
- taking sedatives;
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- obesity;
- pathological processes of the nervous system;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- mental disorders;
- VSD is a provoking factor.
In the elderly
In older people, the manifestations of breathing disorder during sleep can be caused by:
- age-related weakness of the muscular system;
- excessively loose fiber;
- scanty secretion of mucous secretion;
- chronic heart and lung diseases;
- hypertension;
- History of ischemic heart disease.
Why is it dangerous?
Apnea syndrome is dangerous when attacks occur frequently.
This manifests itself in the following:
- the patient complains of frequent headaches;
- chronic drowsiness;
- loss of strength and apathy;
- anxiety;
- depression;
- lack of sexual desire, and in men - impotence;
- nocturnal polyuria;
- decreased perseverance and memory impairment;
- children complain of terrible dreams and nightmares.
- Seemingly harmless conditions worsen the quality of life and provoke the development of secondary diseases.
- In addition, the malignant nature of the pathology, which leads to fear of sleep or causes asthma, cannot be ruled out.
The risk of death is unlikely, but not excluded.
- Chronic nighttime suffocation can cause prolonged spasm of the pharyngeal muscles, while the brain does not have time to react to the impulse.
- The patient does not notice the attacks at night on his own; he only notes poor-quality sleep, attributing it to snoring or nervous tension.
- Clinical picture of respiratory arrest during night rest:
- snore;
- intermittent and noisy breathing;
- desire to take a deep breath;
- sweating;
- Waking up frequently to go to the toilet is a kind of warning factor.
Diagnostics
- Somnologists diagnose and treat the disease.
- There are 2 main diagnostic methods used for both children and adults.
The first technique was developed by scientists. It's called the Epworth scale. This is a questionnaire with a series of questions. The patient is asked to answer questions, but after an external examination and history taking.
Epworth scale questions: “Can you sleep if”:
- reading a newspaper;
- watch TV;
- you are in a public place;
- you are traveling in a car as a passenger;
- had a hearty lunch;
- talking to a person;
- go to bed in the evening;
- you are driving a car or stuck in a traffic jam.
Answer options: I don’t fall asleep - I b, I can doze off - II b, I easily fall asleep, sometimes even instantly - III b.
If the total is more than 14 b, then the patient needs high-quality treatment with medications or other methods. Only a doctor can interpret the results.
The second technique is a polysomnographic examination, which includes the following manipulations:
- patency of the nasal passages;
- blood pressure measurement;
- pulsation;
- urine and blood tests;
- detection of systemic diseases.
The patient is immersed in a medicated sleep, and the condition of the subject is monitored using connected sensors.
The immersion in sleep phases is noted, and periods of cessation of breathing are recorded. During an attack, specialists monitor the person’s behavior and the duration of apnea.
The results indicate the following data:
- chest movements;
- ECG;
- snoring pattern;
- audio recording of sleep;
- electroencephalography;
- electromyography.
Treatment is prescribed in somnology clinics, but not every locality has specialists in this field.
The procedure is expensive and is performed only in private healthcare institutions.
First aid
First aid boils down to trying to awaken the patient. To do this, you need to push the sleeping person, but without making any special physical effort. Next, sit on a chair and open the window.
If asthma attacks occur frequently before bedtime, it is recommended to take a walk in the fresh air and, if possible, sleep with a window slightly open.
You should not pour water on a person or give it to drink, as the risk of repeated spasm increases.
If attempts to wake up are unsuccessful, you should try to shift the patient onto his side and blow a little on his face. From such actions the sleep passes and the patient wakes up.
Treatment
To eliminate the night defect, medications are used and lifestyle adjustments are also made.
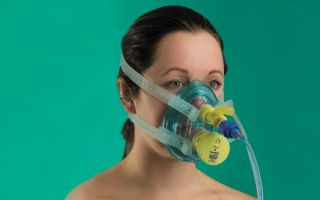
- CPAP is the use of special equipment in the form of a mask, which ensures a sufficient flow of oxygen into the body. This method of treatment is used in severe cases and serious health problems.
- Quitting addictions: smoking, drinking alcohol and overeating. Doctors advise following a diet to normalize weight and reduce the number of asthma attacks.
- Exercise to reduce body fat and gain muscle mass. Patients are recommended to take walks and slow jogs in the open air.
- Drug therapy is reduced to eliminating the cause of the disease, if it is caused by diseases of the respiratory system: vasoconstrictors, immunostimulating. Symptomatic treatment is carried out.
- Surgical treatment consists of removing the adenoids and restoring the structure of the nasal septum.
There are no miracle pills for apnea for adults and children, just like there is no medicine for snoring.
All treatment is symptomatic and aimed at identifying and eliminating the cause.
Recommendations
To prevent attacks of sleep apnea, you must follow a number of simple recommendations:
- change your lifestyle - follow a healthy lifestyle;
- control body weight;
- abandon unnecessary therapy with sleeping pills;
- ventilate the room before going to bed;
- stop watching aggressive TV shows before bed;
- minimize room lighting;
- promptly treat pathologies of the respiratory system, especially the nasopharyngeal cavity.
Nocturnal strangulation occurs in 40% of people, but varies in degree of intensity and form of progression.
Preventive measures for existing tendencies allow you to avoid the disease or prevent its transition to a chronic form.
Source: https://zason.ru/ostanovka-dyhaniya-vo-sne/
Apnea (temporary cessation of breathing during sleep): treatment at home with folk remedies
Apnea is when breathing stops during sleep for at least 10 seconds. One of the signs of pathology is severe snoring, which indicates difficulty in the passage of air flow through the nasal passages.
As soon as breathing stops, there is a lot of carbon dioxide in the tissues, to which the brain reacts by releasing stress hormones, the person wakes up and takes a breath.
You will learn about methods of treating sleep apnea from this article.
Diagnostics
For apnea, that is, temporary cessation of breathing during sleep, treatment depends on the etiology of the disease. Depending on the causes, apnea is divided into three types:
- Central. The reason for holding your breath is dysfunction of the brain structure responsible for respiration. The brain in the deep sleep phase stops sending impulses to the respiratory muscles, and air circulation in the lungs stops.
- Obstructive. Caused by a narrowing of the airways. The muscles of the pharynx are relaxed and do not allow air to pass through, or there is an obstacle in the path of the flow in the form of lymphoid tissue;
- Mixed. It occurs as a result of brain dysfunction and a physical obstruction to the passage of air.
To diagnose the severity of the disease, people living in the same apartment with the patient play an important role. Often the patient is not even aware of the pauses in breathing.
He feels tired and overwhelmed, gets tired quickly, notices a headache and dry mouth in the morning, and problems with cardiac activity may appear.
But it is the relatives who inform the patient that he snores, and this unpleasant sound often stops due to respiratory arrest.
Note! When determining the severity of the disease, the doctor will ask relatives to make a graph on which to note the interval and duration of respiratory pauses.
During the examination, the doctor will determine your body mass index. If the index is above 35, then a diet will be required to bring the weight back to normal. Another important indicator is neck volume (for women it should be up to 40 cm, for men up to 43).
To determine the provoking factors, you will need to consult an otolaryngologist. The doctor should check for a deviated nasal septum, polyps, chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis or rhinitis. The examination of the nasopharynx is carried out using a flexible fiber endoscope and includes:
- pharyngoscopy;
- laryngoscopy;
- rhinoscopy.
A polysomnographic study will show brain function during sleep, the degree of respiratory activity, the duration of breath holds and their number, record cardiac activity, and show the volume of oxygen in the blood. The study lasts at least 8 hours, that is, throughout the entire night's sleep. When analyzing the data, the somnologist will determine the duration of apnea episodes and the degree of their impact on the patient’s body.
There are several degrees of severity of the disease:
- up to five stops per hour - not considered as a pathology;
- up to 15 - mild apnea;
- up to 30 - moderate severity of apnea; more often than 30 - severe apnea.
During the night, the patient may experience more than 100 stops of respiration, which in total gives approximately 3-4 hours of lack of oxygen supply during the night's sleep. This leads to oxygen starvation and increased levels of carbon dioxide in the blood.
to contents ↑
Treatment of sleep apnea
Treatment of sleep apnea involves eliminating the factor that causes breathing to stop. Drug, non-drug and surgical methods are used.
In case of a mild form of the disease, the patient is given general recommendations:
- raise the head end of the bed so that your head is higher than your feet;
- do not sleep on your back;
- to ease breathing, instill xylometazoline into the nasal passages at night;
- gargle with diluted essential oils;
- do not drink alcohol or sleeping pills;
- if necessary, reduce weight.
The attending physician will decide how to treat apnea, having studied the etiology of the disease, and if necessary, refer you to a somnologist or laryngologist.
The tonsils and adenoids are removed during surgery. A deviated nasal septum can also be corrected by septoplasty (it is necessary to straighten, remove or reimplant a part of the septum, performed endoscopically under local anesthesia). If the cause is excess body weight, then the patient requires a balanced diet. Even losing 5 kilograms of weight sometimes helps solve the problem.
Note! For diseases associated with dysfunction of the nervous system, drug treatment is required. Prescribed drugs that stimulate brain and breathing.
For the central form, acetazolamides are prescribed (to reduce carbon dioxide in the blood).
If apnea occurs as a result of a flabby palate, then it can be restored using the radio wave method. The intervention lasts about 20 minutes, the patient can leave the clinic an hour later and sleep at night without debilitating stops in breathing. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, there is no recovery period.
Note! There are other equally effective methods of strengthening the palate, for example, liquid nitrogen or laser, but tissue regeneration takes longer, causing slight discomfort to the patient.
In severe cases of the disease, CPAP therapy is prescribed. Before going to bed, the patient puts on a mask connected to a device that controls the pressure and air supply. This is done to maintain airway pressure so that the walls of the throat do not collapse. This method is considered one of the most effective, however, it does not change the course of the disease.
There are also several treatments for sleep apnea. These are clamps for increasing the clearance of the nasal passages and forcing one to breathe exclusively through the nose, pillows that prevent a person from turning over on his back (the patient sleeps all the time on his side).
Alternative medicine
Traditional medicine will also tell you how to cure obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. It should be used as an addition to conservative treatment. Folk remedies for apnea:
- To improve nasal breathing, it is recommended to rinse the nasal cavity with saline solution. To prepare it, dilute a teaspoon of salt in a glass of water.
- Cabbage juice with honey is also used for treatment (a teaspoon of honey per glass of juice). The drug is drunk for a month.
- Olive oil also has medicinal properties. It has a softening effect, they are recommended to gargle at night.
- Sea buckthorn oil will help remove the inflammatory process in the nasopharynx and restore blood supply. Place 5 drops of oil into your nasal passages for several weeks.
- Eucalyptus oil eliminates infection in the nasopharynx, has an expectorant effect, facilitates breathing, and eliminates snoring. Add a couple of drops of oil to boiling water and inhale the aroma for 5 minutes.
- Thyme will restore the nervous system, which will make your sleep healthier. Add the essential oil from the plant to a container of water and diffuse it daily in the bedroom. Medicinal thyme sprigs can be added to tea.
- Peppermint has a positive effect on the nervous system. The extract helps eliminate mucus from the respiratory tract, relieves inflammation and expands the bronchi. You can drink mint infusion or put a couple of leaves in your favorite tea.
- To eliminate snoring, healers suggest eating baked carrots three times a day before meals.
- Singing is considered the simplest way to help strengthen the muscles of the pharynx. You need to play music for at least 30 minutes a day.
Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pharynx
Special exercises that help strengthen muscles will help you cope with holding your breath during sleep.
- Stick your tongue out as much as possible so that you can feel the tension at its base. Say “and” for two seconds. You need to do the exercise 2 times a day, about 30 times.
- Place your fist on your chin. Your task is to move your jaw forward and then back, while creating slight resistance with your fist. Do twice for 30 approaches.
- Take a pencil with your teeth and, squeezing it, tense the muscles of the pharynx. Do 3-4 minutes.
- Use your lower jaw to trace an imaginary circle, first clockwise, then counterclockwise. Do 15 times.
- Press your tongue as hard as possible on the upper palate. This exercise will not be noticeable to others, but you need to do it until you get tired.
For the treatment of sleep apnea syndrome, pulmonologists, neurologists, otolaryngologists, and cardiologists can be involved. Specialists can only offer nonspecific prevention of the disease, based on maintaining weight within normal limits, quitting smoking, using sleeping pills, psychotropic substances, and timely treatment of nasopharyngeal diseases.
Important! If sleep apnea is not treated, then serious pathology occurs in the cardiovascular system.
Most often, apnea causes strokes in young people, ischemia and myocardial infarction in patients with atherosclerosis. It causes serious complications if chronic lung pathologies are diagnosed. The disease also changes the quality of life. Since the patient wakes up dozens of times a night, he cannot get enough sleep, which increases the risk of injury at home or at work, or getting into an accident.
The disease, as it progresses, can lead to disability or death within the first 5 years (40% of patients), and 94% develop serious health problems within 15 years.
Did the article help you?
Let us know about it - rate it
Loading…
Source: https://opnevmonii.ru/bolezni/apnoe.html
What diseases cause sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common problem that many people face. Full breathing is the basis of human life, and lack of air during sleep causes many problems. It develops suddenly and is characterized by discomfort in the chest area; the person begins to experience panic, a feeling that someone is choking him.
Choking during sleep develops due to a decrease in oxygen concentration in the blood and an increase in carbon dioxide levels. This condition is accompanied by disturbances in the autonomic function of the body, which causes unpleasant symptoms to develop, and subsequently serious health problems are possible.
Causes of sleep apnea
The causes of suffocation during sleep are not always associated with any diseases - rare attacks sometimes occur in the absence of any pathologies after drinking alcohol, psycho-emotional stress, taking certain medications, or in the presence of allergens in the room where a person sleeps. If stopping breathing during sleep occurs constantly, you should pay attention to your own health. The most common factors that cause this pathology include disruptions in the functioning of the body from various systems and organs.
- Dysfunctions of the cardiovascular system (angina pectoris, arrhythmia, vascular crises, acute heart failure). These pathologies are characterized by a violation of the heart’s ability to pump blood normally, which disrupts oxygen metabolism.
- Bronchial asthma. With this pathology, patients often experience shortness of breath, which can develop into nocturnal attacks of respiratory arrest.
- Thyroid diseases. With some endocrine pathologies, there is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which puts pressure on the trachea - for this reason, during sleep, you lose your breath and feel suffocated.
- Sleep apnea. Sleep apnea syndrome is observed due to decreased muscle tone due to excess weight, abuse of sedatives, and enlarged tonsils. During the daytime, this condition is accompanied by drowsiness, a feeling of weakness, headaches in the morning, and surges in blood pressure.
- Panic attacks. Unstable functioning of the nervous system causes panic attacks and symptoms similar to cardiovascular diseases (increased or slow heart rate, chills, severe fear of death).
- Sleep paralysis. This is a condition that causes temporary immobilization. The brain does not send a signal to the rest of the body at the moment of awakening, which is why the person remains conscious, but cannot move or speak, sometimes sees hallucinations and feels intense fear.
If the above pathologies are excluded, the answer to the question of why you suffocate in your sleep should be sought in other factors. A list of secondary causes that can cause sleep apnea includes:
- infectious and inflammatory processes accompanied by swelling of the tonsils, enlarged adenoids, severe runny nose;
- anatomical pathologies of the head, neck, face;
- dysfunction of the digestive system, autoimmune disorders;
- excess weight;
- smoking, including passive smoking.
The first harbinger and another common cause of sleep apnea is constant snoring, which causes changes in the activity of the respiratory system, which is why suffocation develops. Accordingly, people who frequently snore are at risk for developing sleep apnea.
Pregnant women may also suffer from attacks of nocturnal suffocation - this occurs especially often in the last months, when the fetus begins to put pressure on the diaphragm.
This condition does not pose a serious threat to the health of the mother or child, but in order to eliminate discomfort and reduce the risk of oxygen starvation, a woman is recommended to sleep on a bed with the head of the bed raised, or put pillows under her back.
How does it manifest?
The main manifestation is a feeling of suffocation and the inability to take a deep breath, and sometimes breathing stops when falling asleep, and in some cases it stops directly during the night's rest.
Those who have had to deal with this condition describe it as follows: “I wake up from not breathing, or suffocate when I fall asleep, I am afraid of not waking up again, but at the same time I cannot move and ask for help.”
This condition develops in several stages:
- at the first stage, the activity of the respiratory organs is activated, the frequency and depth of breaths increase along with blood pressure and pulse;
- the next phase is characterized by the opposite process - vital signs decrease, fingers and the nasolabial triangle acquire a bluish tint;
- during the third stage, the activity of the respiratory organs is disrupted, breath holding occurs, which lasts from a couple of seconds to 2-3 minutes, reflexes fade, blood pressure drops, convulsions or uncontrolled muscle twitching may develop;
- During the last phase, serious disturbances in the respiratory rhythm occur - breathing becomes short and deep, inhalations become difficult and convulsive, and exhalations become rare.
Some people are unaware that they stop breathing during sleep or when falling asleep. To identify violations, it is necessary to observe the state of the sleeping person - he begins to snore, after which apnea occurs.
Snoring and breathing noise subside, the chest and stomach move, and after 15-30 seconds breathing is restored, the sleeper snores loudly, and normal breathing is restored.
Sleep at this time, as a rule, is very restless - a person rushes about, moves his limbs and tries to say something.
What is the danger of stopping breathing during sleep?
Having discovered apnea, a person first of all thinks: “If I am out of breath when I fall asleep, what consequences can this entail?”
In addition to the serious discomfort that this condition causes, it causes chronic fatigue, decreased performance, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and metabolic processes, and depression.
In addition, people who suffer from sleep apnea have an increased risk of developing hypertension, strokes and heart attacks - pathologies that can be fatal.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of the development of such symptoms is made on the basis of symptoms and anamnesis - identifying diseases that can provoke respiratory arrest. To accurately diagnose pathology, the following methods and procedures are used:
- clinical blood and urine tests to identify inflammatory and infectious processes in the body;
- examination of the respiratory system for tissue changes, areas of compaction, neoplasms and other pathologies (radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, bronchoscopy, thoracoscopy);
- electrocardiogram to assess the activity of the cardiovascular system;
- polysomnography, or long-term recording of brain impulses, respiratory activity and other vital signs of the body during sleep.
The above diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the number and duration of episodes of respiratory arrest, identify changes in body functions during this time, and establish the cause of the pathology.
First aid for choking
The patient should be helped to sit down (in this position the muscles that are responsible for breathing work better), calm him down, and then provide an influx of fresh air - unbutton the clothes on the chest, open a window or vent. If a person continues to sleep during respiratory distress, he should be carefully awakened, sat up, and forced to breathe deeply through his nose.
In cases where the cause of apnea is bronchial asthma, you can put mustard plasters on your chest, a warm compress on your feet, and take a drug orally to dilate the bronchi (for example, Eufilin).
In case of respiratory dysfunction due to laryngeal edema of allergic origin, the patient should be given any antihistamine in the form of tablets or injections, and in case of cardiovascular diseases - Validol, Valocordin or Nitroglycerin.
It is better not to give the patient anything to drink, since the person’s throat is tense after an attack of apnea, and the liquid can provoke a relapse of the pathology and another attack.
Treatment of sleep apnea - CPAP therapy
Treatment for holding your breath during sleep
To completely get rid of attacks of suffocation, you should answer the question of why breathing stops during sleep - consult a somnologist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Treatment of sleep apnea primarily involves eliminating the root cause of the pathology.
If respiratory function is impaired due to drinking alcohol, smoking or using sleeping pills, it is necessary to give up these habits, and soon the patient’s condition will return to normal.
For infectious and inflammatory diseases, therapy with decongestants, antihistamines and vasoconstrictors is necessary, and for obesity, you should normalize your diet, start playing sports and lose excess weight.
Similar recommendations are also suitable for people who suffer from suffocation during sleep due to central nervous system disorders - a correct lifestyle, light physical activity and walks in the fresh air will help normalize sleep function and breathing.
A good effect when breathing stops at night is provided by therapeutic methods that are aimed at artificial ventilation of the lungs (SINAP, VIPAP therapy, etc.), as well as special mouthguards that prevent the tongue from retracting and the muscles of the larynx from relaxing. In case of violations of the anatomical structure of the palate or nasopharynx, surgical intervention is indicated for patients.
Sleep apnea is not a harmless pathology that causes discomfort and interferes with sleep, but a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. To find out how to treat sleep apnea, you should consult a specialist immediately after the first symptoms appear.
Source: https://vosne.info/ostanovka-dyhaniya-vo-sne/
How to treat sleep apnea
Sleep apnea syndrome is characterized by periodic, frequent pauses in breathing during sleep, usually leading to awakening.
Treating sleep apnea is necessary to restore normal breathing at night and avoid daytime sleepiness, decreased performance and immunity.
In addition, sleep apnea causes the development of diseases such as high blood pressure and reduces the risk of heart attack, heart disease, and stroke. Treatment of sleep apnea can reduce the risk of complications.
How to treat apnea: a healthy lifestyle
First of all, traditional advice: a person who has been diagnosed with sleep apnea must change his lifestyle. There are patients who simply need to lose weight to get rid of sleep apnea. Excess body weight is one of the main causes of the disease.
Sleep apnea syndrome and weight are interrelated - 77% of overweight people suffer from various sleep disorders, and 70% of people with sleep apnea are overweight.
It was noticed that even with a slight decrease in weight, the quality of sleep increased, and vice versa: when treating apnea, a person began to lose weight.
In 2009, researchers at Sweden's Karolinska Institute led by Professor Martin Neovius showed that after 9 weeks of a calorie-restricted diet of up to 500 per day, overweight men experienced a reduction in sleep apnea symptoms of up to 21 attacks per hour.
The final study found that over the next year after losing weight, even though the men had gained most of the weight back, the improvement continued.
Even not with such a strict calorie restriction, but only 1200-1500 calories per day, a diet among a study group of 250 people in studies conducted by a professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine showed an improvement in the condition of patients 3 times more often than in the control group.
Be careful about the time before bed. The last solid meal should be no later than 4 hours before bedtime; 2 hours before bedtime, only a light snack in the form of kefir, cookies, or apples is allowed.
You need to give up alcohol before bed and not take sedatives - they cause a decrease in the tone of the pharyngeal muscles.
These factors provoke collapse of the wall of the airway lumen, which causes respiratory arrest.
You need to sleep on your side. Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue to retract during snoring, which again leads to an attack of apnea. To avoid turning over on your back in your sleep, just do a little life hack - sew a pocket on the back of your pajamas and put a tennis ball in it. The ball will put pressure on the back and wake up the sleeping person when turning. After 4 weeks of torment, the body will get used to sleeping on its side.
The pillow also affects the frequency of attacks. On a high pillow, the head takes an incorrect position and the respiratory passages are pinched. The pillow must be replaced with either a flat or orthopedic one. An even better option is to purchase a bed with a slightly raised headboard.
Positive pressure treatment
CPAP therapy, a method based on creating constant positive pressure in the respiratory tract, has recently become widespread for the treatment of sleep apnea - a temporary stop in breathing during sleep. To apply this method, a special CPAP machine is used.
Before going to bed, the patient puts a special mask on his nose and securely fixes it on his head so that it does not slip off during sleep. Through it, oxygen is supplied to the respiratory tract under pressure, which helps maintain the lumen of the respiratory tract in normal working condition.
The pressure level can be individually adjusted to better prevent airway collapse.
Thanks to CPAP therapy, blockage is eliminated, breath holding during sleep stops, sleep is normalized and the patient’s well-being improves from the first night of use.
Regular use of the device reduces the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension.
CPAP therapy is currently the most effective method for treating sleep apnea in patients with moderate to severe forms of obstructive sleep apnea.
In addition to CPAP equipment, more compact devices have been developed and are successfully used, also based on the positive pressure treatment method.
Special Nasal EPAP nasal devices have 2 valves that allow air to enter and prevent it from escaping. Nasal EPAPs are effective for people with mild disease and help reduce it to moderate disease.
They are also used for frequent travelers who have sleep apnea.
Intraoral devices
If blockage of the airways occurs due to retraction of the tongue or other structural features of the lower jaw, patients are recommended to use special intraoral devices during sleep.
All kinds of mouthpieces, mouth guards and other retainers push the lower jaw forward and keep the tongue from retracting. In this position, the airway lumen does not close at night.
These devices only help with mild forms of the disease.
Surgery
If sleep apnea is caused by causes that can be treated surgically, then a variety of surgical treatment methods are used, including:
- correction of the nasal septum;
- removal of tonsils and adenoids;
- Uvulopalatoplasty - changing the shape of the soft palate, partial/complete removal of the uvula, sometimes installing soft palate implants, etc.
To select the method of operation and the site of intervention, a dynamic assessment of the upper respiratory tract is performed using polysomnography or respiratory monitoring or other studies.
For many, single operations are ineffective; the effect can be achieved by multi-level modification of the upper respiratory tract, performed surgically simultaneously or in stages.
The standard protocol is uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (removal of the uvula, part of the soft palate, tonsils) with advancement of the genioglossus muscle, hyoid myotomy and maxillomandibular displacement (increases the space of the posterior airways).
The operations are performed using minimally invasive methods of laser and radio wave surgery.
The main benefit of the operation is that the oxygen saturation of arterial blood increases. In 2008
The Stanford Center for Somnology and Sleep Medicine published studies according to which 93.3% of operated patients achieved a normal level of life.
The surgery resulted in improvements in overall productivity, activity levels, social outcomes, mindfulness, communication, and personal life.
Medicines
Medicines are used primarily to treat central apnea, apnea that has different mechanisms than obstructive apnea.
For treatment, drugs such as acetazolamide or zolpidem and triazolam are used.
Unfortunately, long-term use of acetazolamide is poorly tolerated, and acetazolamide and zolpidem have certain risk factors. Therefore, only the attending physician can make a prescription.
As for obstructive apnea, several approaches to drug therapy have been developed:
- increased respiratory activity;
- tone of the upper respiratory tract;
- threshold of micro-awakenings
- suppression of REM sleep.
The effectiveness of these drugs has not been proven.
Treatment at home
At home, you can reduce the number of apnea attacks, and sometimes even cure if apnea syndrome occurs due to obesity. To do this, you need to follow a diet and give the body the necessary physical activity. For example, daily apnea training of the muscles of the soft palate will help improve muscle tone:
- Move your tongue forward as much as possible, tense it, and hold it for a couple of seconds. Do 30 times in the morning and evening.
- Move your lower jaw up and down, while holding it with your hand (also 30 repetitions).
- Grip a wooden pencil with your teeth as hard as you can for 4 minutes.
- Pronounce vowels clearly and loudly in any order.
With a regular approach and responsible execution, positive results will be visible within a month of training. Regular singing at home will effectively complement this training. During vocal exercises, exactly those muscles that fall during an attack are trained.
Another method of training the tone of the muscles of the upper respiratory tract can be considered ujjayi pranayama, during which the muscles of the nasopharynx and oropharynx are held in a tucked state during inhalation. The exercise is also called snake breathing. With regular yoga practice of “snake breathing”, a stable muscle stereotype is formed.
Some people find that a simple finger massage helps. You need to do it on an empty stomach and in front of a mirror. Open your mouth wide in front of the mirror and with your index finger go behind the tongue and for a couple of minutes (as long as possible) massage the muscles of the soft palate with a pendulum movement. Make more intense movements in the area up to the tongue. A 15-day course strengthens the muscles of the soft palate.
A few more tips:
- before going to bed, rinse your nasal passages with water and sea salt or aquamaris, drawing the solution into yourself;
- To facilitate nasal breathing, drip sea buckthorn oil 4-5 drops into your nose for 3-4 weeks.
List of used literature:
- Vein A. M., Eligulashvili T. S., Poluektov M. G. Sleep apnea syndrome. - M.: Eidos Media, 2002. — 218 p.
- Nikolin K. M. Sleep apnea syndrome (lecture for doctors). — St. Petersburg, 2005 — 21 p.
- Pustozerov V. G., Zhulev N. M. Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders: textbook. - St. Petersburg: SPbMAPO, 2002. — 13 s.
Source: https://PsySon.ru/bolezni-sna/kak-lechit-apnoe-sna.html
Sleep apnea (temporary cessation of breathing during sleep): causes and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome has a peculiarity. It is a risk factor for the progression of life-threatening exacerbations of blood vessels and the heart, such as stroke, impaired cardiac trophism, arrhythmias, and death. Most sleep apnea syndromes occur between 3 and 4 hours. About 80% of attacks are associated with breathing problems.
Causes of pathological apnea during sleep
To treat sleep apnea, your doctor must accurately determine the cause of your sleep apnea. There are a number of anatomical and physiological features that cause temporary cessation of breathing. Causes of apnea:
- pathologies of skull development;
- hypotonia of the muscles located near the respiratory organs;
- retrognathia - protruding lower jaw;
- too large neck due to obesity;
- enlarged tonsils or swelling of the palate;
- narrowness of the upper or lower jaw;
- the presence of polyps or other neoplasms in the respiratory tract;
- obstructive pulmonary diseases;
- defects of the nasal septum;
- The tongue is too large to fit in the mouth.
Also, sleep apnea can be caused by diabetes or obesity.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct causes of apnea, risk factors are also considered that do not guarantee the development of pathology, but increase the risk of sleep apnea. These include:
- Floor . Apnea syndrome occurs much more often in the stronger sex. Doctors attribute this to the fact that men weigh much more and have larger necks. But everything changes with age, since during menopause the female half becomes more vulnerable.
- Age . The peak incidence occurs between 40 and 60 years, but this does not prevent sleep apnea from occurring in a child.
- Genetics . If close relatives have a history of obstructive apnea, the risk of developing the pathology increases significantly.
- Abuse of tobacco products and alcoholic beverages.
Attention! Everyone needs to monitor their body weight, as obesity is a major risk factor.
Symptoms of apnea (OSA)
Reasons for suspecting the presence of sleep apnea syndrome are people’s complaints of poor superficial sleep, lack of a sense of vigor, constant impotence, and headaches. In adults, the ability to work decreases, attention and the ability to concentrate on anything decrease. Such people are very absent-minded and often do not remember what they did.
In addition to these symptoms, the following symptoms may appear:
- insomnia;
- sleep apnea;
- feeling of suffocation at night;
- dyspnea;
- regular nightmares that force you to wake up;
- excessive irritability;
- depression due to lack of sleep;
- severe hyperhidrosis;
- talking in your sleep;
- bruxism – teeth grinding;
- impotence in men and decreased libido in women;
- the need to constantly urinate at night.
Relatives say that night snoring appears. The patient himself cannot notice the cessation of breathing. Treatment of snoring and sleep apnea should be taken very seriously, as if not handled correctly the outcome can be fatal.
Diagnosis of apnea
The diagnosis is based on the patient's complaints and examination data. But since the symptoms are not typical and may not appear at all, additional diagnostics are required.
Many people wonder which doctor to see. The first step is to contact a therapist or take your child to a pediatrician. If the problem is serious, you will need to contact a somnologist.
Experts are more likely to use polysomnography.
With apnea, diagnosis is carried out very carefully. Polysomnography is a long procedure that takes approximately 8 hours.
Using special instruments, doctors examine the patient's sleep throughout the night. This method consists of recording vital signs such as respiratory arrest, brain waves, and their duration.
Based on the results, a final diagnosis is already made.
Apnea in children
Every parent wonders what it is and what threat to life it poses. Apnea in children is when a child stops breathing during the night. It leads to disruption of various parameters of the body's homeostasis.
It is important to know! The disease in children can be either a separate syndrome or a symptom of a disease.
The mechanism of appearance is determined by three types of conditions:
- central;
- obstructive;
- mixed origin.
Central apnea in newborns is associated with disruption of the respiratory center, which is located in the medulla oblongata. The most common reason is its insufficient maturity.
During a night's rest, the metabolic activity of biochemical processes decreases, which causes a decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. It is he who is the activator of the respiratory center. This is why the center shuts down when there is a lack of carbon dioxide.
The development of sleep apnea in children may be due to the fact that the nerve fibers that go to the respiratory muscles have not yet completely undergone the process of myelination. Due to the lack of a specific protein, the speed of impulse transmission from the central nervous system is greatly reduced.
An episode of apnea in children under one year of age of the obstructive type appears when the airway is obstructed. This occurs mainly during sleep. Babies experience relaxation of the smooth muscle fibers that are located around the respiratory tract. The result is a critical narrowing of the larynx. There are also a number of factors that provoke sleep apnea in children:
- serious illnesses and injuries;
- excess weight;
- serious nervous shock;
- conditions after surgery;
- acute inflammatory processes of the respiratory system.
The mixed type in children is observed with airway obstruction.
Stopping breathing is also often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- cyanosis of the skin;
- bradycardia;
- surges in blood pressure.
During treatment, it is very important to protect the child from stress and tension.
Apnea in premature babies
The body of a premature baby is characterized by pronounced immaturity of many organs and systems. This is especially true for the nervous system, which continues to develop over a long period of time. The breathing centers located in the medulla oblongata are no exception.
The process of myelination of nerve fibers plays a special role. In premature babies it is not fully implemented. When a premature baby sleeps, the sensitivity of the respiratory center decreases and the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood decreases.
Apnea in premature babies occurs in most cases. In addition to the physical immaturity of the body, damage to the central nervous system can provoke the development of a pathological condition. Factors include:
- acute inflammatory process of the central nervous system;
- congenital anomalies of the medulla oblongata;
- increased pressure in the cerebral ventricular system;
- consequences of traumatic injury;
- metabolic changes in the blood.
If one of the pathologies described above is detected, it will need to be treated. This is the most effective treatment, after which all symptoms will go away. For severe cases, medications may be prescribed.
How to get rid of apnea
When wondering how to treat apnea, you must first adhere to preventive measures. In mild and not advanced cases, when treating sleep apnea, you must follow simple recommendations:
- Lose excess weight. It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat a balanced diet.
- Avoid eating before bed. More than three hours should pass after dinner.
- Quit smoking and drinking alcohol. If you can’t completely quit, then at least don’t smoke three hours before bedtime.
- When sleeping, take a comfortable position in bed. Most often, apnea attacks occur in those people who prefer to sleep on their back, so you need to learn to sleep on your side.
- Make sure that nasal breathing is free. For this purpose, it is necessary to use special patches.
But for some patients, the above recommendations will not be enough. If the patient has a defect in the nasal septum or has polyps, then surgical intervention will be required. In adults with central apnea due to jaw defects, special devices may be used. They are inserted into the oral cavity and correct the position of the jaw during sleep.
Often, in case of pathology, additional ventilation is used. Using the device, oxygen is released, which prevents the airways from narrowing. The device cannot treat sleep apnea, but it can avoid complications and allow the patient to get enough sleep.
Attention! In case of pathology, it is prohibited to give the patient sleeping pills, as they relax the muscles and the person may simply suffocate.
Having considered what apnea is, you can understand how complex this disease is and what consequences it can entail. Don't think that it's just snoring and just take the problem lightly. In the early stages, the disease can be easily treated at home. And if you consider which doctor treats you, then contact a somnologist. Only he will indicate the cause and treatment.
Source: https://www.ObzorMatrasov.ru/narusheniya-sna/sindrom-obstruktivnogo-apnoe-sna.html