Previous article Next article
Snoring or rhonchopathy is a breathing disorder during sleep, manifested in the form of vibrations of the soft tissues of the palate.
Inhalation is accompanied by a loud rattling noise, which causes a lot of inconvenience to household members and sometimes wakes up the “snoreer” himself. A person almost always knows about his illness, especially if he does not live alone. But only in rare cases is snoring given importance.
The condition must be diagnosed in time to prevent the development of serious diseases and begin treatment.
Ronchopathy and its causes
Snoring, which seems harmless at first glance, leads to chronic respiratory failure. The body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, as a result of which it becomes depleted. Snoring can lead to cardiovascular diseases (including stroke), and fainting often occurs.
Snoring acts as a harbinger of many diseases, including those that can lead to death.
This is a syndrome of apnea, circulatory disorders, heart function, and thyroid disorders. To prevent the condition from getting worse, snoring needs to be controlled. When do you really need to rush to a specialist and start treatment? You should consult a doctor immediately if snoring is accompanied by at least one of the following symptoms:
- constant drowsiness during the daytime;
- suffocation, lack of air during sleep;
- short-term pauses in breathing;
- fainting;
- heart rate disturbances, heart pain.
Treatment of complicated ronchopathy is carried out under the supervision of a physician. Its absence in case of serious breathing problems can lead to progression of the disease, including death.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of rhonchopathy may indicate other diseases, so the examination is carried out especially carefully.
If you complain of attacks of suffocation, oxygen deficiency and sleep apnea, obstructive bronchitis should be excluded. To do this, it is enough to do laboratory tests and a chest x-ray.
Lack of air, after which fainting occurs, also has slightly different causes and is usually not associated with rhonochopathy.
Diagnosis of snoring begins with collecting anamnesis, visual examination of the nasopharynx and listening to breathing.
If necessary, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed. Examination of the body to determine the causes of snoring includes several stages:
- lab tests;
- instrumental examination of the respiratory tract;
- somnological studies.
The results of each of these diagnostic methods will help the doctor diagnose “ronchopathy”, determine the degree of development of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Results of laboratory tests and examination
There are several biological markers that will allow you to accurately say what happened to the patient: fainting, sleep apnea or a heart attack. The doctor will be interested in the following indicators in the blood test:
- red blood cells;
- hemoglobin;
- partial voltage CO2, O2;
- pH in arterial blood.
The quantitative value of these markers allows us to identify impaired gas exchange in the lungs. Laboratory diagnosis is one of the reliable methods to differentiate snoring from other disorders such as fainting and bronchitis.
The inspection is carried out using special tools and apparatus. For example, an otolaryngologist performs an endoscopic examination of the ENT organs to determine the cause of upper airway obstruction.
Somnological studies
Diagnosing snoring is not the most common procedure, because breathing disorders occur at night during sleep. Several devices have been invented that make it possible to track the causes of snoring and record the performance of the heart and blood vessels at this time. Among them are used:
- polysomnography – monitors the main physiological indicators of the human body during sleep for 8 hours. The patient sleeps as usual. Sensors are attached to his body, which do not cause discomfort. The device “records” ECG, EEG, heart rate, EMG, EOG and saturation indicators. The tone of the muscles of the nasopharynx, the nature of abdominal and thoracic breathing, and the patient’s sleep structure are described. The severity of snoring is assessed;
- cardio-respiratory monitoring - monitors ECG, heart rate and saturation, snoring intensity, activity of the pectoral and abdominal muscles during breathing, body position during sleep and air flow passing through the upper respiratory tract;
- pulse oximetry – consists of long-term measurement of saturation in arterial blood and heart rate indicators;
- respiratory monitoring – records snoring, hypopnea and apnea, oxygen saturation indicators. It is a system consisting of a pulse oximeter and a nasal cannula.
What are the reasons for children snoring during sleep?
Snoring is diagnosed on an outpatient basis.
Usually you need to spend a day in the hospital, but if the results are questionable, the procedure may be repeated. After assessing the collected indicators, the doctor will be able to tell exactly why the patient faints or snores. Treatment is prescribed.
Therapy methods
Due to lack of oxygen, fainting may occur and serious neurological disorders may develop. That is why breathing should be normal both day and night. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist after diagnostic procedures. Depending on the severity of the condition, it may be recommended:
Ronchopathy should be treated at the first symptoms: night snoring, fainting, lack of oxygen. The sooner action begins, the easier it will be to overcome the disease.
Previous article Next article
Source: https://hrapless.ru/priznaki-i-simptomy/hrap-diagnostika.html
What tests detect snoring and sleep apnea?
However, diagnosis is really necessary. Only with the help of special overnight studies can doctors reliably determine the form and severity of snoring, establish the causes of the disorder and, as a result, recommend the best and most effective treatment.
Computer pulse oximetry
This is a diagnostic method that is screening. During sleep, a special “clothespin” on the patient’s finger is used to determine the oxygen content in his blood.
The method helps to establish moderate and severe degrees of obstructive apnea, in which a person experiences cyclic drops in oxygen levels due to frequent stops of breathing during sleep.
Pulse oximetry does not claim to be absolutely reliable, but it can be used to identify those who most need help in order to send them for clarifying studies.
Respiratory and cardiorespiratory monitoring
These are more accurate studies, which in most cases are sufficient to diagnose snoring and sleep apnea. During the night, a number of parameters are recorded related to breathing, blood oxygen saturation, and with cardiorespiratory monitoring, also to heart activity.
Polysomnography
Polysomnography (PSG) is the most accurate test with which you can diagnose any sleep disorder. The study is also useful in determining the causes of sleep disorders.
To obtain diagnostic results, 18 sensors are attached to the patient’s body, which record his physiological parameters during sleep. These sensors allow you to find out body position, breathing and cardiac activity, eye and limb movements, chin muscle tone, brain activity, etc.
A cumulative assessment of the above data allows us to draw a conclusion about the presence of any sleep pathology.
PSG is considered the best method for detecting snoring and apnea.
It determines the form, severity of the disease, as well as concomitant sleep disorders that can be combined with these disorders (for example, restless legs syndrome, bruxism, etc.).
Today, only polysomnography makes it possible to study the patient’s condition in more detail and, based on this, prescribe the best treatment.
How to cure snoring and obstructive sleep apnea?
Typically, CPAP therapy is recommended for moderate to severe sleep apnea. This is a hardware technique that prevents snoring and sleep apnea, showing its effect from the first night of treatment.
Uncomplicated snoring and mild apnea can be treated with anti-snoring mouth guards. Among the huge variety of such devices, it is advisable to highlight Sonite, a domestic development made from a thermolabile material.
Sonite can be bought at a pharmacy, it is affordable, easily modeled for a specific person, and it is also the smallest model among anti-snoring guards.
Accordingly, its use is comfortable, safe and in many cases quite effective.
Often, the mechanism of snoring involves a factor such as weakening of the muscles of the tongue, soft palate, and pharynx. To strengthen them, there are special exercises.
Overweight people are advised to take care of their weight to get rid of snoring. Smoking and drinking alcohol often cause snoring; To eliminate the effect of these reasons, it is recommended to give up bad habits.
There are also a variety of sprays, bracelets, and positional treatments.
The most important thing you should know about snoring and obstructive sleep apnea is that they are not easy to treat on your own, and they are difficult to tell apart. To successfully get rid of the problem of snoring and apnea, it is best to consult a doctor. He will identify the causes, form and severity of snoring, recommend relevant treatment and ensure that it is successful.
Source: https://buzunov.ru/articles/hrap-i-sindrom-obstruktivnogo-apnoe-sna/kakie-obsledovaniya-vyiyavlyayut-hrap-i-apnoe-sna/
Snore
Snoring is a specific process that accompanies a person's breathing during sleep and is characterized by a distinct rattling, low-frequency sound and vibration.
This phenomenon has been familiar to every person since time immemorial and in most cases is of a periodic natural nature.
However, in medicine there is such a thing as “ronchopathy”, essentially the same snoring, but described in terms of varieties, etiology and treatment.
Many people tend to joke about a relative or friend who snores, but in fact, this process can lead to serious physiological and mental consequences, as well as death. To answer the question “how to get rid of snoring?”, it is necessary to understand the features of this phenomenon.
Causes of snoring
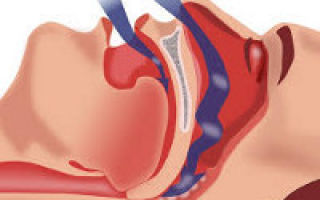
Snoring occurs when air flows through the airways, which are narrowed for one reason or another. At this time, parts of the pharynx come into contact, which creates vibration and rattling.
The causes of snoring can be deviated nasal septums, excess weight, and enlarged tonsils.
In this case, they often resort to surgical intervention, which makes it possible to somewhat correct the physiological characteristics of a person.
The causes of snoring can be congenital, that is, breathing problems are caused by narrow nasal passages, malocclusion, or an elongated uvula. All these signs can be detected at an early age.
Often the problem is provoked by factors such as decreased thyroid function, chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, drinking alcohol or sleeping pills, and smoking.
With age, the muscles of the pharynx lose tone, which can also cause snoring.
If snoring occurs during a cold or after a single excess of alcohol consumption, you don’t have to worry. After proper rest and the necessary treatment of the underlying disease, breathing will quickly recover.
But if this phenomenon repeats frequently and for unknown reasons, then you should seek medical help, because snoring disrupts, first of all, proper sleep. A person feels tired and “broken” all day, and cannot concentrate.
Efficiency noticeably decreases, conflicts begin in the family, since the problem spreads to other family members who are deprived of normal rest due to the loud sound.
Many people become interested in the topic of “how to get rid of snoring” only when the situation becomes critical, or they learn about more serious consequences than lack of sleep and quarrels with loved ones. We are talking about apnea - holding your breath during sleep, which is the result of complicated snoring.
Stopping the natural respiratory process can have different frequency during the night, but at a high frequency, a person suffers from a lack of oxygen in the blood. It has been observed that holding one's breath during sleep often causes heart attack and stroke.
There are also frequent cases of sudden death during sleep, so timely treatment of snoring is required.
Diagnosis of snoring
If oppressive snoring occurs, it is recommended to consult an ENT doctor, who, first of all, will find out the anatomical features of the patient’s respiratory system. It also makes sense to visit an endocrinologist and therapist.
In order to accurately determine the presence of pauses in breathing during sleep as a complication of snoring, they resort to a special modern study - polysomnography.
Sensors are attached to the patient’s skin and connected to various devices, which, in turn, record ECG, brain “waves,” respiratory movements and other parameters of the human body during sleep.
Under the supervision of a specialist, the patient is monitored throughout the night, after which adequate anti-snoring remedies are selected.
If surgery is needed to correct the airway, this study is also necessary to fully monitor the patient’s condition.
The first step in treating snoring is to change your body position while sleeping - on your side. In this position, the walls of the pharynx are less in contact, which somewhat improves sleep. Doctors also recommend purchasing a special orthopedic pillow that fixes the head parallel to the body. You should immediately discard bedding that creates a bend in the cervical region.
Further treatment for snoring directly depends on its cause. About half of people suffering from this type of disorder have problems with nasal breathing. Therefore, to eliminate snoring, it is necessary to restore respiratory function.
To improve sleep, it is recommended to clean the nose with sprays and rinses, but such anti-snoring remedies are not always effective. Radical treatment consists of operations to correct the nasal septum, remove nasal polyps and tonsils.
If a person has a normal structure of the respiratory organs, then a list of measures to reduce excess weight is drawn up, medications or physiotherapeutic treatment are prescribed.
Special oral appliances also help. These anti-snoring remedies increase the clearance of the pharynx by fixing the lower jaw or moving it forward slightly. Unfortunately, not every person can get used to such devices, but the effectiveness of their use is quite high.
Sometimes they resort to nasal dilator strips, which make the wings of the nose a little wider and free up additional space for 30% of the air.
When breathing stops due to snoring, the use of CPAP therapy devices, which are hermetic nasal masks connected to a small compressor, is required.
Thus, during sleep, a person is constantly provided with air passing through a flexible tube under pressure.
As a result of using this device, the airways do not close and the flow of vital air is not blocked.
Source: https://zdorovi.net/bolezni/hrap.html
Snoring: causes, treatment. How to get rid of snoring
The specific low-frequency vibrating sound produced by a person or animal when breathing during sleep is called snoring. The pathological process that causes snoring is caused by excessive relaxation of the muscles of the uvula, palatoglossus, soft palate, and other structures of the pharynx.
More than 30% of adults suffer from snoring, and in people over 60 years of age the frequency increases to 60–65%. This is a very common phenomenon, known to almost every person.
More often, close people of the snorer suffer from snoring, in whom the process of falling asleep is disrupted and various neurological disorders develop. In rare cases, a sharp vibrating sound disturbs the person himself, and he wakes up from it.
In addition to being a problem for others, snoring is dangerous for the snorer, since during sleep his body does not receive enough oxygen, as a result, all organs, especially the brain, experience hypoxia.
The appearance of loud sounds accompanying breathing during sleep is a harbinger of the development and the main symptom of a serious disease called obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA).
This pathology is characterized by a sudden cessation of pulmonary ventilation during sleep. The duration of respiratory arrest ranges from 10 to 30 seconds, less often in severe cases up to 2–3 minutes.
Sometimes such a syndrome leads to the death of a person.
Mechanism of snoring development
The pathogenesis is based on pathological relaxation of the muscles of the oropharynx - palatoglossus arches, uvula, soft palate - or obstruction of the airway due to some obstacle.
The passing air stream, instead of passing directly into the lungs, swirls, causing vibration of the soft structures of the pharynx. This is accompanied by an unpleasant sharp rattling sound.
Further changes in the walls of the respiratory tract lead to the development of OSA.
Causes of snoring
The following factors may impede airflow:
- Thornwald's cyst;
- swelling of the pharynx and tongue due to allergies - urticaria or Quincke's edema;
- inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa during rhinitis, including allergic rhinitis;
- nasal polyps;
- hypertrophy of the tonsils with angina;
- adenoids;
- deviated nasal septum due to injury;
- congenital anomalies of the upper respiratory tract:
- underdevelopment of the upper or lower jaw;
- narrowed lumen of the pharynx;
- elongated uvula;
- Macroglossia is an abnormally enlarged tongue.
- malignant or benign neoplasms of the nasopharynx;
- pathological displacement of the jaw due to injury;
- deposition of fat in the walls of the pharynx, observed in obesity;
Source: https://bezboleznej.ru/hrap
Mouth breathing. Snore
Problems caused by mouth breathing.
Nasal breathing is a normal type of breathing for humans. When we breathe through our nose, most of the suspended particles (dust), bacteria and viruses in the air are first filtered in the nasal cavity. When inhaling air through the nose, the first obstacle to large dust particles is the hairs in the anterior nasal cavity.
Here, with the help of the secretion of the sebaceous and sweat glands, lumps are formed from dust particles, which are subsequently blown out. The leading role in the protective function of the nose belongs to the mucous membrane. The watery mucus produced by the mucous membrane humidifies the inhaled air, and bactericidal substances kill pathogens.
Warming of the air occurs with the help of blood vessels and thin-walled veins located in the nasal cavity. In addition, the air inhaled through the nose puts pressure on the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, which leads to excitation of the respiratory reflex and a greater expansion of the chest than when inhaling through the mouth.
Violation of nasal breathing, as a rule, affects the physical condition of the entire body.
Weakening the tone of the orbicularis oris muscle subconsciously causes mouth breathing. When you breathe through your mouth, all particles, viruses and bacteria contained in the air directly enter your body without going through a strict filtration procedure. A large number of external harmful substances settle on the tonsils.
As you know, tonsils perform barrier and immunogenic functions. Coupled with stimulation by dry and cold air, the load on the tonsils increases many times over, which causes frequent inflammation of the tonsils and their inability to show their protective properties.
As a result, the body's immune system as a whole is weakened.
With chronic inflammation, the tonsils turn from a barrier to infection into a reservoir containing a large number of microbes and their waste products.
The tonsils produce blood lymphocytes, so the infection can spread through the blood throughout the body, causing damage to other organs.
Chronic tonsillitis also directly or indirectly affects the development of collagen diseases (a group of diseases in which there is systemic damage to connective tissue and blood vessels), skin diseases (atopic dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis) and damage to peripheral nerves (sciatica, plexitis).
When people breathe through their mouths, the muscles of the oral cavity are weakened, and accordingly the tongue cannot take its natural position. After falling asleep, muscle tension decreases even more, causing the root of the tongue to move and narrow the airways. Air passing through narrow respiratory tracts causes vibration of relaxed soft tissues, which creates the sound of snoring.
In addition, when the soft tissues in the back of the pharynx collapse and close the airways, and the tongue, under the influence of gravity, finally blocks the passage of air into the lungs, a temporary cessation of breathing occurs, the so-called “Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome.”
If the airways are not completely blocked, “Obstructive Hypnoea” syndrome occurs, characterized by slow, shallow breathing.
The patency of the airways is also impaired by inflammation of the bronchioles. Chronic inflammation of the bronchioles is called “Bronchial asthma”. The results of this disease are a violation of the supply of oxygen to the lungs with air and difficulty in breathing and gas exchange.
Using the Patakara face-building device helps restore the tone of both superficial and deep muscles of the face and neck. The facial muscles overlap and intertwine, but they are all connected to the orbicularis oris muscle.
Therefore, in addition to tensioning the facial muscles, we also strive to restore the normal position of the tongue.
When muscle strength increases, breathing through the nose comes naturally, which will entail positive changes in the body, eliminating problems caused by mouth breathing.
Continuous use of Patakara 4 times every day for 3-5 minutes can significantly improve your current health!
Eliminate snoring, bad breath, dry mouth and sleep apnea with Patakara
Do you snore in your sleep? Do you wake up with a dry mouth? Do you have bad breath? If yes, then there is nothing to congratulate you on - you breathe through your mouth! According to research, about 50% of adults and 80% of children breathe through their mouth rather than their nose (also known as oral respiraton).
Oral breathing is not a natural way of breathing for our body and it leads to many health problems. Mouth breathing is known to cause snoring, bad breath, dry mouth, and sleep apnea (holding your breath). Oral breathing is the process of inhaling air through the mouth.
This increases the evaporation of saliva in the mouth, resulting in bad breath. Saliva is responsible for the breakdown of food, and also has an antibacterial function, limiting and preventing the proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity. When we breathe through our mouths, we essentially remove this protective layer, which inevitably leads to bad breath.
While breathing through the nose (or nasal breathing) is the correct and natural way of breathing for our body. Nasal breathing has many beneficial qualities that mouth breathing does not.
Nasal breathing allows you to filter the inhaled air, remove germs and dust from it, and at the same time regulate the temperature and humidity of the air before entering the body. It also prevents inflammation caused by oral breathing.
The swollen trachea eventually releases once filtered air enters the body. In the video below you can clearly see the difference between nasal breathing and mouth breathing.
The air we inhale is filled with dust, germs and other harmful substances, but nasal breathing has the ability to purify the air we inhale. This function alone prevents bad breath and snoring, since the mucous membrane inside our nose is able to filter out up to 80% of microparticles that are present in the inhaled air.
During nasal breathing, the temperature and humidity of the inhaled air is also regulated. This system prevents our trachea from drying out and microorganisms from multiplying.
If our lungs become too dry or too cold, it becomes difficult for the mucous membrane to effectively process the inhaled air, and as a result, this process affects the efficiency of oxygen absorption.
If we use nasal breathing, the increase in humidity and temperature of the inhaled air prevents a decrease in oxygen consumption even in cold seasons or climates.
When using oral breathing, harmful germs enter directly through the mouth into the trachea and lungs.
This allows microbes to easily attack surrounding tissues, which also leads to decreased oxygen consumption.
During sleep, most of the muscles in our body are relaxed, including our facial muscles. When mouth breathing occurs, the oral tissue surrounding our chest is destroyed, resulting in airway obstruction. This not only causes snoring, but also obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Therefore, it is vital for our health to switch to breathing through the nose.
Additionally, many people have been found to snore after drinking too much alcohol. Large amounts of alcohol cause swelling of the mucous membrane, which leads to suffocation and involuntary oral breathing.
However, compared to nasal breathing, mouth breathing has the same low oxygen consumption efficiency and dissolved oxygen levels in blood cells. People who drink alcohol frequently or have allergies are more likely to suffer a heart attack.
One of the main reasons is the decrease in dissolved oxygen levels in the blood due to mouth breathing.
So how do you switch from mouth to nasal breathing? How to get rid of snoring, bad breath, dry mouth and sleep apnea? The answer is simple, use a special device: Patakara will strengthen your facial muscles.
When we strengthen the facial muscles around the mouth and throat, the tongue rises and touches the roof of the mouth. When this happens, the mouth is naturally closed. As a result, our body switches to nasal breathing.
Thus, it will stop snoring, prevent bad breath, help avoid dry mouth in the morning and stop sleep apnea.
Most people today care about their health and spend a lot of time and money on it. However, exercises for the face and overall health of the body are often overlooked, although our brain and large muscles are in our head. Patakara is a device that stimulates and strengthens all the muscles of the face and neck.
At the same time, it also normalizes/enhances cerebral blood circulation and leads to improved brain function and prevents diseases. The device is non-invasive and requires only 5-15 minutes of training per day. Significant health effects can be seen after just 3-8 weeks of daily exercise.
Use Patakara to treat snoring, sleep apnea, bad breath and dry mouth in the morning!
Mouth breathing does not allow the inhaled air to be filtered, so microorganisms colonize on the trachea, which can lead to inflammation.
Snoring and sudden cessation of breathing during sleep
Snoring is dangerous!
Many people think that the only problem with snoring is how much it disturbs the people around them. This is a very dangerous misconception! The body requires a certain amount of oxygen for its smooth functioning. When health is normal, the body is able to obtain sufficient oxygen.
When there is an obstacle to the passage of air in the respiratory tract, we hear the sound of snoring, and less air enters the body. To prevent hypoxia, the brain forces the respiratory muscles to work with overload, and also connects additional muscle groups.
The worst option is a complete blockage of the airways, which leads to a sudden stop in breathing during sleep - “ sleep apnea ”.
Snoring causes a person's brain and body to suffer from two types of harm simultaneously. The first is that the brain does not get the opportunity to rest during sleep.
There are messages from all parts of the body about hypoxia, this causes the brain to continuously give orders so that the corresponding organs inhale oxygen with greater effort. Another harm is insufficient oxygen in the blood.
Both factors lead to the following diseases: high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, heart attack.
- HISTORY OF A PATIENT suffering from sudden cessation of breathing during sleep (addition: complete absence of teeth):
- Gender: male
- Age: 70 years old
The patient underwent a sleep examination in an inpatient setting (three days and two nights). Sudden apnea during sleep was diagnosed. The doctor recommended n-CPP treatment (treatment using a special device) to the patient.
However, the patient could not sleep with this equipment and abandoned treatment. After 11 months, the patient returned to the doctor, as the problem of sleep apnea still bothered him. The doctor changed his recommendation and referred him to Dr. Hosokawa for treatment.
Hosokawa), a well-known sleep specialist in Japan. Dr. Hosokawa recommended the patient to use the Patakara exercise machine. After 5 weeks of training, the patient again underwent sleep diagnostics in the hospital where he was previously treated.
The results of the examination showed obvious improvements in the oxygen content in the blood, as well as the absence of respiratory arrest during sleep.
Causes of snoring
There is a common belief that the causes of snoring are 50% problems with the nasal cavity, and 50% problems with the oral cavity. However, based on the results of the patients I have recommended using Patakara, I believe the oral cavity is the “main culprit.”
In 2001, the work of Professor Kimu from the University of Southern Carolina was published. He claims that astronauts who do not snore while on Earth begin to snore in space because they are in a state of weightlessness.
This article made me even more confident in my opinion.
When sleeping on your back, the root of the tongue and the tissues of the soft palate, under the influence of gravity, are reduced to the airways, reducing their patency. Since the body needs a strictly defined volume of air, the speed of air flow increases, which causes the sunken tissues of the tongue and soft palate to produce a vibrating sound. This is the sound of snoring.
Source: https://patakara.ru/clauses/informatsiya/rotovoe-dykhanie/
Snore
Snoring is a breathing disorder during sleep, accompanied by vibration of the soft tissues of the larynx and nasopharynx and the production of a low-frequency rattling sound. May indicate the presence of ENT pathology, excess weight or functional disorders.
Snoring is often accompanied by attacks of respiratory arrest (apnea), which leads to oxygen deficiency of vital organs and systems and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Snoring leads to disruption of adequate sleep for the snorer and the people around him.
Snoring is a breathing disorder during sleep, accompanied by vibration of the soft tissues of the larynx and nasopharynx and the production of a low-frequency rattling sound. May indicate the presence of ENT pathology, excess weight or functional disorders.
Snoring is often accompanied by attacks of respiratory arrest (apnea), which leads to oxygen deficiency of vital organs and systems and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Snoring leads to disruption of adequate sleep for the snorer and the people around him.
Every fifth person on Earth snores while sleeping. About 3% of the population suffers from periodic stops in breathing during sleep (sleep apnea).
Due to certain anatomical features of the structure of the respiratory tract, men are more predisposed to snoring. For every woman who constantly snores, there are 10 men.
Every tenth man in the world experiences sleep apnea from time to time. Holding your breath in some cases lasts more than 1 minute.
Snore
In a sleeping person, the muscle tone of the upper respiratory tract decreases. Normally, during inhalation, the pressure in the chest cavity becomes negative and air is “sucked” into the lungs.
An excessive decrease in the tone of the muscles of the larynx and pharynx leads to the fact that the soft tissues of the upper respiratory tract are drawn inward along with the air. The source of sound during snoring is the vibration of the walls of the pharynx, soft palate and root of the tongue.
Apnea occurs when soft tissue closes and blocks the airway during inhalation.
The likelihood of snoring increases with certain diseases and conditions. All causes of snoring and sleep apnea can be divided into two large groups: anatomical and physiological.
Anatomical causes of snoring
The risk of snoring and sleep apnea increases with anatomical narrowing of the upper airways. The airways can become narrowed by a deviated nasal septum, polyps in the nasal cavity, congenital narrowness of the nasal passages and pharynx, enlarged tonsils, adenoids, an elongated uvula, a small, displaced lower jaw, and excess weight.
Functional causes of snoring
Narrowing and decreased muscle tone of the airways can be caused by fatigue, lack of sleep, smoking, drinking alcohol and sleeping pills, and decreased function of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland. The tone of the pharyngeal muscles decreases with age and with the onset of menopause in women.
Snoring, even if it is not complicated by pauses in breathing, can cause multiple micro-awakenings. Episodes of such awakenings are not realized or remembered. Disruption of the normal structure of sleep leads to the fact that the body does not have time to rest during the night. As a result, a person suffering from snoring does not get enough sleep, gets tired quickly, and experiences constant drowsiness.
Snoring that is not accompanied by pauses in breathing does not always disrupt the structure of sleep. Snoring with periodic pauses in breathing in response to a lack of oxygen triggers a cascade of pathological reactions.
Apnea can occur up to 500 times per night and lasts on average 10-20 seconds. Every time breathing stops, the body suffers from a lack of oxygen.
The brain reacts to hypoxia and sends the body a signal to wake up.
Normal sleep consists of several successive phases. With frequent awakenings, the brain does not have time to reach deep stages of sleep - periods of complete muscle relaxation and lower blood pressure.
Constant micro-awakenings activate the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, a person suffering from apnea has increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and sometimes heart rhythm disturbances.
Blockage of the airways during snoring, accompanied by sleep apnea, leads to a sharp decrease in intrathoracic pressure.
The airways collapse during inhalation, the chest continues to exert a suction effect, playing the role of a kind of “bellows”. A “vacuum trap” is created into which blood is sucked.
The limbs and internal organs suffer from a lack of blood, while the heart is overloaded with excess fluid.
The constant effect of these pathological mechanisms on the human body leads to the development of hypertension, arrhythmias, heart attacks and strokes. Patients with snoring accompanied by apnea often experience problems with potency. They are more likely to get into accidents due to drowsiness and decreased attention.
People who snore are prone to abuse of sleeping pills and alcohol. Patients with snoring find themselves in a kind of vicious circle: snoring disrupts sleep, the patient begins to use sleeping pills, the tone of the muscles of the larynx and pharynx decreases even more, and snoring intensifies.
Patients are advised to normalize their weight and stop using sleeping pills. Typically, snoring occurs when a person sleeps lying on their back.
There are special techniques for developing new reflexes - the habit of sleeping on your stomach or side. To prevent snoring, patients can use special devices (various pacifiers and nasal dilators).
For severe snoring and obstructive apnea, a special sleep mask is used. Medicines for snoring are ineffective.
The choice of surgical treatment tactics depends on the cause of snoring. Correction of the nasal septum (septoplasty), removal of nasal polyps with a laser, and removal of enlarged tonsils (tonsillectomy) are performed. Plastic surgeries are performed on the pharynx and soft palate: uvulotomy and uvulopalatoplasty. Classic surgical techniques, laser surgery and radiosurgery are used.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_lor/snoring
Review of the main causes and factors of snoring
Snoring is a common problem, affecting almost 50% of men and 30% of women. It disrupts sleep, causes sleep deprivation, exacerbates stress reactions, affects mental performance and contributes to obesity.
The medical literature identifies the main cause of snoring as weakness and loss of tone in the muscle layer of the upper respiratory tract and neck.
Classic causes of snoring
Analyzing the mechanism of development of pathology, you need to understand what snoring is? This is the vibration of the soft tissues of the respiratory tract as air passes through. Sound occurs due to a combination of factors:
- Excessive softening and sagging of nasopharyngeal tissues, muscle relaxation.
- Narrowing or blocking of the airways in the mouth or nose.
- Excess weight, accumulation of fat in the neck.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol, which causes muscles to relax during sleep.
- Nasal congestion, creating vortex air currents during mouth breathing.
- Retraction of the tongue, which reduces the size of the airway.
Treatment methods involve changes in lifestyle. Sometimes the patient is sent to a dentist, otolaryngologist or surgeon if there is a suspicion of the existence of individual structural features of the jaw, nasopharynx, or post-traumatic changes in tissues. In some cases, snoring is caused by abnormalities in the structure of the nose or mouth: a weak soft palate, a large uvula, turbinate openings, or weak tongue muscles.
Deviations are corrected surgically or with dental aligners. Patients are often referred for a sleep study or polysomnography. The causes of snoring are deeper, affecting dysfunction of the cranial nerves.
Posture of a modern person
Modern lifestyle is associated with changes in posture. Working at a computer, driving, using tablets and smartphones leads to a forward displacement of the head:
- the neck loses normal lordosis;
- the chin moves away from the neck;
- cervical vertebrae become hypermobile.
As a result, the long extensors of the neck relax, the short flexors that push the chin back, and the sternocleidomastoid muscles are overloaded. Overstrain of the suboccipital muscles moves the occipital bone forward, tension in the sternocleidomastoid muscles fixes the temporal bones. As a result, the airways become compressed and severe snoring progresses over time. Stretching the neck further loosens the vertebrae. The cervical region contains important nerves - the phrenic and vagus. They regulate the functioning of internal organs and, most importantly, tighten soft tissues along the way.
To restore their normal function, you need to independently strengthen the long extensors of the neck - return the chin and head back relative to the body:
- Place both hands on the back of your head, press your chin into your neck, applying pressure with your head on your hands.
- Lying down, determine the side in which it is more difficult to turn your head, and, having performed a turn, massage the neck muscles on the opposite side with a soft touch of your knuckles.
One way to work with cranial nerves is osteopathy.
Lower jaw, stuffy nose and snoring
The mandibular joint, formed with the temporal bones, plays an important role in posture, proper functioning of the nasopharynx and neck. The muscles that move the jaw often spasm during times of stress. Overexertion when moving the head forward leads to the following reactions:
- range of motion decreases;
- blood supply to the joint and muscles decreases;
- blood vessels and cranial nerves are blocked;
- lymphatic drainage stops.
As a result, the tissues of the larynx swell, the bones become immobile, and the muscles cannot contract normally. Snoring during sleep or apnea may occur.
To reduce the load on the joint, you need to massage the chewing muscles: open your mouth slightly, feel the painful cords between the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the lower jaw.
Then place your palms on the temporomandibular joint (next to the tragus of the ears), press lightly and lift up, holding for 1-2 minutes, then down with a similar hold.
The condition of the muscles in the mouth area is reflected throughout the body. The facial skull is made up of bones, most of which are very small. Correct rhythmic movement and interaction of all elements of the skull determines healthy breathing:
- sinus drainage;
- free air circulation;
- innervation of pharyngeal tissues.
Trauma to the skull is a common cause of snoring due to limited bone mobility. Dental treatment is an intervention that changes the movement of the upper jaw, palate, and nasal bones. One of the sudden causes of snoring can be the installation of a filling, crown or implant.
Braces can completely change your posture because they shift the position of your head. After traumatic brain injuries and visits to the dentist, osteopathic treatment has long been used in foreign practice.
Dental mouth guards, by helping to keep the jaws in the correct position, prevent snoring, but the cause remains unchanged.
Deviated nasal septum
The nasal septum is formed from bone and cartilage parts. The bone, located behind and above, consists of the vomer and the plate of the ethmoid bone.
The position of these bones is associated with the occiput during the cranial rhythm heard by osteopaths.
Almost 60% of adults have a deviated nasal septum and snoring - this is a combination that is associated with impaired movement of these structures. The causes of violations may be:
- injuries to the face, nose, back of the head;
- infectious diseases of the nasopharynx;
- installation of braces;
- birth injuries (torticollis);
- difficult birth, entanglement with the umbilical cord;
- incorrect posture;
- pneumonia, sore throat and other internal diseases.
Such connections indicate that the nasal bones cannot be considered separately from the skull, neck, chest and body as a whole. Deformation of cartilage tissue can be caused by autoimmune disease and chronic inflammation. The reason is a violation of the innervation of the mucous membranes, overdrying.
Snoring and breathing problems
Allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma are independent factors of snoring and sleep disturbances. There is also another breathing mechanism that is rarely taken into account: diaphragmatic breathing. The diaphragm acts as a pump to fill the lungs. When breathing, the lower ribs expand to the sides.
Without a diaphragm, the chest moves exclusively upward, and lordosis at the level of the thoracolumbar junction increases. As a result, the chest becomes fixed during inhalation and blocks many structures passing through it: the alimentary vein, portal vein, ligaments of the liver and stomach.
Snoring is mentioned in connection with inflammation of the esophagus, heartburn and reflux or the reflux of stomach contents. A spasm of the diaphragm pinches the esophageal tube, tightening it or preventing food from passing through. As a result, the sphincters weaken, the walls of the esophagus become inflamed, and the ligaments spasm more strongly. A dry cough and pressing pain in the area of the xiphoid process appear.
It is enough to restore diaphragmatic breathing, relax the muscles on the side of the neck, and control the lumbar deflection to improve the quality of sleep without snoring.
Mouth breathing in children
The nasopharynx of children has narrow passages. Adenoids perform one of the functions of protecting the body from infection. Mouth breathing is common among children 2-6 years old; almost every tenth child snores.
Mouth breathing is an adaptation, the need to relieve the muscles of the jaw and back of the head, and return the chin to its place.
During childbirth, children may experience injuries associated with compression of the skull by the pelvic bones or the hands of obstetricians. As a result, incorrect patterns of breathing, swallowing, movement and posture are established. If you breathe with your mouth open, the tongue will fall from the upper palate, slide into the throat, blocking the airways.
Restless children's sleep affects behavioral problems, the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and inhibits cognitive development. Enlarged tonsils are the number one cause of childhood snoring during sleep and sleep apnea. Allergies provoke the growth of adenoids, making nasal breathing difficult.
Prolonged mouth breathing affects the narrowing of the facial skull, forms narrow nasal passages and sinuses, and increases the risk of developing rhinitis and sinusitis. Abroad, osteopaths work with snoring children, restoring the mobility of the skull bones as early as possible.
Snoring and sleep position
People who sleep on their backs snore. In fact, this sign indicates weakness of the muscles of the pharynx, hyoid muscles, spasm of the diaphragm, and incorrect posture. The right pillow can reduce snoring by aligning the cervical vertebrae and opening the phrenic nerve. Its pinching disrupts deep breathing and provokes spasm of the scalene muscles.
The side-lying position also causes compression of the shoulder joint and neck, the load falls on only one side of the jaw, and an imbalance develops. Sleeping on your stomach forces you to turn your head to the side and overstretches the muscles on one side of the body. This is the most dangerous position for apnea, disorders of the diaphragm, although it masks the symptoms of snoring.
Diagnosis of sleep apnea
Apnea is a short-term blockage of breathing during sleep, which leads to oxygen starvation, weakness, drowsiness, and deterioration of mental activity. Snoring usually accompanies symptoms of early dysfunction.
The diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea is established on the basis of polysomnography. Using modern acoustic technologies and 3D visualization, doctors take measurements of the respiratory tract, identifying where a person’s snoring comes from.
Orthopedic devices or surgery are used for correction. Hypoglossal nerve stimulation has only recently been tested against sleep apnea.
The hypoglossal nerve emerges from the jugular foramen, forms a loop, and follows the three cervical vertebrae to the muscles attached to the hyoid bone.
It innervates the muscles of the tongue, so its compression is responsible for almost 60% of cases of apnea. The nerve is pinched at the level of the occipital condyle, the junction of the skull and neck. A canal passes through the condylar base.
The work of an osteopath on the first vertebra and occipital bone, strengthening the long extensors of the neck is sufficient to correct the dysfunction.
Snoring correction methods
An otolaryngologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist in the case of thyroid dysfunction can analyze the causes and treatment of snoring. The most common factor is the need to sleep with your mouth open due to nasal congestion. Vasoconstrictors relieve symptoms and make breathing easier through the nose.
A device that fixes the lower jaw replaces the work of the masticatory muscles and allows you to keep your mouth closed. Dental treatment for snoring involves the use of a mouthguard, which changes the shape of the jaw and moves it forward during sleep, opening the airway.
Such devices can hold the tongue and soft palate and resist tissue vibration.
Surgical treatment is carried out after consultation with an ENT surgeon and sleep diagnosis. Excision of the uvula, soft palate with laser or electrocoagulation, and work on the palatine bones are used. Surgeries cause many side effects because they involve invasive intervention. Osteopaths have long figured out what causes snoring, as they study the mobility and structure of the skull. Osteopathic treatment relieves muscle tension, returns normal interaction to the bones, which reduces nasal congestion, frees nerves and blood vessels. In one session, the specialist works with the diaphragm, its innervation, and organs, the prolapse of which can cause loud snoring.
To treat the disorder, you need to change your lifestyle: achieve weight loss, reduce the load on the cardiovascular system, improve joint mobility.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59f9a0235a104fe1e0d6eaf6/5a9ce88300b3dd8810ad8b07