Transurethral resection of the prostate is a minimally invasive operation to remove pathologically overgrown prostate tissue through access through the urethra . Despite the apparent simplicity of the technique, the operation requires high professionalism of the doctor. The likelihood of developing complications after a TUR of the prostate largely depends on the type of instrument and the patient’s health status.
Indications and contraindications for TOUR
The main indication for TUR is hyperplasia (prostate adenoma). The prostate gland hugs the part of the urethra just below the opening of the bladder. As prostate tissue grows, the lumen of the urethra decreases, as a result of which the neck of the bladder suffers from oxygen starvation.
As a result, the man begins to suffer from urinary retention or leakage. TUR involves the removal of excess tissue that interferes with normal urination . The prostate itself (the capsule with tissue remains) remains in place.
It cannot be removed using the TUR method due to the extensive venous network (important venous plexuses will inevitably be damaged).
When is a TURP of the prostate gland recommended?
- Patients for whom maintaining sexual function is important.
- For obesity and the presence of cardiovascular pathologies.
- In case of relapse of adenoma.
- Localized prostate cancer (which can be completely removed from the gland).
TUR is carried out in cases where previous methods (conservative, hyperthermia) were ineffective.
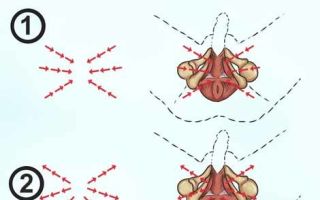
The operation is performed using a resectoscope - a hollow tube through which instruments are brought into the surgical area.
Resectoscope with loop General scheme of TUR
Contraindications for TOUR:
- Arthrosis and other pathologies of the hip joints that prevent the legs from spreading to the sides (this is the position the patient is in during TUR);
- Urethral strictures (impossible to insert the device);
- Bladder capacity less than 100 ml;
- Tumors and defects of the bladder walls;
- Varicose veins of the urethra and bladder neck;
- Severe concomitant diseases.
Advantages of the TOUR:
- There are no cuts or scars.
- Short recovery period.
- The bladder is not injured.
After a TUR, the tissue can be examined for the presence of malignant cells, and after the laser it is completely evaporated.
Types of TOUR
Depending on the type of cutting element (loop), the following types of TUR are distinguished:
- Monopolar : one pole is the knife, the other is the body. To conduct impulses, liquid must constantly circulate between them. An outdated but still used method. It is fraught with severe bleeding, the development of TUR syndrome, and is dangerous for those suffering from cardiovascular diseases. Used only for TUR of the prostate with a volume of no more than 80 cm3 - to quickly remove tissue, otherwise too much electrically conductive solution will be absorbed into the blood.
Urologist, surgeon Maxim Aleksandrovich Ryabov talks about the indications, the course of the operation, and the consequences of transurethral resection of the prostate
- Bipolar : both poles are at the ends of the loop, resulting in a high temperature, effectively sealing the vessels. Saline solution is used as an auxiliary fluid, which is not dangerous to the body. You can spend more time on the operation and remove the nodes better. The method is suitable for excision of formations with a volume of up to 150 cm3, as well as for patients with cardiovascular diseases.
- Plasmokinetic : a “super pulse” is formed around the loop - a plasma corona, which compacts and seals the cut tissue, but does not overheat the surrounding tissue.
Plasmokinetic transurethral resection of prostate adenoma is recognized by most urologists as the least traumatic and most effective method of treating hyperplasia.
Preparation
List of preliminary tests (valid for 30 days):
Be sure to tell your doctor about all the injuries you have suffered to the brain and spinal cord, and about the medications you are taking. Antibiotics are prescribed before and after TUR. You should not eat food 8 hours before; on the day of surgery you must cleanse your intestines.
Operation technique
For TUR, spinal anesthesia is usually used as pain relief - an injection into the spine. During the operation, the patient may feel pressure and touch, but not pain. If there are contraindications, endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the respiratory function is performed by a special apparatus.
Spinal anesthesia before TOUR
The patient is placed on a urological chair or operating table with his legs spread apart, the groin area is treated with an antiseptic solution and covered with sterile sheets. The groin must first be shaved or hair removed using hair removal cream.
Urethral zones
A lubricating antiseptic gel is first injected into the urethra, and then the resectoscope itself. The place to which the device is inserted is indicated in the figure below by number 5 (prostatic part of the urethra):
First, the bladder is examined, the condition of the closing sphincter is assessed, and then the hyperplasia is removed (layer-by-layer excision with a loop). Bleeding vessels are immediately coagulated (cauterized) with a loop.
Cutting tissue during TUR
The doctor monitors all actions on the monitor. In a number of clinics there are two of them, one of which is turned towards the patient if he is under spinal anesthesia and wants to see the progress of the operation.
The process of cutting tissue (real operation) with detailed instructions from the doctor. Schematic video of the TUR prostate operation.
The goal of TUR is to restore the patient’s ability to urinate normally. To do this, it is necessary to clear the urethra of growths. This is done in several ways (depending on the direction of growth of education):
- Removal of a small amount of tissue (10-20%) from the bladder neck or middle lobe of the prostate. This method is called “pseudo-TUR”.
- Excision of 30 to 80% of the tissue (partial TUR), in which a cone-shaped passage is formed.
The removed tissue is pushed into the bladder, and then these remains are washed out and removed through a special channel of the resectoscope. Some of them are sent to the laboratory for histology to rule out cancer through cellular analysis.
With hyperplasia, the PSA level increases. After TUR it will drop (but not to zero), since there will be much less tissue producing this antigen.
Monopolar TUR should last no longer than an hour, otherwise the risk of postoperative complications will significantly increase. It is important not to go beyond the spermatic tubercle (inferior landmark) and the neck of the bladder. Otherwise, the orifices of the ureters and the walls of the bladder will be damaged, which will also lead to serious postoperative complications.
To speed up the healing of the urethral walls after surgery, a catheter is inserted into the bladder - a thin flexible tube through which urine will be drained randomly within 2-3 days. The doctor regularly checks its quality. When the urine becomes light, the catheter is removed.
Postoperative period
After TUR, resuscitation is not required; the patient is immediately transferred to a regular ward. There should be no pain even after recovering from anesthesia. Your legs won't move for about two hours - this is normal. On the first day, it is advisable not to get out of bed to avoid headaches. After 3-4 days the patient is discharged home.
After the catheter is removed, urination will be painful. To relieve symptoms, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed for a week.
Early rehabilitation lasts about two weeks . During this time, it is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of liquid per day to flush out the bladder.
You can have sex and start doing Kegel exercises after 3 weeks.
For 2-4 weeks after TUR, the patient will be bothered by frequent urination and dripping of urine caused by severe irritation of the receptors. There is no need to worry about this as it is a natural phenomenon. The problem of leakage can be solved with the help of urological pads.
Immunologist Ermakov Georgy Aleksandrovich talks about rehabilitation after TUR of prostate adenoma
After excision of hyperlasia, a fairly deep wound remains, covered with burnt tissue.
Subsequently, it will begin to be rejected, which may lead to intravesical bleeding. The patient may detect blood in the urine on days 7, 14 and 21 after TUR.
Complete cleansing of the wound from damaged tissue and restoration of the epithelium occurs after 6-18 months.
For the first 3-6 weeks, you should not lift anything heavier than 2.5 kg or drive. After a TOUR, it is generally advisable to sit less and not on a hard one (it is recommended to use a donut-shaped pillow with a hole for the perineum to avoid pressure). To activate blood flow, you definitely need to move.
It is important to follow nutritional recommendations. No special diet is required, but spicy, salty, smoked and fatty foods, as well as alcohol and coffee should be excluded from the diet to avoid urethral irritation. Eat less potatoes, rice and animal protein to prevent constipation.
Complications after surgery
Complications after TUR are due to the specifics of the technique.
Hyperplasia almost always occurs against the background of chronic prostatitis, therefore, after excision of part of the tissue, inflammation in the remaining tissue often worsens (in 13% of patients).
Damage to the excretory ducts of the gland also occurs, so the organ may become non-functional - the prostate will no longer enrich sperm with its secretion in the same volume, which will complicate natural conception.
Retrograde ejaculation diagram
An obstacle to conception is also retrograde ejaculation, which occurs in 75-93% of patients (when seminal fluid flows into the bladder instead of the urethra). The complication arises due to cutting of the muscle that closes the lumen of the bladder neck (this is necessary to expand the lumen).
The second common problem after TUR is the formation of the so-called pre-bladder. This is a cavity that remains in place of the removed prostate tissue, a widening of the area of the urethra under the bladder.
Chronic inflammation often develops and is maintained in the prevesicle, stones are formed, which is why the patient periodically suffers from painful urination (dysuria).
In this regard, open adenomectomy is better.
Immunologist Ermakov Georgy Aleksandrovich on possible complications after TUR of prostate adenoma
A significant disadvantage of TUR: most clinics use resectoscopes with a large tube caliber (24 or 27), so patients have to bougienage (dilate) the urethra, which is traumatic. When the instrument is forcibly advanced, the mucous membrane is damaged, and scar tissue and strictures subsequently develop (in 18% of patients).
The most dangerous consequence of the operation is TUR syndrome. This is a severe violation of the body’s water and electrolyte balance, fraught with death in the absence of emergency measures. The reason is excessive absorption into the bloodstream of the irrigation fluid used during monopolar TUR.
Life after surgery
Many men are afraid of becoming impotent after a tour. According to doctors, this is possible if the operation is performed with a monopolar instrument in the hands of a not very competent surgeon. If TUR is done correctly, the erection will even improve due to increased blood flow. The quality of orgasm will also not be affected.
As for retrograde ejaculation after TUR, in this case it is necessary to strengthen the tone of the smooth muscles of the bladder neck. Kegel exercises combined with deep squats, as well as special medications, will help.
Urination will be completely restored within a maximum of 6 weeks. During this period, it is important not to fall into depression, otherwise not only erectile function, but also health in general will suffer.
You can drink alcohol (not strong and in small quantities) no earlier than six months later, but it’s better not to. Alcohol provokes inflammation, weakens the effect of medications, slows down the healing process, and weakens the immune system.
Prices and where the operation is performed
Below are approximate prices from clinic websites. The exact cost of the institution is not indicated, since it depends on the category of complexity of the operation, which is determined by the volume of the gland, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Examples of clinics and costs:
- GMS Hospital (Moscow): RUB 385,720;
- Network of “SM-clinics”: from 60 thousand rubles;
- Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy (Moscow): 105 thousand rubles.
In state clinics and city hospitals, the cost of a monopolar TOUR starts from 13 thousand rubles.
Patient reviews
Alexander, 47 years old: “I did a TOUR in Moscow City Clinical Hospital No. 50. My wife is 12 years younger, I thought that the end of my family life had come, but after a couple of months I fully recovered. To eliminate problems with urination, I took a course of Vesicare.”
Evgeniy, 44 years old: “My father had a rather large adenoma removed at the Pirogov clinic in St. Petersburg using a bipolar loop. There were no special complications. We struggled with the natural consequences of urine leakage for about 3 months.”
Conclusion
Doctors consider TUR the most precious operation of all transurethral endosurgery methods, since it requires talent and specific knowledge from the specialist. The effectiveness of the manipulation and the patient’s condition after it depend on this. When choosing a clinic, be sure to clarify what method and who performs the removal (reviews of doctors are on the forums).
Sources:
Source: https://muzhchina.info/prostata/adenoma/tur
Transurethral resection of the prostate and features of the operation
When treating prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia, doctors try to the last to preserve the organ without resorting to surgical treatment. However, this is not always possible, and then transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is used.
The operation is associated with some risks and has its own characteristics. We will talk about who this treatment is indicated for, how to prepare for it and recover from it, in the article.
To whom and when is TURP performed?
Surgical manipulations on the prostate gland affect the functioning of the entire male reproductive system, and therefore should be carried out when indicated.
For acute and chronic prostatitis, doctors first prescribe medications, physiotherapeutic methods, recommend lifestyle changes and monitor the results.
If they are unsatisfactory and the patient’s well-being worsens, surgery may be performed.
Indications for transurethral resection of the prostate are:
- chronic prostatitis, if there is thickening of the prostate tissue;
- calculous prostatitis, especially complicated by stones in the bladder or kidneys;
- prostate adenoma (BPH) in the second or third stage;
- prostate cancer;
- cystic formations on the prostate gland.
TURP is the procedure of choice for men who have previously had open surgery or want to preserve reproductive functions. Also, a similar method is needed in case of acute urinary retention,
Transurethral resection of the prostate helps get rid of dangerous symptoms and prevents metastasis in stage 1 and 2 cancer, but does not cure the disease itself. Therefore, TURP can only be used in complex therapy.
How to prepare for surgery
Successful resection of the prostate gland is impossible without preliminary preparation, during which the man undergoes an examination and changes some aspects of his life. You will need to consult with doctors of various specializations, undergo laboratory tests, and use some instrumental diagnostic methods.
Before TURP, a man undergoes the following types of tests:
- general blood and urine tests;
- coagulogram;
- microflora testing, syphilis;
- blood group and Rh factor;
- allergy tests for anesthetics.
The patient must undergo TRUS of the prostate, fluorography, and ECG. One part of the methods allows one to determine the localization and size of the pathological process, the other allows one to understand which method of anesthesia is permissible to use and whether the patient will tolerate general anesthesia.
Antibiotics may be prescribed at the preparatory stage if an infection is detected and corticosteroids if there is an increased risk of bleeding during surgery. In the latter case, TURP may be delayed for 2-3 months. 2 weeks before the appointed date, some medications are excluded, including those that affect blood clotting.
The man must also prepare for resection, for this the day before he needs:
- provide a light dinner, do not eat after midnight;
- take a shower, shave your pubis, scrotum and perineum;
- do not take medications unless prescribed by a doctor.
Immediately before the operation, the patient is allowed to sign an agreement and is informed about the possible risks. No one will perform surgical treatment without a signature.
How is TURP done?
Transurethral resection has a number of advantages over the suprapubic method - the patient recovers faster and there is less risk of postoperative complications.
Visualization allows excision of diseased tissue with high precision, which could not be achieved with an open approach.
Also, after transurethral resection, there are no traces of surgical intervention; all manipulations are carried out through the urethra and the skin is not disturbed.
The main device is the resectoscope.
This is a complex device, which is a tube about 30 cm long and up to a centimeter in diameter, equipped with a portable telescope and surgical instruments with which tissue is excised and blood vessels are cauterized. Through the same tube, the accumulated fluid is removed before inserting the catheter, as well as excised prostate tissue and stones.
The operation is carried out approximately in the following sequence:
- The man lies down on the operating table.
- After achieving an analgesic effect, a resectoscope is inserted into the urethra.
- The device is directed into the bladder, examined from the inside, and attention is paid to the prostatic urethra.
- After the examination, the doctor uses surgical instruments to remove the affected prostate tissue.
- The bladder cavity of the prostate capsule is inspected for bleeding. The destroyed blood vessels are cauterized by electric current.
- If there is no bleeding, the resectoscope is carefully removed.
- A Foley catheter is inserted through the urethra, which is a multi-channel tube with a balloon at the end into which air is pumped.
A Foley catheter ensures the outflow of urine and fluid from the bladder, prevents bleeding and protects the prostate gland from unwanted pressure from adjacent organs. As soon as blood is no longer visible in the withdrawn fluid, the Foley catheter is removed.
Laser resection of the prostate gland is also performed, which is a more effective method of combating certain prostate disorders. The essence of the operation is the same, but instead of electric current, a laser beam is applied to the organ tissue, therefore the resection is more accurate and the risks of postoperative complications are insignificant.
For whom is TUR of the prostate contraindicated?
Any surgical intervention involves an impact on a number of organ functions, and therefore has its contraindications. Transurethral resection of the prostate is no exception. Some of them are relative and require elimination, while others completely exclude the possibility of such manipulations.
Relative contraindications to TURP are:
- body temperature is higher than normal;
- infectious processes in acute course;
- high blood pressure;
- the need to take drugs that change blood clotting.
In these cases, the operation is performed only after the symptoms disappear, or 2-3 weeks after the end of the course of contraindicated drugs. Some doctors maintain the same period after the last cigarette smoked - smoking is also a relative contraindication.
The following situations and diseases are absolute contraindications to TURP:
- oncological processes, except prostate cancer stages 1 and 2;
- problems with the heart or lungs;
- insufficiency of functions of vital organs (the operation is possible with spinal anesthesia);
- age over 70 years;
- serious pathologies in the intestines;
- conditions in which it is impossible to insert a resectoscope into the urethra.
Contraindications may include enlarged veins in the pelvic area, as well as hemophilia. In these cases, the doctor may opt for laser vaporization or refuse resection altogether.
The final decision on surgical treatment is made by the doctor, so you need to carefully choose a specialist.
Consequences and complications after TU of the prostate
Regardless of the professionalism of the doctor and the technique used, resection of the prostate may fail.
The most common complication after TUR is retrograde ejaculation, a pathological condition in which a man experiences orgasm during sex, but no sperm is released.
This is due to the fact that the direction of movement of the ejaculate changes and the seed enters the bladder. The condition does not threaten the patient's life and does not affect sexual activity, but often causes infertility in men.
In some cases, relapses occur after TUR. To eliminate them, a repeat operation is performed, but not earlier than after 2-3 years.
Transurethral resection, even performed with a laser beam, may have side effects or complications. Most often, postoperative bleeding develops. This condition can be fatal for those who have bleeding problems or are taking medications that affect this. For this reason, after the TUR, the man is under observation in the hospital.
Other complications after surgery may include:
- urinary problems due to urethral stricture;
- proliferation of adhesions and scars with subsequent prostate dysfunction;
- vision problems and disturbances of consciousness due to the fluid used to rinse the cavity during surgery entering the blood;
- inflammation in the prostate, urethra, intestines;
- urinary incontinence, which can occur in most men and is caused by a violation of the innervation of the sphincter.
The last complication in many men goes away on its own after a year. Some require specific treatment.
The development of complications is influenced by the choice of technique, the professionalism of the surgeon, the duration of the operation, the functioning of the body and other factors.
Regardless of the technique chosen by the doctor, after surgery it will take some time to restore normal functions. This period is called rehabilitation.
At this stage, the doctor observes the patient, prescribes certain medications, and orders lifestyle adjustments.
Ignoring the specifics of the rehabilitation period can cause dysfunction or serious complications.
To prevent unpleasant consequences, a catheter is installed in a sick man for 2-10 days, depending on the method of resection of the prostate. With its help, urine is evacuated from the bladder and blood clots and tissue particles are removed from the organ. After removing the catheter, some troubles may begin:
- feeling of discomfort;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pink urine.
These are normal conditions that disappear after a week. During this period, you need to go to the toilet every half hour for the first 3-5 days, then once an hour - you should not allow your bladder to fill.
During the rehabilitation period, water consumption of up to 2-2.5 liters per day is prescribed and the diet is adjusted - the following are prohibited:
- fried and fatty foods;
- smoked meats and marinades;
- highly salted foods.
Preference is given to steamed or boiled food. It is good to include fermented milk products, lean meats and fish, and cereals in your diet.
Physical activity after transurethral resection of the prostate is limited. The first days you can’t get out of bed at all, then you need to move, but carefully. For one and a half months after surgery, the following are prohibited:
- sex in any position;
- lifting weights;
- playing sports, cycling.
Prohibitions can be lifted if prostate resection was done laparoscopically or using laser vaporization, but such an exception remains at the discretion of the doctor.
For men it is recommended:
- to walk outside;
- perform exercises from the exercise therapy complex;
- move without squatting or sudden movements.
For the first two weeks, you need to take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to prevent infection. Laxatives may be prescribed to prevent constipation. You cannot take any medications without a prescription.
Conclusion
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), especially performed with a laser, has the least risk to a man's health. The technique allows you to remove stones from the prostate gland and combat urinary disorders due to prostate adenoma, but is used in complex therapy.
The duration of the operation can reach several hours. Recovery will take about two months, and the man must strictly follow the doctor's instructions and avoid sexual or physical activity.
You might be interested
Source: https://prostatits.ru/lechenie/transuretralnaya-rezektsiya-prostaty.html
Transurethral resection of prostate adenoma (TURP) - preparation for surgery, consequences
If you have been diagnosed with prostatic hyperplasia (Fig. 1), and we are talking about the need for surgical intervention, you should know that in medicine for the treatment of prostate pathology there is transurethral resection of the prostate (TUR).
Transurethral resection of the prostate is the “gold standard” among bloodless laser surgeries and has proven advantages over open cavity and other interventions.
Rice. 1 — Prostate adenoma as an indication for TUR.
This type of surgical treatment uses a laser beam to vaporize or remove hyperplastic prostate tissue. Laser surgery lasts, on average, about an hour. To access the prostate tissue, instead of making an incision in the abdominal wall, natural openings, in particular the urethra, are used.
TUR is an alternative to open interventions on the prostate gland.
Indications for TOUR
Modern means of self-defense are an impressive list of items that differ in their operating principles. The most popular are those that do not require a license or permission to purchase and use. In the online store Tesakov.com, you can buy self-defense products without a license.
When will surgery help?
Common indications for resection are:
- Deterioration in quality of life due to persistent dysuric disorders associated with prostate pathology. Despite the ongoing drug therapy, complaints persist of a weakened urine stream, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, urination at night from 3 to 6 times per night, and the desire to urinate a short time after urination.
- Chronic and acute urinary retention. If acute urinary retention inevitably leads to emergency medical care, then to determine chronic urinary retention it is necessary to perform an ultrasound, according to the results of which the volume of residual urine reaches up to 600-700 ml.
Who can have surgery?
Since this type of treatment for prostate adenoma is considered a gentle method of intervention, the therapy method is suitable both for patients with a large prostate volume without concomitant diseases, and for patients with:
- cardiovascular pathology;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- endocrinological diseases;
- concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system;
- history of surgical interventions on the bladder, intestines, prostate gland;
- desire to maintain erectile function;
- combination of prostate hyperplasia with recurrent inflammation;
- suspicion of oncological pathology in the prostate.
But, like any other surgical procedure, the intervention has strict indications and contraindications, and the final decision on the use of this particular technique is made by the urologist individually, taking into account the condition of each individual patient.
Types of prostate surgery
In urology, there are three types of surgery to treat prostate diseases.
Public method
When carrying out this type of intervention, an incision is made in the suprapubic region, and the hyperplastic prostate gland is removed transvesically, i.e. through the bladder.
Surgery is associated with a large number of complications, requires a long time and has a significant risk for the patient.
During an open operation, blood loss is an impressive amount, which contributes to the further development of anemia in the patient and leads to a lengthening of the rehabilitation period.
Considering the significant area of tissue alteration (damage) and the risk of postoperative bleeding when the walls of the bladder are stretched due to filling with urine, an irrigation system is used to wash away clots, which requires the installation of a urethral catheter and a functioning epicystostomy.
- Hospitalization takes about 4-5 weeks.
- Long-term complications of open prostatectomy include:
- If the patient has severe extragenital diseases, this type of surgical procedure is contraindicated, and as a palliative method of urinary diversion in case of acute urinary retention, epicystostomy was performed - removal of an elastic tube from the bladder through a surgical opening.
- The advantages of the operation include:
- the ability to visualize regional lymph nodes and take material for histological examination, which is important if prostate cancer is suspected to determine the stage of the process and further management tactics.
- radical solution to the problem: with open prostatectomy, the recurrence of further development of hyperplasia (proliferation of gland tissue) was minimal.
Laparoscopic surgery
The laparoscopic type of operation allows the removal of the hyperplastic prostate through small incisions under visual control.
With this surgical procedure, a biopsy from regional lymph nodes is possible if a tumor process is suspected, but, as with open prostatectomy, a complication of the operation is erectile dysfunction and sperm reflux into the bladder (retrograde ejaculation). The percentage of other complications during laparoscopic interventions on the prostate gland is lower.
Transurethral resection
To perform resection (excision), a special surgical instrument, a resectoscope, is inserted into the bladder through the urethra and, using a loop, areas of prostate tissue growth are excised using the destructive effect of a laser beam (see Fig. 2). The operation is performed under spinal anesthesia, which is considered a gentle type of anesthesia for the patient.
Rice. 2 — Transurethral resection of the prostate.
Control over the ongoing manipulations occurs using high-precision optics. To ensure visualization, fluid flows in and out through the resectoscope channels, which significantly reduces tissue trauma.
Surgical interventions on the prostate gland, depending on the laser used, are divided into:
- Laser ablation (vaporization), in which enlarged prostate tissue is burned (evaporated) using a laser;
- Laser enucleation, in which the laser beam replaces the surgeon's scalpel.
Rice. 3 - Result of the operation.
Vaporization is suitable as a surgical aid for small prostate volumes, and for large volumes it is preferable to perform enucleation.
After the operation is completed, a Foley catheter is installed into the bladder through the urethra to create conditions for adequate urine outflow. Unlike other methods of surgery, the duration of the catheter in the bladder does not exceed 2-4 days.
Installing a drainage tube performs the following functions:
- irrigation (prevents the formation of blood clots and blockage of the urethra);
- provides an “empty” bladder condition, which helps prevent bleeding.
Thus, taking into account the minimal percentage of complications, short rehabilitation period, high probability of maintaining sexual function, the possibility of providing assistance to patients with concomitant pathology, the possibility of taking material for biopsy, transurethral resection surgery for prostate pathology is more preferable.
Preparing for surgery
It is necessary to undergo a clinical and urological examination for hospitalization:
- laboratory diagnostics (CBC, OAM, blood biochemistry, blood for syphilis, viral hepatitis B and C, HIV infection, blood for prostate-specific antigen (PSA), feces for I/g).
- instrumental diagnostics include ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder, prostate gland with monitoring of residual urine, uroflowmetry (measurement of urinary flow rate), ECG, FL-graphy.
- consultation with a therapist and other specialists if there are concomitant diseases.
Sometimes, as additional examination methods, survey and excretory urography is prescribed to clarify the functional capacity of the kidneys and pathology of the genitourinary system, and MRI of the pelvic organs.
Recovery period
The recovery period usually proceeds smoothly and without complications. The hospital stay takes 10-12 days.
Spontaneous urination is restored within 2-4 days in almost 100% of cases after removal of the Foley catheter.
Subsequently, the patient goes under the supervision of an outpatient urologist and is on home antibacterial anti-inflammatory therapy.
Consequences of the operation
Undesirable consequences after TOUR are quite rare. But given that laser resection is a surgical intervention, the following complications may occur.
Early postoperative complications
- Postoperative bleeding. Hemostatic agents are prescribed; if ineffective, endoscopic diathermocoagulation is performed;
- Water intoxication syndrome. During surgery, it is possible for a large amount of water to enter the bloodstream; this is extremely rare.
Late postoperative complications
- Rejection of sperm into the bladder;
- Urinary incontinence. In a number of patients, it goes away after 2-3 months against the background of drug therapy (Vesicare, Vesomni, Urotol, Driptan, Spazmex) and special exercises;
- Urethral strictures. The complication occurs in one out of 10 patients, the condition is corrected with bougienage, and if there is no effect, urethroplasty is performed;
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the male genital area. With adequate therapy with antibacterial agents (Tavanic, Floracid, Suprax) they respond quite well to treatment.
Urologist Mishina V.V.
- Is your beard not growing? Or is it not as thick and chic as you would like? All is not lost.
- Cosmetics and accessories for proper care of your beard and mustache. Log in now!
Source: http://MenQuestions.ru/urologiya/transuretralnaya-rezektsiya-prostaty.html
How is transurethral resection of prostate adenoma performed?
Medical statistics show that half of the world's male population is faced with the problem of a benign tumor in the prostate gland.
Today, prostate adenoma is increasingly called benign hyperplasia (BPH). The older a person gets, the higher the risk of getting sick.
With this disease, prostate tissue grows and begins to put pressure on the bladder and squeeze the urethra, which leads to stagnation of urine.
An overfilled bladder leads to cystitis. And squeezing the urethra leads to pain and burning. There is a high probability of sand and stones appearing. Over time, if the adenoma is not treated, it becomes many times larger, causing even more serious complications. To prevent this process, effective treatment is needed. Modern doctors use prostate adenoma tour for this purpose.
What is TOUR?
Tour of prostate adenoma is a surgical intervention on the male gland, which stands for transurethral resection. Today, transurethral resection of prostate adenoma is the most used and effective treatment method. The essence of the procedure is to remove hyperplastic adenoma tissue.
The prognosis of the operation is favorable and allows the patient to forget forever about problems in the reproductive system and the ineffectiveness of the urination process. There are no special recommendations for the operation; it can be practiced for any size and weight of the gland.
When is surgery necessary?
Surgery for prostate adenoma is prescribed for benign tumors, fibrosis and chronic inflammation. In this case, the patient must have the following symptoms:
- Constant desire to go to the toilet “in a small way.” The passage of urine is accompanied by heaviness in the pubic area and severe cutting pain. The pain is diffuse in nature, spreading towards the spinal column and testicles. In advanced cases, urinary incontinence is possible; it is released involuntarily, drip-wise. The urge increases up to 10 times, especially at night.
- Urinary retention.
- The appearance of bloody or purulent inclusions in the urine. The presence of blood in the urine indicates bleeding due to damage to the vasculature. Pus is a sign of inflammation.
- The appearance of residual urine. It is formed due to the fact that urine cannot flow out through the urethral canal, which is narrowed or completely compressed by the prostate adenoma. It accumulates in the bubble, stretching its walls. Long-term disruption of fluid outflow can trigger the process of stone formation in the kidneys.
When choosing a treatment method, the doctor relies on the above symptoms, but this does not mean that a transurethral resection operation will be accurately prescribed. Usually treatment begins with conservative methods and in 80 - 85% of cases it helps.
Source: https://prostatitaid.ru/adenoma-prostaty/lechenie-adenomy/transuretralnaya-rezektsiya.html
Operation transurethral resection (TUR) of the prostate: indications, progress, rehabilitation at the MEDSI clinic
Benign prostate tumor is a common pathology, affecting more than half of men over the age of 50. The disease is successfully treated today. The most modern technique is transurethral resection (TUR) of prostate adenoma.
The technique is especially relevant for young patients. This is due to the fact that TUR of the prostate is an operation that allows you to preserve the organ and all its functions. The intervention is carried out at MEDSI by experienced specialists. Our doctors are fluent in modern techniques of minimally invasive surgery.
What is a TOUR of the prostate?
Transurethral resection of the prostate gland is an intervention that is performed to quickly remove overgrown organ tissue. As a rule, surgery is performed for a benign prostate tumor. At the moment, the technique is rightfully considered the gold standard of treatment.
This is due to the fact that in most cases, after surgery, the tumor disappears forever. In addition, the intervention is minimally invasive, has a short rehabilitation period, and a minimal number of contraindications and side effects.
After surgery, patients recover quickly and can return to their normal lifestyle within a few days. In the future, they are not limited to physical and sexual activity.
Indications for surgery
TUR operation for prostate adenoma is performed in the following pathological conditions of the patient:
- Urinary incontinence
- Large volume (more than 50 cm3) of residual urine (retained in the bladder after voiding)
- Frequent urination at night
- Obstruction of the urinary tract, making it difficult to urinate due to narrowing of the bladder neck or lumen of the ureter
- Painful urge to urinate
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Causing discomfort sagging bladder tissue with the formation of cavities
TUR surgery is often prescribed for patients who regularly suffer from genitourinary tract infections. Intervention is also carried out in cases of suspected malignant degeneration of prostate tissue.
Important! In this case, it is possible to save the organ only with early diagnosis and the general satisfactory state of health of the man. Your doctor will tell you about all the indications for a TUR of the prostate. He will determine whether intervention is required in your case.
Despite the fact that the TUR operation is widely used in urology, it is not performed on everyone. In some cases, other (including medication) methods are used.
Benefits of prostate tour
The main advantage of TUR is that the intervention is minimally invasive. It is performed without tissue incisions.
Thereby:
- Reduces the risk of infection
- Reduces patient rehabilitation time
- Risks of complications are eliminated
The TUR operation for an adenoma is performed without opening the bladder cavity. The integrity of the organ guarantees the rapid restoration of the urination process. If after an open operation the catheter is removed only after a few weeks, then after a TUR - after a couple of days.
TUR (prostate gland) is compared by some to laser removal of the organ. But these are completely different interventions! When exposed to laser, the organ is exposed to heat.
This delays the recovery of the urination process, for example. In addition, during laser surgery, a specialist cannot simultaneously collect material for histology (biopsy).
For this reason, the asymptomatic stage of cancer development may be missed, which will significantly complicate its further treatment.
Intervention technique
The intervention lasts 60-90 minutes. Anesthesia is usually administered by injection into the spine (epidural anesthesia). With this anesthesia, the patient is conscious. During the operation he cannot feel the lower half of his body. If necessary (including if the person being operated on wishes), the intervention is performed under general anesthesia (rather rarely).
Tour of the prostate gland: progress of the operation
Preparation
TOUR is performed on the operating table. The patient is placed on his back, and his legs are spread apart. After this, the genitals are carefully treated with an antiseptic. The patient is covered with sterile linen.
The operation itself
A special instrument is inserted into the patient's urethra. It is called a “resectoscope” and consists of 2 tubes and a working element (electric loop) connected to the prostate. Cutting off the affected organ tissue is ensured by the action of electric current.
A special liquid is supplied through one of the instrument channels. It removes the secreted blood and washes the prostate, providing good opportunities for the surgeon to visually monitor the progress of the intervention. All tissue removed during the intervention is removed using a pump.
End of intervention
The final stage of the operation is to control the integrity of all vessels. The surgeon also stops the bleeding. Only after this the operating instrument is removed from the patient’s urethra.
After completing all the main manipulations, the doctor inserts a catheter with a balloon, which injects a special fluid and tampons the intervention site. The procedure allows you to quickly stop bleeding from all small vessels.
In addition, the bladder is flushed through the catheter. This eliminates the risk of postoperative complications.
Transurethral resection of the prostate: consequences
Important! Despite the fact that upon completion of the intervention the bleeding stops, the risk of bleeding persists for up to 3-4 days. For this reason, the catheter remains in the urethra for the period recommended by the surgeon.
The patient remains in the hospital for about a week. All this time, specialists monitor the urination process.
If the patient experiences difficulty or any delay in urination, additional therapeutic measures are taken.
It is very important to restore the process of urination, since if the outflow of urine is difficult and the bladder is full, the risks of developing an infectious process increase.
Preparation for transurethral resection
The operation of TUR of the prostate gland does not require complex preliminary preparation. The doctor will tell you about all the features.
There are also general recommendations:
- 12 hours before the intervention you should refuse water and food.
- A week before surgery, stop taking aspirin and other medications that can thin the blood. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications that are currently prescribed for you. This will reduce the likelihood of surgical and postoperative complications, the risks of worsening the condition
- On the eve of the intervention, you should not be subjected to physical and emotional stress.
Important! Before TUR, the patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
It includes:
- Taking blood and urine tests
- Ultrasound
- ECG
- X-ray examination of the lungs
- Transrectal examination, etc.
Your doctor will issue a referral for testing. He will also inform you when the results of all tests will be ready. This will allow you to plan the date of the intervention and calmly prepare for it.
Complications
Correctly performed by an experienced surgeon, TUR of an adenoma rarely leads to complications.
However, the following consequences of the intervention may occur:
- Infection . The risk of such a complication with TUR is 30%. Typically, the process of spread of infection begins in the hospital after the intervention and is associated with certain hospital microflora. Microorganisms in hospitals have increased resistance to antiseptics and antibiotics. For this reason, the process of eliminating the infection is often delayed. The latest generation antibiotics are prescribed for prevention and treatment
- Strictures of the urethra . A condition such as narrowing of the urethra is considered very dangerous. This is because it leads to stagnation of urine and increases the risk of infection. Strictures are treated by dilating the urethra. Probes are inserted into the canal. Surgery can also be performed - canal plastic surgery.
- Urinary incontinence . Treatment of such a complication may involve prescribing the patient a number of physical exercises to increase the strength of the pelvic day muscles
- Retrograde ejaculation . This complication occurs quite often (in 70% of cases) and consists of the reflux of seminal fluid into the bladder. There is no threat to the health or life of the patient. Treatment of complications is carried out both conservatively and surgically.
- Impotence . This complication occurs only in 1% of cases. Treatment is carried out mainly by conservative methods. Surgery is prescribed only if therapy does not give the desired result for a long time
If you are at risk of any complications, your doctor will definitely warn you about them and tell you about preventive measures.
Postoperative period in the hospital
The patient remains in the hospital for 1-3 days after surgery. There are no restrictions on food consumption during the rehabilitation period.
Immediately after the intervention, a catheter is installed to ensure the outflow of urine. The duration of use of the catheter is determined individually and depends on the patient’s condition, his individual characteristics, the complexity of the intervention and other factors. Typically, the maximum period for using a catheter is 3 days.
During the day after surgery, there may be blood in the urine. Over time, the urine clears.
To prevent the risk of blockage of blood vessels, a special system is installed to ensure flushing of the bladder. For cleaning, a special solution is used, the composition of which is determined by a specialist.
The first day should be kept in bed. The patient is prohibited from standing up or undergoing physical activity. In order to prevent blood clots, some patients are recommended to perform simple exercises.
Complete rehabilitation after TUR operation usually lasts 3 weeks. After discharge from the hospital, the patient remains at home.
Recovery period
The operation is considered successful if recovery occurs quickly enough and without complications.
Important! Rehabilitation may be delayed if the intervention was carried out for a malignant tumor. The patient is additionally prescribed treatment aimed at reducing the risk of tumor recurrence and metastasis in other organs. Typically, therapy is carried out through irradiation and the introduction of chemicals into the blood.
Surgery TUR of the prostate gland: postoperative period at home
To ensure the fastest possible rehabilitation, the patient should:
- Strictly observe the drinking regime
- Introduce teas, juices and fruit drinks into your diet
- Stick to a diet
- To refuse from bad habits
Surgery TUR of the prostate gland: limitations of the postoperative period
Restrictions in the postoperative period concern not only nutrition and fluid intake, but also:
- Driving a car. You can get behind the wheel no less than a month after discharge from the hospital
- Sexual life. You can return to it a month after the intervention
- Physical activity. They resolve one month after surgery TUR of the prostate gland
The doctor will tell you about all restrictions. He will also determine the desired lifestyle of the patient during the rehabilitation period. If you follow all the recommendations, recovery will take place as quickly as possible and without the risk of complications.
Contraindications
The TUR operation in urology has a number of contraindications and is not performed if:
- Serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system
- Bleeding disorders
- Adenoma in the terminal stage
- Varicocele
- Carcinoma that has affected large volumes of the organ
- Stiffness of the hip joint
- Active inflammatory processes in the body
The doctor will tell you about all contraindications. He will determine whether the TUR technique is suitable for you or whether another operation is necessary.
Advantages of a prostate tour at MEDSI
- Experienced highly qualified doctors
- Competent junior and nursing staff
- Patient management by one specialist
- Comprehensive programs. The price of TUR operation for prostate adenoma is fixed. The cost includes the intervention itself and the patient’s hospital stay.
- High-quality preparation for intervention. Thanks to it, all risks of complications and side effects are reduced
- 24-hour medical care
- Comfortable accommodation in wards with all amenities
- Use of modern drugs
- Using the latest equipment
- Five meals a day, taking into account all medical indications
- Possibility to visit the patient at any time
- Possibility of placing non-resident relatives and friends in the MEDSI sanatorium in Otradnoye
To get a doctor’s consultation before surgery and undergo a full examination, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500 and make an appointment. Our specialists will always answer any of your questions, give you the estimated cost of services, conditions of hospital stay and tell you about all the intricacies of the upcoming intervention.
Source: https://medsi.ru/articles/operatsiya-transuretralnaya-rezektsiya-tur-prostaty-pokazaniya-khod-reabilitatsiya/