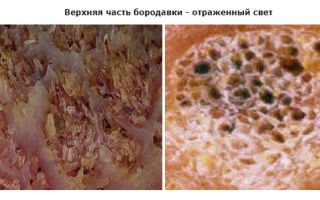
It is important to be able to recognize the disease so as not to miss the onset of a benign tumor.
What does a wart look like?
How to recognize her? A small elevation above the skin in the form of a dense nodule or papilla. The skin around this seal is noticeably lighter or darker than the main tone. The diameter of the formations ranges from 3 to 15 mm. These compactions do not occur alone; most often, a scattering of similar “plaques” forms on the face and limbs.
Areas of rough skin appear near or under the nail plate, and the same neoplasms appear on the sole. They are often oval-shaped and painful to step on. When palpated, they may be rough, flat or smooth. A large number of warts look like a spot or a conglomerate.
Structure of a wart
The top of the formation is covered with a crust, protecting it from external influences. Deep in the skin there is a root, which is penetrated by the finest blood vessels. Their purpose is to deliver nutrients so that cells can divide. This structure leads to profuse bleeding in case of trauma to the surface or root.
External part
The structure of the wart depends on the location. Plantar plants are characterized by their large size, root depth and rigidity. Other types of warts do not go so deep into the dermis, but they rise more above the surface. Therefore, they are easier to damage.
Section of a wart
The following layers and signs of a wart are visible:
- spot - a protruding part above the skin,
- the top layer of skin is the surface of the body,
- dermis,
- roots – located in the deep layers of the skin,
Warts under a microscope
Wart root
The roots are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrition to the outer surface of the formation. It is quite difficult to remove a tumor mechanically; in addition, by getting rid of it in this way, you can expect scars to appear, since the deeper layers of the skin will have to be tightened. It is almost impossible to tear out the root of a formation without leaving a trace.
The only exceptions are very small seals. At the root is a virus. If the growth is removed, the lower part remains. It can go deep and grow wide. Until the virus is removed, it will continue to grow. This is why it is so important to completely remove the root.
When magnified, you can see a black dot on the surface of the formation - this is what the root of a wart looks like. When you remove these seals yourself, you can see thin black veins - this is what the root looks like. If they remain in the wound, then a new spot may form in this place in the future.
Wart formation
Causes of warts
The main cause of compactions is the human papillomavirus, which lurks everywhere. It is transmitted both directly from a person and through objects touched by the patient. The virus is most active in a humid, warm environment: swimming pools, gyms, showers.
In addition, growths often occur for the following reasons.
- Psychosomatics of warts. This is when the problem originates in the head. For example, when a girl is dissatisfied with her body to such an extent that a protest occurs in the body - a new growth appears on the skin. Or a man struggling with some kind of addiction “breaks down” morally or psychologically. For many people, the answer to the question of what warts are is a psychological breakdown in their personal life.
- Low immunity. When everything in the body is balanced, then health is in perfect order. But as soon as your immune system weakens, warts begin to appear, as well as various types of sores and colds.
- Vegetoneurosis is a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Video about the causes of warts.
What causes warts to grow?
Experts believe that the appearance of tumors does not depend in any way on age or gender. The cause of warts on the legs and other parts of the body in most cases is a virus .
Are warts contagious or not?
Viruses penetrate through microcracks in the hands, entering the blood of a healthy person. However, not everyone gets sick - mainly people with reduced immunity are at risk. If there is a scratch on the skin, the virus will not take long to appear.
Can you get infected with warts?
You can become infected not only from a sick person, but also through household items. Since harmful bacteria and viruses persist for a long time on the surface of things.
Important! You should lead a healthy lifestyle and observe the rules of personal hygiene. And to the question of whether warts are contagious, you can give a comprehensive answer to the people around you.
How to distinguish a mole from a wart?
- Form . The tumor should be examined using a magnifying glass. Even a flat wart looks like a growth, while a mole resembles a fly.
- Feel . You need to carefully feel the seal. It is covered with horny growths, so it is unpleasant to touch, whereas moles are always soft.
- Color . Moles are most often dark due to pigmentation. And the sign of the disease has a light color: white, yellowish, pink, gray, etc.
- Quantity . There are significantly more moles on the skin even with the most advanced form of HPV.
Often, growths on the skin in the form of warts confuse people. Under their appearance, corns, calluses and other diseases may be hidden. If a formation similar to a wart is confusing or you have doubts, it is better to immediately go to the doctor - it is sometimes very difficult to distinguish them.
Why are warts dangerous?
- The plantar form causes severe pain when walking.
- Stains located on the hands and other easily accessible places can infect other people. Are warts transmitted by handshakes ? Yes.
- If the lump has changed color, pus or liquid is oozing from it, or the temperature has increased, you should immediately consult a doctor. Infection can provoke urethritis, balanoposthitis, paraproctitis and other diseases.
- The greatest danger lies in the possibility of degeneration into a malignant formation.
- Those at greatest risk are those who have genital warts localized on the scrotum, labia, foreskin, vagina, anus and other places. Doctors advise removing these seals as quickly as possible, eliminating the possibility of developing cancer .
Treatment of warts
Sometimes, with expensive treatment, they are able to actively reproduce, whereas if ignored, they disappear without a trace. Most often, self-healing is typical for children. If left untreated, they can grow, remain static, or disappear.
It is important to understand that modern treatment methods do not get rid of the virus, removing only its manifestations. In order to prevent the “bumps” from appearing again, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system.
Prevention of warts
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. And this is an axiom.
- First of all, you need to pay attention to your lifestyle. Take more vitamins, get enough sleep, avoid nervous situations. Preparations and products containing iodine have a positive effect.
- It is important to maintain good hygiene. After visiting public places, be sure to treat your limbs with special means or at least wash them with soap. Do not use other people’s things, try to touch the handrails less in transport. It’s difficult, but it’s worth trying for your own health, because warts on the hands are very insidious.
- If wounds, cuts, or abrasions appear on your hands, they must be treated with antiseptics. If your partner has the disease, you must wash your hands . Everyone should have their own utensils and household items.
It is important to organize proper nutrition. Eat foods with plenty of vitamins. Try to be less nervous. You can’t put work first; much more attention should be paid to health.
- When visiting public baths, saunas, showers in gyms, you should have replacement shoes. By wearing someone else's slippers or sneakers, there is a risk of becoming infected not only with warts, but also with something worse.
- When working with toxic substances, it is necessary to protect the skin with gloves, since this can also trigger the development of HPV.
- Shoes should be made from natural materials. Synthetics promote increased sweating , which leads to the development of viruses. This advice is especially relevant for young people.
- It is advisable to have a permanent sexual partner, since frequent changes contribute neither to satisfaction nor to maintaining health. Quite the contrary – there is a chance to treat a large number of “interesting” diseases.
- Remember, preventing warts is always easier than visiting a doctor!
Source: https://zdravtelo.com/borodavki/chto-takoe-b.html
Wart roots photo under a microscope
Have you been fighting PAPILLOMAS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of papillomas by taking it every day.
Warts can occur in people at any age and on any part of the body. Each wart differs in color, shape and structure. This disease is caused by the human papillomavirus, which easily enters the body with reduced immunity.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Types of warts
There are these types of warts:
- condylomas;
- plantar warts;
- flat warts;
- senile warts.
Condylomas look like small, sharp nodules with a pinkish tint. They form in the genital area and are prone to constant growth.
Plantar warts are located on the outside of the skin. They look like roots of a dark shade. Cause discomfort and pain when walking.
Common warts are localized on any part of the body and look like dense formations that rise above the surface of the skin. In such a wart there are large vacuolated cells in the granular layer and the Malpighian layer (upper part).
Degenerated cells often contain clumps of keratohyaline granules. The stratum corneum contains parakeratotic cells, which are located above the malpighian layer.
According to some scientists, viral inclusions are represented by eosinophilic bodies located in the nuclei of epidermal cells.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist based on clinical signs characteristic of a certain type of formation. Histological examination is necessary to confirm the benignity of the wart. The genotype of the virus can be determined using a PCR reaction.
Plantar warts are differentiated from ordinary calluses. In addition, differential diagnosis is carried out with epidermal nevus, lichen planus, molluscum contagiosum, etc.
Wart treatment
If there are several warts on the skin at once or one large formation, then surgical treatment, laser therapy, cryotherapy or electrocoagulation are suitable. Each of these methods has its pros and cons. Thus, with surgical treatment, there is a possibility that the root of the wart will remain under the skin, and then the procedure will have to be repeated again. Laser therapy is considered the most effective treatment method. It has practically no contraindications and ensures complete recovery of the patient.
To prevent the occurrence of warts in the future, medications are prescribed to restore immunity. It is necessary to take precautions in public places, do not use other people's personal hygiene items and wash your hands thoroughly after going outside.
Mail (will not be published) (required)
Recent Entries
- Wen on intimate places
- Why do wen appear on the lips and how to deal with them?
- Wen ointment
Everything you need to know about skin cancer: initial stage, photo, what it looks like, treatment methods and prevention
Skin cancer is a lesion of various layers of the epithelium, a malignant tumor that occurs during atypical cell degeneration. Pathology has a large number of varieties. Early stages are successfully treated.
A malignant disease often occurs due to human fault, due to neglect of fairly simple rules. How to avoid cancer? How to recognize skin cancer in time? The information will be useful to any reader, regardless of age.
- Causes
- Symptoms and types of disease
- How to recognize dangerous moles
- Stages and diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment methods and general recommendations
- Prevention and prognosis
Causes
Main causes of skin cancer:
- exposure to radiation;
- prolonged exposure to open sun;
- heredity;
- going to the solarium;
- age 60 years or more;
- senile keratoma;
- exposure to UV rays on unprotected skin;
- injury to moles, including when removed using folk remedies;
- Bowen's disease;
- complications after radiation dermatitis;
- exposure to carcinogens on the surface of the epidermis. The most toxic: tobacco smoke, tar, heavy metals, arsenic;
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- fair skin, an abundance of freckles, birthmarks;
- burns of varying degrees;
- poor nutrition. Frequent consumption of smoked, fried foods, pickled and canned foods.
Oncological diseases of the skin occur in the following cases:
- chronic hepatitis, HIV;
- an abundance of tattoos on the body, especially in places where moles are concentrated;
- living in southern regions with a lot of sunny days;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- melanoma-dangerous nevi;
- work associated with prolonged exposure to the air: field work, going to sea, street trading, and so on;
- chronic dermatological diseases.
Read more about using Metrogyl gel for acne and blackheads on this page.
Symptoms and types of disease
- basal cell;
- squamous;
- melanoma;
- adenocarcinoma.
Each type of malignant pathology has characteristic features. Knowing the symptoms will help you recognize a dangerous disease in time.
Symptoms and signs:
- the shape is marked in places exposed to direct sunlight;
- formations with this variety are constantly increasing.
- a small nodule with a bumpy surface and a dense structure appears on the body;
- color – reddish, brown;
- the surface flakes, peels, crusts appear;
- after a while the nodule looks like cauliflower;
- Erosion and ulcers are visible on the surface, and liquid with a putrid odor is released from the body of the tumor.
- the most dangerous variety;
- quickly spreads to healthy areas of the body;
- the largest number of metastases.
How does melanoma skin cancer manifest? General information:
- a malignant tumor necessarily appears from a benign formation under the influence of negative factors;
- locations - areas with increased accumulation of melanin. Cancer appears from a nevus, freckle, mole;
- the body of the mole becomes denser, often itches, hurts, and swells;
- color changes. The brown tint gives way to bluish, red or white;
- sometimes ulcers appear at the site of a former mole or freckle.
Basal cell carcinoma of the face
- basal cell carcinoma most often appears on the face, disrupting the activity of nearby organs;
- the tumor rarely metastasizes;
- Most patients had a solitary neoplasm.
- shape - hemisphere, color - pearlescent pink or gray, occasionally - natural skin tone;
- the malignant tumor remains quiet for a long time, does not itch, does not become inflamed, and only gradually increases;
- basalioma has a smooth surface, the central part is covered with small scales. There is an erosive zone inside;
- Sometimes multiple neoplasms are noticeable on the face. When they are damaged, droplets of blood appear.
- is quite rare;
- appears in places where sebaceous or sweat glands accumulate - under the breasts, in the folds of the skin, under the armpits.
- the neoplasm resembles a small nodule or tubercle;
- sizes increase gradually, there is no sharp growth in the latent stage;
- when negative processes are activated, adenocarcinoma “reaches” the muscle tissue. An expanded malignant tumor is clearly visible.
Knowledge of the symptoms noted in any form of skin cancer will help to recognize the development of negative processes at an early stage.
Remember these signs:
- constant fatigue even without heavy physical and mental stress;
- sudden weight loss without special diets or increased physical activity;
- loss of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes. Soft “bumps” are easily palpable;
- a slight increase in temperature to 37.1–37.2 degrees for a long period.
How to recognize dangerous moles
- the boundaries of the neoplasms have become blurred, swelling and redness are noticeable around;
- the size, density, and shape of moles have changed, scales, growths, and crusts have appeared on the surface;
- melanoma-dangerous nevus reached 6 mm or more;
- the formations cracked, split in half, clear or bloody discharge, itching, burning appeared;
- the tubercles acquired an unnatural color: they became very dark, or, conversely, light. Often cancerous moles take on a red, bluish or black color.
Stages and diagnosis of the disease
The earlier atypical changes in cells are detected, the easier it is to cure the disease. Cancer is not a death sentence; the survival rate for some types reaches 70–95%.
If you are diagnosed with the initial stage of skin cancer, even such a dangerous disease can be completely cured. Timely contact with a dermato-oncologist increases the chances of a favorable outcome.
If the development of cancer is suspected, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination. The later you seek help, the more tests and examinations you will have to do. Prepare for significant financial expenses. Most procedures are not cheap.
This is interesting: How to remove warts with a laser for children video
After a visual examination, examination of the medical history, palpation of painful areas, and superficial examination of formations on the skin, the dermato-oncologist will prescribe:
- dermatoscopy;
- siascopy;
- Ultrasound of organs located near the tumor;
- cytology;
- histological examination;
- lymph node biopsy.
Sometimes skin cancer is a consequence of damage to internal organs. To identify tumors, clarify the depth of germination of cancer cells, and diagnose distant metastases, the following is prescribed:
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- X-ray of the lungs;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- urography with contrast agent;
- computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain;
- skeletal scintigraphy and other serious studies.
How to treat lichen planus in a person's mouth? Find out the answer by reading this article.
Go here http://vseokozhe.com/bolezni/varikoz/ven.html and read the information about laser treatment of varicose veins.
Stages of skin cancer:
- first. The neoplasms are small, no more than 2 mm. There are no metastases, the lower layers of the epidermis are affected. The treatment gives a good effect, it is often possible to get rid of a dangerous pathology;
- second. The malignant tumor grows, sometimes a slight pain is felt. The lymph nodes are not yet affected; occasionally there is a single metastasis in a lymph node located nearby. With timely detection and treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable;
- third. The lymph nodes are affected, there are no metastases in the organs yet. The tumor enlarges, becomes lumpy, and mobility is limited due to tumor growth deep into the tissue. Patients often have an elevated temperature. The survival rate is reduced to 30%;
- fourth. Advanced cases are very dangerous for the patient. The tumor, often with ulcers, erosions, and bleeding, covers large areas. Metastases grow deeply, affecting cartilage tissue, skeleton, liver, and lungs. The patient constantly experiences severe pain. The body, poisoned by toxins, is unable to resist. Only a fifth of patients survive.
Treatment methods and general recommendations
Meanwhile, it is possible and necessary to fight for life. The initial stage of cancerous tumors on the skin is successfully treated. Even in the second and third stages, active resistance to the disease and faith in one’s strength works wonders.
With adequate treatment, the patient can enjoy life for a long time. Cases have been described in which patients with the most severe, stage four, lived much longer than the doctors had given them.
What you need to know about skin cancer treatment:
- treatment methods are chosen by a dermato-oncologist or a council of doctors (in severely ill patients);
- the patient’s age, the size of the formation, the number of metastases, and the type of pathology are taken into account;
- the main method is removal of atypical cells and tissues, radiation therapy or a combination of both techniques;
- during the operation, areas of healthy skin near the formation are captured;
- control over the complete removal of cancer cells is mandatory. Examination of the edges of the wound using a special device allows you to determine whether the affected tissue has been completely excised.
Basic methods of removing cancerous tumors:
- laser excision. A carbon dioxide or neodymium laser is used. The risk of infection and bleeding is minimal;
- electrocoagulation. The method is suitable for removing small tumors;
- cryodestruction. The destruction of a cancerous tumor using low temperatures is suitable for combating minimally invasive, superficial tumors. A biopsy is required before the procedure to confirm weak rooting of the tumor.
- at the initial stage, small lesion area - close-focus radiotherapy;
- for large superficial neoplasms - irradiation with an electron beam;
- photodynamic therapy;
- chemotherapy of the affected areas with cytostatics (mainly for basal cell carcinoma).
Prevention and prognosis
Studies have shown that the lethal outcome for malignant tumors of the skin is much lower, with similar pathologies of other organs.
- the most dangerous, rapidly progressing form is melanoma;
- The easiest to treat is the superficial type with a rare occurrence of metastases - the basal cell form;
- squamous cell carcinoma, with proper therapy and constant monitoring, gives a high five-year survival rate - up to 95%.
How to protect yourself from skin cancer:
- spend less time in the open sun, especially from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.;
- use sunscreen;
- when working in hazardous areas (thermal radiation, radiation), use protective equipment;
- forget the way to the solarium;
- consume smoked and fried foods as little as possible;
- limit the amount of alcohol, give up cigarettes;
- monitor the condition of the epidermis; if strange moles appear or changes in existing formations, make an appointment with a dermato-oncologist;
- monitor skin health, treat pathologies of internal organs;
- strengthen your immune system, worry less. A weakened body is “easy prey” for various ailments.
Next video. Find out even more details about skin cancer from the TV show “Live Healthy”:
Structure and structure of a wart
In order to successfully resist warts, you need to clearly know their structure and principles of distribution. By their nature, warts are benign formations and under normal conditions do not pose a danger to human health. If they are not injured, they can remain in an unchanged state for many years without increasing in size.
In appearance, it is similar to a callus and is a keratinized area of skin with a compacted structure.
Source: https://womens-life.ru/borodavki/korni-borodavki-foto-pod-mikroskopom.html
Structure of a wart - root and structure
Since many people have these growths on their bodies, it is necessary to be aware of the types and structure of warts.
Warts are benign formations that affect the skin. Despite the fact that such growths are quite harmless and do not pose a particular threat to health, they spoil the appearance of the skin.
Causes and mechanism of occurrence of warty neoplasms
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus. This virus inhabits the bodies of almost all people. However, if you have a strong immune system, the papillomavirus does not make itself felt. There are about 100 types of HPV infection, which leads to various types of diseases.
Penetration of HPV is possible in the presence of abrasions, injuries on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. After entering the cell nucleus, the virus begins to form multiple copies of its own DNA, using the resources of the human cell.
The epidermal cell loses its own identity and stops producing enzymes necessary for its functioning and growth. But HPV solves this problem in its favor. It restores the ability of cells to synthesize DNA, forcing them to actively reproduce. But processes in the structures of the epidermis occur with “imposed” changes.
This is the essence of the oncogenicity of the papillomavirus. This process of tumor development is typical for infection with pathogens of high oncogenic risk.
The most common manifestations of HPV are warts, which are formed as follows.
The corresponding genotype of the virus affects the weakest spot of the skin, resulting in the proliferation of its cells and the formation of a structure that has the shape of papillae (papillae).
Rapid death of the upper part of the skin becomes the stratum corneum. Individual papillae contain blood vessels. As formations die off, new ones grow.
Types of warts and their differences
types of warts
The following types of warts are distinguished:
- flat, or juvenile, which mainly affects teenage children;
- vulgar, or ordinary warts, found on the body of most people;
- plantar papillomas, developing on the soles of the feet and resembling a callus;
- black, or senile, developing mainly in older people;
- thread-like, having a stalk with which they are attached to the body;
- genital warts, which affect only the genital area, namely the mucous membranes.
condyloma, papilloma and wart
These are the main types of warts. They can affect different parts of the body. Any wart has a number of distinctive features. Among them are:
- seals that rise above the skin by several millimeters, and with a diameter of 1-10 mm;
- color ranges from flesh to light or dark brown (the shade depends on the amount of melanin - the skin pigment that is responsible for skin color);
- the shape of warty neoplasms is regular, mostly round;
It is worth remembering: if the growth does not correspond to this description, but has an asymmetrical shape, bleeds, grows, and has an unnatural color, then it may be skin cancer. If you notice such changes, you should immediately consult a dermatologist.
How does a wart work?
structure of a flat wart
Warts are compacted, keratinized areas of skin, which are covered with a protective crust on top. However, formations have one more part - roots. It is impossible to notice what the roots of a wart look like at first glance, since they are located under the skin.
The roots of warts are small cells of the granular layer of the skin that penetrate the deep layers of the dermis. They contain multiple blood vessels that deliver oxygen and nutrients directly to the growth. The roots are black due to the dark color of the blood in the vessels.
Blockage (thrombosis), due to death from compression directly by the growth, root growth and mechanical damage, of blood vessels and capillaries leads to the appearance of wart rods.
Injury to the cutaneous part of the tumor is very dangerous because it leads to damage to blood vessels and, as a rule, to heavy bleeding and infection of the wound.
The roots of the wart create certain difficulties when removing the growth. The size of the root system largely depends on its location.
Thus, in hanging and pointed formations, the roots do not reach large sizes, which leads to their frequent damage. Plantar warts have large roots that penetrate to great depths.
Increased loads and pressure on the legs lead to deepening of the growth and development of its capillary structure.
wart root
Any wart is a living structure, as it is formed from the epidermis of the skin.
Microscopic examination helps to identify a papillary structure, which is innervated by nerve endings and nourished by a network of capillary vessels that penetrates the wart.
It is this structure that provides the unpleasant sensations that a person may experience due to papillomas on the skin, namely itching, and in some cases burning (although this happens quite rarely).
Also, if a wart is mechanically damaged, it begins to bleed, precisely because of the blood vessels in it.
A wart in a section has roots - pathological cells that go deep into the dermis. Papillomas that form on the soles of the feet have more pronounced roots, since during walking the neoplasm is constantly pressed inward. It is precisely because of the remnants of cells that form the roots of the wart that it can be difficult to get rid of papillomas once and for all. Warts often appear again.
Diagnosis and treatment
Although warts are not dangerous to health, their multiple appearance on the skin may indicate a malfunction of the body or a weakened immune system. In this regard, if a person notices the formation of a large number of papillomas on the body, then this is a reason to consult a doctor and undergo a full medical examination.
Warty tumors can be removed using physiotherapeutic procedures, medications and using traditional medicine recipes. Among the physiotherapeutic procedures used to remove warts are:
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- electrocoagulation, or cauterization;
- radio wave method.
The surgical method is also used if the above procedures are unavailable or ineffective.
Medicines used to remove papillomas: “Super celandine” based on alkali, Verrucatsid, Ferozol, Kollomak, oxalic and salicylic ointments, Panavir gel, Cryopharma freezing agent, adhesive plaster based on salicylic acid Salipod. In addition to the listed remedies, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulators and vitamins that increase immunity.
Among the methods of alternative medicine, the most popular are: yellow celandine juice, which should be applied to the wart, wormwood infusion, vinegar or vinegar essence mixed with glycerin, lemon or tea tree essential oils.
They also make a paste of aloe or Kalanchoe and apply it to the affected area. You can prepare an ointment from grated garlic and melted lard.
Remember, to prevent the appearance of papillomas, you need to monitor your lifestyle: eat well, avoid bad habits, and take care of personal hygiene. Then warts will not bother you.
Source: https://vysypanie.ru/herpes/papillomy/stroenie-borodavki.html
Wart under a microscope
Return to list Ask your question
Examining a wart under a microscope in reflected light, you can only see its external structure, but its main part is hidden in the epidermis and dermis, and the root extends into the subcutaneous fat.
It is worth noting that warts are mostly benign skin growths. But sometimes the development of pathological processes in cells activates accelerated growth and transition of the formation to the rank of malignant.
The papillomavirus, which causes this unaesthetic skin defect, has not been fully studied. Some strains are completely harmless, others cause dangerous diseases. One way or another, almost all activate tissue transformation. The virus enters through damaged areas of the skin - scratches, cuts, abrasions.
Therefore, it is important to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene - use a separate razor for each part of the body to avoid self-infection.
Wash your hands after visiting public places - it is known that the papillomavirus can remain for some time outside an environment favorable for development - toilets, saunas, gyms.
To study a wart under a microscope, it is desirable to have a ready-made histological microslide created in special laboratories or in medical institutions. Of course, an amateur biologist cannot prepare such a preparation on his own, because The question will arise where to get the biomaterial.
It is simply impossible to find it or cut it off at home. Even if it was possible to obtain a piece of the sample, the material should be properly processed in an alcohol solution or formaldehyde (fixed, i.e.
stop the microprocesses of tissue decomposition), microtomize, stain, dehydrate and enclose between a slide and cover glass.
Microscopy should be carried out in transmitted light (bright field, illumination from below the stage).
The prepared papilloma preparation is first viewed at low magnification; with a wide field of view, centering and primary focusing are performed. After adjusting the sharpness, you can change the lens to a more powerful one, increasing the overall magnification.
And so we consistently reach 640-800x or 1000x (if the optical device supports research in oil immersion and is equipped with a 100x lens).
If instead of an eyepiece you insert a USB digital camera (video eyepiece) into the eyepiece tube, the image can be displayed on a computer or laptop and then taken using software tools.
Source: http://oktanta.ru/borodavka_pod_mikroskopom_statja
The structure of warts and papillomas
A wart is a benign neoplasm localized on the epidermis or mucous membranes. What does a wart look like? In the shape of a pointed cone, round or flat, with a bumpy, uneven surface. The cause of the growths is HPV. Under the influence of papillomavirus, skin cells change their DNA structure and begin to grow rapidly.
Virus replication will depend on the resistance of the immune system. At the first stage, the course of the clinical picture is sluggish. The growth may be almost invisible. Does not cause much concern to the wearer. Perhaps the wart will not grow further and will remain the same size. The immune system will destroy the strain and there will be no problems.
Referring to statistics in virology, most of the world's population are carriers of papillomavirus. When a certain number of factors coincide or the immune system is weak, the infection manifests itself through intensive growth, modifying the surface of the skin not for the better. Along with an unpleasant aesthetic perception, growths can degenerate into oncology.
Kinds
The causative agent of infection is much smaller than any cell in the body; it can easily penetrate it and manifest itself in any part of the body. A foreign aggressor cannot exist outside the body. Only for some time does it remain on objects, maintaining viability.
Once in a favorable environment, the virus begins to act. The affected cell modifies the nearby healthy one. Subsequently, the chain reaction leads to the formation of different types of warts and papillomas.
The classification is based on the type of pathogen and the form of growth. Types of infectious neoplasms:
- Common (vulgar), species distribution 65% of the total. These are small spherical protrusions above the surface of the epidermis. Pink, non-painful, with clearly defined edges. The most commonly affected localization of growths is the hand; other parts of the body are affected to a lesser extent.
- Plantar (spikes), their percentage is 30% of all warts. Located on the soles of the feet or palms of the hands. The color is yellow or brown with black spots. Plantar neoplasms are characterized by pain. Outwardly they resemble loose compactions, up to 3 centimeters in diameter.
- Juvenile (flat) are rare, accounting for 4%. Externally, the neoplasms have a barely protruding gray shape. The edges are not clearly defined. The surface of the wart is hard. Possible manifestation under the nail plate. This location not only disrupts the appearance of the top of the finger, but also causes pain.
- Acrochords (thread-like), have a pointed shape in the form of a cylinder. At the initial stage they resemble a pine cone, then they lengthen as they grow. The color does not differ from the skin tone. This type is characteristic of older people.
- Condylomas (anogenital), location of the mucous membranes and the genital area. Outwardly they resemble a pointed needle. Appearing in a single copy, they immediately begin to multiply, forming a colony around themselves. There, merging into one whole, it forms a wart, reminiscent of a cauliflower in structure.
- A type of viral tumor acquired through professional activity is called a butcher's wart. They penetrate through damaged skin at the moment of contact with fresh meat. Externally, these are lumpy elevations on the skin of the hands or elbows, light gray in color.
- Seborrheic keratosis is senile warts that are not related to HPV; their nature is not viral. This is a coarsening of the surface of the epidermis in a certain place with subsequent growth. Initially, a yellow spot with an uneven contour appears, then a slight elevation. The final stage - the wart becomes brown, round, dense, and rough to the touch.
Review of the best wart patches
All of them are benign in nature and do not cause any special problems (except for the spine) until they degenerate into cancer cells.
Remember! Any foreign formation deserves attention.
Structural features
On the surface of the epidermis, the structure of the wart can take various forms. It all depends on their type:
- flat;
- threadlike;
- cone-shaped;
- coralliformes.
The color range ranges from flesh to dark brown. The structure is dense, hard, scaly. They can appear in a single version or in several pieces. This is what we see on the surface. General structure of a wart:
- reinforced top;
- skin covering;
- dermis;
- root system of infectious neoplasm;
- fatty tissue.
When examining a wart under a microscope, attention is drawn to its roots.
What is the root
The root base is the microscopic cells that make up the granular layer. The system is equipped with blood vessels that give the dark color to the root. The blood flow to the lower part of the tumor allows it to receive nutrition for cell growth.
The rod, if we look at the wart in cross-section, is healthy blood vessels that have died from blockage due to compression. The more intensively the root grows, the stronger the negative impact on the vascular system, as a result, the appearance of more rods.
What to do if a wart bleeds
If you look at the structure of papillomas in cross-section, their roots do not go deep, they are close to the dermis, and therefore are often subject to mechanical damage with bleeding. Flat growths are more difficult to remove. The structure of plantar warts deserves special attention.
Structure of the spine
This type is localized on the outside of the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. If the tumor is on the legs, it causes a lot of trouble in the form of pain when walking. In its initial manifestation, the spine can be mistaken for a callus. But it does not separate from the skin, increasing in size.
You can divide the growth of a wart on the sole:
- the first stage manifests itself in the form of a “callus”, causing pain when walking, slight itching;
- the second stage begins a month later, a roughness with black spots appears in the center of the protrusion, and the skin thickens at the edges;
- third - the body of the wart is loose with numerous pointed papillomas, grows to the sides with noticeable dynamics, and causes pain.
It can reach two centimeters in width. The roots are often injured and begin to bleed. Bacteria enter open wounds and cause suppuration.
What threat do warts pose to the body?
Benign neoplasms caused by papillomavirus are already an invasion of a foreign agent. And if it begins to actively multiply, it means that the immune system has weakened and cannot cope with it. It is necessary to take measures to strengthen it.
What are warts and where do they come from?
If a plantar wart bothers you and no measures have been taken to remove it, the following consequences are possible:
- In which direction the cells grow, this will be the structure of the spine. After its appearance, time passes, and it begins to actively create new colonies. The root system penetrates deeply into the skin tissue and is firmly strengthened. When walking, the load on the site of its localization contributes to vascular thrombosis and an increase in the number of wart rods. By changing in size itself, it can simultaneously give rise to a new formation.
- When warts appear on the palms of the hands or feet, the aesthetic picture is disrupted. Added to this is stabbing pain, itching and burning.
- This type of virus infects the hard skin surface, forming a wart that tends to degenerate into malignant formations. This is another reason to see a doctor.
Condylomas are another type that require special attention. The variety of the strain that caused their growth is considered the most unpredictable, capable of mutation. The majority of cancer cases associated with papillomavirus are of this variety.
Why warts such as condyloma are dangerous:
- localized on the mucous membrane near the mouth, they affect the appearance, cause discomfort, spreading closer to the throat, and make swallowing difficult;
- single papillomas, combining into a single whole, form candylamotosis, affecting internal organs, it can lead to their complete stop;
- warts in the genital and anal area can degenerate into malignant formations.
In women, when cervical cancer was detected, the presence of papillomavirus was diagnosed in 100% of cases. Like any disease, treatment of warts must begin in the early stages of development.
Source: https://SkinCover.ru/borodavki/stroenie-borodavok-i-papillom.html