The human nervous system is a delicate thing and not fully understood; dysfunctions occur in adults and children of different sexes and ages, and often become chronic. A neurologist is engaged in identifying the causes of the development of disorders and eliminating them.
Neuroscience studies everything related to the central nervous system
What does a neurologist treat?
A neurologist or neuropathologist is a specialist who diagnoses and treats diseases associated with damage to the nervous system.
The doctor’s responsibilities include examining the patient, prescribing medications in accordance with the diagnosis, monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, and identifying possible complications.
At an appointment with a doctor, you can get recommendations on methods for preventing pathologies and rules for preventing relapse of diseases.
What diseases does a neurologist treat:
- osteochondrosis – damage and destruction of intervertebral discs provokes compression of the spinal nerves;
- other pathologies of the spine - intervertebral hernia, pinched spinal nerve, radiculitis, spondylosis;
- ischemic, hemorrhagic stroke - against the background of impaired blood supply to brain neurons, their death occurs;
- insomnia - most often occurs with nervous overstrain, emotional trauma, accompanying mental disorders, neuroses;
- encephalopathy – brain dysfunction;
- meningitis, myelitis, poliomyelitis;
- migraine, neuralgia, multiple sclerosis;
- Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's;
- hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure;
- myopathy;
- spinal cancer, brain tumors.
Migraines are often neurological in nature
In some clinics, a neuropathologist-epileptologist is a highly specialized specialist who studies epilepsy, prescribes medications to treat the disease, prevent relapses, and teaches the patient and loved ones the rules of first aid during attacks.
Pediatric neurologist
A pediatric neurologist examines children immediately after birth to identify abnormalities and assess the state of the nervous system. When diagnosing cerebral palsy, he registers the child, gives recommendations to parents about the specifics of care, prescribes medications and physical procedures.
What does a pediatrician treat:
- Down syndrome, phenylketonuria;
- infectious diseases – encephalitis, meningitis;
- disorders that occur against the background of poisoning of the body due to pathological jaundice in a child;
- consequences of birth injuries of the brain and spinal cord;
- hypoxic lesions.
When to contact a neurologist?
Symptoms of neurological diseases are quite varied; many patients see a neurologist after consultation and examination with a therapist, surgeon, ophthalmologist, or ENT specialist.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- constant or periodic pain in the neck of an aching, pulling, acute nature - appears when the cervical spine or spinal cord is damaged;
- discomfort in the lower back, upper back - occurs when there are problems in the lumbar, thoracic spine, pain radiates to other parts of the body;
- unpleasant sensations in the limbs - signal damage to the spinal and peripheral nerves;
- a feeling of numbness, tingling, crawling in certain parts of the body - paresthesia occurs in the initial stages of the development of many serious diseases of a neurological nature;
- loss of tactile, pain, temperature sensitivity of the skin in certain areas - a sign of stroke, destruction of the peripheral nerve, damage to the spinal cord;
- muscle weakness, complete loss of mobility of the limbs, spine, convulsions, tremors of the limbs - occurs when neurons in the brain and spinal cord are damaged;
- dizziness, fainting;
- impairment of hearing, taste, smell, sharp deterioration of vision, flashing circles before the eyes, periodic loss of visual functions;
- insomnia or drowsiness;
- memory impairment, panic attacks.
If you often feel dizzy, this is a reason to contact a neurologist.
During pregnancy, a consultation with a neurologist is required - active growth of the fetus leads to changes in the shape of the spine, hormonal imbalance disrupts the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, all these factors provoke the development of neurological pathologies.
The most common symptom of nervous system diseases is headache. If discomfort occurs more than once a week, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
Where does he receive it?
There is a neurologist's office or a neurological department in district and city municipal hospitals; appointments and consultations are made at the reception desk. A visit to a specialist is free if you have a policy, but many types of diagnostics are paid. You can call a doctor at home for a bedridden patient; private medical centers provide this service to everyone, but for a fee.
A neurologist also provides consultations in private clinics and diagnostic medical centers, the specialist’s services are paid, the price of an initial consultation is 1.2–1.8 thousand rubles, drawing up an individual treatment plan is 500–2500 rubles.
, the cost of inpatient treatment in the neurology department is calculated on an individual basis. In order not to make a mistake in choosing a specialist and a medical institution, you should read the reviews on the clinic’s website and forums.
What does a neurologist do during an appointment?
At the first visit to a neurologist, the patient needs to tell the doctor in detail and honestly about his complaints, what worries him, how often unpleasant symptoms appear. Based on these data, the doctor will form a general idea of your general health, problems and disorders, and then prescribe the necessary tests.
At the appointment, the doctor palpates areas of the body to identify the nature of the pain.
How the inspection takes place:
- Palpation - feeling various parts of the body and face to determine painful areas.
- Percussion - tapping allows you to assess the state of excitability of peripheral nerves.
- Temperature measurement - an increase in indicators indicates the presence of infectious lesions of the central nervous system, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Measuring blood pressure - hypertension and hypotension are often accompanied by headaches and increase the risk of stroke.
- Tapping with a neurological hammer is a study of tendon reflexes; their nature changes when the central or peripheral nervous system is damaged.
- Hearing assessment using a tuning fork.
- Study of the movement of the eyeballs - the patient fixes his gaze on a pen or hammer, the doctor moves the object in different directions. Normally, the eyeballs move simultaneously, smoothly and evenly.
- Assessment of reaction to light - in the absence of brain pathologies, the pupils reflexively constrict in bright light.
The doctor examines and evaluates the condition of the spine, skin, bones, muscles, joints, and notes signs of atrophy. The neurologist checks muscle tone - the patient sits down, relaxes, the doctor bends the arm at the wrist and elbow, manipulates the other limb, bends and straightens the legs at the knee joint.
A certificate from a neurologist is required to obtain a license, permission to carry a weapon, to register guardianship, admission to educational institutions and when applying for a job.
What diagnostic methods does it use?
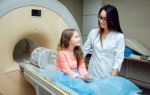
One of the main methods for diagnosing diseases of the nervous system is MRI, CT - during the examination, the monitor displays detailed information about the structure and functioning of the brain and spinal cord.
MRI is often used as a research method.
Examination of cerebrospinal fluid - biological material is taken using a puncture; a puncture is made in the lumbar spine under local anesthesia. The analysis allows us to identify the presence of bacterial and viral pathologies, neoplasms, signs of stroke, and increased intracranial pressure.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- clinical blood test - to determine the degree of the inflammatory process and exclude anemia;
- general urinalysis - allows you to exclude diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- biochemical blood test - shows the condition of the kidneys, liver, pancreas;
- hormonal tests;
- serological research methods make it possible to determine the type of pathogens of infectious processes.
To assess brain function, echoencephalography is performed; if a stroke or brain tumor is suspected, positron emission tomography is performed. Cerebral angiography helps to obtain a clear image of the cerebral vessels, and Doppler scanning helps to identify the presence of stenosis or blockage of the carotid artery.
Recommendations from a neurologist
The nervous system is very vulnerable; various factors can negatively affect its functions, so it is necessary to regularly prevent neurological pathologies.
How to avoid nervous diseases:
- lead an active lifestyle - long walks, regular sports have a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels and brain function;
- give up bad habits - alcohol, nicotine, narcotic drugs destroy neural connections in the brain, impair the elasticity of blood vessels;
- eat right, minimize the consumption of junk food, strong tea, coffee;
- eliminate stress, master meditation and other techniques that relax the nervous system;
- promptly treat all infectious diseases.
To prevent nervous diseases you need a full, relaxed sleep for 8 hours
A full 8-hour night's sleep in a well-ventilated room is one of the best methods for preventing diseases of the nervous system.
Stress, lack of sleep, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, vitamin deficiency are the main causes of the development of neurological diseases. It is much easier and cheaper to adjust your lifestyle than to treat pathologies of the brain and spinal cord.
Find out more on the topic: Doctors
Source: https://lechusdoma.ru/nevrolog/
Doctor - neurologist. What diseases does it treat?
Who is a neurologist? What diseases does it treat, why is it so difficult to diagnose. Methods for identifying diseases, symptoms. At an appointment with a neurologist: how the examination goes, what problems the doctor solves. What symptoms should I treat?
A neurologist is a doctor who considers disruption of the nervous system as the cause of the disease. The older generation is more accustomed to calling a specialist a neurologist, which today is incorrect; this was the case until 1980.
To obtain a certificate in neurology and the ability to see patients, you will need to graduate from medical school and an internship.
Neurology is the science of the occurrence of disorders in the functioning of the human nervous system. The mechanism of development, primary signs and symptoms of the disease are considered. After diagnosis and diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes treatment and prevention.
Causes of nervous system vulnerability
Reasons for the development of pathologies:
- Infection. These can be fungi, parasites, bacteria and viruses.
- During pregnancy. Cytomegalovirus and rubella are transmitted through the placenta.
- Injuries. Bruises of the brain and back.
- Vascular disorders. Formation of blood clots, ruptures and inflammation.
- Heredity and chronic diseases.
Indirect damage to the nervous system is caused by a lack of nutrients and vitamins, heavy metal poisoning, exposure to chemicals, antibiotics, as well as heart and kidney diseases.
What does a neurologist treat: what diseases?
The basis of diseases of the nervous system is a disruption in the functioning of neurons, nerve cells, a weakening of the connection between them, as well as inflammatory processes in the brain and spinal cord.
Diseases treated by a neurologist:
- Arachnoiditis. Infection, including neuroinfection, trauma, and poisoning affects the arachnoid membrane of the brain. Manifested by headaches, seizures, decreased vision, and tinnitus.
- Insomnia.
- Parkinson's disease. A condition in which movements slow down, muscle tone increases and tremors appear at rest.
- Alzheimer's disease. A progressive disease that affects mental functions, there is a violation of memory, thinking, emotions, and identification of a person as an individual. Over time, muscle strength and a sense of balance are lost, and disturbances in the functions of the pelvic organs appear.
- Intracranial hypertension (pressure), hydrocephalus.
- Tension headache. Strong, monotonous, squeezing. It occurs more often in women, and children are also affected. Caused by mental and muscle overstrain, chronic stress.
- Hemorrhagic stroke. A severe form of cerebrovascular accident, accompanied by hemorrhage in the brain.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Sciatica. Neuritis of the sciatic nerve manifests itself as acute pain in the sacrum and lumbar region.
- Ischemic stroke. When cerebral circulation is impaired, brain tissue is damaged, which leads to loss of brain function. The most common stroke.
- Cluster headaches. Sharp, acute, burning pain in the eye or behind it, radiating to the ear, temple, cheek.
- Lumbago. Sharp and sharp, but short-term pain in the lumbar region.
- Meningitis.
- Myasthenia. A genetic disease of a progressive nature, causing pathological fatigue and muscle weakness.
- Migraine.
- Myelitis. A disease in which an infection affects the spinal cord.
- Myopathy. Muscular dystrophy, a degenerative disease caused by damage to muscle fibers.
- Violation of muscle tone in a child.
- Neuralgia. Sharp and piercing pain when a peripheral nerve is damaged.
- Neuritis or neuropathy.
- Tumor of the brain or spine.
- Polio. An infectious disease that affects the spinal cord and leads to paralysis.
- Multiple sclerosis. A progressive chronic disease that destroys the central nervous system.
- Restless legs syndrome or Willis disease. Unpleasant sensations in the limbs force a person to move them, which brings relief.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children and teenagers suffer.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. A combination of several symptoms that are characterized by excessive fatigue that persists for a long time and cannot be relieved by anything.
- Tuberculous meningitis. Inflammation of the meninges develops in patients with tuberculosis.
- Tunnel syndrome. The nerve is pinched and pressed against the protrusions on the bone.
- Chronic cerebrovascular accidents. A slowly progressive disease that leads to the development of microfoci of brain tissue necrosis and brain dysfunction.
- Extrapyramidal disorders. Muscle tone changes, motor activity is disrupted, hyperkinesis (twitching) or hypokinesia (immobility) and their combinations appear.
- Encephalitis.
- Encephalopathy. Diffuse brain damage in various diseases and pathological conditions.
Attention! A neurologist does not treat mental disorders. This is what a psychotherapist does. But diseases of the nervous system can often be accompanied by mental disorders, in which case both specialists provide assistance to the patient at the same time.
Symptoms and complaints to consult a doctor
With peripheral paralysis, there is an almost complete loss of the muscles' ability to contract, the person does not control his body, and is unable to move. Paresis is a partial loss of motor activity in the muscles. In both conditions, atrophy develops, in which muscle volume decreases, tendon reflexes are absent, muscle tissue is relaxed, and elasticity and tone are lost.
With central paralysis, the reverse process occurs, that is, muscle tone increases and the speed of tendon reflexes increases.
When the basal ganglia, which are located in the white matter of the brain, are damaged, the regulation of motor and autonomic function is disrupted, which affects motor skills. They slow down, become involuntary, tremor (trembling) appears, and muscle tone changes.
If the cerebellum suffers, then coordination of movements is impaired, speech becomes slow and unclear, and the limbs weaken.
Attention! Symptoms of a nervous disease can be subtle and minor, be it numbness in the fingers or dizziness; do not take such manifestations of the onset of the disease lightly.
Any disease is easier to prevent and treat at the initial stage. You should consult a doctor if:
- You experience headaches more often than once a week and at the same time vision is impaired, blood pressure changes, nausea and vomiting appear.
- You experience sudden dizziness, uncertainty, and unsteadiness in your gait.
- Short-term or long-term (several hours, days) loss of vision with subsequent recovery.
- Loss of consciousness, convulsive seizure (once or repeatedly).
- Increasing weakness in muscles, the strength of which is not restored during training.
- The motor reaction slowed down, and a feeling of stiffness appeared in the body.
- Trembling in arms and legs.
- Convulsive muscle contractions.
- Pain appeared in the back, shoulders, arms and legs.
- Worrying is a decrease in sensitivity in some areas of the skin, numbness and tingling.
- Memory has deteriorated.
- The sense of smell changed and a disturbance in taste was felt.
- Either constant insomnia or excessive sleep.
- Unreasonable attacks of fear, panic, rapid heartbeat, chills or, conversely, a feeling of heat throughout the body.
At the doctor's appointment: what the patient should know
An experienced doctor can already assess the patient’s condition just by gait and movements. But a careful examination is necessary: visual, tactile and with the help of instruments to make a diagnosis. To assess some reflexes, the condition of the muscles will need to remove some clothing.
So, how does an appointment with a neurologist go:
- The specialist examines the patient’s appearance for the presence of asymmetry of the face and body.
- To study the functioning of the optic nerve, you will need to follow the movements of the hammer without turning your head.
- The doctor can check your reflexes using your facial expressions. The neurologist will ask you to wrinkle your forehead, stick out your tongue, or say “Ah.”
- You can check the sensitivity of your face using a needle. Don’t be scared; you will need to concentrate as much as possible and answer the neurologist’s questions about whether you experience the same sensations when receiving injections in symmetrical zones.
- To determine the condition of the muscles, their tone and reflexes, the doctor will be asked to shake his hand and resist when trying to bend the elbow. Evaluation occurs by assigning points from 1 to 5.
- Deep reflexes of the arms and legs are tested by striking the tendons with a hammer.
- Superficial reflexes are tested by irritating the skin of the abdominal wall with a needle.
- A deep examination of muscles and joints is carried out when the patient's eyes are closed, and the doctor moves his finger in different directions and asks him to name exactly in which direction he is doing it.
- Drawing various figures, letters and numbers on the skin of the patient’s back helps determine the condition of the spinal nerves and paravertebral pain points.
- Coordination of movements is tested by the Romberg pose. The patient stands with his feet together, arms extended forward, eyes closed. The neurologist will ask you to slowly move your index finger to your nose (with each hand). In this study, a person should ideally not stagger to the sides.
- You may need to answer specific questions about counting or dates to assess memory.
Tasks: what does a neurologist do?
Due to the fact that diseases of the nervous system are one of the most extensive and complex areas of medicine, it depends on the neurologist:
- How complete and reliable will the anamnesis be collected and the initial examination performed?
- Diseases associated with nervous system are often accompanied by pain; the doctor must correctly determine the cause.
- To make a final diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes the patient the entire necessary range of studies and tests, consultations (if necessary) with a cardiologist, ophthalmologist and endocrinologist, etc.
Patient examination
Not in all cases it is possible to make a diagnosis based on clinical data. There is a need for additional studies that will provide detailed information about the patient's condition.
- CT scan . Identifies areas of hemorrhage, malformations of arteries or veins. Allows you to see tissue changes, swelling, softening during a heart attack or injury.
- Magnetic resonance imaging . More modern diagnostics provide more detailed and accurate data due to the greater resolution of the device and do not have such a detrimental effect on the patient.
- Angiography . A contrast X-ray examination that reveals pathologies and changes in blood vessels in the brain.
- Ultrasound . Using this study, a detailed image of the large vessels of the neck is obtained.
- Lumbar puncture or cerebrospinal fluid analysis . Conduct a study for meningitis, hemorrhages, tumors of the membranes.
- X-ray . Contrast is used to detect intervertebral disc herniations, proliferation of vertebral bodies, and tumor processes. The study gives a clear picture of the state of the subarachnoid space of the entire spinal cord.
- Electroencephalography . The main test prescribed for patients with suspected epilepsy.
And there are quite a lot of methods and studies that help in diagnosing diseases: biopsy of muscles, nerve tissue, genetic studies, blood tests.
Successful treatment requires finding out the cause of the pain and making the correct diagnosis. And for this you need to contact a neurologist. You shouldn’t let the disease get started; it’s much easier to defeat it in its infancy!
Source: https://proartrit.ru/vrach-nevrolog-kakie-bolezni-lechit/
What does a neurologist treat in adults, when to contact him, and how is the examination performed?
A neurologist studies the nervous system. He analyzes pathological processes associated with improper functioning of the nervous system, and also observes it in a normal state. To give a precise definition of the profession and answer the question “what does a neurologist treat in adults”, you need to know that the doctor must have completed medical education and carry out diagnostics at the highest level.
Neurologist - what kind of doctor is this?
To answer the question - what does a neurologist do, it is important to understand that the human body contains a nervous system, which carries out a huge amount of work and controls almost the entire body. A neurologist is a specialist who studies the functioning of the nervous system, pathologies in its development, and determines a number of preventive measures that can return the nerves to their original state.
Today, a neurologist and a neuropathologist are doing the same thing. Both of them study the peculiarities of the nervous system, brain and nerve plexuses.
The first question that every person asks when going to an appointment is what does a neurologist do? A neurologist treats diseases that affect the human nervous system. Neurologists are available for children and adults. In fact, this is one doctor, just a pediatric neurologist who monitors the child’s nervous system from all sides from birth until he reaches adulthood.
A pediatric specialist has the opportunity to prevent the development of progressive pathologies, and if this is not possible, prescribes preventive measures to maintain the child’s stable condition. The sooner the doctor notices the development of a harmful process, the greater the chance that comprehensive treatment will help eradicate the disease and give the child a comfortable, disease-free life.
An adult neurologist works with patients over 18 years of age. His responsibilities include examining the already formed nervous system.
- The doctor diagnoses the causes of pain in the back, chest, neck, abdomen, and head.
- Among other things, a neurologist treats stuttering in adults.
- Since neurology is closely related to the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system and sensory organs, a neurologist studies the brain. When the brain is damaged, all organs and parts of the body are at risk.
What diseases does a neurologist treat in adults?
What a neurologist treats in adults is presented in the following list:
- any abnormalities that lead to headaches (nervous tic, migraine, tremor);
- Parkinson's disease;
- bleeding in the brain (stroke);
- spinal and head injuries;
- sleep disturbance;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- various seizures;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- intervertebral hernia, protrusion, radiculitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hysteria;
- all types of neuralgia;
- epilepsy.
And this is only a small part of the diseases affected by the profession of a neurologist. What a neurologist treats in adults is damage to the nervous system by various viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
In most cases, complications after suffering a minor illness can lead to irreversible consequences.
Only in rare cases, problems of the peripheral nervous system can be associated with the body's immune response.
When should an adult contact a neurologist?
There are situations when you should contact a neurologist immediately. Each problem has its own symptoms and, due to the fast pace of life, people often leave it without special attention. In case of problems with neurology, symptoms may appear once or repeatedly; one symptom may appear independently or several at the same time. The main thing is to contact a specialist in time.
Symptoms, when they appear, you need to see a specialist and find out what diseases a neurologist treats:
- constant headaches;
- muscle weakness;
- speech disorders;
- sleep disturbance and insomnia;
- pain in the neck, back or head;
- tinnitus and dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- tingling or numbness in various parts of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- pronounced weakness;
- significant deterioration in the perception of reality, poor memory, absent-mindedness.
How does an appointment with an adult neurologist proceed?
To find out what a neurologist treats in adults and what complaints may arise, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. First of all, the doctor must collect an anamnesis of the disease from the patient’s words.
After collecting a general picture of what is happening, the doctor refers the patient to additional studies, if necessary.
At the appointment, the doctor may ask the patient to do a series of physical exercises to determine the degree of impairment.
Additional research that may be needed:
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG) is a study of the condition of muscles and the peripheral part of the nervous system.
- X-ray of organs.
- Ultrasound is an ultrasound examination of certain organs.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a study using a tomograph of the brain and spinal cord.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) is a study that tests the functional state of the human brain by recording its bioelectrical activity.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In this case, examination of the back and brain may be necessary.
- Duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head (DS MAG) – checking the blood vessels of the brain.
How is an adult examined by a neurologist?
You can reliably answer the question of how an examination by a neurologist goes, only after going through the procedure.
So:
- The appointment begins with an examination of the patient by a doctor and a conversation. Thus, the specialist finds out the reason for the visit and the complaint.
- Next, the doctor may ask the patient to do a series of physical exercises to determine the extent of damage to the musculoskeletal system.
- The examination necessarily includes an examination of the muscles and joints; the doctor may tap the kneecap and elbow with a hammer.
- The doctor may palpate some organs to get a complete picture.
The main purpose of the examination is for the specialist to find out what condition the patient’s nervous system is in. Therefore, it will not be possible to do without accompanying procedures.
After the examination, the doctor prescribes a series of tests and additional studies that will help him understand exactly what is happening to the patient.
You should not ignore the doctor’s prescriptions, even if you have to spend a lot of money on it, this is the only way to understand exactly what and how a neurologist treats adults.
What tests does a neurologist prescribe?
Tests for a neurologist play an important role in making a diagnosis. In almost all patients at the first stage, the doctor prescribes 2 main tests:
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine.
Using these indicators, you can understand how the body works and whether there are any deviations from the norm. Further, if necessary, the neurologist can refer you for specific tests, such as:
- determination of the level of various hormones in the blood;
- squirrel.
Often, for testing, blood is taken from a person, but in neurology, cerebrospinal fluid is more informative. To collect it, a puncture is made - a puncture of the disc between the vertebrae in the lumbar region. The procedure is painful, and sometimes there are side effects, but when the risk of developing the disease prevails, there is no choice.
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/chto-lechit-nevrolog-u-vzroslyh-kogda-k-nemu-obrashchatsya-i-kak-prohodit-osmotr
Neurologist - what treats in adults
- Many people are interested in what a neurologist treats in adults and when to contact him.
- A neurologist is a medical specialist who diagnoses and treats pathologies affecting the central and peripheral nervous system.
- To become a neurologist, you need to graduate from a medical school with a degree in general medicine or pediatrics and specialize in neurology.
When to consult a doctor
It is recommended to consult a specialist if:
- headaches and dizziness, especially if they are accompanied by nausea and increased blood pressure;
- shooting pains in the face;
- pain in the limbs, back and neck;
- decreased sensitivity (pain, temperature);
- progressive muscle weakness;
- stiffness in the body;
- trembling, tingling and numbness of the limbs;
- uncontrolled movements of the arms or head;
- convulsions, fainting states;
- insomnia or increased sleepiness;
- constant night awakenings;
- apathy, depression;
- increased nervousness, irritability;
- panic attacks;
- chills or hot flashes;
- loss of balance and ability to coordinate movements, unsteadiness of gait;
- memory impairment;
- violation of taste and smell;
- periodic loss of vision;
- the appearance of tinnitus;
- speech disorders.
Often, diseases of the nervous system manifest themselves with uncharacteristic symptoms. In such cases, a therapist can refer you for a consultation with a neurologist.
It is recommended to visit a specialist annually for preventive purposes.
What diseases does the specialist deal with?
Let's try to find out when a neurologist will help, what he treats in adults.
The doctor treats neurological disorders:
- intracranial hypertension;
- nervous tics, tremors;
- cranial and spinal injuries, as well as their consequences;
- Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases;
- multiple sclerosis;
- stroke and its consequences;
- paresis and paralysis;
- neuralgia, neuritis, plexitis;
- migraines, headaches;
- pain in the neck and back;
- painful prolapses caused by nerve damage;
- seizures, epilepsy;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- torsion dystonia;
- encephalopathy;
- osteochondrosis;
- radiculitis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- Crouzon and Dandy-Walker syndromes;
- arachnoiditis;
- leukodystrophy;
- myasthenia gravis;
- neurofibromatosis;
- blepharospasm;
- syringomyelia;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- meningitis, encephalitis;
- insomnia;
- sleep apnea syndrome;
- tumors of various etiologies.
The listed diseases are often accompanied by changes in mentality and behavior. In this case, it may be necessary to consult a psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
What does a neurologist treat in children?
A pediatric neurologist will help with:
- developmental delay;
- attention deficit symptom;
- Down syndrome;
- hyperactivity;
- convulsions and fainting;
- epilepsy;
- polio;
- hydrocephalus;
- phenylketonuria;
- West syndrome;
- cerebral palsy;
- birth and hypoxic lesions.
The specialist also monitors infants, which allows timely detection and elimination of the slightest pathologies.
How does a neurologist differ from a neurologist?
Now you know who a neurologist is and what he treats in adults. Who is a neurologist, and how does he differ from a neurologist? It turns out that these are two names of the same profession.
In connection with frequent disorders in the functioning of the nervous system, a science was created that studied the structure and functions of the nervous system, clarified the mechanism of failures, and developed methods to cure existing pathologies. It was called neurology, and specialists began to be called neuropathologists. In the 80s of the last century, changes occurred in the Ministry of Health, as a result of which neurologists were renamed neurologists.
How does the consultation work?
At the first appointment, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and collects an anamnesis of the disease.
He asks about age, marital status, characteristics of professional activity, finds out the localization, nature and intensity of pain, factors causing pain, the presence of chronic and hereditary diseases.
Then he examines the patient, conducts palpation and tests to assess visual and olfactory acuity, speech skills, reflexes, coordination of movements, sensitivity, and muscle strength.
Diagnosis and treatment
After a visual examination, the neurologist refers the patient for examination, which may include:
- echoencephalography of the brain;
- neurosonography;
- myelography;
- electroencephalography;
- electroneuromyography;
- cerebral angiography;
- ultrasound encephaloscopy;
- Doppler ultrasound scanning;
- CT, MRI or PET;
- lab tests;
- lumbar puncture.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor makes a diagnosis, determines the cause of the pathology and individually selects the optimal treatment, taking into account the type and stage of the disease, as well as the general condition of the patient and the presence of other diseases.
It includes taking medications, injections, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy, biofeedback therapy, and psychotherapeutic techniques.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
During an exacerbation of the disease, the doctor may prescribe bed rest. During the treatment process, he monitors the patient’s condition and, if necessary, makes treatment adjustments. At the end of the treatment course, the neurologist gives advice to avoid relapses.
Advice from a neurologist
The proper functioning of the nervous system is important for the health of the body, as it controls the coordinated functioning of all organs.
To avoid nervous diseases, it is recommended to follow several rules:
- eat rationally;
- sleep 7-8 hours a day;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- doing physical exercise;
- walk in the fresh air for at least 2 hours.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at Ryazanova Private Office LLC by calling 8 (846) 990-09-44 or using the online form “Request a call back”. Our administrator will call you back and select the best time for you to visit a specialist.
Source: https://clinic63.ru/chto-lechit-vrach-nevrolog.html
Neurologist – what he treats in adults: what complaints are addressed and how is the neurological examination performed?
The science of neurology appeared more than 150 years ago. Its main subject of study is the nervous system, both in pathological and normal states.
Specialists in this area of medicine are called neurologists; they deal with issues related to diseases of the peripheral and central parts of the nervous system , study the mechanisms of their occurrence, methods of prevention and treatment.
Doctor's specialization
In adult patients, the main organs examined are the brain and spinal cord. Nerves and nerve plexuses become important elements of study.
When the brain is damaged or pathological, other important organs and parts of the human body may suffer, so it is believed that neurology is closely related to the endocrine system, the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and the sensory organs.
It is worth visiting a doctor when you feel pain in the back, neck and head, chest and abdomen. In addition, you should consult a neurologist if depression has set in and neuroses, obsessive states and anxiety have appeared.
Neurological diseases can manifest themselves in the form of limb tremors and tics , which also becomes an important reason for quickly contacting a specialist.
It is necessary to consult a specialist if attention deficit disorder or a constant feeling of fear occurs. Such conditions contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain and disruption of its normal activity.
Neurological examination
An appointment with a neurologist begins with a visual examination and identification of the patient’s complaints. To help a specialist correctly diagnose the disease and find out its causes, the patient should be told in detail about the state of health and symptoms, the degree of their severity, and the frequency of occurrence.
How is the reception going? It is carried out individually with each patient separately, it all depends on the type of disease.
It is mandatory to study the medical record, certificates and test results . If the data is insufficient, the doctor prescribes additional tests and examinations to make an accurate diagnosis.
The main purpose of the examination is to determine the state of the nervous system and obtain accurate information about its functioning.
A neurological examination is based on examining parts of the nervous system, from the muscles to the brain. The doctor analyzes the victim’s gait, coordination and reflexes, and cranial nerves. An appointment with a neurologist may also be accompanied by palpation, that is, feeling the patient’s body to detect pathological changes.
Diagnostic tests
After a neurological examination has been carried out, the patient can be referred for examination to make an accurate diagnosis.
Types of research conducted:
- electroneuromyography;
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- computed tomography (CT) of the brain and spinal cord;
- electroencephalography;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the back and brain;
- duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head (DS MAG).
Various laboratory methods for examining the body (general and detailed blood tests, urine tests, etc.) may also be prescribed. When and what tests are prescribed depends only on the patient’s health condition.
Important! It is not recommended to undergo certain diagnostics on your own.
Symptoms of pathologies
A neurologist helps to cope with neurological diseases that are characterized by specific symptoms.
The doctor's competence includes many neurological symptoms that are most often not paid due attention in everyday life.
What complaints do patients turn to a specialist with:
- headaches and muscle weakness;
- speech disorders;
- insomnia, frequent waking up, poor sleep;
- pain in the back and head;
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- sudden loss of consciousness;
- loss of sensitivity, numbness of fingers and toes, soft tissues;
- tingling in the limbs;
- general weakness of the body, fatigue;
- impaired coordination and gait;
- absent-mindedness, deterioration of memory, perception.
With neurological diseases, several symptoms may appear simultaneously, or only one of the above symptoms. Untimely contact with a neurologist can lead to a rapid deterioration of the body’s condition and disruption of the usual rhythm of life.
Types of diseases
Such diseases are considered the most common in the world; they can develop at literally any age and, if not treated in a timely manner, develop into pathologies.
Advice! Neurological diseases cannot be diagnosed and treated independently by the patient; this can only lead to a deterioration in well-being and rapid progression of the disease.
Only qualified specialists determine the type of disease and its stage of development.
Today there are such neurological diseases as:
- Parkinson's disease;
- headaches of different nature and duration (migraines, tremors, nervous tics, etc.);
- stroke and its consequences;
- back and head injuries, as well as their consequences;
- sleep disturbance;
- spasms in different parts of the body;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- radiculitis;
- intervertebral protrusions, hernias;
- multiple sclerosis;
- sciatica;
- hysteria;
- stroke and its consequences;
- neuralgia of various types;
- epilepsy, etc.
In almost all cases, the nervous system is affected by fungal, viral, bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Only in some cases, the main cause of the development of diseases of the peripheral nervous system is the body's immune reaction.
Vascular treatment
An angioneurologist is a doctor who specializes in detecting vascular diseases of the brain , as well as their treatment.
- The specialist’s competence includes improving preventive measures for people of working age.
- In addition, the angioneurologist actively works with other specialties.
- The specialist promotes proper nutrition, avoidance of alcohol abuse and leading an active lifestyle.
- What does an angioneurologist treat?:
- neurological syndrome Parkinsonism;
- pathological changes in the spine;
- chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency;
- determination of repeated, primary risk of stroke;
- disturbance of brain activity in arterial hypertension;
- stroke and its consequences;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- cerebral venous dysfunction;
- disorders of the vascular network of the brain, spinal circulation;
- vascular pathologies;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
Note! An angioneurologist or vascular neurologist may prescribe additional examinations: coagulogram (detection of the degree of blood clotting), lipidogram (indicator of cholesterol in the blood), x-ray of blood vessels.
Difference from a neurologist
The concept of “neurologist” was actively used in the 80s in relation to a specialist who was trained at a medical university in a specialized specialization - neurology.
In modern medicine, such a doctor is usually called a “neurologist,” and no difference in the performance of functional duties, in comparison with a neurologist, has been identified.
We can assume that neurologist and neuropathologist are synonymous words.
Depending on what complaints the patient comes to the specialist with, the initial examination depends. Only a neurologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Specialists will help you cope with many diseases that hinder movement and cause considerable discomfort.
Video: what diseases does a neurologist treat?
Source: https://doktora.guru/nevrologiya/nevrolog-chto-lechit-u-vzroslyh.html
What diseases does a neurologist treat? Find out at DocDoc.ru
A neurologist (neuropathologist) is a doctor who has received a higher medical education and has specialized in neurology.
In Russia, in order to become a neurologist, you need to graduate from a medical institute with a degree in general medicine or pediatrics and complete a residency in neurology.
Neurology is a branch of clinical medicine devoted to the emergence and mechanisms of development of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as studying the clinical signs of these diseases, methods of their diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
What does a neurologist do?
A neurologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases related to the nervous system. These are diseases of the central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral (nerve fibers) nervous systems.
For example: neuralgia, tumors of the brain and spinal cord, encephalitis, neuritis, strokes, discirculatory encephalopathy and various cerebral circulatory disorders, epileptic attacks. Most of these diseases are accompanied by changes in behavior and mental state.
In these cases, psychiatrists and sometimes psychotherapists are involved in treating patients. Pediatric neurology differs significantly from adult neurology. She deals with diseases of the nervous system of children.
Most severe chronic diseases begin in childhood (for example, epilepsy), and the child’s nervous system is so different from that of an adult that it requires a separate field of medicine.
What diseases does a neurologist treat?
What diseases does a neurologist treat? Diseases of the nervous system are often accompanied by paralysis, loss of pain, temperature and other types of sensitivity, convulsions, and mental disorders. The competence of neurologists includes the following problems:
- headache, facial pain (tics, tremors, migraine, Bell's palsy, etc.);
- back pain (osteochondrosis, disc herniation, radiculitis, etc.);
- epilepsy, seizures (loss, disturbances of consciousness);
- stroke (consequences of strokes);
- head injury, back injury (consequences of injuries);
- parkinsonism, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases.
How is the appointment going?
What does a neurologist do? At the appointment, the neurologist asks the patient about complaints about his health, finds out the reasons for previous visits to medical institutions, studies his medical history (collects anamnesis), and conducts an examination.
After the initial consultation, the doctor refers the patient to the necessary tests (for example, an analysis of the functions of the nervous system, an MRI).
Based on the results of the examination, tests and studies, the neurologist prescribes treatment.
How does a neurologist treat? Both conservative and surgical methods are used for treatment. Treatment tactics are determined only by the specialist himself.
Source: https://DocDoc.ru/library/chto_lechit_nevrolog
Neurologist: what diseases he treats and how the examination is carried out
Neurologists are involved in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of a wide range of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, and provide therapy for certain pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Most of the calls to these specialists are related to pathologies such as neuritis, osteochondrosis and radiculitis.
In their practice, doctors always focus on modern methods of examination and treatment, use special instruments and effective drugs. If necessary, neurologists can refer their patients for surgical interventions.
As a rule, surgical treatment is performed for advanced stages of diseases, when conservative therapy does not give the desired effect.
What does a neurologist treat?
Neurologists treat headaches, osteochondrosis (cervical and other parts), spinal hernias, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, etc.
Specialists are contacted when:
- Osteochondrosis of various parts of the spine
- Strokes
- Epilepsy
- Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders
- High and low blood pressure
Professionals deal with disorders associated with genetic disorders caused by fetal hypoxia and other complications during pregnancy and childbirth, injuries, inflammatory diseases (including meningitis), degenerative disorders in the spine, articular cartilage, etc.
Neurologists pay special attention to complications of the perinatal period. Pediatric specialists provide comprehensive diagnostics and treatment for cerebral palsy and other lesions of the nervous system.
Some pathologies (for example, headaches) are eliminated by neurologists together with other doctors. In especially severe cases, councils of doctors gather and decide on conservative therapy or surgical intervention.
Specialists will develop a method for managing the patient, which will ensure the preservation of his health.
When to contact a neurologist?
You should make an appointment with a specialist if:
- Headaches. It is especially important to get an appointment as soon as possible if the pain is sudden and sharp, gradually increases and is not relieved by standard medications.
- Frequent dizziness, pre-syncope and fainting
- Pain in the face, neck, back, limbs, throughout the body
- Muscle weakness
- Disorders of sleep, speech, memory, concentration
- Unsteadiness of gait and general lack of coordination of movements
- Uncontrolled limb movements (including tics)
You should consult a doctor as soon as possible if your child:
- Curls your toes when standing or walking
- Has difficulty falling asleep and wakes up frequently
- Distracted and unable to concentrate
- Gets tired quickly
- Suffering from memory loss
- Doesn't do well at school
- Has difficulty communicating with peers
Important! Don't put off visiting your doctor until later. Some of the diseases that fall under the purview of neurologists progress rapidly and are irreversible. Their effective therapy is possible only in the early stages. At this stage, you can stop the progression of the pathological process and relieve some symptoms.
How is the reception going?
An appointment with a neurologist always begins with a conversation with the patient. It is important for the specialist to collect an anamnesis.
To do this, the patient should inform the doctor about:
- Genetic predisposition to certain diseases
- Worrying symptoms, their severity and frequency of occurrence
- Medicines taken
It is advisable to bring all the results of examinations (if any), extracts and other medical documentation to your appointment with a neurologist. This will allow the doctor to make the most accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time and begin treatment.
Important! If the patient cannot independently express his thoughts clearly, a relative or other representative must come with him to the appointment. It is he who will have to answer all the questions. You should prepare for the consultation in advance.
After the conversation, the doctor conducts an examination.
The neurologist must evaluate:
- Motor activity
- Symmetry of limbs and shoulders
- Features of posture
- The degree of trembling of the hands and body as a whole
The specialist checks reflexes and muscle strength, temperature and pain sensitivity of the skin. Coordination of movements, the ability to correctly assess the spatial position of the body, and stability in various poses are also determined. Today, neurologists have a number of simple tests in their arsenal. They give a general idea of the state of the nervous system.
In some cases, the doctor can immediately make a diagnosis and begin treatment for the identified pathology. If this is not possible, a comprehensive examination is carried out.
Diagnosis by a neurologist
- A comprehensive examination includes both laboratory and instrumental methods.
- Lab tests
- Research:
- Blood (general and biochemical)
- Urine
Instrumental methods
- Vascular ultrasound (Doppler scanning). The study is carried out to assess the blood flow of blood vessels, assess the width of their lumen, and identify stenoses
- Radiography. Such a study makes it possible to assess the condition of musculoskeletal and other structures, identify injuries, detect their consequences, etc.
- CT. Computed tomography is performed to detect atrophy of the cerebral cortex, compression of its structures, hydrocephalus, etc.
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to obtain detailed images of all nerve structures and determine their functionality in order to identify a number of diseases
- Echoencephalography. This study replaces CT and MRI when examining children under 2 years of age and diagnosing hemorrhages in bedridden patients.
- PAT. Such a study is especially informative for strokes, epilepsy, brain tumors
If necessary, other examinations are carried out. Based on their results, the neurologist determines what treatment to prescribe for a particular patient.
Advantages of contacting a MEDSI neurologist
- Experienced specialists. Our neurologists constantly improve their skills and undergo training in leading Russian and foreign centers. Specialists successfully adopt international experience and implement their own proprietary developments into practice
- Traditional and modern diagnostic methods. A comprehensive examination can be completed in just one day. Thanks to this, treatment by a neurologist for any pathology - from headaches to intervertebral hernia - will begin in the near future
- Effective therapy for a wide range of diseases. Only modern methods and drugs are always used for treatment. Therapy is carried out using international protocols and does not cause complications
- Opportunities for consultations with neurologists, traumatologists and neurosurgeons. If necessary, a council of doctors meets
- A wide range of techniques used for therapy. The clinic provides physiotherapeutic treatment, massage, and reflexology methods.
- Availability of modern equipment. We have installations for electromassage and other procedures
If you want to make an appointment with a neurologist and undergo treatment for osteochondrosis of the spine (cervical and other parts), intervertebral hernia, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, tension headaches, migraines and other pathologies, call +7 (812) 336-33-33.
Source: https://spb.medsi.ru/articles/nevrolog-kakie-zabolevanie-lechit-i-kak-provoditsya-osmotr/