Optic nerve atrophy can be congenital or acquired .
In the second case, the causes of atrophy are most often pathological processes in the retina or optic nerve.
The disease can develop after a syphilitic lesion, meningitis, with tumors and multiple sclerosis, with a brain abscess, with various intoxications or poisonings.
The cause of the pathology can also be vascular atherosclerosis, fasting, hypertension, vitamin deficiency, and profuse bleeding.
There are several forms of atrophy:
- Primary atrophy occurs after deterioration of nerve trophism and microcirculation disturbance. This includes descending atrophy of the optic nerve (a consequence of damage to the optic nerve fibers) and ascending atrophy (a consequence of damage to retinal cells).
- Secondary atrophy is the result of damage to the optic nerve head due to pathologies occurring in the retina and optic nerve.
- Not all forms of pathology cause vision loss. For example, with atrophy of peripheral fibers without involvement of the papillomacular bundle, vision is preserved.
- Hereditary Leber atrophy of the gender type is distinguished as a special form . The disease develops mainly in men of the same family aged 13 to 28. The clinical picture is characterized by a sharp decrease in vision in both eyes at once for two to three days.
- Glaucomatous atrophy occurs as a result of collapse of the lamina cribrosa as a result of increased intraocular pressure.
Atrophy can be complete or partial. With complete atrophy, the function of the optic nerve is completely lost. With partial atrophy, visual impairment occurs.
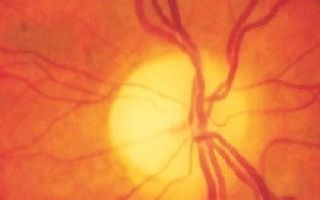
Picture: stages of optic nerve atrophy
During the course of the disease, the nutrition of nerve fibers deteriorates. Vision begins to gradually deteriorate until complete blindness. No vision correction is possible; sometimes, with the rapid development of the process, vision is lost irrevocably within three months.
With atrophy, the symptoms can be of a different nature: narrowing of the visual field, color vision disorder, or the appearance of black spots in the visual field (the most common symptom). In this case, you need to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostics abroad
Abroad, the diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy is carried out using modern techniques:
- The examination begins with ophthalmoscopy.
- Spheroperimetry helps determine the boundaries of vision.
- Computer perimetry is used to identify atrophied areas of the nerve.
- Video ophthalmography helps to identify the nature of the damage.
- Additional examinations, such as skull x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help determine the presence or absence of a brain tumor, which may be one of the causes of the pathology.
- Fluorescein angiography and laser Dopplerography may also be prescribed as an examination.
As a rule, all procedures abroad are carried out in one clinic. The patient also undergoes a mandatory examination to identify hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, etc.
Modern methods of treatment
The pathology is difficult to treat, since the nerve fibers are not restored. Therefore, treatment should begin as quickly as possible before complete destruction of the nerve fibers occurs.
First of all, during treatment the inflammatory process is eliminated, swelling in the optic nerve is removed, trophism and blood circulation are improved.
Ophthalmologists in many countries (Israel, Germany, etc.) have already gained extensive practical positive experience in treating the disease, thanks to close cooperation with research centers around the world.
At the beginning of treatment, it is necessary to provide the nerve with vitamins and nutrition. For this purpose, the most modern medicines are used abroad.
In some cases, a surgical method of delivering nutrients may be used. Physiotherapy allows you to achieve a positive effect. Magnetic stimulation, the effect on the nerve of magnetic alternating fields, helps to improve blood supply and normalize metabolism. Improvement may occur after the first 15 procedures.
In the photo: an eye examination by an ophthalmologist
Laser and electrical stimulation (impacting impulses on the nerve) are also used to treat atrophy. A good effect is observed after just a few sessions.
One of the newest methods of combating the disease is the use of tissue regenerative microsurgery.
Stem cells and the latest advances in nanotechnology are used for treatment, thanks to which nanoparticles are used to deliver nutrients to the optic nerve.
More often, not a single method is used for treatment, but the complex use of several techniques. Thanks to this approach, ophthalmology abroad has achieved outstanding results in the treatment of eye pathologies.
Stem cell treatment
The newest treatment method abroad is stem cell treatment. Stem cells are injected into the optic nerve area. Administration is carried out every 2 hours up to 10 times a day.
A simpler method of introducing stem cells without surgery has been developed.
The method of introducing stem cells consists of injecting them into the patient, with an interval of 3 months to six months for three procedures. A simple lens is used as the basis for the stem cell carrier.
A positive effect is provided by cytokines, interleukins, and growth factors contained in stem cells, which activate restoration processes and support the vital activity of cells.
Where to go?
Treatment of the disease abroad is carried out in leading clinics in Germany, Israel, the USA, Austria, Finland, and Switzerland. Treatment is usually carried out in courses of up to 14 days, based on the diagnosis of the disease, identifying the causes of the pathology and their elimination.
Germany
In Germany, treatment is carried out:
- At the University Clinic of Cologne;
- At the L. Maximilian University Multidisciplinary Clinic in Munich;
- At the ophthalmology clinic of Dr. med. G. Palme in Düsseldorf;
- At the St. Martinus Clinic in Düsseldorf;
- At the ophthalmological medical center at the university clinic in Essen;
- At the University Center for Ophthalmology in Frankfurt am Main;
- At the Clinic for Refractive and Ophthalmic Surgery in Duisburg.
Treatment of optic atrophy in children is carried out at the Clinic for Psychomotor Disorders, Periocular Surgery and Pediatric Ophthalmology in Tübingen.
Israel
In Israel, pathology treatment is carried out:
- At Hadassah University Hospital in Jerusalem by Dr. Yitzhak Hemo;
- At the Ichilov Clinic by Dr. Shimon Kurtz;
- At the Assuta clinic;
- At the Herzliya Medical Center;
- At the medical center. Yitzhak Rabin;
- At the medical center. Souraski;
- At the Rambam medical center.
Austria
In Austria, treatment is carried out:
- At the University Eye Clinic of Vienna by Dr. E. Ergun;
- At the Clinic for Laser Eye Surgery in Vienna by Dr. Reinhard Schranz;
- At the Ophthalmology Center of the Confraternity-Private Clinic Josefstadt by Dr. Christian Lammerhuber.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, qualified and effective treatment can be obtained:
- At the Hirslanden im Park clinic in Zurich;
- At the Cécile Hirslanden clinic in Lausanne;
- At the Hirslanden Clinic in Zurich;
- At the Generale Beaulieu clinic in Geneva;
- At the clinic in Leukerbad.
China
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy in adults and children is successfully carried out in China:
- In Beijing - Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics;
- at Tongren Hospital in Beijing;
- at Daqing People's Hospital.
Infographics: causes, symptoms and treatment of atrophy
Reviews
Natalya : “The child developed optic nerve atrophy due to hydrocephalus. The son was 8 months old, he did not see anything, he only reacted to sunlight. general treatment was carried out by a neuropathologist. After finishing the treatment we went to Ichilov in Israel. As a result of treatment, 70% of vision was restored."
Denis : “At the age of 27, he underwent surgery for basal arachnoiditis of the brain. A year later, a diagnosis of partial atrophy of the optic nerve was made. A year later he began to lose his sight and went with his brother to a Beijing clinic. After treatment, vision stabilized and gradually began to improve.”
Maria : “Atrophy of the optic nerve from birth. As a child, I had surgery to correct strabismus. At the age of 18, she went to the Ikhilov clinic, where she underwent a course of treatment. The eye began to see about a week after the start of treatment.“
Galimov : “I was engaged in karate from the age of 18, received a blow to the head, after which atrophy of the optic nerve began to develop. I went to a clinic in Germany, where after the treatment my vision improved to 90%.“
Source: https://medclinic-tour.com/oftalmologiya/atrofiya-zritelnogo-nerva
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy - how it is done
Damage to the optic nerve, which results in visual impairment, is called atrophy. Previously, there was no way to treat optic nerve atrophy, which led to irreversible blindness.
Table of contents
Methods
Partial
Disability Surgery
Methods
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy is a rather complex and time-consuming process for doctors, since one must remember that it is impossible to restore dead fibers of the optic nerve. In addition, there are many causes of optic nerve atrophy, so the diagnostic search can take a long time.
- Treatment of the disease can be carried out in three directions:
- conservative treatment
- physiotherapeutic treatment
- surgery
- Conservative therapy implies the prescription of symptomatic treatment, including:
- vasodilators;
- drugs that improve blood supply to the optic nerve (aminophylline, trental, no-spa, nicotinic acid, papaverine)
- anticoagulants (ticlid, heparin)
- drugs that improve metabolic processes in nerve tissue (biogenic stimulants, enzymes, amino acids, immunostimulants)
- drugs whose action is aimed at stimulating metabolic processes and resolving pathological processes (preductal), stopping the inflammatory process (hormones), improving the functioning of the nervous system (cavinton, nootropil, emoxypine)
- Electrical, magnetic and laser stimulation of the optic nerve is prescribed as physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Surgical treatment of optic nerve atrophy involves surgery to remove formations compressing it, ligation of the temporal artery, implantation of various biogenic materials that improve blood circulation and vascularization of the nerve.
- Source viewangle.net
- What are the symptoms of optic nerve atrophy?
- Primary glaucoma at the link.
Treatment of open-angle glaucoma with drugs http://ophthalmology.sprvfrm.ru/l4e/otkrytougolnaya-glaukoma.html.
Partial
The prognosis for treatment of partial optic nerve atrophy is favorable.
The main goal of treatment is to stop the changes in the tissue of the optic nerve, aimed at being able to preserve what remains.
It is impossible to completely restore visual acuity, but even without treatment the disease will lead to blindness. The main method of treatment will depend on the cause of optic atrophy.
The drugs used in treatment are drugs to improve blood supply to the nerve, improve metabolism, vasodilators, multivitamins, and biostimulants. These drugs reduce swelling and inflammation in the area of the optic nerve head, improve its nutrition and blood supply, and stimulate the activity of the remaining nerve fibers.
If the patient needs surgical treatment, then it will be the main method of therapy. The emphasis is on treating the underlying disease, eliminating the cause, which led to partial atrophy of the optic nerve.
To achieve a better result, magnetic, electrical, and laser stimulation of the optic nerve, ultrasound, electrophoresis, and oxygen therapy can be prescribed. The earlier treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis of the disease.
Nervous tissue is practically irreparable, so the disease cannot be neglected; it must be treated in a timely manner.
Source ayzdorov.ru
Operation
Surgical treatment - ligation of the temporal artery and implantation of various biogenic materials improve vascularization and blood circulation of the nerve, and decompression surgery of the optic nerve removes excessive compression.
Source zrenue.com
Optic nerve atrophy – is surgery necessary?
It is impossible to restore damaged fibers, so treatment of this disease is focused on maintaining existing vision indicators and stopping the progression of the disease.
Therapy, first of all, begins with eliminating the cause of atrophy, if it is not a hereditary factor.
Afterwards, a traditional treatment regimen is prescribed, consisting of vasodilators, blood circulation tonics, optic nerve trophy surgery and vitamins.
In addition, magnetic, laser or electrical effects are applied to the optic nerve. This helps accelerate tissue regeneration, activate metabolic processes and increase blood supply.
One of the newest methods for treating this pathology is the implantation of an electrical stimulator directly into the orbit of the eye. Despite the high efficiency of this method, it requires large financial investments, requires a long rehabilitation period, and the implant itself only works for a few years.
Source womanadvice.ru
Disability
Optic nerve atrophy is diagnosed based on corresponding changes in the fundus and visual impairment.
With atrophy, blanching of the optic disc, narrowing of the boundaries of the visual field and decreased visual acuity are always noted.
Variable symptoms include narrowing of retinal vessels, a decrease in the number of vessels passing through the edge of the disc, disturbances in color perception and other visual functions.
The severity of atrophy is determined not only by the ophthalmoscopic picture and the degree of visual impairment at the time of the study, but also by whether the process is stable, complete, or in the process of progression. Therefore, when examining patients with optic nerve atrophy, it is necessary to take into account dynamic observation data, reflecting the nature of changes in the peripheral boundaries of the visual field and visual acuity.
The condition of the optic nerve head, changes in the fundus and other symptoms depend on the etiology of atrophy. The etiology of the disease largely determines the severity of the pathology, clinical and occupational prognosis.
The clinical diagnosis for optic nerve atrophy should reflect the etiology of the disease, the form of the clinical course (progressive or stable, non-progressive), the localization of the lesion (optic nerves, chiasm, optic tract), and the state of visual functions.
With a stable, non-progressive form of optic nerve atrophy resulting from poisoning, bleeding and other (sometimes unknown) reasons, patients, in particular, are contraindicated in work associated with the danger of intoxication, especially neurotropic poisons.
Transfer of a patient to another, non-contraindicated job, accompanied by a decrease in qualifications, serves as the basis for determining disability group III.
With progressive forms of optic nerve atrophy, a decrease in visual acuity to 0.2 leads to loss of ability to work in normal working conditions (disability group II). This decrease in vision due to atrophy of the optic nerves is accompanied by a narrowing of the boundaries of the field of vision, often central scotomas, and severe color vision impairment.
Disability group I is assigned to the patient when visual acuity decreases below 0.04, as well as when visual acuity is higher, taking into account the severity of the patient’s general condition, or when the boundaries of the visual field are narrowed, preventing free orientation in space.
Early detection of diseases leading to atrophy of the optic nerves and clinical observation are of great importance for the prevention of profound visual impairment.
Source invalidnost.com
Is the status of a disabled person acquired with optic nerve atrophy?
Yes, with a significant decrease in vision, the issue of assigning a disability group is resolved with the development of an individual rehabilitation program aimed at compensating for the limitations in life activity that arose due to loss of vision.
Source immed.ru
Source: http://ophthalmology.sprvfrm.ru/l4e/lechenie-atrofii-zritelnogo-nerva.html
Optic atrophy
Optic nerve atrophy is a serious ophthalmological disease with a significant decrease in the patient’s visual function. The disease can be triggered by inflammation or dystrophy of the optic nerve, its compression or trauma, leading to damage to the nerve tissue.
Causes of optic nerve atrophy of neurological, infectious, phlebological etiology include brain tumors, meningitis, hypertension, profuse bleeding, atherosclerosis and other diseases. Destruction of the nerve fibers of the optic nerve can also be caused by genetic factors or intoxication of the body.
During the development of optic nerve atrophy, the destruction of nerve fibers gradually occurs, their replacement by connective and glial tissue, and then blockage of the vessels responsible for the blood supply to the optic nerve. As a result, the patient's visual acuity decreases and the optic disc becomes pale.
Reasons for development
Reasons that can cause the development of this eye disease include brain tumors, infectious processes, neurological diseases, and vascular damage.
When optic nerve atrophy forms, the nerve fibers are gradually destroyed, as a result of which they are gradually replaced by connective and glial tissue, and the vessels that supply blood to the optic nerve are blocked. The described phenomenon causes a sharp decline in visual acuity.
Factors contributing to the development of optic nerve atrophy:
- severe intoxication of the body, including drug overdose;
- the presence of congenital pathologies;
- severe alcohol poisoning;
- various viral infections;
- the presence of various eye diseases (glaucoma, neuritis, vascular diseases, retinal pigmentary dystrophy);
- hereditary predisposition;
- presence of profuse bleeding;
- hypertonic disease;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- some diseases of the nervous system (tumor, multiple sclerosis, meningitis, neurosyphilis, serious skull injury).
Classification
We have just found out that the atrophied optic nerve can be either a congenital visual impairment or acquired as a result of certain factors. Hereditary pathology manifests itself in the following forms:
- Autosomal dominant optic atrophy.
- Mitochondrial form of pathology.
- Autosomal recessive form.
In general, a person is born with optic nerve atrophy due to some genetic disorders that arose during fetal development.
For example, Leber's disease, which is caused by a defective RPE65 gene. Because of it, light-sensitive cells in the retina begin to die and are no longer restored. One person in 81,000 suffers from this disease from birth.
The acquired form of nerve death is due to the influence of various etiological factors. These include damage to the fiber structure (descending atrophy), damage to living retinal cells (so-called ascending atrophy). Depending on the course of the disease, primary, secondary, and glaucomatous forms of atrophy are distinguished.
- Primary form. In this case, neurons are compressed throughout the entire visual pathway. The boundaries of the eye disc are still quite clear, it itself is pale, the vessels in the retina narrow somewhat, and excavation may appear. In general, the primary form is considered the simplest and most treatable.
- Secondary form of atrophy. If long-term stagnation occurs in the optic nerve, if it becomes inflamed and is accompanied by signs inherent in the primary form, a deeper disorder is diagnosed. The boundaries of the disc become unclear.
- Glaucomatous form of atrophy. Increased intraocular pressure causes collapse and, as a result, nerve atrophy.
We have already mentioned one hundred percent and partial atrophy of the optic nerve, but now we will consider them in more detail. This is another classification of visual pathology.
From the name itself it is clear that we are talking about one or another scale of damage to nerve cells. With a partial form of atrophy, visual functions are preserved, albeit to an incomplete extent.
For example, there may be disturbances in the area of color perception.
However, this is not the last classification. Atrophy of the nerve endings of the eyes is distinguished by the degree of manifestation. The stationary or non-progressive form is characterized by a stable state of all vision functions, while the progressive form develops quite quickly and is accompanied by a decrease in its quality.
Depending on the scale of the lesion, the pathology can be one-sided (one eye is affected) or two-sided (two nerves of the eyeballs at once).
Optic nerve atrophy in children
Many congenital eye diseases are diagnosed in a child during the first examination in the maternity hospital: glaucoma, cataracts, ptosis of the upper eyelid, etc.
Optic nerve atrophy in children, unfortunately, is not one of them, since its course is often hidden, without external visible symptoms of the disease.
Therefore, the diagnosis of complete damage to the optic nerve or partial atrophy of the optic nerve in children is established, as a rule, in the second month of the child’s life during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
The doctor checks the visual acuity of the newborn, based on the quality of gaze fixation and the child’s ability to follow a moving toy. The infant's field of vision is determined in the same way. If it is not possible to determine visual acuity in this way, then a study of the brain’s reaction to visual stimuli is used.
Using ophthalmological equipment and drugs that dilate the pupil, the baby's fundus is studied. If a clouded optic disc is detected, a diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy is made.
In children, the treatment of the disease follows the same scheme as in adults, with the prescription of vasodilator therapy, nootropics to improve metabolic processes in the brain and courses of light, laser, electrical and magnetic stimulation that stimulate vision.
Symptoms
The main symptom of degenerative processes in the optic nerve is deterioration of vision, defects in visual fields of various locations, loss of clarity of visual perception and completeness of color perception.
With optical neuropathy, the structure of nerve fibers is disrupted, which is replaced by glial and connective tissue. Regardless of the cause of the development of atrophy, it is not possible to restore visual acuity using traditional methods of vision correction (glasses, lenses).
The progressive form of the pathology can last for several months, and in the absence of adequate treatment, end in complete blindness. With incomplete atrophy, degenerative changes reach a certain level and are fixed without further development. Visual function is partially lost.
Alarming symptoms that may indicate that optic nerve atrophy is developing are:
- narrowing and disappearance of visual fields (lateral vision);
- the appearance of “tunnel” vision associated with color sensitivity disorder;
- the occurrence of scotomas;
- manifestation of the afferent pupillary effect.
The manifestation of symptoms can be unilateral (in one eye) or multilateral (in both eyes at the same time).
Complications
The diagnosis of optic atrophy is very serious. At the slightest decrease in vision, you should immediately consult a doctor so as not to miss your chance of recovery. Without treatment and as the disease progresses, vision may disappear completely, and it will be impossible to restore it.
In order to prevent the occurrence of pathologies of the optic nerve, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health and undergo regular examinations by specialists (rheumatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, ophthalmologist). At the first signs of vision deterioration, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
Diagnostics
Self-diagnosis, as well as self-medication (including treatment of optic nerve atrophy with folk remedies) for the disease in question should be completely excluded.
In the end, due to the similarity of the manifestations characteristic of this pathology with manifestations, for example, of a peripheral form of cataract (accompanied initially by impaired lateral vision with subsequent involvement of the central parts) or with amblyopia (a significant decrease in vision without the possibility of correction), it is simply impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis on your own .
What is noteworthy is that even of the listed disease options, amblyopia is not a disease as dangerous as optic nerve atrophy can be for a patient.
Additionally, it should be noted that atrophy can also manifest itself not only as an independent disease or as a result of exposure to another type of pathology, but can also act as a symptom of certain diseases, including diseases that end in death.
Considering the seriousness of the lesion and all possible complications, it is extremely important to promptly begin diagnosing optic nerve atrophy, to find out the reasons that provoked it, as well as to adequately treat it.
The main methods on which the diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy is based include:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- perimetry;
- color vision research method;
- CT scan;
- radiography of the skull and sella turcica;
- NMR scanning of the brain and orbit;
- fluorescein angiography.
Also, a certain information content is achieved to compile a general picture of the disease through laboratory research methods, such as blood tests (general and biochemical), testing for borelliosis or syphilis.
How to treat?
There is a widespread belief in society that “nerve cells do not recover.” This is not entirely correct. Neurocytes can grow, increase the number of connections with other tissues and take on the functions of dead “comrades”. However, they do not have one property that is very important for complete regeneration - the ability to reproduce.
Can optic nerve atrophy be cured? Definitely not. If the trunk is partially damaged, medications can improve visual acuity and fields. In rare cases, even virtually restore the patient's ability to see to normal levels. If the pathological process completely disrupts the transmission of impulses from the eye to the brain, only surgery can help.
To successfully treat this disease, it is necessary, first of all, to eliminate the cause of its occurrence. This will prevent/reduce cell damage and stabilize the course of pathology.
Since there are a large number of factors that cause atrophy, doctors' tactics can vary significantly for different conditions. If it is not possible to cure the cause (malignant tumor, hard-to-reach abscess, etc.)
), you should begin immediately to restore the functionality of the eye.
Modern methods of nerve restoration
Just 10-15 years ago, the main role in the treatment of optic nerve atrophy was given to vitamins and angioprotectors. At present, they have only additional meaning. Medicines that restore metabolism in neurons (antihypoxants) and increase blood flow to them (nootropics, antiplatelet agents and others) come to the fore.
A modern scheme for restoring eye functions includes:
- Antioxidant and antihypoxant (Mexidol, Trimetazidine, Trimectal and others) - this group is aimed at tissue restoration, reducing the activity of damaging processes, and eliminating “oxygen starvation” of the nerve. In a hospital setting, they are administered intravenously; during outpatient treatment, antioxidants are taken in the form of tablets;
- Microcirculation correctors (Actovegin, Trental) - improve metabolic processes in nerve cells and increase their blood supply. These drugs are one of the most important components of treatment. Also available in the form of solutions for intravenous infusions and tablets;
- Nootropics (Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Glutamic acid) are stimulators of blood flow to neurocytes. Accelerate their recovery;
- Drugs that reduce vascular permeability (Emoxipin) - protects the optic nerve from further damage. It was introduced into the treatment of eye diseases not so long ago and is used only in large ophthalmological centers. It is administered parabulbarly (a thin needle is passed along the wall of the orbit into the tissue surrounding the eye);
- Vitamins C, PP, B6, B12 are an additional component of therapy. These substances are believed to improve metabolism in neurons.
The above is a classic treatment for atrophy, but in 2010, ophthalmologists proposed fundamentally new methods for restoring eye function using peptide bioregulators.
At the moment, only two drugs are widely used in specialized centers - Cortexin and Retinalamin.
Studies have shown that they improve vision almost twice.
Their effect is realized through two mechanisms - these bioregulators stimulate the restoration of neurocytes and limit damaging processes. The method of their application is quite specific:
- Cortexin - used as injections into the skin of the temples or intramuscularly. The first method is preferable, since it creates a higher concentration of the substance;
- Retinalamin - the medicine is injected into the parabulbar tissue.
The combination of classical and peptide therapy is quite effective for nerve regeneration, but even this does not always achieve the desired result. You can additionally stimulate recovery processes with the help of targeted physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy for optic atrophy
There are two physiotherapeutic techniques, whose positive effects are confirmed by scientific research:
- Pulsed magnetic therapy (MPT) - this method is not aimed at restoring cells, but at improving their functioning. Thanks to the directed influence of magnetic fields, the contents of neurons are “condensed”, which is why the generation and transmission of impulses to the brain is faster;
- Bioresonance therapy (BT) - its mechanism of action is associated with improving metabolic processes in damaged tissues and normalizing blood flow through microscopic vessels (capillaries).
They are very specific and are used only in large regional or private ophthalmology centers, due to the need for expensive equipment. As a rule, for most patients these technologies are paid, so BMI and BT are used quite rarely.
Prevention
Measures that will reduce the risk of atrophy to a minimum are a standard list:
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner.
- Eliminate the possibility of injury to the brain and visual organs.
- Visit your oncologist regularly to detect cancer early.
- Avoid excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Monitor your blood pressure status.
A periodic examination by an ophthalmologist will help to detect the presence of the disease in time and take measures to combat it. Timely treatment is a chance to avoid complete loss of vision.
Forecast
If optic nerve atrophy was diagnosed and treated at an early stage, vision may be preserved and even slightly improved, but visual function will not be fully restored. With progressive optic nerve atrophy and untreated, complete blindness can develop.
Source: https://p-87.ru/health/atrofiya-zritelnogo-nerva/
Partial optic atrophy: treatment, where it can be cured, descending, symptoms, in children
A rapid decrease in vision may indicate various eye diseases.
But rarely does anyone think that it can be caused by such a dangerous disease as optic nerve atrophy. The optic nerve is an important component in the perception of light information.
Therefore, it is worth taking a closer look at this disease so that it is possible to identify the symptoms in the early stages.
What it is?
The optic nerve is a nerve fiber responsible for processing and transmitting light information. The main function of the optic nerve is to deliver nerve impulses to the brain area.
The optic nerve is attached to retinal ganglion neurocytes, which make up the optic disc. Light rays, converted into a nerve impulse, are transmitted along the optic nerve from the retinal cells to the chiasma (the segment where the optic nerves of both eyes intersect).
Where is the optic nerve located?
Its integrity ensures high visual acuity. However, even the smallest injuries to the optic nerve can lead to serious consequences. The most common disease of the optic nerve is its atrophy.
Optic atrophy is an eye disease in which the optic nerve deteriorates, resulting in decreased vision.
With this disease, the fibers of the optic nerve completely or partially die and are replaced by connective tissue.
As a result, light rays falling on the retina of the eye are converted into an electrical signal with distortions, which narrows the field of view and reduces its quality.
Depending on the degree of damage, optic nerve atrophy can be partial or complete. Partial atrophy of the optic nerve differs from complete atrophy by a less pronounced manifestation of the disease and preservation of vision at a certain level.
Vision correction using traditional methods (spectacle lenses, contact lenses) for this disease is absolutely ineffective, since they are aimed at correcting the refraction of the eye and have nothing to do with the optic nerve.
Causes
Optic nerve atrophy is not an independent disease, but is a consequence of some pathological process in the patient’s body.
Optic atrophy
The main causes of the disease include:
- Eye diseases (diseases of the retina, eyeball, eye structures).
- Pathologies of the central nervous system (brain damage due to syphilis, brain abscess, skull injury, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis).
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (cerebral atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, vascular spasm).
- Long-term toxic effects of alcohol, nicotine and drugs. Alcohol poisoning with methyl alcohol.
- Hereditary factor.
Optic nerve atrophy can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital optic atrophy occurs as a result of genetic diseases (in most cases Leber disease). In this case, the patient has poor quality of vision from birth.
Acquired optic atrophy appears as a result of certain diseases in older age.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of partial visual atrophy may be:
- Deterioration in the quality of vision and the inability to correct it with traditional correction methods.
- Pain when moving the eyeballs.
- Change in color perception.
- Narrowing of visual fields (up to the manifestation of tunnel syndrome, in which the ability to peripherally view is completely lost).
- The appearance of blind spots in the field of vision (scotomas).
Laser vision correction methods can be seen in the material.
Stages of optic nerve atrophy
Diagnostics
Typically, diagnosing this disease does not cause any particular difficulties. As a rule, the patient notices a significant decrease in vision and consults an ophthalmologist, who makes the correct diagnosis. Identifying the cause of the disease is of great importance.
To identify optic nerve atrophy in a patient, a set of diagnostic methods is performed:
- Visometry (visual acuity test).
- Spheroperimetry (determination of visual fields).
- Ophthalmoscopy (detection of pallor of the optic nerve head and narrowing of the fundus vessels).
- Tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure).
- Video-ophthalmography (study of the optic nerve relief).
- Computer perimetry (study of areas of the affected nerve).
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (a study of the brain to identify possible causes of optic atrophy).
Read the article about what computer perimetry determines in ophthalmology.
In addition to an ophthalmological examination, the patient may be prescribed an examination by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. This is necessary because the symptoms of optic nerve atrophy may be symptoms of an incipient intracranial pathological process.
Treatment
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy is quite complex. Destroyed nerve fibers cannot be restored, so first of all it is necessary to stop the process of changes in the tissues of the optic nerve.
Since the nerve tissue of the optic nerve cannot be restored, visual acuity cannot be raised to the previous level. However, the disease must be treated to avoid its progression and blindness.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the timing of the start of treatment, so it is advisable to immediately consult an ophthalmologist when the first symptoms of the disease are detected.
The difference between partial optic nerve atrophy and complete one is that this form of the disease is treatable and it is still possible to restore vision. The main goal in the treatment of partial optic nerve atrophy is to stop the destruction of optic nerve tissue.
The main efforts should be aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. Treatment of the underlying disease will stop the destruction of optic nerve tissue and restore visual function.
During the treatment of the underlying disease that caused optic nerve atrophy, complex therapy is carried out. Additionally, during treatment, medications can be used to improve blood supply and nutrition to the optic nerve, improve metabolism, eliminate swelling and inflammation. It would be a good idea to take multivitamins and biostimulants.
The main drugs used are:
- Vasodilators. These drugs improve blood circulation and trophism in the tissues of the optic nerve. Among the drugs in this group one can highlight complamin, papaverine, dibazol, no-shpu, halidor, aminophylline, trental, sermion.
- Drugs that stimulate the restoration of altered tissues of the optic nerve and improve metabolic processes in it. These include biogenic stimulants (peat, aloe extract), amino acids (glutamic acid), vitamins and immunostimulants (eleuthorococcus, ginseng).
- Drugs that resolve pathological processes and metabolic stimulants (phosphaden, pyrogenal, preductal).
It is necessary to understand that drug therapy does not treat optic nerve atrophy, but only helps to improve the condition of the nerve fibers. To cure optic nerve atrophy, it is necessary to first cure the underlying disease.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, which are used in combination with other treatment methods, are also important. Also, methods of magnetic, laser and electrical stimulation of the optic nerve are effective. They help improve the functional state of the optic nerve and visual functions.
The following procedures are used as additional treatment:
- Magnetic stimulation. During this procedure, the optic nerve is exposed to a special device that creates an alternating magnetic field. Magnetic stimulation helps improve blood supply, saturate the tissues of the optic nerve with oxygen, and activate metabolic processes.
- Electrical stimulation. This procedure is carried out using a special electrode, which is inserted behind the eyeball to the optic nerve and electrical impulses are applied to it.
- Laser stimulation. The essence of this method is non-invasive stimulation of the optic nerve through the cornea or pupil using a special emitter.
- Ultrasound therapy. This method effectively stimulates blood circulation and metabolic processes in the tissues of the optic nerve, improves the permeability of the blood-ophthalmic barrier and the sorption properties of eye tissues. If the cause of optic nerve atrophy is encephalitis or tuberculous meningitis, then the disease will be quite difficult to treat with ultrasound.
- Electrophoresis. This procedure is characterized by the effect of low-power direct current and drugs on the eye tissue. Electrophoresis helps to dilate blood vessels, improve cell metabolism and normalize metabolism.
- Oxygen therapy. This method consists of saturating the tissues of the optic nerve with oxygen, which helps improve metabolic processes in them.
“AMO-ATOS-E” device with “Headband” attachment, combined magnetic therapy and transcranial electrical stimulation
During treatment of optic nerve atrophy, it is imperative to maintain a high-quality diet rich in various vitamins and minerals. It is necessary to consume fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals, meat, and dairy products more often.
See what foods improve vision here.
It is not recommended to treat the disease with folk remedies, since in this case they are ineffective. If you rely only on folk remedies, you can lose precious time when you could still preserve the quality of your vision.
Complications
It must be remembered that optic nerve atrophy is a serious disease and should not be treated on its own. Incorrect self-treatment can lead to dire consequences - complications of the disease.
The most serious complication may be complete loss of vision. Ignoring treatment leads to further development of the disease and a steady decrease in visual acuity, as a result of which the patient will no longer be able to lead his previous lifestyle. Very often, with optic nerve atrophy, the patient becomes disabled.
Also read about heterochromia here.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of optic nerve atrophy, it is necessary to treat diseases in a timely manner, consult an ophthalmologist in a timely manner if visual acuity decreases, and not expose the body to alcohol and drug intoxication. Only if you pay due attention to your health can you reduce the risk of disease.
What is retinal detachment?
What to do if myopia progresses, read this article.
How to treat strabismus in children: https://eyesdocs.ru/zabolevaniya/kosoglazie/detej-pochemu-voznikaet-i-kakim-obrazom-lechitsya.html
Video
conclusions
It is quite possible to stop partial atrophy of the optic nerve in the initial stages of the disease. This disease requires long-term treatment, endurance and patience. And only with the correct identification of the cause of the disease is a complete recovery and preservation of visual acuity at a high level possible.
Symptoms of glaucoma, treatment with folk remedies, follow the link.
Source: https://EyesDocs.ru/zabolevaniya/atrofiya-zritelnogo-nerva/chastichnaya-lechenie.html
Optic nerve atrophy - the most effective treatment methods at the Moscow Eye Clinic. Reasonable prices, experienced doctors!
Causes Symptoms Diagnostics Treatment Our advantages Price
Optic atrophy is a severe, often progressive disease in which there is a gradual irreversible deterioration in visual acuity, up to the development of blindness. According to WHO, the frequency of detection of this disease is growing throughout the world, and this trend is especially noticeable among the population of economically developed countries. Despite the advances of modern medicine, the search for more effective treatments for optic atrophy is still ongoing.
The optic nerve is formed by processes of nerve cells in the retina of the eye. Retinal cells have the ability to perceive light and convert it into nerve impulses, which are then transmitted along the optic nerve to certain areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for the formation of visual images.
Due to the influence of many different factors, the fibers of the optic nerve can gradually deteriorate and die, while the conduction of nerve impulses from the retina to the brain also gradually deteriorates.
For quite a long period of time, the process of destruction of optic nerve fibers remains invisible to the patient, so he does not consult a doctor.
At the same time, the later treatment for optic nerve atrophy is started, the worse the prognosis for the course of the disease, because it will be impossible to restore lost vision.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, partial optic nerve atrophy (PANA ) is distinguished when visual functions are preserved and complete atrophy when vision is absent.
Causes of development of optic nerve atrophy
- Optic nerve atrophy can be caused by a variety of causes, including neuritis, neoplasms, glaucoma, vascular atherosclerosis, poisoning with certain substances (methanol, nicotine), acute viral infections, hypertension, retinal pigmentary dystrophy, etc.
- Based on the reasons, it is customary to distinguish several types of disease:
- Primary optic atrophy
The cause of the development of primary optic nerve atrophy is diseases that are accompanied by impaired microcirculation and trophism of the optic nerve.
It can be observed in atherosclerosis, degenerative diseases of the cervical spine, and hypertension.
Secondary optic atrophy
The pathology occurs as a consequence of swelling of the optic disc due to diseases of the retina or the nerve itself (inflammation, tumor, poisoning with surrogate alcohol, quinine, trauma, etc.).
Symptoms
Patients with optic atrophy may complain of decreased visual acuity and the inability to restore it with glasses or contact lenses; many note pain when moving the eyes, persistent headaches, and deterioration of color vision. Subjectively, patients may note that in the dark they see better than on a sunny day.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic sign of optic nerve atrophy is visual field impairment, detected during an appropriate ophthalmological examination.
When examining the fundus, pronounced pallor of the optic disc, a change in its shape or clarity, and sometimes bulging of the central part of the disc are diagnosed.
Treatment of partial optic atrophy
Drug treatment is aimed at improving microcirculation and trophism in the affected nerve, in order to prevent further progression of pathological changes and slow down the process of vision loss.
Local therapy includes the use of injections of drugs to improve microcirculation, B vitamins, etc. (in the form of subconjunctival, parabulbar, retrobulbar, intravenous and intramuscular injections). Also used are hardware and physiotherapeutic techniques (magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, etc.), laser therapy, and hirudotherapy.
Since in many cases optic nerve atrophy is the outcome of common diseases (atherosclerosis, hypertension), treatment of the underlying disease is mandatory. Patients with degenerative changes in the cervical spine are prescribed various techniques to improve blood circulation in the collar area and relieve muscle-tonic syndrome (massage, mesotherapy, exercise therapy).
Surgical methods for treating optic nerve atrophy are aimed at improving the trophism of the affected nerve (optic nerve revascularization).
Advantages of treatment at MGK
Modern equipment used in our clinic allows our doctors to conduct examinations in the shortest possible time, painlessly and with comfort for the patient, while it is possible to identify any pathologies of the visual apparatus at the initial stage, when there are no symptoms of the disease.
The clinic's doctors have extensive practical experience in treating eye diseases, including optic nerve atrophy. MGC uses the widest range of treatment procedures to preserve vision in patients with optic nerve atrophy.
A comprehensive treatment program has been developed using drug therapy, hardware techniques, hirudotherapy, and physiotherapeutic treatment.
Our specialists are ready to provide highly professional assistance to patients with the most severe forms of optic atrophy.
The specialists of our clinic have developed course treatment programs for patients with optic nerve atrophy, aimed at preserving and restoring visual functions for 10 and 15 days, including the use of medicinal leeches (hirudotherapy).
To improve the quality of treatment and achieve the best results, the clinic operates a hospital (including a day hospital), where patients can receive all necessary treatment in a timely manner and in full, while under the supervision of the attending physician.
Treatment price
The cost of treatment for optic nerve atrophy at MGK is calculated individually and will depend on the volume of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling 8 (495) 505-70-10 and 8 (495) 505-70-15 or online, using Skype consultation on the website, you can also familiarize yourself with the “Prices” section.
Go to the “Prices” section>>>
Source: https://mgkl.ru/uslugi/atrophiya-zritelnogo-nerva