It is easy to get confused in the variety of names of dental diseases. Startsmile divided the most common diseases into three categories and presented a description of dental diseases, their photos and names in a simple and understandable table.
The main cause of dental diseases is the activity of bacteria, which results in caries. But there are other factors that affect oral health:
- heredity and genetic pathologies;
- quality of drinking water;
- ecology of the urban environment;
- nutritional features;
- professional activity.
In most cases, it is impossible to change anything from this list. Therefore, it is important to at least be able to promptly recognize the symptoms of dental disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Classification of dental diseases
Pathologies of teeth eruption and formation
Early detection of dental anomalies makes it easier to carry out subsequent bite correction. Irregularities in the sequence of eruption or asymmetry of opposing teeth should be a reason to contact an orthodontist. Diagnostic accuracy is ensured through x-ray examination.
Edentia
Characterized by partial or complete absence of teeth. The disease can be hereditary or develop throughout life. Sometimes the rudiments of teeth are completely absent from birth.
Supernumerary teeth (hyperdontia)
There are too many teeth in the mouth, and the extra ones can be located both in the dentition, disturbing the arrangement of the remaining teeth, and in atypical places - on the palate or on the front surface of the gums. The anomaly occurs in 5% of the population.
Impacted teeth
The teeth remain in the bone tissue of the jaw and do not erupt completely. In most cases, this is a disease of the molars - eights.
Dystopian teeth
The teeth are located in the wrong places in the jaw, at an angle, and only partially erupt. Pathology refers to diseases of wisdom teeth.
Macrodentia/Microdentia
An increase (or decrease) in the size of teeth compared to the standard norm.
Tooth enamel diseases
There are many chemical processes going on in the mouth that wear down the enamel. Under the influence of food containing dyes or acids, as well as cleaning products, the normal mineralization of teeth is disrupted. Pathologies of the endocrine system and work in hazardous industries are additional unfavorable factors.
Fluorosis
Damage caused by an excess of fluoride in consumed water or food. Fluorosis is commonly referred to as yellow tooth disease.
Enamel hypoplasia
A disease associated with impaired formation of the enamel structure. In most cases, it develops in the first nine months of a child's life.
Wedge-shaped defect
Formation of a “protrusion” at the neck of the tooth on the front side. A disease of the front teeth that can lead to chipping of the entire crown part.
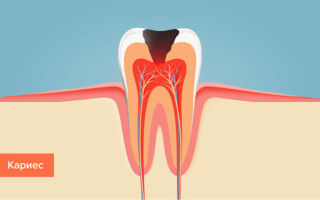
Dental disease caries and its complications
Dental caries occurs in places where microbial plaque lingers and accumulates. The likelihood of developing the disease depends on the individual resistance of both dental tissues and the body as a whole.
Resistance to caries is determined by the structure and composition of the enamel, the degree of its mineralization, as well as the characteristics of the dental system - the structure of the facial skeleton, jaws, bite and location of the teeth.
Caries
A pathology that develops in the hard tissues of the tooth, accompanied by demineralization of the enamel and the formation of a cavity. If left untreated, it provokes the development of inflammation in the pulp and periodontal tissues.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the dental nerve. Characterized by acute pain radiating to the temples. May lead to tooth loss or exacerbation of periodontitis.
Periodontitis
The inflammatory process covers the apex of the tooth root. Without treatment, there is a risk of developing a cyst or abscess. The main manifestations are swelling of the gums, increased temperature.
Periostitis (flux)
Inflammation of the periosteum due to untreated periodontitis. Accompanied by swelling of the gums and severe pain.
Granuloma
Proliferation of inflammatory tissue in the area of the tooth root. Symptoms are redness and swelling of the gums, tooth pain. Ignoring the disease leads to the appearance of a cyst on the root of the tooth, fistula and diseases of the roots of the teeth.
Tooth cyst
A formation in the form of a capsule with pus at the apex of the tooth root, resulting from the penetration of infection into the root canals. The disease is asymptomatic, in some cases there is pain when chewing. The cyst is usually noticed on x-rays.
If you find signs of dental disease presented in the table, you must go to a dental clinic as soon as possible and consult a doctor. The specialist will examine the oral cavity, prescribe diagnostic procedures and draw up an optimal treatment plan for dental diseases to restore the health and beauty of your smile.
Prevention of dental diseases
Some people are not even aware of what dental diseases with inflammatory processes and pathologies are provoked in other vital organs. For those who are not in the know, we inform you: these are gastritis, ulcers, tonsillitis, thrombosis, heart attack and stroke! And the pathogenic bacteria are to blame for everything, which, multiplying in the oral cavity, enter the throat, stomach, blood vessels and even the heart.
To prevent dental diseases, follow simple rules that will help significantly improve your oral health and overall well-being.
- Stop smoking. A bad habit provokes vasoconstriction and deterioration of blood supply to the mucous membrane, which results in a lack of nutrients necessary for teeth and gums.
- Eat a balanced diet. The abundance of flour and sweet foods in the diet contributes to an excessive increase in microorganisms and inevitably leads to caries and its complications. Take care of strengthening your enamel by taking vitamin complexes. Then the disease when “teeth crumble”, which occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body, will not be scary for you.
- Brush your teeth 2 times a day. Regular hygiene is one of the most effective ways to keep your teeth safe and sound. In addition to the traditional use of brushes and pastes, you should not neglect dental floss. Flosses effectively remove food debris between the teeth, preventing the development of many diseases.
- Get preventive examinations once every six months. It is easier to cure any disease if it is detected at the beginning of its development. Some dental diseases in dentistry have symptoms that cannot be identified on their own. For example, caries at the junction of teeth is visible only on an x-ray.
A person is not able to influence factors that cause various types of dental diseases, such as poor ecology, heredity, and stress. However, with a responsible attitude towards hygiene and prevention, the risk of dental diseases can be significantly reduced or, at least, their treatment can be facilitated.
- Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
- Author of the material: Ekaterina Gasparova
- With the support of practicing dentists, magazine experts
Source: https://www.StartSmile.ru/terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya/bolezni-zubov/
From sick teeth to a sick heart: the word of a dentist
AptekaMos.ru
That's all. The doctor successfully placed the filling. The unbearable pain no longer bothers me. You breathe a sigh of relief and return to your previous activities and your previous lifestyle. But in vain. The most ordinary caries leads to serious diseases - heart defects, pneumonia... And at the same time it sends a signal: the body is not in order, it already has diseases that you are not even aware of yet.
After visiting the dentist, it may be worth making an appointment with other specialists: gastroenterologist, cardiologist, neurologist...
What do caries and other oral diseases How to recover with minimal losses?
The story is told by dentist-therapist, candidate of medical sciences, general director of the Italian Dental Center IMEZA Natela Aleksandrovna Lomakina.
In addition to caries, which almost 100% of the adult population and 75% of children have, dental diseases such as pulpitis, periodontitis, and dental cysts can be distinguished.
The most common gum diseases are periodontal disease, periodontitis, gingivitis; diseases of the oral mucosa - stomatitis, xerostomia, cheilitis; inflammation of the tongue - glossitis, periostitis of the jaw, various infections, fungal diseases.
From toothache to... sepsis
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth, nerves and blood vessels, most often due to advanced caries. Characterized by acute or aching pain, swelling, the tooth begins to react to cold, hot, etc. If pulpitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis .
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the roots of the tooth. At this stage of the disease, toothache intensifies, the temperature may rise, and fistulas and cysts may form around the diseased tooth. In this case, saving the tooth is very difficult, sometimes impossible.
And treatment is complex and lengthy.
Another complication of pulpitis is periostitis , purulent inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw. It is characterized by high body temperature, a feeling of fullness near the diseased tooth, and a change in the shape of the face.
Pulpitis has other complications, including sepsis - blood poisoning , so it is necessary and best to treat it in the earliest stages.
Gums and more
In second place after caries in terms of prevalence is periodontitis , an inflammatory infectious disease that affects the periodontium. The periodontium includes not only the gums, but also the bone, as well as the periodontium - the connection between the tooth and the bone. All together this makes up the supporting apparatus of the tooth. Periodontitis destroys this apparatus, which can lead to tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is often confused with periodontitis . This is also a periodontal disease, but it occurs without inflammation and develops over several years. The causes of periodontal disease and periodontitis are local and systemic. Systemic ones include, for example, diabetes mellitus, immune deficiency, and circulatory disorders. For local ones – malocclusion, exposure to certain microorganisms.
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, usually caused by poor oral hygiene.
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. With stomatitis, pain occurs in the affected area (ulcer), white or yellowish plaque, bleeding, and bad breath. There are many causes of stomatitis, but they are all related to the reaction of the immune system. Only a doctor can determine the type of stomatitis and prescribe the correct treatment.
White plaque may also appear with oral candidiasis . Fungi that cause candidiasis are part of the normal microflora of the mouth, but under the influence of pathogenic factors they begin to multiply and lead to disease. Pathogenic factors include low immunity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, taking antibiotics, bad habits, etc.
Xerostomia is insufficient salivation. It appears as a side effect of other diseases, including diabetes, and manifests itself as dryness and burning in the mouth. Treatment of xerostomia is mainly symptomatic.
Cheilitis is an inflammation of the lips; the most striking symptom of this disease is transverse cracks on the lips and in the corners of the mouth. The cause may be vitamin deficiency, environmental exposure, allergic reactions, or the habit of constantly licking your lips. To prevent cheilitis, it is recommended to maintain careful oral hygiene, eat well, and protect your lips from adverse weather conditions.
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue, most often the result of injury. At the same time, the tongue changes color, becomes painful, soft, and may become coated. Antiseptics, analgesics, and a gentle diet are used for treatment.
Stronger immunity means stronger teeth
Among the main reasons for the development of caries, it is necessary to highlight, firstly, poor hygiene. Soft plaque on teeth is a breeding ground for bacteria. Bacteria secrete organic acids that destroy the top layer of enamel - caries develops. But poor hygiene is not the only reason.
An important role is played by heredity (the strength of the enamel and the composition of saliva depend on it), the state of the immune system (whether the body itself is able to fight harmful bacteria), chronic metabolic diseases, and diet.
Why are children forbidden to eat a lot of sweets? Sugar is the best nutrient medium for bacteria; if it is abused, tooth enamel will initially form weak.
To protect yourself, you need not only to follow simple hygiene rules and go to the dentist for a medical examination every six months, but also to improve your immunity and eat right. For dental health, as for the body as a whole, the mineral composition of food and the balance of proteins and carbohydrates are important.
The risk of developing caries increases significantly if there are diseases associated with metabolic disorders in the body. These are, first of all, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and endocrine systems.
If there is a deficiency of immunity, caries develops much faster!
Diets can contribute to the development of caries if they are not balanced in protein and carbohydrate content. The connection is very simple - with metabolic disorders, the absorption and assimilation of useful substances by all organs, including teeth, is reduced. Tooth enamel loses its strength and is more easily destroyed. With weak immunity, the body is not able to effectively fight pathogens.
Another negative factor is the lack of solid food in the diet. Raw vegetables and fruits cleanse enamel, reducing the risk of tooth decay. The simplest way to prevent caries is to eat an apple after every meal.
What minerals do teeth need?
First of all, teeth need calcium and phosphorus. Fluorine, zinc, and selenium play a major role in strengthening enamel. In order for calcium to be well absorbed, you need a sufficient amount of vitamin D.
In general, if we talk about vitamins, they are all important for good health – including teeth. Vitamin C normalizes metabolism, vitamin B6 prevents gum inflammation, vitamin PP reduces the risk of developing stomatitis.
From bad teeth to a bad heart
Caries is dangerous because at first it is asymptomatic. This is why regular medical examinations are needed - to identify the disease in the early stages, when treatment is not yet so painful and expensive. Caries is also dangerous due to its complications – pulpitis and periodontitis.
In addition, caries is a constant source of infection . The blood spreads the infection throughout the body, most often the heart and blood vessels suffer from this.
Once in the heart, pathogenic bacteria destroy the valves, causing infective endocarditis and the development of heart defects. Once in the lungs, they can trigger the development of pneumonia. Getting into the joints – inflammation of the connective tissue and rheumatic diseases.
Why does my jaw crunch?
The jaw joint can click just like any moving joint in the body. This occurs when the head of the joint is displaced from its correct position. The jaw may not just click, but also jam so that the person cannot close his mouth.
The clicks do not have to be audible; sometimes they can only be felt by the patient. The reasons may be different: an incorrectly installed filling, severe spasm of the masticatory muscles, trauma, or malocclusion. In any case, this is a reason to contact an orthodontist.
If there are no teeth, there will be... an ulcer
If you have lost one or more teeth as a result of caries, the load on the digestive system increases significantly, and this can provoke gastritis and peptic ulcers.
The presence of a permanent source of infection often leads to the development of allergic reactions. Caries is much more dangerous than we used to think about it.
Simple rules are best
The causes of stomatitis and other diseases can be different - poor hygiene, bacterial and viral infections, untreated caries, sharp tooth fragments. If we talk about prevention, it should consist of two components: what we can do ourselves, and what the dentist should do.
Simple rules work best: brush your teeth regularly, use dental floss, eat well, don’t eat with dirty hands, and see your dentist on time. Everyone should visit a doctor once every six months - the doctor will assess the condition of the oral cavity, perform professional teeth cleaning, and remove tartar.
Wisdom teeth
At the age when the jaw is already formed, wisdom teeth are cut. Their improper eruption can be accompanied not only by very painful sensations, but also by inflammation, injury to the oral mucosa, malocclusion, etc.
It is impossible to prevent improper eruption of wisdom teeth. Here a lot depends on the structure of the jaw.
What can be done? If teething is accompanied by simply painful sensations, they can be relieved with painkillers. If the pain becomes unbearable and is accompanied by an increase in temperature, you should consult a dentist as soon as possible!
Improper eruption of wisdom teeth is fraught with many complications. Which can only be avoided by removing the tooth.
If you have a tooth removed
Tooth extraction is a serious, sometimes very traumatic operation. To facilitate the healing period of the wound and avoid its infection, dentists advise not to eat for at least 3 hours after removal, to avoid hot, spicy, salty foods, and not to rinse the wound.
During the first 24 hours, you can apply a cold compress. In this case, it is much better to use not ice or a bag of frozen vegetables, but water at borderline temperature (ice water). Apply a heating pad with cold water or a towel soaked in water for 15–20 minutes, repeat if necessary.
If you use an ice pack, be sure to wrap it in a cloth and do not hold it for longer than expected to avoid frostbite.
Due to the fact that blood pressure rises at night, so-called late bleeding may occur. In this case, you need to bite into a clean gauze swab.
If after removal the bleeding does not stop for a long time, if the temperature rises, or the wound begins to become inflamed, consult a doctor immediately!
The longer you delay, the more difficult and expensive the treatment . And the greater the health consequences and risk to life.
Ordinary caries is much more dangerous than we are used to thinking about it...
Altai Ekaterina
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/59673e897ddde8b9364c30b0/59e9ef3e799d9d97fd6d8d36
Dental diseases
Dentistry is a medical discipline that studies the organs of the oral cavity, their physiological and pathological conditions, and also deals with the prevention and treatment of diseases of these organs.
The field of dentistry covers not only diseases of the teeth, but also the entire dental system, as well as the oral mucosa. Along with treatment, modern dentistry pays great attention to the aesthetic side of the issue, striving to create the “ideal smile” for each patient.
Dentists attach particular importance to proper oral care as the most effective method of preventing dental diseases.
- Based on treatment methods, specialized areas are distinguished in dentistry:
- In recent years, new areas of dentistry have received widespread development: implantology and aesthetic dentistry.
- Dentistry covers a wide range of diseases. She treats:
- congenital malformations of the facial area (cleft palate and lip)
- diseases of the salivary glands, etc.
Oral infections serve as a breeding ground for pathogens to spread throughout the body. The state of the oral cavity can be used to judge the overall health of a person.
According to the Russian Dental Association, 87% of Russians need oral sanitation, which, depending on the indications, includes treatment of caries and filling of defects, removal of plaque, stone, roots and teeth, orthodontic and orthopedic treatment.
The most important indicator of the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole is the condition of the teeth. Their formation occurs during the period of intrauterine development, the eruption of milk teeth occurs at approximately six months, and permanent teeth erupt at 6-8 years. Permanent teeth that erupt in childhood are given to a person for the rest of his life, so they require special care and attention at all stages of life.
Today dentistry offers painless, safe and highly effective treatment for various oral diseases. Modern filling materials, as well as tooth-preserving techniques, are used in dental treatment.
They try to resort to tooth extraction as a last resort, when it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection in the oral cavity or when it is impossible to save and restore the tooth.
If, however, the tooth could not be saved, then highly durable and aesthetic denture materials will allow you to accurately recreate the architecture of the tooth and the color of the tooth enamel.
Nowadays, healthy teeth and a beautiful smile are an integral attribute of a person’s well-being and success in society. Aesthetic dentistry works to create the perfect “Hollywood” smile. The scope of activity of this area of dentistry includes aesthetic restoration of teeth, teeth whitening, improvement of shape, size - everything that makes a smile irresistible and flawless.
Today dentistry is one of the most dynamically developing medical sciences: new high-tech techniques and materials appear every year.
However, maintaining oral health depends not only on the dentist and modern technology. It is largely determined by the patient’s lifestyle.
Limiting sweets, eliminating bad habits, good hygiene of teeth and gums, and preventive dental examinations will help keep your teeth beautiful and healthy for many years.
The medical directory of diseases on the “Beauty and Medicine” website will give you the opportunity to learn as much as possible about how you can counter the threat of tooth loss and what to do if this trouble has already happened. Further…
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology
Prevention and treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa
The relevance of the prevention and treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa is due to the high prevalence of this pathology.
Depending on the location of the source of inflammation, stomatitis, glossitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc. are distinguished. A combination of pathological processes is often observed.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity are stomatitis, gingivitis and periodontitis.
Stomatitis
The clinical picture of stomatitis varies depending on the form of the disease.
Allergic stomatitis is characterized by severe hyperemia and moderate swelling of the oral mucosa. Frequently observed itching, burning or dryness may be due to hypersensitivity to a food product or lipstick.
Acute ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis , or Vincent's disease, is manifested by ulcerative-necrotic lesions of the gingival papillae.
With candidiasis (thrush), caused by the yeast-like fungus C. albicans , a white “curdled” coating is observed, rising above the hyperemic mucous membrane.
As the disease progresses, the process may spread to the palate, gums, tonsils, larynx, and gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Candidiasis occurs in weakened children and patients with immunodeficiency states, long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids and antitumor drugs.
Aphthous stomatitis , as a rule, is an indicator of gastrointestinal diseases. Factors that predispose to the development of stomatitis are deficiency of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid. The disease can be triggered by stress or local trauma, and is characterized by the presence of oval erosions (aphthae).
Herpetic stomatitis manifests itself as painful blistering rashes on the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips. Primary acute herpetic infection develops mainly in children aged 1 to 3 years (70% of children at this age experience acute herpetic stomatitis in one form or another).
In case of systemic diseases, the following changes in the oral mucosa may be observed: Koplik spots (measles), blisters (erythema multiforme exudative), hemorrhagic lesions (scurvy, platelet pathology), “crimson” tongue (scarlet fever), hyperemia of the lips and oral mucosa (cutaneous - mucous lymphadenopathy – Kawasaki disease), etc.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Inflammatory or destructive changes in the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, i.e.
Periodontal disease (gums, alveolar processes, cementum) usually begins with gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), which progresses to periodontitis (severe inflammation of the gums up to destruction of the bone tissue of the interdental septa). Periodontitis is the most common cause of tooth loss in adults.
It is believed that the cause of this disease is poor oral hygiene , resulting in the formation of dental plaque (colonies of microorganisms tightly bound to the surface of the tooth); local factors: bite pathology, tartar, incorrectly applied fillings, impaired oral breathing . Gingivitis often develops due to endocrine changes in adolescents and pregnant women. In addition, gingivitis, especially in adolescents, may be an early sign of latent diabetes mellitus.
Characteristic changes in the gums with gingivitis include hyperemia, swelling and bleeding with minimal trauma.
Inflammation is usually chronic, and without treatment, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis , the signs of which are deepening of the gum pockets, an increase in the amount of tartar, bad breath, weakening of the supporting apparatus of the tooth and the onset of bone destruction. Reduction of bone tissue is accompanied by loosening of teeth and gum atrophy. Late stages of the disease are characterized by tooth loss.
Treatment
If the underlying lesion of the oral mucosa is a systemic disease, specific therapy is prescribed. It is necessary to eliminate local and general predisposing factors . In all cases, careful hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity .
For candidiasis, antifungal agents (for example, nystatin suspension), and for bacterial infections, antibiotics . For extensive painful lesions, rinsing the mouth with a 1-2% lidocaine solution or soda solution .
Sometimes medical intervention : removal of tartar, replacement of fillings, surgical plastic surgery of the oral vestibule and frenulum.
One of the local drugs that is effective in the treatment and prevention of this pathology is Imudon , an immunostimulant of bacterial origin.
Imudon is a polyvalent antigenic complex (lyophilized mixture of dry bacteria), the composition of which corresponds to the pathogens that most often cause pathogenic processes in the oral cavity.
Imudon contains the following microorganisms: Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus fermentatum, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus lactis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus sanguis, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Corynebacterium pseudodiphteriticum, Fusiformis fusiformis, Candida al bicans.
- By influencing the immune link of the pathological process, Imudon has the following therapeutic effects:
- • increased phagocytic activity of macrophages;
- • increase in lysozyme content in saliva;
- • stimulation and increase in the number of immunocompetent cells responsible for the production of antibodies;
- • an increase in the content of secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA) in saliva;
- • slowing down the oxidative metabolism of polymorphonuclear cells.
- Thanks to its ability to activate the formation of antibodies and stimulate the defenses of the oral mucosa, Imudon enhances the fight against infection and alleviates the patient’s condition.
Imudon acts locally in the oral cavity; there is currently no data on its systemic absorption. Imudon has both therapeutic and preventive effects. Imudon can be used for the prevention and treatment of infectious complications after tooth extraction and implantation of artificial dental roots.
The tablets should be completely dissolved in the mouth. For acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, the drug is taken 8 tablets per day; The duration of treatment is 10 days. For chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, Imudon is prescribed 6 tablets per day for 20 days. It is recommended to carry out course therapy 2-3 times a year.
When using the drug according to indications in recommended doses, side effects and cases of overdose are currently not described.
It should be noted that, if necessary, you can rinse your mouth no earlier than 1 hour after using Imudon.
When prescribing the drug to patients on a salt-free or low-salt diet, it should be taken into account that one tablet contains 15 mg of sodium. In women during pregnancy or breastfeeding, the drug can be used according to indications.
In a recent study conducted at the Department of Pediatric Therapeutic Dentistry of Moscow State Medical University (headed by Prof. V.M. Elizarova), Imudon was used in 30 children aged 1 to 3 years with acute herpetic stomatitis. Imudon was prescribed on the day the child visited the doctor, 6–8 tablets per day (the tablet was kept in the mouth until it was completely dissolved), and antiviral therapy was also used at the same time.
Imudon reduced symptoms such as pain, inflammation, and bleeding from the gums.
The duration of the course of treatment depended on the severity of the disease: for mild - up to 5-7 days, for moderate - 8-10 days, for severe - 15 days.
We confirmed objective clinical observations indicating positive dynamics in the development of acute herpetic stomatitis by examining the content of lysozyme and secretory IgA in saliva.
- Thus, in the treatment of acute herpetic stomatitis in children, along with antiviral drugs, it is advisable to use Imudon, which significantly improves the condition of patients.
- Imudon can be used along with drugs from other groups without special precautions, since it only acts in the oral cavity and does not interact with other drugs.
- Immunostimulant of bacterial origin:
- Imudon (trade name)
- (SOLVAY PHARMA)
Periodontitis is the most common cause of tooth loss in adults
Source: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/stomatologiya/Profilaktika_i_lechenie_zabolevaniy_slizistoy_obolochki_polosti_rta/
Dental diseases: dental diseases of the oral cavity - main types and their prevention
The list of dental diseases is huge , and all of them are characterized by specific symptoms and arise for certain reasons.
Despite the fact that you can only find out an accurate diagnosis by visiting a dental clinic, every person should familiarize themselves with the signs of the most common dental diseases.
Such information will help to recognize the disease at an early stage and consult a doctor in time.
Caries
This is the name given to a common pathology of hard dental tissues, which is characterized by demineralization and subsequent destruction of the molar. The disease begins with the formation of a small spot on the enamel, which is not even noticeable at first. Then it acquires a yellow-brown color, the affected teeth hurt, and react sharply to hot, cold and sweet foods.
If the development of the disease is not stopped at the initial and middle stages, it will be accompanied by pulpitis (nerve inflammation) and periodontitis, which can cause tooth loss. Also, chronic foci of infection in the form of carious cavities increase the risk of recurrent diseases of the body.
Reasons for development:
Flux has appeared: how to quickly remove a tumor at home
- insufficient oral hygiene (irregular brushing of teeth, ignoring rinses and dental floss after meals);
- poor nutrition, in which carbohydrate foods predominate, with a lack of vegetables, proteins and vitamins;
- hypovitaminosis – a lack of essential microelements in the body;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions, with insufficiently fluoridated water or where food that does not contain phosphorus and calcium predominates;
- improper formation of teeth in children due to rickets, tuberculosis and other diseases;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- a sharp decrease in immunity.
The listed reasons cause changes in the structure of the enamel layer, as a result of which plaque cannot be completely cleared from the surface of the teeth, and the process of bacterial growth accelerates. Caries develops in several stages. As already mentioned, in the initial stage it has the form of a barely noticeable spot on the enamel; it becomes rough, with elements of demineralization.
Further, if the patient does not notice the first sign of pathology, the second stage begins, with a carious cavity forming under the enamel layer with dentin damage. Next, deep caries occurs, with the transition of the inflammatory process beyond the dentin, which is already fraught with various complications.
Starting from the second stage, the destruction process is accompanied by tedious pain that intensifies at night; analgesics help relieve them, but only temporarily
To avoid tooth loss as a result of its complete destruction, it is necessary to consult a dentist in a timely manner. The doctor will determine the degree of development of the problem and select the appropriate treatment method.
At the stain stage, remineralization of the enamel is sufficient (it is restored using a special solution); at the superficial, medium and deep stages, this measure will no longer be enough; treatment followed by filling is necessary.
Diagnostics
The basis for diagnosing dental diseases is examination of the oral cavity using magnifying mirrors and special instruments. Then the patient is sent for an x-ray; the description of the image will indicate the degree of destruction of bone tissue, the presence of periodontal pockets, which will help determine the treatment and prosthetic treatment plan.
Diagnostic methods:
- percussion – using a special temperature stimulus, the sensitivity of the pulp is measured;
- vital staining of enamel - the method allows you to identify caries in the early stages of development;
- electroodontometry – the tooth is exposed to current pulses, the method is used to identify pulpitis;
- Using special instruments, the degree of compression of the jaws is assessed to assess the correctness of the bite;
- panoramic photograph of teeth - allows you to identify the presence of neoplasms in the oral cavity, detect unerupted wisdom teeth, and assess the degree of damage to the roots by caries.
- To identify neoplasms in the oral cavity, a panoramic photograph of the teeth is used.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most informative diagnostic methods; they allow you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the jaw, identify abnormal processes in the development of teeth, and identify root defects.
- From a psychosomatic point of view, dental problems occur in people who often take on many responsibilities; dental problems may indicate an inability to perceive new ideas and poor self-defense.
Pulpitis
The most common dental diseases, in addition to caries, include pulpitis - this is the last stage of its development, when the lesion reaches the nerve area. The pulp is a connective tissue with a fibrous structure, it contains a large number of capillaries, lymphatic vessels and nerves, therefore the main symptom of damage to these tissues is considered to be acute, excruciating pain.
The acute form of the pathology is manifested by attacks of spontaneous acute pain, which can be provoked by hot or cold drinks, sweet food, or frosty air.
If caries pain goes away immediately after eliminating the irritant, pulpitis is distinguished by the persistence of severe discomfort for another 15–20 minutes.
When the disease becomes chronic, acute pain syndrome ceases to bother the person.
Anomalies of the dentition
During exacerbations, attacks can recur, especially when biting an inflamed molar. Reasons for development:
- advanced caries - a huge number of pathogenic bacteria located in the tooth cavity provoke rapid tissue destruction, penetrating into the deepest layers, reaching the pulp;
- poor-quality treatment of a carious lesion - some infected tissue may remain under the installed filling, causing re-inflammation and further destruction;
- thermal burn of deep tissues - while drilling the affected dentin, the dentist may be in a hurry and perform poor cooling, as a result the pulp is burned.
Also, pulpitis can develop not through caries, but, for example, with periodontitis, through infected gum tissue, to the roots of the tooth and above. When a molar is injured, sometimes the pulp tissues die due to the cessation of their blood supply.
Differential diagnosis of caries and its complications
Diagnosis of teeth affected by pulpitis is based on radiographic examination and data from the collected anamnesis (on the frequency of pain attacks and their intensity). Treatment involves removal of the inflamed nerve, root canal treatment and subsequent filling. In this case, pulp removal is carried out using vital (to remove any form of pathology) and deviant (for chronic form) methods.
Traditional methods of treatment
Essential oils are an excellent way to freshen breath, as well as strengthen gums and teeth. We need to prepare a bandage and fir oil .
We cut off a little bandage, roll it up in several layers and soak it in fir oil, then apply it to the jaw for ten minutes. The course lasts one and a half weeks.
Instead of fir, you can take sea buckthorn or peach oils, which are widely used for various purulent diseases.
Linden also copes well with periodontal disease and gingivitis, treats idiopathic diseases of periodontal tissue and all diseases of the gum mucosa.
We make a decoction of linden flowers, oak bark and water in a ratio of 2:1:5. Cook the infusion over low heat for an hour, then remove, put in a dark place and cool.
Rinse your mouth with this liquid twice a day every day, especially in the spring, when inflammatory processes worsen.
Instead of linden, you can take dry sage ; it is also used to treat sore gums. In this case, take part less of the herb than the linden, otherwise the decoction will turn out to be too bitter.
But the most effective method is based on propolis. This product perfectly whitens teeth, freshens breath and cures osteomyelitis. Vodka, which is part of the mixture, quickly disinfects wounds near the teeth or on the tongue. We need to prepare:
- three tablespoons of propolis;
- a glass of vodka;
- five spoons of St. John's wort;
- dark dishes.
We chop the propolis very finely and mix it with vodka, hide the mixture in a dark place for two days, shaking the bottle periodically. You can use it when propolis dissolves in vodka.
Now it’s time for St. John’s wort - pour it into a container and seal the bottle again for two weeks. After this time, we take out and filter our infusion. Use twenty drops per glass of water.
Rinse your mouth with the mixture four times a day for a month.
Source: https://osp-sakhalin.ru/zuby/bolezni-zubov.html
Oral hygiene in a complex of therapeutic measures for periodontal diseases, non-carious lesions and the prevention of dental caries
Home » All about modern dentistry » Prevention of dental diseases » Oral hygiene in the complex of therapeutic measures for periodontal diseases, non-carious lesions and prevention of dental caries
The tactics for managing patients with periodontal diseases include general pathogenetic therapy and local effects on periodontal tissue. The pathogenetic mechanism of therapy includes the prescription of drugs that act at certain points in the development of periodontal diseases and is aimed at strengthening the immune status. The general course of treatment is determined according to the patient’s health status, focusing on eliminating the main pathological process against which periodontal diseases develop. By prescribing local therapy, secondary factors that complicate the patient’s condition and contribute to relapse of the disease are eliminated.
In the treatment and prevention of periodontal diseases, great importance is given to dental care and personal oral hygiene. If you do not follow the necessary recommendations, the effectiveness of treatment may be lost.
At the same time, measures to maintain oral hygiene become more important over time - not only a preventive purpose, but also a therapeutic one.
Based on research data, we came to the conclusion that success in the treatment of periodontal diseases and the prevention of relapses directly depends on the therapeutic measures taken and proper care of the oral cavity.
Of course, you shouldn’t rely only on conscientious implementation of hygiene measures. They are, to a greater extent, characterized by the provision of an auxiliary and reinforcing effect, against the background of the main active intervention of the doctor.
Etiologically and pathogenetically important causes of periodontal diseases are common factors, such as neurodystrophic and metabolic disorders. However, at advanced stages of the process, greater importance is given to local causes (extensive deposition of tartar, the formation of pathological gum pockets, the presence of abundant microflora in the gum pockets, etc.).
Tartars occur in almost 70-90% of patients suffering from periodontal diseases, and proper oral hygiene helps eliminate them.
Compliance with recommendations for oral care in patients with jaw injuries is of great importance.
Limited mobility and functional disorders of chewing are favorable conditions for the accumulation of a significant amount of soft dental deposits, which negatively affect the healing processes of bone and periodontal tissues. Such patients are prescribed special hygiene measures.
Special therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes and rinses are used, which actively promote the dissolution of the protein-lipid structure of soft plaque. Such procedures help reduce inflammatory complications in this group of patients.
Such recommendations are important for people who use dentures and orthodontic patients, especially children, who have used orthodontic equipment for a long period, in connection with the complex treatment of abnormalities of the teeth and jaws. In such cases, teeth cleaning deteriorates, which is a favorable factor for the development of periodontal diseases and oral mucosa. That is why therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes must have a comprehensive effect on periodontal tissue and teeth.
Preventive measures to prevent dental caries should be based on the introduction into the body of drugs that have an anti-caries effect (vitamins, phosphates, microelements) and their use locally in order to increase remineralization (use of special solutions, dental rinsing). The most common method of preventing periodontal disease is the use of special toothpastes containing various anti-caries additives.
Oral hygiene plays an important role in caries prevention. The timely removal of soft plaque helps to normalize the physiological process of “ripening” the enamel, which lasts for seven years from the moment of teething.
If you do not regularly follow the necessary recommendations, plaque can accumulate and block access to the tooth enamel for essential microelements, calcium ions, and phosphorus.
As a result, mineralization is disrupted and, as a result, tooth enamel is subject to the formation of caries.
Regular hygiene measures for the oral cavity, using special therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, contributes to a better mineralization process. Such pastes, which contain fluorides, phosphates, calcium and many other macro- and microelements, are used in combination in the treatment of non-carious dental diseases.
Special toothpastes are widely used for dental diseases such as dentin hypersthesia, pathological tooth wear, enamel hypoplasia and others. During their use, it is recommended not only to rub such pastes into the teeth, but also to apply them to the teeth for 15 minutes several times a month.
Oral hygiene should not be limited to the use of certain toothpastes. To begin with, an assessment of the quality of oral care for patients in the observed group is carried out. This is done using the hygiene index (IG) according to Fedorov-Volodkina.
In this case, the labial surface of the six lower frontal teeth is stained with a potassium iodide solution. When determining the quality of oral hygiene, the studied indicators are assessed in the following order: from 1.2 to 1.5 points - good hygiene; from 1.6 to 2.0 points - satisfactory IG; from 2.1 to 2.5 points - insufficient, irregular IG; from 2.6 to 3.
4 points – bad IG; from 3.5 to 5.0 points - the hygiene index is too poor.
By observing regular and proper oral care, the hygiene index ranges from 1.1 to 1.6 points. Reaching 2.6 or more points, the IG shows that regular dental care is observed, and above 3.5 points indicates a lack of oral care.
Using this hygienic index, they determine not only the quality of teeth cleansing with a certain paste and the assessment of the cleansing effect after using hygiene products, but also the individual degree and quality of teeth cleansing for a particular patient.
It is worth noting that using the proposed hygiene index, you can assess the quality of teeth cleaning simply and affordably, as it is calculated quite quickly and easily. It can also be used as an objective criterion to assess the degree and nature of hygienic oral and dental care among various population groups.
This technique serves as a clear example of the quality of teeth cleaning during hygiene skills training. Long-term studies and observations show that during training in hygienic skills for the purpose of staining dental plaque, it is allowed to use a standard aqueous solution of methylene blue or a 2% fuchsin solution.
When using a methylene blue solution, it is used to treat controlled areas of the dental arch: usually more than 10 accessible teeth of the upper and lower jaw are stained. At the same time, soft dental plaque is perfectly stained and gains better visibility for identification and further cleaning.
The fuchsin solution is used in a volume of up to 12 drops per 15 ml of aqueous solution, which requires rinsing the patient’s mouth for several seconds. After which, the patient spits out the dye and rinses his mouth with clean water. As a result, plaque on the surface of the teeth becomes visible and turns bright red.
We have also developed special solutions and tablets that stain dental plaque in order to demonstrate quality and maintain oral and dental hygiene.
In addition, the patient is taught the rules for caring for the oral cavity and teeth. Cleaning your teeth with a brush and paste should be done twice a day: in the morning and at night. It is recommended to carry out morning cleansing after breakfast in order to remove food debris, preventing them from remaining in the oral cavity for a long time.
Before breakfast, it is recommended to rinse your mouth vigorously. It is advisable to use regular cleansing in combination with finger massage (after therapeutic measures) and it is recommended to rub the paste into the gums using light circular movements. This enhances the effectiveness of therapeutic and prophylactic pastes.
Cleaning the teeth with a brush is done in front along the axis of the tooth, from the side of the chewing surface - from front to back, and from the side of the palate and tongue - also along the axis of the tooth. The brush should produce a “scraping” or “sweeping” motion.
It is believed that the latter are more rational, since they not only clean the teeth, but also gently massage the gums. For such teeth cleaning, it is recommended to spend at least 2-3 minutes, during which about 300-400 cleaning movements of the brush are carried out and the elimination of soft plaque by 66-71% is ensured.
Cleaning your teeth should end with vigorous rinsing of the mouth with special solutions that have a sufficient refreshing and deodorizing effect.
Periodically, using the hygiene index, the results of teaching patients in oral hygiene techniques should be monitored.
Source: http://www.professional-dent.ru/vse-o-sovremennoj-stomatologii/profilaktika-stomatologicheskix-zabolevanij/gigiena-polosti-rta.html