Content:
Endometrial hyperplasia refers to the growth of the inner mucous membrane of the uterus. According to doctors, this is a special condition in which there is a malfunction of the organ caused by hormonal imbalances.
Manifestations of hyperplasia include the appearance of a long delay in menstruation, after which the occurrence of heavy bleeding and spotting in the middle of the cycle is noted.
Often hyperplasia does not manifest itself with any symptoms, and it is detected accidentally during an ultrasound scan.
Endometrial hyperplasia is dangerous because there is a possibility of degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant cancerous tumor. Treatment can be medication or surgery.
Types of endometrial hyperplasia
Based on the changes taking place in the body, several types of endometrial hyperplasia are distinguished:
- glandular,
- cystic,
- glandular-cystic,
- focal,
- atypical.
IRONUS FORM. The glandular form is a benign change and is considered the mildest type of the disease. This means that the likelihood of developing cancerous tumors is small and is only 2-6%.
Active cell division occurs, and the endometrium thickens. The location of the glands is not uniform, but in groups. They can press closely to each other. There are no stromal cells between them. Tubular glands transform from straight to convoluted, they expand.
But at the same time, their contents are freely allocated.
GLANDO-CYSTIS. FORM. In the glandular cystic form, if the cells grow strongly at the mouth of the gland, they block the outflow of mucus. It takes on the appearance of a cyst - a bubble that fills with fluid. These changes occur under the influence of estrogen hormones.
CYSTIC FORM. The cystic form has similar symptoms to the glandular-cystic type of endometrial hyperplasia. There is a strong proliferation of glandular cells, and there is an increase in the size of the glands themselves. They become like a bubble. The interior of the gland is lined with normal epithelium. There is a possibility of such cysts degenerating into cancerous tumors.
FOCAL FORM . In the focal form, endometrial cells do not grow uniformly, but in separate foci. These areas of the mucosa turn out to be more sensitive to the action of hormones, so cell division is more active here.
Elevations with altered glands and formations that look like cysts form on the endometrium. When cells multiply in a polyp, there is a strong increase in size. The diameter of the lesions can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. There is a risk of cancer formation at the site of the lesion.
If changes occur evenly over the entire surface of the endometrium, then this form is called diffuse.
ATYPICAL FORM . The most dangerous form is the atypical form (adenomatosis) of endometrial hyperplasia, since it most often leads to the development of cancer. The risk of degeneration is more than 50%.
Therefore, in this case, removal of the uterus is recommended. Changes can take place not only in the functional, but also in the basal layer. Active division and restructuring of stromal and gland cells occurs. Often mutations occur in them and they become atypical.
Cells change their structure and the structure of the nucleus.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia
- menstrual irregularities . In women of reproductive age and with polyps that arise from a normally functioning endometrium, blood discharge may appear before and after regular menstrual bleeding, and the onset of heavier menstruation is also noted;
- the appearance of bloody spotting between menstruation;
- delayed menstruation with subsequent prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding;
- the occurrence of menorrhagia with fibrous and glandular-fibrous polyps, metrorrhagia with anovulatory cycles and the detection of glandular endometrial polyps;
- detection of infertility , the onset of which is associated with a disruption in the process of egg formation or the impossibility of implantation into the endometrium.
Causes of endometrial hyperplasia
HORMONAL DISTURBANCES . Most often, the development of endometrial hyperplasia is provoked by hormonal disorders. A woman’s reproductive body is subject to cyclical changes, which are most pronounced for the ovaries and endometrium of the uterus.
From the first day after the onset of menstruation, the endometrium enters the proliferation stage, due to which preparations for the onset of a possible pregnancy occur. During the entire cycle, the endometrium thickens, and if a failed pregnancy occurs, the mucous layer of the uterus is rejected, the volume of which increases 10 times during one menstrual cycle.
The endometrium thickens or hypertrophies due to the increase in intercellular substance, the size of epithelial cells, connective and glandular tissue.
In case of hormonal imbalance, disruptions in the cyclic process that occurs in the endometrium are possible: an increase in its volume may begin not due to intercellular fluid, but due to increased reproduction and formation of new cells. Similar hormonal imbalances can be encountered when:
- ovarian dysfunction, which is associated with approaching menopause,
- polycystic disease,
- hormonally active ovarian tumors,
- mastopathy,
- obesity (since excess fat tissue can also produce estrogens).
SOMATIC DISEASES. The reasons for the development of endometrial hyperplasia may include the transfer of certain somatic diseases and conditions:
- obesity,
- chronic stress,
- hypertension,
- liver diseases with its functional failure,
- uterine leiomyomas,
- inflammatory diseases of the endometrium,
- performing abortions,
- curettage for endometrial hyperplasia.
Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia
Ultrasound. The most common method for diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia is ultrasound using an intravaginal sensor. With its help, it is possible to identify thickening of the endometrium, determine the presence and location of polyps in the uterus.
ECHOSALPINGOGRAPHY . Another method for diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia is echosalpingography, which is primarily aimed at studying the patency of the fallopian tubes, but during pregnancy the cavities in the uterus, which are characteristic of polyps and hyperplasia, are quite clearly visible.
BIOPSY . Endometrial hyperplasia can be diagnosed using a biopsy of the uterine mucosa, which is performed in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
Next, the material is examined under a microscope. This method has high results, but it is ineffective in the case of focal distribution of changes, because
There are no guarantees that the material will be collected specifically from the focus of hyperplasia.
HYSTEROSCOPY . One of the most informative methods for studying endometrial hyperplasia is hysteroscopy, thanks to which samples are taken directly from the lesion, and a visual assessment of the condition of the inner lining of the uterus is also possible.
SCRAPPING . The most vivid picture of the degree and nature of the development of hyperplasia is provided by separate diagnostic curettage.
The procedure involves scraping the inner lining of the uterine body and, separately, the cervical canal. Next, a histological examination of the taken material is carried out.
It is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis based on histology results and prescribe treatment.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with drugs
To treat endometrial hyperplasia, drugs can be used, the selection of which takes into account the type of hyperplasia, the age of the patient and her state of health.
HORMONE THERAPY . The basis of drug treatment of the disease is the prescription of hormone therapy, which uses combined oral contraceptives, gestagens or GnRH agonists. Conservative treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is aimed at regulating hormonal levels by reducing estrogen levels, as well as stopping the proliferation of the uterine mucosa and reducing foci of hyperplasia. Often, treatment of hyperplasia with the use of COCs is prescribed to teenage girls or young nulliparous women whose menstruation is heavy and irregular due to the presence of glandular or glandular-cystic hyperplasia. Sometimes, to avoid curettage, COCs may be prescribed for hormonal hemostasis. The course of treatment is 6 months or more. The medications are taken according to a contraceptive regimen. Prescription of treatment with the use of gestagens is possible for women of any age when diagnosing any form of endometrial hyperplasia. Long-term treatment is often provided for 3-6 months. While taking gestagens, intermenstrual bleeding may occur.
DUPHASTON. One of the most effective gestagenic drugs that can be used in the conservative treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is duphaston. It is prescribed for long-term use for 3 or more months from the 16th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle, 2 tablets 3 times a day. If bleeding occurs for 3-4 days, the dose is doubled, then the drug is continued according to the standard regimen.
N ORKOLUT. During the period of illness, Norkolut can be prescribed, which is not an active gestagen, but has a pronounced anti-estrogenic character. For glandular cystic hyperplasia, it is prescribed from the 16th to the 25th day of the menstrual cycle, 1 tablet per day for 3-6 months. To stop bleeding caused by hormone therapy, you need to take 1-2 tablets per day for 6-12 days.
MIRENA. A means of hormonal therapy as a gestagen, which has a local effect, is the Mirena intrauterine device. The advantages of using this method include a long-term (for 5 years) and effective method of preventing unwanted pregnancy and the provision of local therapeutic effects of hormones on the endometrium of the uterus. The disadvantages of using an intrauterine device are the possibility of intermenstrual bleeding in the first few months after its installation, as well as painful menstruation.
AGnRH . The modern and most effective class of drugs that can be used in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia are gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (AGnRH).
Treatment with drugs of this class achieves a high percentage of positive results, there is the possibility of flexible dosing, switching to a convenient regimen of taking the drug - only once a month.
The active ingredients of the drugs block the production of sex hormones, as a result of which the endometrium atrophies and the proliferation of cells and tissues is inhibited. Thanks to the use of AGnRH, as a rule, it is possible to avoid the development of infertility and surgery to remove the uterus.
Surgery for endometrial hyperplasia
Surgical treatment of endometrial hyperplasia can be carried out using various methods and in various volumes.
SCRAPING. The first and almost inevitable stage of treatment of the disease is to perform curettage of the uterine cavity, because removal of the affected endometrium is possible only mechanically.
In addition, sometimes it is necessary to conduct a radioisotope study of the uterus using radioactive phosphorus, with the help of which it is possible to determine not only the presence, nature and extent of the disease, but also its activity.
CRYODESTRATION . To treat and prevent endometrial hyperplasia, cryodestruction can be used, which is based on exposing the affected area to low temperatures. As a result, the hyperplastic layer of the endometrium is rejected. Vessels larger than 2 mm in diameter are not subject to necrosis.
CAUTION . Surgery for endometrial hyperplasia can be performed through cauterization or laser ablation. In this case, the affected area is exposed to an electrosurgical instrument using a laser or high temperature. In this case, the pathological areas are destroyed and the uterine epithelium is naturally restored.
An operation to remove the uterus or perform a hysterectomy is indicated when hyperplasia with a complex atypical form is detected in premenopausal women.
At the same time, the ovaries are preserved, but careful studies of their tissues are carried out regarding the presence of oncological processes.
The uterus along with the appendages is removed if obvious oncological processes are diagnosed, as well as in the case of adenomatosis detected in postmenopausal women.
Combined treatment of endometrial hyperplasia usually includes surgery and subsequent restorative hormone therapy. In some cases, prior administration of hormones is necessary, which significantly reduces the scope of the operation or makes it possible to influence lesions that cannot be removed surgically.
Endometrial hyperplasia and pregnancy
Pregnancy with endometrial hyperplasia is very rare and can result in either miscarriage or the development of serious developmental defects.
In addition, in the case of a long-term disease, there is a possibility of the formation of tumors that were not diagnosed before pregnancy and grow rapidly along with the fetus. If the nature of the tumors is oncological, then this poses a threat to the life of both the child and the mother.
As a rule, endometrial hyperplasia and pregnancy are incompatible, but after undergoing hyperplasia it is possible to restore reproductive function in almost all cases.
If a woman wants to have a child, she will be recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination and prescribed a mandatory course of treatment, after which she can plan a pregnancy 1-3 years later.
Endometrial hyperplasia during menopause
The onset of menopause occurs in women aged 45-60 years. The ovaries stop working and there is no menstruation.
It is during this period that endometrial hyperplasia is often diagnosed during menopause, which refers to the thickening of the inner layer of the uterine mucosa.
The appearance of changes is due to the fact that during this period the body undergoes hormonal changes and an increase in estrogen levels is noted. In addition, after 40 years of age, the likelihood of developing cancer increases.
Prevention
Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia, first of all, lies in the fact that the woman undergoes regular medical examinations, during which a thorough examination of endometrial tissue should be carried out. In addition, for young patients, the doctor may prescribe prophylactic hormonal medications, which significantly reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
Video - endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus
Source: https://LuxMama.ru/giperplaziya-endometriya-lechenie-i-operatsiya
How to treat uterine endometrial hyperplasia: modern treatment methods
The proliferation of the layer of cells on the inner surface of the uterus leads to the development of endometrial hyperplasia. Increased tissue growth is associated with hormonal imbalances and a woman’s menstrual cycle, which can lead to the development of malignant tumors. How to cure uterine endometrial hyperplasia? The attending physician decides which treatment method will give a positive result.
Collapse
Drug treatment is suitable for nulliparous women. Taking medications whose active ingredients are female hormones affects the causes of the disease. Allows treatment of endometrial hyperplasia without curettage.
The doctor determines the possibility of drug treatment based on the woman’s age, the severity of the disease, and existing chronic diseases. Endometrial hyperplasia is treatable with medications in the early stages of the disease.
The course of treatment for endometrial hyperplasia ranges from three months to six months, and consists of several stages:
- bleeding must be stopped
- reduce the growth of the inner surface of the uterus,
- normalize hormonal levels, restore the menstrual cycle. At this stage, magnetic therapy is used for cycle disorders. Magnetic therapy for hyperplasia increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces pain.
- periodic visits to the gynecologist to monitor the condition of the uterus after treatment, to prevent relapses.
Hormone therapy consists of the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Contraceptives containing estrogen and progestogen (COCs). The course of admission is six months. They are prescribed to women under 35 years of age who want to preserve reproductive function. Girls with irregular cycles and heavy bleeding. The drugs are taken according to the same regimen as for the contraceptive effect.
In case of bleeding in girls, treatment of endometrial hyperplasia without curettage is carried out with hormonal contraceptives, 2-3 tablets per day, gradually increasing to 1 tablet. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is used.
These include Janine, Marvelon, Logest, Yarina.
Average price per package 21 tablets. from 400 rub. and higher.
- Contraceptives containing only gestagen (Duphaston, Microlut, Norkolut, Utrozhestan, Orgametril). These drugs do not contain estrogen. They are prescribed to women at any age. Uterine hyperplasia of any type can be treated. The progestogen hormone helps reduce the growth of endometrial cells in the uterus. The course of treatment is up to six months; the drug is taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle for 10 days.
The average price of drugs is from 130 to 600 rubles.It is possible to use a more convenient method of treatment than taking internal medications using the Mirena intrauterine system. It contains the hormone gestagen, which is released in small doses and has a local effect. Mirena is installed for five years; it has no side effects of oral medications. The disadvantage is the high price, from 12,000 rubles.
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (AGnRH).
Drugs in this group (Buserelin, Goserelin, Zoladex) block the action of a hormone that is produced in the pituitary gland and is responsible for the synthesis of sex hormones in the ovaries. As a result, hormonal levels are normalized, estrogen levels decrease, and the disease is cured. Treatment of any type of endometrial hyperplasia with Buserelin is indicated for women over the age of 35 years. The drug is used intramuscularly once a month for six months. The cost of the drug is about 4000 rubles.
Treatment with surgical methods
Treatment methods for endometrial hyperplasia using surgery are used in the following cases:
- treatment of glandular endometrial hyperplasia, which occurs against the background of chronic diseases and occurs with relapses.
- precancerous condition of endometrial cells,
- Treatment without hormones is necessary if a woman has serious contraindications to their use,
- heavy uterine bleeding due to menstrual irregularities,
- age after 40 years.
Separate diagnostic curettage and hysteroscopy
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by combining two procedures, in a hospital setting, under general anesthesia:
- Hysteroscopy.
It is carried out using a hysteroscope device. It allows you to examine the uterine cavity and, thanks to the optical system, identify pathological processes in the endometrium. Hysteroscope - Separate diagnostic curettage is carried out in two approaches. First of all, the cervix is treated, then the uterine cavity.
A woman with endometrial hyperplasia is prescribed a set of tests (general and biochemical blood tests, urine test, smear to detect cancer cells and vaginal microflora, ultrasound, test to detect infectious diseases).
The curettage procedure is carried out using a special spoon - a curette, starting from the cervical canal. The material obtained by scraping is placed in a container for subsequent cell examination. Next, a hysteroscope is inserted, and curettage of the uterine cavity is performed under its control.
Is it possible to cure endometrial hyperplasia without curettage? This can be done with the following modern methods of treating hyperplasia.
More information about curettage can be found in this article.
Cryodestruction
The method is based on the freezing effect of liquid nitrogen. Enlarged areas of the epithelium are treated, the size of the vessels in which does not exceed 2 mm. At the site of nitrogen exposure, tissue cells die, are removed from the surface of the mucosa and come out in the form of clots.
Laser ablation or cauterization
The ablation procedure, in which the endometrial layer is completely removed, is carried out against the background of intravenous analgesics. Treatment is carried out in a short time, without damaging the uterus and leaving no scars on its surface. After ablation, healing of the mucosa occurs quickly.
For treatment the following is used:
- laser pulse,
- high frequency electric current.
Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy)
How to treat uterine endometrial hyperplasia in case of complications, with an atypical form of development? In such cases, surgery to remove the uterus is used.
In preparation for surgery, antibacterial drugs (azithromycin) are prescribed to suppress the inflammatory process, antiviral and immunostimulating agents (Immunomax). In the presence of cancer, in postmenopausal women, the uterus is removed along with the ovaries.
Find out more information in the article: Operations for hyperplasia
An additional method of treating hyperplasia is massage performed by a gynecologist. It helps normalize blood circulation and restore the functions of the reproductive system.
Treatment with folk remedies
Uterine endometrial hyperplasia cannot be treated with traditional medicine. They can be used as an additional treatment to the main method of treatment, as well as during the recovery period after surgery. The following methods are considered the most effective:
- Take freshly squeezed beet and carrot juices, 100 ml once a day. At the same time, douching is carried out with a warm solution of celandine (50 g of herb in 2 liters of boiling water, leave for 12 hours, strain), twice a month.
- Nettle decoction. Has an anti-inflammatory, hemostatic effect, improves immunity. To prepare the decoction, pour two tablespoons of crushed nettle leaves into a glass of boiling water, leave and strain. The product is taken 5 times a day, 60-70 ml.
- Infusion of boron uterus. To prepare the product 1 tbsp. l. the herbs are brewed with two glasses of boiling water, left for 20 minutes, then filtered and taken 125 ml 4 times a day.
- Hirudotherapy. Leeches help relieve swelling, help increase immunity, and have an analgesic effect. Uterine hyperplasia can be treated with leeches only after consulting a gynecologist, a specialist hirudologist.
Read more in the article: Treatment of hyperplasia with traditional methods
Treatment with tampons
Tampons for the treatment of the disease are used either ready-made, purchased at a pharmacy, or made independently. The medicine is Beautiful Life tampons; they contain herbal ingredients. They have anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. They are effective in the early stages, when endometrial hyperplasia is without complications, and are used to prevent relapses.
At home, use cotton-gauze swabs soaked in celandine infusion. (pour 250 ml of boiling water over 30 g of raw materials, leave for half an hour, strain). The infusion has an anti-inflammatory effect, but frequent use can cause burns to the mucous membrane. Exposure time is no more than 10-15 minutes.
The possibility of using tampons in treatment, the duration and frequency of their use should be determined by the gynecologist.
Diet as part of treatment
Uterine hyperplasia, its symptoms and treatment depend on adherence to a certain diet. During this period, support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism (hormones), and normal functioning of the digestive system are necessary.
Principles of nutrition for endometrial hyperplasia:
- Meals should be frequent, in small portions. Dinner 3 hours before bedtime.
- The diet requires vegetables and fruits high in ascorbic acid, which helps reduce endometrial growth.
- taking herbal products that affect the level of hormones in the blood. Foods high in cellulose increase the amount of estrogen. Celery, peas, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, on the contrary, reduce the release of the hormone into the blood.
- To reduce the load on the liver and gall bladder, it is advisable to steam, stew and boil dishes.
- Eating enough varieties of fish rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids can improve uterine contractions and reduce bleeding.
- Avoid eating red meat, the fatty acids of which cause disturbances in hormonal metabolism.
The benefits of physical activity during treatment
Is endometrial hyperplasia combined with physical activity? A properly selected complex and moderate intensity of exercises have a positive effect in the treatment of the disease and on the woman’s health in general.
Regular physical activity helps reduce estrogen in the blood and slow down pathological processes. When playing sports, cell nutrition improves and oxygen supply to tissues increases. And also, endorphins are produced, they relieve pain and lift your mood.
Source: https://vashamatka.ru/patologii/giperplaziya/kak-lechit-giperplaziyu-endometriya-matki.html
Endometrial hyperplasia - laser treatment in Moscow
We use the most gentle and at the same time effective method of treatment, which does not injure the uterine mucosa and does not leave scars!
The laser does not injure the endometrium and avoids relapses, which are the main problem in this disease.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
The inner surface of the uterus is covered with endometrium. A thin layer of mucous membrane, consisting of 3 types of cells (integumentary, glandular and connective), ensures the attachment of the embryo during pregnancy. Endometrial hyperplasia is a pathological growth of the inner lining of the uterus (from lat.
“hyper” - over, “plasia” - formation, formation), manifested by a violation of menstruation and leading to impaired fertility. The thickness of the inner surface of the uterus depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle: the thinnest endometrium is typical for 2–3 days of menstruation, and the thickest is for the 20th day of the cycle.
Normally, the thickness of the uterine mucosa should not exceed 21 mm on the 19th–23rd day of the cycle.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist Normal endometrium Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is not a separate disease, but a benign reaction of the uterine mucosa to internal and external pathological influences. A pertinent question arises: if the changes do not relate to dangerous malignant diseases, then why do gynecologists try to early identify and begin treatment for endometrial hyperplasia?
As they grow, the cells of the mucous membrane can change the genetic program, becoming the background for the malignant degeneration of cellular structures.
The proliferation goes unnoticed by the doctor and the patient: hyperplasia can become the basis of precancer and endometrial cancer, which are extremely difficult to cure.
Therefore, it is important to promptly detect and treat any form of hyperplastic process at an early stage of formation.
Depending on the cellular structure of tissue hyperplasia, the following types of endometrial pathology are distinguished:
- glandular and glandular-cystic hyperplasia (proliferation of integumentary and glandular cells)
- fibrous hyperplasia (growth of connective tissue elements)
- atypical endometrial hyperplasia (precancerous changes in the cellular structures of the uterine mucosa)
Prevalence
Depending on the location and severity of endometrial damage, two forms are distinguished:
- IO focal (single polyp or multiple polyposis of the uterine body)
- II Diffuse hyperplasia (general hyperplastic process of the endometrium)
Significant factors in identifying hyperplasia
The main diagnostic criteria that influence the choice of treatment tactics include:
- the presence or absence of cells with an altered genetic program (tissue atypia);
- preservation or absence of a normal relationship between the constituent elements of the endometrium (structural defects)
simple hyperplasia (the relationship between the structural elements is preserved, the endometrium looks normal, but is thicker than healthy tissue);
complex hyperplasia (heterogeneous accumulations of glands appear in the endometrium);
Both options can be with atypia (the presence of cells with an altered genetic program) or without precancerous changes in the endometrium.
This division is important for predicting uterine cancer in a patient with endometrial hyperplasia. The safest option is a simple form without atypia (the probability of degeneration into cancer is 1%), the most insidious is complex hyperplasia with atypia, which turns into cancer in 1/3 of cases.
-
The most common type of benign endometrial pathology, the basis of which is the proliferation of endometrial cells of the uterine glands.
-
An important difference between the glandular-cystic form is the formation of cystic cavities in the endometrium against the background of a pronounced proliferation of glandular cells
-
A focal variant of hyperplasia is uterine polyps. The growth of fibrous connective tissue elements of the uterine mucosa can reach 6 cm in length and fill the entire uterine cavity
-
Adenomatous hyperplasia is the maximum threat for uterine cancer. The pathology manifests itself in the form of a diffuse or focal form with the obligatory presence of atypical and structural changes in the endometrial tissue
Pathology can occur at any age, but more often girls suffer during the formation of menstrual function and women in the premenopausal period, which is explained simply - the main provoking point in the development of the disease is an imbalance of sex hormones in the body (high levels of estrogen with a relatively low content of progesterone).
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
The following conditions and diseases contribute to the formation of endometrial hyperplasia:
- diabetes
- inflammatory processes of the reproductive system organs
- obesity
- mammary gland pathology
- early onset of menstruation (girls under 12 years old)
- high blood pressure
- late menopause (women over 52)
- Acyclic bleeding A frequent symptom of endometrial hyperplasia is scanty intermenstrual acyclic bleeding. In rare cases, patients complain of heavy uterine bleeding that occurs during menstruation
- Disorders and pain during menstruation Irregular menstrual cycles and premenstrual pain syndrome are signs of pathological changes in the endometrium. Women's problems are associated with vascular disorders and spastic contractions of the uterus
- Impaired reproductive function An important sign of pathology is infertility. Changes in the hormonal balance and structure of the uterine mucosa that occur when endometrial hyperplasia occurs create a significant obstacle to the normal attachment of the embryo after conception.
- Anemia Chronic blood loss associated with frequent menstruation irregularities leads to a weakening of the body with a deterioration in general condition, rapid onset of fatigue, weakness and the development of anemia (anemia)
The main methods to accurately establish the diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia are:
- ultrasonography
- hysteroscopy
- histological examination after diagnostic curettage
The first study if a hyperplastic process is suspected is transvaginal ultrasound. The method allows you to assess the size and condition of the uterus, the thickness of the mucous membrane and the correspondence to the day of the menstrual cycle. Having discovered a thickened endometrium, it is necessary to continue the examination to identify the type of hyperplasia.
Examination of the uterine cavity using a special camera that is inserted into the uterus through the cervical canal.
The accuracy level of the method is 63-97%. Endoscopic diagnosis is carried out before curettage of the uterine mucosa: the doctor can visually assess the location, nature and severity of hyperplasia
Diagnostic curettage is a surgical procedure to obtain endometrial tissue. Histological examination makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, identify the degree of structural abnormalities and prevent the development of uterine cancer
A diagnostic technique for visual examination of the uterine cavity (mini-hysteroscopy), carried out using an ultra-thin optical device, allows you to obtain an enlarged image of the endometrium on the monitor screen. The method is used in a clinic, allowing a diagnosis to be made and the correct therapy to be prescribed.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Depending on the type of endometrial hyperplasia and the age of the patient, conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
The main stages of treatment are:
- stopping bleeding (surgical removal of hyperplastic mucous membrane or use of hormonal tablets)
- a full examination to identify the main cause of the pathology
- course therapy with regular monitoring of the endometrium
- restoration of menstrual and reproductive function in women during the reproductive period
- Hormone therapy:
- An effective and popular method of therapy is the use of hormonal drugs prescribed by a specialist based on the results of ultrasound, hysteroscopy and histological examination.
- Surgical methods
The surgical method is used for a simple form of endometrial hyperplasia without atypia. All overgrown uterine mucosa is removed. Restoration of the endometrium occurs against the background of hormonal therapy prescribed by a doctor.
Laser ablation
A modern, highly effective surgical technique is used for complex endometrial hyperplasia. Laser ablation allows you to destroy and remove affected areas of the endometrium, preventing the risk of precancer formation. Recovery of the mucous membrane must be monitored with hormone therapy and regular visits to the doctor.
Uterus removal
- lack of effect from conservative methods
- relapse of the disease in patients over 35 years of age
- complex hyperplasia with atypia
The volume and technique of the operation are determined by a specialist for each woman on a strictly individual basis.
A high risk of dangerous consequences occurs with atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
Cancer
Benign growths of the endometrium are a background for the development of cancer. After a thorough examination, the doctor will begin conservative treatment, which involves taking hormonal medications, but if there is no effect, surgery must be performed to prevent malignant degeneration.
Infertility
A dangerous complication for women of reproductive age is infertility. There may be difficulties with conceiving and carrying a pregnancy. Problems can be avoided with a timely diagnosis and the correct method of therapy.
Preventive measures to prevent hyperplasia of the uterine mucosa are:
- regular visits to the gynecologist (at least once a year);
- timely and effective treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- correction of gynecological diseases (adenomyosis, uterine fibroids);
- therapy of endocrine and metabolic disorders
Hyperplasia in the endometrium develops less frequently in women who use hormonal contraceptives under the supervision of a physician.
Good results will come from giving up bad habits, regular exercise, fitness classes and normalizing your diet.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Source: https://drugayaginekologiya.ru/lechenie/giperplaziya-endometriya/
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a benign growth of the inner layer of the uterus - the endometrium, leading to thickening and an increase in its volume. The process is based on the increased proliferation of glandular and stromal elements of the endometrium.
Depending on the predominance of certain elements, several types of endometrial hyperplasia are distinguished:
- glandular, glandular-fibrous and fibrous endometrial polyps (focal growths of the endometrium, consisting of glands, in combination of glandular tissue with connective tissue stroma or only connective tissue). This type of hyperplasia is more common than others.
Glandular and glandular fibrous polyps rarely undergo malignancy, but can serve as a favorable background for the development of endometrial cancer.
Causes of endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia occurs in women of all age categories, but more often occurs during adolescence, when hormonal changes occur in the body (in teenage girls or premenopausal women).
Possible causes leading to the development of endometrial hyperplasia include:
- - hormonal disorders - excess estrogen against the background of progesterone deficiency; - concomitant extragenital diseases - diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, obesity, diseases of the thyroid gland, mammary glands and adrenal glands; - inflammatory diseases of the genital organs; - abortions and diagnostic curettages; - adenomyosis and fibroids uterus; - polycystic ovary syndrome;
- - hereditary disposition.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia
The main symptom of all types of endometrial hyperplasia is non-cyclic bleeding. Discharge with hyperplasia appears in the intermenstrual period or after a slight delay in menstruation.
Unlike normal menstruation, the discharge is moderate, sometimes spotting. Less common are heavy breakthrough bleeding with clots, which is typical for hyperplasia of adolescence.
Prolonged bleeding leads to anemia (anemia).
Excess estrogen leads to infertility due to anovulation (a cycle without ovulation). It is extremely rare that hyperplasia does not manifest itself in any way and the absence of a long-awaited pregnancy is the main reason for contacting a gynecologist.
In any case, in case of any alarming bleeding and absence of pregnancy for a year with regular unprotected sexual activity, an in-person consultation with a gynecologist is necessary, since the disease does not go away on its own. As a rule, the symptoms of hyperplasia are often confused with the threat of miscarriage in the early stages and manifestations of uterine fibroids, if the diagnosis was previously established.
Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia
- Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia includes:
- - gynecological examination; - Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with a vaginal sensor (thickening of the endometrium is determined, in the presence of polyps, oval formations in the uterine cavity are visualized); Ultrasound diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia should be considered as screening, since ultrasound records only the thickness of the endometrium.
- Endometrial thickness according to ultrasound data.
| Endometrial structure | Endometrial thickness, mm |
| Unmodified | 9,8 ± 2,1 |
| Hyperplasia | 15,4 ± 0,4 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 20,12 + 2,04 |
- hysteroscopy (examination of the uterine cavity using a special optical device) with separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity. The resulting scraping is sent for histological examination to determine the type of hyperplasia.
Curettage is carried out as planned - on the eve of the expected menstruation. Thus, this method is the most reliable and preferable, since it allows simultaneously making an accurate diagnosis and performing surgical treatment.
The information content of hysteroscopy for endometrial hyperplasia is estimated at 94.5%, transvaginal echography (ultrasound with a vaginal probe) - at 68.6%; - aspiration biopsy of the endometrium - a piece of endometrial tissue is taken and sent for histological examination; - hormonal studies - check the level of estrogen and progesterone, if necessary, examine the hormones of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
It is necessary to treat endometrial hyperplasia in any case, regardless of the patient’s age and the degree of clinical manifestations of the disease.
As already mentioned, hysteroscopy and separate diagnostic curettage is the most effective surgical method for treating and diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia.
If a woman is of reproductive or premenopausal age, as well as in emergency situations - with large blood losses or the presence of a polyp according to ultrasound data, preference should be given to the surgical method. To perform curettage, the patient is sent to the hospital for planned or emergency surgery.
Surgical treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Then, after receiving the results of histological examination, depending on the type of hyperplasia, the patient’s age and concomitant diseases, hormonal therapy is selected (except for fibrous polyps that do not require hormonal treatment). The goal of hormone therapy is to suppress further proliferation (overgrowth) of the endometrium and regulate hormonal imbalance.
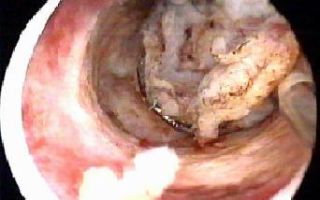
In the photo, electrosurgical resection of the endometrium under the control of a hysteroscope
The following groups of hormones are used to treat endometrial hyperplasia:
- COCs - combined oral contraceptives (Regulon, Zhanin, Yarina) are prescribed for six months according to the contraceptive regimen.
The drugs are suitable for women of reproductive age up to 35 years of age, as well as teenage girls with heavy and/or irregular menstruation with glandular and glandular-cystic types of hyperplasia or polyps.
COCs can be used for “hormonal hemostasis” (taking hormones in large doses) in girls in emergency situations to stop bleeding, so as not to resort to curettage.
COCs are prescribed 2-3 tablets per day, then the dose is reduced, bringing it to 1 tablet per day. The course of treatment is 21 days. If hormonal hemostasis is ineffective - if the bleeding continues and threatens the life of the child, they resort to curettage of the uterine cavity.
- gestagens (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) from the 16th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle are prescribed for 3-6 months. Suitable for women of any age with any type of hyperplasia.
The gestagen-containing contraceptive intrauterine device Mirena is successfully used, which has a local effect on the endometrium, in contrast to gestagens used orally, which have a systemic effect. The spiral is installed for 5 years.
The downside of the IUD is that quite often a side effect occurs in the form of intermenstrual bleeding within 3-6 months after insertion of the IUD. In addition, many patients are confused by the spotting nature of menstrual discharge against the background of Mirena and the presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity;
- GnRH gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists (Zoladex, Buserelin) are the most effective group of hormones. Used in women over 35 years of age and during perimenopause from 3 to 6 months for any form of hyperplasia. An unpleasant side effect of drugs in this group is symptoms of early menopause (hot flashes).
Gonadotropic releasing hormones are formed in the nerve cells of the anterior and middle hypothalamus and regulate the synthesis and release of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland, indirectly the formation of sex hormones in the ovaries.
The mechanism of action of GnRH agonists (as well as natural ones) is to bind to the receptors of pituitary cells that secrete gonadotropic hormones. As a result, a picture develops similar to that observed with hypogonadotropic amenorrhea. This phenomenon is also called “medical castration.”
The process is reversible: after stopping the administration of GnRH agonists, after 14-21 days the function of the entire hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system in women of reproductive age is restored.
GnRH drugs are widely used in gynecological clinics, primarily for estrogen-dependent pathologies: endometrial hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and breast cancer. The drugs are administered once every 28 days for 3-6 months, depending on the nature of the pathological process.
Patients with atypical endometrial hyperplasia require special dynamic monitoring by a gynecologist. Control ultrasound should be performed 3, 6 and 12 months after curettage and the start of taking hormones to assess the effectiveness of treatment. If adenomatosis recurs, removal of the uterus is indicated.
In case of recurrence of endometrial polyps, glandular and glandular-cystic forms of hyperplasia, if hormone therapy is ineffective - if the patient is not interested in childbearing - ablation (resection) of the endometrium is indicated - complete destruction of the endometrium. For this purpose, electrosurgical (with a cutting loop) and laser ablation methods are used under the control of a hysteroscope. The operation is performed under general intravenous anesthesia.
After curettage of the uterine cavity and/or resection of the endometrium, the patient can be discharged home on the day of surgery or the next day. Within 3-10 days after the manipulation, there may be light bleeding from the genital tract. After ablation, the remains of resected tissue usually come out along with the discharge. Such discharge is normal and should not be embarrassing.
In parallel with hormone therapy, for a quick recovery, taking vitamins is indicated: ascorbic acid, B vitamins, iron supplements for anemia (Sorbifer, Maltofer). Sedative therapy (tincture of valerian or motherwort) is prescribed. Physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis) and acupuncture are useful.
Nutrition must be nutritious, it is necessary to observe a regime of work and rest. Sexual abstinence is also recommended for 2 weeks after curettage.
Folk remedies for the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Traditional medicine is also used to treat hyperplasia. It is useful to use folk remedies in the rehabilitation period after curettage. Nettle tinctures are used to replenish hemoglobin and serum iron levels after heavy blood loss.
The plant has a general strengthening and tonic effect. However, it should be borne in mind that folk remedies have no effect on the disease itself; they are used only as symptomatic therapy.
Excessive use of herbal medicine without surgical and drug treatment can lead to complications of the disease.
Complications of endometrial hyperplasia:
- - transition of the atypical form to endometrial cancer; - relapses of the disease (the most common complication); - infertility in reproductive age;
- - chronic anemia.
Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia:
- - regular visits to the gynecologist twice a year; - refusal of abortion; - timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital area and other gynecological diseases (uterine fibroids, adenomyosis); - taking hormonal contraceptives; - treatment of concomitant extragenital diseases - control of blood glucose levels in diabetes, lowering blood pressure for hypertension, losing weight for obesity, and so on;
- - regular exercise and fitness classes.
Questions and answers from an obstetrician-gynecologist on the topic of endometrial hyperplasia
— Will I be able to quickly get pregnant after curettage for endometrial hyperplasia? Yes, if there are no menstrual irregularities;
— I had bleeding. They diagnosed endometrial hyperplasia and recommended curettage. But the discharge disappeared on its own, is it necessary to do curettage? Necessarily. Stopping discharge is not a sign of cure;
— Is it possible to go to a bathhouse or sauna with hyperplasia? Undesirable, any thermal procedures are contraindicated;
— I’m 25 years old, I haven’t given birth. Is it possible to treat hyperplasia with hormones without curettage? No, it's ineffective. Hormones stop the growth of endometrial proliferation, but do not eliminate hyperplastic endometrium;
— If an endometrial polyp is discovered during pregnancy, what do they do with it? How does it affect the fetus? During pregnancy, the polyp is not treated. The polyp does not have a negative effect on the fetus;
“I had curettage twice for endometrial hyperplasia and was treated with hormones. Now they have discovered it again. Why is treatment ineffective? There may be several reasons: the hyperplastic endometrium was not completely removed during curettage, or you have endocrine disorders that contribute to relapse of the disease;
— Is it possible to do hysteroscopy on an outpatient basis or do you have to go to the hospital? Ideally, hysteroscopy is performed in hospitals to provide emergency assistance if necessary. If everything is fine, they may be discharged on the same day;
— Is it possible to have sex if you have endometrial hyperplasia? Yes, you can.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. Christina Frambos.
Source: https://medicalj.ru/diseases/female-illness/12-endometrial-hyperplasia
Uterine endometrial hyperplasia: treatment and diagnosis in Odessa | Medical house Odrex
Uterine endometrial hyperplasia (UGE) is an insidious disease, as it is asymptomatic at first.
The uterine mucosa grows without pain, which creates the deceptive illusion that there is no problem.
However, the disease provokes menstrual irregularities, bleeding, infertility, and is considered by experts as a background process for the development of endometrial cancer.
Uterine hyperplasia is usually understood as excessive growth of its mucous membrane. Failure in this part of the body is due to hormonal imbalances. The mucous membrane loses its ability to shrink after the end of the cycle and takes on a hypertrophied appearance. Symptoms of the disease are menstrual irregularities, spotting and heavy periods.
However, the disease often occurs without pronounced symptoms. The problem of growth of the endometrium of the uterus is relevant for 50% of women aged 30 to 39 years.
Entrust the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia to real professionals
A “silent” but dangerous disease requires high professionalism of the doctor and advanced diagnostic methods. You will find all this at the Odrex medical house, where you will be offered:
- High-precision diagnostics using a Karl Storz hysteroscope without anesthesia and pain;
- Prompt development of an individual treatment plan;
- Treatment methods that work.
Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia at Odrex
The first and mandatory step in diagnosing hyperplasia is an examination of the woman by a gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental tests.
Today, highly effective and gentle diagnostic methods are used in medical practice:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a common method. Modern devices help to see and measure the thickness of the mucous membrane layer with an accuracy of tenths of a millimeter. At the same time, an ultrasound picture in itself, not confirmed by other studies, is not a diagnosis. An ultrasound should be done either in the middle of the cycle or immediately after the end of menstruation.
- MRI of the pelvic organs provides clear visualization due to clear contrast of soft tissues. An indispensable tool for identifying tumor diseases. Magnetic resonance accurately diagnoses adhesions in the pelvis, which cannot be done using ultrasound alone.
- Hysteroscopy is the most informative method that provides accurate and reliable results. Our clinic is equipped with the German optical system Karl Storz, which will perform a targeted biopsy in the place where the focus of cell proliferation is located. If necessary, pathological tissue is cut off. The procedure takes less than an hour and requires hospitalization for half a day. The period of histological examination is from 2 to 14 days.
- Laboratory tests to determine the level of hormones in the blood, adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
Suspicion of hyperplasia appears when the thickness of the endometrium is more than 15-16 mm (according to ultrasound or MRI of the pelvic organs).
How to treat the hyperplastic process?
The treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is influenced by many factors. Among them, the type of endometrial hyperplasia is crucial:
- Simple glandular hyperplasia is characterized by excessive growth of endometrial tissue.
- Adenomatous or complex hyperplasia, in which structures that are not characteristic of it are formed inside the endometrium. Occurs in approximately three out of hundred women.
- Glandular cystic endometrial hyperplasia. It is accompanied by cystic formations and provokes an increase in the volume of the uterus.
- Focal hyperplasia (endometrial polyps). Pathological formations consisting of a body and legs.
- AAtypical endometrial hyperplasia is the most dangerous type, which often leads to malignant formations. It is customary to distinguish focal and diffuse varieties. Sometimes this form is caused by incorrectly selected therapy for glandular hyperplasia.
The main principle of treatment is based on removing the area of pathological mucosa. For this purpose, the following methods have been developed in medicine:
- Hysteroscopic resection (cutting) of the endometrium and removal of polyps is a mandatory first stage of treatment. The advantages of this treatment include low trauma, cost-effectiveness (due to a reduction in the time spent in the clinic), preservation of reproductive function and a reduction in the duration of the intervention.
- Hormonal therapy, which consists of taking medications that normalize the production of estrogen and progesterone. There are general and local drugs (intrauterine). Many regimens for taking such medications have been developed, and the doctor’s task is to choose the best option.
- Surgical intervention is curettage, or in common parlance – curettage. Today it is considered an outdated method. The meaning of the procedure is clear from the name. This operation has numerous disadvantages: severe pain, the need for large dilation of the cervix. the risk of adhesions in the pelvis. It is performed under general anesthesia. The need for hospitalization depends on the patient's physical condition and ability to tolerate anesthesia. Local anesthesia with painkillers is possible.
- Removal of the uterus or hysterectomy is a radical method that is used exclusively for atypical hyperplasia. when there is a high risk of degeneration of benign formations into malignant ones, or with a recurrent form of the disease that does not require therapy.
Remember that treatment for this disease is individual. There is no single panacea that would work with a 100% guarantee in all cases without exception.
And only an experienced gynecologist-endocrinologist will determine the regimen, dose and duration of treatment that will “work” in each specific case.
However, combination treatment is predominantly prescribed, which involves both surgery and hormonal therapy.
Today on the Internet there are a lot of recommendations on how to cure hyperplasia with leeches, celandine, burdock or nettle. However, the effectiveness of these methods against this disease has not been confirmed in official medicine. Therefore, you should not risk your health because of questionable recipes.
The risk of recurrence of this disease is high and occurs in 30% of cases. At the same time, it is impossible to predict the occurrence of relapse: it does not depend either on the course of the disease or on the chosen treatment regimen. Therefore, performing an endometrial biopsy 3-6 months after the end of treatment is a mandatory procedure.
With the disease, there may be no ovulation, and the mucous membrane itself is sometimes unable to accept the embryo. However, after successful treatment, it is possible to become pregnant naturally. Fertility is almost always restored. Therefore, if a woman plans to give birth to a healthy and strong baby, hyperplasia should be cured.
Preventive recommendations in this case are general in nature without specific points. These include regular visits to the gynecologist, treatment of inflammatory sexual diseases, and exercise.
Remember that endometrial hyperplasia is a potential cancer. This has been proven by authoritative foreign and domestic researchers. You should not hope that the overgrown mucous membrane will “resolve” on its own. This disease cannot go away without medical help.
Reviews
I would like to convey my gratitude to gynecologist Olga Nikolaevna Kulish, who performed gynecological surgery on me on January 15, 2018. Thanks a lot! I am very glad that I met such a professional doctor. This is a doctor from God. Dear women, do not look for other ways to improve your health.
If there is at least one chance of recovery, when you contact Olga Nikolaevna, you will get it. And personally, Olga Nikolaevna, my husband and I wish you health, good luck, happiness, prosperity and to have more opportunities to give people the most precious thing - health.
Kuzmicheva Larisa Petrovna
May 12, 2018
I would like to convey my gratitude to gynecologist Olga Nikolaevna Kulish, who performed gynecological surgery on me on January 15, 2018. Thanks a lot! I am very glad that I met such a professional doctor. This is a doctor from God. Dear women, do not look for other ways to improve your health.
If there is at least one chance of recovery, when you contact Olga Nikolaevna, you will get it. And personally, Olga Nikolaevna, my husband and I wish you health, good luck, happiness, prosperity and to have more opportunities to give people the most precious thing - health.
Kuzmicheva Larisa Petrovna
May 11, 2018
Source: https://Odrex.ua/treatment/giperplaziya-endometriya/