Thrush (candidiasis)
Candidiasis, popularly called thrush, is an infectious disease that can affect the skin and mucous membranes of various systems (genital, respiratory, digestive, nervous). Contrary to popular belief, it is not sexually transmitted.
thrush, candidiasis, fungus treatment
Types of thrush (candidiasis)
Depending on the severity of the disease, several types of candidiasis are distinguished:
Superficial – the mildest form. Often called red or double thrush (candidiasis). It is found on the skin, nail plates, mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals. Treatment of fungus at this stage usually does not cause difficulties.
Systemic - the microorganism penetrates the epithelial tissue, affecting the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
Sepsis is a very dangerous stage. The fungus spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. Treatment of candidiasis is particularly difficult. Possible death.
There are several forms of thrush (candidiasis)
- Acute – lasts no more than 2 months. If you make a timely and correct diagnosis, you can quickly cope with the disease.
- Chronic – characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. Usually develops in the absence of treatment or improper therapy of the acute form. In this case, there are 2 types of fungus: systematic, or recurrent, and sluggish, or persistent. According to statistics, a recurrent form of candidiasis occurs in 50% of women.
- Candidate-bearing - there is a huge amount of fungus in the body, but there are no signs of disease.
Depending on the location, candidiasis occurs
- urogenital – affects the mucous membrane of the reproductive and urinary systems;
- visceral – the fungus penetrates the organs of the respiratory, digestive and nervous systems;
- skin and nails - transmitted during fetal development or at birth, which is why it is called congenital thrush.
Nail fungus causes and treatment
Causes of candidiasis (thrush)
The causative agent of the disease is Candida, a representative of yeast-like fungi. Scientists know about 150 species of these microorganisms, but the most common are Candida albicans, tropicalis and globrata.
Fungal cells are round in shape and reach a diameter of 10 micrometers. These microscopic organisms are quite resistant to adverse conditions and are able to live in various environments. But the optimal temperature regime for them is 21-37⁰С.
In its normal state, the fungus lives on the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx and genitals, without revealing itself in any way. But when suitable conditions appear, active, unrestrained reproduction of Candida begins, causing the development of thrush.
The main reason for this situation is a weakened immune system.
Other factors can also provoke rapid growth of the fungus.
- taking strong antibiotics that destroy beneficial microflora;
- use of contraceptives that increase estrogen concentrations;
- stressful state;
- depression;
- nervous tension;
- excessive consumption of baked goods, especially those made from yeast dough, sweets, and beer;
- indigestion (constipation, diarrhea);
- diabetes;
- low-quality tampons and pads;
- poor personal hygiene;
- cheap underwear of low quality.
Click here - all materials on the topic of care for Thrush (candidiasis)
All portal materials on the topic Thrush, Candidiasis at the link above
Signs of candidiasis (thrush)
Thrush is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- cheesy white discharge from the vagina;
- severe itching;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- pain syndrome during intimacy;
- a specific smell reminiscent of curdled milk.
But you should not make a diagnosis yourself and self-treat the fungus , which can only worsen the situation. Other diseases have similar symptoms. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose the pathology. He will prescribe the necessary diagnostics and, based on the results of the study, select the optimal methods for treating thrush .
Recommendations from the attending physician
- abstain from sexual contact for 10 days;
- after each urination, wash with decoctions of medicinal plants, soda or furatsilin solution;
- do not use soap and intimate products;
- in case of severe itching, it is recommended to sprinkle the genitals with baby talcum powder;
- exclude fried foods, smoked foods, salty and spicy foods, sweets;
- increase the consumption of fermented milk products and yoghurts containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals and legumes;
- pay special attention to hygiene during menstruation, it is advisable to temporarily “forget” about tampons, wash your face every three hours and change pads;
- When playing sports and other physical activities, wear underwear made of pure cotton; remove synthetic and tight-fitting underwear from your wardrobe, as they cause excessive sweating.
Melanoma: causes, risks, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
The above tips, together with medications prescribed by the doctor, will help slow down the proliferation of fungi and defeat the insidious disease.
Source: https://old-lekar.com/molochnica-kandidoz-gribok-lechenie/
What kind of fungus is thrush, and what means to cure it
Home => Fungus => What kind of fungus is thrush, and what means to cure it
Many in their lives have encountered manifestations of a fungus, which is popularly called “thrush”. This name is played out in television commercials, where a pretty girl meets a goat in transport - a subtle hint at “fat circumstances.” Why so affectionately and gently, almost deliciously, called a pathogenic fungus that can be dangerous to humans?
“Thrush” was a yeast fungus from the genus Candida . Its species name is C. albicans. It received this name because its most common localization on the mucous membranes resembles curdled flakes.
Indeed, they are very similar to small curds. But if you take such flakes, rub them between your fingers and bring them to your nose, you can clearly smell the mushroom smell.
If thrush appears on the tongue, then when you see it for the first time, it is difficult to get rid of the impression that the person just drank kefir.
This is “cottage cheese with mushrooms”. Now we know what fungus causes thrush. In general, what is the place of candida among other pathogenic fungi, and what diseases does it cause?
A little about the fungus
You shouldn’t be surprised, but Candida lives in the intestines of 80% of healthy people, without causing any signs of disease, not helping us, but not harming us either. Therefore, candida cannot immediately be considered a pathogen, which, when it enters the body, immediately causes thrush. You can rest easy: Candida never left your body.
Therefore, scientists called C. Albicans a conditionally pathogenic pathogen. This means that the fungus that causes thrush is able to exhibit its pathogenic properties only in certain circumstances: when the human body’s defenses, called immunity, are reduced.
Since the candida fungus constantly lives in our mouth and on the mucous membranes, thrush occurs there.
Where is thrush found?
As it became clear, such cheesy discharge is noticeable only on the mucous membranes.
Therefore, babies may experience oral candidiasis: a cheesy coating appears on the tongue, the inner surface of the cheeks, on the gums, and sometimes on the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx.
You shouldn’t be afraid of this: sometimes young parents in a panic search on the Internet what fungus causes thrush, and prepare for serious expenses.
In fact, in simple and uncomplicated cases, an effective remedy for thrush fungus in babies is ordinary baking soda.
It should be diluted in the amount of one teaspoon per glass of warm water, and then gently wipe the plaque with a cotton swab dipped in a soda solution. There is no point in trying to apply force: the main thing is regularity and thoroughness of processing.
This needs to be done twice a day, after feeding, and soon the fungus, once exposed to unfavorable conditions, will disappear.
Does oral thrush occur in adults? Yes, but under special circumstances, which will be discussed below.
In adults, Candida has chosen completely different places. Thus, the thrush fungus in women causes vulvovaginitis, or damage to the genital tract mucosa. The symptoms are as follows:
- cheesy discharge from the genital tract;
- feeling of discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- itching and burning in the intimate area;
- discomfort when urinating.
In men, the thrush fungus also likes to parasitize the genitals, causing balanitis (inflammation of the glans penis), and balanoposthitis - inflammation of the inner layer of the foreskin.
The signs of candidal balanoposthitis are exactly the same manifestations:
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- plaque on the head and inner layer of the foreskin, their hyperemia;
- itching and burning on the head and foreskin;
- curdled discharge.
About severe forms of the disease
If a person’s immunity is very significantly reduced, then candida can colonize internal organs from the border tissues, which are the mucous membranes. In such cases, intestinal candidiasis, and even various forms of visceral candidiasis, affecting internal organs, may develop.
With intestinal candidiasis, “thrush” plaque is found in the stool, bloating, diarrhea occurs, and vitamin deficiency occurs due to inhibition of normal intestinal microflora.
In extreme cases, candidal sepsis may develop. In this case, we can literally say that man has become a substrate for the growth of fungi.
Such severe forms usually develop with HIV infection, which has reached the stage of AIDS, with severe immunodeficiencies of another etiology (for example, with malignant blood tumors).
How to treat thrush
Treatment for thrush involves complete destruction of the fungus . For this purpose, the following means are used: Locally - creams, ointments, rectal and vaginal suppositories, and internally - capsules or tablets.
Tablets for thrush fungus are prescribed together with creams or ointments only if there is reason to think about the presence of immunodeficiency, for example, with diabetes, hypothyroidism, chronic bronchitis. Also, internal administration of antifungal drugs is indicated for relapse of the disease, if only local remedies cannot cure it.
One of the most effective drugs is fluconazole - Diflucan, Mikosist.
How to treat candidal balanoposthitis? You can inject a solution of borax in glycerin into the space between the glans and foreskin, apply Lomexin cream, and, of course, maintain hygiene: thoroughly rinse the glans twice a day before applying the cream.
When treating vaginal candidiasis in women, one Diflucan capsule intravaginally is sometimes sufficient. If a relapse occurs, you can add an oral capsule and repeat the treatment .
About prevention
In order to prevent thrush from returning, you need to strengthen your immune system, observe personal hygiene rules, promptly treat sexually transmitted infections, and refuse sexual contact with dubious people. In the same case, if you refuse beyond all your strength, then you need to use a condom.
Source: http://parazity.info/chto-za-gribok-molochnitsa-i-kakimi-sredstvami-ego-izlechit.html
Candida yeast fungus in women: treatment, causes and symptoms in the photo
According to medical statistics, every third woman in the world experiences vaginal candidiasis. Pathology refers to an infection caused by the yeast Candida.
The disease, which is popularly called thrush, leads to damage to the female genital organs, the development of unpleasant symptoms that cause discomfort, decreased quality of life, stress, nervous tension and frustration.
Timely treatment of yeast fungus eliminates the development of complications and shortens the period of elimination of its symptoms. In the photo you can see a picture of the condition of the mucous membranes of the genital organs in women who have encountered a fungal infection.
A number of compelling factors
Yeast fungus appears in women for a number of reasons. Its development is provoked by:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics that kill beneficial microflora in the intestines and provide the opportunity for Candida fungus to develop intensively in women.
- Treatment with immunosuppressants (immune suppressants).
- Contraceptives, tampons used during menstruation, intimate hygiene products.
- Genetic defects of the immune system of women and a diet rich in carbohydrates, which creates favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of Candida yeast, as well as a deficiency of protein foods.
- Indwelling catheter and other procedures of this kind, causing the appearance of candidiasis and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Failure to comply with basic rules of hygiene and safe sex, as well as exposure to harmful substances and chemicals, causing changes in the immune system.
Causes of yeast fungus in women also include taking steroid medications, diseases of the endocrine and reproductive system. Such factors in the appearance of thrush lead to the diagnosis of fungal infection of the genital organs in girls and women, regardless of their age and status in society.
Manifestation of the disease
Thrush in women manifests itself in the form of unpleasant sensations that cause discomfort and become an obstacle to performing household chores and work duties.
The list of signs of vaginal candidiasis, the development of which is caused by Candida yeast, includes:
- Severe itching of the genitals and pain when urinating.
- The presence of white, grayish discharge with a cheesy consistency.
- The appearance of pain in women during sexual intercourse.
- Burning, redness, swelling of intimate areas.
- Irritation of the perineal area.
In women, the symptoms of thrush cause them a lot of inconvenience, irritation, nervous disorders and lead to a decrease in self-esteem. A fungal infection has distinct symptoms that make it possible to promptly identify the disease at home and begin treatment immediately.
If the activity of yeast fungus in women is reinforced by bacterial infection, additional symptoms of the disease appear in the form of dizziness, depression, fatigue, anxiety, depression, itching in the anus, hyperhidrosis, increased sensitivity of the joints, and aggression.
The fungus should be treated immediately after its first signs appear.
A negligent attitude to the problem leads to the development of a chronic form of vaginal candidiasis, alternating periods of remission with relapses, as well as the spread of pathogenic flora to the skin, nail plates, including the feet, areas between the fingers of the upper and lower extremities, and under the mammary glands.
Recognition and treatment methods
To properly treat yeast fungus, you need to get tested. The research results form the basis for confirming or refuting vaginal candidiasis.
A gynecological examination allows you to determine the causes of the disease, record a cheesy coating on the walls of the genital organs, and swelling of the female genitals. To identify mycelium in a smear in women, a microscopic diagnostic method is used.
To clarify the varieties of Candida fungi that led to the development of pathology, culture seeding is carried out on nutrient media.
Later, the drug to which the detected representatives of the pathogenic flora are sensitive is determined. Vaginal candidiasis is confirmed by the presence of Candida fungi in an amount of 10,000 CFU per 1 cm³ of the test medium.
According to the doctor’s decision, patients can undergo additional types of diagnostics: PCR, bacteriological smear culture, serological and enzyme immunoassay.
The examination results help to identify thrush and determine an effective medication to cure the pathology, prevent relapses, and the development of complications.
How to treat pathology
An integrated approach to solving the problem of candidiasis makes it possible to successfully cure a fungal infection in a short period of time. The treatment regimen aims to relieve unpleasant symptoms, return women to the joy of life, good mood, and full sensations during sexual intercourse. It includes:
- The use of local and systemic pharmaceutical products.
- Organization of a balanced nutritious diet, enriched with vitamins, trace elements, and minerals that are necessary to strengthen the immune system and improve the well-being of women.
- Using traditional medicine recipes.
Self-medication of vaginal candidiasis is unacceptable; you must consult a doctor.
During the treatment of vaginal candidiasis, women are advised to exclude sexual activity, strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene, refuse to wear synthetic underwear, and eat foods high in protein and low in glucose, which is a breeding ground for Candida yeast. Eliminate sugar and all products containing it, white flour products, honey, potatoes, starch and sauces, yoghurts, ketchups based on it, semolina and rice cereals, sweet and semi-sweet wines. It is allowed to eat buckwheat and brown rice, some fruits, except grapes, bananas, figs, dried fruits, dates (they contain a lot of glucose. Such nutrition will reduce the number of fungal colonies in the female body by 80%. Self-medication of vaginal candidiasis is unacceptable. Incorrect or ineffective therapy will cause the transition of thrush to a chronic form of development, subsequent diagnosis of complications.
Medications
In women, thrush can be treated at home. Pharmaceutical local antifungal agents include:
- Vaginal suppositories, cream, gel Miconazole based on miconazole nitrate.
- Decamine ointment with the active ingredient dequalinium chloride.
- Ketoconazole cream based on ketoconazole.
- Vaginal suppositories, Sertaconazole cream based on sertaconazole nitrate.
- Suppositories, Terzhinan tablets, a combination product that contains ternidazole, neomycin sulfate, nystatin, prednisolone, geranium and clove oil.
- Vaginal suppositories, Ginezol cream based on miconazole.
To treat severe forms of candidiasis, systemic medications are prescribed. They allow you to cleanse the female body from pathogenic flora from the inside and speed up recovery. These include tablets and capsules for oral administration of Nystatin, Fluconazole, Levorin, Lamisil, Intraconazole and other antifungal drugs.
Folk remedies
The list of traditional medicine that can enhance the therapeutic effect of medications includes:
1. Herbal decoctions based on chamomile, elecampane, calendula, string, birch buds, lavender, eucalyptus, St. John's wort, which are recommended for douching and treating female genitalia.
2. Solutions prepared from potassium permanganate, soda, honey, alcohol tincture of propolis, chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus allow you to treat candidiasis at home.
3. Essential oils of olive, sea buckthorn, calendula, milk thistle, grape or apricot kernels, used for nightly applications, provide an opportunity to reduce the manifestations of thrush and quickly return to a normal lifestyle.
Following the doctor’s recommendations is the key to successfully solving the problem at home and getting rid of the unpleasant symptoms of a fungal infection as soon as possible.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules of prevention will help minimize the risk of developing candidiasis. Yeast fungus, which occurs under favorable growth factors and the proliferation of pathogenic flora, is always easier to prevent than to treat it.
To do this, it is necessary to regularly carry out hygiene procedures, keep intimate areas clean and dry, and wear underwear made from natural fabrics.
When taking antibacterial drugs, it is necessary to use probiotics, the action of which is aimed at preventing the development of fungal infections. Use protective equipment during sex.
Taking your health seriously will help prevent the development of candidiasis, avoid fungal infections and enjoy life without its unpleasant symptoms.
Source: http://GribkaNet.com/molochnica/drozhzhevoj-gribok-kandida-u-zhenshchin
Thrush
Thrush (vaginal candidiasis) is a fungal infection of the vaginal mucosa. Manifestations of thrush include itching and burning in the vulva, copious curdled discharge, pain during urination and sexual intercourse. It is possible for a fungal infection to spread in the body and become a generalized form, disrupting the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth, and infecting the fetus. Thrush is diagnosed according to a gynecological examination, colposcopy, microscopic and bacteriological examination of a smear. Treatment of thrush is carried out with local and systemic antifungal drugs.
Thrush is an inflammatory lesion of the vaginal mucosa caused by fungi of the genus Candida. It is characterized by burning and itching in the vagina, white cheesy discharge. Thrush is also called neonatal candidiasis, most often manifesting as oral candidiasis.
Thrush is diagnosed by detecting the fungus through microscopy and culture of vaginal smears. To exclude concomitant STIs, ELISA, RIF and PCR studies are performed.
Chronic recurrent thrush is an indication for a complete examination of the patient in order to identify those disorders in the body that could cause such a course of thrush. Treatment is carried out by local and general use of antimycotic drugs.
Yeast-like fungi Candida, which provoke the development of thrush, are opportunistic flora of the vagina of most women and do not cause any pathological symptoms.
Therefore, unlike classic STIs, thrush cannot be 100% classified as a sexually transmitted disease, although Candida fungi can be transmitted from sexual partners.
Clinical gynecology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of candidiasis due to the similarity of its clinical picture with sexually transmitted infections and the frequent cases of a combination of these diseases.
Thrush
The development of thrush is caused by various factors that disrupt the healthy microflora of the vagina. As a result, there is a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria that normally inhibit the growth of fungal flora, and intensive proliferation of fungi. Active growth of fungi leads to the manifestation of their pathogenic properties with the appearance of inflammatory changes in the vaginal mucosa such as colpitis or vaginitis.
Violation of the normal ratio of microorganisms in the vagina with the development of thrush can be caused by treatment with cytostatics and other immunosuppressants, the use of hormonal contraception, decreased immunity due to somatic diseases (HIV, chronic bronchitis, tonsillitis, chronic pyelonephritis, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.), hormonal abnormalities ( diabetes mellitus, ovarian dysfunction, menopause, hypothyroidism, obesity), anorexia, pregnancy, stressful situations, sudden climate change.
Long-term or frequent antibiotic therapy, the use of antibacterial drugs without additional probiotics primarily cause intestinal dysbiosis. Since the intestines are a reservoir of Candida fungi, its diseases (dysbacteriosis, colitis, etc.) lead to the spread of Candida to other organs and primarily to the vagina with the development of thrush.
Various local factors can have an adverse effect on the vaginal biocenosis with the appearance of thrush: poor personal hygiene, irregular change of pads and vaginal tampons, the use of local contraceptives, the use of deodorized pads and scented colored toilet paper, wearing synthetic underwear. Frequent use of antibacterial products (antibacterial soap, intimate gel, vaginal spray) for hygienic purposes often leads to a decrease in local natural immunity and can provoke the occurrence of thrush.
Some women experience thrush after wearing wet underwear, visiting a pool or swimming in open water. This is due to the beneficial effect of a humid environment on the vital activity of Candida fungi. Poor diet with excess consumption of sweets can also contribute to the development of thrush.
Newborns born to mothers with thrush may develop thrush as a result of infection during the fetal period or passage through the birth canal.
The development of thrush in such cases is facilitated by the weakened state of the child’s body due to birth trauma, premature birth, hemolytic disease, intrauterine hypoxia, and asphyxia of the newborn.
Thrush is manifested by severe burning and itching in the area of the external genitalia and vagina. These symptoms are accompanied by the appearance of a white discharge characteristic of candidiasis.
Thrush is characterized by a heterogeneous consistency of discharge with small lumps resembling grains of cottage cheese. The discharge may have a sour odor.
Many women suffering from thrush note an increase in the amount of discharge after sexual intercourse, water procedures, and at night. Redness of the labia minora is often observed, and sometimes swelling of the labia minora and majora is observed, which can reach the anus.
Swelling and inflammatory changes in the vaginal mucosa during thrush lead to pain during sexual intercourse. There may be painful urination.
Quite often there is an erased course of thrush, when its clinical manifestations are mild or only one of the indicated symptoms is present. Symptoms of thrush can spontaneously resolve with the appearance of menstrual flow, since during this period the vaginal environment shifts to an alkaline side, less favorable for fungi.
However, thrush can also become chronic. Its relapses, as a rule, occur at least 4 times a year and usually occur a week before the start of menstruation. Chronic thrush is much more difficult to treat and can lead to complications.
A combination of thrush with other infectious lesions of the vagina (ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, genital herpes, etc.) is possible.
The most common manifestation of thrush in newborns is candidiasis of the gums (gingivitis), soft palate, buccal mucosa (stomatitis) and tongue (glossitis). It is manifested by the appearance of areas or spots covered with a white coating on the mucous membrane.
When the plaque is removed, the red and inflamed mucous membrane underneath is exposed. A newborn suffering from thrush is restless, often cries, sucks poorly and may refuse to breastfeed. Less commonly, neonatal thrush manifests itself in the form of candidal conjunctivitis.
The consequence of intrauterine infection can be pneumonia caused by fungi.
Chronic thrush can cause a number of complications.
Primarily, they are caused by the spread of fungal infection to structures located near the vagina: the cervix with the development of cervicitis, the urethra with the development of urethritis, and the bladder with the development of cystitis. The combination of thrush with other STIs with a long-term recurrent course can lead to the development of infertility in women.
As a rule, patients with symptoms of thrush consult a gynecologist. The doctor performs an examination on the chair and a colposcopy, takes smears from the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina. Microscopic examination of smears for thrush reveals the presence of fungal mycelium in the preparation.
This is a quick research method, but it does not provide accurate information about what type of fungus caused the disease. To answer this question, a smear is cultured on special nutrient media, followed by a study of the grown colonies and determination of the susceptibility of the isolated Candida fungi to antimycotic drugs.
In this case, the quantitative characteristics of the identified Candida colonies are taken into account, since their small number is normal for a healthy vaginal microflora.
Clinical observations show that thrush quite often occurs against the background of other sexually transmitted infections and can “mask” their presence. Therefore, if thrush is detected, it is advisable to additionally consult a venereologist and undergo testing for STIs. Typically, complex PCR diagnostics are used, which, if necessary, can be supplemented by ELISA and RIF.
Since the development of thrush is usually associated with certain disorders occurring in the body, when it is detected, a complete examination of the woman is necessary. This is especially true in cases where thrush does not respond well to treatment or takes a chronic course.
Thrush is often the first symptom of diabetes. Therefore, a woman needs to take a blood test for sugar and, if an increase is detected, contact an endocrinologist.
An examination by a gastroenterologist is also recommended: analysis for dysbacteriosis, coprogram, gastroscopy, radiography of the stomach, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, irrigoscopy, X-ray examination of the small intestine.
If complications of thrush develop in the urinary tract, it is necessary to consult a urologist, examine urine and smear from the urethra, Zimnitsky's test, and ultrasound of the bladder. Differential diagnosis of thrush should be made with bacterial vaginosis, gonorrhea, genital herpes, and trichomoniasis.
Local treatment of thrush can be carried out in case of its primary occurrence and uncomplicated course.
It is carried out with vaginal suppositories or tablets containing antifungal drugs: miconazole, clotrimazole, isoconazole, natamycin. Treatment of acute thrush lasts from 1 day to a week, depending on the drug prescribed.
Its effectiveness reaches 80-90%. During treatment, it is necessary to carefully observe intimate hygiene and abstain from sexual intercourse.
Broad-spectrum vaginal preparations containing nystatin should not be used in the local treatment of thrush. They suppress the beneficial microflora of the vagina and often lead to the development of gardnerellosis.
For mild thrush, local treatment can be replaced with a single dose of fluconazole. The disappearance of thrush symptoms is not always a sign of cure.
After treatment, a repeat examination of the vaginal smear is necessary.
In case of insufficient effectiveness of local therapy or chronic thrush, systemic oral administration of antifungal drugs is indicated. Fluconazole is most often used for this purpose.
After antifungal therapy, it is necessary to restore healthy vaginal microflora. For this purpose, eubiotics are prescribed.
However, their use is advisable only after laboratory confirmed elimination of candidiasis.
Treatment of chronic thrush can last several months.
It should include therapy for concomitant diseases, correction of intestinal dysbiosis, restoratives, exclusion of provoking factors (taking antibiotics, oral contraceptives, etc.).
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used in the treatment of recurrent thrush: SMT, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, laser therapy, darsonvalization.
Treatment of thrush in newborns in most cases is carried out by local treatment of the oral cavity with a solution of chlorhexidine or sodium bicarbonate. General antifungal therapy is used only in complicated cases.
Thrush occurs in more than half of pregnant women. Its treatment requires an integrated approach, taking into account the contraindications that exist during pregnancy. It is important to identify diseases and pathological conditions that can provoke thrush.
In pregnant women, thrush is treated mainly with local remedies. Most often these are suppositories with miconazole or clotrimazole. If systemic antifungal therapy for thrush in pregnant women is necessary, natamycin can be used, since it does not have an embryotoxic effect.
During pregnancy, it is possible to use traditional methods of treating thrush. These include washing with a decoction of oak bark, calendula or soda solution, soda-iodine baths, etc. These methods are weakly effective in completely curing thrush, but can help relieve its symptoms during pregnancy.
Prevention of thrush includes adequate antibiotic therapy along with the mandatory administration of probiotics; timely and correct treatment of chronic diseases, STIs, hormonal disorders; maintaining intimate hygiene; wearing cotton underwear.
You should avoid the use of hygiene and intravaginal products that can change the pH of the vagina from the acidic side or cause an imbalance in its microflora.
To prevent thrush from developing from improper use of tampons and pads, women should remember that they need to be changed every 3-4 hours.
Women whose thrush is caused by a humid environment should dry themselves thoroughly after swimming, avoid wearing a wet swimsuit, and use a spare dry swimsuit when relaxing on a pond.
Prevention of thrush in newborns is facilitated by a complete examination of women when planning pregnancy, early detection and treatment of thrush in pregnant women.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/molochnica
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is an infectious disease of a fungal nature. The causative agent is the opportunistic fungus Candida, which is normally present on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. Its growth is limited by beneficial microflora, but when conditions favorable for development occur, the microorganism multiplies intensively, which leads to the development of thrush.
Causes
The leading role in the development of candida lesions belongs to the immune system - in most cases, the fungus is activated against the background of its weakening under the influence of provoking factors. Among the numerous common causes that are the trigger for the occurrence of thrush, the following can be identified:
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- overwork;
- stressful situations;
- injury to mucous membranes;
- sudden change in climatic conditions;
- unbalanced diet, predominance of simple carbohydrates;
- diabetes;
- disruption of the functional activity of the endocrine glands.
Each type of pathology has its own specific provoking factors.
Thus, the cause of urogenital thrush in women can be wearing tight synthetic underwear, abuse of intimate hygiene products, and hormonal disorders. And damage to the nail plate can occur as a result of prolonged exposure of hands or feet to dampness.
Forms and types of candidiasis
There are three forms of candidiasis:
- Spicy. Manifests itself with pronounced signs.
- Chronic. It is characterized by alternating periods of remission and relapse (of varying intensity).
- Carriage. The fungus is detected as a result of diagnosis, but there are no signs of pathology. There is no treatment.
Depending on the location of the affected tissues, several types of thrush are distinguished:
- urogenital;
- skin, nails, feet, palms;
- lungs and other internal organs;
- thrush of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oral cavity;
- ears, eyes and so on.
Urogenital
The urogenital type of the disease affects the mucous membrane and skin of the genital organs and urinary tract. When the disease is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, the child is often born with signs of thrush. Transmission of infection also occurs during sexual contact.
Most often, the symptoms of the urogenital variety are fully manifested in women, and men are carriers. However, males are also susceptible to pathology, and the fungus can spread to the prostate gland.
Oral candidiasis
The development of oral thrush is most often diagnosed in young children. The main reason is the presence of fungus in the mother's birth canal. In adults, in addition to the above factors, improperly performed prosthetics can cause the growth of candida.
Source: https://venerolog-info.ru/kandidoz/
7 Symptoms of Candida Overgrowth (And Treatment)
- Generally, the beneficial bacteria in your body keep Candida levels in check.
- However, if levels of beneficial bacteria are disrupted or the immune system is compromised, Candida may begin to overgrow.
- Below are several factors that can lead to Candida overgrowth (3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8):
- Taking antibiotics
- Diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- High level of alcohol consumption
- Weakened immune system
- Taking oral contraceptives
- Diabetes
- High stress levels
When Candida overgrowth occurs, it can lead to various health problems.
This article discusses 7 signs and symptoms of Candida overgrowth and treatments.
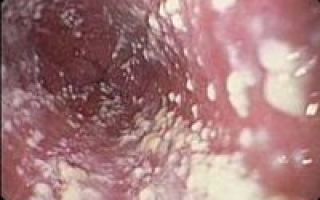
1. Symptoms of Candida in the mouth and throat
- Candidiasis that develops in the mouth or throat is called thrush.
- This condition most often occurs in newborns, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems (9).
- People with poor oral hygiene or removable dentures are also at increased risk (10).
- People with Candida overgrowth in the mouth usually develop white, bumpy patches on the tongue, cheeks, gums, tonsils, or throat (11).
- The lesions may be painful and may bleed slightly when scraped.
- Oral thrush is also often associated with redness or soreness of the tongue and mouth (12).
- In very bad cases, it can spread to the esophagus (candida esophagitis) and cause pain or difficulty swallowing.
Conclusion:
When there is too much Candida fungus in the mouth, it can cause white, bumpy lesions, redness, and pain in the mouth and throat. This condition is also known as oral thrush.
2. Fatigue
- One of the most common symptoms associated with Candida is fatigue.
- While there is no evidence that Candida causes fatigue, there are several ways the fungus may contribute to it.
- First, candidiasis is often accompanied by nutritional deficiencies, such as magnesium, vitamin B6, and essential fatty acids (13).
- Magnesium deficiency in particular is known to cause fatigue (14).
- Secondly, candida infections usually occur when the immune system is weakened.
- A poorly functioning immune system itself can make you feel tired.
- One study suggests that long-term intestinal candidiasis may even be a potential cause of chronic fatigue syndrome (15).
Conclusion:
Candidiasis most often occurs in people with weakened immune systems and can be accompanied by various problems in the absorption of nutrients. This may make you feel tired.
3. Recurrent genital or urinary tract infections
- Candida is found in the vaginal tract of most women.
- Overgrowth of this fungus can lead to vaginal candidiasis, also known as a yeast infection.
- It is estimated that 75% of all women will experience at least one vaginal yeast infection in their lifetime, and half of them will have at least one recurrence (16).
- Men can also get genital yeast infections, but this is much less common.
- Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis include:
- Redness
- Edema
- Itching
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Thick white vaginal discharge
- Although much less common, Candida can also cause a urinary tract infection (UTI).
- Candida-related urinary tract infections most often occur in the elderly, hospitalized, or immunocompromised people (17).
- Symptoms of a UTI include:
- Burning feeling when urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Cloudy, dark, or strange-smelling urine
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen
Although other bacteria, such as E. coli, are more likely to cause UTIs.
However, if you suffer from recurring infections and think they are the result of Candida overgrowth, you may want to test your urine to find out.
Conclusion:
Candida can cause genital and urinary tract infections, which can lead to pain and discomfort.
4. Problems with the digestive system
- The health of your digestive system depends largely on a good balance between the “good” and “bad” bacteria that live in your gut.
- "Good" bacteria, which are normally found in your gut, are important for digestion as they help break down starches, fiber and some sugars.
- When the balance of gut bacteria is disrupted, you may experience digestive problems including constipation, diarrhea, nausea, flatulence, cramping and bloating.
- Recent research shows that Candida overgrowth is associated with several gastrointestinal diseases, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease (18).
Conclusion:
It is normal to have small amounts of Candida in the intestines. However, if this fungus grows in excess, it can cause various gut-related symptoms.
5. Sinus infections
- Chronic sinus infections affect one in eight adults (19).
- Common symptoms include a runny nose, nasal congestion, loss of smell and headaches.
- Although short-term sinus infections are mostly caused by bacteria, many chronic sinus infections are considered fungal.
- A study from the Mayo Clinic looked at a group of 210 people with chronic sinus infections and found that 96% of them had fungi in their mucus (20).
Antibiotics are a common treatment for sinus infections.
This treatment may work for acute bacterial sinus infections, but not for chronic fungal infections.
In fact, treating a chronic sinus infection with antibiotics may even make the situation worse.
If you have a sinus infection that lasts more than one month, Candida may be to blame.
Conclusion:
Many chronic sinus infections are thought to be caused by fungi. If you have a sinus infection that lasts longer than one month, Candida may be the cause.
6. Fungal infections of the skin and nails
- Just like your gut, your skin has bacteria that prevent Candida from growing out of control.
- All bacteria grow under different conditions, including different temperatures, humidity levels, or acidity levels.
- This is why changing the environment on your skin can lead to Candida overgrowth.
- For example, cosmetics, soaps, and moisturizers can change skin conditions, especially if they have antibacterial properties.
- While cutaneous thrush can affect any part of the body, warm and moist areas such as the armpits and groin are especially susceptible to infection.
- Itching and a visible rash are the two most common symptoms of fungal skin infections.
- Candida overgrowth can cause conditions such as athlete's foot, ringworm, and nail fungus (21).
- Although fungal skin infections are not life-threatening, they can be very uncomfortable and can significantly reduce quality of life.
Conclusion:
Overgrowth of Candida on the skin can cause conditions such as athlete's foot, ringworm, and nail fungus.
7. Joint pain
- If a Candida infection enters your bloodstream and spreads throughout your body, it can infect your joints and cause arthritis (22).
- This usually only occurs after surgery or when Candida overgrowth is left untreated for a long period of time.
- Thrush arthritis is associated with pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints.
- The hips and knees tend to be the areas most likely to become infected.
- Candida can also cause bone infections or osteomyelitis, which can cause pain and tenderness in the infected area (23).
- Bone and joint infections are not very common, but once they become infected they can be very difficult to get rid of.
Conclusion:
If Candida overgrowth is left untreated, the fungus can enter your bloodstream and spread throughout your body. When this happens, Candida can infect the bones and joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Treatment of candidiasis
- The best way to treat candidiasis and prevent recurrent infections is to address the root cause.
- The food you eat plays an important role in maintaining the balance of good and bad bacteria in your gut.
- Refined sugar, carbohydrates, and high-lactose dairy products can stimulate the growth of Candida and other “bad” microorganisms (24).
- If you have a suppressed immune system, eating too many of these foods may contribute to the development of an infection.
- On the other hand, certain foods have been shown to stimulate the growth of “good” bacteria and inhibit the growth of Candida.
- The following foods help fight Candida-related infections:
- Garlic . Garlic contains an antifungal substance called allicin, which has been found to work against Candida yeast in animal and test tube studies (25, 26).
- Coconut oil . Coconut oil contains high amounts of lauric acid, which has been found in numerous test tube studies to fight Candida infections (27, 28).
- Curcumin . Test-tube studies show that curcumin can kill Candida yeast or at least reduce its growth (29, 30, 31, 32).
- Xylitol . In one test-tube study, xylitol helped fight candida by reducing its ability to stick to surfaces and cause infection (33).
- Aloe vera . Aloe vera gel can inhibit the growth of Candida in the mouth and prevent infections (34).
- Pomegranate . A test-tube study found that plant compounds in pomegranate are beneficial against Candida yeast (35).
- Kombucha . The kombucha drink is rich in polyphenols and acetic acid, which have been shown to kill Candida in test-tube studies (36).
- Probiotics . Probiotics, such as Lactobacillus, may reduce the growth of Candida and protect against infections (37).
- Unfortunately, dietary changes do not always help, in which case antifungal medications are the most common form of treatment.
- If you need medication, talk to your doctor.
- Candida is generally not life-threatening, but if left untreated, this fungal infection can spread and eventually reach the bloodstream.
- When the fungus circulates throughout the body, it can attack vital organs such as the brain and heart and cause more serious complications, including death (38, 39).
Conclusion:
Limiting your intake of refined sugars and carbohydrates can help prevent Candida overgrowth. In case of infection, certain foods, probiotics, and antifungal medications may help.
Summarize
- Candida is the most common cause of fungal infections in people.
- A few key symptoms can help you determine if you have Candida overgrowth.
- The most common signs and symptoms of infection include: oral thrush, recurrent genital yeast infections, digestive problems, and fungal infections of the skin and nails.
- It is extremely important to begin treatment for candidiasis promptly to prevent its spread and more serious complications.
Source: https://www.magicworld.su/bolezni/simptomy-boleznej/1031-7-simptomov-izbytochnogo-rosta-gribka-kandida-i-lechenie.html