Polycystic syndrome in women (PCOS) is a pathology that causes concern among gynecologists, as it affects the ability to conceive. The incidence of the disease is increasing every year. Women of childbearing age (18–40 years) are mainly affected. What are the signs to suspect the presence of PCOS? What diagnostic methods do specialists use?
What is polycystic disease
With polycystic disease, as a result of ovulation disorders, multiple cysts are formed in both ovaries, which are follicles that did not rupture in time with liquid contents and unformed eggs.
The disease has other names: PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome), polycystic ovary disease, primary polycystic ovaries, Stein-Leventhal syndrome, scleropolycystic ovaries.
In polycystic disease, the structure of the ovary is heterogeneous
The development of polycystic disease begins during puberty as a result of active hormonal processes. During this period, it is very important not to overlook the developing pathology and take all measures to eliminate it.
Diagnosis and treatment of benign ovarian tumor: https://medvoice.ru/dobrokachestvennyie-opuholi-yaichnikov/
The exact causes and mechanisms of formation of the syndrome are still unclear. Factors contributing to its development can be identified:
- obesity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- heredity;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- dysfunctions of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
What you need to know about polycystic ovary syndrome - video
Symptoms and signs of the disease in women: the nature of menstruation, the appearance of acne, hair loss and others
Like any other disease, polycystic disease can be characterized by vague symptoms or their absence. Therefore, detecting it at an early stage is quite problematic, especially if it occurs during puberty, which is characterized by hormonal instability.
At an early stage, polycystic disease may be asymptomatic
What you should be wary of:
- Irregularity of the menstrual cycle. Characteristic are long breaks between menstruation (35–40 days), irregularity of regularity during five cycles. There may be an absence of menstruation for two to three months or more with their sudden onset. The nature of the discharge can be different: from very scanty to abundant, long-lasting and painful;
- obesity. Develops as a result of impaired glucose tolerance and the occurrence of hyperinsulinemia. It is considered the main symptom and main cause of polycystic disease. Most often, obesity develops according to the male type, when adipose tissue intensively accumulates in the abdominal cavity and lower abdomen;
- high production of male sex hormones. This contributes to the appearance of signs of hirsutism (increased hair growth in male areas of the body). In advanced cases, it is possible to develop masculinization (secondary male sexual characteristics: rough voice, increased muscle mass, increased hair growth, enlargement of the clitoris, hair loss on the head up to the formation of a bald spot);
- increased greasiness of skin and hair;
- the appearance of acne, fine wrinkles, age spots;
- stretch marks on the hips, buttocks and abdomen due to rapid weight gain;
- chronic pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- infertility. Occurs as a result of lack of ovulation;
- depression, apathy, mood swings;
- swelling;
- drowsiness;
- apnea (stopping breathing during sleep);
- changes in the structure of the ovaries on ultrasound.
A characteristic picture for polycystic disease: hirsutism, acne, swelling Obesity in PCOS is characterized by the deposition of adipose tissue mainly in the abdominal area Hirsutism is manifested by hair growth in women in uncharacteristic places Polycystic pain is accompanied by chronic pain in the lower abdomen and lower back
As a rule, an experienced doctor will not have difficulty diagnosing polycystic disease. But the final diagnosis will be made when the woman undergoes a series of certain examinations.
What is chronic fatigue syndrome: https://medvoice.ru/sindrom-hronicheskoy-ustalosti/
What the gynecologist will do:
- he can suspect polycystic disease if a woman presents characteristic complaints for this disease;
- will conduct a gynecological examination on a chair. During palpation (feeling) of the appendage area, the doctor will detect enlarged ovaries and determine the heterogeneity of their structure.
In order to identify the causes of the syndrome and see the changes occurring in the ovaries, the doctor will prescribe a number of additional examinations.
Basal temperature measurement
Measured over several months. This is necessary in order to understand whether a woman is ovulating or not.
Measuring basal temperature helps determine the presence of ovulation
Before its onset, in the middle of the cycle there is a sharp rise in temperature, and it remains at this level until the end of the second phase. In the absence of ovulation, the temperature remains at the same level throughout the entire cycle.
It is carried out on the 4th–6th day of the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
Hormone levels in women - table
| Hormone | Description | Norm | Level for polycystic disease |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Regulates the production of prolactin by the pituitary gland. | from 1.1 to 8.7 mIEMl | Overpriced |
| Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) | Stimulates the formation of follicles. | from 1.8 to 11.3 mIEMl | Demoted |
| With PCOS, the ratio of luteinizing hormone to follicle-stimulating hormone increases by more than 2.5 times. | |||
| 17-Hydroxyprogesterone (17-OP) | This is an adrenal hormone, from which the hormone cortisol is then formed. | from 1.24 to 8.24 nmol/l | Overpriced |
| Prolactin | Pituitary hormone. | from 65 to 700 mMEL | Promoted. But with an increase in prolactin levels, it is necessary to exclude other pathologies associated with the function of the pituitary gland. |
| Estradiol | Produced by the maturing follicle. | from 15 to 160 ng/l | Demoted |
| Testosterone | Produced in the adrenal glands and ovaries. | from 0.3 to 3.8 nmol/l | Overpriced |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEAS) | Produced in the adrenal glands. From it, estrogens and testosterone are subsequently produced. Shows the severity of hyperandrogenism. | from 2700 to 11000 nmol/l | Overpriced |
| SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin) | This is a liver protein that transports estradiol and testosterone into the blood. The analysis is prescribed when the level of testosterone and estrogen does not correspond to the external manifestations of hirsutism. | from 32 to 128 nmol/l | Demoted |
Ultrasound (echoscopy): characteristics of the endometrium in the disease
carried out with a transvaginal sensor for a clearer picture of the pathology.
On the monitor, the doctor clearly sees multiple cysts throughout the ovarian tissue, and due to their presence, the structure of the organ is heterogeneous, and it itself is enlarged by 2-3 times.
This is what polycystic ovary looks like on ultrasound
The characteristic volume for polycystic ovaries is more than 8 cm3. the capsule in which they are located is smooth and thickened, its area is also increased, there is increased blood flow and an abundant vascular network (visible when using Doppler ultrasound).
the number of follicles in the ovary with a diameter of up to 10 mm is at least ten. in the uterus there is a heterogeneous, hyperplastic (thickened) endometrium due to irregular menstruation and hormonal disorders. Normally, its thickness at the beginning of the cycle ranges from 3 to 6 mm.
with hyperplasia it is always larger.
diagnosis and treatment of hydrosalpinx disease: https://medvoice.ru/gidrosalpinks-sleva-chto-eto-takoe/
allows you to study the ovaries from the inside. their surface is smooth, shiny, lumpy. they themselves are increased in size.
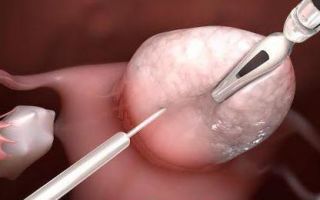
As a rule, laparoscopy is used both as a diagnosis and as a treatment at the same time.
laparoscopy is the most informative and accurate diagnostic method
This method is used when drug treatment has not produced any results. It is performed by inserting instruments into the abdominal cavity through three small incisions.
Using a laparoscope, follicular formations are removed, thereby creating conditions for the maturation of a new follicle.
subsequently it can become dominant, an egg is formed from it, resulting in ovulation.
hysterography
This is a radiological test. used for irregular uterine bleeding. the uterus is filled with a contrast agent and examined with a hysteroscope. the nature of hyperplasia is established. with polycystic disease it is most often glandular.
blood test for genetic markers
as a rule, it is used quite rarely. The method allows you to determine a woman’s tendency to polycystic disease.
allows you to identify metabolic disorders, in particular insulin resistance. Basal and stimulated levels of glucose and insulin are determined in the blood by taking 50 g of glucose.
If after a couple of hours the glucose level becomes normal, but there is no insulin, then this indicates the presence of insulin resistance. if after the same period of time glucose and insulin remain elevated, this already indicates impaired glucose tolerance.
With insulin resistance, signs such as:
- obesity (accumulation of fatty tissue on the abdomen);
- increased insulin in the blood after taking glucose;
- fasting insulin level 12.2 mmU/L or more.
lipid profile
necessary to determine metabolic disorders. in obesity it is always impaired.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by a decrease in high-density lipoproteins (HDL) in the blood, an increase in low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL).
this can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, and subsequently to complications associated with it.
differential diagnosis
Polycystic ovary syndrome is differentiated from conditions such as:
- premature loss of ovarian function;
- pregnancy;
- adrenal hyperplasia;
- hyperprolactinemia;
- hypothyroidism;
- ovarian tumors;
- Cushing's syndrome.
To do this, the examinations performed are analyzed and compared with signs characteristic of these diseases.
To exclude adrenal hyperplasia and endometrial cancer, additional studies are carried out:
- ACTH test. Adrenocorticotropic hormone regulates the production of steroid hormones and stimulates the activity of the adrenal glands. To identify the cause of hyperandrogenism, it is administered parenterally (by injection). With polycystic disease, as a result of the administration of ACTH, the level of androgens in the blood increases slightly. With adrenogenital syndrome (hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex), there is a sharp upward jump in androgenic indicators.
- Test with Dexamethasone. When Dexamethasone is administered, the production of ACTH is reduced, as a result of which the work of the adrenal glands and their production of hormones slows down. With polycystic disease, after the test the level of androgens in the blood remains almost unchanged. With hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex, a sharp drop in the values of these hormones occurs.
- Endometrial biopsy. Indicated for those who have acyclic bleeding and endometrial hyperplasia. This procedure is necessary to exclude endometrial cancer, since women with polycystic ovaries are at high risk of developing it.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is not such a simple pathology. Due to its manifestations and consequences, it requires careful diagnosis and competent treatment. At the slightest suspicion of polycystic disease, you should immediately contact your gynecologist for help, since the disease can lead not only to unpleasant sensations in the future, but also cause infertility.
Source: https://medvoice.ru/sindrom-polikistoznyih-yaichnikov-simptomyi-i-diagnostika/
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): what it is, causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment:
The diagnosis of PCOS refers to a hormonal disease that affects the ovaries. As a result, their structure is disrupted and the glands malfunction. During reproductive age, polycystic ovary syndrome is diagnosed most often. Despite the widespread prevalence of the disease, the causes of its occurrence are still not fully understood.
What it is?
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) is a pathology characterized by the formation of multiple cystic cavities in the glands. They may be filled with clotted blood or pus. According to statistics, every fifth woman suffers from the disease.
In gynecology, PCOS is considered a serious problem. This is due to the fact that most patients who consult a doctor complain about the inability to get pregnant.
This occurs due to the fact that enlarged ovaries cause increased production of luteinizing hormone and male sexually active substances.
The consequence is an increase in estrogen levels and a decrease in progesterone concentrations.
The natural results of these processes are the following violations:
- there is a malfunction of the ovaries;
- their blood supply deteriorates;
- the paired glands do not receive vital components in sufficient quantities;
- ovulation does not appear;
- the endometrium of the uterus thickens;
- the menstrual cycle becomes irregular;
- Uterine bleeding may occur periodically.
In gynecology, PCOS is classified according to several criteria.
According to etiology, it can be:
- Primary. Another name for the disease is Stein-Leventhal syndrome. Primary polycystic ovary syndrome can be congenital, or it develops during the formation of the menstrual cycle.
- Secondary. In this case, the disease is a consequence of an existing endocrine disease.
According to pathogenesis, the syndrome can have the following forms:
- Typical, in which the synthesis of male sex hormones is significantly increased.
- Central, characterized by rapid weight gain.
- Mixed, combining features of both forms.
In addition, polycystic ovary syndrome can be of two types. In the first case, the glands increase in size, in the second - not.
You need to know that PCOS is a disease that needs to be treated. It significantly reduces the likelihood of pregnancy, but with timely consultation with a doctor, it is possible to successfully carry and give birth to a child. If you ignore the alarming symptoms, the pathology will lead not only to infertility, but also to other serious complications.
Causes
You need to know that PCOS is a disease that is a consequence of a hormonal disorder. It, in turn, occurs due to the production of large amounts of testosterone, which inhibits the ovulation process.
The reasons for this situation may be:
- hereditary predisposition;
- a state of constant psycho-emotional stress;
- depression;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- unsatisfactory environmental conditions in the area of permanent residence;
- metabolic disorders;
- decreased sensitivity of body cells to insulin;
- neurohumoral disorders;
- infectious diseases of a chronic nature;
- excess body weight;
- climate change.
Under the influence of one or more of the above factors, the process of development and formation of follicles is inhibited. At the same time, the ovarian capsules thicken and increase in size, under which numerous cystic formations begin to form.
Symptoms
Every woman needs to know that PCOS is a disease that can occur in different ways. The severity of symptoms depends only on the individual characteristics of the organism.
The first signs of PCOS may appear when a pathological process has been developing in the ovaries for a long time.
In this regard, most women do not even suspect the presence of polycystic disease and seek medical help if numerous attempts to become pregnant have been unsuccessful. In this case, the symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome is infertility.
The following signs may also indicate the disease:
- menstrual irregularities;
- amenorrhea;
- increased hair growth on the face, neck, arms;
- acne;
- baldness;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- obesity (body weight increases sharply by 10 kg or more);
- uterine bleeding;
- increased oily skin and hair;
- pain in the lower abdomen, often radiating to the lower back or pelvic area;
- Rectal body temperature remains unchanged throughout the entire cycle (it should increase during ovulation).
Important! Most of the above symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome may not be signs indicating the presence of pathology in women during or before menopause and in girls during adolescence. This is due to the fact that in both cases, cycle disruption and manifestations of excess androgen production may be normal physiological conditions.
After examination by a doctor, a diagnosis of PCOS may be made if the symptoms are persistent and persist for a long time after the first menstrual bleeding. As for women whose bodies are preparing for or are in menopause, the likelihood of having the syndrome is extremely high if they have already noticed signs of the disease at a younger age.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor needs to carefully collect anamnesis. At the initial appointment, he should receive answers to the following questions:
- what alarming symptoms bother the patient;
- body type;
- body mass index;
- whether the condition of the skin and mucous membranes is impaired;
- type of hair growth.
Then the doctor performs a vaginal examination on a gynecological chair and performs palpation. This is necessary in order to assess the size and density of the glands.
To make an accurate diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome are prescribed:
- A blood test to determine the level of the following hormones: progesterone, prolactin, testosterone, cortisol, FSH, LH, DHEA-S, estradiol, androstenedione. They are produced by the adrenal glands, pituitary gland and ovaries.
- Blood test to determine lipid concentrations. This is necessary to identify metabolic disorders.
- Blood sugar test. Most women with polycystic ovary syndrome suffer from diabetes or are at risk for developing it. To obtain more accurate information, a glucose tolerance test may be prescribed.
- Ultrasound. During the study, the speed of blood flow, the size of the ovaries, and the density of the capsules are assessed. The diagnosis of PCOS is confirmed by ultrasound if a specialist finds 25 or more formations, the diameter of which varies between 2-9 mm. In addition, with polycystic disease, the volume of the ovary exceeds 10 ml.
- MRI. With its help, the doctor is able to find out whether the glands are affected by tumors.
- Laparoscopy. In PCOS, the method allows you to visually assess the condition of the ovaries, which is impossible with a vaginal examination. In addition, the doctor can collect biomaterial for further analysis.
Blood tests are prescribed for all patients. Based on their results, the most suitable instrumental diagnostic methods are selected.
Conservative treatment
According to clinical recommendations, PCOS recedes with an integrated approach to getting rid of the disease. Due to this, it is possible to create favorable conditions for pregnancy and gestation.
According to the same medical document, the following steps should be present in the treatment of PCOS:
- Loss of body weight. The fight against obesity involves adjusting your diet and increasing the intensity of physical activity. The use of hypoglycemic drugs is also indicated, among which doctors prefer Metformin.
- Restoration of ovulation and normalization of the menstrual cycle. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed whose active ingredient is clomiphene citrate. Therapy is carried out over 6 cycles. If the drug does not lead to positive results, gonadotropin preparations or GnRH agonists are additionally prescribed. If they also prove ineffective, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
- Reducing androgen levels, eliminating male pattern hair growth. Therapy involves taking combined oral contraceptives. To get rid of the manifestations of hirsutism (excessive hair growth), the drug Spironolactone is usually prescribed. The course of treatment is 6 months. As for COCs, a huge number of items are sold on the pharmaceutical market. The choice of contraceptive is made only by a doctor, taking into account the results of all studies. After discontinuation, the drug should provoke the process of maturation of several follicles.
Thus, the treatment tactics for PCOS come down to normalizing the cycle, restoring fertility, eliminating metabolic disorders or reducing their manifestations to a minimum, getting rid of cosmetic defects, and reducing body weight.
Diet
It is impossible to get rid of polycystic ovary syndrome forever. But if it is not treated periodically, health-threatening conditions will begin to develop over time.
The patient’s diet is of great importance in pathology.
In most cases, it is the diet for PCOS that can enhance the positive effects of medications, especially if the disease is accompanied by a significant increase in body weight.
Basic principles of nutrition for polycystic disease:
- The caloric content of the diet should be reduced to 2000 kcal per day. It should not be less than 1200 kcal, as this is dangerous to health. The doctor can calculate the ideal calorie content of the daily diet for the patient using special formulas. She can do this on her own.
- You need to eat food that contains an acceptable amount of calories. The basis of the diet should be: fruits, vegetables, lean meats, herbs, fish, dairy products, seafood.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of carbohydrates entering the body. At the same time, you need to increase your intake of foods rich in proteins.
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of animal fats, replacing them with vegetable ones.
- It is necessary to exclude from the diet sweet, salty, smoked, pickled, spicy foods, as well as any alcohol-containing drinks.
- To cleanse the body, it is important to arrange fasting days 1-2 times a week.
Compliance with these recommendations, coupled with physical activity and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, is the key to getting rid of the disease as quickly as possible.
Surgical treatment
Currently, the main method of surgical intervention is laparoscopy. This is due to the fact that the method is effective and low-traumatic.
Its essence is as follows: the doctor makes several incisions on the wall of the abdomen (usually 3 or 4 of them, the length of each does not exceed 2 cm), through which manipulators of various actions are introduced into the body. During the operation, the surgeon has the opportunity to change instruments.
The main types of manipulators used for polycystic disease are: a coagulator designed to cauterize blood vessels; forceps necessary to grasp the gland; endoscopic scissors.
Thus, the surgeon does not perform any manipulations with his hands inside the abdominal cavity. Thanks to the camera built into the instrument, the progress of the operation is displayed on the monitor.
The main goal of laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome is to restore ovulation. Due to this, the patient has the opportunity to become pregnant naturally.
The operation can be performed in several ways:
- Cauterization. During surgery, the doctor grabs the ovary with forceps. Then, using a laser, he makes incisions on its capsule, the depth of which does not exceed 1 cm. The choice of the location for the incisions is not random: the surgeon first examines the gland to detect translucent follicles. After laparoscopy, they should mature and release an egg. The operation does not involve significant blood loss; it does not exceed 10 ml.
- Wedge resection. After grasping the ovary with forceps, the surgeon coagulates the area whose tissue will be removed. Then, using endoscopic scissors, he cuts out part of the gland and cauterizes the vessels. After this, the edges of the wound are sewn together with one suture.
- Decortication. The essence of the method is to remove a dense section of the capsule with a coagulator.
It is important to know that PCOS is a disease that will constantly recur. On average, after surgery, fertility is restored for 1 year. Then the capsule begins to gradually thicken again. In this regard, the patient needs to conceive a child in the near future after laparoscopy.
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic disease?
It is important to understand that for successful conception it is necessary that the ovulation process periodically starts in a woman’s body. With PCOS, pregnancy is almost impossible, since a mature egg cannot escape from the gland due to the thickening of the capsule. Gradually, the follicle fills with fluid and a cyst forms from it.
The presence of polycystic disease does not mean that a woman is infertile, but without timely treatment, all chances are reduced to almost zero. Over time, the situation worsens more and more, since with each cycle the number of cystic formations increases.
The greatest difficulty is the situation in which the ovarian tissue does not react in any way to the action of hormonal drugs. This condition is a consequence of a disruption in the functioning of receptors. In this case, simultaneously with PCOS, the doctor diagnoses “ovarian resistance syndrome.”
In the presence of this disease, restoration of ovulation is impossible, since no drug or surgical intervention will achieve changes in a positive direction. The only solution for women with pathology is in vitro fertilization.
But it requires donor material, since with resistance syndrome it is impossible to obtain eggs suitable for IVF.
If not treated?
Polycystic disease is a consequence of hormonal imbalance, and its course is accompanied by the absence of the ovulation process. If you ignore alarming symptoms, the disease can cause infertility. Statistically, PCOS is one of the most common reasons why women cannot become pregnant naturally.
In addition, a long course of polycystic ovary syndrome without regular courses of therapy significantly increases the likelihood of developing cancer of the cervix, mammary glands and other organs. The risk of a malignant process increases many times over if the patient suffers from diabetes and obesity.
The following diseases can also be complications of PCOS:
- atherosclerosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke.
Timely diagnosis makes it possible to detect pathology at the earliest stage of its development, thereby minimizing the likelihood of dangerous complications.
Finally
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a serious illness that not only significantly reduces the quality of life of every woman, but also prevents the desired pregnancy.
The main symptoms of the disease are: disruption of the menstrual cycle (up to amenorrhea), male pattern hair growth, acne, seborrhea, pain, increased oiliness of hair and skin.
The difficulty of making a diagnosis may lie in the fact that not every patient experiences several characteristic symptoms at once; some may have none at all. To diagnose the disease, both laboratory and instrumental methods are used, including: blood tests, ultrasound, MRI, laparoscopy.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes medications, the action of which is aimed at restoring fertility, normalizing the menstrual cycle, and reducing the manifestations of cosmetic defects. If they do not bring the desired effect, surgical intervention is indicated. The operation is performed laparoscopically.
After it, the ovulation process is restored and it is important for the patient to become pregnant in the coming months. This is due to the fact that it is impossible to get rid of the disease forever; relapses will occur periodically. Without courses of treatment, it can provoke the appearance of infertility and various malignant processes.
Source: https://www.syl.ru/article/364590/sindrom-polikistoznyih-yaichnikov-spkya-chto-eto-takoe-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnostika-i-lechenie
What are the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome: who is at risk and how the disease can be cured
- Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the reasons for the lack of conception, but it is diagnosed in 10% of women of reproductive age.
- This is a serious disease, which does not mean that it is impossible to treat it and become a mother.
- Of course, the sooner appropriate therapy is carried out, the greater the chance that the disease will subside and conception will occur.
- Every woman should know about this disease, understand the causes of its occurrence and understand the principles of treatment.
The essence of pathology
- The term “polycystic ovary syndrome” refers to the pathology of the female gonads, which concerns organ dysfunction and is associated with a malfunction in estrogen synthesis, increased production of androgens, which leads to the formation of small cystic formations on the surface of the ovary.
- In this case, the egg cannot leave the follicle (because it does not rupture), and, consequently, infertility develops.
- This hormonal pathology was first described by Leventhal and Stein, which is why polycystic disease is sometimes called Stein-Leventhal syndrome.
- Polycystic disease of both ovaries can be primary or secondary.
In the first case, the disease occurs in women whose body weight is within normal limits, and when the disease develops, insulin does not increase.
This form is practically not amenable to drug treatment; moreover, surgical treatment is also not always effective.
Most often, the process of pathology formation occurs during the girl’s puberty, that is, at 10-12 years old..
Secondary polycystic disease is more often diagnosed in adult women who are overweight and insulinemic. In some cases, the secondary form is observed in women during menopause. With a competent approach, such a pathology can be eliminated using conservative methods.
In addition, polycystic disease is distinguished as follows:
- ovarian – signs of ovarian dysfunction prevail;
- adrenal - symptoms of an imbalance in the ratio of estrogen and androgens are clearly visible;
- diencephalic - signs are expressed that indicate disruptions in endocrine functionality.
Symptoms of polycystic disease
The symptoms of polycystic disease are varied, and they do not have any specific specifics - the manifestations of the disease are very similar to the manifestations of other hormonal disorders.
Signs:
- The first sign that makes a woman worry is a disruption in the menstrual cycle. Menstruation may be infrequent - every 3 or more months, and then replaced by prolonged bleeding and spotting. In this case, the cycle can be more than 35 days. There may be a delay.
- Hyperandrogenism. Since androgens are synthesized in large quantities in polycystic disease, women may experience male-type hair growth, an enlarged clitoris, a low voice, and hypoplasia of the mammary gland. Hair thinning and alopecia are very common.
- The skin with polycystic disease is usually oily, the pores are enlarged, and there is a tendency to acne. Hair quickly becomes greasy and dirty, even if you take very good care of it.
- In most cases, a woman with this pathology is obese or overweight; fatty tissue is distributed in the thighs and abdomen.
- Infertility. Since almost all cycles anovulatory conception is impossible.
- Often polycystic disease is accompanied by concomitant ailments - hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, atherosclerosis.
Precursors of the disease
Precursors of the disease can appear at any age, so you need to listen very carefully to your body, and at the slightest sign of polycystic disease, immediately consult a doctor.
The very first signs may be:
- the appearance of acne and deterioration of hair condition;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- weight gain;
- pain of unknown etiology.
- Also, polycystic disease may be accompanied by swelling of the mammary glands, swelling, dark spots on the skin, and a large number of skin folds..
- In some cases, the pathology leads to cessation of breathing during sleep, which provokes awakening, and subsequently to headaches.
- In adulthood, polycystic disease does not pose a serious threat to health; the pathological danger lies in the development of infertility, so young girls need to take the warning signs of the disease very seriously.
Causes
Until now, scientists have not been able to figure out exactly what causes contribute to the development of polycystic disease.
The mechanism of development of the pathology is a violation of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, ovaries and adrenal glands . In addition, a disorder in the synthesis of thyroid and pancreatic hormones can provoke the disease.
An important role is played by decreased sensitivity to insulin, which leads to insulin resistance.
As a result, a large amount of insulin appears in the blood, and this provokes the ovaries to produce more estrogens, and, consequently, androgens.
There is another development option. Ovarian tissue increases its sensitivity to insulin, but fat and muscle tissue respond normally to insulin .
Thus, a normal amount of insulin is diagnosed in the blood, but the ovaries still intensively produce estrogens and androgens.
The following factors can lead to the development of the disease::
- heredity;
- excess weight;
- frequent stress;
- chronic infectious processes;
- a large number of abortions;
- difficult pregnancy and childbirth;
- absence or irregularity of sexual activity;
- diseases of endocrine organs;
- poor environmental conditions;
- gynecological problem.
Scientists have already reliably established that harmful substances released from plastic dishes have a negative effect on sex hormones.
The elements that are used in the production of plastic containers affect the body in the same way as estrogen, and therefore can provoke infertility and oncological processes.
Polycystic disease is associated with hormonal dysregulation, which is why it leads to inhibition of follicle maturation, as a result of which the egg cannot be released, and the cycle becomes anovulatory. Unruptured follicles remain on the surface of the ovary and transform into cysts.
This process can be provoked by a variety of factors, including obesity. If you have extra pounds, polycystic disease is diagnosed in half of the cases.
In addition, stressful situations, infectious diseases, and even changes in climatic conditions can give impetus to the development of pathology.
Who is at risk?
Since the exact causes of polycystic disease are still unknown, scientists suggest that women who have been diagnosed with this pathology in their family are at risk.
And it doesn’t matter on which line – maternal or paternal – the disease occurred. In addition, a family history of diabetes also increases the risk of developing polycystic disease.
Thus, girls with:
- obesity;
- family history of diabetes mellitus;
- with irregular menstrual cycles;
- with male pattern hair.
Is PCOS dangerous?
- Firstly, polycystic disease leads to infertility, but in some cases pregnancy still occurs, but in this case the risk of miscarriage in the early stages increases sharply.
- Also, during pregnancy it is possible to develop diabetes mellitus and eclampsia, which is extremely dangerous for both the mother and the fetus.
- Another danger of the disease is sudden weight gain, oily skin, hair loss, and excessive hair growth in places uncharacteristic for a woman.
- All this provokes depression, anxiety disorders, and eating disorders.
- In addition, the risk of arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, apnea increases.
- All these factors together can provoke oncological processes in the endometrium.
Can it be completely cured?
- Unfortunately, polycystic disease cannot be completely cured..
- Even with timely and correct therapy, the disease will recur.
- Treatment of the pathology is aimed at creating favorable conditions for pregnancy, as well as eliminating the negative clinical picture.
- Therapy for polycystic disease can be medicinal (taking hormonal drugs) or surgical ( laparoscopy ) .
- A woman should understand that in some cases, taking hormonal medications will be lifelong, and the maximum period for conceiving after surgery is no more than a year, after which polycystic disease returns and conception will not occur.
Hormone therapy
To stimulate ovulation, a woman can be prescribed Antiestrogen, Clomiphene, Duphaston.
These medications are taken according to a specific regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If Clomiphene does not give results, it can be replaced with Humegon or Pergonal.
- It is very important that ovulation stimulation is carried out under ultrasound control and taking into account basal temperature readings .
- The doctor may also recommend Clostilbegit or Utrozhestan, however, when prescribing them, it is necessary to take into account a large number of contraindications.
- If a woman does not plan to conceive, she is prescribed oral contraceptives - Yarina, Diane-35, Zhanine, and so on.
- Oral contraceptives for polycystic disease do not eliminate the causes of the disease, and only stabilize hormonal levels, which leads to normalization of the cycle.
- As soon as these drugs are stopped, the disease will return.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis, the following examination is necessary:
- general examination of the patient – body type, hair pattern, etc.;
- gynecological examination to determine if there is an increase in the size of the ovaries;
- Ultrasound, which allows you to accurately determine the size of the ovaries, as well as visualize the presence of multiple cystic neoplasms;
- blood test for hormones - prolactin, FSH, progesterone, L, testosterone, estradiol, androgen, cortisol and others;
- MRI to exclude the presence of tumors in the ovaries (the image is shown in the photo);
- identification of lipid metabolism disorders;
- determination of glucose and insulin concentrations;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
Basic treatment methods
In some cases, hormonal treatment may be contraindicated. Then the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy, means to increase local immunity, and vitamins.
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used:
- massage of the collar area;
- electrophoresis;
- galvanophoresis;
- magnet therapy;
- hirudotherapy.
- Traditional medicine is used - taking decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs - boron uterus, red brush, sage, mint, dandelion, burdock and others.
- If conservative treatment remains unsuccessful, surgical intervention is prescribed.
- As a rule, this is laparoscopy - a gentle organ-preserving treatment method, the recovery period after which takes only a month.
- The disadvantage of this method is that it does not have a long-term effect - if conception does not occur within a year, the pathology recurs.
Conclusion and conclusions
- Polycystic disease of the left or right ovary is a serious pathology, the treatment of which can be very long.
- Despite the fact that it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, with the right approach to treatment, you can achieve stabilization of the menstrual cycle, improve the general well-being of the patient, stimulate ovulation, promote conception, and also prevent possible negative consequences.
- It is very important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner, especially for the primary form of the disease - it is necessary to carefully monitor the girl’s health during puberty.
Source: https://zhenskoe-zdorovye.com/ginekologija/bolezni-yaichnikov/polikistoz-yaich/simptomy-neduga.html
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most common gynecological diseases. This pathology is characterized by disruption of the endocrine and generative function of both ovaries.
We distinguish between primary polycystic ovaries (Stein-Leventhal disease) and secondary polycystic disease, which occurs with various diseases that impair ovarian function (adrenogenital syndrome, polycystic ovaries of central origin).
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome begins with a medical history. The patient's complaints and the presence of main clinical symptoms are clarified.
In most cases, polycystic ovary syndrome is manifested by menstrual irregularities: rare menstruation or its complete absence, acyclic uterine bleeding; anovulatory infertility or a history of miscarriages; pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, obesity (with polycystic disease of central origin it can reach stage III-IV); hirsutism - increased hair growth on the body, face, and limbs.
An important point for the differential diagnosis of various forms of polycystic ovary syndrome is to establish the period of onset of symptoms and the dynamics of their changes from the moment of occurrence.
In polycystic ovary syndrome with adrenogenital syndrome, hirsutism develops early and precedes menstrual irregularities, while in primary polycystic disease (Stein-Leventhal disease), hirsutism develops later.
Polycystic ovary syndrome of central origin is characterized by the appearance of symptoms after injury or infection, with rapid progression of symptoms. With primary polycystic disease, it is impossible to accurately determine the period of onset of symptoms; the development of this pathology itself is characterized by a slow course.
The next stage of diagnosis is examination of the patient. During a general examination, attention is paid to the general development of the body, the degree of development of adipose tissue (as mentioned above, polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by obesity), the location and type of hair growth on the body.
With adrenogenital syndrome (the disease is determined by the production of androgens by the adrenal cortex), hirsutism is sometimes very pronounced, while with polycystic disease of central origin, hirsutism is weakly expressed and completely absent.
Other dermatological signs are also noted: the presence of acne (acne), seborrhea (excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands), the presence of stretch marks on the skin. A special examination is carried out by a specialist gynecologist. The purpose of the examination is to determine the type and level of development of the external genitalia.
With adrenogenital syndrome (prepubertal form), there is underdevelopment of the external genitalia, as well as signs of hermaphroditism.
The next stage of diagnosis is a special clinical examination of the patient. The purpose of this diagnostic stage is to determine the condition of the patient’s reproductive system organs. In some cases, with a bimanual stroke of the vagina, enlarged and hardened ovaries can be palpated (healthy ovaries, as a rule, are not palpable).
Gynecological examination and diagnosis helps to form a preliminary idea of the patient’s hormonal status. The cervical mucus stretch test and its crystallization, as well as a cytological smear of the cells of the vaginal mucosa, reveal insufficiency (or excess) of estrogen content.
The clinical diagnosis stage guides the patient, helps him draw up a plan for further research and provides the necessary information for making a differential diagnosis.
The next stage in the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome is paraclinical (laboratory and instrumental) research methods.
Ultrasound (ultrasound) is most often used in the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome. A more informative transvaginal (through the vagina) examination is preferable.
Diagnostic criteria for polycystic ovary syndrome during ultrasound examination are: ovarian volume more than 9 cubic cm, thickening of the ovarian capsule, ovarian stroma hyperplasia, the presence of more than 10 atretic follicles (cysts) with a diameter of up to 10 mm.
The high information content and accessibility of ultrasound make it an indispensable tool for diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome.
Hormonal studies serve to clarify the diagnosis and treatment regimen. The following hormonal test results are typical for polycystic ovary syndrome:
- An increase in the level of luteotropic hormone (LH) and an increase in the LH/FSH ratio (FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone) more than 2.5;
- Increased concentration of male sex hormones (testosterone)
To determine the source of androgens, special tests are performed:
- Test with dexamethasone. The essence of this test is that when dexamethasone is prescribed, the release of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) by the pituitary gland, which stimulates the adrenal cortex, is reduced. As a result, the production of hormones by these glands is reduced. With adrenogenital syndrome (one of the causes of secondary polycystic ovary syndrome), there is an increased secretion of androgens by the adrenal cortex, therefore, when dexamethasone is prescribed, there is a sharp decrease in androgens in the blood and their metabolites in the urine. In primary polycystic ovary disease (this disease is characterized by the synthesis of androgens in the ovaries and adipose tissue), the administration of dexamethasone only slightly reduces the concentration of androgens in the blood. Thus, a dexamethasone test helps differentiate various forms of polycystic ovary syndrome.
- ACTH test. As mentioned above, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates adrenal function and the synthesis of steroid hormones. In adrenogenital syndrome, the administration of ACTH causes a sharp increase in the level of androgens in the blood, while in Stein-Leventhal disease the level of androgens in the blood increases slightly. The diagnostic value of this test is the same as that of the above-described test with dexamethasone.
Another stage of diagnosis is the determination of metabolic disorders. To do this, tests are performed to determine the blood lipid profile. Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by the following disorders of fat metabolism: a decrease in the HDL (high-density lipoprotein) fraction and an increase in the VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein) and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) fractions.
Determination of the lipid profile is important for predicting and timely treatment of complications from the cardiovascular system.
In particular, a decrease in the concentration of the protective HDL fraction and an increase in the atherogenic LDL fraction is a factor in the development of atherosclerosis and all its accompanying complications (coronary heart disease, cerebral stroke, thrombosis, renal failure, etc.)
Determination of carbohydrate metabolism disorders is carried out using a glucose tolerance test.
High levels of glycemia (blood glucose) 2 hours after taking 50 grams of dissolved glucose indicate the presence of insulin resistance, which, accordingly, requires treatment. Also, an increase in the concentration of insulin in the blood testifies in favor of insulin resistance.
In some cases, laparoscopic diagnosis (introduction of a fiber-optic imaging system into the abdominal cavity).
As a rule, this diagnostic method is used for differential diagnosis and treatment of various forms of infertility (for example, tubal infertility, endometriosis).
During laparoscopic examination, the polycystic ovaries are enlarged, their surface is tuberous, and the capsule has a characteristic pearl color. If necessary and if there are appropriate indications, laparoscopic diagnosis can become a treatment method.
In particular, this method makes it possible to carry out certain types of surgical interventions for the treatment of polycystic ovaries (electrocoagulation of the ovaries, laser evaporation, etc.) or other causes of infertility (elimination of adhesions compressing the fallopian tubes, coagulation of foci of endometriosis).
In the presence of acyclic uterine bleeding and changes in the mammary glands, additional research methods are used to establish the form of concomitant diseases.
The examination of the uterus begins with hysterography (radiological examination with the introduction of contrast into the uterine cavity). Establishing the nature of the endometrial hyperplastic process is carried out using diagnostic curettage and histological analysis of tissue.
The most common form of endometrial pathology in polycystic ovary syndrome is glandular or adenomatous hyperplasia.
The examination of the mammary glands is aimed at establishing the form of mastopathy. For this purpose, mastography, thermography and ultrasound examination of the mammary gland are performed.
- In some cases, a patient with polycystic ovary syndrome needs specialized neurological diagnostics to establish the causes and forms of nervous disorders (depression, sleep apnea, etc.)
- A comprehensive diagnosis of the patient helps to establish an accurate diagnosis (form of the disease, stage, presence of complications), as well as draw up an effective treatment plan.
- Bibliography:
- Gilyazutdinov I.A. Clinical and radiological diagnosis of neuroendocrine syndromes and diseases of central origin in women Kazan: Karpol, 1997
- Vikhlyaeva E.M. Guide to endocrine gynecology, M.: Medical information agency, 2006
- Taranov A.G. Laboratory diagnostics in obstetrics and gynecology, M., EliksKom, 2004
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Source: https://www.tiensmed.ru/diagnoz6.html