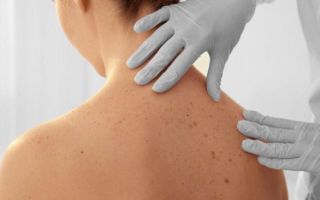
A malignant wart is a pathological skin neoplasm that occurs as a result of human infection with human papillomavirus infection. Basically, this type of formation occurs only in one area of the body, without affecting nearby healthy areas of the skin. In addition, skin tumors can be observed in both women and men, and also have different structures and sizes. Warts are almost always benign tumors and do not cause any discomfort to a person.
However, in some cases, skin growths can become malignant, and thus can cause harm to health.
Malignant warts can form on the human body as a result of constant damage to pathological growths, as well as in the event of untimely or unqualified medical care.
In this case, surgical removal of the skin tumor may be required.
Classification of growths and causes of their occurrence
Tumor skin neoplasms are dense small nodules and are divided into the following types:
- Pointed. This type of wart looks like a pointed formation of pale pink color.
- Flat. Flat warts look like small round spots that protrude slightly above the surface of the affected area of the epidermis. Unlike neoplasms with a pointed shape, flat ones have a brighter color.
The main and main factor that disrupts the processes of epithelial cell division is the presence of papillomavirus infection in the human body.
Depending on the type of human papillomavirus (HPV), various types of warts appear on the body.
Although these types of formations are benign, you should not refuse to visit a doctor, because some varieties of this virus are not safe for health and can cause various pathological processes both on the surface of the epidermis and inside the body itself.
HPV is characterized by great viability to the influence of various external factors and, once it enters the human body, it can remain dormant for a fairly long period of time without causing any manifestations.
The human papillomavirus begins to manifest itself only after the body’s protective functions have been significantly weakened for some reason, which is a favorable condition for the intensive reproduction of the viral infection.
Infection with human papillomavirus infection occurs directly after close contact with a person who is a carrier of this pathological microorganism.
Infection mainly occurs through sexual contact, but in some cases the infection can also be contracted through household contact.
Most often, the spread of a pathological microorganism is facilitated by non-compliance with basic hygiene standards and promiscuous sexual intercourse without contraceptives.
In addition, the following contributes to the development of a pathological process on the skin:
- the presence of various types of hormonal disorders in a person, which can arise as a result of long-term use of hormonal medications, or during pregnancy;
- weakening of the human immune system;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- impact on the human body of strong stressful situations of a constant nature.
Diagnosis and treatment of malignant warts
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the attending physician must first examine the skin tumor and prescribe a number of additional procedures, which include:
- Dermoscopy. A procedure that allows you to examine the affected area of the epidermis using a microscope.
- Cytological examination. This method allows you to examine the tissue that makes up the malignant tumor using a special scraping.
- Histological examination. Carrying out this procedure makes it possible to determine the stage of development at which the pathological process is located.
After carrying out all the necessary procedures to clarify the diagnosis of the pathological process, a comprehensive course of treatment is prescribed, which involves strengthening the body’s immune system and removing the malignant wart. You can remove a wart using procedures such as:
- Electrocoagulation. This method of removing skin pathological neoplasms is carried out by exposing the affected area of the epidermis to a directed electric current. Moreover, after electrocoagulation, the likelihood of scars and other defects on the skin is almost zero, and the operation itself takes no more than 15 minutes.
- Cryodestruction. This procedure allows you to remove a wart by exposing it to liquid nitrogen.
- Laser destruction. This method of eliminating a malignant tumor involves exposing it to laser radiation, which allows the pathological growth to be cut off layer by layer.
- Surgical removal. Surgical removal is used in severe cases and involves cutting off the growth using a scalpel.
The method of eliminating a malignant growth is chosen only by a doctor, based on the characteristics of a particular skin tumor and the individual characteristics of the structure of the human body.
What can cause a malignant wart and how to get rid of it Link to main publication
Source: https://1papillom.ru/borodavki/zlokachestvennaya-borodavka.html
Warts - benign neoplasms: types and features
There is a strong belief that warts can only appear on unkempt skin. This is far from true; such neoplasms can occur in a wide variety of skin types and on skin that is regularly cared for.
This neoplasm is one of the most common skin problems. With the exception of the so-called senile warts, their appearance is caused by a virus. This virus is called HPV - human papillomavirus.
Manifestations such as moles and warts are often confused.
This is not surprising - even professional dermatologists cannot visually distinguish these neoplasms. However, there are still several criteria by which they can be recognized without resorting to histological studies:
- According to the structure of the neoplasm. The mole is always dense and hard. The structure of the wart is looser and softer, which can be determined by touch;
- If you look closely at the shape of the neoplasm, a wart always looks like a growth rising above the skin;
- Another criterion by which these two neoplasms can be distinguished is color. In the vast majority of cases, neoplasms in the form of moles, or they are also called nevi, have a darker color;
- A mole consists only of skin cells. A wart contains capillaries in its body. This can also be determined visually.
Well, the main difference between these tumors lies in the methods of treatment. If you can get rid of a mole only by removing it, then warts can be cured both with medication and surgery.
Warts of viral origin ↑
In medical practice, there are 5 main types of formations, the origin of which is viral in nature. Separation criteria are the shape, color and localization of the tumor.
- Common wart . This variety is the most common. The preferred places where this type of formation prefers to be localized are the dorsum of the hands, fingers and toes. The neoplasm appears in the form of keratinized dense papules. Their size varies from 1 to 10 mm in diameter. A special feature of this variety is the ability to change color;
- Viral warts of the flat type . This type is very difficult to diagnose. The reason is the color, which is identical to the color of the skin. Often occur during hormonal changes. A characteristic feature is the fact that this type of wart is never localized on the palms and soles of the feet. In addition, they are quite rarely found in people over 40 years of age;
- Plantar type of viral warts . The name itself speaks about the place in which such neoplasms can appear. In addition to the soles of the feet, they can be localized on the palms. The reason for this selectivity of this type of neoplasm is the density of the skin. The strain of the virus that provokes their appearance prefers to be localized in areas with dense and thick skin. The shape of such neoplasms is quite clear. The size does not exceed about 2 cm in diameter. At the same time, they are slightly higher than the main layer of skin. This elevation is no more than 2 mm;
- Acrochords or filamentous variants of viral warts . These warts look like a thread-like or round body. The places where they most often appear are characterized by thin, sensitive skin and high moisture content. That is, these are skin folds, areas of the armpits, groin, etc. Unlike some other varieties, acrochords do not disappear on their own. They, if necessary, require drug treatment or complete removal. Due to the fact that in the places where they are located there is an increased risk of injury to such a neoplasm, they should either be treated or removed;
- Viral warts of the genital type (condylomas) . Most often, this type of wart develops on the mucous membranes. In addition, a neoplasm can develop on the skin, which is characterized by a rather thin and sensitive layer. The predominant location of this neoplasm is the anogenital area. If left untreated, they can grow to impressive sizes. They appear in the form of pointed small growths. They are similar in appearance to the top part of a cauliflower.
Keratomas or senile warts ↑
The only type of neoplasm that can be confidently attributed to warts, but their appearance is in no way related to HPV. They appear as a result of processes that occur in the epidermis as we age.
They appear on the skin at the age of 50+ and look like small growths. In the initial stage, senile keratoma appears as a yellow or pink growth. Over time, its color changes from dark brown to black.
In the vast majority of cases, the nature of the neoplasm is benign.
Papillomas ↑
This neoplasm is the result of the manifestation of the activity of the papilloma virus. That is, as in the case of warts, we are talking about the manifestation of HPV. This virus manifests itself in different ways. Papilloma is one of the variants of such manifestations. It is quite difficult to distinguish a viral wart from a papilloma. If we talk about visual differences, papilloma can be recognized by the following criteria:
- Location. If viral warts are localized in open areas, then papillomas appear in the folds of the skin - in the armpits, groin, under the breasts. They can often be found in the genital area;
- Geometry of the neoplasm. Papillomas have a rough surface and ragged, irregular edges. While an ordinary wart has a more regular shape and a smooth surface;
- Base. Papilloma has a base in the form of a stalk or thread. Warts do not have this feature.
Other types of neoplasms ↑
While these manifestations of the virus are quite similar in appearance, they differ more seriously in their internal structure and effect on the body. Currently, there have been some changes in the classification of neoplasms. In particular, some types of papillomas, which were previously classified as viral warts, are classified as a separate group.
Today, more than a hundred strains of HPV are quite well known in modern medicine. Depending on which species provoked the appearance of the formation, certain changes occur.
It must be said that the strain of the virus, which manifests itself on the skin in the form of papillomas, warts and other neoplasms, can be treated quite successfully. In addition, some types of the virus are completely harmless to our body. However, along with these varieties, there are strains with a high degree of oncogenicity.
Simply put, these strains are highly likely to influence the formation of malignant tumors.
It is according to these criteria that some types of neoplasms, previously classified as viral warts, are now classified as papillomas. These are papilloma of the bladder, cervix, larynx and anogenital warts. Bladder papilloma appears as a thin growth with a heterogeneous surface.
In some cases, it has a pronounced clinical picture, which manifests itself in bleeding and difficulty urinating. But, in most cases, this benign neoplasm does not manifest its presence in the body.
Its detection is possible only during a routine examination of the genitourinary system using ultrasound.
Another type that does not manifest itself in any way and is therefore considered quite dangerous is cervical papilloma. It manifests itself in numerous growths on the walls of this internal organ. If this type of papilloma is detected, mandatory treatment or complete removal of the formation is indicated.
Laryngeal papilloma
Source: http://plastic-beauty.ru/pap/borodavki-dobrokachestvennye-novoobrazovaniya-vidy-i-osobennosti.html
What types of skin growths are there? Types and methods of removal
Currently, there is a tendency towards an increase in the incidence of various neoplasms on the skin. The greatest concern is the high rate of malignant tumors in both men and women.
Causes of skin growths
The development of skin tumors is caused by pathological growth of the dermis. It is possible not only to increase cells and their number, but also to modify the structures of the epidermis. Genetic predisposition and structural features of the skin (for example, light type) play one of the determining roles in the occurrence of a tumor. The main factors contributing to the appearance of tumors on the skin:
- All types of radiation (sun rays, x-rays, etc.).
- Exposure to chemicals.
- Constant traumatization.
- Chronic skin pathology.
- Various infections (bacterial, viral).
- Reduced immunity is evident.
A benign or malignant formation on the skin can be determined by conducting a histological examination.
Types of benign neoplasms
According to most experts, benign formations do not pose a threat to the patient’s life. However, in some cases it is possible that they can transform into a malignant tumor. This can be facilitated by exposure to various factors (for example, ultraviolet radiation, carcinogens, etc.).
The main types of benign formations on the skin:
- Pigmented nevus (mole).
- Papilloma (wart).
- Lipoma.
- Hemangioma.
- Atheroma.
- Fibroma.
We list the criteria that may indicate that a tumor on the skin is benign:
- The tumor grows slowly. The increase in size occurs gradually.
- There is no spread of cellular elements beyond the neoplasm.
- Tumor growth into surrounding healthy tissue is not detected.
- Despite the atypical structure, there is no tendency to metastasize.
Types of warts
In accordance with medical terminology, a wart is a benign tumor-like growth of the skin. The cause is the papilloma virus. Occurs in almost every person (up to 90%). According to the clinical classification, the following types of warts are distinguished:
- Flat. They are also called youthful. They have a flat appearance, flesh-colored or light brown in color. They can be either small or quite large in size. However, they rise above the skin only 1-2 millimeters. Location: face and back of hands. Occurs in childhood and adolescence.
- Vulgar (ordinary). Mostly young people suffer. The formations rise above the skin (up to about 5 millimeters), have a round shape, and are prone to growth. The rashes are multiple. May exist for several months. As a rule, they then go away on their own.
- Thread-like. At first they have a thread-like shape, then they become elongated oval. They usually occur in places where the skin is delicate and thin, there are natural folds and there is high humidity. Favorite localization is the face, neck, groin area, armpits, under the mammary glands.
- Genital (genital warts). Formations similar to growing cauliflower. The main location is the inguinal and anal areas, as well as the perineum. The size of genital warts is 10-15 millimeters. During the development of the disease, it causes severe itching.
- Senile. The reason for their appearance is the formation of seborrheic keratotic growths on the skin of older people. The skin growths are greyish, brown or black. Seborrheic scales are visible on the surface. They can merge into a massive warty conglomerate.
Nevi
A mole or nevus refers to benign formations that appear on the skin in the form of pigmentation. They can be congenital and acquired, single and multiple. They are a cluster of cells that contain a large amount of melanin (pigment). Clinical manifestations of nevus:
- Pigmented, slightly raised spots that are brown or black in color are revealed.
- The surface is smooth or papillomatous (warty).
- The sizes, number and location of nevi are very diverse.
- Hair may grow on some lesions.
- Depending on the location, borderline, intradermal and mixed nevi are distinguished.
It should be noted that pigmented borderline nevi are considered the most dangerous in terms of transition to melanoma (skin cancer). These are flat nodules of dark brown or black color.
They have an uneven surface with no hair on it. Mostly observed from birth, but can be acquired.
The risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor and location in an inconvenient place are the main reasons for removing moles.
Many nevi are observed in people suffering from actinic dermatitis, which develops due to increased exposure to sunlight on the skin.
Hemangioma: red raised spot
A neoplasm that arises from vascular tissue is called hemangioma. There are such forms as:
- Capillary.
- Venous.
- Cavernous.
Often this is a congenital tumor that increases as the baby grows. Capillary hemangiomas are dilated and increased in number of capillaries. The sizes can be different (from a few millimeters to huge ones, occupying half the face). They look like a red raised spot.
Dilated, tortuous and dense blood vessels located above the skin form the basis of venous hemangioma. Rise above the surface of the skin. They can reach sizes up to 5-7 centimeters.
Such tumors are located more deeply than capillary hemangiomas. As the tumor grows, the skin becomes thin and easily injured, which often leads to bleeding.
At the same time, cavernous hemangioma is characterized by varicose vessels and periodic bleeding.
Atheromas: ball-shaped growths
A tumor arising from the sebaceous gland is an atheroma. Most often it is located in the head, neck, forehead, tailbone, etc. As a rule, it occurs in mature and elderly people. Atheroma rises above the surrounding tissues, resembling a ball. The consistency is dense or elastic. It grows quite slowly. The skin over the neoplasm is of normal color.
If you squeeze the atheroma, a cheese-like mass or thick liquid is released. If the tumor becomes inflamed, it becomes painful and the skin above it becomes noticeably red. It is necessary to remove the atheroma with a capsule, otherwise a relapse (recurrence of the disease) cannot be avoided.
Malignant tumors
The incidence of skin cancer is approximately 10% of all malignant tumors. Over the past 10 years in Russia, patients with oncological pathology of the skin have increased 3 times.
Elderly people are most often affected. It has been clinically proven that if a person has fair skin and lives in a region with a hot, sunny climate, the risk of developing a malignant skin tumor increases dramatically.
Types of skin cancer:
- Basal cell (basal cell carcinoma).
- Squamous.
- Melanoma.
- Adenocarcinoma.
To confirm the diagnosis, a cytological or histological examination is required. If you notice that any formations have appeared on your body, do not hesitate to consult a doctor. Early diagnosis allows you to effectively cope with the tumor and count on a favorable prognosis.
Cancer with excess keratinization
In the tumor type of squamous cell skin cancer, a node or plaque of red-pink or flesh-colored color with excessive keratinization (hyperkeratic form) is determined. However, there may also be warty growths on the surface of the tumor. Over the course of several months, cancer grows into the dermis and fatty tissue. The resulting node, up to two to three centimeters in size, has a dense consistency, is inactive and prone to ulceration. It also bleeds easily with minor injury. It should be noted that with the ulcerative type of squamous cell skin cancer, excessive keratinization is not observed.
What kind are on the face?
Any formations on the skin of the face look extremely unattractive and bring severe psychological discomfort. The most common types of neoplasms that appear on the face are:
- Warts and papillomas.
- Moles (pigmented nevi).
- Milia.
- Keratomas.
- Cutaneous horn.
- Lipoma.
- Atheroma et al.
In medical reference books you can find quite a lot of photos with various neoplasms on the skin.
Removal methods
We list the situations when it is necessary to contact a specialist and get rid of benign tumors:
- In a small area there is a cluster of nevi (15-20), which is considered a fairly high risk of developing a malignant tumor such as melanoma.
- The formation is located on the face, neck, hands, which are often exposed to ultraviolet rays, which contributes to the degeneration of the tumor into a malignant tumor.
- One of your close relatives had skin cancer, since the presence of a hereditary factor is important in the development of the tumor.
- The neoplasm is often injured.
Today, the following methods are used to remove benign and malignant formations on the skin:
- Surgery. Benign, precancerous or malignant tumors can be eliminated. The removed tissues are sent for histological examination.
- Cryodestruction. The tumor is eliminated using liquid nitrogen. After some time, dead cells peel off and are replaced by scar tissue.
- Laser exposure. Benign skin growths (for example, warts, pigmented nevi, papillomas, etc.) are effectively removed.
- Electrocoagulation. At the moment, it is considered one of the most common methods of removing various skin formations. However, the method does not allow the removed material to be sent for histological examination, which is a significant drawback.
The choice of the optimal treatment method is determined by the attending doctor, taking into account the type, size and location of the tumor.
Source: https://MoyaKoja.ru/onkologiya/drugie/novoobrazovaniya-na-kozhe.html
Types of warts
Warts are growths on the skin, the formation of which is caused by the proliferation of the surface layers of the epithelium. They belong to the group of benign neoplasms resulting from infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are different types of warts, each with characteristic features.
General characteristics of human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common infections. According to statistics, 90% are its carriers, but not in every case does it cause characteristic symptoms of the lesion.
HPV belongs to the papillomavirus family. It is resistant to temperatures and external factors. Papillomavirus affects the epithelial layer of the skin and mucous membranes. It is transmitted through sexual contact, household contact, vertical transmission and from mother to child during pregnancy or childbirth.
Attention! Currently, about 130 strains of HPV are isolated. Some of them are safe and do not cause significant harm to human health, while others belong to the group of papillomas with an increased risk of oncogenicity.
The human papillomavirus causes the formation of warts on the body.
What is a wart and how does it differ from condyloma?
Warts are benign growths on the skin that are formed when the human papillomavirus enters the body. Externally, they look like small papillae or nodules.
The prognosis for the appearance of such formations is in most cases favorable. In approximately 50% of cases, their resolution occurs spontaneously. However, the possibility of their malignancy or relapse cannot be ruled out.
Papillomas differ from condylomas. Unlike the first type of formation on the skin, condylomas cause an inflammatory process. Most often, this type is localized in areas of the skin that are subject to friction with clothing or shoes.
All condylomas are classified into the following types:
- wide neoplasms attached to the skin with a large base;
- genital warts - have a thin stalk and are characterized by a lobular structure. They often affect the mucous membranes of the reproductive system and are transmitted through sexual contact from an infected partner.
Unlike condylomas, papillomas look like flat nodules.
Important! The main differences between condylomas and papilloma are not only in appearance, but also in the method of transmission. The former arise as a result of infection through domestic or sexual contact, and the latter – through contact and household contact.
Risk of oncogenicity
- Different types of warts are dangerous to health in their own way, but there are certain types of them that are characterized by an increased risk of oncogenicity.
- Strains with an average level of oncogenicity are 31, 33, 35, 52, 58.
- Highly oncogenic types of warts include strains –16, 18, 36, 39, 45, 51,56, 59, 68.
- Oncogenic papillomas can be distinguished by symptoms:
- inflammation of the tumor;
- change in the size, shape, structure of the wart;
- pain, itching and burning sensation in the area of the growth;
- formation of purulent masses;
- bleeding from a wart.
Unlike types of papillomas with a high risk of oncogenicity, ordinary warts do not cause any discomfort, are characterized by small sizes, and protrude slightly above the surface of the skin.
Classification of warts
The most common types of warts are:
- flat, or juvenile, is one of the most common types of papillomas that usually appear on the face. Neoplasms are located on the neck, arms and legs, back, and dorsum of the hands. They often appear next to abrasions, scratches, and cuts. Their appearance is associated with hormonal changes in the body of adolescents. Papillomas are oval or round in shape, their surface is smooth. Color – light brown or pinkish. The diameter of such formations varies from 0.5 to 3 mm. Typically, flat warts appear several at a time. Occurs in children and adolescence. Flat warts are not a symptom of a serious disease and do not require specific treatment;
- vulgar, or simple - a characteristic feature of the species is that the neoplasm rises approximately 5 mm above the surface of the skin. Its color is white, flesh or brown. The nodules have different diameters and appear mainly on the toes and hands, and on the outside of the hands. Appearance of warts: a large number of small neoplasms form around the so-called “maternal” papilloma. Warts are difficult to treat, but can spontaneously disappear from the surface of the body. A type of vulgar wart is plantar. They are usually found on the feet and have a dense, keratinized structure. Such papillomas are formed in places where shoe pressure is applied. Growths of this type are the most painful and cause particular discomfort when walking. They can be flat or, conversely, protrude greatly above the surface of the skin;
- filamentous - have an elongated, oval or round shape, can reach 10 mm in length. They form in skin folds, on the face and neck, in the armpits, along the hairline. In women, filamentous papillomas are localized under the mammary glands. Such warts are observed in patients over 35 years of age. Growths of this type are easy to treat;
- senile - these neoplasms are also called seborrheic keratomas. This is the only type of wart whose formation is not associated with HPV. The reason is age-related changes in the skin layers. They grow quite slowly. In the initial stages, a small brown spot forms, which gradually increases to 6 mm. At the last stage, the color of the keratoma becomes saturated (dark brown), it rises significantly above the surface of the skin. Senile warts form mainly on closed areas of the body, but the possibility of their appearance on the neck, limbs, and face cannot be ruled out.
The causes of warts are not limited to the presence of HPV. To activate it, predisposing conditions are necessary, which include stress, the presence of infections, reduced immunity, and nutrient deficiency in the body.
ICD 10 code
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), human papillomavirus infection, which causes the formation of warts on the skin, has code B97.7.
Warts are benign skin growths that arise as a result of activation of the human papillomavirus. If such nodules are detected, you should consult a dermatologist, since some strains can become malignant and lead to the development of cancer.
Types of warts Link to main publication
Source: https://dermatologiya.su/virusnye/vpch/raznovidnosti-borodavok
Warts, benign and malignant
- 01 August
- 0 views
- 0 rating
Contents: [hide]
- Causes of malignancy
- Signs of a malignant nevus
- Photos of malignant moles and warts
- How to distinguish a benign mole?
- Which doctor should I contact?
- How is diagnosis carried out?
- Treatment of the disease
- How often should I be examined after removal?
- Forecast
- Add a comment Cancel reply
- Popular:
- Causes of warts
- Types of warts
- Malignant warts
- Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
- Treatment methods for malignant growths
- Routes of infection with papillomavirus
- When can a wart develop into cancer?
- Wart turned into cancer: symptoms
- Stages of development of cancerous tumors
- Diagnosis
- Examination of the skin
- Laboratory examination
- Instrumental diagnostic technique
- Cancer detected, how to treat?
- Treatment for the initial and first stages of cancer
- Second, third and last stage of oncology
- Chemotherapy
- Video on topic
But under the influence of pathological factors, nevi can degenerate into a malignant tumor - melanoma. It is one of the fastest growing tumors in the body.
The disease (especially in its advanced form) is difficult to treat. It is important to recognize dangerous symptoms in time and begin therapy.
Causes of malignancy
Any mole or wart can develop into cancer. This requires prolonged exposure to adverse factors. Basic prerequisites:
- ultraviolet radiation (solar or artificial);
- history of sunburn;
- injury to education;
- the presence of a certain type of nevus (complex, borderline, blue, intradermal melanocytic);
- a large number of moles (more than 50);
- age over 50 years;
- skin cancer in relatives or in the patient himself in the past.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/borodavki-dobrokachestvennye-i-zlokachestvennye.html
Do warts turn into cancer?
Since the end of the last century, warts and condylomas have ceased to be considered solely a cosmetic defect. It has already been proven that they play a leading role in the occurrence of cancer, in particular, cancer of the cervix, breast, rectal intestine, and melanoma.
The cause of the appearance of neoplasms is papillomavirus. It can be detected in many people, but not everyone develops warts or other growths. The virus is in an inactive form in the body, but when the immune defense is reduced or exposed to negative factors, it begins to multiply intensively.
The virus has the ability to change the skin and mucous membranes by disrupting cell growth. It is transmitted through contact of injured skin with an infectious agent, sexual intercourse, or the use of household objects.
What causes warts?
The incubation period, when the virus is inactive, can last several months or years. Its intensive reproduction, and the appearance of warts most often occurs when:
- weakened immunity due to another viral illness or its chronicity;
- long-term self-medication with drugs that are not pathogenetic treatment of any disease (immunosuppressants, hormonal drugs);
- taking antibacterial medications or cytostatics;
- excessive exposure to open sunlight during the period of maximum activity;
- frequent influence of stress factors, due to which the psycho-emotional state of a person changes;
- hormonal imbalance.
As soon as the body is weakened, the papillomavirus provokes the formation of condylomas, warts or papillomas.
The risk of developing cancer from warts
There are quite a few viral strains that have a tropism for a specific location in the body. For example, type 16, 18 predisposes to cancer of the oral cavity, male and female reproductive organs.
Oncological condyloma can form as a result of activation of types 6 and 11. Even in the case of a benign process, effective treatment is required, since neoplasms are a source of infection, especially when they are traumatized.
When do warts turn into cancer?
To prevent warts from becoming malignant, it is necessary to pay special attention to them. Traumatization of the formation significantly increases the risk of cancerous degeneration of cells. This is possible when it is localized in areas of high friction (belt area, cuffs, sock), due to mechanical damage during shaving or with a washcloth during bathing.
If you notice that you have torn off a wart, you need to treat the wound surface with an antiseptic solution, for example, hydrogen peroxide or brilliant green. You should not wet it with water or cover it with a band-aid in the next couple of days.
In cases where the integrity of the growth has only been compromised, but remains attached to the skin, it is recommended to consult a doctor, because trauma can provoke malignant transformation.
Among other factors predisposing to cancer, it is worth highlighting:
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- excess body weight;
- hormonal imbalance;
- psycho-emotional failure;
- immunodeficiency.
The virus is especially often activated in the presence of a concomitant sexually transmitted infectious disease.
How can you tell if a wart has turned into cancer?
Suspicion of malignant degeneration can be noticed only with careful observation of changes in the wart. If the following symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible:
- rapid increase;
- violation of integrity in the form of cracks;
- itching, tingling, aching sensations in the area of the tumor;
- inflammation around the formation in the form of a rim;
- disturbance of the skin or vascular pattern around the wart;
- loss of clear boundaries;
- color change;
- the appearance of superficial droplets of blood.
In addition to changes in the characteristics of the wart, it is necessary to palpate nearby lymph nodes. During the cancer process, they may thicken, enlarge, become immobile and adhere to the surrounding tissues.
Skin cancer can manifest itself as:
- basal cell type, affecting the superficial layers of the skin most often in open areas of the body (face, neck, scalp). It can be localized in the area of the nasolabial triangle, on the nasal wings, in the corners of the eyes and temples.
- squamous cell type, located in the area of the lower lip and external genitalia. The patient complains of a tumor formation or ulcerative defect that is rapidly increasing in size. Diffuse skin lesions are accompanied by pain due to a pronounced inflammatory process.
- melanoma is considered the most aggressive, because it often metastasizes to regional and distant areas of the body. Secondary foci of cancer cell screening are formed, which, when multiplying, form metastases. Visually, melanoma is similar to a mole, but is distinguished by uneven borders, increasing size and uneven color.
To differentiate between a benign neoplasm and cancer, cytological and histological examination is considered the most effective method. After a thorough study of the cellular composition, a final diagnosis is established, on the basis of which treatment tactics are determined.
Treatment
Treatment can be carried out surgically by excising the wart within healthy tissue and removing the lymph nodes if they have changed. In addition, laser treatment, cryotherapy or electrocoagulation are possible.
If necessary, chemotherapy, antiviral and immunomodulators are used. They help prevent metastasis, strengthen immune defense and fight papillomavirus.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to completely rid the body of papillomavirus, so it is necessary to follow some recommendations to prevent the initial appearance of a wart or relapse of the disease:
- undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist, mammologist or urologist;
- maintain immunity by normalizing a nutritious diet, proper rest and sleep;
- avoid stressful situations;
- control hormonal levels;
- pay attention to existing warts in order to promptly identify their changes.
If you find warts on your body, you should not be upset, because almost every person has papillomas, moles, nevi and other formations on their skin. Particular attention should be paid to formations that are exposed to traumatic factors and, of course, to warts localized in open areas of the body.
Source: https://orake.info/borodavki-perexodyat-v-rak/