Neurosonography (or ultrasound examination of the brain) is a diagnostic procedure that replaced magnetic resonance imaging.
The article explains how ultrasound differs from MRI of the brain and which is better, how and why the examination is carried out, what indicators are normal, what indicates pathology and up to what age the examination is performed.
Why is NSG better than MRI?
The difference between the old and new examination method is that MRI is far from a harmless procedure; it has many contraindications. In particular, it cannot be carried out if:
- the patient has pacemakers, metal implants, braces, an artificial heart valve;
- the patient is pregnant in the early stages;
- have a disease of the pituitary gland;
- the patient suffers from allergies, heart failure, and cerebrovascular accident.
At the same time, there was no alternative method for diagnosing brain pathologies in the early stages. It was neurosonography - a fairly accurate and safe procedure.
Neurosonography – what is it?
For people far from medicine, neurosonography means ultrasound of the brain . However, this is only one area of research, albeit the most widespread. The term “neurosonography” itself is a general concept for a whole complex of ultrasound studies of the state of the nervous system.
Neurosonography allows you to determine the condition:
- spinal cord;
- vessels supplying these organs;
- scalp;
- cranial bones;
- spine.
Important! The procedure is mainly performed on children, especially newborns, but is sometimes performed on adults, for example, during operations or injuries.
Ultrasound examination shows:
- damage to bone tissue;
- soft tissue defects;
- state of nerves;
- cysts and tumors;
- symptoms of increased intracranial pressure and other pathologies.
In what cases is neurosonography prescribed?
Neurosonography is rarely done in adults. Brain ultrasound is performed if:
- there was a head or spinal injury;
- there are circulatory disorders;
- there is a possibility of damage to the central nervous system;
- there are tumors, cysts, hernias;
- undergo brain surgery;
- inflammation was detected.
Source: https://MediGid.com/uzi/vidy/nejrosonografiya.html
Neurosonography – what is it, prices
Neurosonography is an examination of the state of the brain of newborn children using ultrasound. The method is safe, convenient and informative - these are the characteristics that are important for examining children.
The advent of neurosonography was a revolutionary revolution in the study of brain pathologies in newborns. In many ways, it resembles a conventional ultrasound, but the examination is carried out through cartilaginous “fontanelles” that have not yet had time to ossify. That is why the procedure cannot be performed on older children and adults.
The method allows you to understand whether the child’s brain is formed correctly and how effectively it is developing.
Neurosonography is a procedure recommended by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and is included in the list of comprehensive examinations of newborn children. Therefore, at least one session is recommended for absolutely all babies under the age of one year.
Why is it important to screen a young child?
Neurosonography of the brain can be performed until the child is 1.5 years old - later the “fontanelles” close and the necessary information can only be obtained using electroencephalography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
It is in the first year of life that the child’s brain and nervous system go through active stages of development. And any developmental pathologies are most successfully corrected at this time. If a teenager has 99% of his nerve cells, then a newborn baby has only 25%.
The child’s body is susceptible to external influences and proper treatment can correct health problems and preserve it for many years.
The essence of the method
When performing neurosonography of newborns, a special sensor creates ultrasound waves of the required frequency and length. This is a special spectrum of sound waves that is not detected by the human ear. They are sent in a narrowly directed beam through the moving bones of the baby’s skull, reflected from the tissues and structures of the brain, and returned back to the sensor.
Thus, the doctor can see with his own eyes those changes whose presence he could only assume. And successful treatment always begins with the correct diagnosis.
Is neurosonography safe?
Like any ultrasound, the procedure has no contraindications, complications or side effects. Devices intended for ultrasound examination are manufactured under strict quality and safety control.
Interesting: ultrasonic waves are produced by many representatives of wildlife, such as dolphins, without any harm to themselves and their offspring.
How is neurosonography performed?
Most often, neurosonography is performed through the anterior fontanel, which is located between the frontal bone and the crown. But depending on the situation, you can use the lateral temporal fontanelles and the greater occipital fontanel, located at the base of the neck.
The sequence of actions when performing neurosonography is as follows:
- the baby is placed on the couch in a supine position;
- the doctor precisely applies a small amount of a special gel to the child’s head, ensuring comfortable sliding and maximum fit of the sensor;
- by making slight sequential movements with the sensor, the specialist scans measurements of the state of individual parts of the baby’s brain;
- ultrasonic pulses enter the receiving apparatus, are converted and display a moving image on the monitor screen;
- Based on the data obtained, the doctor assesses the state of the baby’s brain and makes a conclusion.
The baby does not need to be specially prepared for the procedure. Before the examination, it is recommended to feed the baby so that he feels as comfortable as possible and allows himself to be examined.
- But even if a small patient behaves restlessly for some reason, this will not affect the results of the examination.
- Some babies may not like the cool gel, but an experienced doctor will conduct the test quickly and comfortably for the baby.
- The ideal option is to carry out the procedure while the child is sleeping.
Before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking antispasmodic and painkillers. The drugs can change the size of the blood vessels in the brain and the examination data will be inaccurate.
Who needs examination
Neurosonography should be performed on all newborn babies aged 1-2 months and older, before the age of 1.5 years. Since the procedure is harmless, on the recommendation of a doctor it can be repeated as many times as the specific situation requires.
However, there are children for whom the examination is extremely necessary. These include:
- premature babies (born before the 37th week of pregnancy inclusive);
- children who suffered from birth trauma or were injured after birth (for example, falling from a crib);
- babies born by caesarean section;
- if, in the absence of illnesses, the child is inactive, has poor appetite and digestion, is indifferent or cries frequently;
- with frequent shallow sleep of the baby, causeless crying;
- with pronounced tremor of the arms, legs or chin;
- strabismus;
- if there are signs of increased intracranial pressure (the child often cries, throws back his head and arches;
- with signs of poor hearing or vision (cannot focus on a toy or parents’ faces);
- with fainting, convulsions;
- with high blood pressure;
- in case of coordination problems;
- if the child throws his head back sharply;
- children with low birth weight (less than 2700 g);
- babies born with facial asymmetry;
- children who have suffered severe viral infections;
- children who are undergoing heart or vascular surgery;
- babies born as a result of difficult births, which were accompanied by fetal hypoxia and Rh conflict.
Neurosonography will help identify brain tumors and monitor the process of their treatment.
What does neurosonography show?
During the examination, the doctor evaluates a number of factors:
- How symmetrical is the shape of the cerebral hemispheres? If the hemispheres have differences, this may signal the development of pathologies.
- Are the grooves and convolutions of the cortical layer of the brain clearly visible? In a healthy child, they have clear and even contours, without the presence of fluid in the brain space;
- What are the sizes of the ventricles and cistern of the brain. The doctor checks the normal values using tables.
Neurosonography standards:
- the lateral ventricles (anterior horns) should not exceed 2 mm (2-4 mm after reaching three months of age);
- lateral ventricles (occipital horns) - no more than 10-15 mm;
- body of the lateral ventricles - no more than 4 mm;
- volume of the third ventricle - 3-5 mm;
- the volume of the fourth ventricle is up to 4 mm.
- interhemispheric fissure - 3-4 mm;
- cistern magna – up to 10 mm;
- subarachnoid space - up to 3 mm.
Attention: depending on the individual data of each baby, the indicators may have errors. For example, for a child with low weight, the size of the brain regions will be smaller than the similar parameters of a “hero”.
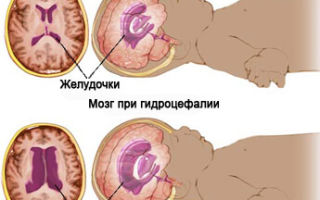
Pathologies detected by neurosonography
If your baby looks healthy and is developing harmoniously, this is not a reason to refuse the procedure. Anomalies of brain development, if they are not total, do not always manifest themselves in an obvious way. It is important that the child’s health status is assessed by a specialist.
Timely neurosonography will identify dangerous conditions that need correction:
- brain cysts, including arachnoid cysts - they do not resolve on their own and such neoplasms must be treated;
- dropsy of the brain;
- aneurysms - areas with dilated vessels that interfere with proper cerebral circulation;
- cerebral ischemia, characterized by oxygen deficiency and death of nerve cells in the brain. Without treatment, this results in a very severe disease called leukomalacia;
- brain tumors;
- meningitis is an infectious disease accompanied by deformation of the membranes of the brain;
- cerebral palsy;
- hematomas.
During the examination, it is possible to identify some physiological or functional disorders that do not require treatment, but require attention and understanding from the parents. Over time, subject to the standards of mental hygiene and careful treatment of the baby, neurophysiological processes return to normal.
It is important that the examination can promptly identify diseases that require regular monitoring and treatment. For example, hydrocephalus.
If deviations are detected
If problems are identified during the examination of the baby, there is no need to panic. Contact a neurologist, he will assess how serious the pathology is, whether urgent treatment is necessary or whether monitoring the child’s development is sufficient.
Your doctor may refer you for re-examination. Indeed, despite the fact that neurosonography is an accurate medical instrument, the possibility of error cannot be excluded.
If the diagnosis is confirmed and the doctor has prescribed treatment for your baby, strictly follow all medical recommendations. Remember that a significant part of pathologies are successfully cured during the first year of a child’s life.
Source: https://www.polyclin.ru/uslugi/nejrosonografiya/
Studies of blood vessels and brain structures: key diagnostic methods
The brain, like any structure of the human body, is susceptible to serious diseases.
Sad statistics show that mortality from strokes accounts for 12–15% of total mortality, ranking 3rd after heart disease and malignant tumors.
According to WHO, for every 100 million people in the world there are 500 thousand strokes and cerebral vascular crises per year. To protect yourself from brain diseases and their severe consequences, you should undergo timely examinations and diagnose problems.
Methods for studying the human brain: from ultrasound to MRI
The most common brain diseases include: stroke, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, epilepsy, and brain oncology. In Russia, up to 400 thousand cases of stroke are registered annually and 35% of them end in death from the disease itself or its consequences.
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no tendency to improve the situation.
In addition, diseases associated with cerebral vessels (subarachnoid hemorrhages, cerebral hemorrhages, thrombosis, embolism, malignant brain tumors, atherosclerosis, hypertension and others) affect today not only older people, but also very young people.
Scientists attribute this to an unfavorable environment, an aggressive information environment, unsatisfactory biochemical indicators and personal risk factors: smoking, alcoholism, unbalanced poor-quality nutrition, and an unhealthy lifestyle in general.
The risk group includes people over 50 years of age and those who are regularly exposed to psycho-emotional and physical stress - they are recommended to have a brain scan. It can also be prescribed:
- with diabetes mellitus, which causes destructive changes in the functioning of many organs and provokes the development of atherosclerosis;
- with atherosclerosis, which is dangerous because over time it causes complete or partial blockage of blood vessels in the brain;
- with inadequate blood supply to the brain. Impaired coordination of movements, persistent severe headaches, vomiting, general weakness and poor health are symptoms of this ailment;
- when a tumor is detected in the brain;
- in a pre-stroke state;
- with vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- for traumatic brain injuries and bruises of the head and spine;
- before undergoing planned cardiac surgery.
The doctor determines the diagnostic method depending on the purpose of the study, but in any case, the specialist needs to know:
- whether there are blockages or narrowing of blood vessels in the brain;
- how the patient's disease affects blood flow;
- Is the tone of the vascular walls okay?
- whether aneurysm, deformation, vasospasm and congenital abnormalities are present in the structure of cerebral vessels.
This is interesting. The prototypes of modern brain diagnostics have existed since ancient times. Thus, in France, during archaeological excavations, a skull was discovered with a competent, even by modern standards, trepanation of the skull. The age of the find was determined to be 7000 years. What the primitive surgeon was trying to find out - either to diagnose the brain of his fellow tribesman in this way, or to relieve unbearable headaches - remained a mystery. Now there is no need to make a hole in the skull unless absolutely necessary. Modern methods of diagnosing the brain and blood vessels open up opportunities for doctors that no one imagined even a few decades ago.
Study of cerebral vessels
There are many modern diagnostic methods that can be used to check the condition of the blood vessels in the brain. Let's take a closer look at them.
Ultrasound Dopplerography (USDG)
The examination is based on a combination of ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound. Due to its informativeness, safety, and effectiveness, the method has gained recognition in the medical community.
With its help, you can establish the speed of blood flow, narrowing in the lumens of blood vessels and atherosclerotic formations, blockage of blood vessels, the presence of changes in the direction of blood flow caused by osteochondrosis or tissue deformation, and also identify cerebral aneurysms.
The only drawback of ultrasound scanning is its inaccessibility. Only in modernly equipped clinics can you undergo this examination. Despite all the information content of the method, there are practically no contraindications to its implementation.
Only the patient's serious condition and inability to lie down can prevent the procedure from being performed. Ultrasound ultrasound does not require special training.
Rheoencephalography (REG)
The principle of operation is similar to the method of electroecephalography (which will be discussed below). According to her testimony, the doctor evaluates blood circulation in the brain, vascular tone and the state of blood supply. When performing REG, no special preparation is required, the method is harmless, and there are no contraindications.
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
The method is most informative when studying small structures of the brain. Extremely accurately determines the condition of the nerve trunks of blood vessels and the medulla.
Much depends on the device used; the power for such a study is high (0.3 Tesla). The doctor will refer you for this examination if there are disturbances in the functioning of the vessels of the neck and brain, such as micro-strokes and thrombosis.
MRA has the same contraindications as MRI, which will be discussed below.
If the attending physician needs a comprehensive “picture” about hemodynamics, blood flow rate, functionality and vascular filling with blood, he suggests that the patient undergo Doppler ultrasound.
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound uses digital examination, and the depth of passage of ultrasound beams increases to 9 cm.
The scan takes place in “slices”, which provides a complete and detailed visualization of the condition of the arteries and veins of the head.
When duplex scanning of head vessels, the principle of spectral analysis and Doppler digital coding is used. The procedure helps to display the color “picture” of the lumen of blood vessels, the tone and structure of the walls of blood vessels, branching and deformation of blood vessels, the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques and their sizes.
Doppler sonography, like duplex brain scanning, is so harmless that this study can be performed on young patients.
Diagnosis of diseases of brain structures
Echoencephalography (EchoEg) is an ultrasound examination of the brain. A special device is used - an oscilloscope, which records the state of the brain using ultrasound and reproduces the result in the form of a diagram. The doctor receives information about the condition of the blood vessels in the head, the performance of all parts of the brain, and brain activity.
Neurosonography (NSG) is also called the pediatric method because it is applicable to newborns and young children. It is absolutely harmless. NSG allows you to determine the condition of the brain matter, soft tissues, brain vessels, the presence of aneurysms, tumors, and various pathologies.
Electroencephalography (EEG) involves recording electrical impulses from the brain. The method is well studied and tested by generations of doctors.
Examines brain activity and degree of functionality, carries out a comprehensive examination of the brain, the cerebral circulatory system and the network of nerve fibers. Before the procedure, you must stop taking antispasmodics and anticonvulsants.
The method is harmless for all age categories. Indications, in addition to diagnosing the condition of the vascular system, may include sleep disorders, mental disorders, and brain injuries.
Craniography is an X-ray diagnostic method that “tells” the attending physician everything about the patient’s skull: its structure, changes due to injuries and diseases of the brain.
Suitable for diagnosing Paget's disease, identifying myelomas, neoplasms, and indirect signs of intracranial hypertension.
Since craniography is often performed using contrast agents injected into the cerebrospinal fluid containers (brain ventricles), this procedure is poorly tolerated by the patient. Today, doctors prefer to replace this research method with CT or MRI.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG) is a research method that evaluates the passage of impulses along the nerves. It will determine the area where the conduction of nerve impulses is insufficient or absent altogether.
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a modern diagnostic method based on the use of radiopharmaceuticals. Creates a three-dimensional “reconstruction” of processes occurring in the brain. Diagnoses, unlike all other methods, the functional activity of the brain.
Another common name for PET is “functional tomography”. PET is highly appreciated by oncologists. Tumors measuring 1 cm or more and not having obvious clinical manifestations can be diagnosed and differentiated into benign and malignant. In most cases, glucose is used as a radiopharmaceutical.
It has been observed that neoplasm cells consume glucose more intensively than normal tissues. Glucose is unevenly distributed throughout the body, and this allows the doctor to make the right conclusions. PET, in addition to diagnosing oncology, is also used to determine Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, ischemic disorders, and the consequences of concussions.
A categorical contraindication for PET scanning is pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Indications for referral for computed tomography (CT) examination cover many conditions, because CT can detect almost all pathologies:
- inflammatory processes in the substances of the brain and membrane;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- brain cysts, neoplasms, organ development abnormalities;
- multiple sclerosis and others.
A CT scan “shows” the state of the necessary brain structures layer by layer. A tomogram allows the doctor with a very high probability to make a final diagnosis and begin therapy.
The condition of the white and gray matter of the brain, pituitary gland, hippocampus, membrane, ventricular system, cranial nerves, blood vessels - the study will objectively show. The method is safe, radiation exposure is low.
CT scans are also allowed for children.
The magnetic resonance imaging method is as informative as a CT scan, and it also takes layer-by-layer images of the brain. The essence of the method is different than with CT. The object is affected not by X-rays, but by radio waves. The research object is placed in the created magnetic field.
In this way, resonant vibrations are created in molecular nuclei, which are recorded by the program. The result is a series of black and white tomograms with high contrast, each of them is a “slice” of the brain. The images are taken in different planes; the device allows you to see the brain in three-dimensional format.
Thus, the specialist receives comprehensive information about the structure of the brain.
Indications for MRI:
- uncertainty of the result when conducting other research methods;
- complaints of severe headaches, convulsions and other “general cerebral” symptoms;
- increased intracranial pressure and head injuries;
- neoplasms and inflammatory diseases of the brain, abnormalities in the structure of the brain and blood vessels;
- examination before surgery.
No special preparation is required for the study. Possible for children. The method has contraindications. For example, its implementation in the presence of metal prostheses, implants, and pacemakers in the human body is impossible.
“Food for the Mind” The scientific journal “Psycholoqy Today” published the results of studies on which foods help improve brain function. As it turned out, fish, which is traditionally considered the best “food for the mind,” is not the leader of the rating. Cranberries take first place on the list. Next come blueberries, beets, cabbage. Spinach is in fourth position. The top five is rounded out by oily fish. Anchovies or sprat will not help you become smarter. Only salmon, tuna, sardines and other fish containing fatty acids are able to break down harmful enzymes. These same foods contain phosphorus, which nourishes the brain.
Which brain research method is right for you?
Statistics show that the most popular methods for studying the brain are MRI, CT, ultrasound, PET, while CT is more suitable for studying bone structures, and MRI for soft tissues. The doctor’s prescription when choosing a research method remains a decisive factor, but the informativeness and safety of the method and the amount you plan to spend on treatment are no less important.
Source: https://www.eg.ru/digest/diagnostika-golovnogo-mozga.html
Neurosonography – what is it and why is it performed? At what age can a baby have the procedure and is it safe? Find out at the MEDSI clinic
Unfortunately, childbirth does not always go perfectly. In approximately 80% of cases, some kind of problem occurs. They can relate to both weak labor and entanglement of the baby with the umbilical cord, prolonged labor, painful pushing, etc.
Any difficulties that arise are usually eliminated without harm to the newborn and his mother.
If for some reason the problems have not been eliminated and there is a possibility that the child will be damaged or have congenital brain abnormalities, neurosonography (NSG) is performed.
What is neurosonography?
Neurosonography of the brain is a diagnostic procedure that began to be performed relatively recently. It allows you to study the newborn's brain using ultrasound.
NSG is carried out both in the direction of a neonatologist and for the purpose of a preventive examination. Previously, such diagnostics were carried out only in the most dangerous cases.
Today, neurosonography of the brain in children is prescribed almost everywhere. The technique replaced MRI.
Important! Magnetic resonance imaging is quite dangerous for the weakened body of infants and can provoke a number of serious complications.
Unlike MRI, neurosonography of the brain of newborns is as safe as possible. It can be carried out in the very first minutes of the baby’s life. Modern diagnostics have made it possible to significantly reduce the mortality rate of newborns due to the rapid detection of brain pathologies in them.
Indications for examination
Neurosonography of newborns is carried out to determine the following conditions:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Vessels
- Skull bones
- scalp
- Spine
Ultrasound examination can detect:
- Cysts
- Damage to bone tissue and soft tissue defects
- Tumors
Also during diagnosis, symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, the condition of the nerves are determined, and various pathologies are identified. As a rule, undergoing NSG is recommended for preventive purposes.
Neurosonography may be prescribed to a child if:
- Complicated labor
- Birth defects
- Genetic diseases
- Post-term pregnancy
- After caesarean section
- Use of obstetric forceps during childbirth
- Using drugs to induce contractions
- Prematurity
- Intrauterine infection
- Infant skull injury
- Newborn resuscitation
The study is carried out not only for babies in the first days of life. Neurosonography is often prescribed monthly or annually. In some cases, diagnosis is carried out even in adult patients. The research method used is no longer called “neurosonography”, but “ultrasound of the brain”. The modern research method is used for injuries and during surgical interventions or after their completion.
Is the examination safe?
Neurosonography of the brain is a study that is absolutely safe. Ultrasound diagnostics is painless. In this case, the child does not need special preparation or recovery after the procedure.
There is no proven evidence that ultrasound examinations have a negative impact on the health of children in the long term.
Thanks to this, neurosonography is performed on all babies (even those in intensive care incubators).
Types of neurosonography
There are several options for performing neurosonography. The method of execution depends on how diagnostic procedures are carried out.
The following types of neurosonography are distinguished:
- Through the fontanel . This procedure can only be performed on infants. It can be done until the fontanel is overgrown
- Transcranial . This procedure can be performed on children, adolescents and even adults. The examination is carried out through the bones of the skull. Typically the sensor is installed in the temple area
- Transcranial-transfontanelle . Such a study is characterized by increased accuracy and reduces the risk of diagnostic errors. It should be understood that this type of examination is usually the longest
- Examination through bone defects : holes, cracks, etc. (including those performed during surgical interventions)
The choice in favor of one or another type of study is made by the doctor. This choice depends on the patient’s age, his individual characteristics, diagnostic methods and its goals.
Features of the procedure
The main feature of the procedure is that it can only be performed through the fissures of the skull. This is due to the fact that ultrasonic waves do not pass through stronger bones. This makes it easier to perform newborn screening.
Neurosonography is an effective technique that has no contraindications.
Its advantages also include:
- Non-invasive – no need to damage skin and tissues
- High speed (usually 15-20 minutes)
- Accuracy of the results obtained
- Minimal risks of errors during research
- Wide range of indications
Neurosonography allows you to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis, adjust the treatment, and identify hidden pathologies that cannot be detected by other examinations. Moreover, the technique is easy to implement and accessible to many.
How is it carried out?
The examination is carried out using a standard ultrasound machine.
To carry out the examination, it is necessary to remove a cap or other headdress, hairpins, bows, etc. from the head. It is most convenient to hold the child in your arms. This way the baby will calm down and will not make unnecessary movements during the procedure.
The doctor will apply a special gel to the area of study (it is absolutely safe and does not cause allergic reactions), which improves the conductivity of ultrasound. After this, the specialist will perform a direct diagnosis. He will move the sensor over the head, but these movements will not cause any unpleasant sensations in the baby.
On the monitor, the specialist will see a dynamic image of all internal structures.
At the end of the examination, you will receive a conclusion about the condition of the brain and tissues. To interpret the results obtained, you should contact the doctor who is observing your child or who has given you a referral for neurosonography.
Do you need to prepare for diagnosis?
The procedure does not require additional preparation.
The mother or other person who came for the examination with the baby should:
- Pre-feed the baby. This way the baby will be as calm as possible.
- Stay close to the little patient all the time and, if necessary, entertain him with his favorite toys. If the child is relaxed, the study will be as accurate and reliable as possible.
- Try not to allow sudden movements of the baby
No additional recommendations are issued. There is no need to feed your child in any special way or limit his fluid intake. The study is no different from traditional ultrasound.
Explanation of research indicators
A specialist must decipher the results of the study. This is due to the fact that when assessing all indicators, the doctor focuses on the child’s weight and other individual characteristics, already identified pathologies and past diseases. It should also be noted that in almost 70% of cases newborns exhibit some abnormalities in brain development.
They are not critical and do not indicate dangerous pathological conditions. During the first year of life, all indicators usually return to normal. This does not have negative consequences for the health of the baby. As a rule, minor deviations become a reason for regular monitoring of the baby’s condition. The doctor will inform you about the need (if any) for constant monitoring.
When deciphering research indicators, attention is paid to such important parameters as:
- Structure of the cerebellum
- The structure of the cerebral hemispheres
- Presence/absence of neoplasms
- Pathological conditions
- Features of intracranial fluid
Norms and deviations of indicators
In the study protocol, the doctor indicates:
- The shape of the brain tissue (symmetrical or asymmetrical). In the absence of deviations from the norm, brain tissue has an absolutely symmetrical structure
- Visualization of the sulci and convolutions of the brain
- Absence/presence of inclusions in the ventricles of the brain. Normally, these sections are homogeneous and absolutely identical.
- The shape of the tentorium cerebellum . Normally it is symmetrical and trapezoidal
- Absence/presence of fluid in the space between the two hemispheres. Normally, no fluid is detected, and the vascular plexuses have a homogeneous structure
Important! Your doctor will definitely tell you about deviations from the norm. He will also explain all the results of the examination. Do not try to decrypt it yourself. For a non-specialist, all the numbers and various descriptions are completely incomprehensible. In addition, there are differences in indicators depending on the age of the small patient.
Where is the diagnosis carried out?
Neurosonography is a diagnostic that is carried out today in all major perinatal centers. It is carried out free of charge immediately after the birth of the baby (if indicated). For preventive purposes, research is carried out only on a paid basis. The price of neurosonography of the brain of newborns and other patients depends on a number of factors. You can always clarify it in advance.
Important! Paid diagnostics should be carried out only in well-known medical institutions with modern equipment. It is very important to clarify in advance who is conducting the research. The doctor must have all the necessary professional knowledge and skills.
Advantages of diagnostics at MEDSI
- Highly qualified doctors . The study is carried out by a specialist with the necessary knowledge and skills, in accordance with the established medical protocol
- No queues . You don't have to bother or worry your baby
- New generation ultrasound systems . Expert class equipment is used for the research. It meets WHO requirements for accuracy and safety
- High speed and quality . The research is carried out as quickly as possible. This eliminates the risk of discomfort for the baby.
- Instant issuance of a conclusion . You don't have to wait for additional processing
- Comfortable conditions. Neurosonography in Moscow in our clinics is carried out in modern rooms. They are convenient for both the little patient and his parents or other accompanying persons.
To sign up for the study, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500.
The specialist will tell you the exact cost of the diagnosis and tell you how it is carried out in our clinic.
Source: https://medsi.ru/articles/neyrosonografiya-chto-eto-takoe-i-dlya-chego-ee-provodyat/
Ultrasound neurosonography
Content :
- The concept of neurosonography
- Neurosography technique
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound, including neurosonography, is an increasingly widespread diagnostic technique for a wide range of diseases.
This method is most often used in young children, usually infants, but modern technologies make it possible to use modified versions in adults. The method makes it possible to evaluate the structure of the brain and its individual structures, to identify various types of anomalies and defects.
Such an examination is usually carried out as planned, as part of a comprehensive diagnosis if any disturbances in the structure of the child’s brain are suspected.
Neurosonography of the head is usually prescribed for children under one year of age, since during this time the fontanel on the child’s head has not yet closed, usually at the age of one and a half to two months.
Often, such diagnostics are also needed for premature babies, as well as children whose birth was associated with a high risk of perinatal complications, especially from the brain (for example, those who suffered hemorrhages in the ventricles of the brain after childbirth, birth injuries, and so on).
Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography) for adults: what is it? Contrary to popular belief, neurosonography is not only available for infants. There are several options for conducting research, and transfontanelle is only one of them.
Also, for relatively young children, a type of neurosonography such as a mixed form, or transcranial-transfontanelle, can be used. For adults, varieties such as transcranial and studies through bone defects are available.
Consequently, depending on the indications and characteristics of the clinical situation, the most suitable option for each case is selected.
Neurosonography and ultrasound of the brain: differences in methods. Often patients, and even some specialists, call these two concepts synonymous. However, this opinion is somewhat erroneous.
It would be more accurate to say that neurosonography is one of the branches of ultrasound diagnostics.
To avoid confusion, most often the term “neurosonography” is used to refer to transfontanelle research, that is, applicable to young children, and the concept “ultrasound of the brain” is used to refer to adults and older children.
Ultrasound (neurosonography) of the brain in adults is used both routinely at the diagnostic stage and urgently, for example, during an operation in which the integrity of the skull bones is violated; the study is carried out to detail the damage and help in determining the tactics of further surgical and conservative treatment. Such an ultrasound is routinely performed when visiting a neurologist or therapist with complaints of headaches, migraine attacks, dizziness, the appearance of focal neurological symptoms and many other complaints and symptoms.
Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) does not require special preparation of the patient. Only recommendations are given regarding diet and lifestyle.
It is also necessary to warn the patient that it is not recommended to take potent, especially vascular, drugs, since this may affect some study parameters, for example, the elasticity and resistance of blood vessels.
If drugs are used for health reasons, then they cannot be interrupted, but a specialist is warned about this so that he can correctly evaluate the results obtained.
Ultrasound of the head (neurosonography) is performed in a lying or sitting position, which depends on the general condition of the patient and his physical capabilities. The total duration of the procedure is no more than half an hour, but in most cases 15 minutes is enough.
This parameter depends on many factors, in particular, on the experience of the specialist, the diagnostic capabilities of the equipment, and the complexity of the clinical case.
In adults, such an ultrasound is usually performed through the area of the temporal bones; a special gel is first applied to the scalp.
When a situation arises that an urgent need to examine a child or an adult, the question often arises: where to do neurosonography and how to get to the examination? The study can be carried out in almost any large medical center, especially those specializing in the pathology of the central nervous system.
Research institutes, public and private medical institutions are also involved in such research. Only a doctor should refer for neurosonography if he has precise indications and reasons for doing so. Most often this is a neurologist, but in the absence of a specialist, this can be done, for example, by a pediatrician or neonatologist if we are talking about children.
The procedure is performed by a doctor specializing in neuroimaging techniques.
Neurosonography shows a good result (patient reviews indicate this) if you consult a doctor in a timely manner if there is any suspicion of the development of brain pathology.
Often only a specialist can suspect these in children, so preventive visits to the pediatrician, especially at an early age, are extremely necessary and should not be missed.
For some diseases, already in the maternity hospital, parents are told that a thorough additional examination of the child is necessary, and in particular, neurosonography at one time or another. This helps make the diagnosis as informative as possible and determine treatment tactics more precisely.
There is another type of neurosnography, such as electroneurosonography, the conclusion of which is also a description of the state of brain structures, including cranial nerves.
The need for this manipulation is also determined only by the attending physician.
Despite the safety of all types of neuroimaging through neurosonography, all studies must be carried out strictly according to indications.
Neurosography technique
Neurosonography: method of procedure and features of its implementation. As is known, neurosonography is safe for a child of any age, and experts note that the study is highly informative.
This type of diagnosis can be carried out not only on an awake child, but also on a sleeping child, which greatly simplifies the procedure for children. In addition, neurosonography can be performed not only in a hospital setting, but also on an outpatient basis.
Given that the procedure is non-invasive, no anesthesia or sedation is required, even for the youngest patients.
If neurosonography is indicated for a child, it is done in different ways depending on the age of the child. So, if this is a child under one year old, then his fontanel has not yet ossified, so it is possible to conduct research through the tissue of the fontanel. Moreover, the younger the child, the greater the diagnostic capabilities of the method, since every month the fontanel becomes smaller.
This is due to the predominant conduct of neurosonography in the first months of a child’s life. After the fontanel closes, an ultrasound of the child’s brain can be performed transcranially, that is, through the bones of the skull.
If the first neurosonography revealed any changes, then, if necessary, to assess the state of the brain in dynamics, a study through the bones of the skull or, for example, magnetic resonance imaging can be used. Indications for a particular type of study are determined only by a doctor, based on clinical data and the age of the child.
For example, in some pathologies, the fontanel does not close pathologically for a long time, which makes it possible to conduct neurosonography through the fontanel even at an older age.
Neurosonography does not take much time, usually no more than 15 minutes. The child is lying down at this time; you don’t even have to take him out of the incubator during the ultrasound. To ensure that the head remains motionless during the examination, one of the parents or a health care worker gently holds the head to fix it.
As with a regular ultrasound, a special gel is applied to the fontanel area to improve the glide of the transducer and provide better contact between the skin and the transducer to obtain a good image.
By changing the position of the sensor and its tilt, the doctor receives the necessary image from the angles he needs, visualizing the structures of the brain.
Video: Neurosonography in the daily practice of a neurologist
Source: https://prodiagnostics.ru/nejrosonografiya.html
NSG (neurosonography) of the brain in newborns: what it shows and how it is done, explanation and table of norms
04/09/2016 Editorial site Ultrasound during pregnancy 0
Ultrasound diagnostics is used in various fields of medicine. Pediatrics is no exception. Neurosonography is prescribed to newborns to identify brain pathologies. This research method has many advantages - high information content, lack of radiation exposure, non-invasiveness, and the ability to conduct multiple examinations.
When is neurosonography prescribed?
Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography) is prescribed for newborns according to indications and for all infants at the age of one month . Neurosonography is included in the list of studies during preventive medical examinations of minors.
Neurosonography of the newborn’s brain is performed once every 1 month of life, but can be carried out until the child’s fontanelle closes and as long as necessary (according to indications and to assess the effectiveness of treatment).
Phakomatoses: causes, types, diagnosis and treatment
The sutures and fontanelles of a newborn’s skull are capable of transmitting ultrasound, so while the fontanelles have not closed, it is possible to conduct neurosonography. The sutures of the child’s skull close soon after birth, and the large fontanelle usually closes by the end of the first year of life (from 9 months to 1.5 years).
Neurosonography of a newborn: Ultrasound of the infant's brain
Who is NSG indicated for?
This is the main method for detecting structural pathology of the brain in newborns. The main indication for diagnosis is a deviation in the infant’s neurological status coupled with a violation of a number of laboratory parameters.
- The method is invaluable if the child’s condition is severe and it is not possible to transport him to the functional diagnostics department for an MRI.
- Neurosurgical operations carry a high risk, since orientation in the cranial cavity and brain structures is difficult.
- Ultrasonography can help the surgeon ensure that the surgical instrument hits the target as quickly and accurately as possible, using a minimum of technical means.
- Ultrasound helps determine the location, depth, size of the surgical target, and select the optimal access with a minimal operating window.
Children of the first month of life
It is carried out if the pediatrician or neonatologist suspects or has diagnosed the following conditions:
- intrauterine infection;
- prematurity;
- history of hypoxia (during pregnancy or childbirth);
- abnormalities in the development of organs or systems;
- anomalies in the development of the bones of the facial and cerebral parts of the skull;
- infectious diseases have been detected in the mother or child.
Children under one year old
In older children, the study helps to track the timeliness of brain development and identify the cause of neurological symptoms (convulsions, pain, etc.).
It is worth remembering when conducting NSG that the older the child, the smaller the fontanel and the narrower the acoustic window. Consequently, a smaller viewing angle for the sensor.
For children up to one year old, the method of ultrasonography is available - visualization of the structures of the spinal cord. Spinal ultrasonography is used before lumbar punctures, as a screening method for diagnosing spinal canal pathology.
Can it be done by adults?
Rarely, but it happens. In adults, the bones of the skull are connected by sutures, the fontanelles are closed, and there is no cartilage between the bones of the cerebral part of the skull. Ultrasound cannot penetrate the cranial cavity, which makes research impossible (in the traditional sense - research through the fontanelles).
In adults, transcranial ultrasonography is possible. It is possible to diagnose cerebral edema, dislocation, and enlargement of the third ventricle. But in some cases, in adults, the brain is not accessible for research due to a narrow “acoustic window.”
The use of ultrasonography results and interpretation of the clinical picture makes it effective to diagnose intracranial hematomas, which are often present in adult patients with cerebrovascular accidents.
But the main method of neuroimaging in adults and older children is CT and MRI.
Why is a newborn's brain examined?
Neurosonography allows the doctor to obtain a complete picture of the brain structures, blood flow, and identify possible hemorrhages (for example, during childbirth or if the child hit his head hard during a fall), structural anomalies or other pathological changes.
The examination is especially indicated:
- newborns with a low Apgar score (less than 7 points at 5 minutes);
- if you suspect a neurological disorder accompanied by frequent regurgitation and/or vomiting, convulsions;
- restless children who constantly cry, have difficulty sleeping at night, or often startle in their sleep;
- bulging of a large fontanel (suspicion of intracranial pressure);
- if you suspect cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy);
- if the child’s head circumference does not correspond to normal indicators: the head is too large (hydrocephalus) or children with a small head (microcephaly), with an unusual skull shape;
- born from mothers with various forms of feto-placental insufficiency (FPI);
- premature babies (born before 36 weeks) with low birth weight (less than 2800 g);
- if there is a Rhesus conflict between mother and child during pregnancy, when the mother is Rhesus negative and the fetus is Rhesus positive;
- if the mother suffered infectious diseases during pregnancy (toxoplasmosis, herpes virus, rubella during pregnancy, etc.).
How much does the examination cost and where to get it done?
The cost of the study varies depending on the location and qualification category of the doctor. In government institutions, NSG is carried out free of charge. In private clinics and offices, the average cost of a service is 2,500 rubles. In Moscow, the price of an examination is 2000–6000 rubles. In Kaliningrad and St. Petersburg it is about 4,000 rubles. In Novosibirsk no more than 2000 rubles.
Neurosonography is a fast, simple and accurate method for diagnosing pathologies of the nervous system in newborns. With its help, it is possible to identify the disorder in the early stages and begin timely therapy.
Source: https://neuro-orto.ru/bolezni/mozg/nejrosonografiya-novorozhdennyh.html