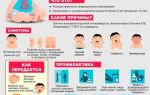
Among prostate diseases, BPH is far from the last place, and after 40 years, the risk of developing this pathology only increases. What is BPH of the prostate gland and why does it occur? This, as well as methods of treating the disease and measures to prevent it, will be discussed in the article.
BPH of the prostate gland: what it is, causes, treatment and prevention
Characteristics of the disease
BPH is the abbreviation for benign prostatic hyperplasia, better known as prostate adenoma. This designates a condition in which small formations (nodules) form in the prostate, gradually increasing in size. Their pathological growth leads to compression of the urinary canal, which is manifested by serious disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system.
The disease is benign, that is, it does not metastasize, although under the influence of a number of factors it can develop into prostate cancer.
But even if this does not happen, the presence of a tumor in the gland negatively affects men’s health and the entire body as a whole, significantly reducing the quality of life.
BPH is rare in young men, but after 50-60 years it is diagnosed in every third case. By the age of eighty, the risk of developing the disease increases to 70%.
Characteristics of BPH
The prostate gland consists of three types of tissues - muscle, glandular and connective, and any of them can be involved in the pathological process.
Typically, the lesion is located in the central part of the organ and affects the lateral lobes; in some cases, it may shift to one side or the other.
Tissue growth most often occurs in one direction, as a result of which three forms of pathology are distinguished.
Table. Forms of BPH by growth type
Form of pathologyMain characteristics| Subvesical | It is considered the most common. The tissues grow towards the rectum , as a result of which the motility of the prostatic part of the urethra deteriorates, and urine does not come out completely. This form does not greatly affect the process of urination. |
| Intravesical | The tissue grows towards the bladder. The tumor blocks the lumen of the bladder through the urethra, compresses the internal sphincter and partially or completely disrupts its functioning. |
| Retrotrigonal | Rarely observed. The tumor forms between the internal outlet of the urethra and the orifices of the ureters. The most severe form, characterized by a simultaneous deterioration in the outflow of urine and difficulty in its passage through the mouth. |
The focus of the disease is often single, although multiple ones are not so rare. Depending on this, the manifestations of pathology also change. The size of the tumor in the most advanced cases can exceed 80 mm in diameter, but usually varies between 10-40 mm.
Tumor size varies depending on the stage and form of BPH
The development of BPH occurs in stages, and experts distinguish three stages of pathology:
- compensated – early stage, developing over 1-3 years. Characterized by mild urination disorders, slight enlargement of the gland, changes in its density;
- subcompensated - disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system are more pronounced, the bladder does not empty completely, and thickening of its walls is observed. The gland itself increases 1.5 times, its tissues become much denser;
- decompensated – the most severe stage with pronounced disturbances in the functioning of the bladder. In many men, it is accompanied by renal failure with typical manifestations.
Stages of development of BPH
Each stage has its own characteristic manifestations and, accordingly, requires different treatment methods.
Causes and symptoms of BPH
The main cause of the pathology is considered to be hormonal changes in the male body, which disrupt the balance of testosterone and estrogen. This leads to uncontrolled growth of prostate cells, as a result of which adenoma develops. Among the risk factors, the main one is the natural decline of sexual functions, which begins at about 50 years of age.
The main reason for the development of BPH is considered to be age-related changes in a man’s hormonal levels.
Less commonly, the development of BPH occurs for other reasons:
- the presence of chronic genitourinary diseases;
- infectious lesions of the urinary tract;
- injuries;
- the presence of cancer tumors and metastases.
Chronic diseases and inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system can also provoke the development of prostate adenoma
At an early stage, only a specialist can determine the development of adenoma, because the first symptoms are mild and similar to the manifestations of other prostate diseases. Later, when nodules begin to form in the tissues of the gland, general signs appear, which are already a reason to consult a doctor:
- the urge to urinate occurs more often, especially at night, and the urine stream is noticeably weaker than before;
- urinary control deteriorates and incontinence may occur;
- general weakness and apathy periodically occur, body weight decreases;
- constipation is more common;
- erection decreases.
Symptoms of BPH
With the development of BPH, the symptoms worsen, a pain syndrome occurs, the nature and severity of which depends on the shape of the tumor, the stage of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies in the body.
Often the disease is accompanied by the formation of stones in the prostate, which significantly complicates the treatment process.
In patients with an advanced form of BPH, the urine is cloudy, often mixed with blood, and is excreted in small portions.
Diagnostic methods
Based on these symptoms, you cannot independently diagnose yourself and select treatment, because this can lead to the most severe consequences.
A urologist specializes in the treatment of BPH, and he also prescribes all the tests necessary to make a diagnosis.
To accurately determine the presence of a tumor, its location, size, and possible complications, several complex diagnostic methods are used at once.
Table. Methods for diagnosing BPH
Research methodCharacteristics| Rectal diagnostics | Using a digital examination, the specialist determines the presence of lumps in the prostate, its size, and pain. Additionally, this allows you to take for analysis the secretion of the gland, which is released when massaging the lobules. |
| Transrectal ultrasound | The use of an ultrasound sensor allows you to obtain an accurate image of the diseased organ and determine the size of the nodules, the localization of the tumor focus, and the presence of stones in the gland. |
| Radiography | This method helps to accurately assess the condition of the genitourinary system, identify possible complications such as stones in the bladder and kidneys, the formation of diverticula, and so on. The study can be carried out either with or without the use of contrast. |
| Laboratory diagnostics | It must include a biochemical and general blood test, a urine test, and, if necessary, a prostate secretion or smear (if an infection is suspected) is examined. |
| Uroflowmetry | Non-invasive method for assessing the condition of the urethra. It is performed during urination and involves measuring the flow rate and some other parameters. |
If a malignant nature of the disease is suspected, the doctor prescribes a biopsy. In some cases, an additional MRI of the pelvic organs may be prescribed, especially if the disease is advanced and accompanied by severe impairment of the kidneys.
If a malignant form of the tumor is suspected, a prostate biopsy is prescribed
Treatment of BPH
In modern medicine, several highly effective methods are used to treat BPH. The choice of the optimal treatment method depends, first of all, on the stage and form of the disease, as well as on the presence of complications and the general condition of the body.
Drug therapy
In the first stage of BPH, medications are not always prescribed, since therapeutic exercises and diet are usually sufficient to normalize the functioning of the genitourinary system. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which suppress tumor growth in the prostate. The most effective drugs in this group include: Avodart, Penester, Urofin.
Instructions for use of avodart
For the second stage, taking medications is the main type of therapy, as it allows you to eliminate pain, normalize the outflow of urine, and slow down the growth of nodules.
In addition to alpha-reductase inhibitors, the patient is shown adrenergic blockers and herbal-based drugs that have an antispasmodic effect.
The most famous of them are “Omnik”, “Kornam”, “Kardura”, pumpkin and chamomile extracts.
"Omnic": instructions for use
At the third stage, medications are prescribed as an auxiliary therapy before and after surgery. The type of drugs is selected exclusively by a specialist, depending on the condition of the prostate itself and the urinary system.
Tablets "Kardura"
Non-operative methods
The list of conservative treatment methods includes:
- ultrasound therapy;
- implantation of special dilating stents into the urethra;
- cryotherapy;
- radiofrequency treatment with the introduction of special needles through the urethra.
Microwave coagulation of the prostate
In addition to these procedures, physical therapy is of great importance (especially at an early stage of the disease), which helps improve blood circulation in the affected tissues, fluid outflow, and eliminate congestion in the gland. The doctor also selects a set of exercises, and they must be performed regularly over a long period of time.
A set of exercises for BPH
Surgical treatment
Surgery is also performed in different ways. In severe advanced cases, open surgery is performed to remove the tumor. If the formations are not too large and there are no complications, minimally invasive methods are used, for example, laser vaporization. After surgical treatment, the patient is given a catheter to divert urine and prescribed drug therapy and diet.
Laser vaporization for BPH
Prevention of BPH
Prevention of the disease plays an important role, which has already been proven by many years of research in urology. Preventing the development of BPH is not so difficult if you adhere to the following rules:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- If possible, stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- pay more attention to physical activity;
- consult a doctor about problems in the genitourinary area in a timely manner, do not neglect the disease;
- undergo regular examinations with a urologist after 40 years.
For prostate health, you should limit your intake of alcohol, junk food and spend less time on the couch.
But the most important thing is not to engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, because in most cases this leads to a deterioration in health, the development of side complications and a decrease in the chances of a full recovery of men’s health.
Video - BPH of the prostate gland: what it is, causes, treatment and prevention
Provided that BPH is detected early and treated appropriately, the prognosis for this disease is usually favorable. But delaying a visit to the doctor can lead to the development of a malignant form of the tumor, which is much more difficult to cure. How prostate cancer manifests itself and how effective its treatment is, you can read on our website.
Source: https://prostatit-doc.ru/dgpzh-predstatelnoj-zhelezy-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny-lechenie-i-profilaktika/
List of prostate diseases in men: possible causes of prostate problems and treatment methods
The prostate is an important and at the same time vulnerable organ.
She is susceptible to a number of diseases that arise due to an unhealthy lifestyle and a man’s inattention to his health.
Most pathologies are of an inflammatory nature. You can learn more about what prostate diseases are, as well as the causes of diseases and methods of their treatment in this article.
Hide content
Common Causes
The following factors influence the likelihood of developing prostate diseases:
- congestive processes in the pelvis caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- nervous and physical overload of the body, reducing its defenses;
- abstaining from sex for too long;
- promiscuous sex life;
- smoking, alcohol consumption;
- improper diet with an excess of fatty, spicy and salty foods;
- the prostate is cold and provokes acute and chronic inflammation;
- infectious lesions of the body. They can be either bacterial in nature (streptococcus, tuberculosis, gonorrhea) or viral (influenza, papilloma);
- Traumatic lesions of the prostate occur with fractures of the pelvic bones, for example, with strong blows to the groin crotch. Prostate injuries can be caused by bougienage of the urethra, improper massage of the prostate and other diagnostic procedures performed in violation of the rules.
You can find out more about the causes of prostate pain here.
Symptoms
The main symptom of prostate disease is pain. They can have different localization and severity, but most often pain is observed in the genitals, in the scrotum, in the pubic area, and in the lower abdomen.
Sometimes a man experiences pain in the areas of the sacrum, rectum and kidneys. Unpleasant sensations intensify after urination and sex. The nature of the pain can be short-term shooting, constant aching and cutting.
With a prostate infection, a man experiences general malaise, weakness, lack of appetite, and body temperature rises.
Prostate adenoma and the presence of stones in the prostate gland are characterized by an increased urge to urinate with a simultaneous decrease in fluid secretion. Over time, a man needs more and more effort to empty his bladder.
REFERENCE! A urologist diagnoses and treats prostate diseases. The science that studies the functioning of the prostate gland and its disorders is called andrology.
Prostate diseases
The following prostate diseases in men are distinguished:
- Prostatitis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the prostate gland. It can be either infectious or non-infectious in nature. Non-infectious prostatitis occurs due to stagnation of prostate secretions or due to circulatory disorders. Infection in the prostate gland is a consequence of sexually transmitted diseases, and can also occur as a complication of systemic infections.
The development of prostatitis leads to complications:
- fibrosis. Characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue. The disease causes the prostate gland to put pressure on the urinary tract and make it difficult to empty the bladder;
- cyst. A fluid-filled cavity that occurs in the prostate tissue. The fluid may be sterile or infected;
- scarring. They are a consequence of infectious lesions (especially sexually transmitted ones).
- abscesses are purulent formations that can lead to sepsis during their development.
The listed disorders are caused not only by prostatitis. They can also arise due to other pathogenic factors.
-
BPH. Another name is benign prostatic hyperplasia. The diseased prostate increases in size. It may be a consequence of prostatitis, or it may have a nature independent of it.
The exact causes of prostate disease in men have not yet been established. The chance of developing an adenoma increases significantly with age and reaches 20% by the age of 50-60. This connection is explained by hormonal changes in the body as it ages.
ATTENTION! The main danger of the diagnosis for a person is that the prostate, as it enlarges, increasingly compresses the urinary canals, which leads to dysfunction of the bladder and kidneys.
There are three stages of prostate adenoma:
- at the first stage, the stream of urine becomes sluggish, and the urge to urinate becomes more frequent, but there is no liquid left in the bladder, it empties completely;
- in the second stage, urination becomes even more difficult, and the bladder no longer empties completely. Kidney failure develops;
- at the third stage, the bladder is greatly stretched, urine is released drop by drop, and blood appears in it.
- Stones in the prostate. They arise due to stagnant processes in the gland or due to urine entering it. The composition of stones can be urate, phosphate, calcium. Read our article about calcifications. The symptoms are similar to those of prostatitis: pain, decreased libido.
- Prostate tuberculosis is a disease of the prostate gland, which is characterized by pain and a decrease in the size of the gland. Caused by the entry of Koch's bacillus through the urinary tract or other means.
- Prostate cancer. Unlike adenoma, it is a malignant formation. During its development, it gives metastases, leading to human death. Treatable in the early stages.
Prostate diseases in men can be treated with physical exercise, conservative and surgical methods.
REFERENCE! Physical activity is useful because it improves blood circulation in the pelvic area and improves the flow of gland secretions. Particular attention should be paid to squats, bending, running and other exercises that involve the legs and pelvic muscles.
Conservative treatment of prostate disease involves taking medications. For infectious diseases, antibiotics and antiviral drugs are taken. For other inflammations, alpha-1 adrenergic blockers, hormonal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and herbal medicines are prescribed.
Surgical methods vary in their invasiveness. Transvesical adenectomy is the most effective, but also the most difficult method.
- It provides a reliable cure for adenoma, but requires a long recovery of the body.
- Also in modern surgery, adenoma is eliminated using a laser.
- It is performed without incisions, as the high-frequency laser is directed into the prostate through the urethra.
Embolization is another minimally invasive method. During this operation, the vessels of the prostate are blocked with medical polymers.
Other non-surgical methods include cryodestruction, ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, and thermotherapy.
Consequences
If infectious lesions of the prostate are not treated, the disease can spread throughout the body and cause serious systemic complications. Tuberculosis has the greatest likelihood of developing systemic complications.
IMPORTANT! Prostatitis can become chronic and lead to the appearance of cysts, abscesses and adenomas.
If the adenoma develops to the third stage, then there is a possibility of developing kidney failure and rupture of the bladder, and this is deadly.
In general, all problems with the prostate are very unpleasant for a man, since even in the absence of serious complications they significantly worsen his quality of life.
Prevention
To minimize the likelihood of developing prostate diseases, you need to:
- strengthen immunity;
- lead a moderate and orderly sex life;
- get checked regularly for STDs;
- exercise;
- to eat healthy food;
- minimize stress.
- Do not delay emptying your bladder for a long time.
Source: https://samec.guru/zabolevaniya/urologiya/zabolevaniya-prostaty
Prevention of the prostate gland
Content:
- Prevention of prostate diseases
- Controllable causes of prostate disease
- Nutrition
- Sex life
- Tobacco smoking
- Taking hormonal medications
- Preventive actions
- Proper nutrition
- Physical exercise
- Regular sexual activity
- Weight loss
- Examination by a specialist
- Sexual hygiene
- Warm
Diseases of the prostate (prostate gland) are much more common than other male ailments. According to statistics, this disease affects more than half of men of retirement age, and also affects about a third of the working-age male population.
Without professional help, prostate disease can develop into cancer. In some cases, no treatment can help. To avoid such an outcome, it is necessary to think about the state of your own health as early as possible, and also take all possible measures to prevent prostate diseases.
Controllable causes of prostate disease
There are a number of factors that can negatively affect men's health. They need to be known and taken into account for better implementation of preventive actions. These factors include: Ecology.
The most susceptible to the development of prostate diseases, as well as concomitant cancer diseases, are men whose profession is associated with hazardous industrial production. Also at risk are males engaged in agriculture, welders, mechanics, etc.
In this case, the option of the negative influence of the environment in which a person regularly lives, and not other other factors, is considered.
Nutrition
It has been established that excessive saturated fat content in food can negatively affect men's health, as the risk of prostate diseases increases. According to statistics, men who consume foods or various dishes that are high in calories and high in fat are most likely to develop prostate cancer.
Sex life
You need to be very careful about your sex life.
A large number of sexual partners is likely to lead to various sexually transmitted diseases, and this in turn increases the risk of developing prostate cancer.
A man who has had a sexually transmitted disease at least once has a much greater risk of developing prostate cancer than those who have never been infected or sick with anything like that.
The more sexual partners a man has during his life, the higher the risk of developing prostate disease. According to statistics, even males who have two or three sexual partners in their lives are much more likely to develop prostate cancer than a man who has only had one sexual partner.
There is also research that shows that men who have sex with more than thirty partners are more likely to develop more severe prostate cancer.
Tobacco smoking
Among smokers, many more young people are prone to developing prostate cancer. Among men under 60 years of age who underwent surgery to remove the prostate gland due to cancer, the majority were smokers.
Taking hormonal medications
When consuming large doses of DHEA, there is a risk of enlargement of the prostate gland, as well as the formation of a malignant tumor. DHEA supplements are often used as drugs to slow down the aging process, reduce weight, increase muscle size, and also as immunostimulants. But the positive effect of these drugs has not yet been identified.
Preventive actions
There are several principles that, if followed, will help maintain the normal functioning and health of the prostate gland, as well as the entire male body.
Proper nutrition
Eating healthy foods and eating properly can minimize the risk of developing prostate disease.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of foods high in fat, and you should also strive to ensure that the majority of your diet consists of plant foods.
But don't exclude unsaturated fats. They are the basis for the body’s production of useful enzymes, which reduce the risk of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland.
Products with a large amount of unsaturated fats are: sea fish, as well as olive and flaxseed oils.
Other vegetable oils contain Omega-6 (fatty acids), which, on the contrary, should be excluded from the main diet.
It is also necessary to completely avoid foods that negatively affect the condition of the kidneys. These include very spicy or salty foods, alcoholic drinks, and caffeine.
Eating enough fruits and vegetables has a positive effect on the functioning of the prostate, not necessarily every day, but it is advisable to consume them as often as possible, as well as some other foods that can maintain men's health:
- Tomatoes. This vegetable is high in the antioxidant lycopene, which gives tomatoes their bright red color. Dishes prepared with tomatoes, tomatoes themselves, and other foods containing lycopene can reduce the likelihood of developing prostate cancer. When cooked, foods containing lycopene have much higher protective properties than when eaten raw.
- Soy. Isoflavones, which are contained in soy and soy foods, have a positive effect on maintaining optimal levels of the hormones testosterone and estrogen. Soy is useful as a product that protects against the formation of prostate cancer, because prostate diseases develop due to too active testosterone, and soy products reduce the risk of cancer.
- Green tea. Green tea contains a substance called epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which is similar to polyphenols found in vegetables and red wine. EGCG is considered an antitumor substance that prevents the development of enzymes that form a malignant tumor.
- Garlic. This product contains a huge amount of sulfur, which helps strengthen the human immune system. It also provides the body with enzymes that block the formation of tumors, thereby reducing the rate of cancer development.
Physical exercise
The main principle of physical exercise is not the amount of load on the muscles, but the regularity of exercise
Men who lead a predominantly sedentary and sedentary lifestyle most often suffer from various diseases and inflammatory processes in the prostate gland. That is why it is necessary to devote enough time to physical activity and do exercises regularly.
For the prostate gland, exercises that involve the pelvis, buttocks and lower limbs are considered the most beneficial. The main principle of physical exercise is not the amount of load on the muscles, but the regularity of exercise.
There is a set of exercises that are used as one of the stages of treating the disease, as they help reduce pain if the disease is already present, and are also an excellent prevention of prostate diseases:
- Exercise No. 1. It is necessary to take a sitting position, squeeze your knees and draw in your stomach. Maintain this position for some time. You need to do at least 50 repetitions. Then rest for about 15 minutes.
- Exercise No. 2. In a lying position, raise your legs about 30 degrees and try to hold them in this position for as long as possible. The exercise should be repeated several times a day.
- Exercise No. 3. Moving on the floor on the buttocks. You need to sit on the floor and straighten your legs in front of you. Next, use your gluteal muscles to move along the floor without touching it with your hands.
- Exercise No. 4. Squats. You need to bend forward a little and put your hands on your knees, resting on them. Then squat down, get up and straighten up. Several repetitions are necessary.
Regular sexual activity
The prostate gland belongs to the group of genital organs; therefore, an important condition for maintaining its health is regular sex.
If this condition is not taken into account as a prevention of prostate diseases, then this can lead to stagnation of prostate secretions, which can lead to the onset of inflammatory processes in the gland and the development of various diseases.
During orgasm, blood vessels dilate and blood circulation in the prostate gland increases. In addition, regular sex has a healing effect on the entire body as a whole.
It helps increase the level of immunoglobulin, which provides the body with antitumor immunity. The number of sexual acts for each is determined individually. But on average, sex should not be less than twice a week.
Weight loss
According to statistics, men with prostate diseases in most cases had extra pounds. Too large a percentage of adipose tissue in the human body quite significantly reduces the level of male sex hormones. This often causes the development of prostate diseases.
Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor your weight, control it by adhering to proper nutrition and regular exercise or exercise.
Examination by a specialist
All men need regular examination by a urologist. This is especially true for older men, that is, after forty years. One visit to the doctor per year is enough.
This should be done to identify any inflammatory processes and diseases of the prostate gland in the early stages in order to be able to start treatment on time. You need to be very careful about your health.
Even if there are no symptoms or they seem minor, you should not ignore it. At the first suspicion of problems with the prostate gland, you should seek help or advice from a qualified specialist who, if necessary, will prescribe treatment.
In no case should you engage in self-diagnosis of the disease and its treatment, as this can lead to a deterioration in the general condition, as well as to irreparable consequences.
Sexual hygiene
It is necessary to be very careful about the choice of sexual partners, as well as their number. Unprotected sex can lead to many different sexually transmitted diseases and infections.
And this will negatively affect the health of the prostate gland, as various inflammatory processes may develop.
That is why it is preferable to choose a permanent and trusted sexual partner.
Prostate diseases are very common in men who prefer winter fishing
Warm
Cold has a strong negative effect on the prostate gland. In the cold, blood vessels narrow, which leads to poor blood circulation in the prostate gland.
Prostate diseases are very common in men who prefer winter fishing. It is very important to always ensure that there is no hypothermia.
You need to dress as warmly as possible in the winter season, wear the warmest, waterproof shoes possible.
By following a few easy-to-follow rules and recommendations, you can achieve a good result, namely high-quality and long-lasting functioning of the prostate gland. It is always better to use preventative measures than to waste time, money and nerves on treating the disease.
Source: https://funkit.ru/predstatelnaya_zheleza/profilaktika-predstatelnoj-zhelezy.html
Symptoms of major prostate diseases
Symptoms of prostate disease in men appear against the background of infections, hormonal imbalance, genetic predisposition, age and congestion in the genitourinary tract.
The most common disease is prostatitis.
This is inflammation of the prostate gland of various etiologies. In addition to prostatitis, men can suffer from other diseases of this organ.
Among them are prostatic vesiculitis.
Only men can suffer from prostatitis, since women do not have this organ. However, they have a vestigial gland - the skin, which is located in the distal third of the urinary canal.
Its inflammation leads to a disease called skineitis, which causes similar symptoms.
Types of prostatitis
The American National Institute of Health has developed a classification of types of prostatitis .
According to her, this disease occurs :
The second, in turn, is divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory .
Inflammatory prostatitis manifests itself in an increased content of leukocytes in the secretions of the prostate gland. Its other name is chronic inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome.
Non-inflammatory prostatitis does not cause such symptoms. It is called chronic non-inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome.
An acute form of bacterial prostatitis appears when various pathogens enter the prostate (Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, Proteus, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus). These microorganisms are opportunistic, which are found in the natural microflora of the digestive tract and on the skin.
When the immune system weakens for some reason and the appropriate conditions exist, bacteria can provoke acute inflammatory processes in the prostate. This form is much less common than the chronic form.
Clinical picture
In the acute form of prostatitis in men, symptoms of general intoxication of the body occur quite often . He feels weak in the body, fever, shivering, headaches, and aches in the joints. This is accompanied by severe pain in the groin, perineal area and during trips to the toilet. Prostate diseases are characterized by rare or frequent urination.
The appearance of a chronic form of prostatitis can be triggered by genetic causes. Frequent hypothermia, prolonged abstinence from urination, and long breaks in sexual activity lead to the disease. The risk group includes men who move little, have various diseases of the genitourinary system and pathologies that are sexually transmitted.
Chronic prostatitis in most cases has a hidden development . It is not always accompanied by any symptoms. The disease may not manifest itself for several years. At a certain point, an exacerbation occurs, after which the symptoms subside, and later recur with renewed vigor.
A man may feel a frequent urge to urinate, which can cause discomfort and does not bring noticeable relief. Another symptom is pain in the suprapubic region and groin. In addition, prostatitis negatively affects erection and causes huge problems during sexual intercourse.
Often men suffer from chronic prostatitis of non-bacterial origin . The pathology can appear at different ages, but most often it affects people over 30 years of age. This form of the disease also causes frequent urination in small portions, pain and problems with erection. Symptoms and treatment of the pathology depend on its severity and causes.
Video: “Pathogenesis of prostatitis”
Course of vesiculitis
Another disease in men is vesiculitis . This is an inflammatory lesion of the seminal vesicles. It occurs mainly as a consequence of prostatitis, urethritis and other diseases. Vesiculitis rarely appears on its own. This pathology, like prostatitis, can be acute or chronic. It is provoked by the pathogen entering the posterior urethra, genital tract and prostate area.
Vesiculitis is manifested by pain in the groin , which intensifies during bowel movements and radiates to the rectum. During ejaculation, a man experiences severe pain, and blood clots are present in the semen itself.
At the same time, sexual intercourse becomes more complicated, since vesiculitis is characterized by rapid ejaculation. With a chronic form of the disease, the symptoms vary.
Pain can be felt in different places and in different situations, which is associated with the severity of the disease and its causes.
Development of adenoma
Prostate adenoma causes hyperplasia and an increase in the size of the organ . This is not a tumor in the strict sense of the word. It appears in men over 50 years of age.
At this age, a quarter of the stronger sex suffers from adenoma, and by the age of 65 this is already half. Over the years, the likelihood of getting sick increases rapidly. This problem negatively affects a man’s quality of life.
Significant restrictions appear in sexual relations and in usual daily activities.
With an adenoma, the functions of the bladder are impaired , and a frequent urge to urinate appears, which can be so strong that the man cannot stand it.
It happens that a person is not able to empty the bladder without strong strain. The flow of liquid becomes weak and intermittent.
After the process itself, urine is released from the urethra in small drops for a long time, and the man does not feel complete relief.
Prostate adenoma develops slowly. An exacerbation can be caused by hypothermia, alcohol abuse, nervous overload, and the development of a chronic form of prostatitis. How much the patient suffers from difficulty urinating depends on the degree of hyperplasia and its direction.
The severity of the disorders in the bladder itself matters. An enlarged prostate in the middle lobe can create a kind of valve, which will become an obstacle to the removal of urine from the body. If hyperplasia is observed in the lateral sections towards the rectum, then no such symptoms may appear for a long time.
Adenoma develops in 3 stages.
At the first stage, the patient feels a weak urinary stream, frequent and strong urges at night, and difficulties when trying to urinate. At the second stage the jet becomes weak. About 1/2 of the volume of liquid drunk remains in the body, and stagnation develops. Kidney function may be impaired.
At the last stage, paradoxical ischuria appears, which is characterized by overfilling of the bladder and loss of muscle tone. The man completely loses the ability to urinate. The fluid comes out of the urethra on its own in small drops. In this case, a strong expansion of the urinary canals occurs.
Oncological pathologies
Under the influence of certain factors, a man may develop prostate cancer . More often it originates in the peripheral zones of the organ, less often in the central and transitional parts. More than 2/3 of all men after reaching 80 years of age suffer from various forms of this disease.
The likelihood of getting sick increases if close people have the same diagnosis. The more relatives there were affected by the disease, the greater the chance of getting sick yourself. The influence of human diet on the development of cancer is controversial. According to some observations, men who consume a lot of animal fats and are overweight are more likely to get sick.
It is important to identify this disease before its symptoms occur . The presence of noticeable manifestations may mean that the process is very neglected.
Medicine has reliable diagnostic methods that make it possible to determine the diagnosis at an early stage.
The symptoms themselves begin to appear in the later stages of the disease, when metastases already appear in the lymph nodes, bones, lungs or liver.
At a certain stage, a man begins to suffer from urinary problems and urinary incontinence. Blood clots appear in seminal fluid and urine, and impotence occurs.
This is all accompanied by constant discomfort in the lower abdomen and lower back. If the cancer has metastasized, then pain in the bones may occur, and the legs begin to swell due to stagnation of lymph. In especially severe cases, paralysis of the lower body may occur due to pinching of the spine.
With a severely advanced disease, cachexia, anemia, lack of appetite, and severe loss of strength can occur.
Development of sarcoma
A rare disease in men is sarcoma . It is more common at younger ages.
Half of the cases are observed in children, young people are less at risk and older men are slightly more at risk. According to histology, fibrosarcoma, lymphosarcoma and myosarcoma are distinguished.
They are the most common. Less common are myxosarcoma, chondrosarcoma and rhabdomysarcoma.
At the initial stages of the disease, symptoms are not detected or make themselves felt by minor urinary disorders. Often, due to compression of the urinary tract by a tumor, men experience acute urinary retention .
In the later stages, sarcoma grows into adjacent tissues and metastases appear. At the same time, cachexia begins, pain in the lower abdomen and perineum. Examination of the prostate through the rectum shows a woody density of a lumpy or smooth nature, while the prostate is slightly painful.
Video: “What prostate diseases are there?”
Other organ pathologies
In some cases, stones may form . They are primary and secondary, mostly round and measure about 2.5 cm in diameter.
The stones themselves do not often cause noticeable symptoms, but can serve as favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogens of other diseases.
This disorder is called calculous prostatitis , which tends to worsen frequently.
In the chronic course of the pathology, a person feels pain above the pubis, in the perineum and sacral area after ejaculation or physical exertion. They often radiate into the penis and scrotum. Blood appears in the seminal fluid, and the man feels a frequent urge to urinate.
Fibrosis or sclerosis of the prostate gland is characterized by shrinkage of connective tissues, which increase in size. In this case, the prostate compresses the urinary and vas deferens, the neck of the bladder and the ureters. This causes problems with urination and disorders of the reproductive system.
As the disease progresses, problems with urination worsen, and dysfunction of the genitourinary system appears. In the most advanced stages, terminal changes occur in the kidneys, ureters, bladder and vas deferens.
With a prostate abscess, a small area of purulent tissue damage appears. This disease can be primary or secondary. The primary form occurs when the infection is transmitted through blood from other places, and the secondary form is a consequence of infectious prostatitis, which is the most common cause of the disease.
Men with weakened immune systems and diabetics are most susceptible to abscesses. The disease can cause congestion in the pelvic veins and severe hypothermia.
In this case, the disease is manifested by symptoms of general intoxication of the body, such as fever, loss of strength and chills.
If the prostate gland is affected, symptoms of the disease may be as follows: discomfort in the lower abdomen, problems with urination, retention of feces and gases.
Empyema of the seminal vesicle
A rare type of prostate disease in men is empyema seminal vesicle . It is characterized by purulent lesions and can be a complication of acute or chronic forms of vesiculitis. Symptomatically, the male disease manifests itself in the form of general intoxication with increased body temperature, painful sensations in the rectum and perineum. Other signs of pathology are also possible.
A man experiences pain during ejaculation, problems with urination, and spontaneous ejaculations with purulent and bloody inclusions. On rectal examination, a pronounced formation is observed, which causes severe pain and has an elevated temperature. After such a pathology of the prostate is detected in men, a surgical operation is performed, opening the seminal vesicle and pumping out the pus.
It is difficult to diagnose tuberculosis of the prostate gland . This pathology is actually not detected during laboratory tests and clinical examinations. Very often it accompanies pulmonary tuberculosis and is extremely rarely diagnosed during the patient’s lifetime, since there are no signs of the disease.
A phthisio-urologist diagnoses and treats prostate tuberculosis. Symptoms of the disease include difficulty urinating and pain.
In the analysis of urine and prostate secretions, a large number of leukocytes and the presence of red blood cells can be detected. The difficulty for diagnosis is the very rare identification of the causative agent of the disease.
This is caused by long-term use of antibacterial drugs.
More often, the pathogen is detected in tests of rural residents, since city residents are more susceptible to self-medication with antibacterial agents . In most patients, this male disease occurs together with nephrotuberculosis.
Sometimes tuberculous lesions of the testicles and their appendages are noted. More often, genitourinary tuberculosis and concomitant damage by its pathogen to many body systems are detected.
Only in a twentieth of patients, prostate tuberculosis is localized in one place.
Conclusion
The prostate gland is a sensitive organ found only in men. He is susceptible to a large number of diseases.
One of the most common is prostatitis, which in turn can contribute to the development of many other serious diseases - adenoma and prostate cancer. Such diseases are asymptomatic and the presence of manifestations indicates advanced forms.
Therefore, it is very important to diagnose them in the early stages, which can only be done by a specialist when examining the patient.
Source: https://kakbyk.com/simptomy/simptomy-osnovnykh-zabolevanij-predstatelnoj-zhelezy.html