Prostate adenoma (abbreviated prostate adenoma ) is now more commonly referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia ("BPH").
The initial stage of the disease is the appearance of a small nodule or group of nodules on the gland. As the disease progresses, they rapidly increase in size and number. Unlike cancer, an adenoma does not metastasize to other organs, that is, it is a benign tumor. This urological disease is most often diagnosed in men over 50 years of age.
Causes
The causes of prostate adenoma in men have not yet been clarified. The only thing that has been proven and beyond doubt is the direct connection between age and the presence of the disease.
As men age, the function of producing testosterone, which is the main male hormone, is disrupted, and estradiol estradiol (a hormone that can stimulate an increase in the speed and intensity of reproduction of prostate cells) begins to be produced in large quantities. Thus, the closer the critical age of 50 years, the higher the likelihood of diagnosing prostate adenoma in men.
It has been proven that the following factors provoke the occurrence of the disease; their presence significantly increases the risk of disease:
- inactivity, a sedentary lifestyle and excess weight - these circumstances contribute to the accumulation of excess adipose tissue - in which estrogens are produced, disrupting the balance of testosterone and estrogen in a man’s body;
- poor heredity - if among your immediate relatives there were patients diagnosed with prostate adenoma, then the risk of the disease increases;
- frequent inclusion of the wrong foods in the diet, abuse of fast food and processed foods, content in the diet of a large amount of food with spices, fried and fatty foods.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma
In men, the symptoms of the disease vary. Their development and manifestation are influenced by the progression of the disease, the age and social status of the patient, as well as his mental and somatic state.
The first characteristic sign of the disease is considered to be a delay in the initial stage of urination and the manifestation of a false urge to urinate. Along with these symptoms, an intermittent stream of urine is usually observed.
Over time, the alarming symptoms begin to intensify: the patient complains of problems with eliminating need. To urinate, you need to strain the abdominal muscles.
In the cavity of the bladder, residual urine is observed - the amount of urine that did not come out due to a decrease in the tone of the muscular lining of the bladder (detrusor). It consists of mutually intertwining layers, forming a single muscle.
Normal contraction of this tissue is an important indicator of men's health.
If left untreated at this stage of the disease, this symptom becomes predominant. This process is characterized by a decrease in the amount of urine emitted from normal to extremely scanty, the urine stream is sometimes reduced to a drop-shaped stream. In some cases, detrusor tension drops so much that the volume of fluid in the bladder becomes critical - more than a liter.
Treatment is often complicated by the fact that many patients consider the listed symptoms of prostate adenoma to be normal for their age and do not rush to consult a specialist. But against the backdrop of subsequent problems due to sexual dysfunction, men still go to see a urologist.
Obstructive and irritative syndromes of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Such signs are also called symptoms of irritation. These include frequent urination or an empty urge to urinate, and urinary incontinence. Often the patient is forced to go to the toilet at night - getting up 2 or 3 times to relieve himself. Such signs depend on the severity of the bladder muscle disorder.
Now science knows for certain that as a result of age-related hormonal changes in the body, oxygen starvation of the muscles of the pelvic organs greatly progresses. This condition is called bladder instability.
The listed irritative symptoms complicate a man’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and timely, high-quality treatment, they are least dangerous.
The difficulty is that the patient can simultaneously experience both irritative and obstructive symptoms of the disease. The classic clinical picture is characterized by the presence of both groups of signs.
When symptoms of prostate adenoma appear in men, the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the prostate has a great influence on the formation of the clinical picture of the disease.
With swelling of the prostate tissue, deterioration in the erectile function of the penis is often observed. Chronic prostatitis often manifests itself as urinary disorders.
The presence of this syndrome increases the number of postoperative complications in patients with different stages of disease development.
The ability to make an accurate diagnosis is often complicated by the fact that the clinical picture is also formed by pathological processes in the body that are not related to BPH.
It follows that not every patient needs surgery, given the fact that patients with moderate obstructive symptoms usually do not improve after surgery.
Stages of the disease
Experts divide the development of prostate adenoma into three stages:
- The compensated stage usually manifests itself in a slight increase in the organ. The changes have minor consequences: the boundaries of the prostate are clearly defined, palpation does not provoke pain. The density of the organ remains normal. The median groove is detected upon palpation. The patient does not exhibit residual urine retention.
- Subcompensated stage. It is characterized by severe enlargement of the prostate, to the point where it begins to have a strong impact on bladder function. The symptoms are as follows: portioned and incomplete emptying of the bladder, the walls of the bladder swell and become much thicker than the walls of the organ in a normal state, when the bladder is full, partial urination often occurs, which is uncontrollable.
Often the urine becomes opaque, cloudy, and sometimes sediment appears. In some cases, the urine contains a suspension of blood.
- Decompensated stage. This is an extreme degree of development of prostatitis. Patients have a critical volume of residual urine, urination is extremely difficult and occurs drop by drop, the bladder muscles are extremely weak due to a constantly enlarged condition. Often this stage is complicated by a lack of hemoglobin in the blood - anemia. The patient's breath smells of urine.
Diagnostics
After listening to the patient’s own complaints, the doctor begins to collect an anamnesis and begins to examine the state of health of the body. The first method used in drawing up a clinical picture is palpation and visual inspection.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the specialist resorts to ultrasound. It can be transrectal - to determine the exact problem area of the prostate, or include an external examination of the bladder - to determine the stage of development of the disease, you need to know the volume of residual urine.
The patient needs to undergo several tests:
- First of all, a general analysis of urine and blood is performed. It provides information about the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the body and clarifies the picture of the patient’s general health;
- The level of PSA (specific antigen) in the body - the level of its content in the body clearly indicates the presence or absence of malignant cells in the neoplasm;
- on creatinine level. This analysis is a qualitative indicator of the condition of the upper urinary ducts;
- The uroflowmetry method is a qualitative way to determine urinary problems and their causes.
Treatment of prostate adenoma in men
According to research results, treatment of prostate adenoma can be of the following types:
- medicinal;
- minimally invasive (another common name is HIFU therapy);
- surgical. (variations are possible here - transurethral resection of the prostate gland, laser intervention or vaporization).
Drug treatment (medicines)
Various medications are an effective method of combating the disease in the early stages of its development. The most well-known types of medications used in the treatment of prostate adenoma are considered to be:
- Alpha adrenergic blockers - their main function is to improve urine flow in case of prostate adenoma and relieve pain when urinating;
- blockers. Medicines of this type inhibit the production of the toxic hormone dihydrotestosterone - it has a detrimental effect on the process of its increase, speeding up this process many times over. Medicines, blocking the effect of this substance, make it possible to slightly reduce it. In some cases, this process is irreversible and persists.
Diet
In case of benign prostatic hyperplasia, the patient's diet should be carefully monitored. In addition, compliance with the rules below serves as a good prevention of this disease, and many others. It is necessary to use more often:
- a variety of fresh fruits, berries and vegetables;
- foods containing fiber;
- foods rich in unsaturated fatty acids;
- raw pumpkin seeds - they contain many substances beneficial to the male body.
And, on the contrary, you should reduce or completely abandon:
- red meat and rich bone broths;
- offal and entrails;
- easily digestible (“fast”) carbohydrates;
- legumes and peas;
- canned food, semi-finished products;
- alcohol;
- sweets, in particular chocolate in any form;
- hot seasonings and spices.
The patient’s diet must meet the main rule - you need to eat like any adequate person who is not indifferent to the state of his health.
Surgery
With prostate adenoma, it increases in volume - to a greater or lesser extent. The extent to which the size of the organ has changed corresponds to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and, accordingly, a change in his treatment plan.
The indicators of the universal scale of correspondence between the size of the tumor and the need for surgery are considered to be:
- 30-55 mm – surgical treatment is not necessarily required. Conservative treatment based on medication is possible;
- 40-60 mm in diameter - conservative treatment can be successful, but in combination with surgical removal of part of the prostate, possibly using laparoscopy;
- 60-80 mm – at such a scale of gland enlargement, operations are performed in 100% of cases.
Absolute and urgent indications for surgical intervention include:
- inability to relieve natural need even after catheterization of the urethral valve;
- persistently recurring extensive hematuria;
- chronic or acute renal failure;
- chronic inflammation of the genitourinary ducts, or acute development of such conditions;
- diverticula of the pelvic muscles;
- stones in the bladder or one (both) kidneys.
Complementary and alternative treatments at home
Often, so-called alternative treatment methods are used in the treatment of prostate adenoma. They are either homemade or non-traditional. Sometimes such methods give good chances.
Among the recipes of traditional healers and connoisseurs, the most popular are the following:
- infusion of birch leaves. 2 tablespoons of fresh or dried leaves are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water, left for two hours and taken half a glass three times a day before meals.
- burdock root decoction. To do this, steam 2 tablespoons of roots in boiling water for three to four hours and drink 0.5 cups several times a day.
- onion heads. Sometimes, to relieve the symptoms of inflammation, it is enough to eat one head of fresh onion;
- pumpkin seeds. It is necessary to consume the peeled seeds of this plant every day.
The use of these methods should not be independent - individually they will not bring the desired result, and may even do a poor job - with self-medication, you can skip the development of the disease and skip the stage at which it is still possible to solve the problem without surgical intervention. However, when combining alternative and traditional remedies prescribed by specialists, a good treatment result is possible.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence and development of prostate adenoma in men, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. It will be useful to take the following measures:
- engage in physical education. A few minutes of exercise a day will help prevent congestion;
- adhere to the correct diet;
- monitor your body weight. The risk of prostate adenoma is directly proportional to the increase in body mass index and the appearance of excess fat deposits;
- visit a urologist annually for examination;
- avoid hypothermia;
- try to defecate at the first urge, do not create situations in which the bladder or intestines are full.
Forecast
The prostate gland in men is treated if the problem is detected at an early stage. But in advanced cases, when the disease has not been recognized for a long time, the quality of life deteriorates sharply. One should not lose sight of the moral and ethical side of the issue.
With timely consultation with a specialist, correct diagnosis and strict adherence to the treatment plan, the prognosis is very favorable.
But when the disease is detected in the later stages, experts give a sharply positive prognosis. The diseases are complicated by concomitant chronic infections of the genitourinary system, the formation of stones, sand and other deposits in the bladder and kidneys.
Do not forget that there is always a risk of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one - prostate cancer. It is this risk that is the fundamental factor in the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Prevention and timely detection of diseases of the genitourinary system, including benign prostatic hyperplasia, is an important part of maintaining the health of the male body.
It should be remembered that only careful care of your own health, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and, if necessary, strict adherence to doctor’s instructions significantly increases your chances of living a life free from diseases and disorders.
Videos on the topic
Source: https://tvojajbolit.ru/urologiya/adenoma-prostatyi-adenoma-predstatelnoy-zhelezyi-prichinyi-simptomyi-i-lechenie-u-muzhchin/
Features of prostate adenoma in men
Prostate adenoma in men, according to its morphological characteristics, is a benign process of proliferation of prostate tissue.
In other words, an adenoma is hyperplasia, which implies excessive growth and division of prostate gland cells. The tumor is benign, but in some cases it can become malignant.
Prostate adenoma is dangerous due to its complications, which affect many systems of the male body.
Causes
All representatives of the stronger sex are interested in what causes prostate adenoma in men and whether it is possible to avoid the onset of the disease.
The prostate gland consists of many small glands united by ducts; between the glands there are layers of smooth muscle and connective tissue that form the stroma (base) of the organ. Hyperplasia of prostate tissue leads to a significant increase in its volume.
The pathogenesis of prostate adenoma is based on the following processes:
- Testosterone through 5 alpha reductase is transformed into a metabolite - dihydrotestosterone, which in turn penetrates into the cells of the prostate gland, binds to the nucleus and provokes excessive division of glandular elements.
- In smooth muscles, the number and activity of alpha-adrenergic receptors increases, which leads to spasm.
- The proportions of testosterone and estrogen are disrupted, which leads to the proliferation of connective tissue at the base of the organ.
- Impaired blood flow in the prostate gland due to age-related and pathological changes leads to changes in microcirculation and varicose veins.
The development of hyperplastic processes of the prostate gland in adulthood and old age is inevitable.
But the pathological process can be prevented or stopped at the first stage with the help of medications and timely diagnostic tests.
Age-related prostate adenoma develops regardless of the presence of pathologies such as sexually transmitted infections, smoking, and diabetes mellitus.
Acceleration of the development of hyperplastic processes in the gland can be provoked by irregular sex life, stagnant processes in the pelvis.
If the emptying of the prostate glands occurs irregularly, preconditions for stagnant processes arise.
In addition, impaired microcirculation in the pelvis due to various diseases and a sedentary lifestyle also leads to accelerated development of adenoma in men.
Symptoms and signs
The first signs of prostate adenoma are initiated by compression of the urethra. How does prostate adenoma manifest itself, and by what signs can one suspect the disease? Hyperplasia is described by two types of symptoms:
- obstructive;
- irritative.
Obstructive signs mean the presence of symptoms of adenoma due to compression and narrowing of the urethra:
- urinary retention - the appearance of a stream after straining;
- lethargy, weakening of the stream;
- a feeling of incomplete emptying, intermittent urination, dripping of urine at the end.
Irritative symptoms mean the appearance of changes due to irritation of the bladder sphincter:
- false urges;
- increased urge during the day and at night;
- pain syndrome.
Important!
The normal number of urinations per day is 4-6, but with prostate adenoma it increases to 20-25 times.
At night, the urge to go to the toilet normally does not bother men. The first sign of illness is often the need to get up at night. Often prostate adenoma occurs against the background of prostatitis - inflammation of the gland in men.
In addition, prostatitis often becomes a complication of hyperplasia. It is not easy to differentiate the symptoms of prostatitis and prostate adenoma in men, since anatomically these two processes affect the same areas.
Signs of prostatitis and prostate adenoma occurring simultaneously, in addition to impaired urination, are described by fever, impotence, urethritis, pain in the rectum, perineum, especially in a sitting position.
Source: https://prostatitaid.ru/adenoma-prostaty/o-zabolevanii-adenomy/u-muzhchin.html
About the symptoms of prostate adenoma in men
Prostate adenoma is a benign hyperplasia (overgrowth) of glandular, fibrous (read about prostate fibrosis) or muscle tissue (true, fibroadenoma and myoadenoma, respectively).
At the same time, the increase in the mass of the gland sometimes amounts to more than 200 g. At the initial stage, the growth process can be stopped using conservative therapy methods. The difficulty of early diagnosis is that the symptoms of prostate adenoma depend on the direction of its growth.
Often, hyperplasia is detected in the later stages during an examination for a completely different reason.
Groups of adenoma symptoms
The appearance of adenoma is mainly typical for men after 50 years of age.
Under the influence of hormonal changes in the body, iron loses its functionality and increases in size (therefore, for older men, an increase in PSA to 6 ng/ml is normal).
In young men, adenoma rarely develops, usually as a consequence of underlying endocrine pathology. In old age, symptoms are more pronounced as the compensatory functions of organs decrease.
The formation of an adenoma begins with a small nodule, which grows over time, absorbing more and more functional prostate tissue, displacing it to the walls of the gland capsule. Gradually, the prostate becomes a solid adenomatous node, which puts pressure on neighboring organs, provoking certain symptoms.
Signs of adenoma appear depending on the prevalence of the process and the duration of its course. Main groups of symptoms:
- Pathological changes in the lower urinary tract;
- Disorders of the kidneys and upper urinary tract;
- Complications of adenoma.
The prostate is closely connected to the bladder, so symptoms are primarily related to urination. Adenomatous nodes sooner or later begin to put pressure on the prostatic part of the urethra, causing blockage of the urethra under the bladder - at this time the clinical picture of the disease appears. Symptoms are caused by two factors:
- Static – mechanical compression of the urethra. Causes obstructive symptoms of adenoma.
- Dynamic – irritation, hyperactivity of alpha receptors of the bladder neck. Provokes impaired reflexes.
The main components of the clinical picture of adenoma
Due to compression of the urethra, problems arise with emptying the bladder: the stream is sluggish, periodically interrupted . To push urine out, you have to push, and in the end drops come out for a long time.
However, these problems do not begin immediately. The first sign is an increase in the time of urination, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
This happens when you have to endure the urge for too long, and then the process of urination becomes forced: urine has to be pushed out in portions.
The second group of symptoms is associated with impaired functionality of the walls of the bladder and the contractility of its muscles. Normally, urine should not stagnate for a long time, but due to the compressed urethra, complete and timely emptying does not occur.
In response to this, the bladder detrusor (the muscle that expels urine) becomes hyperactive and fires even when it is only slightly full.
As a result, the urge to urinate becomes unreasonably frequent (pollakiuria) and practically uncontrollable (impossible to adequately tolerate).
One of the leading symptoms of adenoma is urination more than 3 times at night (nocturia). However, in older men, this can also occur due to weakened kidney function. Gradually their concentration ability decreases.
How often do you urinate at night?
Source: https://muzhchina.info/prostata/adenoma/simptomy-dgpzh
Prostate adenoma (Prostatic hyperplasia)
In modern medicine, the growth of the prostate gland due to active tissue growth is called prostate adenoma .
Although some experienced specialists and older patients still use terms such as prostate adenoma or urinary retention.
To be fair, we note that this name has another synonym: benign prostatic hyperplasia (hereinafter referred to as BPH).
In any case, the essence of the disease is an increase in the size of the prostate, which leads to the appearance of nodes in it that interfere with normal urination. Benign nature implies the absence of metastases , which distinguishes the disease from prostate cancer.
Prostate adenoma is rightfully considered a disease of older men. Every second man by the age of 50 experiences problems with urination, which, after examination by a specialist, are attributed to this disease.
The incidence increases with age, and by the age of 70, three out of four men experience the same problems. According to medical research, at most 15% of men are not susceptible to BPH.
At the same time, the likelihood of the disease increases every year.
Causes of prostate adenoma
All causes of prostate adenoma can be divided into two groups.
The first group includes reasons due to a person’s lifestyle, which increase the likelihood of prostate enlargement. For example, this could be sedentary work or active mental stress in the absence of physical activity. That is why the role of regular physical exercise cannot be overestimated.
The second group includes objective reasons that do not depend on a person’s lifestyle. It has been proven that prostate adenoma occurs due to changes in the hormonal background of a man. If we consider that these changes inevitably occur in old age , we can come to the conclusion that only some men are lucky enough to avoid problems with the prostate gland.
To be fair, it is worth noting that the causes of prostate adenoma are still not fully understood. Scientists regularly conduct research aimed at identifying correlations with other diseases or with the characteristics of a person’s personal life, but so far all these studies have not yielded significant results.
Although, for example, it was possible to refute the opinion that prostatitis and prostate adenoma are interconnected. As statistics show, both diseases can occur completely independently or, on the contrary, simultaneously.
Therefore, despite the various hypothetical causes of prostate adenoma, the only proven factor that increases the risk of incidence is age.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma
Initially, when the canal just begins to narrow under external influences, the first symptoms of prostate adenoma appear. They consist of a change in sensations when urinating. Healthy men experience a pleasant sensation when emptying their bladder, and this is quite normal. The disappearance of these sensations can serve as the first alarm bell.
Unfortunately, men tend to attribute detected changes to anything other than an illness, so at the first stage they rarely turn to doctors. Meanwhile, BPH progresses to the next form. More noticeable symptoms of prostate adenoma appear.
In particular, a noticeable contraction of the urethra leads to a decrease in the force of the jet. When there is little urine (in the final stages of emptying), it becomes vertical or even breaks up into separate drops.
Naturally, the bladder is not completely emptied. The patient has to strain the abdominal muscles, thus squeezing the bladder, and the urine remaining there will, after a short time, cause another urge to urinate.
These are also the main signs of prostate adenoma.
If left untreated, new symptoms similar to enuresis . Thus, a man can no longer go without urinating at night, and the time he can “tolerate” is significantly reduced, up to complete incontinence.
The importance of timely contacting a specialist when the first signs are detected is also due to the fact that without proper treatment, prostate adenoma can have serious complications, which will be discussed further.
Complications of prostate adenoma
As you understand, prostate adenoma leads to problems with urination. And this, in turn, causes a serious blow to the kidneys.
Their gradual defeat can be manifested by frequent headaches, irritability, constant thirst and a feeling of dry mouth.
The fact that urine lingers in the bladder for too long significantly increases the likelihood of developing urinary tract infections, such as pyelonephritis , urethritis and others, as well as the appearance of urolithiasis .
It must be admitted that these are by no means the most terrible complications of prostate adenoma. Unimpeded development of prostate nodes can lead to complete occlusion of the urethra.
In this case, urine accumulates in the bladder with no outlet, which results in severe pain and a threat to life for the man.
If such signs occur, a catheter is installed to drain urine or, in case of urgent need, immediate surgery is performed.
The danger is that complete closure of the urethra can occur even in the initial stages of the disease. It all depends on a certain combination of provoking factors, such as hypothermia , alcohol abuse , abstinence from urination and others.
Unfortunately, these are not all complications of prostate adenoma. Sometimes an overgrowth of the prostate gland leads to blood in the urine .
The difficulty in diagnosing this complication lies in the low concentration of blood, which cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Therefore, taking a urine test allows you to identify the disease by the presence of blood clots during microscopic examination of the sediment.
Such a variety of complications, each of which in itself is quite severe for the body, necessitates timely diagnosis of the disease in the early stages.
Diagnosis of prostate adenoma
It will not be an exaggeration if we say that successful diagnosis of prostate adenoma directly depends on the patient himself. At the earliest stages, it is the survey that can provide the indicators by which a specialist can suspect the presence of a disease. A digital examination of the prostate is added to the survey .
For laboratory tests, material (that is, prostate secretions and smears from the urethra) is taken after prostate massage. The attending physician can obtain certain information through an ultrasound, which determines the presence of stones, the volume of residual urine after a bowel movement, and the size of the prostate.
An additional research method is uroflowmetry . Literally, the name of the term is translated as a measurement of the speed of the urine stream. In addition to speed, a number of other parameters are measured, thanks to which the diagnosis of prostate adenoma becomes more accurate.
Although prostate adenoma does not always lead to oncological consequences, for men who are at risk, that is, who have reached the age of 50, a mandatory blood test is required.
Based on the results of a laboratory test, traces of the presence of a malignant tumor can be identified, or evidence of its absence can be obtained. It is from this age that it is recommended to make a blood test a regular annual procedure.
If there is a suspicion of oncological problems, specific additional studies are carried out.
Treatment of prostate adenoma
Drug treatment involves taking certain medications. They are presented in large quantities on the market today, so the prescription is at the discretion of the doctor.
All medications are aimed either at relaxing the muscle fibers of the prostate gland or at reducing the volume of the prostate gland. In both cases, the compression of the urethra is reduced, and the normal flow of urine is restored.
Unfortunately, medications can only help in the initial stages, and their effect is not always sufficient. In this case, most likely, the patient will be offered surgical intervention. Surgical treatment of prostate adenoma can be performed either openly or without an incision, when the surgeon performs all manipulations through the urethra.
non-surgical methods can be an alternative to surgery . All of them are aimed at once again expanding the urethra. This is done either by influencing the channel itself (balloon dilatation or prostatic stents), or by influencing the prostate gland (thermotherapy or microwave coagulation ).
As for preventive methods, unfortunately, there are no effective recommendations that could guarantee protection against prostate adenoma. In fact, all preventive measures come down to leveling factors that increase the risk of disease, that is, poor nutrition, alcohol abuse, and other bad habits.
The doctors
Medicines
Diet, nutrition for prostate adenoma
List of sources
- Hinman F. Operative urology: atlas / Hinman F.; Ed. Yu. G. Alyaeva, V. A. Grigoryan. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007;
- Emergency surgery. Diagnosis and treatment of acute surgical pathology: V. N. Chernov - St. Petersburg, Phoenix, 2007;
- Portnoy A. S. Surgical treatment of adenoma and prostate cancer. - L.: Medicine, 1988;
- Nephrology and urology. Textbook: A. S. Chizh, V. S. Pilotovich, V. G. Kolb - Moscow, Book House, 2004.
Source: https://medside.ru/adenoma-prostaty
Prostate adenoma in men: symptoms and treatment of the prostate gland, causes of the disease
A disease such as prostate adenoma develops very slowly and affects every second man over 40 years of age.
Unfortunately, most men, for psychological reasons, do not like to visit a doctor and undergo regular routine examinations.
Therefore, people often learn about the disease only when serious treatment is already required not only for the adenoma, but for the accompanying complications. Knowledge of symptoms and treatment methods will allow men to listen to their body and consult a doctor in time.
Because with early diagnosis, it is possible to successfully and quickly treat the disease. Now we will describe the symptoms of adenoma and treatment of the prostate gland; the size of the tumor is an extremely important indicator.
What is prostate adenoma?
BPH is a benign neoplasm of the paraurethral glands located around the urethra in its prostatic section. The main symptom of prostate adenoma is difficulty urinating due to gradual compression of the urethra by one or more growing nodules.
With adenoma, the organ enlarges, which causes compression of the bladder and urethra. This disrupts the flow of urine and leads to the accumulation of residual urine. Additionally, a man may develop a genital tract infection, urolithiasis and cancer. The increase occurs painlessly, which is dangerous for the rapid diagnosis of the disease.
Prostate gland: what is it?
The prostate gland, also known as the prostate, is an organ located slightly below the bladder.
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce a specific secretion that is part of sperm.
The secretion of the prostate gland, determining the consistency of the ejaculate (in particular, contributing to its liquefaction), contains vitamins, enzymes, immunoglobulin, zinc ions, etc.
The prostate gland for men is the “second heart”, which is responsible for sexual function, psycho-emotional state and general health.
The main functions of the prostate gland include:
- liquefaction of sperm - thanks to this, sperm acquire active motility and generally become viable;
- secretion production - it contains enzymes, proteins, fats and hormones, without which the reproductive system will not function normally;
- ejection of semen - the smooth muscles of the prostate gland are capable of contraction, which ensures the entry of semen into the urethra, and this is how ejaculation occurs.
Prostate tumor prevention
You can reduce the likelihood of developing a prostate tumor by:
- Healthy eating. It is advisable to avoid foods high in fat, giving preference instead to vegetables, fruits, and whole grain bread. Some evidence suggests that green tea may have a preventative effect. However, a large-scale clinical analysis of the anticancer properties of the drink has not been carried out to date.
- Active lifestyle and sports. Regular exercise can improve your health, keep your weight in check and improve your mood.
- Watch your weight. If your current body weight is within normal limits, you need to maintain it in this state. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help with this.
- Constant examinations. If a man turns 45, he should have his PSA levels checked every year, which helps diagnose cancer (if present) at an early stage, when the disease is easier to treat. If people are in a certain risk group, they need to check their body for PSA every year and visit a proctologist.
We looked at how prostate cancer progresses. You also had the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the photo.
Causes
Prostate adenoma develops and grows gradually. Although this disease occurs mainly among older men, the initial symptoms can be detected as early as 30-40 years of age. It is interesting that at first cell nodules form en masse and only after a long time begin to grow in size.
Reasons for development:
- The first group includes reasons due to a person’s lifestyle, which increase the likelihood of prostate enlargement. For example, this could be sedentary work or active mental stress in the absence of physical activity. That is why the role of regular physical exercise cannot be overestimated.
- The second group includes objective reasons that do not depend on a person’s lifestyle. It has been proven that prostate adenoma occurs due to changes in the hormonal background of a man. If we consider that these changes inevitably occur in old age, we can come to the conclusion that only some men are lucky enough to avoid problems with the prostate gland.
There are a number of associated factors that may contribute to the development of adenoma. These include:
- Excess weight (accumulation of adipose tissue contributes to the production of female hormones);
- Hereditary factor;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys and urethra;
- Physical inactivity and poor nutrition;
- High blood pressure.
Diagnostic signs
At the first sign of problems with urination, you should consult a urologist. The doctor can detect the adenoma by palpation: both lobes of the prostate are rounded, the groove between them is smoothed. The same picture is observed in acute prostatitis, but the hyperplastic gland is usually painless. Adenomas that are too small or located in the anterior section are not detected by palpation.
TRUS is an inexpensive and informative diagnostic method. With adenoma, an increase in the size of the prostate is recorded (in 75% of cases in the anteroposterior direction). The structure of the formation itself is homogeneous (one color), there are areas of echo seals (light spots). An adenoma formed by fibrous tissue gives a bright echo signal (light color).
Lubricants - purpose and use of intimate gel lubricants
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Lyubov Mikhailovna Kovshutina on the benefits of TRUS of the prostate gland
Even with ultrasound it can be difficult to distinguish a nodular adenoma from cancer, so the most accurate diagnostic method in such cases is MRI with contrast.
Types of prostate adenoma
Based on their structure and location, there are three types of adenoma:
- The tumor penetrates the bladder through the urethra, deforming the internal sphincter and disrupting its function.
- The tumor enlarges towards the rectum, urination is slightly impaired, but the loss of contractility of the prostatic part of the urethra does not allow the bladder to be completely emptied.
- With uniform compaction of the prostate under the pressure of the adenoma without its enlargement, neither urinary retention in the bladder nor urinary disturbances are observed. This is the most favorable type of adenoma.
Erectile dysfunction
With a prostate tumor, erectile dysfunction may occur after surgery. Its likelihood is determined by the stage of cancer and the extent of surgery, the state of erection before treatment and the age of the person. Often an erection is restored, but this process is not quick - it can last from several months to a couple of years.
To combat erectile dysfunction, medications are used (Tadalafil, Vardenafil, Sildenafil), various implants placed in the penis, and vacuum devices.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma in men
There are two groups of symptoms of prostate adenoma: irritative and obstructive.
The first group of symptoms for prostate adenoma includes:
- increased frequency of urination,
- persistent (imperative) urge to urinate,
- nocturia,
- urinary incontinence.
The group of obstructive symptoms characteristic of prostate adenoma includes:
- difficulty urinating,
- delayed onset and increased time of urination,
- feeling of incomplete emptying,
- urination in an intermittent sluggish stream,
- the need for straining.
The first signs you need to pay attention to:
- The first signs of prostate adenoma are a sluggish stream of urine, an increased urge to urinate, which does not always result in emptying the bladder.
- As the tumor acquires serious dimensions, the patient no longer has the desire to find out what the causes of prostate adenoma are; he is more concerned about how to get rid of the disturbing symptoms. Urination becomes difficult, you need to strain to urinate, engage your abdominal muscles.
With the complication of prostate adenoma and its transition to a severe stage, all symptoms will intensify, which will negatively affect the patient’s life. In severe cases, only surgery can help, which is why it is so important to pay attention to the symptoms. Even if they are repeated 1-2 times, you need to undergo a full examination.
Prostate adenoma in men goes through several stages, each of which is accompanied by increasing symptoms and complications.
Compensated form
The most characteristic changes in urination at this stage:
- more frequent
- less free
- not as intense as before (the stream of urine no longer looks like a characteristic parabola, but falls almost vertically).
As the prostate continues to grow and pressure on the urethra increases, the following symptoms appear:
The use of heparin ointment to improve male potency
- increased urge to urinate during the day,
- decrease in urine output,
- increased incidence of an uncontrollable desire to urinate (the so-called imperative urge),
- participation of auxiliary muscles: the patient, for better emptying, strains the abdomen from time to time at the beginning or end of urination.
Subcompensated stage
Subcompensated - prostate enlargement has reached levels where it has severely affected the function of the bladder to remove urine from the body. Violations occur:
- the bladder is released in portions,
- the walls of the bladder increase in thickness,
- some urine is retained,
- when the bladder is full, involuntary release of urine may occur,
- urine may be cloudy and contain blood.
Stage 3 prostate adenoma - decompensated
There is a decrease in the contractility of the bladder to minimal limits, and an increase in residual urine can be of the order of two liters. Also relevant is a sharp stretching of the bladder, in which its contours are visible in an oval or spherical shape, reaching the navel, and in some cases rising much higher.
Meanwhile, at night, and then during the day, urine is systematically or constantly released, this happens in an involuntary manner, due to drops from a full bladder.
Associated symptoms of adenoma:
- weakness,
- nausea and lack of appetite,
- constipation,
- thirst and dry mouth.
What names does this disease have?
Changes characterized by benign growth of the prostate gland have several names in the Russian-language literature.
“Prostate adenoma” and “prostate adenoma” are names more familiar to the patient’s hearing.
However, new names - BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) more fully reflect the essence of this change.
In books and articles written by Russian urologists of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the disease is called “prostatic hypertrophy.”
The term “hypertrophy” means an abnormal increase in something (organ, cells).
At the beginning of the 20th century, the term “prostate adenoma” also appeared in urology, which indicated that the growing tissue was nothing more than a benign tumor of the prostate gland - an adenoma.
- At the same time, a number of scientists began to use the term “hyperplasia” (with hypertrophy of an organ or cells, their size simply increases, and with hyperplasia, the organ increases due to an increase in the number of cells).
- Subsequently, discrepancies appeared in Russian-speaking and English medicine.
- Already in the middle of the 20th century, in reference books and textbooks the disease was called Benign prostatic hyperplasia - BPH, which can be translated into Russian as “benign prostatic hyperplasia”.
Soviet surgeons used the terms “prostate adenoma” and “prostate adenoma”, considering them correct. Such terms are still used today; they are more familiar to patients. However, in the last 10-15 years, doctors in medical institutions in patient records call the disease not “prostate adenoma”, but BPH (in another version - BPH).
REFERENCE! The replacement of terms occurred because the new name correctly and fully reflects the essence of the disease; it is literally translated into English and is currently used by urologists in all CIS countries. Doctors also use other names for this disease according to the recommendations of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10, item No. N40).
Consequences for a man
Complications of prostate adenoma:
- Acute urinary retention. The complication appears at stages 2 or 3 of the disease due to compression of the urethra by the hypertrophied prostate gland.
- Inflammation of the urinary tract. Stagnant processes in the bladder lead to the proliferation of bacteria. They provoke the development of cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis.
- Urolithiasis disease. Incomplete emptying of the bladder leads to the appearance of microliths, stones, or mineral deposits in the bladder. They can cause bladder blockage and urinary retention.
- Hematuria. The appearance of red blood cells in the urine, which is caused by varicose veins in the neck of the bladder.
Source: https://erekto.ru/zdorove/adenoma-prostaty-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Prostate adenoma: symptoms and causes
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common disease in elderly and senile men in the Russian Federation.
According to epidemiological studies, 25 percent! Men over 50 years of age experience distressing symptoms associated with prostate adenoma.
And in the age group of 70 years and more, every second person suffers from them.
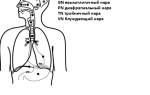
The prostate gland is a very important organ of the male reproductive system; normally it is the size of a walnut and is located between the bladder and the penis. The localization of the prostate allows it to be palpated through the rectum.
The secretory function of the pancreas is to produce a special secretion, which after ejaculation ensures the liquefaction of sperm and preserves the viability of sperm due to the presence of nutrients such as fructose and zinc citrate.
The secretion of the prostate makes up 20-30 percent of the volume of seminal fluid (sperm). Another special function of the pancreas is the metabolism of male sex hormones, in particular testosterone, which, under the influence of the enzyme 5α-reductase, is converted into the active form - Dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Symptoms of prostate adenoma:
With pronounced growth of the prostate gland - in particular, the tissues around the prostatic urethra, a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra inevitably occurs - with the development of infravesical (subvesical) obstruction (IVO).
The consequence of this is problems with urination - the so-called “emptying symptoms”. In addition, IVO leads to a reflex increase in the tone of the muscles of the internal urethral sphincter and an increase in the sensitivity (irritability) of the nerve endings in the area of the bladder neck.
This, in turn, leads to “storage symptoms”: increased urge to urinate, getting up to go to the toilet at night, etc.
Main complaints with prostate adenoma:
- frequent urination in small portions is one of the most common symptoms presented when talking with men suffering from BPH. However, it is necessary to distinguish between frequent urination caused by polyuria, when there are large volumes of urine released, for this purpose you can fill out urination diaries.
- getting up to go to the toilet more than once a night, a symptom that significantly reduces the quality of life due to sleep disturbances,
- weak pressure of the urine stream leads to the fact that the duration of urination can reach several minutes,
- intermittent urination,
- imperative urge to urinate, in other words very strong and sudden with a feeling of fear about possible urinary incontinence,
- sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder, sometimes may not depend on the volume of urine released
- the need to strain to start urinating. In patients with cardiovascular diseases, this symptom can lead to syncope (loss of consciousness, fainting) or even the development of a cerebral stroke.
- blood in the urine (hematuria), long-term chronic urinary retention, due to IVO, leads to complications such as stones and bladder infections
To standardize, quantify patient complaints and determine the severity of prostate adenoma, a special questionnaire is used - the International Index of Prostatic Symptoms (IPSS). This tool, despite its apparent simplicity, has high sensitivity and specificity (more than 80%). According to the IPSS, the severity of prostate hyperplasia is assessed as follows:
- up to 7 points – EASY,
- 8-19 points – MODERATE,
- 20-35 points – HEAVY.
The symptoms described above are just the tip of the iceberg.
Sooner or later, a serious complication of prostate adenoma occurs - acute urinary retention (inability to urinate due to narrowing of the lumen of the urethra and the inability of the bladder to adequately contract).
In addition, the development of prostate adenoma is accompanied by a gradual increase in the amount of “residual urine,” that is, urine that is not evacuated from the bladder during urination.
This contributes, on the one hand, to the development of infection and the formation of stones in the bladder, and on the other hand, it disrupts the outflow of urine from the kidneys through the ureters.
Unfortunately, as hyperplasia progresses, a stage of decompensation (irreversible depletion) of the muscular wall of the bladder begins, which is forced to make great efforts, “squeezing out” urine.
Subsequently, hydronephrosis gradually develops - expansion of the renal cavity system, which ultimately leads to chronic renal failure (CRF).
Stages of prostate adenoma (prostate adenoma):
Currently, it is customary to distinguish the following stages in the course of prostatic hyperplasia:
- Stage I – compensation (minor urination disorders, absence of residual urine),
- Stage II – subcompensation (moderate or severe complaints, presence of residual urine, onset of damage to the upper urinary tract (kidneys), risk of acute urinary retention, urinary tract infections and other complications),
- Stage III – decompensation (bladder exhaustion, hydronephrosis, development of renal failure).
Causes of development of prostate adenoma (prostate adenoma)
The causes of prostate adenoma are not completely clear to this day. The most common theories indicate that development is a consequence of age-related hormonal imbalance.
According to one theory, as men age, the level of Dihydrotestosterone in the blood increases, which stimulates the growth of glandular tissue of the prostate.
Another theory suggests that the balance of the hormones testosterone and estrogen plays a major role in the development of the disease. In young men, testosterone levels are higher than estrogen levels, and with age this ratio shifts in the other direction. Relatively high levels of estrogen can stimulate the proliferation of pancreatic tissue.
It is important to note that adenoma, prostatitis and prostate cancer are completely different diseases (having different causes and mechanisms of development). Therefore, an adenoma cannot “transition” into cancer, just as prostatitis cannot turn into BPH.
Risk factors for prostate adenoma
According to some studies, patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia, in addition, suffered from arterial hypertension (AH) and diabetes mellitus (DM). However, the above pathologies are most likely natural processes of natural aging, and there is no direct relationship between these three diseases.
Source: https://uroportal.ru/services/giperplaziya-predstatelnoy-zhelezy/adenoma-predstatelnoy-zhelezy-simptomy-i-prichiny/