With proper treatment, the cough goes away in about a week. If the attacks last much longer, the disease becomes chronic. There are many reasons for this, ranging from improper treatment of the patient to an incorrect diagnosis made by a doctor. If a cough does not go away for a long time in adults, how to treat it and in what dosage, you can find out below.
What causes cough in adults?
The causes of persistent cough in adults vary. This condition may occur due to bronchial asthma. The sick person is tormented by attacks of dry cough, and he has difficulty breathing. The disease appears due to allergies or a cold. Stress and severe emotional stress can also lead to sudden attacks. In this case, the help of a neurologist will help.
Another cause of this condition is lung cancer. This cancer often resembles bronchitis. The patient coughs constantly, sometimes even to the point of vomiting.
In this case, you need to contact a medical institution for diagnosis as soon as possible. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract can lead to frequent coughing attacks.
This condition is caused by increased acidity of gastric juice. It causes irritation after entering the esophagus.
Stagnation of blood in the lungs can occur due to heart failure. Then a cough appears in adults, which does not go away for a long time. The attacks intensify when the person is in a horizontal position. To cope with this problem, you need to consult a cardiologist.
The cause of prolonged coughing attacks is chronic non-infectious bronchitis. It appears due to cigarettes that the sick person constantly smokes. Bacterial secondary inflammation occurs. It should be remembered that if a cough does not go away for a long time in adults, a specialist will decide how to treat it. Self-administration of any medications can cause harm to health.
How to treat a long lasting cough?
Experts recommend using the following medications:
- Gerbion. This product contains an extract from plantain leaves, which is famous for its anti-inflammatory and antitussive effect. The drug removes mucus from the upper respiratory tract and strengthens the immune system, thanks to a large amount of vitamin C. Take 2 tsp. medications up to 5 times a day.
- Bronholitin. This syrup effectively removes mucus from the bronchi. Take 10 ml 3 times a day.
- Libexin. These tablets are taken orally with plenty of water (1 piece 3 times a day). The product fights pathogenic microorganisms and removes mucus from the bronchi.
- Fluimucil. Helps thin mucus and facilitates its separation. Take 1 tablet once a day, dissolving it in half a glass of warm water. Possible side effects include hives, tinnitus, heartburn and nausea. Prescribed with caution for gastric ulcers.
- Fluditek. This syrup is used 1 tbsp. up to 3 times a day. This remedy copes with a lingering cough and removes bronchial secretions from the upper respiratory tract.
All of the medications listed are sold without a prescription. Before treating a cough with them, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Residual cough: how to deal with it?
You can remove residual cough that has not completely gone away after a cold with Sinekod. This drug contains butamirate citrate, which relieves inflammation and dilates the bronchi. In addition, the drug blocks the activity of the cough center. This medicine can be taken by pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimester.
Tusuprex can cope with this condition. The drug expands the lumen of the bronchi and inhibits the cough center. Do not use during pregnancy or during breastfeeding.
Erespal is considered no less effective. This medicine has antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator effects. Not prescribed while waiting for a baby. Available in the form of tablets and syrup.
As for codeine-based products, despite their proven effectiveness, experts do not recommend the use of such drugs. Codeine-containing products have a negative impact on health.
Medicines to relieve prolonged cough
If a cough does not go away for a long time in adults, how to treat such a condition? If doctors have established the cause of a prolonged cough, then, depending on this, they prescribe antibiotics, antifungal and antiviral agents.
Medications containing plant extracts will help you cope with a wet cough. This is Breast collection or Pectusin. In addition, you can use synthetic-based drugs (Lazolvan, Bromhexine, ACC).
These medications help quickly remove mucus accumulated in the bronchi.
Doctor Mom, Mucaltin and Gerbion will help you cope with a lingering dry cough. These drugs have an expectorant effect. They help thin mucus and speed up the process of its evacuation from the bronchi.
If the cause of the cough is a respiratory tract infection, antibiotics are prescribed. These are Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin or Azithromycin. Eleutherococcus extract, Rhodiola rosea, ginseng or succinic acid will help strengthen the body weakened by cough.
The most effective folk remedies
Not only medications, but also folk remedies will help to cope with a cough that has dragged on for a long time:
- Warming up has gained well-deserved popularity. For example, in hot water. To do this, you need to pour it into a basin and stir the mustard in it, and then lower your feet. The procedure should last until the water cools completely. Then you should put on warm socks and lie down under the blanket. It is best to do this warming up before bed.
- Mustard plasters can be used to warm the chest. Before applying them, apply a thin layer of vegetable oil or fatty cream to the skin. Each mustard plaster must be immersed in warm water for a few seconds and applied to the chest. In this case, the heart area should be avoided. Keep mustard plasters on your body for no more than 10 minutes. If allergic reactions occur in the form of red spots or rashes, this treatment should be abandoned.
- In addition to the above remedies, a warm compress will help. To do this, you need to boil the peeled potatoes and grind them to a puree. Place a cotton cloth, folded in half, on the patient’s chest, and potato mass on it. It needs to be well leveled. The top of the puree is covered with another layer of fabric. Keep the potatoes until they cool completely.
Another effective way to get rid of coughing attacks that do not go away for a long time is badger fat. This remedy is used to rub the chest and back area between the shoulder blades.
Then the patient is covered with a sheet and a warm blanket on top. The procedure takes from 4 to 8 hours (you can leave the fat on the body overnight).
This remedy warms up the organs of the respiratory system and removes mucus from the bronchi.
Other methods to combat a persistent cough
Inhalations will help cope with a prolonged cough. They will help warm the airways and remove mucus from them. One of the most effective is inhalation with soda (3 tsp of soda is added to 2 liters of water).
Bring the mixture to a boil and cool slightly. Breathe over the steam, covering your head with a towel for 20 minutes. Inhalation over boiled potatoes will help relieve a prolonged cough and warm up the bronchi.
This procedure is carried out by analogy with that described above.
Using raw beets against cough is no less effective. To do this, one medium root vegetable is peeled and grated. Take 2 tsp. every two hours. This remedy will not only relieve prolonged coughing attacks, but also cope with severe sore throat.
In addition to the above remedies, drinking warm water will help. Particularly popular in the treatment of this symptom are onions fried in butter and mixed with honey. All components of the product are taken in equal proportions. You need to take this home remedy 1 tsp. from 3 to 4 times a day.
If a cough does not go away for a long time in adults, what to treat, a specialist will tell you based on the diagnosis. Therapy must be comprehensive and include a full range of procedures.
Source: https://lechu-kashel.ru/kashel-dolgo-ne-prohodit-u-vzroslyh-chem-lechit/
What should you do if a dry cough does not go away for a long time in an adult?
A cough that lasts more than one week depletes the body
A frequent manifestation of many respiratory diseases is coughing. In most cases, after the disease is cured, the cough disappears. But sometimes a dry cough does not go away for a long time in an adult, and this becomes an alarming symptom that can lead to serious health problems.
This article will aim to explain the reasons why a cough can last for a long time, as well as advice on diagnosing possible diseases.
Cough that lasts for a long time
Coughing is a reflex aimed at clearing the respiratory tract of dust and phlegm.
It comes in two types:
- Dry cough - without mucus production, exhausts the body with prolonged attacks and irritates the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
- A wet cough - with sputum production - is more productive, since during the process of removing phlegm the body heals itself.
Both dry and wet coughs can suddenly develop into a lingering cough, which will not allow the body to fully recover from the illness it has just suffered.
Diseases and conditions that can cause a persistent cough
The most common reason why a dry cough does not go away is considered to be an incorrect diagnosis, and as a result, treatment that is not suitable in this case. It is not uncommon for a cough to persist after a long time due to self-medication.
Many people go to work with a cough, take their children to children's educational institutions, and do not even think about the fact that they need the help of a specialist. Instead, they prefer to buy the syrup that a friend recommended, or take several inhalations.
If the condition has improved slightly, then such dangerous self-medication is also stopped. None of the above is strictly forbidden! Only a doctor knows how to diagnose the disease and what medications to choose to improve the condition and complete recovery.
So:
- If a dry cough does not go away after a cold, this indicates that the development of the disease has been delayed. Ideally, a dry cough appears during a cold in the first days of the acute period of the disease, and then turns into a wet cough, gradual discharge of sputum begins, the bronchi are cleared and the person gets better. If the dry cough still lasts and does not turn into a wet one, this indicates that the bronchi are unable to cope with the load, which means you need to consult a pulmonologist.
- It happens that a dry cough with pharyngitis does not go away for a long time. Pharyngitis is a disease in which the mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes inflamed. The cough can be of a different nature: dry, paroxysmal, throaty, tormenting only at night. Most often, the cough does not go away due to errors in treatment, namely, treatment for pharyngitis is stopped as soon as the cough disappears. And this is fundamentally wrong, because an interrupted course will lead to complications in the form of recurring coughing attacks.
- Smoker's cough is another reason why a dry cough does not go away for a long time. Most smokers may not even notice a cough, believing that it is nothing serious, and therefore there is no need to consult a doctor. However, such coughing may indicate chronic bronchitis, which has developed as a result of systematic exposure to nicotine and other toxic substances contained in cigarettes. Advanced chronic bronchitis in smokers eventually leads to emphysema, and then to pulmonary failure.
- Allergic cough - if you have asked yourself the question - why a dry cough does not go away, perhaps you have become one of the many people with allergies. Allergic reactions to dust, wool, fluff, and seasonal allergies to the flowering of various plants are very common. Dry cough, sneezing, itchy nose - all these are symptoms that may accompany this disease.
- If you are suffering from a dry, persistent cough and at this time you are taking any medications, there is a high probability that the cough is a reaction of the body caused by these medications. In 30% of patients with cardiovascular diseases, a dry cough occurs while taking medications to lower blood pressure. After stopping the drug, the cough goes away on its own.
- Tuberculosis - this serious diagnosis is worth thinking about if a dry cough has not gone away for a month (see What is a cough with tuberculosis and how to distinguish it from a cold). Koch's bacillus, which is the causative agent of this disease, is found in the body of almost every person by the age of 30, but thanks to the protective forces of the immune system, the disease does not develop. With a sharp decrease in immunity, constant stress and nervous tension, as well as poor nutrition, tuberculosis can develop. Manifestations of tuberculosis are considered to be low-grade body temperature and increased sweating at night, obsessive coughing, which over time turns into a dry, unproductive cough.
If a cough does not go away for more than a month, this is a serious reason to see a doctor.
- Helminthic infestations - there are cases of ascariasis, in which the larvae move through the pulmonary circulation and linger in the bronchi, trachea or lungs. The larvae irritate cough receptors and provoke a prolonged dry cough.
- Cough caused by occupational hazards. When a dry cough in an adult does not go away, there is reason to think about working conditions. When working near toxic substances, household chemicals, or in coal mines, a dry cough may develop, and in some cases even respiratory failure. The simplest solution to this problem is to change your job and consult a pulmonologist. After all, no matter how high the salary, the price of your health is much higher.
What diseases does the duration of cough indicate:
| Causes of cough | Duration | Additional symptoms |
| Self-medication | Up to 3 weeks | – |
| Allergy | Up to a month or seasonally | Runny nose, watery eyes |
| Smoking | From 1 month and longer | – |
| Pharyngitis | 2-3 weeks | Sore throat |
| ARVI | 1-2 weeks | – |
| Worm infestations | 1-2 weeks while the larvae are in the respiratory system | – |
| Tuberculosis | More than 1 month | Temperature, sweating |
| Occupational hazards | From 1 week and longer | – |
How to improve your health with a dry cough?
If a dry cough does not go away for a long time, the main goal is to visit a doctor.
Note! Only a doctor will be able to check whether the diagnosis is correct and the treatment selected, adjust it if necessary and conduct a diagnosis.
You may need to have blood tests or chest x-rays. The instructions for completing this procedure are quite simple, you just need to take a certain position for a few minutes and not move while the device takes pictures.
Helpful Tips:
- Treatment of dry cough should be aimed at removing sputum, i.e. so that it turns into a wet cough.
- Drink more than 2 liters of liquid daily - teas, fruit drinks, herbal infusions, mineral water. As an option, you can drink warm milk, to which honey, figs, banana, as well as butter or mineral water are added. All these components soften cough, reduce the frequency of attacks and envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from irritation.
- Include light foods rich in calories in your daily diet and reduce the consumption of fatty and fried foods, so as not to overload the body, which is fighting the disease.
- Conduct a course of inhalations. Inhalations can be done with potatoes, essential oils or medicinal herbs. Add a couple of drops of essential oil or pre-brewed herbs to hot water - thyme, mint or eucalyptus are suitable, then lower your head over a container of water and inhale the steam. It is advisable to cover your head together with the container with a terry towel so that the beneficial substances from the steam enter only the respiratory tract and do not disperse throughout the room. With the help of photos posted on the Internet, you can learn how to do it correctly.
Thanks to the video posted in this article, you can learn more about possible treatment methods, the reasons why a dry cough does not go away for a long time in an adult, and what minimal interventions can be applied before visiting a doctor.
Source: https://Kashel.su/problemy/ne-prohodit/suhoj-kashel-dolgo-ne-prohodit-u-vzroslogo-223
Why does an adult’s cough not go away for a long time and what to do?
If an adult’s cough does not go away, it is most often caused by improper treatment of the existing disease.
The most common causes include self-medication or lack of treatment for colds. Treatment of patients with diseases accompanied by coughing attacks is often carried out at home, only in severe cases it is carried out in a hospital.
Why does an adult’s cough not go away for a long time?
In addition to diseases of the respiratory tract, a lingering cough can appear with pathologies of other organs and systems. Frequent reasons for its development are presented in the table.
- Table. Diseases that may be accompanied by a prolonged cough
- Pathologies of the respiratory tract
- Diseases of other organs and systems
- Inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system
- Neoplasms of the respiratory tract
- Otorhinolaryngological pathologies can also cause the development of a cough that does not go away for a long time; its appearance is usually caused by the flow of mucous secretions down the back wall of the pharynx.
If a person smokes, he may develop smoker's bronchitis, in which coughing attacks are observed for a long time, almost constantly. In turn, this can lead to the development of lung cancer and emphysema, which are also characterized by this symptom.
The cause may be unfavorable environmental factors, hypothermia, inhalation of too dry and/or dusty air, or the use of certain medications. Cough attacks develop when foreign bodies and substances enter the respiratory tract, in the presence of allergies.
Prolonged cough and accompanying symptoms in various diseases
The cough can be dry or wet depending on the presence of mucus in the respiratory tract. A wet cough is characteristic of diseases of the lower respiratory tract. The absence of sputum is often observed in the initial stages of acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. With bronchitis, sputum begins to separate a few days after the onset of the disease.
With pharyngitis, pain, a feeling of dryness and a sore throat are observed, the pain intensifies when swallowing. There is a slight increase in body temperature, nasal discharge, and headache. Further spread of the infectious process involving the respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi) is possible.
With laryngitis, the patient has a prolonged barking cough. Patients may also experience dryness and/or sore throat, voice disturbance, difficulty breathing, pain when swallowing, and cyanosis of the skin.
With tracheitis, in addition to coughing, which usually worsens at night and in the morning, the patient may experience increased body temperature, sore throat and/or chest pain.
With bronchitis, an intense chest cough occurs (in the chronic form of the disease, this symptom can be observed for several months), pain in the chest and difficulty breathing may also be noted.
With pneumonia, both scanty sputum and a large amount of mucus can be released, in which impurities of pus can be detected. Patients also experience increased body temperature, harsh breathing, wheezing, and chest pain.
In the atypical form of the disease, sputum may not be separated; patients experience:
- headache;
- sore throat;
- muscle pain;
- weakness and fatigue.
Bronchial asthma
With bronchial asthma, the patient often experiences coughing attacks, which can turn into attacks of suffocation. After an attack, the patient often produces glassy sputum. Attacks are triggered by contact with an allergen and physical activity.
Tuberculosis and oncological diseases of the respiratory tract
The patient is bothered by a prolonged, painful cough, and blood is found in the sputum. There is an unmotivated decrease in body weight, constant fatigue, and rapid fatigue.
Painful coughing attacks are observed with whooping cough. Most often, this disease develops in childhood, but in some cases it also occurs in adults. If there is a sick child in the house, the risk of developing infection among adults in contact with him is approximately 30%.
Cough attacks during whooping cough can be accompanied by rhinitis, cyanosis of the skin, and vomiting. After the disappearance of other clinical signs of the disease, a person’s cough may continue for several weeks.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
With chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, patients experience:
- prolonged wet cough;
- cyanosis of the skin;
- dyspnea;
- airway obstruction;
- wheezing;
- participation of additional muscles in the breathing process, etc.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease and gastritis with high acidity
In these conditions, the cough reflex is caused by stomach contents refluxing into the esophagus and entering the respiratory tract. Patients also experience bloating, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, bad breath, and sour belching.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Unpleasant sensations in the throat and a prolonged shallow cough may occur if the patient has strained neck muscles or cervical osteochondrosis. Symptoms are worse in the morning or evening.
Congestive heart failure
The cough worsens when the body is horizontal, often at night.
The patient also has:
- dyspnea;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract;
- dizziness;
- acrocyanosis;
- chest pain;
- swelling of the neck veins.
Taking medications to regulate blood pressure
While taking antihypertensive drugs, some patients develop a dry cough, which accompanies the entire time the drug is used.
Thyroid diseases
Pain in the throat without signs of inflammation of the mucous membranes is observed with disorders of the thyroid gland. A prolonged dry cough is caused by pressure from the enlarged thyroid gland on the trachea and larynx. It is accompanied by dry skin, chills, and increased excitability.
What to do if an adult’s cough does not go away for a long time
What medications need to be used to treat a cough that does not go away for a long time depends on the cause of its occurrence, accompanying symptoms, contraindications and other parameters, and is therefore determined by the doctor.
For respiratory diseases the following are prescribed:
- antitussive drugs (used in the absence of accumulations of sputum in the respiratory tract);
- mucolytic, expectorants (help thin and remove mucus);
- bronchodilators (relieve bronchospasm);
- antihistamines (used for allergic reactions).
If infection is present, anti-infective drugs (antibiotics, antiviral, antifungal agents) may be prescribed.
Inhalations, which can be carried out using an inhaler or nebulizer in a medical facility or at home, are effective. To perform steam inhalation at home, you can simply breathe steam over a container with a solution.
Physiotherapeutic techniques, warm compresses, mustard plasters, breathing exercises, and drainage massage can speed up the healing process.
When a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, bronchoscopy is usually resorted to. Surgical treatment may be indicated for gastroesophageal reflux disease, cancer, and some pathologies of the ENT organs.
Any treatment methods can be used only after consultation with the attending physician and examination.
To speed up recovery, you must follow the general rules:
- give up bad habits, especially smoking;
- spend more time outdoors;
- Healthy food;
- strengthen the drinking regime (preferably warm drinks: tea with lemon, milk, compotes, fruit drinks, water);
- carry out regular cleaning, ventilate living spaces, control air humidity.
Treatment with folk remedies
In some cases, you can supplement the main therapy with folk remedies (consultation with a doctor is required):
- Milk . You can take milk with honey (1 teaspoon of honey per 1 glass of milk), with soda (1 pinch of soda per glass) or cocoa butter (0.5 teaspoon per 1 glass). It is recommended to drink these milk-based products before bed.
- A mixture of black radish juice and honey . Squeeze the black radish juice and mix with honey in a 1:1 ratio. Adults should take 1 tablespoon, and children 1 teaspoon 3-4 times a day.
- Ginger with green tea in milk . Grated ginger root (3-4 cm long) and 2 tablespoons of green tea are poured into 1.5 liters of milk, brought to a boil, removed from heat and left for about 25 minutes. The product should be drunk several times a day warm.
- Fat + honey + butter + cocoa. Mix 200 g of melted pork fat and honey, 100 g of butter, 2 tablespoons of cocoa powder. The product is taken 3-4 times a day by melting 1 teaspoon of the mixture in 1 glass of warm milk.
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article.
Education: 2004-2007 “First Kiev Medical College”, specialty “Laboratory diagnostics”.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
Over the course of a lifetime, the average person produces no less than two large pools of saliva.
A person taking antidepressants will, in most cases, become depressed again. If a person has coped with depression on his own, he has every chance to forget about this condition forever.
Dentists appeared relatively recently. Back in the 19th century, pulling out diseased teeth was the responsibility of an ordinary hairdresser.
The highest body temperature was recorded in Willie Jones (USA), who was admitted to the hospital with a temperature of 46.5°C.
The human brain weighs about 2% of the total body weight, but it consumes about 20% of the oxygen entering the blood. This fact makes the human brain extremely susceptible to damage caused by a lack of oxygen.
An educated person is less susceptible to brain diseases. Intellectual activity promotes the formation of additional tissue that compensates for the disease.
Tooth decay is the most common infectious disease in the world, which even the flu cannot compete with.
The first vibrator was invented in the 19th century. It was powered by a steam engine and was intended to treat female hysteria.
Scientists from Oxford University conducted a series of studies in which they came to the conclusion that vegetarianism can be harmful to the human brain, as it leads to a decrease in its mass. Therefore, scientists recommend not completely excluding fish and meat from your diet.
- Each person has not only unique fingerprints, but also tongue prints.
- Our kidneys are capable of purifying three liters of blood in one minute.
- In 5% of patients, the antidepressant Clomipramine causes orgasm.
In the UK there is a law according to which a surgeon can refuse to perform an operation on a patient if he smokes or is overweight. A person must give up bad habits, and then, perhaps, he will not need surgical intervention.
74-year-old Australian resident James Harrison has donated blood about 1,000 times. He has a rare blood type whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
Partial absence of teeth or even complete edentia can be a consequence of injury, caries or gum disease. However, lost teeth can be replaced with dentures.
Prolonged cough in adults and children: causes
Prolonged cough is a nonspecific symptom, that is, it occurs in many diseases. To find out its cause, a doctor's examination is required, and often additional studies.
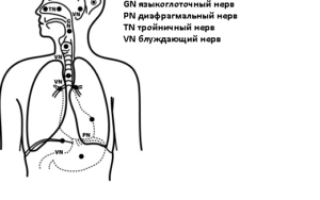
The causes of a prolonged cough may be associated with excitation of the centers of the brain (for example, with neurosis) or irritation of sensitive endings located outside the respiratory tract (in the esophagus, middle ear). However, most often this symptom occurs in diseases of the respiratory system.
This symptom is almost always accompanied by lesions of the larynx, trachea, and large bronchi, since these areas have the most sensitive receptors. Information about their irritation is transmitted through the nerves to the brain, where signals are generated to the muscles of the chest. A protective reaction is formed aimed at removing the irritant from the respiratory tract.
Most common reasons
Prolonged cough persists for 3 weeks or more. If this symptom appears, you should consult a doctor. Possible reasons:
- chronic laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis;
- lung abscess;
- pleurisy of various origins;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchiectasis;
- emphysema and pneumosclerosis;
- pulmonary tuberculosis, sarcoidosis;
- tumors of the bronchi, lungs, mediastinum, metastases or primary tumor lesions of the pleura;
- enlarged thoracic lymph nodes;
- aortic aneurysm;
- diffuse pulmonary diseases;
- dyskinesia of the trachea and bronchi;
- foreign body in the respiratory tract;
- whooping cough;
- tuberculous bronchoadenitis;
- chronic heart failure, causing stagnation of blood in the pulmonary vessels.
The main causes of prolonged cough that cannot be treated:
- lungs' cancer;
- tracheobronchial dyskinesia;
- bronchiectasis;
- polyp or foreign body of the bronchus;
- compression of the bronchus by enlarged intrathoracic lymph nodes.
Prolonged cough in adults
Almost all diseases accompanied by this symptom can be observed in both adults and children. However, the incidence of these diseases varies at different ages. Therefore, we will separately consider conditions that are more typical for people over and under 18 years of age.
Upper respiratory tract diseases
Source: https://kgkb6.ru/kashel/kashel-dolgo-ne-prohodit-u-vzroslogo-chto-delat-chem-lechit.html
Dry cough does not go away for a long time in an adult
A cough is the body’s response to contact with the mucous epithelium of the respiratory tract by any irritant of a viral or bacterial allergic nature or evidence of the presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract.
The causes of a dry cough should be sought among multiple diseases or allergens.
A dry cough in an adult can occur due to a common cold or as a result of cancer. Even heart pathologies can cause this phenomenon.
But in this case we are talking about reasons that are somehow related to the human respiratory system. So, cough can be caused by the following diseases:
- ARVI – parainfluenza, influenza, MS infection;
- atypical pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- measles;
- pharyngitis;
- whooping cough;
- tracheitis;
- laryngitis;
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- false croup;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- oncological diseases of the respiratory system.
The main factors of dry cough not associated with inflammation in the respiratory system:
- inhalation of toxic substances;
- allergic reaction;
- professional dry cough;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- helminthic infestations;
- taking medications;
- entry of a foreign body.
And now about each reason in more detail.
Acute respiratory infections
The flu is a viral infection that affects the nose, throat, and in some cases the lungs. The main signs of the disease are:
- dry cough;
- general weakness;
- fever;
- runny nose;
- a sore throat.
Parainfluenza is an acute respiratory viral infection of an anthroponotic nature. Signs of this disease include:
- dry, barking cough;
- runny nose;
- feeling of dryness and sore throat;
- subfebrile (up to 38℃) or normal body temperature.
Respiratory syncytial infection is a viral pathology that usually affects the lower respiratory tract. This disease is characterized by a dry cough, which turns into a wet cough within 3-5 days. The patient's temperature is either normal or low-grade.
If a person experiences this syndrome, the patient must be provided with bed rest and plenty of warm fluids. To relieve acute symptoms, symptomatic treatment is carried out, antiviral drugs are prescribed and medications are given to reduce fever.
If a dry cough does not go away after a few days, the patient is prescribed expectorants.
It is necessary to treat ARVI, since an advanced disease can result in serious complications. Therefore, you need to contact a medical facility.
Pleurisy, pneumonia, whooping cough
If the cough does not go away for a long time, it may indicate a disease called pleurisy. Pleurisy is a disease of the pleural layers, accompanied by the deposition of fibrin on them or the accumulation of exudative fluid in the pleural cavity.
What syndrome is characteristic of pleurisy?
- Dry cough.
- Dyspnea.
- Painful sensations when breathing.
- Weakness.
- Cyanosis.
- Slight increase in temperature.
Treatment can only be carried out by a doctor after establishing the true cause of the disease. Most often, the patient is prescribed antibacterial or anti-tuberculosis drugs. Anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating and desensitizing medications may be prescribed as additional therapy.
Atypical pneumonia is a disease with an unusual symptomatic course. The factors that provoke atypical pneumonia are atypical pathogens.
Symptoms of the disease:
- dry cough that does not go away for a long time;
- headache;
- fever;
- extrapulmonary symptoms characteristic of these pathogens.
Since drugs for most atypical pathogens have not yet been created, treatment is carried out with broad-spectrum antibiotics, antivirals and glucocorticosteroids.
Whooping cough is an infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets. The pathology is bacterial in nature and is accompanied by a spasmodic paroxysmal cough that does not go away for a long time. This symptom is accompanied by a slight runny nose and a slight increase in temperature.
Treatment consists of taking antihistamines, bronchodilators and antitussives.
Pharyngitis, measles, laryngitis, false croup
The disease should be treated with inhalations, gargling, systemic antibiotics and plenty of warm drinks.
The next cause of dry cough is measles. This disease is caused by a virus and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dry, persistent cough;
- a significant increase in body temperature, up to 40℃;
- runny nose;
- photophobia;
- characteristic rash;
- hoarseness.
Treatment consists of taking mucolytic, antipyretic, expectorant, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. Measles has serious consequences, which is why if you suspect this pathology, you should immediately call a doctor at home. Measles itself never goes away; adequate treatment is required.
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat. The disease can be suspected by the following signs:
- long and severe dry cough;
- difficulty breathing;
- loss of voice;
- soreness;
- there is pain when swallowing.
Treatment for laryngitis is quite simple. The patient should limit himself to talking and irritating spicy foods, drink as much warm liquid as possible, do inhalations and gargle. To prevent the disease from becoming chronic, it must be treated.
Source: https://0p3.ru/kasel/suhoj-kashel-dolgo-ne-prohodit-u-vzroslogo.html
How to treat a dry cough in an adult that lasts for a long time without fever
A severe dry cough without fever in an adult can turn into the worst nightmare if it does not go away for a long time, and especially if we do not know about the reasons for its origin.
Do not underestimate these minor ailments; sometimes they can be the cause of something larger, for example, inflammatory processes associated with pulmonary diseases.
Today we want to tell you about the reasons that can cause irritation of receptors located along the entire respiratory tract and how to treat a dry cough in an adult (medicines, folk remedies) at home.
Causes of a severe dry cough
Anything can cause it to occur; even a small speck of dust that gets into the throat can cause irritation and become the starting point. The reasons for the appearance are a variety of viral ailments: influenza, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.
Also, a severe cough in an adult without fever can be caused by the following factors and diseases:
- smoking tobacco . Tobacco tar causes irritation in the bronchi;
- dust . People who are often in dusty rooms with very dry air may soon complain of a sore throat;
- foreign bodies . When such a body enters the respiratory tract, the urge to cough begins. These are often dust particles;
- asthma . It appears at night with painful sensations in the abdomen and bust;
- deviations of ENT organs of a chronic nature. Many are born with abnormalities of the nasopharynx: acute tracheitis, frontal sinusitis , sinusitis in which a dry cough is normal. It is triggered by mucus running down the throat from the mouth;
- allergy. Cases of dry cough due to a reaction to animal fur, pollen of certain plants, and chemicals are not exceptional;
- viral infections. All kinds of diseases: bronchitis, influenza, ARVI, whooping cough;
- oncological pathologies . Scientists believe that if a dry cough is tormented for a long period, which is accompanied by a strong fever, then the patient should immediately be examined by an oncologist. There is a possibility of cancer of the throat, bronchi, lungs or trachea;
- thyroid diseases. If growths have appeared in the thyroid gland, then the cough occurs as a result of pressure on the trachea;
- heart failure. Ailments of the heart muscle manifest themselves due to extreme physical exertion, accompanied by shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. Sometimes, during an acute form of cardiac abnormalities, blood mucus is released when coughing;
- ailments of the intestines and stomach. Due to the occurrence of a fistula in the esophageal-tracheal cavity or other similar diseases, a reflex dry cough arises after eating;
- tuberculosis. If there is a strong cough to the point of vomiting in an adult, this may be a signal for the presence of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Regarding tuberculosis, the disease arises as a result of decreased immunity, and Koch’s bacillus begins to become active in the body. 80% of the country's residents, people over 30, have it.
Kinds
Depending on the basis for its occurrence, cough is divided into physiological and pathological.
Physiological cough is considered a normal life process. This type of cough is not harmful, and is even a necessary phenomenon. It is necessary to remove accumulated sputum, accidentally introduced foreign bodies, food particles, etc.
Occurs periodically and goes away quickly. Same type. Freely diagnosed.
A pathological cough occurs due to respiratory tract diseases. Has a complex character. Completely depends on the nature of the disease. To diagnose and treat, characteristics must be established.
Depending on the duration of the symptoms, there are varieties of cough, such as:
- spicy. From one to 2 weeks;
- protracted. From a week to 30 days;
- subacute. From a month to 2;
- chronic. Lasts up to 8 weeks.
Most often, a dry cough in an adult manifests itself and exposes the symptoms of many respiratory ailments.
Severe coughing is spread by viruses, microbes, diseases of vital organs - the stomach, heart and lungs.
An acute cough is detected due to acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections. Classified as common. It develops quickly against the background of a respiratory illness.
Appears within two hours. Characteristic: adult tracheitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, etc.
The most important characteristics of an acute cough:
- gradual formation over two hours, days;
- the presence of various symptoms: rhinitis, high fever, weakness, etc.;
- conversion from dry to wet cough.
A constant cough is a sign of chronic diseases of the pulmonary tract and lungs. It is considered a symptom of cystic fibrosis , tuberculosis or laryngeal papillomatosis, where it develops into a persistent dry cough.
Cough is like an alarm bell
A severe cough in an adult manifests itself as a symptom of the disease. Doctors can quickly make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment using it. There are main criteria by which the disease is determined:
Source: https://tvojajbolit.ru/populyarnoe/chem-lechit-suhoy-kashel-u-vzroslogo-cheloveka-protekayushhiy-dolgoe-vremya-bez-temperaturyi/
How long does it take for a cough to go away, how to speed up treatment?
To find out how long a cough lasts during ARVI, you need to determine the nature of the disease. The symptom occurs due to damage to the nasopharyngeal mucosa by an infection - adenovirus, rhinovirus, coronavirus, etc.
In the absence of complications, already 2 days after infection, a dry cough becomes productive and completely disappears within 3-4 days. But if the infection penetrates the lower respiratory tract, the symptomatic picture is replenished with new signs.
The cough becomes dry, barking, paroxysmal, suffocating, prolonged or chronic.
How long does a cough with ARVI last and why does it not go away for a long time?
ARVI is a group of viral respiratory diseases characterized by an acute course. Viral cough occurs as a result of damage to the upper respiratory tract by respiratory syncytial infection, coronaviruses, reoviruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, etc.
During the initial period of the disease, viruses multiply in the mucous membrane of the nose and larynx. This leads to rhinitis (runny nose), coughing attacks, and burning sensation in the laryngopharynx. You can understand how long it takes for a cough to go away with an uncomplicated ARVI by the presence of mucous discharge. With timely initiation of therapy, the symptom completely disappears within 5-6 days.
Very often, ARVI in adults is complicated by bacterial infections. Their penetration into the lower respiratory tract leads to inflammation of the bronchi, larynx, and trachea. Because of this, the cough becomes:
- Protracted – lasts from 21 days to 3 months. Occurs as a result of bacterial damage to the ENT organs or allergic reactions to the penetration of irritating substances into the mucosa.
- Chronic – lasts more than 3 months. Often becomes a symptom of chronic pathology.
The greatest health hazard is chronic cough, as it is provoked by the following diseases:
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- myocardial failure;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- postnasal drip.
For a long time, tuberculosis may no longer manifest itself, so if coughing attacks occur, you should consult a doctor.
Sometimes a cough is a symptom of allergic manifestations that occur against the background of rhinoconjunctivitis and hay fever. In this case, the disease is accompanied by lacrimation, sore throat, and severe swelling of the mucous membranes of the ENT organs.
Types of cough due to viral infections
Cough during a viral infection belongs to the category of catarrhal (inflammatory) manifestations of ARVI. Its character depends on several factors:
- type of pathogen;
- virus reproduction rates;
- immune status;
- presence of chronic diseases.
At the initial stage of ARVI, the cough is unproductive, that is, during coughing, sputum is not separated from the ENT organs. When taking mucolytic drugs, it becomes moist (productive), which ensures the cleansing of the airways from bronchopulmonary mucus (sputum).
Dry
An unproductive cough, a burning sensation in the throat and nasal cavity are the first symptoms of ARVI in adults. They arise as a result of non-purulent inflammation of the ciliated epithelium, which covers the surface of the nasopharynx and hypopharynx. To make the patient feel better, antitussives are prescribed.
A nonproductive cough during ARVI in an adult is accompanied by a feeling of sore and sore throat. When coughing, the sputum does not come out, but a deep chest sound occurs. Its appearance is associated with an increase in the sensitivity of cough receptors against the background of inflammation of the laryngopharyngeal mucosa.
A dry cough during ARVI is sometimes accompanied by a paroxysmal course. If his productivity does not increase within 2-3 days, the patient is prescribed mucolytics. They dilute bronchopulmonary mucus, which accelerates its removal from the ENT organs.
Wet
A productive cough during a cold indicates the beginning of recovery. In uncomplicated ARVI, sputum viscosity decreases 3-4 days after infection. A wet cough speeds up the clearing of viscous mucus from the respiratory system and also prevents its accumulation in the bronchi.
With non-purulent inflammation, the amount of mucus in the respiratory tract increases 7-10 times. If cough productivity does not increase within 3 days, the patient is prescribed mucolytics.
Their untimely intake is fraught not only with the accumulation of sputum in the bronchi, but also with the addition of a bacterial infection. To speed up the coughing up of mucus during ARVI, take expectorant medications.
They thin the mucus, increasing the amount of water in it. This helps to quickly remove mucus from the lungs.
Suffocating
If coughing attacks are accompanied by suffocation, this indicates complications of ARVI. The symptom occurs against the background of such diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- laryngitis;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- obstructive pulmonary disease.
A suffocating cough during ARVI in young children becomes a manifestation of false croup, tracheobronchitis, and whooping cough. The appearance of foamy sputum indicates esophageal-bronchial fistulas.
Difficulty breathing indicates insufficient airway patency, that is, swelling of the mucous membranes. Similar manifestations of ARVI occur with severe complications - bronchitis, pneumonia.
Barking
A barking viral cough in a child is accompanied by chest pain, burning in the laryngopharynx, and hoarseness. It occurs as a complication of ARVI and signals tracheitis or laryngitis. The symptom indicates an infection of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, larynx and trachea.
Cough attacks during colds are caused by the following factors:
Source: https://kashelproch.ru/interesnoe/skolko-dlitsya-kashel