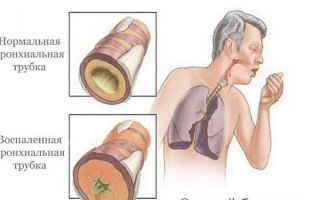
Cough is the most common symptom of respiratory and heart diseases. It helps remove phlegm and foreign substances from the respiratory tract.
The cough reflex occurs as a result of involuntary compression of the vocal cords, relaxation of the diaphragm and increased tone of the long-lasting muscles. These processes lead to increased pressure inside the chest.
During the opening of the vocal cords, air quickly escapes through the narrow passage of the trachea and open vocal cords. The difference between the pressure inside the chest and the atmosphere provokes a cough.
What causes
A cough is the result of an infectious process, exposure to chemical irritants on the body, or a sharp change in air temperature. Paroxysmal cough occurs with coughing up mucus, which varies in smell, color and consistency.
Causes of paroxysmal cough:
- Acute bronchitis. Most often, this disease is a consequence of acute respiratory viral infections. Attacks of dry cough are accompanied by itching and burning in the throat or chest. Often the attacks are so severe that they cause headaches and loss of consciousness. Short-term fainting occurs due to a sharp compression in the sternum, reducing the flow of blood to the heart. After 48 hours, a large volume of viscous secretion is released, the patient feels general weakness, chills, headache and muscle pain, and body temperature may rise. When listening with a stethoscope, difficulty breathing and wheezing are felt. There is severe shortness of breath, a blue tint to the skin and mucous membranes, the sputum is viscous and difficult to separate, the cough reflex does not effectively remove it, wheezing is heard in the lungs, especially when exhaling in a lying position.
Severe coughing attacks in an adult with the release of mucous secretions, elevated body temperature, rapid pulse and breathing indicate the transition of acute bronchitis to the stage of bronchopneumonia. This disease, when auscultated, is characterized by a quiet, vague and high-frequency sound with wheezing.
- Lobar pneumonia. At the initial stage of the disease, the coughing attack is dry and painful; after 48 hours, when coughing, a rust-colored secretion is noted. The patient shudders, the body temperature rises, the skin of the face turns red, the lips and nose turn blue, rashes in the form of herpes may appear on the face, breathing slows down in the affected part of the sternum. When breathing, the patient experiences pain, rapid heartbeat and breathing. During a medical examination, a trembling voice and bronchophony, hard breaths with wheezing are observed.
- Influenza pneumonia begins with a dry cough, later purulent-mucous blood discharge is coughed up. The patient often feels nauseous, the body temperature rises, the general condition worsens, and severe pain is felt in the chest area. Muscle weakness, shortness of breath, bluish skin and painful, rapid heartbeat appear. In especially severe cases, changes in blood composition, development of collapse, pulmonary edema, coughing up blood and difficulty breathing are observed.
- Acute lung abscess (lung gangrene). The patient suffers from a paroxysmal cough with a single release of a large volume of secretion with a characteristic fetid odor. The patient feels nauseous, chills, has a high fever, shortness of breath and bluish skin.
- Bronchiectactic disease. The cough is prolonged with copious mucus mixed with pus. The patient's temperature rises, there is weight loss, nausea, enlargement of the tips of the fingers and toes (symptom of drumsticks), deformation of the nail plates (symptom of “watch glasses”), enlargement of the intercostal space, the sternum is difficult to compress. When listening, hard, weak breathing with scattered dry rales is observed.
- Bronchial asthma. The patient is overcome by a coughing attack, which is stopped with bronchodilator medications. A cough also occurs at the end of an attack of bronchial asthma, and a small amount of clear secretion may be released.
- Pleurisy is dry. It is characterized by sharp acute pain in the sternum, which intensifies with a cough reflex and full inspiration. Breathing in the affected part of the chest is slow, and pleural friction sounds are heard.
- Pulmonary edema. The patient continues to have shortness of breath, a blue tint to the skin, a dry cough appears, turning into a wet cough with secretion. In case of lung pathology, the patient feels better after coughing; in case of heart failure, no improvement is observed. Moist rales are clearly audible above the lungs.
- Bronchopulmonary malignant formations. In the vast majority of patients with this diagnosis, paroxysmal cough manifests itself at the earliest stage of the disease. This is due to the neoplasm and transformation of the bronchi under the influence of the inflammatory process and compression of the lung. The cough is wet, with pus and blood. Lung cancer can be recognized if there is a prolonged dry debilitating cough, chest pain, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, and fever. Later, the tumor grows and compresses neighboring organs. The patient may experience a hoarse voice, swelling of the face, and severe wheezing.
- Neoplasms in the lumen of the bronchi. A paroxysmal cough may be the root cause of a tumor of the lungs or bronchi. Large tumors block the normal functioning of the bronchi and trachea, small ones provoke suffocation, pressure and severe coughing with blood. When the lumen of the lungs is blocked, inflammation of the damaged tissue appears, and when the blockage is complete, the lung collapses and is excluded from gas exchange.
- Mediastinal syndrome is a disease caused by inflammation or neoplasm in the mediastinum. At an early stage, breathing is impaired, the trachea and bronchi are compressed, which provokes paroxysmal coughing and shortness of breath. The reflex is strong, painful, sometimes with vomiting. You can hear whistling noisy breathing, the pressure of the veins, arteries and recurrent nerve increases, the voice changes and disappears.
- Pulmonary tuberculosis. With this disease, the nature of the cough varies - from minor morning cough to paroxysmal cough.
Symptoms accompanying cough
Patients often experience wheezing when breathing. The reasons for these sounds are explained by excess pus and sputum in the enlarged bronchi.
Wheezing can be heard very clearly using a phonendoscope, and strong wheezing can be heard even at some distance from the patient without medical devices.
The patient feels internal vibrations in the chest, which periodically disappear after a coughing attack. There are other symptoms:
- Shortness of breath most often occurs in the progressive stages of the disease. The reasons are caused by difficulty in the passage of air to the alveoli.
- Chest pain always appears during exacerbations, when the inflammation process occurs in an acute form and pus accumulates. When this process reaches the pleura, which has nerve endings, people complain of chest pain. The sensations manifest themselves in different ways: from dull, weak attacks that persist for several days, to an acute sharp jolt during inhalation. The lungs do not have nerve endings, so pain is not felt from this area.
- Heat. This symptom means an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of toxins entering the blood. Microparticles are released by microbes at the source of the disease, and also enter the period of resorption of pus. The forced formation of pus increases the temperature to 39. Antipyretics help alleviate the condition a little, but it is unlikely that it will be possible to establish a temperature that corresponds to the norm.
- Hippocratic fingers - an increase in the size of the terminal phalanges of the fingers, which occurs as a result of the development of respiratory failure. This symptom rarely occurs in people under 45 years of age. The reasons for it are not fully understood. It is generally accepted that the nail phalanx becomes more porous due to oxygen deficiency and, accordingly, expands. The symptom most often appears on the hands, but minor changes may also be visible on the toes. During the period of manifestation, a person’s fingers look like drumsticks. The nail plates swell, transforming into a dome-shaped shape. Sometimes this phenomenon is called the “watch glass symptom” due to its external similarity. A person’s nails will never return to their previous shape and will remain that way for the rest of their lives.
- If a person has close contact with allergens, exacerbations occur more often. Difficulty breathing prevents oxygen from entering the body in the required amount, so the patient feels depressed and exhausted, suffers from migraines and feels dizzy. Intoxication further aggravates this process.
- Thin. During the period of illness, a purulent process occurs, and with it a loss of appetite. During an exacerbation, the patient looks weak and thin.
First aid
If foreign objects penetrate the trachebronchial tree, the patient is hospitalized in a surgical or otorhinolaryngological hospital. With pneumonia they are sent to the therapeutic department, with gangrene of the lungs - to a therapeutic or surgical hospital, depending on the advanced stage of the disease. The determination of hospitalization for other diseases is determined by the general clinical picture of the patient.
For allergic cough, asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis, allergic and polypous rhinosinusopathy, treatment is carried out by an allergist. An otolaryngologist treats aspiration, ENT pathology, asthma and chronic bronchitis. A pulmonologist prescribes treatment for interstitial lung diseases, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, pleurisy, and lung gangrene.
A gastroenterologist treats gastroesophageal reflux and other types of cough caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The thoracic surgeon prescribes treatment for bronchiectasis and lung gangrene.
If the cough is of a cardiovascular nature, a cardiologist's opinion is necessary; for tuberculosis and sarcoidosis, a phthisiatrician is needed. The oncologist will answer all questions regarding malignant tumors. An endocrinologist treats pathological processes of the thyroid gland. A psychoneurologist will give advice on psychogenic cough.
Olga Kondratyuk
Sources: medscape.com, health.harvard.edu, medicalnewstoday.com.
Source: https://globalmedclub.ru/kashel/vidy/pristupoobraznyj.html
Illnesses with coughing attacks
Coughing attacks in an adult or child most often act as a protective reaction of the human body to irritation of the mucous layer of the upper respiratory tract. In the vast majority of cases, such a sign is part of the clinical picture of a limited range of pathological conditions. In addition, there are harmless factors of occurrence, for example, inhalation of dry air.
Most often, a severe coughing attack is accompanied by the production of sputum, which may vary in color and consistency. There is also shortness of breath, attacks of suffocation and pain in the chest area.
A pulmonologist can make the correct diagnosis after studying the results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic measures, as well as on the basis of information obtained during a thorough examination of the patient.
Treatment of coughing attacks is carried out using conservative methods, in particular by taking medications. However, medical intervention may sometimes be required to eliminate the underlying disease.
Etiology
To date, not many factors are known that cause coughing attacks, which greatly simplifies the process of establishing the correct diagnosis.
The most common causes of this manifestation in adults and children are:
- inflammatory lung disease;
- localization of the inflammatory process in the bronchi - it is noteworthy that coughing attacks with bronchitis quite often occur at night;
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchial spasm, which most often occurs under the influence of one or another irritant in allergies;
- compression of the respiratory tract by lymph nodes that have changed in size;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- enlargement or swelling of the thyroid gland;
- the formation of a malignant or benign tumor in the upper respiratory tract;
- penetration of a foreign object into the respiratory system;
- exposure to mechanical irritants - this includes inhaling dust along with air;
- unfavorable working or living conditions, which is why a person is forced to constantly breathe various chemicals that have a strong odor or cigarette smoke;
- the influence of thermal factors, namely inhalation of excessively cold or extremely hot air.
It is not uncommon for a child or an adult to develop a severe cough at night - it is noteworthy that etiological factors may differ depending on the age category.
For example, coughing attacks at night in adults are caused by:
- gastric reflux, in which the contents of the stomach are thrown into the larynx;
- bronchial asthma;
- heart failure;
- sinusitis;
- a wide range of colds;
- lack of iron in the body.
Nocturnal coughing attacks in a child are represented by the following provoking sources:
- an allergic reaction to surrounding objects, in particular to the fluff that fills pillows or a large amount of dust in the sleeping area;
- croup - the danger of the disease lies in the fact that it is sudden. When it manifests itself at night, the child often gets scared, which can only intensify the attack of suffocation, which is why children subsequently refuse to sleep;
- the course of one of the above diseases;
- uncomfortable body position during sleep, especially if the mattress is insufficiently rigid;
- dry and cold air in the child’s room.
Classification
Experts in the field of pulmonology identify several main options for expressing this symptom, which is why cough occurs:
- dry or unproductive - characterized by the absence of sputum;
- wet or productive - accompanied by the release of moisture from the bronchi.
Division depending on time of occurrence:
- morning - most typical for people who abuse tobacco smoking, including passive smoking. It is also observed in COPD, bronchial asthma, infectious and inflammatory processes, lung abscesses or bronchiectasis;
- night - in the vast majority of cases, attacks of allergic cough are observed, as well as the formation of a similar symptom in pulmonary tuberculosis or asthma;
- regularly repeated throughout the day - often expressed in pneumonia and bronchitis.
According to the nature of their manifestation, sudden coughing attacks are divided into:
- loud and barking - may indicate whooping cough, compression of the trachea by a neoplasm, laryngeal disease or hysteria;
- quiet - very often indicates inflammatory damage to the ligaments;
Source: https://lkray-promo.ru/kashel/bolezni-s-pristupami-kashlya/
How to treat dry paroxysmal cough in adults
A dry paroxysmal cough is a convulsive contraction of the muscles of the bronchopulmonary system. It is accompanied by suffocation, vomiting, and chest pain. To get rid of obsessive attacks, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease manifested by this symptom.
Features
A dry paroxysmal cough lasts 1-2 minutes. All this time the patient cannot take a deep breath and relax the body. He sits in a tense position, leaning forward. Such attacks deplete the body of an adult. Therefore, without treatment, the underlying disease progresses, and inflammation spreads to neighboring organs.
Vomiting during a paroxysmal dry cough does not always indicate digestive disorders. The reason for this concomitant symptom is the proximity of the cough and vomiting centers in the cerebral cortex.
In case of allergies, attacks of dry cough are accompanied by lacrimation, rhinitis, sneezing, and swelling of the throat. The intensity of symptoms increases upon contact with the allergen. And the inability to clear the throat causes pain in the chest and throat in an adult.
An increase in paroxysmal dry cough at night is characteristic of bronchial asthma, whooping cough, and parawhooping cough. In the morning hours, this symptom becomes more active in adult heavy smokers. During the day, attacks bother people suffering from pleurisy.
First aid for paroxysmal cough
Diseases that manifest themselves as paroxysmal dry coughs often require complex long-term treatment. Therefore, an adult needs to know how to provide first aid, stop an attack and ease breathing.
- Take a sitting position.
- Unbutton the collar of your clothing.
- Open the window (during the warm season).
- Place a wet towel on the radiator (during the cold season).
- Drink warm milk with soda, suck a teaspoon of honey or cough drops.
There are medications (Omnitus, Sinekod) that can stop an attack, regardless of the cause of its occurrence. They act directly on the cough center of the brain, inhibiting its activity. This method of first aid is justified in extreme cases, since the pills do not cure the disease, but only stop the debilitating symptom.
You can stop the attack with the help of inhalation drugs (Berotec, Berodual). The medicinal liquid in them is in a steel cylinder. When you press the lid, it is converted into tiny particles of steam, which enter the respiratory tract with pressure. The medicine instantly relieves bronchospasm and makes breathing easier, but it also does not eliminate the cause of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
At the appointment, the doctor asks about the characteristics of the attacks and accompanying symptoms. He examines an adult patient, listens to his breathing through a phonendoscope, and taps the lungs using percussion. Next, the doctor prescribes laboratory diagnostics:
- urine and blood analysis;
- fluorography;
- examination of sputum, throat smear;
- bronchoscopy.
If the presence of a neoplasm is suspected, a computed tomography scan of the chest is prescribed.
What diseases cause paroxysmal cough
Attacks of dry cough are a symptom of many diseases of the respiratory system. They arise after an attack by various pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, allergens) and disappear after long-term complex treatment.
Bronchial asthma
A dry paroxysmal cough leading to vomiting is characteristic of the early stage of bronchial asthma. It appears in adults whose bronchi show hypersensitivity to allergens. After contact with dust, mold or other irritants, they spasm, which causes attacks.
As first aid, inhaled medications are prescribed to relieve spasms. The main treatment includes taking anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, and immunostimulating drugs. An adult should avoid contact with the allergen and remove spicy, hot and cold foods from the diet.
Whooping cough and parawhooping cough with dry cough
The cause of the development of these diseases is the attack of pertussis and parapertussis bacteria. They enter the adult body by airborne droplets and settle in the bronchioles and alveoli. Constant irritation of the respiratory tract receptors causes a dry paroxysmal cough leading to vomiting.
Whooping cough is considered a more severe disease. Its treatment is carried out inpatiently in the clinic, and parawhooping cough is most often cured after home therapy. In both cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as antitussives and expectorants.
Dry pleurisy
Pleurisy or inflammation of the pleura occurs due to unsuccessful surgery, trauma, and also as complications of other diseases of the respiratory system. In the dry type of the disease, the cause of paroxysmal cough is exposure to allergens and digestive enzymes (in acute pancreatitis).
To treat dry pleurisy in an adult, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition, effective methods of combating the disease are tight bandaging of the lower parts of the chest, application of an iodine mesh, warm compresses, and switching to a special diet.
Malignant and benign tumor
A dry paroxysmal cough is sometimes a symptom of the appearance of a neoplasm in the organs of the respiratory system. The growing tumor compresses them and irritates the cough receptors. Without treatment, it can clog the lumen of the bronchi, make breathing difficult, and lead to attacks of vomiting.
During diagnosis, the location, size and nature of the tumor are determined. Next, surgery is performed to remove the tumor. If the cancer is inoperable, symptomatic treatment of cough with anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating drugs is prescribed.
Inflammation of the trachea and paroxysmal cough in adults
The causative agents of the disease can be bacteria, viruses, allergens. Initially they attack the nasopharynx of an adult. But if treated incorrectly, the inflammation spreads to the trachea. The disease is manifested by paroxysmal cough, high fever, weakness, and loss of appetite.
During diagnosis, the pathogen is determined. Next, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, antihistamines or antiviral drugs. Anti-inflammatory aerosols are used as first aid for attacks. During treatment, an adult limits physical activity and switches to a gentle diet.
Preventive measures
After successful treatment of a disease manifested by paroxysmal dry cough, it is important to prevent relapse. To do this, you need to get rid of bad habits and take simple preventive measures.
- Treat colds in a timely manner.
- Do fluorography annually.
- Do physical exercise and sports.
- Take regular walks.
- Carry out hardening procedures.
- Ventilate the apartment.
- Take vitamin complexes.
If all the rules are followed, the immunity of an adult is strengthened. His body responds better to treatment and recovers faster from an attack by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Source: https://stop-kashel.ru/kak-lechit-suhoj-pristupoobraznyj-kashel-u-vzroslyh/
What diseases can a cough be a symptom of?
Cough, it would seem, like a runny nose, is one of the most common symptoms of a cold. But don’t think that dry and wet coughs are treated in the same way. After all, there are as many types of it as there are treatment methods. How to determine which disease symptoms are attacks of dry and wet cough and what should be done in each case?
Causes of cough
What are the causes of cough? The surface of the bronchial “tree” is covered with a layer of mucus, which has the ability to absorb everything that a person inhales - particles of dust and dirt, including bacteria and viruses. In addition, the surface of the bronchi is covered with ciliated epithelium - a kind of cilia, which, thanks to rhythmic vibrations, promote the movement of mucus upward and thus rid the body of harmful substances coming with the air.
In case of respiratory tract disease, the epithelium cannot cope with its functions, the mucus becomes viscous and accumulates in the bronchi. Therefore, it turns out that the cough reflex is a useful ability of the upper respiratory tract to cleanse itself.
With its help, the body is cleansed of unwanted microparticles and phlegm. This is why you should not suppress it with medication at the first sign of cough. The primary task is to transform a dry cough into a wet, productive one.
And the sooner this happens, the sooner the patient will return to normal life.
The role of the virus in the occurrence of dry cough: ARVI
Cough symptoms vary, and there is no one universal cure for all types. The main goal of treating a cough at any stage is to prevent it from going “lower” in the respiratory system. Cough can be caused by various diseases.
ARVI is most often an “upper” cough. It usually appears due to the virus entering the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. With a common viral infection, the cough is dry, throaty, paroxysmal and debilitating.
It causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient - it causes anxiety, interferes with normal sleep, and even annoys others with its loudness. However, this type of cough is considered superficial and the safest.
With a dry, recently developed cough, there is practically no phlegm, but mucus accumulates in the nasopharynx, which, moving along the back wall of the pharynx, causes a cough reflex.
At first, intensive treatment of such a cough is not required; in this situation it is necessary:
- warmth and peace - home mode;
- drink plenty of water - warm milk with honey, a pinch of soda, as well as a piece of butter, tea with lemon, raspberries and black currants, warm mineral water.
You can rinse your nose with a saline solution (one teaspoon per glass of boiled water, cooled to room temperature), and also gargle with herbal infusions or a solution of baking soda (half a teaspoon per glass of water).
First aid for laryngitis and tracheitis
If the patient is bothered by a sore throat, hoarseness, and the cough becomes “barking,” then most likely the inflammatory process has spread to the larynx, and this disease is called “laryngitis.”
Source: https://MedAboutMe.ru/zdorove/publikacii/stati/sovety_vracha/simptomom_kakikh_bolezney_mozhet_yavlyatsya_kashel/
Coughing attack
A coughing attack is the body’s response to the influence of any irritant. Coughing during attacks can be convulsive - due to cough impulses following one after another, the patient cannot take a breath. In some cases, severe attacks result in disturbances in heart rhythm and breathing, fainting, or vomiting.
Cough as a symptom of disease
Before deciding how to relieve a coughing attack, you should determine which symptoms of the disease they relate to. Treatment of symptoms is ineffective if the cause of their occurrence is not eliminated.
A cough in an adult can be a symptom of acute respiratory infections, respiratory diseases (tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, tumor diseases of the lungs, etc.), bacterial and viral infections, allergies, problems with the cardiovascular or nervous systems.
A cough without sputum is called dry. Most often it is a sign of pathologies in organs that are not part of the respiratory system (inflammation of the external ear, heart defects, pericarditis, diseases of the nervous system).
A wet cough is caused only by diseases of the respiratory system. Accompanied by copious sputum secretion due to increased formation of bronchial secretions.
In terms of duration and frequency of occurrence, the cough can be constant or periodic, representing isolated urges and severe attacks.
Chronic and acute cough are determined by the duration of its existence. Acute is considered to be one that is observed for 3 months, and chronic is one that lasts more than 3 months.
Causes
Factors that cause coughing attacks in adults can be divided into 4 groups:
- Inflammatory and allergic factors: increased sputum production, bronchial spasms, edema, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract;
- Thermal factors - irritation of the respiratory tract by too cold or hot air;
- Mechanical factors: foreign body in the larynx or ear canal, enlarged lymph nodes, formation of tumors compressing the bronchi and trachea;
- Chemical factors: gaseous substances and medications inhaled along with air, in which periodic coughing can be a side effect.
Coughing attacks in a child
Coughing attacks in a child should be treated with special care, since young children, as a rule, cannot correctly talk about their condition and accompanying symptoms. The most likely causes of attacks are mechanical and inflammatory factors.
If a cough is accompanied by general weakness, fever, rhinitis, lacrimation, loss of appetite and sleep disturbance, it is most likely due to a cold.
If it intensifies only when the baby goes to bed, then most likely it is due to excessive salivation during teething.
In some cases, the cause of coughing attacks in a child is accidental inhalation of a foreign body, which can result in suffocation.
If your cough is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, painful appearance, general weakness, pain when coughing, increased frequency of breaths, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to relieve a coughing attack
Taking medications that help thin the mucus will help it separate more easily and be cleared from the lungs more quickly. The best way to thin mucus is to drink plenty of fluids. In addition, cough syrups containing guaifenesin can be used to loosen sticky mucus.
It is not recommended to abuse cough suppressants. This may not be advisable, especially if there is excessive mucus production. If the mechanism for releasing sputum from the body is disrupted, it will accumulate in the lungs.
If you suffer from severe coughing attacks that prevent you or your household from sleeping peacefully, you can use some antitussives for a while, but this should be done within reasonable limits.
To reduce pain and irritation in your throat, use saline gargles. To prepare such a solution, dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of fine table salt in a glass of warm water.
A cough may occur and become worse due to smoking tobacco. Therefore, if you want to recover, you need to give up this bad habit.
To get rid of a lingering cough, ask your doctor to prescribe you medications with a bronchodilator effect. Such remedies will speed up the process of cleansing the lungs and help eliminate coughing.
Dry air irritates the lungs, which leads to increased coughing. Using household appliances designed to humidify indoor air will help you significantly alleviate your condition.
When to see a doctor
Periodic coughing attacks, as a rule, do not cause any concern. However, if it is accompanied by the following symptoms, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible:
- the cough continues for more than a week, but there is no relief;
- heat;
- attacks of suffocation;
- general weakness and weight loss;
- specific sputum (thick, mixed with blood, green or yellow);
- cough is accompanied by pain in the chest.
Source: https://dolgojit.net/pristup-kashlia.php
Cough for no reason in adults: causes
If there are no recognizable symptoms of influenza and ARVI such as fever, runny nose, aching joints, but a cough for no reason is bothering you, in an adult this may mean allergies, a latent form of bronchitis, asthma, helminthic infestation and many other diseases. In addition, the manifestation of a reflex expectorant attack may indicate the entry of a foreign body, water, or mucus flowing down the walls of the nasopharynx into the respiratory organs.
In any case, you should immediately seek advice from your family doctor (general practitioner), who, if necessary, will issue a referral to a specialist - otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, allergist, cardiologist to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe medications.
To have an idea of how dangerous a cough for no reason is, we list all sorts of hidden factors that cause its appearance.
Why might a person suddenly cough?
How to recognize the etiology of cough without an obvious cause in an adult? Doctors distinguish more than 50 factors in the occurrence of attacks, and almost all of them indicate illness.
However, coughing can also be a reflex pushing reaction to remove foreign bodies and liquids from the body that accidentally enter the respiratory tract. Or jerky exhalations begin due to irritation (chemical, thermal, physical) of the mucous membrane of the larynx.
Coughing causes cleansing of the bronchi, throat, and lungs, so you should not try to hold it back.
A cough of unknown visual etiology - causeless - may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- tracheitis,
- laryngitis,
- pharyngitis,
- allergy,
- asthma,
- pleurisy,
- bronchitis,
- pneumonia,
- tuberculosis,
- lung abscess,
- gastroesophageal reflux,
- neurosis,
- heart failure.
Depending on the type of disease, it can be barking, wet, dry, night, morning, day, and a separate definition of the type is that it occurs during physical stress. Occurs during the formation of inflammatory processes, as well as during narrowing and decreased patency of the respiratory channels due to swelling and overflow with mucus.
A sudden attack can be triggered by tobacco or other acrid smoke, gas, or the smell of perfume (for COPD, asthma, bronchitis).
Excessively hot food and air or, on the contrary, too cold ambient temperatures also contribute to the occurrence of attacks if a person suffers from pulmonary, cardiac, or allergic diseases.
The presence of high concentrations of dust and plant pollen in the air causes the development of cough in allergies and asthma.
Determining a possible illness by the nature of coughing
A qualified doctor can establish the correct diagnosis not only based on test results, but also on the timbre of sound, duration, and also the painful sensations experienced by the patient during an attack. The main differences between coughs are:
Source: https://GorloUhoNos.ru/gorlo/bolezni/kashel-bez-prichiny-u-vzroslyx.html
What diseases cause cough?
Many people associate a cough with a cold, and they uncontrollably take antiviral drugs. However, such a symptom accompanies a variety of diseases, and inadequate treatment only aggravates the condition and leads to complications.
It is a mistake to think that spastic exhalations are characteristic only of bronchopulmonary diseases. Among the reasons are problems in various organs:
- heart;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- nasopharynx;
- endocrine and nervous system.
How does cough manifest itself in various diseases?
- ARVI. Bronchospasm does not occur immediately, but 2–4 days after the high temperature was noted. Its companions are sneezing, runny nose, and sore throat.
- Bronchitis. A sharp cough is one of the main symptoms of this disease. However, in 5–10% of cases it may be absent. The clinical picture includes wheezing and chest pain, fatigue, and fever.
- Pneumonia. The type of cough and accompanying symptoms differ depending on the form of pneumonia. With a viral disease, dry bronchospasms and symptoms such as headache and muscle pain, fatigue, and difficulty breathing are observed. The bacterial form is characterized by a wet cough, fever, shortness of breath, and sweating.
- Pharyngitis. Dry, painful exhalations intensify at night, making it difficult to sleep. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes moist. The patient has a sore throat and complains of itching and foreign body sensation.
- Tracheitis. The cough is loud, painful, and contains sputum. It is accompanied by weakness, and the temperature rises.
- Bronchial asthma. In addition to coughing with viscous mucus, there are attacks of suffocation.
- Allergy. Spasmodic exhalations occur immediately after contact with the irritant. Allergy coughs are accompanied by lacrimation, itching, and nasal discharge.
Spasms of the respiratory tract are a common occurrence in gastrointestinal diseases.
They are associated with disruption of the muscles that regulate the movement of food through the esophagus. During such a malfunction, gastric juice irritates the mucous membrane, and this causes a reaction in the form of a cough, which intensifies after eating. With gastroesophageal reflux disease, wheezing, heartburn, and sore throat are observed.
In diseases of the thyroid gland, the cough is accompanied by a pressing sensation in the neck and difficulty swallowing. Attacks of suffocation, heart pain and headaches may occur.
Sometimes the cause of bronchospasms is a stressful condition or a psychosomatic disorder. This cough is characterized as sharp and loud. At night it does not bother the patient.
What diseases cause coughing with sputum?
The release of clear mucus during bronchospasm is a signal of a pathological process in the body. When making a diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to the color and consistency of the sputum.
Viscous white mucus is characteristic of allergic reactions and colds. It is observed in asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia. The patient is prescribed medications that thin the mucus and help remove it.
Green sputum indicates an inflammatory process in the bronchi and lungs. This condition is typical for:
- lobar pneumonia;
- bronchitis;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- oncological disease.
The patient needs a thorough comprehensive examination.
Pink sputum indicates internal bleeding. This is a symptom of such dangerous diseases as:
- pneumococcal pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- pulmonary embolism;
- cancer.
In this case, immediate medical attention is required.
To properly treat a cough, you need to know what disease it is a symptom of. Doctors at the Private Practice clinic will carefully examine you, make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary therapy. Proper treatment will eliminate not only the cough, but also the reasons that caused it.
Source: https://www.chpr.ru/info/kashel-zabolevaniya/